343:(KPI). These KPIs are specific to the racial disparity issues which the population served identifies with (i.e. low reading, financial literacy, unemployment, etc). In an effort to prevent the logic model itself from being cluttered with an overwhelming number of KPIs, the KPIs are arranged by category and only the category is displayed on the logic model. The extensive list of KPIs are an appendix to the logic model. Organizations identify the KPIs and corresponding outcomes by first conducting a needs assessment and/or community focus groups. This helps to ensure that the logic model remains focused on improving the real-time needs of people to remove racial barriers. The POSLM can help to make more clear the intended outcomes and the casual pathways leading to them; both of which help to connect and compose a logical companion "if, then"
258:
172:
examine if the intermediate outcomes progress as planned. In addition, the pathways of numerous outcomes are still largely misunderstood due their complexity, their unpredictability and lack of scientific / practical evidences. Therefore, with proper research design, one may not only assess the progress of intermediate outcomes, but evaluate as well if the program theory of change is accurate, i.e. is successful change of an intermediate outcomes provokes the hypothesized subsequent effects in the causal pathway. Finally, outcomes may easily be achieved through processes independent of the program and an evaluation of those outcomes would suggest program success when in fact external outputs were responsible for the outcomes.
277:, which is a graphical depiction of at-risk population and its social environment behaviors (factors) leading to the health problem and their respective causal pathways (attitudes, beliefs, skills, etc.). This may include as well at-risk population physical environment related causes such as pollutants or lack of physical activity infrastructure and their respective causes, i.e. environmental agents behaviors leading to the physical environment causes and their respective causal pathways;
25:
316:
67:
86:
application are various, e.g. waste management, poultry inspection, business education, heart disease and stroke prevention. Since they are used in various contexts and for different purposes, their typical components and levels of complexity varies in literature (compare for example the W.K. Kellogg
Foundation presentation of logic model, mainly aimed for evaluation, and the numerous types of logic models in the
157:. It is easy to measure the amount of money spent on a program, but this is a poor indicator of outcomes. Likewise it is relatively easy to measure the amount of work done (e.g. number of workers or number of years spent), but the workers may have just been 'spinning their wheels' without getting very far in terms of ultimate results or outcomes.
359:
can be drawn from any of the steps. One of the key insights of the logic model is the importance of measuring final outcomes or results, because it is quite possible to waste time and money (inputs), "spin the wheels" on work activities, or produce outputs without achieving desired outcomes. It is
269:
approach of
Bartholomew et al. makes an extensive use of the logic model through the whole life-cycle of a health promotion program. Since this method can start from as far as a vague desired outcome (author's example is a city whose actors decide to address "health issues" of the city), planners go
98:
Citing
Funnell and Rogers's account (2011), Joy A. Frechtling's (2015) encyclopedia article traces logic model underpinnings to the 1950s. Patricia J. Rogers's (2005) encyclopedia article instead traces it back to Edward A. Suchman's (1967) book about evaluative research. Both encyclopedia articles
338:
outcomes. To measure the progress towards outcomes, this type of logic model states short, intermediate and long-term outcomes as "stage 1", "stage 2" and "stage 3. Each stage is uniquely defined and used to depict the percentage of KPIs achieved at each stage or the percentage of people who reach
171:
By making clear the intended outcomes and the causal pathways leading to them, a program logic model provides the basis upon which planners and evaluators can develop a measurement plan and adequate instruments. Instead of only looking at the outcome progress, planners can open the "black box" and
112:
One of the most important uses of the logic model is for program planning. It is suggested to use the logic model to focus on the intended outcomes of a particular program. The guiding questions change from "what is being done?" to "what needs to be done"? McCawley suggests that by using this new
81:
leading to an outcome of interest (e.g. prevalence of cardiovascular diseases, annual traffic collision, etc). While they can be in a narrative form, logic model usually take form in a graphical depiction of the "if-then" (causal) relationships between the various elements leading to the outcome.
85:
Logic models are used by planners, funders, managers and evaluators of programs and interventions to plan, communicate, implement and evaluate them. They are being employed as well by health scientific community to organize and conduct literature reviews such as systematic reviews. Domains of
242:
Many refinements and variations have been added to the basic template. For example, many versions of logic models set out a series of outcomes/impacts, explaining in more detail the logic of how an intervention contributes to intended or observed results. Others often distinguish short-term,
384:
Program logic is no guarantee of actual logic in how the program may work. The world is complex, and some situations cannot be ascertained before they are implemented, so some programs may even progress against the "logic" of the
270:
through various steps in order to develop effective interventions and properly evaluate them. There are distinguishable but closely interwoven logic models with different purposes that can be developed through the process:
140:
through the logic model to identify how best to achieve the desired results. Here it helps managers to 'plan with the end in mind', rather than just consider inputs (e.g. budgets, employees) or the tasks that must be done.
