38:
73:. Time complexity is commonly estimated by counting the number of elementary operations performed by the algorithm, supposing that each elementary operation takes a fixed amount of time to perform. Thus, the amount of time taken and the number of elementary operations performed by the algorithm are taken to be related by a
5489:
problems like 3SAT etc. take exponential time. Indeed, it is conjectured for many natural NP-complete problems that they do not have sub-exponential time algorithms. Here "sub-exponential time" is taken to mean the second definition presented below. (On the other hand, many graph problems represented
3241:
comes earlier in alphabetical order than the middle word of the whole dictionary--we continue the search in the same way in the left (i.e. earlier) half of the dictionary, and then again repeatedly until the correct word is found. Otherwise, if it comes after the middle word, continue similarly with
5517:
is used to express that the running time of some algorithm may grow faster than any polynomial but is still significantly smaller than an exponential. In this sense, problems that have sub-exponential time algorithms are somewhat more tractable than those that only have exponential algorithms. The
3718:
Linear time is the best possible time complexity in situations where the algorithm has to sequentially read its entire input. Therefore, much research has been invested into discovering algorithms exhibiting linear time or, at least, nearly linear time. This research includes both software and
2611:
has to be performed to locate it. In a similar manner, finding the minimal value in an array sorted in ascending order; it is the first element. However, finding the minimal value in an unordered array is not a constant time operation as scanning over each
92:
of the size of the input. Since this function is generally difficult to compute exactly, and the running time for small inputs is usually not consequential, one commonly focuses on the behavior of the complexity when the input size increases—that is, the
5618:
5040:
in terms of machine model changes. (For example, a change from a single-tape Turing machine to a multi-tape machine can lead to a quadratic speedup, but any algorithm that runs in polynomial time under one model also does so on the other.) Any given
6693:
6306:
5471:
3242:
the right half of the dictionary. This algorithm is similar to the method often used to find an entry in a paper dictionary. As a result, the search space within the dictionary decreases as the algorithm gets closer to the target word.
5947:
2648:
Despite the name "constant time", the running time does not have to be independent of the problem size, but an upper bound for the running time has to be independent of the problem size. For example, the task "exchange the values of
6399:
88:, which is the average of the time taken on inputs of a given size (this makes sense because there are only a finite number of possible inputs of a given size). In both cases, the time complexity is generally expressed as a
7701:
Grohe, Martin; Neuen, Daniel (2021). "Recent advances on the graph isomorphism problem". In
Dabrowski, Konrad K.; Gadouleau, Maximilien; Georgiou, Nicholas; Johnson, Matthew; Mertzios, George B.; Paulusma, Daniël (eds.).
3235:
5675:. This definition allows larger running times than the first definition of sub-exponential time. An example of such a sub-exponential time algorithm is the best-known classical algorithm for integer factorization, the
6517:
3179:
5526:
A problem is said to be sub-exponential time solvable if it can be solved in running times whose logarithms grow smaller than any given polynomial. More precisely, a problem is in sub-exponential time if for every
3099:
5490:
in the natural way by adjacency matrices are solvable in subexponential time simply because the size of the input is the square of the number of vertices.) This conjecture (for the k-SAT problem) is known as the
5295:
There are some problems for which we know quasi-polynomial time algorithms, but no polynomial time algorithm is known. Such problems arise in approximation algorithms; a famous example is the directed
4681:
5800:
3340:
6113:
6021:
1631:
529:
3715:. For example, a procedure that adds up all elements of a list requires time proportional to the length of the list, if the adding time is constant, or, at least, bounded by a constant.
5738:
4603:
1758:
2481:
1329:
3927:
819:
5360:. Although quasi-polynomially solvable, it has been conjectured that the planted clique problem has no polynomial time solution; this planted clique conjecture has been used as a
2353:
2294:
2235:
1915:
3809:
5552:
3123:
5209:
3953:
4959:
The concept of polynomial time leads to several complexity classes in computational complexity theory. Some important classes defined using polynomial time are the following.
4544:
1002:
970:
7117:
Holm, Jacob; Rotenberg, Eva (2020). "Fully-dynamic planarity testing in polylogarithmic time". In
Makarychev, Konstantin; Makarychev, Yury; Tulsiani, Madhur; Kamath, Gautam;
4403:
3885:
1798:
368:
6614:
6543:
4061:
2786:
1941:
1153:
649:
327:
207:
5339:
4748:
3451:
3386:
3012:
593:
2035:
859:
353:
1366:
937:
769:
7613:
4500:
4368:
4327:
4284:
4224:
4180:
4142:
4104:
3607:
2852:
2819:
1831:
1211:
169:
6056:
4462:
3511:
2948:
2895:
2516:
2415:
1556:
703:
7009:
6231:
5673:
5393:
5096:
4918:
2099:
2000:
1500:
1415:
905:
245:
2127:
1665:
1270:
1241:
5290:
5236:
4878:
4006:
2154:
1692:
730:
5982:
5845:
3980:
2381:
1528:
1443:
3682:
3653:
3284:
3045:
2707:
2681:
1085:
1051:
458:
287:
129:
5264:
3843:
3709:
5873:
2643:
2601:
2572:
6335:
6905:
5811:
It makes a difference whether the algorithm is allowed to be sub-exponential in the size of the instance, the number of vertices, or the number of edges. In
3684:. Informally, this means that the running time increases at most linearly with the size of the input. More precisely, this means that there is a constant
260:
Algorithmic complexities are classified according to the type of function appearing in the big O notation. For example, an algorithm with time complexity
5498:
make the assumption that NP-complete problems do not have quasi-polynomial time algorithms. For example, see the known inapproximability results for the
2603:(the complexity of the algorithm) is bounded by a value that does not depend on the size of the input. For example, accessing any single element in an
7972:
5095:
An algorithm that uses exponential resources is clearly superpolynomial, but some algorithms are only very weakly superpolynomial. For example, the
3728:
7785:
7451:
3188:
5494:. Since it is conjectured that NP-complete problems do not have quasi-polynomial time algorithms, some inapproximability results in the field of
6427:
2954:
increases. An algorithm that must access all elements of its input cannot take logarithmic time, as the time taken for reading an input of size
7366:
Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on
Discrete Algorithms, SODA 2017, Barcelona, Spain, Hotel Porta Fira, January 16-19
7257:
3132:
2645:
time. If the number of elements is known in advance and does not change, however, such an algorithm can still be said to run in constant time.
1948:
7936:
7760:
7721:
7597:
7552:
7391:
7232:
7148:
6865:
3058:
2950:
algorithm is considered highly efficient, as the ratio of the number of operations to the size of the input decreases and tends to zero when
5012:: The complexity class of decision problems that can be solved with 1-sided error on a probabilistic Turing machine in polynomial time.
5020:: The complexity class of decision problems that can be solved with 2-sided error on a probabilistic Turing machine in polynomial time
4923:
All the basic arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and comparison) can be done in polynomial time.
7536:
7323:
6985:
6771:
5361:
4426:
3568:
Algorithms that search for local structure in the input, for example finding a local minimum in a 1-D array (can be solved in
7977:
5805:
4989:
4765:). No general-purpose sorts run in linear time, but the change from quadratic to sub-quadratic is of great practical importance.
84:, which is the maximum amount of time required for inputs of a given size. Less common, and usually specified explicitly, is the
7967:
7877:
7814:
6564:
the list until it is found to be sorted. In the average case, each pass through the bogosort algorithm will examine one of the
4828:
3547:
3543:
7357:
7080:
Bradford, Phillip G.; Rawlins, Gregory J. E.; Shannon, Gregory E. (1998). "Efficient matrix chain ordering in polylog time".
6814:
3396:
2608:
7533:
Fundamentals of
Computation Theory: 14th International Symposium, FCT 2003, Malmö, Sweden, August 12-15, 2003, Proceedings
5037:
7750:
7123:
Proceedings of the 52nd Annual ACM SIGACT Symposium on Theory of
Computing, STOC 2020, Chicago, IL, USA, June 22-26, 2020
5754:
4615:
6219:. Problems which admit exponential time algorithms on a deterministic Turing machine form the complexity class known as
5001:
4977:
4930:
3610:
3400:
58:
7917:(1975). "Quantifier elimination for real closed fields by cylindrical algebraic decomposition". In Brakhage, H. (ed.).
7339:
6585:
6124:
5491:
5113:, but the input size must become impractically large before it cannot be dominated by a polynomial with small degree.
3520:
commonly refers to randomized algorithms that sample a small fraction of their inputs and process them efficiently to
3392:
2966:
2420:
2299:
539:
7680:
Oded Regev (2004). "A Subexponential Time
Algorithm for the Dihedral Hidden Subgroup Problem with Polynomial Space".
4606:
3289:
1952:
6065:
5990:
5348:
Other computational problems with quasi-polynomial time solutions but no known polynomial time solution include the
1577:
5676:
5045:
will have a complexity class corresponding to the problems which can be solved in polynomial time on that machine.
4934:
3724:
2159:
2039:
488:
478:
7169:
5518:
precise definition of "sub-exponential" is not generally agreed upon, however the two most widely used are below.
7311:
7082:
6852:. Graduate Studies in Mathematics. Vol. 117. Providence, RI: American Mathematical Society. pp. 82–86.
5747:
5345:
being the number of vertices), but showing the existence of such a polynomial time algorithm is an open problem.
2048:
7706:. London Mathematical Society Lecture Note Series. Vol. 470. Cambridge University Press. pp. 187–234.
7531:
Moser, P. (2003). "Baire's
Categories on Small Complexity Classes". In Andrzej Lingas; Bengt J. Nilsson (eds.).
7439:
5812:
5683:
5495:
4939:
4549:
3252:
1719:
80:
Since an algorithm's running time may vary among different inputs of the same size, one commonly considers the
66:
6149:
variables, cannot be solved in time 2. More precisely, the hypothesis is that there is some absolute constant
2441:
1696:
7827:
7627:
Kuperberg, Greg (2005). "A Subexponential-Time
Quantum Algorithm for the Dihedral Hidden Subgroup Problem".
6573:
6142:
5155:
3562:
3521:
2616:
in the array is needed in order to determine the minimal value. Hence it is a linear time operation, taking
1847:
1294:
85:
5613:{\displaystyle {\text{SUBEXP}}=\bigcap _{\varepsilon >0}{\text{DTIME}}\left(2^{n^{\varepsilon }}\right)}
3890:
787:
6715:
5299:, for which there is a quasi-polynomial time approximation algorithm achieving an approximation factor of
5029:
4245:
3732:
3613:
where the algorithm receives a large input and queries to local information about some valid large output.
2855:
2320:
2241:
2177:
1877:
1279:
599:
89:
42:
3754:
7607:
6703:
6572:
items. If the items are distinct, only one such ordering is sorted. Bogosort shares patrimony with the
5146:
3104:
2521:
2043:
1370:
1163:
81:
37:
6688:{\displaystyle {\mbox{2-EXPTIME}}=\bigcup _{c\in \mathbb {N} }{\mbox{DTIME}}\left(2^{2^{n^{c}}}\right)}
5165:
3932:
1094:
6956:
Calude, Cristian S. and Jain, Sanjay and
Khoussainov, Bakhadyr and Li, Wei and Stephan, Frank (2017).
5485:
problem asks if all problems in NP have polynomial-time algorithms. All the best-known algorithms for
4511:
975:
943:
5296:
4373:
3852:
3524:
infer properties of the entire instance. This type of sublinear time algorithm is closely related to
3408:
2604:
1851:
1764:
1090:
466:
373:
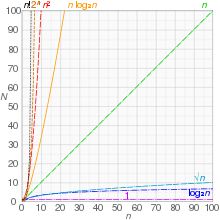
The following table summarizes some classes of commonly encountered time complexities. In the table,
6845:
6522:
4021:
2741:
2683:" is called constant time even though the time may depend on whether or not it is already true that
1920:
1113:
613:
296:
176:
7776:
7435:
5985:
5383:
consists of all problems that have quasi-polynomial time algorithms. It can be defined in terms of
5302:
5130:
4702:
4610:
4015:
3414:
3349:
2985:
2163:
1559:
1455:
556:
94:
31:
5158:, a type of behavior that may be slower than polynomial time but yet is significantly faster than
2006:
825:
332:
7868:
7864:
7707:
7681:
7662:
7636:
7369:
7194:
7126:
7062:
7003:
6991:
6938:
6418:
6301:{\displaystyle {\text{EXP}}=\bigcup _{c\in \mathbb {R_{+}} }{\text{DTIME}}\left(2^{n^{c}}\right)}
5466:{\displaystyle {\mbox{QP}}=\bigcup _{c\in \mathbb {N} }{\mbox{DTIME}}\left(2^{\log ^{c}n}\right)}
3720:
3539:
2979:
2729:
2424:
2303:
1704:
1700:
1335:
910:
735:
546:
7026:
5126:
4832:
4467:
4335:
4294:
4251:
4191:
4147:
4109:
4071:
3571:
2824:
2791:
1803:
1178:
136:
6026:
4432:
3472:
2918:
2865:
2487:
2386:
1535:
673:
7932:
7914:
7756:
7717:
7654:
7593:
7558:
7548:
7387:
7319:
7228:
7144:
6981:
6861:
6767:
6719:
5642:
5512:
4887:
4835:
states that polynomial time is a synonym for "tractable", "feasible", "efficient", or "fast".
