2613:
259:
2205:
2608:{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}q_{n-1}&=\lambda _{1}+\dots +\lambda _{n-1}=\mathrm {tr} Q=2|E|\\q_{n-2}&=\lambda _{1}\lambda _{2}+\lambda _{1}\lambda _{3}+\dots +\lambda _{n-2}\lambda _{n-1}\\q_{2}&=\lambda _{1}\dots \lambda _{n-2}+\lambda _{1}\dots \lambda _{n-3}\lambda _{n-1}+\dots +\lambda _{2}\dots \lambda _{n-1}\\q_{1}&=\lambda _{1}\dots \lambda _{n-1}\\\end{aligned}}}
1309:
857:
610:
First notice that the
Laplacian matrix has the property that the sum of its entries across any row and any column is 0. Thus we can transform any minor into any other minor by adding rows and columns, switching them, and multiplying a row or a column by −1. Thus the cofactors are the same up to sign,
1050:
1455:
in the resulting expression represents a spanning tree consisting of the edges corresponding to the indeterminates appearing in that monomial. In this way, one can obtain explicit enumeration of all the spanning trees of the graph simply by computing the determinant.
2149:
1158:
1123:
follows from
Kirchhoff's theorem as a special case, since every vector with 1 in one place, −1 in another place, and 0 elsewhere is an eigenvector of the Laplacian matrix of the complete graph, with the corresponding eigenvalue being
701:
245:
914:
1403:
Kirchhoff's theorem can be strengthened by altering the definition of the
Laplacian matrix. Rather than merely counting edges emanating from each vertex or connecting a pair of vertices, label each edge with an
1935:
1737:
2210:
2006:
1304:{\displaystyle {\begin{bmatrix}n-1&-1&\cdots &-1\\-1&n-1&\cdots &-1\\\vdots &\vdots &\ddots &\vdots \\-1&-1&\cdots &n-1\\\end{bmatrix}}.}
1447:
The determinant of the modified
Laplacian matrix by deleting any row and column (similar to finding the number of spanning trees from the original Laplacian matrix), above is then a
1795:
2692:
562:
1638:
2198:
1971:
434:
852:{\displaystyle E={\begin{bmatrix}1&1&0&0&0\\-1&0&1&1&0\\0&-1&-1&0&1\\0&0&0&-1&-1\\\end{bmatrix}}.}
2730:
1998:
1856:
1829:
1451:(the Kirchhoff polynomial) in the indeterminates corresponding to the edges of the graph. After collecting terms and performing all possible cancellations, each
1471:, so Kirchhoff's theorem provides a formula to count the number of bases in a graphic matroid. The same method may also be used to count the number of bases in
165:
1045:{\displaystyle \det \left(M_{11}\right)=\sum _{S}\det \left(F_{S}\right)\det \left(F_{S}^{\mathrm {T} }\right)=\sum _{S}\det \left(F_{S}\right)^{2}}
2949:
2866:
2825:
2902:
1094:− 1 edges of the original graph, and it can be shown that those edges induce a spanning tree if and only if the determinant of
3021:
2789:
O'Toole, J.B. "On the
Solution of the Equations Obtained from the Investigation of the Linear Distribution of Galvanic Currents".
88:
Kirchhoff's theorem relies on the notion of the
Laplacian matrix of a graph, which is equal to the difference between the graph's
1590:
that contains all vertices and is cycle-free, i.e., there is at most one path between each pair of vertices. Given such a forest
1864:
3011:
20:
1643:
1101:
is +1 or −1, and that they do not induce a spanning tree if and only if the determinant is 0. This completes the proof.
51:
1487:
Kirchhoff's theorem can be modified to count the number of oriented spanning trees in directed multigraphs. The matrix
2749:
112:
2144:{\displaystyle q_{k}=\sum _{\{i_{1},\dots ,i_{n-k}\}\subset \{1\dots n-1\}}\lambda _{i_{1}}\dots \lambda _{i_{n-k}}.}
1416:)-th entry of the modified Laplacian matrix be the sum over the indeterminates corresponding to edges between the
3026:
2759:
2733:
680:
74:
905:
600:
1587:
1405:
1129:
2911:
Maurer, Stephen B. (1976), "Matrix generalizations of some theorems on trees, cycles and cocycles in graphs",
1138:
Alternatively, note that as Cayley's formula counts the number of distinct labeled trees of a complete graph
250:
An
English translation of Kirchhoff's original 1847 paper was made by J. B. O'Toole and published in 1958.
3016:
1745:
1448:
604:
2764:
1576:
124:
97:
2647:
453:
258:
1597:
1365:
1120:
1115:
78:
2637:= 1 case corresponds to the original Kirchhoff theorem since the weight of every spanning tree is
262:
The Matrix-Tree
Theorem can be used to compute the number of labeled spanning trees of this graph.
2769:
2165:
1943:
108:
with 1's at places corresponding to entries where the vertices are adjacent and 0's otherwise).