82:
However, the logic model is more than the graphical depiction: it is also the theories, scientific evidences, assumptions and beliefs that support it and the various processes behind it.
168:, outcomes are usually in the long-term and may requires numerous intermediate changes (attitudes, social norm, industry practices, etc.) to advance progressively toward the outcomes.
153:
or not-for-profit organizations, where the mission and vision are not aimed at achieving a financial benefit. Traditionally, government programs were described only in terms of their
160:
However, nature of outcomes varies. To measure the progress toward outcomes, some initiatives may require an ad hoc measurement instrument. In addition, in programs such as in
552:
Anderson LM, Petticrew M, Rehfuess E, Armstrong R, Ueffing E, Baker P, Francis D, Tugwell P (March 2011). "Using logic models to capture complexity in systematic reviews".
257:
360:
these outcomes (impacts, long-term results) that are the only justification for doing the work in the first place. For commercial organizations, outcomes relate to
284:. This is a model of behavioral changes (performance objectives) that should happen and their corresponding necessary changes higher up in the cause-effects chain.
706:
291:
is developed. This model describes the various activities that will happen and the cascades of effects they are expected to cause toward the desired outcome.
597:"Developing and Optimising the Use of Logic Models in Systematic Reviews: Exploring Practice and Good Practice in the Use of Programme Theory in Reviews"
90:
framework). In addition, depending on the purpose of the logic model, elements depicted and the relationships between them is more or less detailed.
261:
Logic Model of the
Problem for Management information Decision Support Epilepsy Tool (MINDSET program) from Ruiter, DeSmet and Schneider (2007).
811:
328:
1163:
1035:
994:
905:
872:
839:
682:
536:
498:
347:
statement. Again, more research is needed and currently being conducted as more nonprofits, philanthropic and governments use this model.
675:
Development of a logic model and an evaluation framework of the
Canadian Food Inspection Agency's Modernized Poultry Inspection Program
1304:
Stinchcomb JB (2001). "Using logic modeling to focus evaluation efforts: Translating operational theories into practical measures".
1084:
949:
1334:
1228:
70:
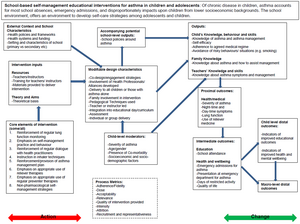
Example of a logic model for a school-based self-management educational interventions for asthma in children and adolescents.
655:
331:
when developing program logic models. More testing and research is needed in order to verify the validity of this model.
1102:"Clinic-Based Mobile Health Decision Support to Enhance Adult Epilepsy Self-Management: An Intervention Mapping Approach"
37:
1414:
1419:
710:
380:
There are some potential disadvantages of logic models due to tendencies toward oversimplification. These include:
340:
369:
1383:
Unrau YA (2001). "Using client exit interviews to illuminate outcomes in program logic models: A case example".
966:
334:
The POSLM approach makes use of the logic model with a strong focus on tracking progressive improvement towards
768:"Adapting logic models over time: the Washington State Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention Program experience"
323:
The
Progressive Outcomes Scale Logic Model (POSLM) approach was developed by Quisha Brown in response to the
365:
356:
295:
Evaluators thereafter use the logic model of the intervention to design a proper evaluation plan to assess
1262:
Julian DA (1997). "The utilization of the logic model as a system level planning and evaluation device".
1283:
McLaughlin JA, Jordan GB (1999). "Logic models: A tool for telling your program's performance story".
608:
266:
252:
87:
1198:
National
Evaluation of the Comprehensive Community Mental Health Services and their Families Program
361:
113:
reasoning, a logic model for a program can be built by asking the following questions in sequence:
1370:
1321:
1045:
748:
726:"Putting theory-oriented evaluation into practice: A logic model approach for evaluating SIMGAME"
700:
577:
427:
304:
300:
296:
236:
e.g. increased skills/ knowledge/ confidence, leading in longer-term to promotion, new job, etc.
355:
By describing work in this way, managers have an easier way to define the work and measure it.
1193:
1169:
1159:
1133:
1080:
1031:
1000:
990:
945:
941:
911:
901:
878:
868:
845:
835:
789:
688:
678:
636:
569:
532:
494:
422:
324:
1249:
Hernandez M (2000). "Using logic models and program theory to build outcome accountability".