4754:
3404:
2068:
1969:
1859:
1469:
1384:
874:
214:
2105:
1637:
1246:
1217:
7922:
7886:
7836:
7794:
7646:
7585:
7540:
7460:
7379:
7266:
7220:
7212:
7186:
7165:
7136:
7091:
7054:
6973:
6965:
6922:
6914:
6853:
6823:
6737:
6709:
5848:
5373:
5369:
5269:
5215:
5159:
5117:
5042:
5016:
4996:
4973:
4969:
4926:
4853:
4819:
4815:
4414:
4239:
3985:
3525:
2132:
1670:
709:
397:
7946:
7900:
7850:
7731:
7474:
7401:
7280:
7103:
6934:
6875:
5955:
5818:
3958:
2359:
1506:
1421:
7942:
7896:
7846:
7818:
7727:
7470:
7397:
7276:
7099:
7050:
6930:
6889:
6871:
6553:
5942:{\displaystyle {\text{SUBEPT}}={\text{DTIME}}\left(2^{o(k)}\cdot {\text{poly}}(n)\right).}
5008:
4984:
4951:
These two concepts are only relevant if the inputs to the algorithms consist of integers.
4505:
3846:
3658:
3629:
3558:
3554:
3260:
3021:
1275:
1061:
1027:
1006:
434:
263:
105:
74:
7249:
7041:(1993). "BPP has subexponential time simulations unless EXPTIME has publishable proofs".
5243:
3822:
2686:
2660:
7919:
Automata Theory and Formal
Languages: 2nd GI Conference, Kaiserslautern, May 20–23, 1975
6394:{\displaystyle {\text{E}}=\bigcup _{c\in \mathbb {N} }{\text{DTIME}}\left(2^{cn}\right)}
3955:
and thus run faster than any polynomial time algorithm whose time bound includes a term
3691:
2534:"Constant time" redirects here. For programming technique to avoid a timing attack, see
7514:
7415:
6893:
6759:
6325:
5353:
5349:
5121:
5066:
5028:: The complexity class of decision problems that can be solved with 2-sided error on a
4964:
4843:
4823:
4774:
4758:
4410:
3126:
2859:
2613:
2061:
1570:
1451:
1159:
656:
535:
98:
7891:
7872:
7823:"The complexity of the word problems for commutative semigroups and polynomial ideals"
7360:; Kun-Ko, Young; Rubinstein, Aviad; Weinstein, Omri (2017). "ETH hardness for densest-
2619:
2577:
2548:
7982:
7961:
7841:
7822:
7271:
7118:
7038:
7030:
6942:
6926:
6827:
6787:
6156:
such that 3SAT cannot be decided in time 2 by any deterministic Turing machine. With
2909:
2535:
1098:
773:
7666:
7519:
7066:
6995:
5129:
posits that these algorithms are impractical, and in many cases they are. Since the
5000:: The complexity class of decision problems that can be solved with zero error on a
3513:. In particular this includes algorithms with the time complexities defined above.
7746:
7217:
Proceedings of the 2019 ACM Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing (PODC)
5357:
6897:
3609:
time using a variant of binary search). A closely related notion is that of
7589:
7544:
7198:
7420:
7177:
6841:
5631:
is not part of the input and each ε may have its own algorithm for the problem.
5486:
5482:
5365:
5134:
4784:
4418:
4288:
3727:. This concept of linear time is used in string matching algorithms such as the
2905:
1855:
1447:
17:
7921:. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 33. Springer. pp. 134–183.
7383:
6172:
5859:
is the class of all parameterized problems that run in time sub-exponential in
2862:
to big O classification, the standard usage for logarithmic-time algorithms is
7650:
7095:
7034:
6732:
4788:
4762:
4235:
4227:
3529:
97:
of the complexity. Therefore, the time complexity is commonly expressed using
7927:
7658:
7562:
7224:
7140:
6969:
6605:
6561:
5499:
5036:
P is the smallest time-complexity class on a deterministic machine which is
4692:
4231:
4065:
3230:{\displaystyle w<D\left(\left\lfloor {\frac {n}{2}}\right\rfloor \right)}
2434:
70:
7799:
7780:
7686:
7465:
7190:
6962:
Proceedings of the 49th Annual ACM SIGACT Symposium on Theory of Computing
6957:
6512:{\displaystyle n!\leq n^{n}=2^{n\log n}=O\left(2^{n^{1+\epsilon }}\right)}
4144:
in expectation on the worst-case input. Its non-randomized version has an
7641:
6549:
6160:
denoting the number of clauses, ETH is equivalent to the hypothesis that
4818:
for which a deterministic polynomial-time algorithm exists belong to the
4761:), but more advanced algorithms can be found that are subquadratic (e.g.
4185:
3174:{\displaystyle w=D\left(\left\lfloor {\frac {n}{2}}\right\rfloor \right)}
2965:
An example of logarithmic time is given by dictionary search. Consider a
1010:
666:
3719:
hardware methods. There are several hardware technologies which exploit
7539:. Vol. 2751. Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag. pp. 333–342.
7489:
7295:
7058:
6918:
3185:
is exactly in the middle of the dictionary--then we are done. Else, if
3094:{\displaystyle D\left(\left\lfloor {\frac {n}{2}}\right\rfloor \right)}
2904:
Algorithms taking logarithmic time are commonly found in operations on
2897:
regardless of the base of the logarithm appearing in the expression of
2313:
7368:. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics. pp. 1326–1341.
6977:
6857:
5162:. The worst case running time of a quasi-polynomial time algorithm is
6722:
takes at least double exponential time, and can be done in this time.
6311:
Sometimes, exponential time is used to refer to algorithms that have
5092:
requires superpolynomial time (more specifically, exponential time).
6850:
An epsilon of room, II: Pages from year three of a mathematical blog
5109:-bit inputs; this grows faster than any polynomial for large enough
5088:
For example, an algorithm that runs for 2 steps on an input of size
4988:: The complexity class of decision problems that can be solved on a
7712:
7374:
7131:
5364:
to prove the difficulty of several other problems in computational
5085:
is the input parameter, typically the number of bits in the input.
3535:
Other settings where algorithms can run in sublinear time include:
5952:
More precisely, SUBEPT is the class of all parameterized problems
5543:
5384:
36:
7364:-subgraph with perfect completeness". In Klein, Philip N. (ed.).
5116:
An algorithm that requires superpolynomial time lies outside the
4933:
can be found in polynomial time. In some contexts, especially in
6138:
4791:
expression in the size of the input for the algorithm, that is,
7342:(1965). "The intrinsic computational difficulty of functions".
6424:. Factorial time is a subset of exponential time (EXP) because
3557:
on the input structure. An important example are operations on
3055:
is in the dictionary may be done in logarithmic time: consider
6221:
5024:
254:
69:
that describes the amount of computer time it takes to run an
5750:, which the best known algorithm from 1982 to 2016 solved in
5639:
Some authors define sub-exponential time as running times in
7576:
Miltersen, P.B. (2001). "Derandomizing Complexity Classes".
3051:
th entry. Under these hypotheses, the test to see if a word
5534:
there exists an algorithm which solves the problem in time
4182:
running time only when considering average case complexity.
7248:
Naik, Ashish V.; Regan, Kenneth W.; Sivakumar, D. (1995).
6548:
An example of an algorithm that runs in factorial time is
6319:) = 2, where the exponent is at most a linear function of
5623:
This notion of sub-exponential is non-uniform in terms of
5538:(2). The set of all such problems is the complexity class
7125:. Association for Computing Machinery. pp. 167–180.
6964:. Association for Computing Machinery. pp. 252–263.
6790:; Naher, Stefan (1990). "Bounded ordered dictionaries in
4425:-sized array one by one. Since the insert operation on a
4411:
Big O notation § Family of Bachmann–Landau notations
3546:(allowing them to read the entire input), but sub-linear
5815:, this difference is made explicit by considering pairs
4106:, in its randomized version, has a running time that is
6698:
Well-known double exponential time algorithms include:
6552:, a notoriously inefficient sorting algorithm based on
7781:"Which problems have strongly exponential complexity?"
7344:
Proc. Logic, Methodology, and Philosophy of Science II
6647:
6619:
5808:
2016 a quasi-polynomial time algorithm was presented.
5426:
5398:
5154:
algorithms are algorithms whose running time exhibits
4618:
2689:
2663:
2622:
2580:
2551:
6617:
6525:
6430:
6338:
6234:
6203:. More formally, an algorithm is exponential time if
6068:
6029:
5993:
5958:
5876:
5821:
5757:
5686:
5645:
5555:
5396:
5305:
5272:
5246:
5218:
5168:
4890:
4856:
4705:
4552:
4514:
4470:
4435:
4376:
4338:
4297:
4254:
4194:
4150:
4112:
4074:
4024:
3988:
3961:
3935:
3893:
3855:
3825:
3757:
3694:
3661:
3632:
3574:
3475:
3417:
3352:
3292:
3263:
3191:
3135:
3107:
3061:
3024:
2988:
2921:
2868:
2827:
2794:
2744:
2490:
2444:
2389:
2362:
2323:
2244:
2180:
2135:
2108:
2071:
2009:
1972:
1923:
1880:
1806:
1767:
1722:
1673:
1640:
1580:
1538:
1509:
1472:
1424:
1387:
1338:
1297:
1249:
1220:
1181:
1116:
1064:
1030:
978:
946:
913:
877:
828:
790:
738:
712:
676:
616:
559:
491:
437:
335:
299:
266:
217:
179:
139:
108:
6141:, the satisfiability problem of Boolean formulas in
4676:{\textstyle T(n)=2T\left({\frac {n}{2}}\right)+O(n)}
1089:
Finding the smallest or largest item in an unsorted
7873:"Real quantifier elimination is doubly exponential"
5795:{\displaystyle 2^{O\left({\sqrt {n\log n}}\right)}}
3018:th entry of the dictionary in a constant time. Let
369:
Computational complexity of mathematical operations
6687:
6537:
6511:
6393:
6300:
6107:
6050:
6015:
5976:
5941:
5839:
5794:
5732:
5667:
5612:
5465:
5333:
5284:
5258:
5230:
5203:
4912:
4872:
4742:
4675:
4597:
4538:
4494:
4456:
4397:
4370:running time is simply the result of performing a
4362:
4321:
4278:
4218:
4174:
4136:
4098:
4055:
4011:Algorithms which run in quasilinear time include:
4000:
3974:
3947:
3921:
3879:
3837:
3803:
3703:
3676:
3647:
3601:
3505:
3445:
3380:
3334:
3278:
3229:
3173:
3117:
3093:
3039:
3006:
2942:
2889:
2846:
2813:
2780:
2701:
2675:
2637:
2595:
2566:
2510:
2475:
2409:
2375:
2347:
2288:
2229:
2148:
2121:
2093:
2029:
1994:
1935:
1909:
1825:
1792:
1752:
1686:
1659:
1625:
1550:
1522:
1494:
1437:
1409:
1360:
1323:
1264:
1235:
1205:
1147:
1079:
1045:
996:
964:
931:
899:
853:
813:
763:
724:
697:
643:
587:
523:
452:
347:
321:
281:
239:
201:
163:
123:
6604:. Such algorithms belong to the complexity class
30:"Running time" redirects here. For the film, see
6145:with at most three literals per clause and with
5065:) is not bounded above by any polynomial. Using
7520:Class SUBEXP: Deterministic Subexponential-Time
7300:(4th ed.). Pearson Education. p. 186.
6958:"Deciding parity games in quasipolynomial time"
6164:SAT cannot be solved in time 2 for any integer
3335:{\displaystyle O{\bigl (}(\log n)^{k}{\bigr )}}
27:Estimate of time taken for running an algorithm
6108:{\displaystyle 2^{f(k)}\cdot {\text{poly}}(n)}
6016:{\displaystyle f:\mathbb {N} \to \mathbb {N} }
1626:{\displaystyle 2^{O(\log n)}={\text{poly}}(n)}
7612:: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of March 2024 (
4838:Some examples of polynomial-time algorithms:
3327:
3298:
655:Amortized time per operation using a bounded
524:{\displaystyle O{\bigl (}\alpha (n){\bigr )}}
516:
497:
8:
7008:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
6906:Journal of the European Mathematical Society
3112:
3108:
3395:can be solved in polylogarithmic time on a
2520:Deciding the truth of a given statement in
6323:. This gives rise to the complexity class
6171:. The exponential time hypothesis implies
3111:
390:
7926:
7890:
7840:
7798:
7711:
7685:
7640:
7464:
7373:
7270:
7130:
6898:"Primality testing with Gaussian periods"
6764:Introduction to the Theory of Computation
6671:
6666:
6661:
6646:
6640:
6639:
6632:
6618:
6616:
6524:
6491:
6486:
6457:
6444:
6429:
6378:
6365:
6359:
6358:
6351:
6339:
6337:
6286:
6281:
6268:
6260:
6259:
6256:
6254:
6247:
6235:
6233:
6091:
6073:
6067:
6028:
6009:
6008:
6001:
6000:
5992:
5957:
5917:
5899:
5885:
5877:
5875:
5820:
5770:
5762:
5756:
5733:{\displaystyle 2^{{\tilde {O}}(n^{1/3})}}
5715:
5711:
5693:
5692:
5691:
5685:
5650:
5644:
5598:
5593:
5580:
5568:
5556:
5554:
5445:
5440:
5425:
5419:
5418:
5411:
5397:
5395:
5316:
5304:
5271:
5245:
5217:
5184:
5173:
5167:
4901:
4889:
4864:
4855:
4731:
4704:
4644:
4617:
4598:{\displaystyle \log(n!)=\Theta (n\log n)}
4551:
4513:
4469:
4434:
4375:
4337:
4296:
4253:
4193:
4149:
4111:
4073:
4038:
4023:
3987:
3966:
3960:
3934:
3904:
3892:
3857:
3856:
3854:
3824:
3786:
3756:
3693:
3660:
3631:
3573:
3474:
3428:
3416:
3363:
3351:
3326:
3325:
3319:
3297:
3296:
3291:
3262:
3209:
3190:
3153:
3134:
3106:
3073:
3060:
3023:
2987:
2920:
2867:
2832:
2826:
2799:
2793:
2743:
2688:
2662:
2621:
2579:
2550:
2500:
2495:
2489:
2455:
2454:
2449:
2443:
2399:
2394:
2388:
2367:
2361:
2329:
2328:
2322:
2271:
2258:
2243:
2203:
2179:
2140:
2134:
2113:
2107:
2076:
2070:
2019:
2014:
2008:
1977:
1971:
1922:
1896:
1891:
1879:
1811:
1805:
1772:
1766:
1753:{\displaystyle 2^{{\text{poly}}(\log n)}}
1728:
1727:
1721:
1678:
1672:
1645:
1639:
1609:
1585:
1579:
1537:
1514:
1508:
1483:
1471:
1429:
1423:
1398:
1386:
1346:
1337:
1301:
1296:
1248:
1219:
1180:
1130:
1115:
1063:
1029:
983:
977:
951:
945:
912:
888:
876:
845:
827:
791:
789:
752:
737:
711:
675:
615:
570:
558:
515:
514:
496:
495:
490:
436:
334:
310:
298:
265:
228:
216:
190:
178:
138:
107:
41:Graphs of functions commonly used in the
7294:Sedgewick, Robert; Wayne, Kevin (2011).