2978:
2945:
2862:
2831:
2821:
283:
2968:
2920:
2854:
2798:
867:
298:
101:
67:
43:
2932:
2928:
1472:
1468:
93:
55:
1432:, and the negative sum over all indeterminates corresponding to edges emanating from the
2708:
1976:
1834:
1807:
82:
475:
3005:
2973:
2644:
The proof can be done analogously to the proof of
Kirchhoff's theorem. An invertible
271:
89:
47:
2754:
240:{\displaystyle t(G)={\frac {1}{n}}\lambda _{1}\lambda _{2}\cdots \lambda _{n-1}\,.}
105:
31:
59:
27:
2858:
1327:
152:
2982:
2835:
2802:
2695:
871:
607:
argument for
Kirchhoff's theorem can be found on page 654 of Moore (2011).)
63:
1391:
by same methods produced above, since a simple graph is a multigraph with
2996:
1452:
2702:-component spanning forest with a choice of vertex for each component.
2924:
1739:
to be the product of the number of vertices in each component. Then
77:
of the Laplacian matrix. Kirchhoff's theorem is a generalization of
2897:
Harris, John M.; Hirst, Jeffry L.; Mossinghoff, Michael J. (2008),
257:
1940:
The last factor in the polynomial is due to the zero eigenvalue
1459:
For a proof of this version of the theorem see Bollobás (1998).
611:
and it can be verified that, in fact, they have the same sign.
155:
of its Laplacian matrix. Then the number of spanning trees of
1135: − 1, so there are no other non-zero eigenvalues.
1145:
we need to compute any cofactor of the Laplacian matrix of
2959:
Chaiken, S.; Kleitman, D. (1978), "Matrix Tree Theorems",
1930:{\displaystyle (x+\lambda _{1})\dots (x+\lambda _{n-1})x.}
1548:
The number of oriented spanning trees rooted at a vertex
1732:{\textstyle w(F)=|V(F_{1})|\cdot \dots \cdot |V(F_{k})|}
1552:
is the determinant of the matrix gotten by removing the
641:
matrix, which may be defined as follows: suppose that (
2711:
2168:
1979:
1946:
1837:
1810:
1646:
1600:
1167:
716:
2650:
2208:
2009:
1867:
1748:
1161:
917:
704:
614:
We proceed to show that the determinant of the minor
456:
286:
168:
2820:. Oxford England New York: Oxford University Press.
447:. For example, deleting row 1 and column 1 yields
2724:
2686:
2629:−1 case states that the sum of the eigenvalues of
2607:
2192:
2143:
1992:
1965:
1929:
1850:
1823:
1789:
1731:
1632:
1467:The spanning trees of a graph form the bases of a
1303:
1044:
851:
556:
428:
239:
683:for understanding this modified incidence matrix
81:which provides the number of spanning trees in a
2621:−1 components corresponds to a single edge, the
1571:Kirchhoff's theorem can be generalized to count
1482:
1014:
973:
952:
918:
2694:submatrix of the incidence matrix corresponds
1583:-component spanning forest is a subgraph with
1372:Cayley's formula for a complete multigraph is
629:the number of its edges. The incidence matrix
54:, showing that this number can be computed in
1078:− 1) matrix whose columns are those of
579:), which is 8 for the diamond graph. (Notice
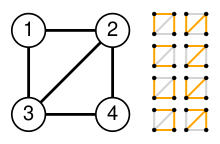
8:
2187:
2169:
2090:
2072:
2066:
2028:
1483:Kirchhoff's theorem for directed multigraphs
1475:, a generalization of the graphic matroids (
625:be the number of vertices of the graph, and
2944:, Cambridge University Press, p. 138,
1364:when counting the degree of a vertex, all
1128:. These vectors together span a space of
16:On the number of spanning trees in a graph
2972:
2961:Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A
2716:
2710:
2649:
2589:
2576:
2559:
2539:
2526:
2501:
2485:
2472:
2453:
2440:
2423:
2403:
2387:
2368:
2358:
2345:
2335:
2312:
2299:
2291:
2274:
2259:
2240:
2217:
2209:
2207:
2167:
2124:
2119:
2104:
2099:
2054:
2035:
2027:
2014:
2008:
1984:
1978:
1951:
1945:
1906:
1881:
1866:
1842:
1836:
1815:
1809:
1778:
1753:
1747:
1724:
1715:
1700:
1686:
1677:
1662:
1645:
1624:
1605:
1599:
1162:
1160:
1036:
1026:
1008:
990:
989:
984:
963:
946:
929:
916:
711:
703:
621:counts the number of spanning trees. Let
474:
461:
455:
297:
285:
233:
221:
208:
198:
184:
167:
866:can be factored into the product of the
443:by deleting any row and any column from
254:An example using the matrix-tree theorem
2781:
2732:are up to sign the coefficients of the
1321:
1152:. The Laplacian matrix in this case is
70:; specifically, the number is equal to
1476:
1399:Explicit enumeration of spanning trees
675:= −1, and all other entries in column
266:First, construct the Laplacian matrix
7:
1790:{\displaystyle \sum _{F}w(F)=q_{k},}
1314:Any cofactor of the above matrix is
1105:Particular cases and generalizations
890:with its first row deleted, so that
687:). For the preceding example (with
2913:SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics
1322:Kirchhoff's theorem for multigraphs
2903:Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics
2791:IRE Transactions on Circuit Theory
2633:is twice the number of edges. The
2278:
2275:
1059:ranges across subsets of of size
991:
14:
2687:{\displaystyle (n-k)\times (n-k)}
599:(The proof below is based on the
567:Finally, take the determinant of
46:is a theorem about the number of
1804:-component spanning forests and
557:{\displaystyle Q^{\ast }=\left.}
2750:List of topics related to trees
1633:{\textstyle F_{1},\dots ,F_{k}}
1353:is the number of edges between
653:th edge of the graph, and that
40:Kirchhoff's matrix tree theorem
2997:A proof of Kirchhoff's theorem
2899:Combinatorics and Graph Theory
2681:
2669:
2663:
2651:
2300:
2292:
1973:. More explicitly, the number
1918:
1893:
1887:
1868:
1768:
1762:
1725:
1721:
1708:
1701:
1687:
1683:
1670:
1663:
1656:
1650:
1326:Kirchhoff's theorem holds for
178:
172:
1:
2886:. Cambridge University Press.
