259:) of an infectious disease is the time interval between the beginning of infection in an individual (infector) to the time that person transmits to another individual (infectee). The generation time specifies how fast infections are spreading in the community with the passing of each generation. In contrast, the effective reproductive number determines in what number the infections are spreading in the community with the passing of each generation. The latent period and the infectious period helps determine the generation time of an infection. The mean generation time is equal to the sum of the mean latent period and one-half of the mean infectious period, given that infectiousness is evenly distributed across the infectious period.
243:) will generally be larger, regardless of the infectiousness of the disease. For example, even though HIV/AIDS has a very low transmission potential per sexual act, its basic reproduction number is still very high because of its unusually long infectious period spanning many years. From the viewpoint of controlling an epidemic, the goal is to reduce the effective infectious period either by treatment or by isolating the patient from the community. Sometimes a treatment can paradoxically increase the effective infectious period by preventing death through supportive care and thereby increasing the probability of infection of other individuals.
153:. Moreover, at a certain point in time after infection, the host becomes capable of transmitting pathogens to others, i.e. they become infectious or communicable. Depending on the disease, the host individual may or may not be infectious during the incubation period. The incubation period is important in the dynamics of disease transmission because it determines the time of case detection relative to the time of infection. This helps in the evaluation of the outcomes of control measures based on symptomatic surveillance. The incubation period is also useful to count the number of infected people.
226:, the infectious period begins approximately 2 days before the onset of symptoms and 44% of the secondary infections may happen during this pre-symptomatic stage. In these kinds of cases with a significant number of pre-symptomatic (asymptomatic) transmissions, symptomatic surveillance-based disease control measures (such as isolation, contact tracing, enhanced hygiene, etc.) are likely to have their effectiveness reduced, because a significant portion of the transmission may take place before the onset of symptoms and this has to be taken into account when designing
31:
180:), defined as the period from the end of the pre-infectious period or the latent period until the time when the host can no longer transmit the infection to other individuals. During the infectious period, a host may or may not show symptoms, but they are capable of infecting other individuals. The duration of the infectious period depends on the ability of the infected host individual to mount an immune response.
164:. During the pre-infectious or latent period, a host may or may not show symptoms (i.e. the incubation period may or may not be over), but in both cases, the host is not capable of infecting other hosts i.e. transmitting pathogens to other hosts. The latent period, rather than the incubation period, has more influence on the spreading dynamics of an infectious disease or epidemic.
267:
is defined as the period of time between the onset of clinical symptoms in the first host (infector) and the onset of analogous clinical symptoms in the second host (infectee). Just like the generation time, the length of the serial interval depends on the lengths of the latent period, the infectious
262:
Since the precise moment of infection is very difficult and almost impossible to detect, the generation time is not properly observable for two successive hosts. Generally, in infectious disease statistics, the onset of clinical symptoms for all the hosts are reported. For two successive generations
208:
However, for some infectious diseases, the symptoms of the clinical disease may appear after the host becomes infectious. In this case, the pre-infectious or latent period has a shorter duration than the incubation period, the infectious period begins before the end of the incubation period and the
292:), the term "latency period" is used to indicate the time that passes between being exposed to something that can cause disease (such as radiation or a virus) and having symptoms. Doctors and medical journals may speak of "latent" tumors, which are present but not active or causing symptoms.
188:
In some cases, the pre-infectious or latent period and the incubation period coincide and are mostly of the same duration. In this case, the infected individual becomes infectious at around the same time they start showing symptoms. In certain other infectious diseases such as
132:
of the body and to multiply or replicate after having traveled to their favored sites within the host’s body (tissue invasion and tropism). When the pathogens become sufficiently numerous and toxic to cause damage to the body, the host begins to display
197:, the host becomes infectious after the onset of symptoms. In this case, the latent period is longer than the incubation period. In these two cases, the disease can be effectively controlled using symptomatic surveillance. A related term is the
221:
of the disease. For example, in HIV/AIDS, the incubation period lasts years longer than the latent period. So an HIV infected individual can show no symptoms and unwittingly infect other susceptible individuals for many years. In
280:
or
Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary) as being the time interval between infection by a pathogen and the onset of symptoms, i.e., as a synonymous term for the epidemiologically different concept of "incubation period".