7215:(2019). "Local Computation Algorithms".
6754:
6752:
2476:{\displaystyle 2^{2^{{\text{poly}}(n)}}}
7786:Journal of Computer and System Sciences
7452:Journal of Computer and System Sciences
7250:"On quasilinear-time complexity theory"
6748:
5137:problems require superpolynomial time.
5097:Adleman–Pomerance–Rumely primality test
3887:. Quasilinear time algorithms are also
7605:
7430:
7428:
7001:
4753:For example, simple, comparison-based
4609:. They also frequently arise from the
4546:comparisons in the worst case because
3688:such that the running time is at most
2713:such that the time required is always
1324:{\displaystyle n{\text{poly}}(\log n)}
293:and an algorithm with time complexity
7021:
7019:
5133:is unresolved, it is unknown whether
3922:{\displaystyle O(n^{1+\varepsilon })}
814:{\displaystyle {\text{poly}}(\log n)}
465:Finding the median value in a sorted
7:
6596:) is upper bounded by 2, where poly(
6545:. However, it is not a subset of E.
6195:) is upper bounded by 2, where poly(
5266:this gives polynomial time, and for
2348:{\displaystyle 2^{{\text{poly}}(n)}}
2289:{\displaystyle n!,n^{n},2^{n\log n}}
2230:{\displaystyle O(n)!=2^{O(n\log n)}}
1910:{\displaystyle O(2^{n^{\epsilon }})}
5481:In complexity theory, the unsolved
4920:and is a polynomial-time algorithm.
4827:, which is central in the field of
3804:{\displaystyle T(n)=O(n\log ^{k}n)}
3729:Boyer–Moore string-search algorithm
45:, showing the number of operations
7318:. Reading, Mass.: Addison-Wesley.
4574:
4515:
4377:
3611:Local Computation Algorithms (LCA)
3542:that have linear or greater total
3453:time per insert/delete operation.
3118:{\displaystyle \lfloor \;\rfloor }
2709:. However, there is some constant
1951:unless EXPTIME (see below) equals
25:
7537:Lecture Notes in Computer Science
7490:"A not-quite-exponential dilemma"
5863:and polynomial in the input size
5742:where the length of the input is
5542:which can be defined in terms of
5362:computational hardness assumption
5204:{\displaystyle 2^{O(\log ^{c}n)}}
4464:time, the entire algorithm takes
4427:self-balancing binary search tree
4421:by inserting each element of the
3948:{\displaystyle \varepsilon >0}
363:Table of common time complexities
7578:Handbook of Randomized Computing
7488:Aaronson, Scott (5 April 2009).
5477:Relation to NP-complete problems
5352:problem in which the goal is to
5053:An algorithm is defined to take
4990:non-deterministic Turing machine
4539:{\displaystyle \Omega (n\log n)}
3655:time, if its time complexity is
2607:takes constant time as only one
1371:Multipoint polynomial evaluation
997:{\displaystyle n^{\frac {2}{3}}}
965:{\displaystyle n^{\frac {1}{2}}}
7973:Computational complexity theory
7878:Journal of Symbolic Computation
7779:; Paturi, R.; Zane, F. (2001).
7752:Parameterized Complexity Theory
5356:in the union of a clique and a
4829:computational complexity theory
4398:{\displaystyle \Theta (\log n)}
3880:{\displaystyle {\tilde {O}}(n)}
3743:An algorithm is said to run in
3723:to provide this. An example is
3461:An algorithm is said to run in
3346:. Another way to write this is
3250:An algorithm is said to run in
1793:{\displaystyle n^{\log \log n}}
257:needed to represent the input.
7580:. Combinatorial Optimization.
7421:Class QP: Quasipolynomial-Time
6815:Information Processing Letters
6538:{\displaystyle \epsilon >0}
6102:
6096:
6083:
6077:
6058:and an algorithm that decides
6045:
6039:
6005:
5971:
5959:
5928:
5922:
5909:
5903:
5834:
5822:
5725:
5704:
5698:
5660:
5654:
5328:
5309:
5196:
5177:
4907:
4894:
4779:An algorithm is said to be of
4737:
4724:
4715:
4709:
4670:
4664:
4628:
4622:
4592:
4577:
4568:
4559:
4533:
4518:
4489:
4474:
4451:
4439:
4392:
4380:
4357:
4342:
4316:
4301:
4273:
4258:
4213:
4198:
4169:
4154:
4131:
4116:
4093:
4078:
4056:{\displaystyle O(n\log ^{2}n)}
4050:
4028:
3916:
3897:
3874:
3868:
3862:
3798:
3776:
3767:
3761:
3671:
3665:
3642:
3636:
3596:
3593:
3587:
3578:
3500:
3494:
3485:
3479:
3440:
3421:
3397:parallel random-access machine
3375:
3356:
3316:
3303:
3273:
3267:
3034:
3028:
2937:
2925:
2884:
2872:
2781:{\displaystyle T(n)=O(\log n)}
2775:
2763:
2754:
2748:
2632:
2626:
2590:
2584:
2561:
2555:
2536:Timing attack § Avoidance
2466:
2460:
2340:
2334:
2222:
2207:
2190:
2184:
2086:
2080:
1987:
1981:
1936:{\displaystyle \epsilon >0}
1904:
1884:
1745:
1733:
1620:
1614:
1601:
1589:
1489:
1476:
1404:
1391:
1318:
1306:
1200:
1185:
1148:{\displaystyle O(n\log ^{*}n)}
1142:
1120:
1040:
1034:
894:
881:
842:
829:
808:
796:
758:
745:
692:
680:
644:{\displaystyle O(\log \log n)}
638:
620:
600:Distributed coloring of cycles
582:
563:
511:
505:
447:
441:
322:{\displaystyle O(n^{\alpha })}
316:
303:
276:
270:
234:
221:
202:{\displaystyle O(n^{\alpha })}
196:
183:
158:
143:
118:
112:
1:
7892:10.1016/S0747-7171(88)80004-X
7704:Surveys in combinatorics 2021
6846:"1.11 The AKS primality test"
5334:{\displaystyle O(\log ^{3}n)}
4937:, one differentiates between
4880:operations for some constant
4743:{\displaystyle T(n)=o(n^{2})}
4409:times (for the notation, see
3622:An algorithm is said to take
3446:{\displaystyle O(\log ^{3}n)}
3381:{\displaystyle O(\log ^{k}n)}
3007:{\displaystyle 1\leq k\leq n}
2734:An algorithm is said to take
588:{\displaystyle O(\log ^{*}n)}
7842:10.1016/0001-8708(82)90048-2
7590:10.1007/978-1-4615-0013-1_19
7584:. Kluwer Academic Pub: 843.
7545:10.1007/978-3-540-45077-1_31
7438:; Paturi, Ramamohan (2001).
7272:10.1016/0304-3975(95)00031-Q
7258:Theoretical Computer Science
6828:10.1016/0020-0190(90)90022-P
6556:. Bogosort sorts a list of
5002:probabilistic Turing machine
4978:deterministic Turing machine
2047:formerly-best algorithm for
2030:{\displaystyle 2^{\sqrt{n}}}
1532:Naive multiplication of two
854:{\displaystyle (\log n)^{2}}
348:{\displaystyle \alpha >0}
59:theoretical computer science
49:as the result of input size
7170:"Sublinear time algorithms"
6584:An algorithm is said to be
6409:An algorithm is said to be
6183:An algorithm is said to be
6131:exponential time hypothesis
6125:Exponential time hypothesis
6119:Exponential time hypothesis
5679:, which runs in time about
5492:exponential time hypothesis
4810:for some positive constant
3811:for some positive constant
3181:--that is to say, the word
2541:An algorithm is said to be
2421:matrix chain multiplication
1361:{\displaystyle n\log ^{2}n}
932:{\displaystyle 0<c<1}
764:{\displaystyle \log(n^{2})}
384:, i.e., polynomial in
7999:
7592:(inactive 18 March 2024).
7384:10.1137/1.9781611974782.86
7312:Papadimitriou, Christos H.
6122:
5746:. Another example was the
5677:general number field sieve
5292:it gives sub-linear time.
5144:
4772:
4495:{\displaystyle O(n\log n)}
4363:{\displaystyle O(n\log n)}
4322:{\displaystyle O(n\log n)}
4279:{\displaystyle O(n\log n)}
4219:{\displaystyle O(n\log n)}
4175:{\displaystyle O(n\log n)}
4137:{\displaystyle O(n\log n)}
4099:{\displaystyle O(n\log n)}
3725:content-addressable memory
3602:{\displaystyle O(\log(n))}
2847:{\displaystyle \log _{b}n}
2814:{\displaystyle \log _{a}n}
2727:
2533:
2300:traveling salesman problem
2160:traveling salesman problem
1826:{\displaystyle n^{\log n}}
1206:{\displaystyle O(n\log n)}
366:
164:{\displaystyle O(n\log n)}
82:worst-case time complexity
29:
7755:. Springer. p. 417.
7651:10.1137/s0097539703436345
7629:SIAM Journal on Computing
7096:10.1137/S0097539794270698
7083:SIAM Journal on Computing
6927:21.11116/0000-0005-717D-0
6766:. Course Technology Inc.
6051:{\displaystyle f\in o(k)}
5748:graph isomorphism problem
5077:) time for all constants
4457:{\displaystyle O(\log n)}
3506:{\displaystyle T(n)=o(n)}
2943:{\displaystyle O(\log n)}
2890:{\displaystyle O(\log n)}
2511:{\displaystyle 2^{2^{n}}}
2410:{\displaystyle 2^{n^{2}}}
1551:{\displaystyle n\times n}
698:{\displaystyle O(\log n)}
469:of numbers. Calculating
419:Examples of running times
357:polynomial time algorithm
7928:10.1007/3-540-07407-4_17
7635:(1). Philadelphia: 188.