2617:Since a spanning forest with
1540:minus the number of loops at
1318:, which is Cayley's formula.
2974:10.1016/0097-3165(78)90067-5
1518:is the number of edges from
21:Kirchhoff's integral theorem
2193:{\textstyle \{1,\dots ,n\}}
1966:{\textstyle \lambda _{n}=0}
1491:is constructed as follows:
587:) is the (1,1)-cofactor of
3043:
2816:Moore, Cristopher (2011).
2154:where the sum is over all
1800:where the sum is over all
1594:with connected components
1579:in an unweighted graph. A
1113:
862:Recall that the Laplacian
277:(see image on the right):
18:
2859:10.1007/978-1-4612-0619-4
2818:The nature of computation
2760:Markov chain tree theorem
2734:characteristic polynomial
681:oriented incidence matrix
439:Next, construct a matrix
3022:Theorems in graph theory
2905:(2nd ed.), Springer
2803:10.1109/TCT.1958.1086426
1334:is modified as follows:
429:{\displaystyle Q=\left.}
19:Not to be confused with
2849:Bollobás, Béla (1998).
1536:equals the indegree of
1109:
3012:Algebraic graph theory
2884:Algebraic Graph Theory
2853:. New York: Springer.
2726:
2688:
2609:
2194:
2145:
1994:
1967:
1931:
1852:
1831:is the coefficient of
1825:
1791:
1733:
1634:
1449:homogeneous polynomial
1305:
1046:
853:
558:
430:
263:
241:
2940:Tutte, W. T. (2001),
2765:Minimum spanning tree
2727:
2689:
2610:
2195:
2146:
1995:
1968:
1932:
1853:
1826:
1792:
1734:
1635:
1556:th row and column of
1306:
1047:
854:
559:
431:
261:
242:
2709:
2648:
2206:
2166:
2162:-element subsets of
2007:
1977:
1944:
1865:
1835:
1808:
1746:
1644:
1640:, define its weight
1598:
1588:connected components
1575:-component spanning
1330:as well; the matrix
1159:
915:
906:Cauchy–Binet formula
702:
601:Cauchy–Binet formula
454:
284:
166:
2851:Modern graph theory
2000:can be computed as
996:
908:allows us to write
882:. Furthermore, let
36:Kirchhoff's theorem
2882:Biggs, N. (1993).
2725:{\textstyle q_{k}}
2722:
2684:
2605:
2603:
2190:
2141:
2094:
1993:{\textstyle q_{k}}
1990:
1963:
1927:
1858:of the polynomial
1851:{\textstyle x^{k}}
1848:
1824:{\textstyle q_{k}}
1821:
1787:
1758:
1729:
1630:
1567:-component forests
1563:Counting spanning
1424:-th vertices when
1301:
1292:
1042:
1013:
980:
951:
849:
840:
591:in this example.)
