651:
632:
38:
666:
696:
681:
1045:
861:
1184:
Allowing empty trees makes some definitions simpler, some more complicated: a rooted tree must be non-empty, hence if empty trees are allowed the above definition instead becomes "an empty tree or a rooted tree such that ...". On the other hand, empty trees simplify defining fixed branching factor:
41:
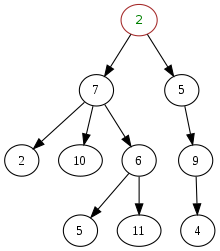
This unsorted tree has non-unique values (e.g., the value 2 existing in different nodes, not in a single node only) and is non-binary (only up to two children nodes per parent node in a binary tree). The root node at the top (with the value 2 here), has no parent as it is the highest in the tree
1219:
This is different from the formal definition of subtree used in graph theory, which is a subgraph that forms a tree – it need not include all descendants. For example, the root node by itself is a subtree in the graph theory sense, but not in the data structure sense (unless there are no
70:
node, which has no parent (i.e., the root node as the top-most node in the tree hierarchy). These constraints mean there are no cycles or "loops" (no node can be its own ancestor), and also that each child can be treated like the root node of its own subtree, making
799:
over the entirety of a tree; nodes are traversed level by level, where the root node is visited first, followed by its direct child nodes and their siblings, followed by its grandchild nodes and their siblings, etc., until all nodes in the tree have been traversed.
839:
can be implemented as a list of lists: the head of a list (the value of the first term) is the left child (subtree), while the tail (the list of second and subsequent terms) is the right child (subtree). This can be modified to allow values as well, as in Lisp
506:). Thus the root node has depth zero, leaf nodes have height zero, and a tree with only a single node (hence both a root and leaf) has depth and height zero. Conventionally, an empty tree (tree with no nodes, if such are allowed) has height −1.
812:
records with pointers to their children, their parents, or both, as well as any associated data. If of a fixed size, the nodes might be stored in a list. Nodes and relationships between nodes might be stored in a separate special type of
108:(ADT) can be represented in a number of ways, including a list of parents with pointers to children, a list of children with pointers to parents, or a list of nodes and a separate list of parent-child relations (a specific type of
83:, many trees cannot be represented by relationships between neighboring nodes (parent and children nodes of a node under consideration, if they exist) in a single straight line (called edge or link between two adjacent nodes).
844:, where the head (value of first term) is the value of the node, the head of the tail (value of second term) is the left child, and the tail of the tail (list of third and subsequent terms) is the right child.
89:
are a commonly used type, which constrain the number of children for each parent to at most two. When the order of the children is specified, this data structure corresponds to an
1989:
775:
of the tree. Often, an operation might be performed when a pointer arrives at a particular node. A walk in which each parent node is traversed before its children is called a
452:. Typically siblings have an order, with the first one conventionally drawn on the left. Some definitions allow a tree to have no nodes at all, in which case it is called
1265:
A parent can have multiple child nodes. ... However, a child node cannot have multiple parents. If a child node has multiple parents, then it is what we call a graph.
376:
1424:. Section 10.4: Representing rooted trees, pp. 214–217. Chapters 12–14 (Binary Search Trees, Red–Black Trees, Augmenting Data Structures), pp. 253–320.
2559:
1438:
66:. Each node in the tree can be connected to many children (depending on the type of tree), but must be connected to exactly one parent, except for the
2235:
1982:
2090:
1066:
882:
1145:
which determines the direction on the edges (arrows point away from the root; given an edge, the node that the edge points from is called the
2529:
1714:
1313:
1258:
1921:
1185:
with empty trees allowed, a binary tree is a tree such that every node has exactly two children, each of which is a tree (possibly empty).
1975:
2068:
1465:
498:
of a node is the length of the longest downward path to a leaf from that node. The height of the root is the height of the tree. The
2603:
2468:
1421:
1389:
1092:
908:
2598:
1199:
1581:
2258:
1379:
787:
traversal. (This last scenario, referring to exactly two subtrees, a left subtree and a right subtree, assumes specifically a
2263:
2155:
1070:
886:
783:
walk; a walk in which a node's left subtree, then the node itself, and finally its right subtree are traversed is called an
2228:
2073:
821:, nodes are typically represented as table rows, with indexed row IDs facilitating pointers between parents and children.
128:
2145:
577:
The level of a node is the number of edges along the unique path between it and the root node. This is the same as depth.