233:
The infectious period is a very important element in the infectious disease spreading dynamics. If the infectious period is long, then the measure of secondary infections (represented by the
740:
209:
host can infect others for some time without showing any noticeable symptoms. This early or mild stage of infection whose symptoms stay below the level of clinical detection is called
172:
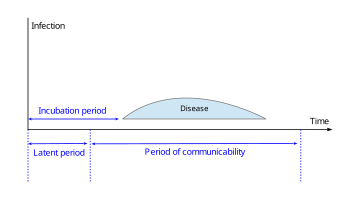
The time interval during which the host is infectious, i.e. the pathogens can be transmitted directly or indirectly from the infected host to another individual, is called the
548:
145:
The time interval from the time of invasion by an infectious pathogen to the time of onset (first appearance) of symptoms of the disease in question is called the
2062:
1616:
733:
726:
205:, which is defined as the time duration during which a host or patient excretes pathogens through saliva, urine, feces or other bodily fluids.
2397:
2384:
998:
754:
1669:
112:
The infection of a disease begins when a pathogenic (disease-causing) infectious agent, or a pathogen, is successfully transmitted from one
2186:
1644:
38:. In such cases, a person can transmit infection without showing any signs of the disease and is called subclinically infectious or an
2389:
1819:
1814:
268:
period and the incubation period. Therefore the serial interval is often used as a proxy measure to estimate the generation time.
1898:
1305:
921:
227:
1492:
2233:
1831:
1550:
1528:
276:
Outside the confines of epidemiology, the term "latent period" may be defined in some general-purpose dictionaries (e.g. the
899:
2201:
2450:
2228:
1624:
1381:
859:
124:
and after coming into contact (exposure) with a new susceptible host, they enter the host's body through an appropriate
2270:
2141:
2077:
2045:
1993:
1290:
1272:
50:
576:
1826:
1239:
979:
636:
277:
2330:
2320:
2015:
1951:
1674:
1639:
1018:
959:
337:
235:
2148:
2010:
1885:
1739:
854:
844:
2335:
2253:
2119:
1649:
1447:
1323:
1154:
1092:
926:
894:
657:
581:, National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
563:
Systematic review on the incubation and infectiousness/shedding period of communicable diseases in children
1922:
1707:
1457:
1330:
936:
793:
783:
289:
74:
2445:
2358:
2243:
1875:
1744:
1252:
1159:
1078:
542:
211:
1502:
2325:
2218:
2164:
2092:
2082:
1774:
1629:
1442:
1419:
1109:
342:
217:
125:
121:
39:
117:
2412:
2402:
2368:
1973:
1424:
1411:
1393:
1247:
1058:
2136:
2131:
2040:
2020:
1654:
1497:
1462:
1316:
1282:
832:
86:
30:
2422:
2363:
2223:
2176:
1978:
1480:
1149:
1139:
1129:
931:
914:
705:
592:
530:
484:
317:
312:
98:
94:
35:
610:
73:
and when that individual becomes infectious, i.e. capable of transmitting pathogens to other
2417:
2353:
2340:
2169:
2158:
2050:
2030:
1865:
1779:
1754:
1485:
1371:
1262:
1205:
1011:
909:
837:
695:
687:
520:
474:
466:
718:
2285:
2280:
2124:
2072:
1880:
1857:
1702:
1679:
1063:
1028:
904:
849:
332:
327:
129:
106:
102:
455:"On the relationship between serial interval, infectiousness profile and generation time"
2315:
2248:
2191:
1963:
1852:
1844:
1722:
1717:
1664:
1388:
1169:
1164:
1124:
1073:
1038:
876:
812:
700:
479:
454:
322:
156:
The period from the time of infection to the time of becoming infectious is called the
113:
2439:
2196:
2153:
2112:
2005:
1988:
1946:
1659:
1210:
1179:
1023:
800:
34:
In some diseases, as depicted in this diagram, the latent period is shorter than the
27:
Time interval between infection by a pathogen and the individual becoming infectious
2407:
2345:
2107:
2087:
2035:
1983:
1934:
1734:
1684:
1295:
1068:
866:
46:
128:. Upon entering the new host, they take a period of time to overcome or evade the
565:, Stockholm: European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, 2016, p. iv
2300:
2102:
2025:
2000:
1749:
1729:
1634:
1594:
1432:
889:
805:
788:
691:
2238:
2213:
2181:
1958:
1939:
1929:
1917:
1764:
1376:
1348:
1174:
1134:
1006:
525:
508:
17:
2310:
1789:
1114:
822:
817:
750:
66:
709:
534:
488:
470:
303:" refers to asymptomatic periods with different degrees of infectiousness.
