445:
485:
307:
417:
496:, is the largest of the horns. It extends anteriorly from the atrium beneath the thalamus and terminates at the amygdala. The collateral eminence and hippocampus form the floor, which is separated from the hippocampus by a white matter layer called the alveus, whereas the roof is formed by the thalamus, the caudate nucleus, and tapetum. The stria terminalis forms the remainder of the roof, which is narrower than at the body, and the choroid plexus occupies the medial wall.
377:
644:
656:
231:
223:
41:
29:
516:
The lateral ventricles, similarly to other parts of the ventricular system of the brain, develop from the central canal of the neural tube. Specifically, the lateral ventricles originate from the portion of the tube that is present in the developing prosencephalon, and subsequently in the developing
543:
During development, pressure from exterior structures causes a number of concave bulges to form within the lateral ventricles, which can be extremely variable in their degree of development; in some individuals they are ill-defined, while in others they can be prominent:
499:
The tapetum for the temporal lobe comprises the lateral boundary of the inferior horn, on its way to join the main tapetum above the body of the ventricle (passing over the caudate nucleus as it does so). The majority of the inferior horn's floor is formed by the
392:. The tail of the caudate nucleus forms the upper portion of the lateral edge, but it is not large enough to cover the whole boundary. Immediately below the tail of the caudate nucleus, the next portion of the lateral edge is formed by the comparatively narrow
1065:
Mortazavi, M. M.; Adeeb, N.; Griessenauer, C. J.; Sheikh, H.; Shahidi, S.; Tubbs, R. I.; Tubbs, R. S. (2013). "The ventricular system of the brain: a comprehensive review of its history, anatomy, histology, embryology, and surgical considerations".
624:, where right-handed people have been found to have a larger right lateral ventricle and a longer left posterior horn, whereas left-handed people have been found to have longer right posterior horns. A severe asymmetry, or an asymmetry with
330:. This portion of the lateral ventricle impinges on the frontal lobe, passing anteriorly and laterally, with slight inclination inferiorly. It is separated from the anterior horn of the other lateral ventricle by a thin neural sheet -
278:, and sits above the tapetum; a small number of further connections passing through the occipital tapetum to join the putamen to portions of the caudate nucleus tail adjoining the anterior horn. Below the putamen sits the
977:
Kempton, Matthew J.; Geddes, John R.; Ettinger, Ulrich; Williams, Steven C. R.; Grasby, Paul M. (2008-09-01). "Meta-analysis, Database, and Meta-regression of 98 Structural
Imaging Studies in Bipolar Disorder".
238:
Each lateral ventricle takes the form of an elongated curve, with an additional anterior-facing continuation emerging inferiorly from a point near the posterior end of the curve; the junction is known as the
259:(anterior, posterior, or inferior), or sometimes by the lobe of the cerebral cortex into which they extend. Though somewhat flat, the lateral ventricles have a vaguely triangular cross-section.
524:, the central canal expands into lateral, third, and fourth ventricles, connected by thinner channels. In the lateral ventricles, specialized areas – choroid plexuses – appear, which produce
528:. The neural canal that does not expand and remains the same at the level of the midbrain superior to the fourth ventricle forms the cerebral aqueduct. The fourth ventricle narrows at the
464:
continues to form the roof, which due to the lilt is also the lateral edge. However, the posterior and anterior ends of the corpus callosum are characterized by tighter bundling, known as
508:
itself. As with the posterior horn, the remainder of the boundary (in this case, the lateral side of the floor) is directly in contact with the white matter of the surrounding lobe.