554:
545:
426:
417:
264:
237:
2951:978-0-521-79489-3
2868:978-0-387-98488-9
2827:978-0-19-923321-2
2705:The coefficients
2023:
1749:
1004:
942:
192:
141:, ...,
3034:
3027:Gustav Kirchhoff
2985:
2976:
2954:
2935:
2906:
2888:
2887:
2879:
2873:
2872:
2846:
2840:
2839:
2813:
2807:
2806:
2786:
2731:
2729:
2728:
2723:
2721:
2720:
2693:
2691:
2690:
2685:
2614:
2612:
2611:
2606:
2604:
2600:
2599:
2581:
2580:
2564:
2563:
2550:
2549:
2531:
2530:
2512:
2511:
2496:
2495:
2477:
2476:
2464:
2463:
2445:
2444:
2428:
2427:
2414:
2413:
2398:
2397:
2373:
2372:
2363:
2362:
2350:
2349:
2340:
2339:
2323:
2322:
2303:
2295:
2281:
2270:
2269:
2245:
2244:
2228:
2227:
2199:
2197:
2196:
2191:
2150:
2148:
2147:
2142:
2137:
2136:
2135:
2134:
2111:
2110:
2109:
2108:
2093:
2065:
2064:
2040:
2039:
2019:
2018:
1999:
1997:
1996:
1991:
1989:
1988:
1972:
1970:
1969:
1964:
1956:
1955:
1936:
1934:
1933:
1928:
1917:
1916:
1886:
1885:
1857:
1855:
1854:
1849:
1847:
1846:
1830:
1828:
1827:
1822:
1820:
1819:
1803:
1796:
1794:
1793:
1788:
1783:
1782:
1757:
1738:
1736:
1735:
1730:
1728:
1720:
1719:
1704:
1690:
1682:
1681:
1666:
1639:
1637:
1636:
1631:
1629:
1628:
1610:
1609:
1586:
1582:
1574:
1473:regular matroids
1436:-th vertex when
1390:
1310:
1308:
1307:
1302:
1297:
1296:
1121:Cayley's formula
1116:Cayley's formula
1110:Cayley's formula
1051:
1049:
1048:
1043:
1041:
1040:
1035:
1031:
1030:
1012:
1000:
995:
994:
988:
972:
968:
967:
950:
938:
934:
933:
868:incidence matrix
858:
856:
855:
850:
845:
844:
603:. An elementary
563:
561:
560:
555:
550:
546:
466:
465:
435:
433:
432:
427:
422:
418:
270:for the example
246:
244:
243:
238:
232:
231:
213:
212:
203:
202:
193:
185:
151:be the non-zero
102:adjacency matrix
79:Cayley's formula
68:Laplacian matrix
44:Gustav Kirchhoff
3042:
3041:
3037:
3036:
3035:
3033:
3032:
3031:
3002:
3001:
2993:
2988:
2958:
2952:
2939:
2925:10.1137/0130017
2910:
2896:
2892:
2891:
2881:
2880:
2876:
2869:
2848:
2847:
2843:
2828:
2815:
2814:
2810:
2788:
2787:
2783:
2778:
2770:Prüfer sequence
2746:
2712:
2707:
2706:
2646:
2645:
2602:
2601:
2585:
2572:
2565:
2555:
2552:
2551:
2535:
2522:
2497:
2481:
2468:
2449:
2436:
2429:
2419:
2416:
2415:
2399:
2383:
2364:
2354:
2341:
2331:
2324:
2308:
2305:
2304:
2255:
2236:
2229:
2213:
2204:
2203:
2164:
2163:
2120:
2115:
2100:
2095:
2050:
2031:
2010:
2005:
2004:
1980:
1975:
1974:
1947:
1942:
1941:
1902:
1877:
1863:
1862:
1838:
1833:
1832:
1811:
1806:
1805:
1801:
1774:
1744:
1743:
1711:
1673:
1642:
1641:
1620:
1601:
1596:
1595:
1584:
1580:
1572:
1569:
1534:
1500:
1485:
1469:graphic matroid
1465:
1428:does not equal
1401:
1373:
1343:
1324:
1291:
1290:
1279:
1274:
1266:
1257:
1256:
1251:
1246:
1241:
1235:
1234:
1226:
1221:
1210:
1201:
1200:
1192:
1187:
1179:
1163:
1157:
1156:
1150:
1143:
1118:
1112:
1107:
1099:
1074:− 1)-by-(
1068:
1063:− 1, and
1022:
1018:
1017:
976:
959:
955:
925:
921:
913:
912:
900:
839:
838:
830:
822:
817:
812:
806:
805:
800:
795:
787:
779:
773:
772:
767:
762:
757:
752:
743:
742:
737:
732:
727:
722:
712:
700:
699:
673:
666:
620:
597:
544:
543:
538:
530:
521:
520:
512:
507:
498:
497:
489:
481:
470:
457:
452:
451:
416:
415:
410:
402:
394:
388:
387:
379:
374:
366:
357:
356:
348:
340:
335:
326:
325:
320:
312:
304:
293:
282:
281:
256:
217:
204:
194:
164:
163:
150:
146:
140:
133:
94:diagonal matrix
66:of the graph's
56:polynomial time
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
3040:
3038:
3030:
3029:
3024:
3019:
3014:
3004:
3003:
3000:
2999:
2992:
2991:External links
2989:
2987:
2986:
2967:(3): 377–381,
2956:
2950:
2937:
2919:(1): 143–148,
2908:
2893:
2890:
2889:
2874:
2867:
2841:
2826:
2808:
2780:
2779:
2777:
2774:
2773:
2772:
2767:
2762:
2757:
2752:
2745:
2742:
2719:
2715:
2683:
2680:
2677:
2674:
2671:
2668:
2665:
2662:
2659:
2656:
2653:
2598:
2595:
2592:
2588:
2584:
2579:
2575:
2571:
2568:
2566:
2562:
2558:
2554:
2553:
2548:
2545:
2542:
2538:
2534:
2529:
2525:
2521:
2518:
2515:
2510:
2507:
2504:
2500:
2494:
2491:
2488:
2484:
2480:
2475:
2471:
2467:
2462:
2459:
2456:
2452:
2448:
2443:
2439:
2435:
2432:
2430:
2426:
2422:
2418:
2417:
2412:
2409:
2406:
2402:
2396:
2393:
2390:
2386:
2382:
2379:
2376:
2371:
2367:
2361:
2357:
2353:
2348:
2344:
2338:
2334:
2330:
2327:
2325:
2321:
2318:
2315:
2311:
2307:
2306:
2302:
2298:
2294:
2290:
2287:
2284:
2280:
2277:
2273:
2268:
2265:
2262:
2258:
2254:
2251:
2248:
2243:
2239:
2235:
2232:
2230:
2226:
2223:
2220:
2216:
2212:
2211:
2200:. For example
2189:
2186:
2183:
2180:
2177:
2174:
2171:
2152:
2151:
2140:
2133:
2130:
2127:
2123:
2118:
2114:
2107:
2103:
2098:
2092:
2089:
2086:
2083:
2080:
2077:
2074:
2071:
2068:
2063:
2060:
2057:
2053:
2049:
2046:
2043:
2038:
2034:
2030:
2026:
2022:
2017:
2013:
1987:
1983:
1962:
1959:
1954:
1950:
1938:
1937:
1926:
1923:
1920:
1915:
1912:
1909:
1905:
1901:
1898:
1895:
1892:
1889:
1884:
1880:
1876:
1873:
1870:
1845:
1841:
1818:
1814:
1798:
1797:
1786:
1781:
1777:
1773:
1770:
1767:
1764:
1761:
1756:
1752:
1727:
1723:
1718:
1714:
1710:
1707:
1703:
1699:
1696:
1693:
1689:
1685:
1680:
1676:
1672:
1669:
1665:
1661:
1658:
1655:
1652:
1649:
1627:
1623:
1619:
1616:
1613:
1608:
1604:
1568:
1561:
1546:
1545:
1532:
1527:
1498:
1484:
1481:
1464:
1461:
1400:
1397:
1370:
1369:
1362:
1341:
1323:
1320:
1312:
1311:
1300:
1295:
1289:
1286:
1283:
1280:
1278:
1275:
1273:
1270:
1267:
1265:
1262:
1259:
1258:
1255:
1252:
1250:
1247:
1245:
1242:
1240:
1237:
1236:
1233:
1230:
1227:
1225:
1222:
1220:
1217:
1214:
1211:
1209:
1206:
1203:
1202:
1199:
1196:
1193:
1191:
1188:
1186:
1183:
1180:
1178:
1175:
1172:
1169:
1168:
1166:
1148:
1141:
1114:Main article:
1111:
1108:
1106:
1103:
1097:
1082:with index in
1066:
1053:
1052:
1039:
1034:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1016:
1011:
1007:
1003:
999:
993:
987:
983:
979:
975:
971:
966:
962:
958:
954:
949:
945:
941:
937:
932:
928:
924:
920:
898:
886:be the matrix
860:
859:
848:
843:
837:
834:
831:
829:
826:
823:
821:
818:
816:
813:
811:
808:
807:
804:
801:
799:
796:
794:
791:
788:
786:
783:
780:
778:
775:
774:
771:
768:
766:
763:
761:
758:
756:
753:
751:
748:
745:
744:
741:
738:
736:
733:
731:
728:
726:
723:
721:
718:
717:
715:
710:
707:
671:
664:
618:
596:
593:
565:
564:
553:
549:
542:
539:
537:
534:
531:
529:
526:
523:
522:
519:
516:
513:
511:
508:
506:
503:
500:
499:
496:
493:
490:
488:
485:
482:
480:
477:
476:
473:
469:
464:
460:
437:
436:
425:
421:
414:
411:
409:
406:
403:
401:
398:
395:
393:
390:
389:
386:
383:
380:
378:
375:
373:
370:
367:
365:
362:
359:
358:
355:
352:
349:
347:
344:
341:
339:
336:
334:
331:
328:
327:
324:
321:
319:
316:
313:
311:
308:
305:
303:
300:
299:
296:
292:
289:
255:
252:
248:
247:
236:
230:
227:
224:
220:
216:
211:
207:
201:
197:
191:
188:
183:
180:
177:
174:
171:
148:
144:
138:
131:
83:complete graph
48:spanning trees
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3039:
3028:
3025:
3023:
3020:
3018:
3017:Spanning tree
3015:
3013:
3010:
3009:
3007:
2998:
2995:
2994:
2990:
2984:
2980:
2975:
2970:
2966:
2962:
2957:
2953:
2947:
2943:
2938:
2934:
2930:
2926:
2922:
2918:
2914:
2909:
2904:
2900:
2895:
2894:
2885:
2878:
2875:
2870:
2864:
2860:
2856:
2852:
2845:
2842:
2837:
2833:
2829:
2823:
2819:
2812:
2809:
2804:
2800:
2796:
2792:
2785:
2782:
2775:
2771:
2768:
2766:
2763:
2761:
2758:
2756:
2753:
2751:
2748:
2747:
2743:
2741:
2739:
2735:
2717:
2713:
2703:
2701:
2697:
2678:
2675:
2672:
2666:
2660:
2657:
2654:
2642:
2640:
2636:
2632:
2628:
2624:
2620:
2615:
2596:
2593:
2590:
2586:
2582:
2577:
2573:
2569:
2567:
2560:
2556:
2546:
2543:
2540:
2536:
2532:
2527:
2523:
2519:
2516:
2513:
2508:
2505:
2502:
2498:
2492:
2489:
2486:
2482:
2478:
2473:
2469:
2465:
2460:
2457:
2454:
2450:
2446:
2441:
2437:
2433:
2431:
2424:
2420:
2410:
2407:
2404:
2400:
2394:
2391:
2388:
2384:
2380:
2377:
2374:
2369:
2365:
2359:
2355:
2351:
2346:
2342:
2336:
2332:
2328:
2326:
2319:
2316:
2313:
2309:
2296:
2288:
2285:
2282:
2271:
2266:
2263:
2260:
2256:
2252:
2249:
2246:
2241:
2237:
2233:
2231:
2224:
2221:
2218:
2214:
2201:
2184:
2181:
2178:
2175:
2172:
2161:
2157:
2138:
2131:
2128:
2125:
2121:
2116:
2112:
2105:
2101:
2096:
2087:
2084:
2081:
2078:
2075:
2069:
2061:
2058:
2055:
2051:
2047:
2044:
2041:
2036:
2032:
2024:
2020:
2015:
2011:
2003:
2002:
2001:
1985:
1981:
1960:
1957:
1952:
1948:
1924:
1921:
1913:
1910:
1907:
1903:
1899:
1896:
1890:
1882:
1878:
1874:
1871:
1861:
1860:
1859:
1843:
1839:
1816:
1812:
1784:
1779:
1775:
1771:
1765:
1759:
1754:
1750:
1742:
1741:
1740:
1716:
1712:
1705:
1697:
1694:
1691:
1678:
1674:
1667:
1659:
1653:
1647:
1625:
1621:
1617:
1614:
1611:
1606:
1602:
1593:
1589:
1578:
1566:
1562:
1560:
1559:
1555:
1551:
1543:
1539:
1535:
1528:
1525:
1521:
1517:
1513:
1509:
1505:
1502:for distinct
1501:
1494:
1493:
1492:
1490:
1480:
1478:
1474:
1470:
1462:
1460:
1457:
1454:
1450:
1445:
1443:
1439:
1435:
1431:
1427:
1423:
1419:
1415:
1411:
1408:and let the (
1407:
1406:indeterminate
1398:
1396:
1394:
1388:
1384:
1380:
1376:
1368:are excluded.
1367:
1363:
1360:
1356:
1352:
1348:
1344:
1337:
1336:
1335:
1333:
1329:
1319:
1317:
1298:
1293:
1287:
1284:
1281:
1276:
1271:
1268:
1263:
1260:
1253:
1248:
1243:
1238:
1231:
1228:
1223:
1218:
1215:
1212:
1207:
1204:
1197:
1194:
1189:
1184:
1181:
1176:
1173:
1170:
1164:
1155:
1154:
1153:
1151:
1144:
1136:
1134:
1131:
1127:
1122:
1117:
1104:
1102:
1100:
1093:
1089:
1086:. Then every
1085:
1081:
1077:
1073:
1070:denotes the (
1069:
1062:
1058:
1037:
1032:
1027:
1023:
1019:
1009:
1005:
1001:
997:
985:
981:
977:
969:
964:
960:
956:
947:
943:
939:
935:
930:
926:
922:
911:
910:
909:
907:
902:
897:
893:
889:
885:
881:
877:
873:
869:
865:
846:
841:
835:
832:
827:
824:
819:
814:
809:
802:
797:
792:
789:
784:
781:
776:
769:
764:
759:
754:
749:
746:
739:
734:
729:
724:
719:
713:
708:
705:
698:
697:
696:
694:
690:
686:
682:
678:
674:
667:
660:
656:
652:
648:
644:
640:
636:
632:
628:
624:
617:
612:
608:
606:
602:
595:Proof outline
594:
592:
590:
586:
582:
578:
574:
570:
551:
547:
540:
535:
532:
527:
524:
517:
514:
509:
504:
501:
494:
491:
486:
483:
478:
471:
467:
462:
458:
450:
449:
448:
446:
442:
423:
419:
412:
407:
404:
399:
396:
391:
384:
381:
376:
371:
368:
363:
360:
353:
350:
345:
342:
337:
332:
329:
322:
317:
314:
309:
306:
301:
294:
290:
287:
280:
279:
278:
276:
273:
272:diamond graph
269:
260:
253:
251:
234:
228:
225:
222:
218:
214:
209:
205:
199:
195:
189:
186:
181:
175:
169:
162:
161:
160:
158:
154:
147:
137:
130:
126:
122:
118:
114:
109:
107:
103:
99:
95:
91:
90:degree matrix
86:
84:
80:
76:
73:
69:
65:
61:
57:
53:
49:
45:
41:
37:
33:
29:
22:
2964:
2960:
2942:Graph Theory
2941:
2916:
2912:
2898:
2883:
2877:
2850:
2844:
2817:
2811:
2794:
2790:
2784:
2755:BEST theorem
2737:
2704:
2699:
2643:
2638:
2634:
2630:
2626:
2622:
2618:
2616:
2202:
2159:
2155:
2153:
1939:
1799:
1591:
1570:
1564:
1557:
1553:
1549:
1547:
1541:
1537:
1530:
1523:
1519:
1515:
1511:
1507:
1503:
1496:
1488:
1486:
1466:
1458:
1446:
1441:
1437:
1433:
1429:
1425:
1421:
1417:
1413:
1409:
1402:
1392:
1386:
1382:
1378:
1374:
1371:
1358:
1354:
1350:
1346:
1339:
1331:
1325:
1315:
1313:
1146:
1139:
1137:
1132:
1125:
1119:
1095:
1091:
1087:
1083:
1079:
1075:
1071:
1064:
1060:
1056:
1054:
903:
895:
891:
887:
883:
879:
875:
863:
861:
692:
688:
684:
676:
669:
662:
658:
654:
650:
646:
642:
638:
634:
630:
626:
622:
615:
613:
609:
598:
588:
584:
580:
576:
572:
568:
566:
444:
440:
438:
274:
267:
265:
249:
156:
142:
135:
128:
120:
116:
111:For a given
110:
106:(0,1)-matrix
87:
71:
42:named after
39:
35:
32:graph theory
28:mathematical
25:
2696:bijectively
1477:Maurer 1976
1328:multigraphs
679:are 0 (see
153:eigenvalues
60:determinant
3006:Categories
2797:(1): 4–7.
2776:References
1529:The entry
1495:The entry
1338:The entry
1090:specifies
571:to obtain
100:) and its
96:of vertex
2983:0097-3165
2836:180753706
2676:−
2667:×
2658:−
2594:−
2587:λ
2583:…
2574:λ
2544:−
2537:λ
2533:…
2524:λ
2517:⋯
2506:−
2499:λ
2490:−
2483:λ
2479:…
2470:λ
2458:−
2451:λ
2447:…
2438:λ
2408:−
2401:λ
2392:−
2385:λ
2378:⋯
2366:λ
2356:λ
2343:λ
2333:λ
2317:−
2264:−
2257:λ
2250:⋯
2238:λ
2222:−
2179:…
2129:−
2117:λ
2113:…
2097:λ
2085:−
2079:…
2070:⊂
2059:−
2045:…
2025:∑
1949:λ
1911:−
1904:λ
1891:…
1879:λ
1751:∑
1698:⋅
1695:⋯
1692:⋅
1615:…
1285:−
1277:⋯
1269:−
1261:−
1254:⋮
1249:⋱
1244:⋮
1239:⋮
1229:−
1224:⋯
1216:−
1205:−
1195:−
1190:⋯
1182:−
1174:−
1130:dimension
1006:∑
944:∑
872:transpose
833:−
825:−
790:−
782:−
747:−
649:) is the
605:induction
533:−
525:−
515:−
502:−
492:−
484:−
463:∗
405:−
397:−
382:−
369:−
361:−
351:−
343:−
330:−
315:−
307:−
226:−
219:λ
215:⋯
206:λ
196:λ
113:connected
64:submatrix
58:from the
30:field of
2744:See also
1514:, where
1510:equals −
1463:Matroids
1453:monomial
1420:-th and
1349:, where
1345:equals −
904:Now the
874:, i.e.,
870:and its
691:= 4 and
125:vertices
123:labeled
75:cofactor
2933:0392635
1577:forests
1440:equals
661:. Then
134:,
98:degrees
26:In the
2981:
2948:
2931:
2865:
2834:
2824:
1055:where
695:= 5):
633:is an
127:, let
115:graph
2698:to a
1395:= 1.
1366:loops
668:= 1,
657:<
119:with
92:(the
62:of a
52:graph
50:in a
2979:ISSN
2946:ISBN
2863:ISBN
2832:OCLC
2822:ISBN
1506:and
1357:and
637:-by-
2969:doi
2921:doi
2855:doi
2799:doi
2736:of
1533:i,i
1522:to
1499:i,j
1479:).