637:""Latency Period". National Cancer Institute's Dictionary of Cancer Terms"
2293:
2208:
1784:
1769:
1759:
1712:
1257:
1053:
1033:
827:
770:
300:
296:
223:
190:
90:
70:
2097:
1968:
1221:
778:
134:
509:"Temporal dynamics in viral shedding and transmissibility of COVID-19"
2305:
1870:
1523:
1119:
285:
1534:
1046:
658:""Latent". National Cancer Institute's Dictionary of Cancer Terms"
93:, three important time periods should be carefully distinguished:
81:
Relationship with related concepts in infectious disease dynamics
1518:
987:
884:
507:
He X, Lau EHY, Wu P, Deng X, Wang J, Hao X; et al. (2020).
453:
Lehtinen, Sonja; Ashcroft, Peter; Bonhoeffer, Sebastian (2021).
194:
722:
435:
An
Introduction to Mathematical Modeling of Infectious Diseases
387:(3rd ed.), Jones & Bartlett Learning, p. 135-136
65:) is the time interval between when an individual or host is
101:. Two other relevant and important time period concepts are
149:. After the incubation period is over, the host enters the
137:
of a clinical disease (i.e. the host becomes symptomatic).
116:
to another. Pathogens leave the body of one host through a
383:
Kenrad E. Nelson; Carolyn
Masters Williams, eds. (2014),
299:(a sexually transmitted infectious disease), the term "
385:
Infectious disease epidemiology: Theory and
Practice
2377:
2269:
2061:
1910:
1897:
1802:
1693:
1615:
1587:
1573:
1559:
1543:
1511:
1473:
1402:
1364:
1357:
1339:
1271:
1238:
1231:
1195:
1188:
1100:
1091:
978:
875:
769:
762:
437:, Springer International Publishing AG, p. 25
263:(or cases or hosts) in a chain of infection, the
407:An Introduction to Infectious Disease Modelling
678:Patrick French (20 January 2007), "Syphilis",
502:
500:
498:
734:
8:
547:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
400:
398:
396:
394:
85:To understand the spreading dynamics of an
1907:
1361:
1235:
1192:
1097:
766:
741:
727:
719:
448:
446:
444:
405:Emilia Vynnycky; Richard G. White (2010),
215:and the individual concerned is called an
699:
524:
478:
378:
376:
374:
372:
370:
368:
366:
364:
362:
360:
358:
29:
1815:Ear-Nose-Throat/Upper respiratory tract
988:Access to water, sanitation and hygiene
354:
2398:Infectious disease (medical specialty)
2290:Antimicrobial resistance surveillance
540:
459:Journal of the Royal Society Interface
409:, Oxford University Press, p. 2-3
272:Usage of the term outside epidemiology
97:, pre-infectious or latent period and
7:
1645:Compartmental models in epidemiology
428:
426:
424:
422:
420:
418:
416:
49:, particularly in the discussion of
25:
2394:Economics of Infectious Diseases
2403:Infectious disease informatics
2234:Transmission-based precautions
1:
1820:Chest/Lower respiratory tract
1595:Ocular (Eye) mucosal membrane
956:Behavioral/lifestyle factors
1382:Aerosol-generating procedure
1160:Silent/Subclinical infection
860:Multidrug-resistant bacteria
2046:Vaccine-preventable disease
1994:Monoclonal antibody therapy
692:10.1136/bmj.39085.518148.BE
51:infectious disease dynamics
2467:
2187:Respiratory source control
278:Collins English Dictionary
2331:Global Health Initiatives
2321:Evolutionary epidemiology
2016:Post-exposure prophylaxis
1952:Antimicrobial stewardship
1675:Multiplicity of infection
1640:Basic reproduction number
1416:Percutaneous inoculation
900:Host–pathogen interaction
526:10.1038/s41591-020-0869-5
338:Basic reproduction number
236:basic reproduction number
178:period of communicability
2149:Protective sequestration
2011:Pre-exposure prophylaxis
1302:Generational difference
855:Horizontal gene transfer
845:Antimicrobial resistance
2336:Microbial phylogenetics
2254:Wastewater surveillance
1775:Geographic distribution
1650:Critical community size
1448:Surgical site infection
1296:Iatrogenic/Medical care
1215:Microbial translocation
1211:Endogenous reactivation
1206:Normal flora overgrowth
1155:Opportunistic infection
927:Opportunistic infection
680:British Medical Journal
75:susceptible individuals
2408:Microbial bioterrorism
2031:efficacy/effectiveness
1439:Surgical intervention
1331:Breakthrough infection
953:Genetic predisposition
937:Susceptible individual
784:Germ theory of disease
471:10.1098/rsif.2020.0756
465:(174). Royal Society.