7316:Computational complexity
7043:Computational Complexity
6702:Decision procedures for
6600:) is some polynomial in
6417:is upper bounded by the
6199:) is some polynomial in
5813:parameterized complexity
5668:{\displaystyle 2^{o(n)}}
5496:approximation algorithms
4976:that can be solved on a
4940:strongly polynomial time
4913:{\displaystyle O(n^{2})}
4607:Stirling's approximation
4242:, etc. in the worst case
3711:for every input of size
3518:sublinear time algorithm
2860:multiplier is irrelevant
2094:{\displaystyle 2^{O(n)}}
2040:Best classical algorithm
1995:{\displaystyle 2^{o(n)}}
1495:{\displaystyle O(n^{3})}
1410:{\displaystyle O(n^{2})}
900:{\displaystyle O(n^{c})}
253:is the size in units of
240:{\displaystyle O(2^{n})}
67:computational complexity
7978:Computational resources
7828:Advances in Mathematics
7225:10.1145/3293611.3331587
7141:10.1145/3357713.3384249
7049:(4). Berlin, New York:
6970:10.1145/3055399.3055409
6580:Double exponential time
6574:infinite monkey theorem
6143:conjunctive normal form
5156:quasi-polynomial growth
4884:. Thus it runs in time
4783:if its running time is
4246:Fast Fourier transforms
3405:determined to be planar
2982:. We suppose that, for
2431:double exponential time
2122:{\displaystyle 1.1^{n}}
1848:approximation algorithm
1660:{\displaystyle n^{2}+n}
1265:{\displaystyle \log n!}
1236:{\displaystyle n\log n}
86:average-case complexity
7968:Analysis of algorithms
7800:10.1006/jcss.2001.1774
7466:10.1006/jcss.2000.1727
7440:"On the complexity of
6716:Quantifier elimination
6689:
6539:
6513:
6395:
6302:
6215:(2) for some constant
6109:
6052:
6017:
5978:
5943:
5841:
5796:
5734:
5669:
5614:
5467:
5335:
5286:
5285:{\displaystyle c<1}
5260:
5232:
5231:{\displaystyle c>0}
5205:
5030:quantum Turing machine
4945:weakly polynomial time
4914:
4874:
4873:{\displaystyle An^{2}}
4744:
4677:
4599:
4540:
4496:
4458:
4399:
4364:
4323:
4280:
4220:
4176:
4138:
4100:
4057:
4002:
4001:{\displaystyle c>1}
3976:
3949:
3923:
3881:
3839:
3805:
3705:
3678:
3649:
3603:
3555:guaranteed assumptions
3507:
3447:
3382:
3336:
3280:
3231:
3175:
3119:
3095:
3041:
3008:
2944:
2891:
2848:
2815:
2782:
2703:
2677:
2639:
2597:
2574:time) if the value of
2568:
2512:
2477:
2411:
2377:
2349:
2290:
2231:
2150:
2149:{\displaystyle 10^{n}}
2123:
2095:
2058:(with linear exponent)
2031:
1996:
1937:
1911:
1827:
1794:
1754:
1688:
1687:{\displaystyle n^{10}}
1661:
1627:
1558:matrices. Calculating
1552:
1524:
1496:
1439:
1411:
1362:
1325:
1280:Fast Fourier transform
1266:
1237:
1207:
1149:
1081:
1047:
998:
966:
933:
901:
855:
815:
765:
726:
725:{\displaystyle \log n}
699:
645:
589:
538:per operation using a
525:
454:
349:
323:
283:
241:
203:
165:
125:
54:
43:analysis of algorithms
7191:10.1145/954092.954103
6704:Presburger arithmetic
6690:
6540:
6514:
6396:
6303:
6110:
6053:
6018:
5984:for which there is a
5979:
5977:{\displaystyle (L,k)}
5944:
5842:
5840:{\displaystyle (L,k)}
5797:
5735:
5670:
5615:
5468:
5379:The complexity class
5336:
5287:
5261:
5233:
5206:
5152:Quasi-polynomial time
5147:Quasi-polynomial time
5141:Quasi-polynomial time
5067:little omega notation
4915:
4875:
4846:sorting algorithm on
4745:
4678:
4600:
4541:
4497:
4459:
4400:
4365:
4324:
4281:
4221:
4177:
4139:
4101:
4058:
4003:
3977:
3975:{\displaystyle n^{c}}
3950:
3924:
3882:
3849:these algorithms are
3840:
3806:
3747:(also referred to as
3706:
3679:
3650:
3604:
3553:Algorithms that have
3508:
3448:
3393:matrix chain ordering
3383:
3337:
3281:
3232:
3176:
3120:
3096:
3042:
3014:, one may access the
3009:
2945:
2892:
2849:
2816:
2783:
2728:Further information:
2704:
2678:
2657:if necessary so that
2640:
2598:
2569:
2522:Presburger arithmetic
2513:
2478:
2412:
2378:
2376:{\displaystyle 2^{n}}
2350:
2291:
2232:
2151:
2124:
2096:
2044:integer factorization
2032:
1997:
1938:
1912:
1828:
1795:
1755:
1711:quasi-polynomial time
1697:Karmarkar's algorithm
1689:
1662:
1628:
1553:
1525:
1523:{\displaystyle n^{3}}
1497:
1440:
1438:{\displaystyle n^{2}}
1412:
1363:
1326:
1267:
1238:
1208:
1164:polygon triangulation
1150:
1082:
1048:
999:
967:
934:
902:
856:
816:
766:
727:
700:
646:
590:
526:
455:
367:Further information:
350:
324:
291:linear time algorithm
284:
242:
204:
166:
126:
40:
7436:Impagliazzo, Russell
6615:
6560:items by repeatedly
6523:
6428:
6336:
6232:
6066:
6027:
5991:
5956:
5874:
5819:
5755:
5684:
5643:
5553:
5506:Sub-exponential time
5394:
5303:
5297:Steiner tree problem
5270:
5244:
5216:
5166:
5055:superpolynomial time
5049:Superpolynomial time
4888:
4854:
4757:are quadratic (e.g.
4703:
4616:
4550:
4512:
4468:
4433:
4374:
4336:
4295:
4252:
4234:, binary tree sort,
4192:
4148:
4110:
4072:
4022:
3986:
3959:
3933:
3891:
3853:
3823:
3755:
3692:
3677:{\displaystyle O(n)}
3659:
3648:{\displaystyle O(n)}
3630:
3572:
3473:
3415:
3350:
3290:
3279:{\displaystyle T(n)}
3261:
3246:Polylogarithmic time
3237:--i.e., if the word
3189:
3133:
3105:
3059:
3040:{\displaystyle D(k)}
3022:
2986:
2919:
2866:
2825:
2792:
2742:
2702:{\textstyle a\leq b}
2687:
2676:{\textstyle a\leq b}
2661:
2620:
2578:
2549:
2488:
2442:
2387:
2360:
2321:
2242:
2178:
2133:
2106:
2069:
2007:
1970:
1960:sub-exponential time
1921:
1878:
1867:sub-exponential time
1852:Steiner tree problem
1804:
1765:
1720:
1671:
1638:
1578:
1536:
1507:
1470:
1422:
1385:
1336:
1295:
1247:
1218:
1179:
1114:
1080:{\displaystyle 2n+5}
1062:
1046:{\displaystyle O(n)}
1028:
976:
944:
911:
875:
826:
788:
780:polylogarithmic time
736:
710:
674:
614:
557:
547:iterated logarithmic
489:
453:{\displaystyle O(1)}
435:
333:
297:
282:{\displaystyle O(n)}
264:
215:
177:
137:
124:{\displaystyle O(n)}
106:
7865:Davenport, James H.
6712:(in the worst case)
6568:! orderings of the
5986:computable function
5354:find a large clique
5259:{\displaystyle c=1}
5131:P versus NP problem
4611:recurrence relation
4332:In many cases, the
4016:In-place merge sort
3929:for every constant
3838:{\displaystyle k=1}
3733:Ukkonen's algorithm
3540:Parallel algorithms
2978:entries, sorted in
2958:is of the order of
2856:constant multiplier
2164:dynamic programming
1962:(second definition)
1858:solver, best known
1560:partial correlation
1106:"n log-star n" time
422:Example algorithms
95:asymptotic behavior
32:Running Time (film)
7915:Collins, George E.
7687:quant-ph/0406151v1
7059:10.1007/BF01275486
6890:Lenstra, H. W. Jr.
6720:real closed fields
6685:
6651:
6645:
6623:
6586:double exponential
6535:
6509:
6419:factorial function
6391:
6364:
6298:
6267:
6105:
6048:
6013:
5974:
5939:
5837:
5792:
5730:
5665:
5627:in the sense that
5610:
5579:
5463:
5430:
5424:
5402:
5331:
5282:
5256:
5228:
5201:
5032:in polynomial time
5004:in polynomial time
4992:in polynomial time
4980:in polynomial time
4955:Complexity classes
4910:
4870:
4850:integers performs
4755:sorting algorithms
4740:
4687:Sub-quadratic time
4673:
4595:
4536:
4492:
4454:
4395:
4360:
4319:
4276:
4216:
4172:
4134:
4096:
4053:
3998:
3972:
3945:
3919:
3877:
3835:
3801:
3704:{\displaystyle cn}
3701:
3674:
3645:
3599:
3565:in a sorted array.
3516:The specific term
3503:
3443:
3378:
3342:for some constant
3332:
3276:
3227:
3171:
3115:
3091:
3037:
3004:
2980:alphabetical order
2940:
2887:
2844:
2811:
2778:
2730:Logarithmic growth
2699:
2673:
2635:
2593:
2564:
2508:
2473:
2425:brute-force search
2407:
2373:
2345:
2304:brute-force search
2286:
2227:
2146:
2119:
2091:
2027:
1992:
1933:
1907:
1869:(first definition)
1823:
1790:
1750:
1705:AKS primality test
1701:linear programming
1684:
1657:
1623:
1548:
1520:
1492:
1456:Direct convolution
1435:
1407:
1358:
1321:
1262:
1233:
1203:
1145:
1095:Kadane's algorithm
1077:
1043:
994:
962:
929:
897:
851:
811:
761:
722:
695:
641:
585:
521:
450:
345:
329:for some constant
319:
279:
237:
199:
161:
121:
55:
7938:978-3-540-07407-6
7762:978-3-540-29952-3
7723:978-1-009-01888-3
7599:978-1-4613-4886-3
7554:978-3-540-40543-6
7393:978-1-61197-478-2
7234:978-1-4503-6217-7
7213:Rubinfeld, Ronitt
7166:Rubinfeld, Ronitt
7150:978-1-4503-6979-4
6867:978-0-8218-5280-4
6650:
6628:
6622:
6368:
6347:
6342:
6271:
6243:
6238:
6094:
5920:
5888:
5880:
5849:decision problems
5784:
5701:
5635:Second definition
5583:
5564:
5559:
5429:
5407:
5401:
4974:decision problems
4927:Maximum matchings
4697:subquadratic time
4652:
4508:require at least
3865:
3817:linearithmic time
3217:
3161:
3081:
2854:are related by a
2638:{\textstyle O(n)}
2596:{\textstyle T(n)}
2567:{\textstyle O(1)}
2545:(also written as
2527:
2526:
2458:
2332:
2049:graph isomorphism
2024:
1860:graph isomorphism
1850:for the directed
1731:
1612:
1304:
1274:Fastest possible
1171:linearithmic time
991:
959:
794:
479:inverse Ackermann
53:for each function
16:(Redirected from
7990:
7951:
7950:
7930:
7911:
7905:
7904:
7894:
7861:
7855:
7854:
7844:
7819:Meyer, Albert R.
7811:
7805:
7804:
7802:
7773:
7767:
7766:
7742:
7736:
7735:
7715:
7698:
7692:
7691:
7689:
7677:
7671:
7670:
7644:
7642:quant-ph/0302112
7624:
7618:
7617:
7611:
7603:
7573:
7567:
7566:
7528:
7522:
7511:
7505:
7504:
7502:
7500:
7494:Shtetl-Optimized
7485:
7479:
7478:
7468:
7448:
7443:
7432:
7423:
7412:
7406:
7405:
7377:
7363:
7354:
7348:
7347:
7346:. North Holland.
7336:
7330:
7329:
7308:
7302:
7301:
7291:
7285:
7284:
7274:
7254:
7245:
7239:
7238:
7209:
7203:
7202:
7174:
7161:
7155:
7154:
7134:
7114:
7108:
7107:
7077:
7071:
7070:
7023:
7014:
7013:
7007:
6999:
6953:
6947:
6946:
6919:10.4171/JEMS/861
6913:(4): 1229–1269.