2608:
338:
317:
311:
176:
2342:
2325:
1118:
641:
196:
180:
2135:
1055:
871:
2541:
2308:
2303:
1546:
1412:
267:
1074:
1059:
890:
875:
290:
2298:
1931:
809:
397:
277:
2178:
2337:
2332:
2291:
2221:
2193:
1487:
97:. A value or pointer to other data may be associated with every node in the tree, or sometimes only with the
2572:
2549:
2140:
2112:
1194:
413:
349:
327:
63:
2019:
1330:
779:
walk; a walk in which the children are traversed before their respective parents are traversed is called a
2554:
2354:
2183:
2150:
2031:
1458:
767:
Stepping through the items of a tree, by means of the connections between parents and children, is called
749:
739:
2480:
2397:
2170:
2127:
1625:
360:
302:
297:
221:
80:
650:
2420:
2063:
2058:
2036:
1615:
1570:
1399:
825:
796:
437:
190:
184:
2593:
2188:
2024:
1729:
1505:
1136:
1020:
818:
733:
322:
282:
153:
120:
2463:
1585:
2448:
2313:
2273:
2204:
2085:
1896:
1855:
1681:
1671:
1550:
1353:
922:
307:
273:
249:
208:
105:
55:
2160:
1109:, generally with values attached to each node. Concretely, it is (if required to be non-empty):
119:
Trees as used in computing are similar to but can be different from mathematical constructs of
2382:
2281:
2107:
2048:
1790:
1491:
1451:
1417:
1385:
1309:
1278:
1254:
847:
Ordered trees can be naturally encoded by finite sequences, for example with natural numbers.
401:
261:
124:
2405:
1881:
1403:
1395:
1345:
1329:
L. Afanasiev; P. Blackburn; I. Dimitriou; B. Gaiffe; E. Goris; M. Marx; M. de Rijke (2005).
1246:
1166:
1132:
239:
47:
2425:
2367:
2011:
1998:
1825:
1575:
631:
365:
172:
808:
There are many different ways to represent trees. In working memory, nodes are typically
333:
Trees can be used to represent and manipulate various mathematical structures, such as:
37:
2517:
2495:
2320:
2244:
2002:
1778:
1773:
1656:
1590:
1407:
1125:
814:
762:
665:
416:
is a structure which may contain data and connections to other nodes, sometimes called
243:
113:
109:
76:
59:
1967:
828:, with relationships between them determined by their positions in the array (as in a
368:
used to identify which subroutines in a program call other subroutines non recursively
355:
Tree structures are often used for mapping the relationships between things, such as:
2587:
2490:
2387:
2372:
2102:
1926:
1906:
1749:
1638:
1565:
213:
157:
1500:
1886:
1850:
1666:
1661:
1643:
1555:
1374:
1357:
1106:
841:
695:
147:
140:
94:
90:
345:), by making multiple nodes in the tree for each graph node used in multiple paths
553:
For a given node, its number of children. A leaf, by definition, has degree zero.
2485:
2410:
2053:
1936:
1901:
1891:
1805:
1739:
1734:
1724:
1633:
1482:
1114:
1044:
1016:
860:
836:
829:
788:
680:
609:
A rooted tree in which an ordering is specified for the children of each vertex.
253:
235:
86:
2473:
2377:
1946:
1916:
1876:
1719:
1648:
1595:
1515:
1434:
1303:
1250:
396:
documents can be thought of as trees, but are typically represented by nested
342:
202:
1349:
1281:
17:
2415:
2362:
1951:
1911:
1758:
1686:
1676:
1286:
1170:
541:
A node reachable by repeated proceeding from parent to child. Also known as
383:
372:
167:
The mechanism used to allocate and link blocks of data on the storage device
161:
72:
2512:
1840:
1530:
2458:
2286:
1956:
1830:
1810:
1783:
1768:
1520:
2507:
2453:
1941:
1845:
1820:
1763:
1610:
1540:
1535:
1510:
1443:
659:: undirected cycle 1-2-4-3. 4 has more than one parent (inbound edge).
428:, which are below it in the tree (by convention, trees are drawn with
2502:
2443:
1860:
1835:
1815:
1800:
1709:
1600:
1525:
1173:), particularly always having two child nodes (possibly empty, hence
448:, such as the parent's parent. Child nodes with the same parent are
112:). Representations might also be more complicated, for example using
2213:
1704:
1605:
1560:
36:
1142:
with a distinguished root (one vertex is designated as the root),
561:
The degree of a tree is the maximum degree of a node in the tree.
2524:
2117:
2041:
1696:
432:
going downwards). A node that has a child is called the child's
393:
389:
229:
31:
2217:
1971:
1447:
1117:
with the "away from root" direction (a more narrow term is an "
1038:
854:
569:
The number of edges along the shortest path between two nodes.
509:
Each non-root node can be treated as the root node of its own
225:
1308:. Pacific Grove, CA: Brooks/Cole Publishing Co. p. 694.