1392:
1313:
1292:
1271:
1237:
1214:
1123:
1113:
1023:
937:
779:
740:
626:
616:
561:
524:
486:
456:
407:
344:
46:
397:
They do not necessarily establish causality. Many factors exert influence upon the effects.
1057:
417:
335:
315:
66:
99:
and LeCroy (2018) mention increasing interest, usage and publications about the subject.
725:
612:
280:
Once the most relevant behaviors and causal pathways are identified, planners develop a
24:
1345:
1128:
1101:
784:
767:
631:
596:
490:
165:
1396:
1296:
1275:
898:
Evaluative
Research: Principles and Practice in Public Service and Social Action Progr
460:
1408:
1325:
1226:
Conrad KJ, Randolph FL (1999). "Creating and using logic models: Four perspectives".
1073:
1205:
Alter C, Murty S (1997). "Logic modeling: A tool for teaching practice evaluation".
752:
581:
185:
Many authors and guides use the following template when speaking about logic model:
1218:
621:
412:
865:
Purposeful program theory: Effective use of theories of change and logic models
528:
1358:"Assessing Impact to Inform Decisions: A Toolkit on Measures for Policymakers"
1027:
391:
It is a representation of reality, not reality itself. Programs are not linear
150:
1357:
1173:
1142:
The full intervention mapping based protocol is available in the full article
1118:
882:
849:
744:
692:
1371:"A set of three online evaluation tools that includes a Logic Model Builder"
1004:
243:
medium-term and long-term results, and between direct and indirect results.
161:
78:
1137:
793:
640:
573:
1317:
1241:
915:
372:, outcomes relate to successful achievement of mission or program goals.
126:
What knowledge or skills do people need before the behavior will change?
120:
What will it look like when we achieve the desired situation or outcome?
394:
Normally, it does not include effects besides those initially expected.
154:
129:
What activities need to be performed to cause the necessary learning?
1156:
The logic model guidebook : better strategies for great results
832:
Planning health promotion programs: an intervention mapping approach
565:
447:
Renger R (2002). "A Three-Step
Approach to Teaching Logic Models".
136:
By placing the focus on ultimate outcomes or results, planners can
483:
International
Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences
314:
256:
677:. Canada. Health Canada. Food Safety Assessment Program. . 2003.
654:
Industrial Economics, Incorporated (IEc) Evaluation Team (2010).
233:
e.g. number of booklets produced, workshops held, people trained
1075:
Evaluation Research. Methods for Assessing Program Effectiveness
1194:"Crafting logic models for systems of care: Ideas into action."
132:
What resources will be required to achieve the desired outcome?
123:
What behaviors need to change for that outcome to be achieved?
18:
834:(Fourth ed.). San Francisco, CA: John Wiley & Sons.
830:
Eldredge LK, Markham CM, Ruiter RA, Kok G, Parcel GS (2016).
319:
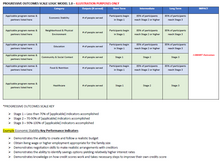
Sample Progressive Outcomes Scale Logic Model (POSLM) (2021)
867:(1st ed.). San Francisco, CA: John Wiley & Sons.
766:
Sitaker M, Jernigan J, Ladd S, Patanian M (April 2008).
117:
What is the current situation that we intend to impact?
42:
1335:"The Logic Model for Program planning and Evaluation"
813:
W.K. Kellogg Foundation Logic Model Development Guide
181:
The Inputs → Activities → Outputs → Outcomes template
1079:. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall, Inc.
663:. EPA's Office of Policy, Economics, and Innovation.
327:
to aid organizations in the immediate need to add a
221:
the changes or benefits that result from the program
968:
The logic model for program planning and evaluation
388:
It is a partial representation of a complex system.
1369:
1072:
476:
474:
472:
470:
230:e.g. development of materials, training programs
1376:Innovation Network's Point K Logic Model Builder
825:
823:
311:Progressive Outcomes Scale Logic Models (POSLM)
1022:. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. pp. 62–87.
339:each stage as they progress on pre-identified
77:are hypothesized descriptions of the chain of
1154:Knowlton LW, Phillips CC, Phillips C (2013).
8:
724:Hense J, Kriz WC, Wolfe J (February 2009).
595:Kneale D, Thomas J, Harris K (2015-11-17).
705:: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (
1127:
1117:
989:(7th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
783:
630:
620:
216:what is produced through those activities
1356:Savitz S, Matthews M, Weilant S (2017).