6902:
6886:
6880:
6879:
6838:
6832:
6831:
6811:
6800:
6784:
6778:
6777:
6756:
6738:Space complexity
6694:
6692:
6691:
6686:
6684:
6680:
6679:
6678:
6677:
6676:
6675:
6652:
6648:
6644:
6643:
6624:
6620:
6544:
6542:
6541:
6536:
6518:
6516:
6515:
6510:
6508:
6504:
6503:
6502:
6501:
6471:
6470:
6449:
6448:
6400:
6398:
6397:
6392:
6390:
6386:
6385:
6369:
6366:
6363:
6362:
6343:
6340:
6307:
6305:
6304:
6299:
6297:
6293:
6292:
6291:
6290:
6272:
6269:
6266:
6265:
6264:
6263:
6239:
6236:
6211:) is bounded by
6185:exponential time
6179:Exponential time
6170:
6155:
6114:
6112:
6111:
6106:
6095:
6092:
6087:
6086:
6057:
6055:
6054:
6049:
6022:
6020:
6019:
6014:
6012:
6004:
5983:
5981:
5980:
5975:
5948:
5946:
5945:
5940:
5935:
5931:
5921:
5918:
5913:
5912:
5889:
5886:
5881:
5878:
5846:
5844:
5843:
5838:
5803:
5801:
5799:
5798:
5793:
5791:
5790:
5789:
5785:
5771:
5745:
5741:
5739:
5737:
5736:
5731:
5729:
5728:
5724:
5723:
5719:
5703:
5702:
5694:
5674:
5672:
5671:
5666:
5664:
5663:
5619:
5617:
5616:
5611:
5609:
5605:
5604:
5603:
5602:
5584:
5581:
5578:
5560:
5557:
5533:
5522:First definition
5472:
5470:
5469:
5464:
5462:
5458:
5457:
5450:
5449:
5431:
5427:
5423:
5422:
5403:
5399:
5374:machine learning
5370:property testing
5340:
5338:
5337:
5332:
5321:
5320:
5291:
5289:
5288:
5283:
5265:
5263:
5262:
5257:
5239:
5237:
5235:
5234:
5229:
5210:
5208:
5207:
5202:
5200:
5199:
5189:
5188:
5160:exponential time
5118:complexity class
5104:
5043:abstract machine
4970:complexity class
4919:
4917:
4916:
4911:
4906:
4905:
4879:
4877:
4876:
4871:
4869:
4868:
4820:complexity class
4809:
4749:
4747:
4746:
4741:
4736:
4735:
4682:
4680:
4679:
4674:
4657:
4653:
4645:
4604:
4602:
4601:
4596:
4545:
4543:
4542:
4537:
4506:Comparison sorts
4501:
4499:
4498:
4493:
4463:
4461:
4460:
4455:
4424:
4415:binary tree sort
4413:). For example,
4408:
4404:
4402:
4401:
4396:
4369:
4367:
4366:
4361:
4328:
4326:
4325:
4320:
4285:
4283:
4282:
4277:
4240:patience sorting
4225:
4223:
4222:
4217:
4181:
4179:
4178:
4173:
4143:
4141:
4140:
4135:
4105:
4103:
4102:
4097:
4062:
4060:
4059:
4054:
4043:
4042:
4007:
4005:
4004:
3999:
3981:
3979:
3978:
3973:
3971:
3970:
3954:
3952:
3951:
3946:
3928:
3926:
3925:
3920:
3915:
3914:
3886:
3884:
3883:
3878:
3867:
3866:
3858:
3844:
3842:
3841:
3836:
3814:
3810:
3808:
3807:
3802:
3791:
3790:
3745:quasilinear time
3739:Quasilinear time
3714:
3710:
3708:
3707:
3702:
3687:
3683:
3681:
3680:
3675:
3654:
3652:
3651:
3646:
3608:
3606:
3605:
3600:
3526:property testing
3512:
3510:
3509:
3504:
3452:
3450:
3449:
3444:
3433:
3432:
3387:
3385:
3384:
3379:
3368:
3367:
3345:
3341:
3339:
3338:
3333:
3331:
3330:
3324:
3323:
3302:
3301:
3285:
3283:
3282:
3277:
3240:
3236:
3234:
3233:
3228:
3226:
3222:
3218:
3210:
3184:
3180:
3178:
3177:
3172:
3170:
3166:
3162:
3154:
3124:
3122:
3121:
3116:
3100:
3098:
3097:
3092:
3090:
3086:
3082:
3074:
3054:
3050:
3046:
3044:
3043:
3038:
3017:
3013:
3011:
3010:
3005:
2977:
2973:
2961:
2957:
2953:
2949:
2947:
2946:
2941:
2900:
2896:
2894:
2893:
2888:
2853:
2851:
2850:
2845:
2837:
2836:
2820:
2818:
2817:
2812:
2804:
2803:
2787:
2785:
2784:
2779:
2736:logarithmic time
2724:Logarithmic time
2719:
2712:
2708:
2706:
2705:
2700:
2682:
2680:
2679:
2674:
2656:
2652:
2644:
2642:
2641:
2636:
2602:
2600:
2599:
2594:
2573:
2571:
2570:
2565:
2517:
2515:
2514:
2509:
2507:
2506:
2505:
2504:
2482:
2480:
2479:
2474:
2472:
2471:
2470:
2469:
2459:
2456:
2416:
2414:
2413:
2408:
2406:
2405:
2404:
2403:
2382:
2380:
2379:
2374:
2372:
2371:
2354:
2352:
2351:
2346:
2344:
2343:
2333:
2330:
2310:exponential time
2295:
2293:
2292:
2287:
2285:
2284:
2263:
2262:
2236:
2234:
2233:
2228:
2226:
2225:
2155:
2153:
2152:
2147:
2145:
2144:
2128:
2126:
2125:
2120:
2118:
2117:
2100:
2098:
2097:
2092:
2090:
2089:
2056:exponential time
2036:
2034:
2033:
2028:
2026:
2025:
2023:
2015:
2001:
1999:
1998:
1993:
1991:
1990:
1942:
1940:
1939:
1934:
1916:
1914:
1913:
1908:
1903:
1902:
1901:
1900:
1845:
1832:
1830:
1829:
1824:
1822:
1821:
1799:
1797:
1796:
1791:
1789:
1788:
1759:
1757:
1756:
1751:
1749:
1748:
1732:
1729:
1693:
1691:
1690:
1685:
1683:
1682:
1666:
1664:
1663:
1658:
1650:
1649:
1632:
1630:
1629:
1624:
1613:
1610:
1605:
1604:
1557:
1555:
1554:
1549:
1529:
1527:
1526:
1521:
1519:
1518:
1501:
1499:
1498:
1493:
1488:
1487:
1444:
1442:
1441:
1436:
1434:
1433:
1416:
1414:
1413:
1408:
1403:
1402:
1367:
1365:
1364:
1359:
1351:
1350:
1330:
1328:
1327:
1322:
1305:
1302:
1287:quasilinear time
1271:
1269:
1268:
1263:
1242:
1240:
1239:
1234:
1212:
1210:
1209:
1204:
1154:
1152:
1151:
1146:
1135:
1134:
1086:
1084:
1083:
1078:
1057:
1052:
1050:
1049:
1044:
1003:
1001:
1000:
995:
993:
992:
984:
971:
969:
968:
963:
961:
960:
952:
938:
936:
935:
930:
906:
904:
903:
898:
893:
892:
867:fractional power
860:
858:
857:
852:
850:
849:
820:
818:
817:
812:
795:
792:
770:
768:
767:
762:
757:
756:
731:
729:
728:
723:
704:
702:
701:
696:
663:logarithmic time
650:
648:
647:
642:
594:
592:
591:
586:
575:
574:
530:
528:
527:
522:
520:
519:
501:
500:
472:
459:
457:
456:
451:
416:
414:
402:Time complexity
398:Complexity class
391:
383:
354:
352:
351:
346:
328:
326:
325:
320:
315:
314:
288:
286:
285:
280:
252:
248:
246:
244:
243:
238:
233:
232:
210:
208:
206:
205:
200:
195:
194:
172:
170:
168:
167:
162:
132:
130:
128:
127:
122:
21:
18:Logarithmic time
7998:
7997:
7993:
7992:
7991:
7989:
7988:
7987:
7958:
7957:
7954:
7939:
7913:
7912:
7908:
7863:
7862:
7858:
7813:
7812:
7808:
7777:Impagliazzo, R.
7775:
7774:
7770:
7763:
7744:
7743:
7739:
7724:
7700:
7699:
7695:
7679:
7678:
7674:
7626:
7625:
7621:
7604:
7600:
7575:
7574:
7570:
7555:
7530:
7529:
7525:
7512:
7508:
7498:
7496:
7487:
7486:
7482:
7446:
7441:
7434:
7433:
7426:
7413:
7409:
7394:
7361:
7358:Braverman, Mark
7356:
7355:
7351:
7338:
7337:
7333:
7326:
7310:
7309:
7305:
7293:
7292:
7288:
7252:
7247:
7246:
7242:
7235:
7211:
7210:
7206:
7172:
7163:
7162:
7158:
7151:
7116:
7115:
7111:
7079:
7078:
7074:
7051:Springer-Verlag
7025:
7024:
7017:
7000:
6988:
6955:
6954:
6950:
6900:
6894:Pomerance, Carl
6888:
6887:
6883:
6868:
6858:10.1090/gsm/117
6840:
6839:
6835:
6802:
6791:
6786:
6785:
6781:
6774:
6760:Sipser, Michael
6758:
6757:
6750:
6746:
6729:
6667:
6662:
6657:
6653:
6613:
6612:
6582:
6554:trial and error
6521:
6520:
6487:
6482:
6478:
6453:
6440:
6426:
6425:
6407:
6374:
6370:
6334:
6333:
6282:
6277:
6273:
6255:
6230:
6229:
6181:
6165:
6150:
6127:
6121:
6069:
6064:
6063:
6025:
6024:
5989:
5988:
5954:
5953:
5895:
5894:
5890:
5872:
5871:
5851:and parameters
5817:
5816:
5766:
5758:
5753:
5752:
5751:
5743:
5707:
5687:
5682:
5681:
5680:
5646:
5641:
5640:
5637:
5594:
5589:
5585:
5551:
5550:
5528:
5524:
5513:sub-exponential
5508:
5479:
5441:
5436:
5432:
5392:
5391:
5312:
5301:
5300:
5268:
5267:
5242:
5241:
5214:
5213:
5212:
5211:for some fixed
5180:
5169:
5164:
5163:
5149:
5143:
5127:Cobham's thesis
5100:
5051:
4957:
4897:
4886:
4885:
4860:
4852:
4851:
4833:Cobham's thesis
4792:
4781:polynomial time
4777:
4771:
4769:Polynomial time
4727:
4701:
4700:
4689:
4640:
4614:
4613:
4548:
4547:
4510:
4509:
4466:
4465:
4431:
4430:
4422:
4406:
4372:
4371:
4334:
4333:
4293:
4292:
4250:
4249:
4190:
4189:
4146:
4145:
4108:
4107:
4070:
4069:
4034:
4020:
4019:
3984:
3983:
3962:
3957:
3956:
3931:
3930:
3900:
3889:
3888:
3851:
3850:
3847:soft O notation
3821:
3820:
3812:
3782:
3753:
3752:
3749:log-linear time
3741:
3712:
3690:
3689:
3685:
3657:
3656:
3628:
3627:
3620:
3570:
3569:
3559:data structures
3471:
3470:
3465:(often spelled
3463:sub-linear time
3459:
3457:Sub-linear time
3424:
3413:
3412:
3359:
3348:
3347:
3343:
3315:
3288:
3287:
3259:
3258:
3253:polylogarithmic
3248:
3238:
3205:
3201:
3187:
3186:
3182:
3149:
3145:
3131:
3130:
3103:
3102:
3069:
3065:
3057:
3056:
3052:
3048:
3020:
3019:
3015:
2984:
2983:
2975:
2974:which contains
2969:
2959:
2955:
2951:
2917:
2916:
2898:
2864:
2863:
2828:
2823:
2822:
2795:
2790:
2789:
2740:
2739:
2732:
2726:
2717:
2710:
2685:
2684:
2659:
2658:
2654:
2650:
2618:
2617:
2576:
2575:
2547:
2546:
2539:
2532:
2496:
2491:
2486:
2485:
2450:
2445:
2440:
2439:
2395:
2390:
2385:
2384:
2363:
2358:
2357:
2324:
2319:
2318:
2267:
2254:
2240:
2239:
2199:
2176:
2175:
2136:
2131:
2130:
2109:
2104:
2103:
2072:
2067:
2066:
2057:
2010:
2005:
2004:
1973:
1968:
1967:
1961:
1919:
1918:
1892:
1887:
1876:
1875:
1868:
1836:
1807:
1802:
1801:
1768:
1763:
1762:
1723:
1718:
1717:
1674:
1669:
1668:
1641:
1636:
1635:
1581:
1576:
1575:
1567:polynomial time
1534:
1533:
1510:
1505:
1504:
1479:
1468:
1467:
1425:
1420:
1419:
1394:
1383:
1382:
1342:
1334:
1333:
1293:
1292:
1276:comparison sort
1245:
1244:
1216:
1215:
1177:
1176:
1126:
1112:
1111:
1060:
1059:
1055:
1026:
1025:
1007:Range searching
979:
974:
973:
947:
942:
941:
909:
908:
884:
873:
872:
841:
824:
823:
786:
785:
748:
734:
733:
708:
707:
672:
671:
612:
611:
606:log-logarithmic
566:
555:
554:
487:
486:
470:
433:
432:
405:
403:
374:
371:
365:
331:
330:
306:
295:
294:
262:
261:
250:
224:
213:
212:
211:
186:
175:
174:
173:
135:
134:
133:
104:
103:
102:
75:constant factor
63:time complexity
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
7996:
7994:
7986:
7985:
7980:
7975:
7970:
7960:
7959:
7953:
7952:
7937:
7906:
7885:(1–2): 29–35.
7856:
7835:(3): 305–329.
7815:Mayr, Ernst W.
7806:
7793:(4): 512–530.
7768:
7761:
7737:
7722:
7693:
7672:
7619:
7598:
7568:
7553:
7523:
7515:Complexity Zoo
7506:
7480:
7459:(2): 367–375.
7424:
7416:Complexity Zoo
7407:
7392:
7349:
7331:
7324:
7303:
7286:
7265:(2): 325–349.
7240:
7233:
7204:
7156:
7149:
7119:Chuzhoy, Julia
7109:
7090:(2): 466–490.
7072:
7039:Wigderson, Avi
7031:Fortnow, Lance
7015:
6986:
6948:
6881:
6866:
6833:
6822:(4): 183–189.