674:: cycle B→C→E→D→B. B has more than one parent (inbound edge).
533:
A node reachable by repeated proceeding from child to parent.
1139:(any two vertices are connected by exactly one simple path),
475:) is any node of a tree that has child nodes. Similarly, an
2097:
2080:
502:
of a node is the length of the path to its root (i.e., its
359:
Components and subcomponents which can be visualized in an
440:). All nodes have exactly one parent, except the topmost
175:
or "inheritance tree" showing the relationships among
1031:(tree with root node with given value and children).
1241:
Subero, Armstrong (2020). "3. Tree Data
Structure".
689:: cycle A→A. A is the root but it also has a parent.
513:, which includes that node and all its descendants.
2540:
2434:
2396:
2353:
2272:
2251:
2169:
2126:
2010:
1869:
1748:
1695:
1624:
1481:
1416:, Second Edition. MIT Press and McGraw-Hill, 2001.
1158:
an ordering on the child nodes of a given node, and
1149:and the node that the edge points to is called the
727:
Adding a new item at a certain position on the tree
139:Trees are commonly used to represent or manipulate
1165:Often trees have a fixed (more properly, bounded)
644:parts, A→B and C→D→E. There is more than one root.
1105:Viewed as a whole, a tree data structure is an
491:) is any node that does not have child nodes.
2229:
1983:
1459:
8:
1439:Dictionary of Algorithms and Data Structures
379:), of designs in various types of cars, etc.
375:, of source code by software projects (e.g.
238:store data in a way that makes an efficient
1073:. Unsourced material may be challenged and
933:is defined, using the abstract forest type
889:. Unsourced material may be challenged and
156:used to organize subdirectories and files (
2236:
2222:
2214:
1990:
1976:
1968:
1466:
1452:
1444:
1161:a value (of some data type) at each node.
1093:Learn how and when to remove this message
909:Learn how and when to remove this message
444:, which has none. A node might have many
34:, a specific type of tree data structure.
824:Nodes can also be stored as items in an
314:with sections of increasing specificity.
1392:. Section 2.3: Trees, pp. 308–423.
1384:, Third Edition. Addison-Wesley, 1997.
1338:Journal of Applied Non-Classical Logics
1243:Codeless Data Structures and Algorithms
1233:
1212:
1202:(catalogs types of computational trees)
424:. Each node in a tree has zero or more
160:create non-tree graphs, as do multiple
27:Linked node hierarchical data structure
1305:Discrete Mathematics with Applications
1181:child nodes), hence a "binary tree".
7:
1071:adding citations to reliable sources
887:adding citations to reliable sources
736:: Removing a whole section of a tree
601:A set of one or more disjoint trees.
518:
371:Inheritance of DNA among species by
937:(list of trees), by the functions:
116:or ancestor lists for performance.
742:: Adding a whole section to a tree
25:
1200:Category:Trees (data structures)
1043:
859:
694:
679:
664:
649:
630:
101:, which have no children nodes.
2205:List of graph search algorithms
1380:The Art of Computer Programming
721:Enumerating a section of a tree
622:Examples of trees and non-trees
585:The number of nodes in a level.
293:trees used to simulate galaxies
129:trees in descriptive set theory
58:that represents a hierarchical
701:Each linear list is trivially
164:to the same file or directory)
143:data in applications such as:
1:
745:Finding the root for any node
516:Other terms used with trees:
382:The contents of hierarchical
1023:defined by the constructors
795:walk effectively performs a
757:Traversal and search methods
617:Number of nodes in the tree.
318:Hierarchical temporal memory
312:Dewey Decimal Classification
216:for generating conversations
2560:Directed acyclic word graph
2326:Double-ended priority queue
1302:Susanna S. Epp (Aug 2010).
377:Linux distribution timeline
337:Paths through an arbitrary
197:Natural language processing
181:object-oriented programming
2625:
1413:Introduction to Algorithms
760:
268:Computer-generated imagery
29:
2568:
2202:
1251:10.1007/978-1-4842-5725-8
929:with values of some type
925:, the abstract tree type
718:Enumerating all the items
278:binary space partitioning
207:Modeling utterances in a
2604:Knowledge representation
2292:Retrieval Data Structure
1922:Left-child right-sibling
1382:: Fundamental Algorithms
1350:10.3166/jancl.15.115-135
1245:. Berkeley, CA: Apress.