433:Michael Y. Li (2018),
290:non-infectious disease
120:, are carried by some
42:
2244:Universal precautions
1202:Endogenous overgrowth
1054:Poultry and livestock
295:In the discussion of
284:In the discussion of
212:subclinical infection
158:pre-infectious period
63:pre-infectious period
33:
2346:Genomic reassortment
2326:Genetic epidemiology
2165:Health communication
2093:Flattening the curve
2083:Disease surveillance
1866:Systemic/Generalized
1630:Animal disease model
1110:Asymptomatic carrier
343:Asymptomatic carrier
218:asymptomatic carrier
199:duration of shedding
122:mode of transmission
40:asymptomatic carrier
2451:Infectious diseases
2413:Pandemic prevention
2369:Viral phylodynamics
2350:Re-emerging disease
2239:Travel restrictions
1443:Postoperative wound
1412:Blood-borne disease
1394:Respiratory droplet
1306:Vertical/Congenital
1291:Nosocomial/Hospital
1248:Spillover infection
615:Merriam-Webster.com
257:generation interval
57:(also known as the
2359:Selection pressure
1655:Force of infection
1283:Contagious disease
1218:Endogenous seeding
1115:Chain of infection
1039:Injection drug use
950:Vaccination status
833:Case fatality rate
751:infectious disease
597:Collins Dictionary
151:symptomatic period
87:infectious disease
43:
2433:
2432:
2423:Tropical medicine
2364:Synthetic biology
2265:
2264:
2224:Social distancing
2177:Outbreak response
1798:
1797:
1625:Agent-based model
1611:
1610:
1607:
1606:
1603:
1602:
1150:Natural reservoir
1140:Infectious period
1130:Incubation period
1087:
1086:
1043:Natural disaster
1012:Tropical diseases
995:Biodiversity loss
932:Risk of infection
922:Microbiome health
915:Immunosuppression
686:(7585): 143–147,
617:. Merriam-Webster
578:HIV/AIDS Glossary
318:Infectious period
313:Incubation period
174:infectious period
168:Infectious period
147:incubation period
141:Incubation period
99:infectious period
95:incubation period
36:incubation period
16:(Redirected from
2458:
2418:Tropical disease
2354:Reverse zoonosis
2341:One Health Model
2170:Health education
2159:Community health
2078:Cordon sanitaire
2051:Ring vaccination
2021:Repurposed drugs
1908:
1827:Gastrointestinal
1670:Machine learning
1474:Gastrointestinal
1425:Intravenous line
1362:
1276:/Cross-infection
1263:Reverse zoonosis
1236:
1193:
1098:
1079:War and conflict
947:Nutrition status
910:Immunodeficiency
767:
743:
736:
729:
720:
713:
712:
703:
675:
669:
668:
666:
664:
654:
648:
647:
645:
643:
633:
627:
626:
624:
622:
607:
601:
600:
589:
583:
582:
573:
567:
566:
559:
553:
552:
546:
538:
528:
504:
493:
492:
482:
450:
439:
438:
430:
411:
410:
402:
389:
388:
380:
53:(modeling), the
21:
2466:
2465:
2461:
2460:
2459:
2457:
2456:
2455:
2436:
2435:
2434:
2429:
2373:
2286:Antigenic shift
2281:Antigenic drift
2272:
2261:
2125:Barrier nursing
2073:Contact tracing
2064:
2057:
1902:
1900:
1893:
1804:
1794:
1695:
1689:
1680:Serial interval
1599:
1583:
1574:Cervico-vaginal
1569:
1560:Trans-placental
1555:
1539:
1507:
1469:
1405:Vascular system
1404:
1398:
1353:
1341:
1335:
1275:
1267:
1227:
1184:
1102:
1083:
974:
905:Immune response
871:
850:Drug resistance
794:Infectious dose
758:
747:
717:
716:
677:
676:
672:
662:
660:
656:
655:
651:
641:
639:
635:
634:
630:
620:
618:
611:"Latent Period"
609:
608:
604:
591:
590:
586:
575:
574:
570:
561:
560:
556:
539:
506:
505:
496:
452:
451:
442:
432:
431:
414:
404:
403:
392:
382:
381:
356:
351:
333:Serial interval
328:Generation time
309:
274:
265:serial interval
253:generation time
249:
247:Generation time
242:
203:shedding period
186:
170:
143:
130:immune response
126:portal of entry
107:serial interval
103:generation time
83:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2464:
2462:
2454:
2453:
2448:
2438:
2437:
2431:
2430:
2428:
2427:
2426:
2425:
2415:
2410:
2405:
2400:
2395:
2392:
2387:
2381:
2379:
2375:
2374:
2372:
2371:
2366:
2361:
2356:
2351:
2348:
2343:
2338:
2333:
2328:
2323:
2318:
2316:Emergent virus
2313:
2308:
2303:
2298:
2297:
2296:
2288:
2283:
2277:
2275:
2267:
2266:
2263:
2262:
2260:
2259:
2256:
2251:
2249:Vector control
2246:
2241:
2236:
2231:
2226:
2221:
2216:
2211:
2206:
2205:
2204:
2199:
2194:
2192:N95 respirator
2184:
2179:
2174:
2173:
2172:
2167:
2162:
2151:
2146:
2145:
2144:
2134:
2129:
2128:
2127:
2117:
2116:
2115:
2110:
2105:
2095:
2090:
2085:
2080:
2075:
2069:
2067:
2065:pharmaceutical
2059:
2058:
2056:
2055:
2054:
2053:
2048:
2043:
2038:
2033:
2023:
2018:
2013:
2008:
2003:
1998:
1997:
1996:
1986:
1981:
1976:
1971:
1966:
1961:
1956:
1955:
1954:
1944:
1943:
1942:
1932:
1927:
1926:
1925:
1914:
1912:
1911:Pharmaceutical
1905:
1895:
1894:
1892:
1891:
1888:
1883:
1878:
1873:
1868:
1863:
1862:Cardiovascular
1860:
1855:
1850:
1847:
1842:
1841:Nervous system
1839:
1836:
1835:
1834:
1824:
1823:
1822:
1817:
1808:
1806:
1800:
1799:
1796:
1795:
1793:
1792:
1787:
1782:
1777:
1772:
1767:
1762:
1757:
1752:
1747:
1742:
1737:
1732:
1727:
1726:
1725:
1720:
1710:
1705:
1699:
1697:
1691:
1690:
1688:
1687:
1682:
1677:
1672:
1667:
1665:Infection rate
1662:
1657:
1652:
1647:
1642:
1637:
1632:
1627:
1621:
1619:
1613:
1612:
1609:
1608:
1605:
1604:
1601:
1600:
1598:
1597:
1591:
1589:
1585:
1584:
1582:
1581:
1577:
1575:
1571:
1570:
1568:
1567:
1563:
1561:
1557:
1556:
1554:
1553:
1547:
1545:
1541:
1540:
1538:
1537:
1531:
1526:
1521:
1515:
1513:
1509:
1508:
1506:
1505:
1500:
1495:
1490:
1489:
1488:
1477:
1475:
1471:
1470:
1468:
1467:
1466:
1465:
1460:
1452:
1451:
1450:
1445:
1437:
1436:
1435:
1430:
1427:
1422:
1420:Injection site
1414:
1408:
1406:
1400:
1399:
1397:
1396:
1391:
1389:Dental aerosol
1386:
1385:
1384:
1374:
1368:
1366:
1359:
1355:
1354:
1352:
1351:
1345:
1343:
1337:
1336:
1334:
1333:
1328:
1327:
1326:
1321:
1320:
1319:
1314:
1311:
1300:
1299:
1298:
1293:
1285:
1279:
1277:
1273:Human-to-human
1269:
1268:
1266:
1265:
1260:
1255:
1250:
1244:
1242:
1233:
1229:
1228:
1226:
1225:
1219:
1216:
1213:
1208:
1203:
1199:
1197:
1190:
1186:
1185:
1183:
1182:
1177:
1172:
1170:Super-spreader
1167:
1165:Superinfection
1162:
1157:
1152:
1147:
1142:
1137:
1132:
1127:
1122:
1117:
1112:
1106:
1104:
1095:
1089:
1088:
1085:
1084:
1082:
1081:
1076:
1074:Vector control
1071:
1066:
1061:
1056:
1051:
1050:
1049:
1041:
1036:
1031:
1026:
1021:
1016:
1015:
1014:
1009:
1003:Climate zones
1001:
999:Climate change
996:
993:
990:
984:
982:
976:
975:
973:
972:
971:
970:
967:
964:
963:
962:
954:
951:
948:
945:
942:
934:
929:
924:
919:
918:
917:
912:
902:
897:
892:
887:
881:
879:
873:
872:
870:
869:
864:
863:
862:
857:
852:
842:
841:
840:
835:
830:
825:
815:
813:Quorum sensing
810:
809:
808:
798:
797:
796:
786:
781:
775:
773:
764:
760:
759:
748:
746:
745:
738:
731:
723:
715:
714:
670:
649:
628:
602:
584:
568:
554:
519:(5): 672–675.