424:
The trigone of the lateral ventricle is the area where the part of the body forms a junction with the inferior horn and the posterior horn. This area is referred to as the
294:. The thalamus primarily communicates with the structures bounding the lateral ventricles via the globus pallidus, and the anterior extremities of the fornix (the
139:
1357:
1135:
327:
199:
1440:
384:
The body of the lateral ventricle, or central part is the part of the ventricle between the anterior horn and the trigone. Its roof is bound by the
643:
460:
in a posterior direction, initially laterally but subsequently curving medially and lilting inferiorly on the lateral side. The tapetum of the
787:
115:
655:
472:
form the upper part of the medial side of the posterior horn. The remainder of the medial edge of the ventricle is directly in contact with
290:, a cleft-like opening would be all that lay between the lateral ventricle and the thalamus; this cleft constitutes the lower part of the
1408:
211:
1242:
892:
1128:
146:
385:
134:
533:
397:
1482:
1121:
356:
1296:
343:
620:, in the size of the lateral ventricles is found in about 5–12% of the population. This has been associated with
606:
360:. The remaining boundary - that facing interior to the ventricle curvature - comprises the posterior edge of the
334:, which thus forms its medial boundary. The boundary facing exterior to the ventricle curvature is formed by the
1291:
1279:
1271:
444:
73:
1430:
484:
306:
936:
847:
282:, with which it connects. These structures bounding the lateral ventricles form a frame curving around the
672:
610:
122:
110:
803:
Unger, S; Salem, S; Wylie, L; Shah, V (February 2011). "Newborn frontal horn cysts: cause for concern?".
432:. As a triangular surface feature of the floor of this part of the lateral ventricle it is known as the
264:
416:
1252:
1015:"Ventricular Enlargement as a Surrogate Marker of Alzheimer Disease Progression Validated Using ADNI"
617:
521:
865:
90:
1422:
1340:
1237:
1177:
1013:
Nestor, S; Rupsingh, R; Borrie, M; Smith, M; Accomazzi, V; Wells, J; Fogarty, J; Bartha, R (2008).
582:
525:
401:
180:
176:
376:
1445:
1225:
1144:
1099:
828:
501:
168:
286:, which itself constitutes the main structure bounding the third ventricle. Were it not for the
908:
Glonek, M; Kedzia, A; Derkowski, W (2003). "Planar measurements of foetal lateral ventricles".
1435:
1320:
1247:
1194:
1091:
1083:
1044:
995:
956:
917:
888:
820:
783:
760:
578:
389:
365:
331:
33:
Scheme showing relations of the ventricles to the surface of the brain; oriented facing left.
1461:
1387:
1301:
1262:
1172:
1075:
1034:
1026:
987:
948:
812:
750:
742:
731:"The Lateral Ventricles: A Detailed Review of Anatomy, Development, and Anatomic Variations"
602:
560:
393:
295:
45:
Drawing of a cast of the ventricular cavities, viewed from the side; oriented facing right.
1378:
1362:
1325:
1220:
1204:
461:
361:
335:
323:
279:
275:
230:
203:
186:
Each lateral ventricle resembles a C-shaped cavity that begins at an inferior horn in the
183:
contains a lateral ventricle, known as the left or right lateral ventricle, respectively.
935:
Wright IC, Rabe-Hesketh S, Woodruff PW, David AS, Murray RM, Bullmore ET (January 2000).
1113:
597:
The volume of the lateral ventricles is enlarged in some neurological diseases, such as
404:
forms the next narrow portion of the lateral boundary, which is completed medially by a
234:
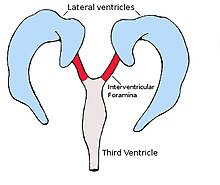
The lateral ventricles connected to the third ventricle by the interventricular foramina
1403:
1383:
1039:
1014:
755:
730:
684:
457:
429:
405:
291:
287:
207:
1476:
1345:
1335:
1284:
1230:
1167:
625:
598:
191:
187:
1103:
1215:
832:
679:
629:
473:
468:(due to the resulting shape), to curve around the central sulci; the edge of these
319:
195:
848:"Trigone of the lateral ventricle | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org"
103:
78:
1187:
1148:
729:
Scelsi CL, Rahim TA, Morris JA, Kramer GJ, Gilbert BC, Forseen SE (April 2020).
574:
from the hippocampus against the inferior horn (on the medial floor of the horn)
564:
537:
505:
991:
589:
Fetal lateral ventricles may be diagnosed using linear or planar measurements.