1035:Mathematical terminology
187:produces non-tree graphs
62:with a set of connected
30:Not to be confused with
2599:Trees (data structures)
2573:List of data structures
2550:Binary decision diagram
2113:Monte Carlo tree search
1752:data partitioning trees
1710:C-trie (compressed ADT)
1331:"PDL for ordered trees"
1195:Distributed tree search
328:Hierarchical clustering
308:Hierarchical taxonomies
75:a useful technique for
2555:Directed acyclic graph
771:, and the action is a
750:lowest common ancestor
350:mathematical hierarchy
303:Nested set collections
222:Document Object Models
193:for computer languages
81:linear data structures
43:
2171:Minimum spanning tree
810:dynamically allocated
724:Searching for an item
593:The number of leaves.
361:exploded-view drawing
191:Abstract syntax trees
121:trees in graph theory
40:
2421:Unrolled linked list
2156:Shortest path faster
2064:Breadth-first search
2059:Bidirectional search
2005:traversal algorithms
1932:Log-structured merge
1475:Tree data structures
1400:Charles E. Leiserson
1067:improve this section
883:improve this section
819:relational databases
797:breadth-first search
185:multiple inheritance
2609:Abstract data types
2469:Self-balancing tree
2091:Iterative deepening
1027:(empty forest) and
339:node-and-edge graph
323:Genetic programming
283:Digital compositing
154:Directory structure
125:trees in set theory
2449:Binary search tree
2314:Double-ended queue
2086:Depth-first search
1897:Fractal tree index
1492:associative arrays
1279:Weisstein, Eric W.
923:abstract data type
479:(also known as an
463:(also known as an
274:Space partitioning
250:binary search tree
209:generative grammar
106:abstract data type
56:abstract data type
44:
2581:
2580:
2383:Hashed array tree
2282:Associative array
2211:
2210:
2108:Jump point search
2049:Best-first search
1965:
1964:
1315:978-0-495-39132-6
1260:978-1-4842-5724-1
1153:), together with:
1131:whose underlying
1103:
1102:
1095:
982:with the axioms:
919:
918:
911:
713:Common operations
79:. In contrast to
54:is a widely used
16:(Redirected from
2616:
2406:Association list
2238:
2231:
2224:
2215:
1992:
1985:
1978:
1969:
1468:
1461:
1454:
1445:
1404:Ronald L. Rivest
1396:Thomas H. Cormen
1362:
1361:
1335:
1326:
1320:
1319:
1299:
1293:
1292:
1291:
1274:
1268:
1267:
1238:
1221:
1217:
1167:branching factor
1133:undirected graph
1098:
1091:
1087:
1084:
1078:
1047:
1039:
1030:
1026:
1011:
1007:
1003:
997:
993:
989:
978:
974:
970:
964:
958:
954:
948:
944:
936:
932:
928:
914:
907:
903:
900:
894:
863:
855:
769:walking the tree
730:Deleting an item
704:
698:
688:
683:
673:
668:
658:
653:
639:
634:
525:Parent or child.
366:Subroutine calls
240:search algorithm
224:("DOM tree") of
48:computer science
21:
2624:
2623:
2619:
2618:
2617:
2615:
2614:
2613:
2584:
2583:
2582:
2577:
2564:
2536:
2430:
2426:XOR linked list
2392:
2368:Circular buffer
2349:
2268:
2247:
2245:Data structures
2242:
2212:
2207:
2198:
2165:
2122:
2006:
1996:
1966:
1961:
1865:
1744:
1691:
1620:
1616:Weight-balanced
1571:Order statistic
1485:
1477:
1472:
1431:
1371:
1369:Further reading
1366:
1365:
1333:
1328:
1327:
1323:
1316:
1301:
1300:
1296:
1277:
1276:
1275:
1271:
1261:
1240:
1239:
1235:
1230:
1225:
1224:
1218:
1214:
1209:
1191:
1099:
1088:
1082:
1079:
1064:
1048:
1037:
1028:
1024:
1019:, a tree is an
1009:
1005:
1001:
995:
991:
987:
976:
972:
968:
962:
956:
952:
946:
942:
934:
930:
926:
915:
904:
898:
895:
880:
864:
853:
806:
804:Representations
765:
759:
715:
710:
709:
708:
707:
706:
702:
699:
691:
690:
686:
684:
676:
675:
671:
669:
661:
660:
656:
654:
646:
645:
637:
635:
624:
614:
606:
598:
590:
582:
574:
566:
558:
550:
538:
530:
522:
410:
173:Class hierarchy
137:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2622:
2620:
2612:
2611:
2606:
2601:
2596:
2586:
2585:
2579:
2578:
2576:
2575:
2569:
2566:
2565:
2563:
2562:
2557:
2552:
2546:
2544:
2538:
2537:
2535:
2534:
2533:
2532:
2522:
2521:
2520:
2518:Hilbert R-tree
2515:
2510:
2500:
2499:
2498:
2496:Fibonacci heap
2493:
2488:
2478:
2477:
2476:
2471:
2466:
2464:Red–black tree
2461:
2456:
2446:
2440:
2438:
2432:
2431:
2429:
2428:
2423:
2418:
2413:
2408:
2402:
2400:
2394:
2393:
2391:
2390:
2385:
2380:
2375:
2370:
2365:
2359:
2357:
2351:
2350:
2348:
2347:
2346:
2345:
2340:
2330:
2329:
2328:
2321:Priority queue
2318:
2317:
2316:
2306:
2301:
2296:
2295:
2294:
2289:
2278:
2276:
2270:
2269:
2267:
2266:
2261:
2255:
2253:
2249:
2248:
2243:
2241:
2240:
2233:
2226:
2218:
2209:
2208:
2203:
2200:
2199:
2197:
2196:
2194:Reverse-delete
2191:
2186:
2181:
2175:
2173:
2167:
2166:
2164:
2163:
2158:
2153:
2148:
2146:Floyd–Warshall
2143:
2138:
2132:
2130:
2124:
2123:
2121:
2120:
2115:
2110:
2105:
2100:
2095:
2094:
2093:
2083:
2078:
2077:
2076:
2071:
2061:
2056:
2051:
2046:
2045:
2044:
2039:
2034:
2022:
2016:
2014:
2008:
2007:
1997:
1995:
1994:
1987:
1980:
1972:
1963:
1962:
1960:
1959:
1954:
1949:
1944:
1939:
1934:
1929:
1924:
1919:
1914:
1909:
1904:
1899:
1894:
1889:
1884:
1879:
1873:
1871:
1867:
1866:
1864:
1863:
1858:
1853:
1848:
1843:
1838:
1833:
1828:
1823:
1818:
1813:
1808:
1803:
1798:
1781:
1776:
1771:
1766:
1761:
1755:
1753:
1746:
1745:
1743:
1742:
1737:
1732:
1730:Ternary search
1727:
1722:
1717:
1712:
1707:
1701:
1699:
1693:
1692:
1690:
1689:
1684:
1679:
1674:
1669:
1664:
1659:
1654:
1646:
1641:
1636:
1630:
1628:
1622:
1621:
1619:
1618:
1613:
1608:
1603:
1598:
1593:
1588:
1578:
1573:
1568:
1563:
1558:
1553:
1543:
1538:
1533:
1528:
1523:
1518:
1513:
1508:
1503:
1497:
1495:
1479:
1478:
1473:
1471:
1470:
1463:
1456:
1448:
1442:
1441:
1430:
1429:External links
1427:
1426:
1425:
1408:Clifford Stein
1393:
1370:
1367:
1364:
1363:
1344:(2): 115–135.
1321:
1314:
1294:
1269:
1259:
1232:
1231:
1229:
1226:
1223:
1222:
1211:
1210:
1208:
1205:
1204:
1203:
1197:
1190:
1187:
1163:
1162:
1159:
1156:
1155:
1154:
1143:
1140:
1129:
1126:directed graph
1101:
1100:
1051:
1049:
1042:
1036:
1033:
1021:inductive type
1013:
1012:
1000:children(node(
998:
980:
979:
965:
959:
949:
917:
916:
867:
865:
858:
852:
849:
815:adjacency list
805:
802:
763:Tree traversal
761:Main article:
758:
755:
754:
753:
746:
743:
737:
731:
728:
725:
722:
719:
714:
711:
700:
693:
692:
685:
678:
677:
670:
663:
662:
655:
648:
647:
636:
629:
628:
627:
626:
625:
623:
620:
619:
618:
615:
613:Size of a tree
612:
610:
607:
604:
602:
599:
596:
594:
591:
588:
586:
583:
580:
578:
575:
572:
570:
567:
564:
562:
559:
557:Degree of tree
556:
554:
551:
548:
546:
539:
536:
534:
531:
528:
526:
523:
520:
471:for short, or
446:ancestor nodes
409:
406:
387:
386:
380:
369:
363:
353:
352:
346:
331:
330:
325:
320:
315:
305:
300:
294:
287:
286:
285:
280:
265:
258:
257:
256:
244:tree traversal