6788:Mehlhorn, Kurt
6779:
6772:
6747:
6745:
6742:
6741:
6740:
6735:
6728:
6725:
6724:
6723:
6713:
6706:
6696:
6695:
6683:
6674:
6670:
6665:
6660:
6656:
6642:
6638:
6635:
6631:
6627:
6581:
6578:
6534:
6531:
6528:
6507:
6500:
6497:
6494:
6490:
6485:
6481:
6477:
6474:
6469:
6466:
6463:
6460:
6456:
6452:
6447:
6443:
6439:
6436:
6433:
6411:factorial time
6406:
6405:Factorial time
6403:
6402:
6401:
6389:
6384:
6381:
6377:
6373:
6361:
6357:
6354:
6350:
6346:
6309:
6308:
6296:
6289:
6285:
6280:
6276:
6262:
6258:
6253:
6250:
6246:
6242:
6180:
6177:
6123:Main article:
6120:
6117:
6104:
6101:
6098:
6090:
6085:
6082:
6079:
6076:
6072:
6047:
6044:
6041:
6038:
6035:
6032:
6011:
6007:
6003:
5999:
5996:
5973:
5970:
5967:
5964:
5961:
5950:
5949:
5938:
5934:
5930:
5927:
5924:
5916:
5911:
5908:
5905:
5902:
5898:
5893:
5884:
5836:
5833:
5830:
5827:
5824:
5788:
5783:
5780:
5777:
5774:
5769:
5765:
5761:
5727:
5722:
5718:
5714:
5710:
5706:
5700:
5697:
5690:
5662:
5659:
5656:
5653:
5649:
5636:
5633:
5621:
5620:
5608:
5601:
5597:
5592:
5588:
5577:
5574:
5571:
5567:
5563:
5523:
5520:
5507:
5504:
5478:
5475:
5474:
5473:
5461:
5456:
5453:
5448:
5444:
5439:
5435:
5421:
5417:
5414:
5410:
5406:
5350:planted clique
5330:
5327:
5324:
5319:
5315:
5311:
5308:
5281:
5278:
5275:
5255:
5252:
5249:
5227:
5224:
5221:
5198:
5195:
5192:
5187:
5183:
5179:
5176:
5172:
5145:Main article:
5142:
5139:
5050:
5047:
5034:
5033:
5021:
5013:
5005:
4993:
4981:
4956:
4953:
4949:
4948:
4924:
4921:
4909:
4904:
4900:
4896:
4893:
4867:
4863:
4859:
4844:selection sort
4775:P (complexity)
4773:Main article:
4770:
4767:
4759:insertion sort
4739:
4734:
4730:
4726:
4723:
4720:
4717:
4714:
4711:
4708:
4695:is said to be
4688:
4685:
4672:
4669:
4666:
4663:
4660:
4656:
4651:
4648:
4643:
4639:
4636:
4633:
4630:
4627:
4624:
4621:
4594:
4591:
4588:
4585:
4582:
4579:
4576:
4573:
4570:
4567:
4564:
4561:
4558:
4555:
4535:
4532:
4529:
4526:
4523:
4520:
4517:
4491:
4488:
4485:
4482:
4479:
4476:
4473:
4453:
4450:
4447:
4444:
4441:
4438:
4394:
4391:
4388:
4385:
4382:
4379:
4359:
4356:
4353:
4350:
4347:
4344:
4341:
4330:
4329:
4318:
4315:
4312:
4309:
4306:
4303:
4300:
4286:
4275:
4272:
4269:
4266:
4263:
4260:
4257:
4243:
4215:
4212:
4209:
4206:
4203:
4200:
4197:
4183:
4171:
4168:
4165:
4162:
4159:
4156:
4153:
4133:
4130:
4127:
4124:
4121:
4118:
4115:
4095:
4092:
4089:
4086:
4083:
4080:
4077:
4063:
4052:
4049:
4046:
4041:
4037:
4033:
4030:
4027:
3997:
3994:
3991:
3969:
3965:
3944:
3941:
3938:
3918:
3913:
3910:
3907:
3903:
3899:
3896:
3876:
3873:
3870:
3864:
3861:
3834:
3831:
3828:
3800:
3797:
3794:
3789:
3785:
3781:
3778:
3775:
3772:
3769:
3766:
3763:
3760:
3740:
3737:
3700:
3697:
3673:
3670:
3667:
3664:
3644:
3641:
3638:
3635:
3619:
3616:
3615:
3614:
3598:
3595:
3592:
3589:
3586:
3583:
3580:
3577:
3566:
3551:
3502:
3499:
3496:
3493:
3490:
3487:
3484:
3481:
3478:
3467:sublinear time
3458:
3455:
3442:
3439:
3436:
3431:
3427:
3423:
3420:
3377:
3374:
3371:
3366:
3362:
3358:
3355:
3329:
3322:
3318:
3314:
3311:
3308:
3305:
3300:
3295:
3275:
3272:
3269:
3266:
3247:
3244:
3225:
3221:
3216:
3213:
3208:
3204:
3200:
3197:
3194:
3169:
3165:
3160:
3157:
3152:
3148:
3144:
3141:
3138:
3127:floor function
3114:
3110:
3089:
3085:
3080:
3077:
3072:
3068:
3064:
3036:
3033:
3030:
3027:
3003:
3000:
2997:
2994:
2991:
2939:
2936:
2933:
2930:
2927:
2924:
2908:or when using
2886:
2883:
2880:
2877:
2874:
2871:
2843:
2840:
2835:
2831:
2810:
2807:
2802:
2798:
2777:
2774:
2771:
2768:
2765:
2762:
2759:
2756:
2753:
2750:
2747:
2725:
2722:
2698:
2695:
2692:
2672:
2669:
2666:
2634:
2631:
2628:
2625:
2592:
2589:
2586:
2583:
2563:
2560:
2557:
2554:
2531:
2528:
2525:
2524:
2518:
2503:
2499:
2494:
2483:
2468:
2465:
2462:
2453:
2448:
2437:
2432:
2428:
2427:
2417:
2402:
2398:
2393:
2370:
2366:
2355:
2342:
2339:
2336:
2327:
2316:
2311:
2307:
2306:
2296:
2283:
2280:
2277:
2274:
2270:
2266:
2261:
2257:
2253:
2250:
2247:
2237:
2224:
2221:
2218:
2215:
2212:
2209:
2206:
2202:
2198:
2195:
2192:
2189:
2186:
2183:
2173:
2171:
2170:factorial time
2167:
2166:
2156:
2143:
2139:
2116:
2112:
2101:
2088:
2085:
2082:
2079:
2075:
2064:
2059:
2053:
2052:
2037:
2022:
2018:
2013:
2002:
1989:
1986:
1983:
1980:
1976:
1965:
1963:
1957:
1956:
1945:
1943:
1932:
1929:
1926:
1906:
1899:
1895:
1890:
1886:
1883:
1873:
1870:
1864:
1863:
1833:
1820:
1817:
1814:
1810:
1787:
1784:
1781:
1778:
1775:
1771:
1760:
1747:
1744:
1741:
1738:
1735:
1726:
1715:
1712:
1708:
1707:
1694:
1681:
1677:
1656:
1653:
1648:
1644:
1633:
1622:
1619:
1616:
1608:
1603:
1600:
1597:
1594:
1591:
1588:
1584:
1573:
1568:
1564:
1563:
1547:
1544:
1541:
1530:
1517:
1513:
1502:
1491:
1486:
1482:
1478:
1475:
1465:
1463:
1459:
1458:
1452:Insertion sort
1445:
1432:
1428:
1417:
1406:
1401:
1397:
1393:
1390:
1380:
1378:
1377:quadratic time
1374:
1373:
1368:
1357:
1354:
1349:
1345:
1341:
1331:
1320:
1317:
1314:
1311:
1308:
1300:
1290:
1288:
1284:
1283:
1272:
1261:
1258:
1255:
1252:
1232:
1229:
1226:
1223:
1213:
1202:
1199:
1196:
1193:
1190:
1187:
1184:
1174:
1172:
1168:
1167:
1157:
1155:
1144:
1141:
1138:
1133:
1129:
1125:
1122:
1119:
1109:
1107:
1103:
1102:
1087:
1076:
1073:
1070:
1067:
1053:
1042:
1039:
1036:
1033:
1023:
1021:
1017:
1016:
1004:
990:
987:
982:
958:
955:
950:
939:
928:
925:
922:
919:
916:
896:
891:
887:
883:
880:
870:
868:
864:
863:
861:
848:
844:
840:
837:
834:
831:
821:
810:
807:
804:
801:
798:
783:
781:
777:
776:
771:
760:
755:
751:
747:
744:
741:
721:
718:
715:
705:
694:
691:
688:
685:
682:
679:
669:
664:
660:
659:
657:priority queue
653:
651:
640:
637:
634:
631:
628:
625:
622:
619:
609:
607:
603:
602:
597:
595:
584:
581:
578:
573:
569:
565:
562:
552:
550:
543:
542:
536:Amortized time
533:
531:
518:
513:
510:
507:
504:
499:
494:
484:
482:
475:
474:
463:
460:
449:
446:
443:
440:
430:
428:
424:
423:
420:
417:
400:
395:
364:
361:
344:
341:
338:
318:
313:
309:
305:
302:
278:
275:
272:
269:
236:
231:
227:
223:
220:
198:
193:
189:
185:
182:
160:
157:
154:
151:
148:
145:
142:
120:
117:
114:
111:
99:big O notation
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
7995:
7984:
7981:
7979:
7976:
7974:
7971:
7969:
7966:
7965:
7963:
7956:
7948:
7944:
7940:
7934:
7929:
7924:
7920:
7916:
7910:
7907:
7902:
7898:
7893:
7888:
7884:
7880:
7879:
7874:
7870:
7866:
7860:
7857:
7852:
7848:
7843:
7838:
7834:
7830:
7829:
7824:
7820:
7816:
7810:
7807:
7801:
7796:
7792:
7788:
7787:
7782:
7778:
7772:
7769:
7764:
7758:
7754:
7753:
7748:
7747:Grohe, Martin
7741:
7738:
7733:
7729:
7725:
7719:
7714:
7709:
7705:
7697:
7694:
7688:
7683:
7676:
7673:
7668:
7664:
7660:
7656:
7652:
7648:
7643:
7638:
7634:
7630:
7623:
7620:
7615:
7609:
7601:
7595:
7591:
7587:
7583:
7579:
7572:
7569:
7564:
7560:
7556:
7550:
7546:
7542:
7538:
7534:
7527:
7524:
7521:
7517:
7516:
7510:
7507:
7495:
7491:
7484:
7481:
7476:
7472:
7467:
7462:
7458:
7454:
7453:
7445:
7437:
7431:
7429:
7425:
7422:
7418:
7417:
7411:
7408:
7403:
7399:
7395:
7389:
7385:
7381:
7376:
7371:
7367:
7359:
7353:
7350:
7345:
7341:
7335:
7332:
7327:
7325:0-201-53082-1
7321:
7317:
7313:
7307:
7304:
7299:
7298:
7290:
7287:
7282:
7278:
7273:
7268:
7264:
7260:
7259:
7251:
7244:
7241:
7236:
7230:
7226:
7222:
7219:. p. 3.
7218:
7214:
7208:
7205:
7200:
7196:
7192:
7188:
7184:
7180:
7179:
7171:
7167:
7164:Kumar, Ravi;
7160:
7157:
7152:
7146:
7142:
7138:
7133:
7128:
7124:
7120:
7113:
7110:
7105:
7101:
7097:
7093:
7089:
7085:
7084:
7076:
7073:
7068:
7064:
7060:
7056:
7052:
7048:
7044:
7040:
7036:
7032:
7028:
7027:Babai, László
7022:
7020:
7016:
7011:
7005:
6997:
6993:
6989:
6987:9781450345286
6983:
6979:
6975:
6971:
6967:
6963:
6959:
6952:
6949:
6944:
6940:
6936:
6932:
6928:
6924:
6920:
6916:
6912:
6908:
6907:
6899:
6895:
6891:
6885:
6882:
6877:
6873:
6869:
6863:
6859:
6855:
6851:
6847:
6843:
6837:
6834:
6829:
6825:
6821:
6817:
6816:
6809:
6805:
6798:
6794:
6789:
6783:
6780:
6775:
6773:0-619-21764-2
6769:
6765:
6761:
6755:
6753:
6749:
6743:
6739:
6736:
6734:
6731:
6730:
6726:
6721:
6717:
6714:
6711:
6710:Gröbner basis
6707:
6705:
6701:
6700:
6699:
6681:
6672:
6668:
6663:
6658:
6654:
6636:
6633:
6629:
6625:
6611:
6610:
6609:
6607:
6603:
6599:
6595:
6591:
6587:
6579:
6577:
6575:
6571:
6567:
6563:
6559:
6555:
6551:
6546:
6532:
6529:
6526:
6505:
6498:
6495:
6492:
6488:
6483:
6479:
6475:
6472:
6467:
6464:
6461:
6458:
6454:
6450:
6445:
6441:
6437:
6434:
6431:
6423:
6420:
6416:
6412:
6404:
6387:
6382:
6379:
6375:
6371:
6355:
6352:
6348:
6344:
6332:
6331:
6330:
6328:
6327:
6322:
6318:
6314:
6294:
6287:
6283:
6278:
6274:
6251:
6248:
6244:
6240:
6228:
6227:
6226:
6224:
6223:
6218:
6214:
6210:
6206:
6202:
6198:
6194:
6190:
6186:
6178:
6176:
6174:
6168:
6163:
6159:
6153:
6148:
6144:
6140:
6136:
6132:
6126:
6118:
6116:
6099:
6088:
6080:
6074:
6070:
6061:
6042:
6036:
6033:
6030:
5997:
5994:
5987:
5968:
5965:
5962:
5936:
5932:
5925:
5914:
5906:
5900:
5896:
5891:
5882:
5870:
5869:
5868:
5866:
5862:
5858:
5854:
5850:
5831:
5828:
5825:
5814:
5809:
5807:
5786:
5781:
5778:
5775:
5772:
5767:
5763:
5759:
5749:
5720:
5716:
5712:
5708:
5695:
5688:
5678:
5657:
5651:
5647:
5634:
5632:
5630:
5626:
5606:
5599:
5595:
5590:
5586:
5575:
5572:
5569:
5565:
5561:
5549:
5548:
5547:
5545:
5541:
5537:
5531:
5521:
5519:
5516:
5514:
5505:
5503:
5501:
5497:
5493:
5488:
5484:
5476:
5459:
5454:
5451:
5446:
5442:
5437:
5433:
5415:
5412:
5408:
5404:
5390:
5389:
5388:
5386:
5382:
5377:
5375:
5371:
5367:
5363:
5359:
5355:
5351:
5346:
5344:
5325:
5322:
5317:
5313:
5306:
5298:
5293:
5279:
5276:
5273:
5253:
5250:
5247:
5225:
5222:
5219:
5193:
5190:
5185:
5181:
5174:
5170:
5161:
5157:
5153:
5148:
5140:
5138:
5136:
5132:
5128:
5124:
5123:
5119:
5114:
5112:
5108:
5103:
5098:
5093:
5091:
5086:
5084:
5080:
5076:
5072:
5068:
5064:
5060:
5056:
5048:
5046:
5044:
5039:
5031:
5027:
5026:
5022:
5019:
5018:
5014:
5011:
5010:
5006:
5003:
4999:
4998:
4994:
4991:
4987:
4986:
4982:
4979:
4975:
4971:
4967:
4966:
4962:
4961:
4960:
4954:
4952:
4946:
4942:
4941:
4936:
4932:
4928:
4925:
4922:
4902:
4898:
4891:
4883:
4865:
4861:
4857:
4849:
4845:
4841:
4840:
4839:
4836:
4834:
4830:
4826:
4825:
4821:
4817:
4813:
4807:
4803:
4799:
4795:
4790:
4786:
4785:upper bounded
4782:
4776:
4768:
4766:
4764:
4760:
4756:
4751:
4732:
4728:
4721:
4718:
4712:
4706:
4698:
4694:
4686:
4684:
4667:
4661:
4658:
4654:
4649:
4646:
4641:
4637:
4634:
4631:
4625:
4619:
4612:
4608:
4589:
4586:
4583:
4580:
4571:
4565:
4562:
4556:
4553:
4530:
4527:
4524:
4521:
4507:
4503:
4486:
4483:
4480:
4477:
4471:
4448:
4445:
4442:
4436:
4428:
4420:
4416:
4412:
4389:
4386:
4383:
4354:
4351:
4348:
4345:
4339:
4313:
4310:
4307:
4304:
4298:
4291:calculation,
4290:
4287:
4270:
4267:
4264:
4261:
4255:
4247:
4244:
4241:
4237:
4233:
4229:
4210:
4207:
4204:
4201:
4195:
4187:
4184:
4166:
4163:
4160:
4157:
4151:
4128:
4125:
4122:
4119:
4113:
4090:
4087:
4084:
4081:
4075:
4067:
4064:
4047:
4044:
4039:
4035:
4031:
4025:
4017:
4014:
4013:
4012:
4009:
3995:
3992:
3989:
3967:
3963:
3942:
3939:
3936:
3911:
3908:
3905:
3901:
3894:
3871:
3859:
3848:
3832:
3829:
3826:
3818:
3795:
3792:
3787:
3783:
3779:
3773:
3770:
3764:
3758:
3750:
3746:
3738:
3736:
3734:
3730:
3726:
3722:
3716:
3698:
3695:
3668:
3662:
3639:
3633:
3625:
3617:
3612:
3590:
3584:
3581:
3575:
3567:
3564:
3563:binary search
3560:
3556:
3552:
3549:
3545:
3541:
3538:
3537:
3536:
3533:
3531:
3527:
3523:
3522:approximately
3519:
3514:
3497:
3491:
3488:
3482:
3476:
3468:
3464:
3456:
3454:
3437:
3434:
3429:
3425:
3418:
3410:
3409:fully dynamic
3406:
3402:
3398:
3394:
3391:For example,
3389:
3372:
3369:
3364:
3360:
3353:
3320:
3312:
3309:
3306:
3293:
3270:
3264:
3256:
3254:
3245:
3243:
3223:
3219:
3214:
3211:
3206:
3202:
3198:
3195:
3192:
3167:
3163:
3158:
3155:
3150:
3146:
3142:
3139:
3136:
3128:
3087:
3083:
3078:
3075:
3070:
3066:
3062:
3031:
3025:
3001:
2998:
2995:
2992:
2989:
2981:
2972:
2968:
2963:
2934:
2931:
2928:
2922:
2913:
2911:
2910:binary search
2907:
2902:
2881:
2878:
2875:
2869:
2861:
2858:, and such a
2857:
2841:
2838:
2833:
2829:
2808:
2805:
2800:
2796:
2772:
2769:
2766:
2760:
2757:
2751:
2745:
2737:
2731:
2723:
2721:
2716:
2696:
2693:
2690:
2670:
2667:
2664:
2646:
2629:
2623:
2615:
2610:
2606:
2587:
2581:
2558:
2552:
2544:
2543:constant time
2537:
2530:Constant time
2529:
2523:
2519:
2501:
2497:
2492:
2484:
2463:
2451:
2446:
2438:
2436:
2433:
2430:
2429:
2426:
2422:
2418:
2400:
2396:
2391:
2368:
2364:
2356:
2337:
2325:
2317:
2315:
2312:
2309:
2308:
2305:
2301:
2297:
2281:
2278:
2275:
2272:
2268:
2264:
2259:
2255:
2251:
2248:
2245:
2238:
2219:
2216:
2213:
2210:
2204:
2200:
2196:
2193:
2187:
2181:
2174:
2172:
2169:
2168:
2165:
2161:
2157:
2141:
2137:
2114:
2110:
2102:
2083:
2077:
2073:
2065:
2063:
2060:
2055:
2054:
2051:
2050:
2045:
2041:
2038:
2020:
2016:
2011:
2003:
1984:
1978:
1974:
1966:
1964:
1959:
1958:
1954:
1950:
1946:
1944:
1930:
1927:
1924:
1897:
1893:
1888:
1881:
1874:
1871:
1866:
1865:
1861:
1857:
1854:, best known
1853:
1849:
1843:
1839:
1834:
1818:
1815:
1812:
1808:
1785:
1782:
1779:
1776:
1773:
1769:
1761:
1742:
1739:
1736:
1724:
1716:
1713:
1710:
1709:
1706:
1702:
1698:
1695:
1679:
1675:
1654:
1651:
1646:
1642:
1634:
1617:
1606:
1598:
1595:
1592:
1586:
1582:
1574:
1572:
1569:
1566:
1565:
1561:
1545:
1542:
1539:
1531:
1515:
1511:
1503:
1484:
1480:
1473:
1466:
1464:
1461:
1460:
1457:
1453:
1449:
1446:
1430:
1426:
1418:
1399:
1395:
1388:
1381:
1379:
1376:
1375:
1372:
1369:
1355:
1352:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1332:
1315:
1312:
1309:
1298:
1291:
1289:
1286:
1285:
1281:
1277:
1273:
1259:
1256:
1253:
1250:
1230:
1227:
1224:
1221:
1214:
1197:
1194:
1191:
1188:
1182:
1175:
1173:
1170:
1169:
1165:
1161:
1158:
1156:
1139:
1136:
1131:
1127:
1123:
1117:
1110:
1108:
1105:
1104:
1100:
1099:Linear search
1096:
1092:
1088:
1074:
1071:
1068:
1065:
1054:
1037:
1031:
1024:
1022:
1019:
1018:
1015:
1013:
1008:
1005:
988:
985:
980:
956:
953:
948:
940:
926:
923:
920:
917:
914:
889:
885:
878:
871:
869:
866:
865:
862:
846:
838:
835:
832:
822:
805:
802:
799:
784:
782:
779:
778:
775:
774:Binary search
772:
753:
749:
742:
739:
719:
716:
713:
706:
689:
686:
683:
677:
670:
668:
665:
662:
661:
658:
654:
652:
635:
632:
629:
626:
623:
617:
610:
608:
605:
604:
601:
598:
596:
579:
576:
571:
567:
560:
553:
551:
548:
545:
544:
541:
537:
534:
532:
508:
502:
492:
485:
483:
480:
477:
476:
468:
464:
461:
444:
438:
431:
429:
427:constant time
426:
425:
421:
418:
412:
408:
401:
399:
396:
393:
392:
389:
387:
382:
378:
370:
362:
360:
358:
342:
339:
336:
311:
307:
300:
292:
273:
267:
258:
256:
229:
225:
218:
191:
187:
180:
155:
152:
149:
146:
140:
115:
109:
100:
96:
91:
87:
83:
78:
76:
72:
68:
64:
60:
52:
48:
44:
39:
33:
19:
7955:
7918:
7909:
7882:
7876:
7869:Heintz, Joos
7859:
7832:
7826:
7809:
7790:
7784:
7771:
7751:
7745:Flum, Jörg;
7740:
7703:
7696:
7675:
7632:
7628:
7622:
7608:cite journal
7581:
7577:
7571:
7532:
7526:
7513:
7509:
7497:. Retrieved
7493:
7483:
7456:
7450:
7414:
7410:
7365:
7352:
7343:
7340:Cobham, Alan
7334:
7315:
7306:
7296:
7289:
7262:
7256:
7243:
7216:
7207:
7185:(4): 57–67.
7182:
7176:
7159:
7122:
7112:
7087:
7081:
7075:
7046:
7042:
6961:
6951:
6910:
6904:
6884:
6849:
6842:Tao, Terence
6836:
6819:
6813:
6807:
6803:
6796:
6792:
6782:
6763:
6708:Computing a
6697:
6601:
6597:
6593:
6589:
6583:
6569:
6565:
6557:
6547:
6421:
6414:
6410:
6408:
6324:
6320:
6316:
6312:
6310:
6220:
6216:
6212:
6208:
6204:
6200:
6196:
6192:
6188:
6184:
6182:
6166:
6161:
6157:
6151:
6146:
6134:
6130:
6128:
6059:
5951:
5864:
5860:
5856:
5852:
5810:
5804:However, at
5638:
5628:
5624:
5622:
5546:as follows.
5539:
5535:
5529:
5525:
5511:
5509:
5480:
5387:as follows.
5380:
5378:
5358:random graph
5347:
5342:
5294:
5151:
5150:
5120:
5115:
5110:
5106:
5101:
5094:
5089:
5087:
5082:
5078:
5074:
5070:
5062:
5058:
5054:
5052:
5035:
5023:
5015:
5007:
4995:
4983:
4963:
4958:
4950:
4944:
4938:
4935:optimization
4881:
4847:
4837:
4822:
4811:
4805:
4801:
4797:
4793:
4780:
4778:
4752:
4696:
4690:
4504:
4331:
4010:
3819:is the case
3816:
3748:
3744:
3742:
3717:
3623:
3621:
3534:
3517:
3515:
3466:
3462:
3460:
3390:
3257:if its time
3251:
3249:
3125:denotes the
3047:denote this
2970:
2964:
2914:
2906:binary trees
2903:
2735:
2733:
2714:
2647:
2542:
2540:
2298:Solving the
2158:Solving the
2046:
1841:
1837:
1011:
540:disjoint set
410:
406:
385:
380:
376:
372:
356:
290:
259:
249:etc., where
101:, typically
79:
62:
56:
50:
46:
7178:SIGACT News
7053:: 307–318.
5487:NP-complete
5483:P versus NP
5366:game theory
5135:NP-complete
4947:algorithms.
4419:binary tree
4289:Monge array
3721:parallelism
3624:linear time
3618:Linear time
1856:parity game
1835:Best-known
1448:Bubble sort
1166:algorithm.
1020:linear time
7962:Categories
7713:2011.01366
7499:2 December
7375:1504.08352
7297:Algorithms
7132:1911.03449
6978:2292/31757
6744:References
6733:L-notation
6137:) is that
4789:polynomial
4763:shell sort
4417:creates a
4405:operation
4236:smoothsort
4228:merge sort
3530:statistics
2967:dictionary
1862:algorithm
1462:cubic time
7659:1095-7111
7563:0302-9743
7035:Nisan, N.
7004:cite book
6943:127807021
6801:time and
6795:(log log
6637:∈
6630:⋃
6621:2-EXPTIME
6606:2-EXPTIME
6562:shuffling
6527:ϵ
6499:ϵ
6465:
6438:≤
6356:∈
6349:⋃
6252:∈
6245:⋃
6089:⋅
6034:∈
6006:→
5915:⋅
5779:
5699:~
5600:ε
5570:ε
5566:⋂
5510:The term
5502:problem.
5500:set cover
5452:
5416:∈
5409:⋃
5323:
5191:
5099:runs for
4693:algorithm
4587:
4575:Θ
4557:
4528:
4516:Ω
4484:
4446:
4387:
4378:Θ
4352:
4311:
4268:
4232:introsort
4208:
4164:
4126:
4088:
4066:Quicksort
4045:
3937:ε
3912:ε
3863:~
3793:
3585:
3435:
3370:
3310:
3113:⌋
3109:⌊
2999:≤
2993:≤
2932:
2879:
2839:
2806:
2788:. Since
2770:
2694:≤
2668:≤
2609:operation
2435:2-EXPTIME
2279:
2217:
1947:Contains
1925:ϵ
1898:ϵ
1816:
1783:
1777:
1740:
1596:
1543:×
1353:
1313:
1254:
1228:
1195:
1137:
1132:∗
836:
803:
743:
717:
687:
633:
627:
577:
572:∗
503:α
337:α
312:α
192:α
153:
71:algorithm
7871:(1988).
7821:(1982).
7749:(2006).
7667:15965140
7314:(1994).
7168:(2003).
7121:(eds.).
7067:14802332
6996:30338402
6896:(2019).
6844:(2010).
6812:space".
6762:(2006).
6727:See also
6588:time if
6550:bogosort
6519:for all
6062:in time
5105:time on
5081:, where
5069:, it is
4816:Problems
4186:Heapsort
3982:for any
3845:. Using
3220:⌋
3207:⌊
3164:⌋
3151:⌊
3101:, where
3084:⌋
3071:⌊
2419:Solving
1917:for all
667:DLOGTIME
90:function
7947:0403962
7901:0949111
7851:0683204
7732:4273431
7475:1820597
7402:3627815
7281:1355592
7104:1616556
6935:3941463
6876:2780010
3561:, e.g.
3411:way in
3403:can be
3401:a graph
2715:at most
2614:element
2314:EXPTIME
1014:-d tree
65:is the
7945:
7935:
7899:
7849:
7759:
7730:
7720:
7665:
7657:
7596:
7561:
7551:
7473:
7400:
7390:
7322:
7279:
7231:
7197:
7147:
7102:
7065:
6994:
6984:
6941:
6933:
6874:
6864:
6770:
6173:P ≠ NP
6154:> 0
5879:SUBEPT
5857:SUBEPT
5558:SUBEXP
5540:SUBEXP
5532:> 0
5372:, and
5038:robust
4968:: The
4931:graphs
4502:time.