1079:
621:
85:
1087:
999:
428:
of the lateral ventricle, and is where the choroid plexus is enlarged as the
127:
1095:
1048:
1030:
960:
921:
824:
764:
255:
in Latin); they are usually referred to by their position relative to the
952:
283:
260:
97:
152:
816:
746:
632:
early in life, particularly in cases of a longer right posterior horn.
271:
388:- and is separated medially from the other lateral ventricle by the
270:
Between the inferior horn and the main body of the ventricle is the
222:
504:(from which the fornix emerges), and then, more anteriorly, by the
40:
28:
483:
443:
415:
375:
305:
229:
221:
172:
61:
346:(the reflected portion of the corpus callosum), while nearer the
1350:
661:
Drawing of a cast of the ventricular cavities, viewed from above
529:
314:
The anterior horn of the lateral ventricle is also known as the
267:, line the ventricular system including the lateral ventricles.
1117:
368:
are sometimes found on the frontal horn as a normal variant.
206:. Along the path, a posterior horn extends backward into the
202:
where each lateral ventricle connects to the single, central
937:"Meta-analysis of regional brain volumes in schizophrenia"
571:, for visual reasons) on the lower medial side of the horn
342:
at the limit of the ventricle is the upper surface of the
243:. The centre of the superior curve is referred to as the
1060:
1058:
1454:
1421:
1396:
1371:
1310:
1270:
1261:
1203:
1155:
133:
121:
109:
96:
84:
72:
60:
55:
50:
21:
649:Position of lateral ventricles (shown in red)
247:, while the three remaining portions are known as
16:Two largest ventricles in each cerebral hemisphere
492:The inferior horn of the lateral ventricle, or
1129:
452:The posterior horn of lateral ventricle, or
8:
885:Human Embryology & Developmental Biology
1267:
1136:
1122:
1114:
563:against the posterior horn - creating the
552:against the posterior horn - creating the
420:Trigone of lateral ventricle shown in red.
39:
27:
1038:
972:
970:
754:
724:
722:
720:
581:against the inferior horn - creating the
354:consists of the posterior surface of the
718:
716:
714:
712:
710:
708:
706:
704:
702:
700:
696:
639:
532:(in the caudal medulla), to become the
440:Posterior horn of the lateral ventricle
380:Body of lateral ventricle shown in red.
302:Anterior horns of the lateral ventricle
214:extends farther into the frontal lobe.
480:Inferior horn of the lateral ventricle
150:
18:
628:or diffuse enlargement, may indicate
476:of the cortex of the occipital lobe.
274:, which emerges from the head of the
7:
556:on the upper medial side of the horn
322:. The anterior horn connects to the
198:, and ultimately terminates at the
735:American Journal of Neuroradiology
14:
585:on the lateral floor of the horn.
520:During the first three months of
654:
642:
412:Trigone of the lateral ventricle
408:, which serves both ventricles.
241:trigone of the lateral ventricle
190:, travels through a body in the
147:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
980:Archives of General Psychiatry
386:tapetum of the corpus callosum
1:
870:braininfo.rprc.washington.edu
372:Body of the lateral ventricle
448:Posterior horn shown in red.
398:superior thalamostriate vein
226:Lateral ventricles and horns
887:. Mosby. pp. 237–238.
554:bulb of the posterior cornu
488:Inferior horn shown in red.
310:Anterior horn shown in red.
1499:
992:10.1001/archpsyc.65.9.1017
883:Carlson, Bruce M. (1999).
670:
1441:Interventricular foramina
1080:10.1007/s00381-013-2321-3
607:major depressive disorder
567:(historically called the
200:interventricular foramina
145:
38:
26:
1292:Inferior medullary velum
1280:Superior medullary velum
782:. Elsevier. p. 32.
328:interventricular foramen
805:Journal of Perinatology
400:. The main part of the
318:as it extends into the
1068:Child's Nervous System
778:Crossman, A R (2005).