233:
219:
218:
217:
211:
205:
194:
188:
170:
169:
168:
165:
158:symbolic links
136:
133:
110:adjacency list
77:tree traversal
60:tree structure
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2621:
2610:
2607:
2605:
2602:
2600:
2597:
2595:
2592:
2591:
2589:
2574:
2571:
2570:
2567:
2561:
2558:
2556:
2553:
2551:
2548:
2547:
2545:
2543:
2539:
2531:
2528:
2527:
2526:
2523:
2519:
2516:
2514:
2511:
2509:
2506:
2505:
2504:
2501:
2497:
2494:
2492:
2491:Binomial heap
2489:
2487:
2484:
2483:
2482:
2479:
2475:
2472:
2470:
2467:
2465:
2462:
2460:
2457:
2455:
2452:
2451:
2450:
2447:
2445:
2442:
2441:
2439:
2437:
2433:
2427:
2424:
2422:
2419:
2417:
2414:
2412:
2409:
2407:
2404:
2403:
2401:
2399:
2395:
2389:
2388:Sparse matrix
2386:
2384:
2381:
2379:
2376:
2374:
2373:Dynamic array
2371:
2369:
2366:
2364:
2361:
2360:
2358:
2356:
2352:
2344:
2341:
2339:
2336:
2335:
2334:
2331:
2327:
2324:
2323:
2322:
2319:
2315:
2312:
2311:
2310:
2307:
2305:
2302:
2300:
2297:
2293:
2290:
2288:
2285:
2284:
2283:
2280:
2279:
2277:
2275:
2271:
2265:
2262:
2260:
2257:
2256:
2254:
2250:
2246:
2239:
2234:
2232:
2227:
2225:
2220:
2219:
2216:
2206:
2201:
2195:
2192:
2190:
2187:
2185:
2182:
2180:
2177:
2176:
2174:
2172:
2168:
2162:
2159:
2157:
2154:
2152:
2149:
2147:
2144:
2142:
2139:
2137:
2134:
2133:
2131:
2129:
2128:Shortest path
2125:
2119:
2116:
2114:
2111:
2109:
2106:
2104:
2103:Fringe search
2101:
2099:
2096:
2092:
2089:
2088:
2087:
2084:
2082:
2079:
2075:
2072:
2070:
2069:Lexicographic
2067:
2066:
2065:
2062:
2060:
2057:
2055:
2052:
2050:
2047:
2043:
2040:
2038:
2035:
2033:
2030:
2029:
2028:
2027:
2023:
2021:
2018:
2017:
2015:
2013:
2009:
2004:
2000:
1993:
1988:
1986:
1981:
1979:
1974:
1973:
1970:
1958:
1955:
1953:
1950:
1948:
1945:
1943:
1940:
1938:
1935:
1933:
1930:
1928:
1925:
1923:
1920:
1918:
1915:
1913:
1910:
1908:
1907:Hash calendar
1905:
1903:
1900:
1898:
1895:
1893:
1890:
1888:
1885:
1883:
1880:
1878:
1875:
1874:
1872:
1868:
1862:
1859:
1857:
1854:
1852:
1849:
1847:
1844:
1842:
1839:
1837:
1834:
1832:
1829:
1827:
1824:
1822:
1819:
1817:
1814:
1812:
1809:
1807:
1804:
1802:
1799:
1796:
1794:
1788:
1786:
1782:
1780:
1777:
1775:
1772:
1770:
1767:
1765:
1762:
1760:
1757:
1756:
1754:
1751:
1747:
1741:
1738:
1736:
1733:
1731:
1728:
1726:
1723:
1721:
1718:
1716:
1713:
1711:
1708:
1706:
1703:
1702:
1700:
1698:
1694:
1688:
1685:
1683:
1682:van Emde Boas
1680:
1678:
1675:
1673:
1672:Skew binomial
1670:
1668:
1665:
1663:
1660:
1658:
1655:
1653:
1651:
1647:
1645:
1642:
1640:
1637:
1635:
1632:
1631:
1629:
1627:
1623:
1617:
1614:
1612:
1609:
1607:
1604:
1602:
1599:
1597:
1594:
1592:
1589:
1587:
1583:
1579:
1577:
1574:
1572:
1569:
1567:
1564:
1562:
1559:
1557:
1554:
1552:
1551:Binary search
1548:
1544:
1542:
1539:
1537:
1534:
1532:
1529:
1527:
1524:
1522:
1519:
1517:
1514:
1512:
1509:
1507:
1504:
1502:
1499:
1498:
1496:
1493:
1489:
1484:
1480:
1476:
1469:
1464:
1462:
1457:
1455:
1450:
1449:
1446:
1440:
1436:
1433:
1432:
1428:
1423:
1422:0-262-03293-7
1419:
1415:
1414:
1409:
1405:
1401:
1397:
1394:
1391:
1390:0-201-89683-4
1387:
1383:
1381:
1376:
1373:
1372:
1368:
1359:
1355:
1351:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1332:
1325:
1322:
1317:
1311:
1307:
1306:
1298:
1295:
1289:
1288:
1283:
1280:
1273:
1270:
1266:
1262:
1256:
1252:
1248:
1244:
1237:
1234:
1227:
1220:descendants).