494:
440:
412:
390:
353:
352:
350:
347:
346:
345:
340:
335:
330:
325:
323:Viral shedding
320:
315:
308:
305:
273:
270:
248:
245:
240:
185:
182:
169:
166:
142:
139:
118:portal of exit
82:
79:
59:latency period
26:
24:
18:Latency period
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2463:
2452:
2449:
2447:
2444:
2443:
2441:
2424:
2421:
2420:
2419:
2416:
2414:
2411:
2409:
2406:
2404:
2401:
2399:
2396:
2393:
2391:
2388:
2386:
2383:
2382:
2380:
2376:
2370:
2367:
2365:
2362:
2360:
2357:
2355:
2352:
2349:
2347:
2344:
2342:
2339:
2337:
2334:
2332:
2329:
2327:
2324:
2322:
2319:
2317:
2314:
2312:
2309:
2307:
2304:
2302:
2299:
2295:
2292:
2291:
2289:
2287:
2284:
2282:
2279:
2278:
2276:
2274:
2268:
2257:
2255:
2252:
2250:
2247:
2245:
2242:
2240:
2237:
2235:
2232:
2230:
2229:Sterilization
2227:
2225:
2222:
2220:
2217:
2215:
2212:
2210:
2207:
2203:
2200:
2198:
2197:Surgical mask
2195:
2193:
2190:
2189:
2188:
2185:
2183:
2180:
2178:
2175:
2171:
2168:
2166:
2163:
2160:
2157:
2156:
2155:
2154:Public health
2152:
2150:
2147:
2143:
2140:
2139:
2138:
2135:
2133:
2130:
2126:
2123:
2122:
2121:
2118:
2114:
2111:
2109:
2106:
2104:
2101:
2100:
2099:
2096:
2094:
2091:
2089:
2086:
2084:
2081:
2079:
2076:
2074:
2071:
2070:
2068:
2066:
2060:
2052:
2049:
2047:
2044:
2042:
2039:
2037:
2034:
2032:
2029:
2028:
2027:
2024:
2022:
2019:
2017:
2014:
2012:
2009:
2007:
2006:Phage therapy
2004:
2002:
1999:
1995:
1992:
1991:
1990:
1989:Immunotherapy
1987:
1985:
1982:
1980:
1977:
1975:
1972:
1970:
1967:
1965:
1962:
1960:
1957:
1953:
1950:
1949:
1948:
1947:Antimicrobial
1945:
1941:
1938:
1937:
1936:
1933:
1931:
1928:
1924:
1921:
1920:
1919:
1916:
1915:
1913:
1909:
1906:
1904:
1896:
1889:
1887:
1884:
1882:
1879:
1877:
1874:
1872:
1869:
1867:
1864:
1861:
1859:
1856:
1854:
1851:
1848:
1846:
1843:
1840:
1838:Genitourinary
1837:
1833:
1830:
1829:
1828:
1825:
1821:
1818:
1816:
1813:
1812:
1810:
1809:
1807:
1801:
1791:
1788:
1786:
1783:
1781:
1778:
1776:
1773:
1771:
1768:
1766:
1763:
1761:
1758:
1756:
1753:
1751:
1748:
1746:
1743:
1741:
1738:
1736:
1733:
1731:
1728:
1724:
1721:
1719:
1716:
1715:
1714:
1711:
1709:
1706:
1704:
1701:
1700:
1698:
1696:in population
1692:
1686:
1683:
1681:
1678:
1676:
1673:
1671:
1668:
1666:
1663:
1661:
1660:Herd immunity
1658:
1656:
1653:
1651:
1648:
1646:
1643:
1641:
1638:
1636:
1633:
1631:
1628:
1626:
1623:
1622:
1620:
1618:
1614:
1596:
1593:
1592:
1590:
1586:
1579:
1578:
1576:
1572:
1565:
1564:
1562:
1558:
1552:
1549:
1548:
1546:
1544:Genitourinary
1542:
1536:
1532:
1530:
1527:
1525:
1522:
1520:
1517:
1516:
1514:
1510:
1504:
1501:
1499:
1496:
1494:
1491:
1487:
1486:Contamination
1484:
1483:
1482:
1479:
1478:
1476:
1472:
1464:
1461:
1459:
1456:
1455:
1454:Vector-borne
1453:
1449:
1446:
1444:
1441:
1440:
1438:
1434:
1431:
1428:
1426:
1423:
1421:
1418:
1417:
1415:
1413:
1410:
1409:
1407:
1401:
1395:
1392:
1390:
1387:
1383:
1380:
1379:
1378:
1375:
1373:
1370:
1369:
1367:
1363:
1360:
1356:
1350:
1347:
1346:
1344:
1338:
1332:
1329:
1325:
1322:
1318:
1315:
1312:
1309:
1308:
1307:
1304:
1303:
1301:
1297:
1294:
1292:
1289:
1288:
1286:
1284:
1281:
1280:
1278:
1274:
1270:
1264:
1261:
1259:
1256:
1254:
1251:
1249:
1246:
1245:
1243:
1241:
1240:Cross-species
1237:
1234:
1230:
1223:
1220:
1217:
1214:
1212:
1209:
1207:
1204:
1201:
1200:
1198:
1194:
1191:
1187:
1181:
1180:Window period
1178:
1176:
1173:
1171:
1168:
1166:
1163:
1161:
1158:
1156:
1153:
1151:
1148:
1146:
1145:Latent period
1143:
1141:
1138:
1136:
1133:
1131:
1128:
1126:
1123:
1121:
1118:
1116:
1113:
1111:
1108:
1107:
1105:
1099:
1096:
1094:
1090:
1080:
1077:
1075:
1072:
1070:
1067:
1065:
1062:
1060:
1057:
1055:
1052:
1048:
1045:
1044:
1042:
1040:
1037:
1035:
1032:
1030:
1027:
1025:
1024:Deforestation
1022:
1020:
1017:
1013:
1010:
1008:
1005:
1004:
1002:
1000:
997:
994:
991:
989:
986:
985:
983:
981:
977:
969:Stress levels
968:
965:
961:
958:
957:
955:
952:
949:
946:
943:
940:
939:
938:
935:
933:
930:
928:
925:
923:
920:
916:
913:
911:
908:
907:
906:
903:
901:
898:
896:
893:
891:
888:
886:
883:
882:
880:
878:
874:
868:
865:
861:
858:
856:
853:
851:
848:
847:
846:
843:
839:
836:
834:
831:
829:
826:
824:
821:
820:
819:
816:
814:
811:
807:
804:
803:
802:
801:Pathogenicity
799:
795:
792:
791:
790:
787:
785:
782:
780:
777:
776:
774:
772:
768:
765:
761:
756:
752:
744:
739:
737:
732:
730:
725:
724:
721:
711:
707:
702:
697:
693:
689:
685:
681:
674:
671:
659:
653:
650:
638:
632:
629:
616:
612:
606:
603:
598:
594:
588:
585:
580:
579:
572:
569:
564:
558:
555:
550:
544:
536:
532:
527:
522:
518:
514:
510:
503:
501:
499:
495:
490:
486:
481:
476:
472:
468:
464:
460:
456:
449:
447:
445:
441:
436:
429:
427:
425:
423:
421:
419:
417:
413:
408:
401:
399:
397:
395:
391:
386:
379:
377:
375:
373:
371:
369:
367:
365:
363:
361:
359:
355:
348:
344:
341:
339:
336:
334:
331:
329:
326:
324:
321:
319:
316:
314:
311:
310:
306:
304:
302:
298:
293:
291:
287:
282:
279:
271:
269:
266:
260:
258:
254:
246:
244:
238:
237:
231:
229:
225:
220:
219:
214:
213:
206:
204:
200:
196:
192:
184:Latent period
183:
181:
179:
175:
167:
165:
163:
162:latent period
159:
154:
152:
148:
140:
138:
136:
131:
127:
123:
119:
115:
110:
108:
104:
100:
96:
92:
88:
80:
78:
76:
72:
68:
64:
60:
56:
55:latent period
52:
48:
41:
37:
32:
19:
2446:Epidemiology
2137:Notification
2108:Hand washing
2103:Food hygiene
2088:Disinfection
1984:Immunization
1935:Anthelmintic
1923:prophylactic
1811:Respiratory
1735:Hyperendemic
1685:WAIFW matrix
1340:Environment-
1144:
1093:Transmission
1069:Urbanization
867:Host tropism
763:Determinants
749:Concepts in
683:
679:
673:
661:. Retrieved
652:
640:. Retrieved
631:
619:. Retrieved
614:
605:
596:
587:
577:
571:
562:
557:
543:cite journal
516:
512:
462:
458:
434:
406:
384:
294:
283:
275:
264:
261:
256:
252:
250:
234:
232:
216:
210:
207:
202:
198:
187:
177:
173:
171:
161:
157:
155:
150:
146:
144:
111:
84:
62:
58:
54:
47:epidemiology
44:
2390:Eradication
2301:Biosecurity
2026:Vaccination
2001:Inoculation
1979:Drug safety
1974:Combination
1901:and Control
1849:Soft tissue
1803:Anatomical
1770:Seasonality
1750:Mesoendemic
1730:Holoendemic
1723:Farr's laws
1635:Attack rate
1433:Animal bite
1429:Insect bite
1365:Respiratory
992:Air quality
980:Environment
890:Comorbidity
806:Attack rate
789:Infectivity
2440:Categories
2273:infections
2214:Sanitation
2182:Quarantine
2041:resistance
1959:Antiseptic
1940:Ascaricide
1930:Antifungal
1918:Antibiotic
1899:Prevention
1832:Intestinal
1765:Prevalence
1745:Inequality
1694:Occurrence
1493:Breastmilk
1377:Bioaerosol
1349:Sapronosis
1324:Horizontal
1196:Endogenous
1175:Viral load
1135:Index case
349:References
230:measures.
2385:Discovery
2311:Disease X
2271:Emerging
2219:Screening
2120:Isolation
1964:Antiviral
1790:Twindemic
1740:Incidence
1617:Modelling
1580:Perinatal
1512:Cutaneous
1403:Linked to
1313:Perinatal
1232:Exogenous
1224:formation
966:Pregnancy
823:Endotoxin
818:Virulence
2294:EARS-Net
2209:Safe sex
2161:services
2132:Lockdown
1903:measures
1805:location
1785:Syndemic
1780:Sporadic
1760:Pandemic
1755:Outbreak
1713:Epidemic
1566:Prenatal
1458:Mosquito
1342:to-human
1317:Neonatal
1310:Prenatal
1258:Zoonosis
1103:concepts
1034:Humidity
1019:Commerce
895:Diabetes
828:Exotoxin
710:17235095
593:"Latent"
535:32296168
489:33402022
307:See also
297:syphilis
224:COVID-19
191:smallpox
176:(or the
135:symptoms
91:epidemic
71:pathogen
67:infected
2098:Hygiene
2036:booster
1969:Asepsis
1708:Endemic
1703:Cluster
1287:Source
1222:Biofilm
1059:Poverty
1029:Ecology
1007:El Niño
960:Smoking
838:factors
779:Biofilm
755:Outline
701:1779891
663:23 June
642:23 June
621:23 June
513:Nat Med
480:7879757
286:cancers
228:control
201:or the
160:or the
61:or the
2306:CRISPR
2258:Zoning
2113:Gloves
1524:Fomite
1358:Routes
1253:Vector
1120:Fomite
1101:Basic
1064:Travel
944:Gender
708:
698:
533:
487:
477:
301:latent
89:or an
2378:Other
1886:Fetus
1881:Mouth
1876:Tooth
1871:Blood
1858:Joint
1718:Curve
1588:Other
1535:wound
1533:Open
1503:Feces
1498:Water
1189:Modes
1047:Flood
771:Agent
69:by a
2142:list
2063:Non-
1853:Bone
1845:Skin
1529:Soil
1519:Burn
1481:Food
1463:Tick
1125:Host
885:Burn
877:Host
706:PMID
665:2021
644:2021
623:2021
549:link
531:PMID
485:PMID
255:(or
251:The
195:SARS
114:host
105:and
2202:PPE
1890:Eye
1551:Sex
1372:Air
941:Age
696:PMC
688:doi
684:334
521:doi
475:PMC
467:doi
288:(a
239:, R
193:or
45:In
2442::
704:,
694:,
682:,
613:.
595:.
545:}}
541:{{
529:.
517:26
515:.
511:.
497:^
483:.
473:.
463:18
461:.
457:.
443:^
415:^
393:^
357:^
109:.
77:.
757:)
753:(
742:e
735:t
728:v
690::
667:.
646:.
625:.
599:.
551:)
537:.
523::
491:.
469::
241:0
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.