673:anatomical terminology
489:
449:
421:
396:, which sits upon the
381:
350:of the ventricle, the
311:
235:
227:
593:Clinical significance
487:
447:
419:
379:
309:
265:neuroepithelial cells
233:
225:
67:ventriculus lateralis
1253:Posterior commissure
1031:10.1093/brain/awn146
953:10.1176/ajp.157.1.16
618:anatomical variation
522:prenatal development
456:, impinges into the
167:are the two largest
1431:Blood–brain barrier
1423:Cerebrospinal fluid
1341:Hypoglossal trigone
1238:Hypothalamic sulcus
1221:Infundibular recess
1178:Collateral eminence
611:Alzheimer's disease
583:collateral eminence
526:cerebrospinal fluid
402:fornix of the brain
181:cerebral hemisphere
177:cerebrospinal fluid
1483:Ventricular system
1446:Perilymphatic duct
1226:Suprapineal recess
1157:Lateral ventricles
1145:Ventricular system
910:Folia Morphologica
817:10.1038/jp.2010.79
747:10.3174/ajnr.A6456
671:This article uses
502:fimbria hippocampi
490:
450:
434:collateral trigone
422:
382:
366:Frontal horn cysts
312:
236:
228:
165:lateral ventricles
22:Lateral ventricles
1470:
1469:
1436:Cerebral aqueduct
1417:
1416:
1321:Facial colliculus
1248:Subfornical organ
1195:Septum pellucidum
789:978-0-443-10036-9
636:Additional images
579:collateral sulcus
569:hippocampus minor
390:septum pellucidum
332:septum pellucidum
161:
160:
156:
1490:
1462:Ventriculomegaly
1268:
1263:Fourth ventricle
1173:Stria terminalis
1138:
1131:
1124:
1115:
1108:
1107:
1062:
1053:
1052:
1042:
1025:(9): 2443–2454.
1010:
1004:
1003:
974:
965:
964:
932:
926:
925:
905:
899:
898:
880:
874:
873:
862:
856:
855:
846:Marsh, Phillip.
843:
837:
836:
800:
794:
793:
775:
769:
768:
758:
726:
658:
646:
616:Asymmetry as an
603:bipolar disorder
561:calcarine sulcus
394:stria terminalis
296:mamillary bodies
153:edit on Wikidata
43:
31:
19:
1498:
1497:
1493:
1492:
1491:
1489:
1488:
1487:
1473:
1472:
1471:
1466:
1450:
1413:
1392:
1388:Lateral/Luschka
1379:Median/Magendie
1367:
1363:Sulcus limitans
1358:Medial eminence
1326:Locus coeruleus
1306:
1257:
1205:Third ventricle
1199:
1184:Occipital horn
1151:
1142:
1112:
1111:
1064:
1063:
1056:
1012:
1011:
1007:
976:
975:
968:
941:Am J Psychiatry
934:
933:
929:
907:
906:
902:
895:
882:
881:
877:
864:
863:
859:
845:
844:
840:
802:
801:
797:
790:
777:
776:
772:
728:
727:
698:
693:
676:
669:
662:
659:
650:
647:
638:
595:
517:telencephalon.
514:
482:
462:corpus callosum
442:
414:
374:
362:caudate nucleus
336:corpus callosum
324:third ventricle
304:
292:choroid fissure
280:globus pallidus
276:caudate nucleus
220:
204:third ventricle
157:
46:
34:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1496:
1494:
1486:
1485:
1475:
1474:
1468:
1467:
1465:
1464:
1458:
1456:
1452:
1451:
1449:
1448:
1443:
1438:
1433:
1427:
1425:
1419:
1418:
1415:
1414:
1412:
1411:
1409:Tela choroidea
1406:
1404:Rhomboid fossa
1400:
1398:
1394:
1393:
1391:
1390:
1384:Lateral recess
1381:
1375:
1373:
1369:
1368:
1366:
1365:
1360:
1355:
1354:
1353:
1348:
1343:
1338:
1330:
1329:
1328:
1323:
1314:
1312:
1308:
1307:
1305:
1304:
1299:
1294:
1289:
1288:
1287:
1276:
1274:
1265:
1259:
1258:
1256:
1255:
1250:
1245:
1243:Tela choroidea
1240:
1235:
1234:
1233:
1228:
1223:
1218:
1209:
1207:
1201:
1200:
1198:
1197:
1192:
1191:
1190:
1182:
1181:
1180:
1175:
1170:
1161:
1159:
1153:
1152:
1143:
1141:
1140:
1133:
1126:
1118:
1110:
1109:
1054:
1005:
966:
927:
900:
893:
875:
857:
838:
795:
788:
770:
741:(4): 566–572.