1216:
1213:
1206:
1201:
1198:
1196:
1193:
1192:
1188:
1186:
1182:
1180:
1176:
1172:
1168:
1160:
1157:
1152:
1148:
1144:
1141:
1138:
1134:
1130:
1127:
1123:
1122:
1121:"), meaning:
1120:
1116:
1112:
1111:
1110:
1108:
1097:
1094:
1086:
1076:
1072:
1068:
1062:
1061:
1057:
1052:This section
1050:
1046:
1041:
1040:
1034:
1032:
1022:
1018:
999:
985:
984:
983:
966:
960:
950:
940:
939:
938:
924:
913:
910:
902:
892:
888:
884:
878:
877:
873:
868:This section
866:
862:
857:
856:
850:
848:
845:
843:
842:S-expressions
838:
833:
831:
827:
822:
820:
816:
811:
803:
801:
798:
794:
790:
786:
782:
778:
774:
770:
764:
756:
751:
747:
744:
741:
738:
735:
732:
729:
726:
723:
720:
717:
716:
712:
697:
682:
667:
652:
643:
633:
621:
616:
611:
608:
603:
600:
595:
592:
587:
584:
579:
576:
571:
568:
563:
560:
555:
552:
547:
544:
540:
535:
532:
527:
524:
519:
517:
514:
512:
507:
505:
501:
497:
492:
490:
489:terminal node
486:
482:
478:
477:external node
474:
470:
466:
462:
461:internal node
457:
455:
451:
450:sibling nodes
447:
443:
439:
435:
431:
427:
423:
419:
415:
407:
405:
403:
399:
395:
391:
385:
381:
378:
374:
370:
367:
364:
362:
358:
357:
356:
351:
347:
344:
340:
336:
335:
334:
329:
326:
324:
321:
319:
316:
313:
309:
306:
304:
301:
299:
296:Implementing
295:
292:
288:
284:
281:
279:
275:
272:
271:
269:
266:
263:
260:Representing
259:
255:
252:is a type of
251:
247:
246:
245:
242:possible via
241:
237:
234:
231:
227:
223:
220:
215:
214:Dialogue tree
212:
210:
206:
204:
201:
200:
198:
195:
192:
189:
186:
182:
178:
174:
171:
166:
163:
159:
155:
152:
151:
149:
146:
145:
144:
142:
134:
132:
130:
126:
122:
117:
115:
111:
107:
102:
100:
96:
92:
88:
84:
82:
78:
74:
69:
65:
61:
57:
53:
49:
39:
33:
19:
18:Internal node
2435:
2343:Disjoint-set
2136:Bellman–Ford
2025:
1792:
1784:
1649:
1582:Left-leaning
1488:dynamic sets
1483:Search trees
1474:
1411:
1378:
1375:Donald Knuth
1341:
1337:
1324:
1304:
1297:
1285:
1272:
1264:
1242:
1236:
1215:
1183:
1178:
1174:
1164:
1150:
1146:
1119:arborescence
1107:ordered tree
1104:
1089:
1080:
1065:Please help
1053:
1015:In terms of
1014:
981:
920:
905:
896:
881:Please help
869:
846:
834:
823:
807:
792:
784:
780:
776:
772:
768:
766:
752:of two nodes
748:Finding the
605:Ordered tree
542:
515:
510:
508:
503:
499:
495:
493:
488:
484:
480:
476:
472:
468:
464:
460:
458:
453:
449:
445:
441:
433:
429:
425:
421:
417:
411:
402:dictionaries
388:
354:
332:
310:such as the
276:, including
262:sorted lists
236:Search trees
148:File systems
141:hierarchical
138:
135:Applications
118:
103:
98:
95:graph theory
91:ordered tree
87:Binary trees
85:
67:
51:
45:
2486:Binary heap
2411:Linked list
2054:Beam search
2020:α–β pruning
1882:Exponential
1870:Other trees
1435:Description
1115:rooted tree
1017:type theory
986:value(node(
851:Type theory
837:binary tree
830:binary heap
793:level-order
789:binary tree
473:branch node
434:parent node
430:descendants
426:child nodes
408:Terminology
343:multigraphs
341:(including
254:binary tree
203:Parse trees
2594:Data types
2588:Categories
2474:Splay tree
2378:Hash table
2259:Collection
2141:Dijkstra's
1826:Priority R
1576:Palindrome
1228:References
1083:April 2022
961:nil: () →
951:children:
899:April 2022
781:post-order
687:Not a tree
672:Not a tree
657:Not a tree
640:: two non-
638:Not a tree
537:Descendant
481:outer node
465:inner node
384:namespaces
291:Barnes–Hut
162:hard links
99:leaf nodes
42:hierarchy.
