293:
44:
365:
329:
353:
305:
341:
317:
59:
becomes a significant factor in the high-energy environment of the earliest stage of the universe, and general relativity on its own fails to make accurate predictions. In response to the inaccuracy of considering only general relativity, as in the traditional model of the Big Bang, alternative
103:, however their modifications with only one bounce (as opposed to cyclic series of bounces) circumvent this problem (particularly if the contracting phase is empty, i.e. compactified
83:
Various new models of what preceded and caused the Big Bang have been proposed as a result of the problems created by quantum mechanics. One model, using
108:
292:
283:
126:, and has budded off from another universe (e.g., one that macroscopically looks like static empty space) as a result of
390:
119:
100:
72:
207:
24:
91:, in which quantum fluctuations cause the universe to expand. This use of loop quantum gravity also predicts a
260:
31:
to have existed before the Big Bang. The instant immediately following the initial singularity is part of the
233:
84:
357:
127:
95:
of universes, with a new universe being created after an old one is destroyed, each with different
154:
345:
333:
184:
52:
385:
96:
56:
309:
60:
theoretical formulations for the beginning of the universe have been proposed, including a
55:
to predict what happened in the beginnings of the universe has been heavily criticized, as
28:
68:, enormous membranes much larger than the universe, collided, creating mass and energy.
43:
369:
297:
379:
61:
364:
321:
131:
92:
32:
104:
71:
Although there is no direct evidence for a singularity of infinite density, the
123:
88:
234:"What If the Big Bang Wasn't the Beginning? New Study Proposes Alternative"
115:
87:, aims to explain the beginnings of the universe through a series of
75:
is evidence that the universe expanded from a very hot, dense state.
65:
316:
42:
99:. These proposals have been criticized as inconsistent with the
16:
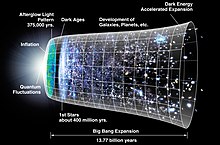
Time period of seeming infinite density just after the Big Bang
35:, the earliest period of time in the history of our universe.
155:"The Big Bang: What Really Happened at Our Universe's Birth?"
107:, and (2+1)-dimensional, due to the inherent stabilizing
122:(CMB) states that the universe is but one of many in a
281:
134:, as opposed to our universe being all that exists.
148:
146:
8:
178:
176:
261:"Thinking About Time Before the Big Bang"
288:
208:"Branes, Crunches, and Other Big Ideas"
142:
159:The History & Future of the Cosmos
47:The traditional model of the Big Bang
7:
185:"What Happened Before The Big Bang?"
39:Traditional models of our universe
14:
212:What existed before the big bang?
363:
351:
339:
327:
315:
303:
291:
259:Atkinson, Nancy (13 June 2008).
27:predicted by some models of the
109:rigidity of vacuum in this case
79:Alternatives to the singularity
153:Wall, Mike (21 October 2011).
1:
114:Another possibility based on
206:Lamb, Robert (12 May 2010).
120:cosmic microwave background
101:Borde-Guth-Vilenkin theorem
73:cosmic microwave background
407:
183:Penn State (2 July 2007).
64:-based model in which two
118:and observations of the
48:
46:
128:quantum fluctuations
85:loop quantum gravity
21:initial singularity
391:Physical cosmology
97:physical constants
53:general relativity
49:
240:. 5 December 2017
57:quantum mechanics
398:
368:
367:
356:
355:
354:
344:
343:
342:
332:
331:
330:
320:
319:
308:
307:
306:
296:
295:
287:
277:
276:
274:
272:
267:. Universe Today
256:
250:
249:
247:
245:
230:
224:
223:
221:
219:
203:
197:
196:
194:
192:
180:
171:
170:
168:
166:
150:
51:The use of only
406:
405:
401:
400:
399:
397:
396:
395:
376:
375:
374:
362:
352:
350:
340:
338:
328:
326:
314:
304:
302:
290:
282:
280:
270:
268:
258:
257:
253:
243:
241:
232:
231:
227:
217:
215:
214:. HowStuffWorks
205:
204:
200:
190:
188:
182:
181:
174:
164:
162:
152:
151:
144:
140:
81:
41:
29:Big Bang theory
17:
12:
11:
5:
404:
402:
394:
393:
388:
378:
377:
373:
372:
360:
348:
336:
324:
312:
300:
279:
278:
265:Universe Today
251:
225:
198:
187:. ScienceDaily
172:
141:
139:
136:
80:
77:
40:
37:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
403:
392:
389:
387:
384:
383:
381:
371:
366:
361:
359:
349:
347:
337:
335:
325:
323:
318:
313:
311:
301:
299:
294:
289:
285:
266:
262:
255:
252:
239:
235:
229:
226:
213:
209:
202:
199:
186:
179:
177:
173:
160:
156:
149:
147:
143:
137:
135:
133:
129:
125:
121:
117:
112:
110:
106:
102:
98:
94:
90:
86:
78:
76:
74:
69:
67:
63:
62:string theory
58:
54:
45:
38:
36:
34:
30:
26:
22:
358:Solar System
269:. Retrieved
264:
254:
242:. Retrieved
237:
228:
216:. Retrieved
211:
201:
189:. Retrieved
163:. Retrieved
158:
132:quantum foam
113:
93:cyclic model
82:
70:
50:
33:Planck epoch
20:
18:
346:Outer space
334:Spaceflight
161:. Space.com
89:Big Bounces
25:singularity
380:Categories
138:References
124:multiverse
310:Astronomy
271:April 16,
238:Space.com
218:April 16,
191:April 16,
165:April 16,
386:Big Bang
130:such as
116:M-theory
370:Science
298:Physics
284:Portals
244:2 April
66:branes
322:Stars
105:Milne
23:is a
273:2012
246:2018
220:2012
193:2012
167:2012
19:The
111:).
382::
263:.
236:.
210:.
175:^
157:.
145:^
286::
275:.
248:.
222:.
195:.
169:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.