695:
694:
692:
689:
688:
687:
685:Choroid plexus
682:
668:
665:
664:
663:
660:
653:
651:
648:
641:
637:
634:
594:
591:
587:
586:
575:
572:
557:
513:
510:
481:
478:
458:occipital lobe
454:occipital horn
441:
438:
430:choroid glomus
413:
410:
406:choroid plexus
373:
370:
303:
300:
288:choroid plexus
219:
216:
208:occipital lobe
159:
158:
149:
143:
142:
137:
131:
130:
125:
119:
118:
113:
107:
106:
101:
94:
93:
88:
82:
81:
76:
70:
69:
64:
58:
57:
53:
52:
48:
47:
44:
36:
35:
32:
24:
23:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1495:
1484:
1481:
1480:
1478:
1463:
1460:
1459:
1457:
1453:
1447:
1444:
1442:
1439:
1437:
1434:
1432:
1429:
1428:
1426:
1424:
1420:
1410:
1407:
1405:
1402:
1401:
1399:
1395:
1389:
1385:
1382:
1380:
1377:
1376:
1374:
1370:
1364:
1361:
1359:
1356:
1352:
1349:
1347:
1346:Area postrema
1344:
1342:
1339:
1337:
1336:Vagal trigone
1334:
1333:
1331:
1327:
1324:
1322:
1319:
1318:
1316:
1315:
1313:
1309:
1303:
1300:
1298:
1295:
1293:
1290:
1286:
1283:
1282:
1281:
1278:
1277:
1275:
1273:
1269:
1266:
1264:
1260:
1254:
1251:
1249:
1246:
1244:
1241:
1239:
1236:
1232:
1231:Pineal recess
1229:
1227:
1224:
1222:
1219:
1217:
1214:
1213:
1211:
1210:
1208:
1206:
1202:
1196:
1193:
1189:
1186:
1185:
1183:
1179:
1176:
1174:
1171:
1169:
1168:Lamina affixa
1166:
1165:
1163:
1162:
1160:
1158:
1154:
1150:
1146:
1139:
1134:
1132:
1127:
1125:
1120:
1119:
1116:
1105:
1101:
1097:
1093:
1089:
1085:
1081:
1077:
1073:
1069:
1061:
1059:
1055:
1050:
1046:
1041:
1036:
1032:
1028:
1024:
1020:
1016:
1009:
1006:
1001:
997:
993:
989:
985:
981:
973:
971:
967:
962:
958:
954:
950:
946:
942:
938:
931:
928:
923:
919:
915:
911:
904:
901:
896:
894:0-8151-1458-3
890:
886:
879:
876:
871:
867:
861:
858:
853:
849:
842:
839:
834:
830:
826:
822:
818:
814:
811:(2): 98–103.
810:
806:
799:
796:
791:
785:
781:
774:
771:
766:
762:
757:
752:
748:
744:
740:
736:
732:
725:
723:
721:
719:
717:
715:
713:
711:
709:
707:
705:
703:
701:
697:
690:
686:
683:
681:
678:
677:
674:
666:
657:
652:
645:
640:
635:
633:
631:
627:
626:midline shift
623:
619:
614:
612:
608:
604:
600:
599:schizophrenia
592:
590:
584:
580:
576:
573:
570:
566:
562:
558:
555:
551:
547:
546:
545:
541:
539:
535:
534:central canal
531:
527:
523:
518:
511:
509:
507:
503:
497:
495:
494:temporal horn
486:
479:
477:
475:
471:
467:
463:
459:
455:
446:
439:
437:
435:
431:
427:
418:
411:
409:
407:
403:
399:
395:
391:
387:
378:
371:
369:
367:
363:
359:
358:
353:
349:
345:
341:
337:
333:
329:
325:
321:
317:
308:
301:
299:
297:
293:
289:
285:
281:
277:
273:
268:
266:
262:
258:
254:
250:
246:
242:
232:
224:
217:
215:
213:
212:anterior horn
209:
205:
201:
197:
193:
192:parietal lobe
189:
188:temporal lobe
184:
182:
178:
174:
170:
166:
154:
148:
144:
141:
138:
136:
132:
129:
126:
124:
120:
117:
114:
112:
108:
105:
102:
99:
95:
92:
89:
87:
83:
80:
77:
75:
71:
68:
65:
63:
59:
54:
49:
42:
37:
30:
25:
20:
1216:Optic recess
1156:
1074:(1): 19–35.