1385:−1)
1342:i,j
1015:det
974:det
953:det
919:det
159:is
104:(a
72:any
38:or
3008::
2977:,
2965:24
2963:,
2929:MR
2927:,
2917:30
2915:,
2901:,
2861:.
2830:.
2793:.
2740:.
2641:.
2625:=
1444:.
1412:,
1381:−(
931:11
901:.
899:11
894:=
892:FF
880:EE
878:=
672:jk
665:ik
645:,
619:11
149:−1
85:.
34:,
2971::
2955:.
2936:.
2923::
2907:.
2871:.
2857::
2838:.
2805:.
2801::
2795:5
2738:Q
2718:k
2714:q
2700:k
2682:)
2679:k
2673:n
2670:(
2664:)
2661:k
2655:n
2652:(
2639:n
2635:k
2631:Q
2627:n
2623:k
2619:n
2597:1
2591:n
2578:1
2570:=
2561:1
2557:q
2547:1
2541:n
2528:2
2520:+
2514:+
2509:1
2503:n
2493:3
2487:n
2474:1
2466:+
2461:2
2455:n
2442:1
2434:=
2425:2
2421:q
2411:1
2405:n
2395:2
2389:n
2381:+
2375:+
2370:3
2360:1
2352:+
2347:2
2337:1
2329:=
2320:2
2314:n
2310:q
2301:|
2297:E
2293:|
2289:2
2286:=
2283:Q
2279:r
2276:t
2272:=
2267:1
2261:n
2253:+
2247:+
2242:1
2234:=
2225:1
2219:n
2215:q
2188:}
2185:n
2182:,
2176:,
2173:1
2170:{
2160:k
2158:−
2156:n
2139:.
2132:k
2126:n
2122:i
2106:1
2102:i
2091:}
2088:1
2082:n
2076:1
2073:{
2067:}
2062:k
2056:n
2052:i
2048:,
2042:,
2037:1
2033:i
2029:{
2021:=
2016:k
2012:q
1986:k
1982:q
1961:0
1958:=
1953:n
1925:.
1922:x
1919:)
1914:1
1908:n
1900:+
1897:x
1894:(
1888:)
1883:1
1875:+
1872:x
1869:(
1844:k
1840:x
1817:k
1813:q
1802:k
1785:,
1780:k
1776:q
1772:=
1769:)
1766:F
1763:(
1760:w
1755:F
1726:|
1722:)
1717:k
1713:F
1709:(
1706:V
1702:|
1688:|
1684:)
1679:1
1675:F
1671:(
1668:V
1664:|
1660:=
1657:)
1654:F
1651:(
1648:w
1626:k
1622:F
1618:,
1612:,
1607:1
1603:F
1592:F
1585:k
1581:k
1573:k
1565:k
1558:Q
1554:i
1550:i
1544:.
1542:i
1538:i
1531:q
1526:;
1524:j
1520:i
1516:m
1512:m
1508:j
1504:i
1497:q
1489:Q
1442:j
1438:i
1434:i
1430:j
1426:i
1422:j
1418:i
1414:j
1410:i
1393:m
1389:)
1387:n
1383:n
1379:n
1377:(
1375:m
1361:;
1359:j
1355:i
1351:m
1347:m
1340:q
1332:Q
1316:n
1299:.
1294:]
1288:1
1282:n
1272:1
1264:1
1232:1
1219:1
1213:n
1208:1
1198:1
1185:1
1177:1
1171:n
1165:[
1149:n
1147:K
1142:n
1140:K
1133:n
1126:n
1098:S
1096:F
1092:n
1088:S
1084:S
1080:F
1076:n
1072:n
1067:S
1065:F
1061:n
1057:S
1038:2
1033:)
1028:S
1024:F
1020:(
1010:S
1002:=
998:)
992:T
986:S
982:F
978:(
970:)
965:S
961:F
957:(
948:S
940:=
936:)
927:M
923:(
896:M
888:E
884:F
876:L
864:L
847:.
842:]
836:1
828:1
820:0
815:0
810:0
803:1
798:0
793:1
785:1
777:0
770:0
765:1
760:1
755:0
750:1
740:0
735:0
730:0
725:1
720:1
714:[
709:=
706:E
693:m
689:n
685:E
677:k
670:E
663:E
659:j
655:i
651:k
647:j
643:i
639:m
635:n
631:E
627:m
623:n
616:M
589:Q
585:G
583:(
581:t
577:G
575:(
573:t
569:Q
552:.
548:]
541:2
536:1
528:1
518:1
510:3
505:1
495:1
487:1
479:3
472:[
468:=
459:Q
445:Q
441:Q
424:.
420:]
413:2
408:1
400:1
392:0
385:1
377:3
372:1
364:1
354:1
346:1
338:3
333:1
323:0
318:1
310:1
302:2
295:[
291:=
288:Q
275:G
268:Q
235:.
229:1
223:n
210:2
200:1
190:n
187:1
182:=
179:)
176:G
173:(
170:t
157:G
145:n
143:λ
139:2
136:λ
132:1
129:λ
121:n
117:G
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.