2530:Hash tree
2416:Skip list
2363:Bit array
2264:Container
2184:Kruskal's
2179:Borůvka's
2151:Johnson's
1912:iDistance
1791:implicit
1779:Hilbert R
1774:Cartesian
1657:Fibonacci
1591:Scapegoat
1586:Red–black
1437:from the
1287:MathWorld
1282:"Subtree"
1179:non-empty
1171:outdegree
1054:does not
870:does not
777:pre-order
642:connected
504:root path
485:leaf node
442:root node
373:evolution
232:documents
73:recursion
2459:AVL tree
2338:Multiset
2287:Multimap
2274:Abstract
2074:Parallel
1927:Link/cut
1639:Binomial
1566:Interval
1189:See also
785:in-order
740:Grafting
565:Distance
543:subchild
529:Ancestor
521:Neighbor
438:superior
289:Storing
2513:R+ tree
2508:R* tree
2454:AA tree
1887:Fenwick
1851:Segment
1750:Spatial
1667:Pairing
1662:Leftist
1584:)
1556:Dancing
1549:)
1547:Optimal
1358:1979330
1175:at most
1075:removed
1060:sources
941:value:
891:removed
876:sources
734:Pruning
589:Breadth
511:subtree
264:of data
177:classes
114:indexes
2542:Graphs
2503:R-tree
2444:B-tree
2398:Linked
2355:Arrays
2189:Prim's
2012:Search
1937:Merkle
1902:Fusion
1892:Finger
1816:Octree
1806:Metric
1740:Y-fast
1735:X-fast
1725:Suffix
1644:Brodal
1634:Binary
1420:
1406:, and
1388:
1356:
1312:
1257:
1147:parent
967:node:
921:As an
703:a tree
597:Forest
549:Degree
496:height
127:, and
2436:Trees
2309:Queue
2304:Stack
2252:Types
2161:Yen's
1999:Graph
1947:Range
1917:K-ary
1877:Cover
1720:Radix
1705:Ctrie
1697:Tries
1626:Heaps
1606:Treap
1596:Splay
1561:HTree
1516:(a,b)
1506:2–3–4
1354:S2CID
1334:(PDF)
1207:Notes
1151:child
1135:is a
1008:)) =
994:)) =
826:array
817:. In
791:.) A
581:Width
573:Level
500:depth
487:, or
469:inode
454:empty
422:links
418:edges
398:lists
298:heaps
150:for:
64:nodes
2525:Trie
2481:Heap
2299:List
2118:SSS*
2042:SMA*
2037:LPA*
2032:IDA*
2003:tree
2001:and
1952:SPQR
1831:Quad
1759:Ball
1715:Hash
1687:Weak
1677:Skew
1652:-ary
1418:ISBN
1386:ISBN
1310:ISBN
1255:ISBN
1177:two
1137:tree
1058:any
1056:cite
1029:node
874:any
872:cite
773:walk
494:The
436:(or
414:node
400:and
394:YAML
392:and
390:JSON
348:Any
230:HTML
228:and
104:The
68:root
52:tree
50:, a
32:Trie
2333:Set
1957:Top
1811:MVP
1769:BSP
1521:AVL
1501:2–3
1346:doi
1247:doi
1069:by
1025:nil
885:by
832:).
459:An
420:or
226:XML
179:in
93:in
46:In
2590::
2098:D*
2081:B*
2026:A*
1942:PQ
1856:VP
1846:R*
1841:R+
1821:PH
1795:-d
1787:-d
1764:BK
1611:UB
1536:B*
1531:B+
1511:AA
1410:.
1402:,
1398:,
1377:.
1352:.
1342:15
1340:.
1336:.
1284:.
1263:.
1253:.
1124:A
1113:A
1004:,
990:,
975:→
971:×
955:→
945:→
835:A
483:,
467:,
456:.
412:A
404:.
270::
248:A
199::
183:;
131:.
123:,
2237:e
2230:t
2223:v
1991:e
1984:t
1977:v
1861:X
1836:R
1801:M
1797:)
1793:k
1789:(
1785:k
1650:d
1601:T
1580:(
1545:(
1541:B
1526:B
1494:)
1490:/
1486:(
1467:e
1460:t
1453:v
1360:.
1348::
1318:.
1290:.
1249::
1169:(
1128:,
1096:)
1090:(
1085:)
1081:(
1077:.
1063:.
1010:f
1006:f
1002:e
996:e
992:f
988:e
977:T
973:F
969:E
963:F
957:F
953:T
947:E
943:T
935:F
931:E
927:T
912:)
906:(
901:)
897:(
893:.
879:.
705:.
545:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.