4429:takes
3399:, and
2162:using
1872:SUBEXP
1160:Seidel
907:where
61:, the
7708:arXiv
7682:arXiv
7663:S2CID
7637:arXiv
7447:(PDF)
7444:-SAT"
7370:arXiv
7253:(PDF)
7199:65359
7195:S2CID
7173:(PDF)
7127:arXiv
7063:S2CID
6992:S2CID
6939:S2CID
6901:(PDF)
6649:DTIME
6367:DTIME
6270:DTIME
6187:, if
6023:with
5887:DTIME
5582:DTIME
5544:DTIME
5428:DTIME
5385:DTIME
5240:When
4787:by a
4605:, by
3751:) if
3626:, or
3548:depth
3469:) if
3407:in a
3129:. If
2738:when
2605:array
1091:array
1009:in a
467:array
375:poly(
355:is a
289:is a
7983:Time
7933:ISBN
7757:ISBN
7718:ISBN
7655:ISSN
7614:link
7594:ISBN
7559:ISSN
7549:ISBN
7501:2009
7388:ISBN
7320:ISBN
7229:ISBN
7145:ISBN
7010:link
6982:ISBN
6862:ISBN
6768:ISBN
6530:>
6415:T(n)
6139:3SAT
6129:The
6093:poly
5919:poly
5806:STOC
5573:>
5515:time
5277:<
5223:>
4943:and
4842:The
4800:) =
3993:>
3940:>
3731:and
3544:work
3528:and
3255:time
3196:<
2821:and
2653:and
2457:poly
2423:via
2331:poly
2302:via
2042:for
1928:>
1840:(log
1730:poly
1699:for
1611:poly
1303:poly
924:<
918:<
793:poly
549:time
481:time
471:(−1)
394:Name
379:) =
340:>
255:bits
7923:doi
7887:doi
7837:doi
7795:doi
7647:doi
7586:doi
7541:doi
7461:doi
7380:doi
7267:doi
7263:148
7221:doi
7187:doi
7137:doi
7092:doi
7055:doi
6974:hdl
6966:doi
6923:hdl
6915:doi
6854:doi
6824:doi
6718:on
6462:log
6413:if
6237:EXP
6222:EXP
6169:≥ 3
6135:ETH
5847:of
5776:log
5443:log
5314:log
5182:log
5057:if
5025:BQP
5017:BPP
4997:ZPP
4972:of
4929:in
4699:if
4691:An
4584:log
4554:log
4525:log
4481:log
4443:log
4384:log
4349:log
4308:log
4265:log
4205:log
4161:log
4123:log
4085:log
4036:log
3784:log
3582:log
3426:log
3361:log
3307:log
3286:is
2929:log
2915:An
2876:log
2830:log
2797:log
2767:log
2276:log
2214:log
2111:1.1
1949:BPP
1813:log
1780:log
1774:log
1737:log
1593:log
1344:log
1310:log
1251:log
1225:log
1192:log
1162:'s
1128:log
833:log
800:log
740:log
714:log
684:log
630:log
624:log
568:log
150:log
57:In
7964::
7943:MR
7941:.
7931:.
7897:MR
7895:.
7881:.
7875:.
7867:;
7847:MR
7845:.
7833:46
7831:.
7825:.
7817:;
7791:63
7789:.
7783:.
7728:MR
7726:.
7716:.
7661:.
7653:.
7645:.
7633:35
7631:.
7610:}}
7606:{{
7557:.
7547:.
7535:.
7518::
7492:.
7471:MR
7469:.
7457:62
7455:.
7449:.
7427:^
7419::
7398:MR
7396:.
7386:.
7378:.
7277:MR
7275:.
7261:.
7255:.
7227:.
7193:.
7183:34
7181:.
7175:.
7143:.
7135:.
7100:MR
7098:.
7088:27
7086:.
7061:.
7045:.
7037:;
7033:;
7029:;
7018:^
7006:}}
7002:{{
6990:.
6980:.
6972:.
6960:.
6937:.
6931:MR
6929:.
6921:.
6911:21
6909:.
6903:.
6892:;
6872:MR
6870:.
6860:.
6848:.
6820:35
6818:.
6751:^
6608:.
6576:.
6422:n!
6329:.
6225:.
6175:.
6115:.
5867::
5855:.
5400:QP
5381:QP
5376:.
5368:,
5125:.
5009:RP
4985:NP
4831:.
4814:.
4750:.
4683:.
4248:,
4238:,
4230:,
4226:,
4188:,
4068:,
4018:,
4008:.
3815:;
3735:.
3532:.
3388:.
2962:.
2912:.
2901:.
2720:.
2383:,
2138:10
2129:,
1955:.
1953:MA
1800:,
1714:QP
1703:.
1680:10
1667:,
1562:.
1454:.
1450:.
1282:.
1278:.
1243:,
1101:.
1097:.
1093:.
1058:,
972:,
732:,
473:.
462:10
388:.
359:.
77:.
7949:.
7925::
7903:.
7889::
7883:5
7853:.
7839::
7803:.
7797::
7765:.
7734:.
7710::
7690:.
7684::
7669:.
7649::
7639::
7616:)
7602:.
7588::
7582:9
7565:.
7543::
7503:.
7477:.
7463::
7442:k
7404:.
7382::
7372::
7362:k
7328:.
7283:.
7269::
7237:.
7223::
7201:.
7189::
7153:.
7139::
7129::
7106:.
7094::
7069:.
7057::
7047:3
7012:)
6998:.
6976::
6968::
6945:.
6925::
6917::
6878:.
6856::
6830:.
6826::
6810:)
6808:n
6806:(
6804:O
6799:)
6797:N
6793:O
6776:.
6682:)
6673:c
6669:n
6664:2
6659:2
6655:(
6641:N
6634:c
6626:=
6602:n
6598:n
6594:n
6592:(
6590:T
6570:n
6566:n
6558:n
6533:0
6506:)
6496:+
6493:1
6489:n
6484:2
6480:(
6476:O
6473:=
6468:n
6459:n
6455:2
6451:=
6446:n
6442:n
6435:!
6432:n
6388:)
6383:n
6380:c
6376:2
6372:(
6360:N
6353:c
6345:=
6341:E
6326:E
6321:n
6317:n
6315:(
6313:T
6295:)
6288:c
6284:n
6279:2
6275:(
6261:+
6257:R
6249:c
6241:=
6217:k
6213:O
6209:n
6207:(
6205:T
6201:n
6197:n
6193:n
6191:(
6189:T
6167:k
6162:k
6158:m
6152:c
6147:n
6133:(
6103:)
6100:n
6097:(
6084:)
6081:k
6078:(
6075:f
6071:2
6060:L
6046:)
6043:k
6040:(
6037:o
6031:f
6010:N
6002:N
5998::
5995:f
5972:)
5969:k
5966:,
5963:L
5960:(
5937:.
5933:)
5929:)
5926:n
5923:(
5910:)
5907:k
5904:(
5901:o
5897:2
5892:(
5883:=
5865:n
5861:k
5853:k
5835:)
5832:k
5829:,
5826:L
5823:(
5802:.
5787:)
5782:n
5773:n
5768:(
5764:O
5760:2
5744:n
5740:,
5726:)
5721:3
5717:/
5713:1
5709:n
5705:(
5696:O
5689:2
5661:)
5658:n
5655:(
5652:o
5648:2
5629:ε
5625:ε
5607:)
5596:n
5591:2
5587:(
5576:0
5562:=
5536:O
5530:ε
5460:)
5455:n
5447:c
5438:2
5434:(
5420:N
5413:c
5405:=
5343:n
5341:(
5329:)
5326:n
5318:3
5310:(
5307:O
5280:1
5274:c
5254:1
5251:=
5248:c
5238:.
5226:0
5220:c
5197:)
5194:n
5186:c
5178:(
5175:O
5171:2
5122:P
5111:n
5107:n
5102:n
5090:n
5083:n
5079:c
5075:n
5073:(
5071:ω
5063:n
5061:(
5059:T
4965:P
4908:)
4903:2
4899:n
4895:(
4892:O
4882:A
4866:2
4862:n
4858:A
4848:n
4824:P
4812:k
4808:)
4806:n
4804:(
4802:O
4798:n
4796:(
4794:T
4738:)
4733:2
4729:n
4725:(
4722:o
4719:=
4716:)
4713:n
4710:(
4707:T
4671:)
4668:n
4665:(
4662:O
4659:+
4655:)
4650:2
4647:n
4642:(
4638:T
4635:2
4632:=
4629:)
4626:n
4623:(
4620:T
4593:)
4590:n
4581:n
4578:(
4572:=
4569:)
4566:!
4563:n
4560:(
4534:)
4531:n
4522:n
4519:(
4490:)
4487:n
4478:n
4475:(
4472:O
4452:)
4449:n
4440:(
4437:O
4423:n
4407:n
4393:)
4390:n
4381:(
4358:)
4355:n
4346:n
4343:(
4340:O
4317:)
4314:n
4305:n
4302:(
4299:O
4274:)
4271:n
4262:n
4259:(
4256:O
4214:)
4211:n
4202:n
4199:(
4196:O
4170:)
4167:n
4158:n
4155:(
4152:O
4132:)
4129:n
4120:n
4117:(
4114:O
4094:)
4091:n
4082:n
4079:(
4076:O
4051:)
4048:n
4040:2
4032:n
4029:(
4026:O
3996:1
3990:c
3968:c
3964:n
3943:0
3917:)
3909:+
3906:1
3902:n
3898:(
3895:O
3875:)
3872:n
3869:(
3860:O
3833:1
3830:=
3827:k
3813:k
3799:)
3796:n
3788:k
3780:n
3777:(
3774:O
3771:=
3768:)
3765:n
3762:(
3759:T
3713:n
3699:n
3696:c
3686:c
3672:)
3669:n
3666:(
3663:O
3643:)
3640:n
3637:(
3634:O
3597:)
3594:)
3591:n
3588:(
3579:(
3576:O
3550:.
3501:)
3498:n
3495:(
3492:o
3489:=
3486:)
3483:n
3480:(
3477:T
3441:)
3438:n
3430:3
3422:(
3419:O
3376:)
3373:n
3365:k
3357:(
3354:O
3344:k
3328:)
3321:k
3317:)
3313:n
3304:(
3299:(
3294:O
3274:)
3271:n
3268:(
3265:T
3239:w
3224:)
3215:2
3212:n
3203:(
3199:D
3193:w
3183:w
3168:)
3159:2
3156:n
3147:(
3143:D
3140:=
3137:w
3088:)
3079:2
3076:n
3067:(
3063:D
3053:w
3049:k
3035:)
3032:k
3029:(
3026:D
3016:k
3002:n
2996:k
2990:1
2976:n
2971:D
2960:n
2956:n
2952:n
2938:)
2935:n
2926:(
2923:O
2899:T
2885:)
2882:n
2873:(
2870:O
2842:n
2834:b
2809:n
2801:a
2776:)
2773:n
2764:(
2761:O
2758:=
2755:)
2752:n
2749:(
2746:T
2718:t
2711:t
2697:b
2691:a
2671:b
2665:a
2655:b
2651:a
2633:)
2630:n
2627:(
2624:O
2591:)
2588:n
2585:(
2582:T
2562:)
2559:1
2556:(
2553:O
2538:.
2502:n
2498:2
2493:2
2467:)
2464:n
2461:(
2452:2
2447:2
2401:2
2397:n
2392:2
2369:n
2365:2
2341:)
2338:n
2335:(
2326:2
2282:n
2273:n
2269:2
2265:,
2260:n
2256:n
2252:,
2249:!
2246:n
2223:)
2220:n
2211:n
2208:(
2205:O
2201:2
2197:=
2194:!
2191:)
2188:n
2185:(
2182:O
2142:n
2115:n
2087:)
2084:n
2081:(
2078:O
2074:2
2062:E
2021:3
2017:n
2012:2
1988:)
1985:n
1982:(
1979:o
1975:2
1931:0
1905:)
1894:n
1889:2
1885:(
1882:O
1846:-
1844:)
1842:n
1838:O
1819:n
1809:n
1786:n
1770:n
1746:)
1743:n
1734:(
1725:2
1676:n
1655:n
1652:+
1647:2
1643:n
1621:)
1618:n
1615:(
1607:=
1602:)
1599:n
1590:(
1587:O
1583:2
1571:P
1546:n
1540:n
1516:3
1512:n
1490:)
1485:3
1481:n
1477:(
1474:O
1431:2
1427:n
1405:)
1400:2
1396:n
1392:(
1389:O
1356:n
1348:2
1340:n
1319:)
1316:n
1307:(
1299:n
1260:!
1257:n
1231:n
1222:n
1201:)
1198:n
1189:n
1186:(
1183:O
1143:)
1140:n
1124:n
1121:(
1118:O
1075:5
1072:+
1069:n
1066:2
1056:n
1041:)
1038:n
1035:(
1032:O
1012:k
989:3
986:2
981:n
957:2
954:1
949:n
927:1
921:c
915:0
895:)
890:c
886:n
882:(
879:O
847:2
843:)
839:n
830:(
809:)
806:n
797:(
759:)
754:2
750:n
746:(
720:n
693:)
690:n
681:(
678:O
639:)
636:n
621:(
618:O
583:)
580:n
564:(
561:O
517:)
512:)
509:n
506:(
498:(
493:O
448:)
445:1
442:(
439:O
415:)
413:)
411:n
409:(
407:O
404:(
386:x
381:x
377:x
343:0
317:)
308:n
304:(
301:O
277:)
274:n
271:(
268:O
251:n
247:,
235:)
230:n
226:2
222:(
219:O
209:,
197:)
188:n
184:(
181:O
171:,
159:)
156:n
147:n
144:(
141:O
131:,
119:)
116:n
113:(
110:O
51:n
47:N
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.