1071:
1067:
1022:
1018:
1008:
983:
979:
947:(1): 16–25.
944:
940:
930:
916:(3): 263–5.
913:
909:
903:
884:
878:
869:
860:
851:
841:
808:
804:
798:
780:Neuroanatomy
779:
773:
738:
734:
680:Colpocephaly
630:brain injury
615:
596:
588:
568:
553:
549:
542:
519:
515:
498:
493:
491:
474:white matter
469:
465:
453:
451:
433:
425:
423:
383:
355:
351:
347:
339:
320:frontal lobe
316:frontal horn
315:
313:
269:
263:, which are
256:
252:
248:
244:
240:
237:
196:frontal lobe
185:
175:and contain
164:
162:
116:A14.1.09.272
104:birnlex_1263
66:
1188:Calcar avis
1149:human brain
986:(9): 1017.
866:"BrainInfo"
852:Radiopaedia
565:calcar avis
538:spinal cord
512:Development
506:hippocampus
56:Identifiers
691:References
622:handedness
326:, via the
169:ventricles
86:NeuroNames
1372:Apertures
1302:Fastigium
1212:Recesses
1088:0256-7040
1000:0003-990X
577:from the
559:from the
548:from the
218:Structure
210:, and an
1477:Category
1285:Frenulum
1104:13815435
1096:24240520
1049:18669512
961:10618008
922:14507062
825:20616785
765:32079598
667:See also
284:thalamus
261:Ependyma
98:NeuroLex
1455:Related
1147:of the
1040:2724905
833:9691516
756:7144651
609:, and
550:forceps
536:of the
470:forceps
466:forceps
344:rostrum
272:putamen
179:. Each
171:of the
79:D020547
51:Details
1332:Lower
1317:Upper
1297:Taenia
1102:
1094:
1086:
1047:
1037:
998:
959:
920:
891:
831:
823:
786:
763:
753:
426:atrium
338:- the
253:cornua
1397:Other
1311:Floor
1164:Body
1100:S2CID
1019:Brain
829:S2CID
340:floor
249:horns
173:brain
151:[
140:78448
62:Latin
1351:Obex
1272:Roof
1092:PMID
1084:ISSN
1045:PMID
996:ISSN
957:PMID
918:PMID
889:ISBN
821:PMID
784:ISBN
761:PMID
530:obex
357:genu
352:roof
348:body
257:body
245:body
194:and
163:The
128:5639
111:TA98
74:MeSH
1386:to
1076:doi
1035:PMC
1027:doi
1023:131
988:doi
949:doi
945:157
813:doi
751:PMC
743:doi
298:).
135:FMA
123:TA2
91:209
1479::
1098:.
1090:.
1082:.
1072:30
1070:.
1057:^
1043:.
1033:.
1021:.
1017:.
994:.
984:65
982:.
969:^
955:.
943:.
939:.
914:62
912:.
868:.
850:.
827:.
819:.
809:31
807:.
759:.
749:.
739:41
737:.
733:.
699:^
613:.
605:,
601:,
540:.
436:.
364:.
100:ID
1137:e
1130:t
1123:v
1106:.
1078::
1051:.
1029::
1002:.
990::
963:.
951::
924:.
897:.
872:.
854:.
835:.
815::
792:.
767:.
745::
675:.
251:(
155:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.