985:Rossi PH, Lipsey MW, Freeman HE (2004).
932:LeCroy CW (2018-06-25). "Logic Models".
816:. Battle Creek: W.K. Kellogg Foundation.
187:
65:
16:Method of depicting causal relationships
987:Evaluation : a systematic approach
942:10.1093/acrefore/9780199975839.013.1273
863:Funnell SC, Rogers PJ (February 2011).
514:
512:
510:
439:
1053:
1043:
1018:McLaughlin JA, Jordan G (2015-10-14).
698:
481:Frechtling JA (2015). "Logic Models".
211:what activities the program undertakes
1158:(2nd ed.). Los Angeles: SAGE C.
927:
925:
900:. New York: Russell Sage Foundation.
805:
803:
7:
1251:Education and Treatment of Children
1192:Hernandez M, Hodges S (July 2003).
657:Evaluation of the WasteWise Program
1306:Journal of Offender Rehabilitation
491:10.1016/b978-0-08-097086-8.10549-5
449:The American Journal of Evaluation
14:
247:Intervention mapping logic models
149:The logic model is often used in
36:to comply with Knowledge (XXG)'s
1207:Journal of Social Work Education
974:. University of Idaho Extension.
810:W.K. Kellogg Foundation (1998).
523:. Sage Publications, Inc. 2005.
206:what resources go into a program
23:
1385:Evaluation and Program Planning
1285:Evaluation and Program Planning
1264:Evaluation and Program Planning
289:logic model of the intervention
1229:Alcoholism Treatment Quarterly
1219:10.1080/10437797.1997.10778856
485:. Elsevier. pp. 299–305.
1:
1397:10.1016/S0149-7189(01)00029-5
1342:University of Idaho Extension
1297:10.1016/S0149-7189(98)00042-1
1276:10.1016/S0149-7189(97)00002-5
461:10.1016/s1098-2140(02)00230-8
227:e.g. money, staff, equipment
176:Various types of logic models
1100:Shegog R, Begley CE (2017).
622:10.1371/journal.pone.0142187
235:
232:
229:
226:
219:
214:
209:
204:
934:Encyclopedia of Social Work
896:Suchman E (December 1968).
1436:
1106:Frontiers in Public Health
772:Preventing Chronic Disease
554:Research Synthesis Methods
529:10.4135/9781412950558.n321
521:Encyclopedia of Evaluation
370:governmental organizations
341:Key Performance Indicators
275:Logic model of the problem
250:
1028:10.1002/9781119171386.ch3
1119:10.3389/fpubh.2017.00256
745:10.1177/1046878107308078
49:may contain suggestions.
34:may need to be rewritten
733:Simulation & Gaming
103:Uses of the logic model
94:History of logic models
320:
262:
71:
1318:10.1300/J076v33n02_04
1242:10.1300/J020v17n01_02
709:) CS1 maint: others (
318:
282:logic model of change
260:
69:
1351:on 17 November 2010.
1333:McCawley PF (2001).
965:McCawley PF (1995).
357:Performance measures
267:intervention mapping
253:Intervention mapping
88:intervention mapping
613:2015PLoSO..1042187K
329:racial equity focus
1415:Evaluation methods
1020:Using Logic Models
428:Thought experiment
321:
263:
79:causes and effects
72:
1420:Conceptual models
1165:978-1-4522-1675-1
1071:Weiss CH (1972).
1037:978-1-119-17138-6
996:978-0-7619-0894-4
907:978-0-87154-863-4
874:978-0-470-47857-8
841:978-1-119-03556-5
684:978-0-662-35161-0
538:978-0-7619-2609-2
500:978-0-08-097087-5
423:Scenario planning
325:racial wealth gap
240:
239:
200:Outcomes/impacts
64:
63:
38:quality standards
1427:
1400:
1379:
1373:
1365:
1352:
1350:
1344:. Archived from
1339:
1329:
1300:
1279:
1258:
1245:
1222:
1201:
1178:
1177:
1151:
1145:
1144:
1131:
1121:
1097:
1091:
1090:
1078:
1068:
1062:
1061:
1055:
1051:
1049:
1041:
1015:
1009:
1008:
982:
976:
975:
973:
962:
956:
955:
929:
920:
919:
893:
887:
886:
860:
854:
853:
827:
818:
817:
807:
798:
797:
787:
763:
757:
756:
730:
721:
715:
714:
704:
696:
671:
665:
664:
662:
651:
645:
644:
634:
624:
607:(11): e0142187.
592:
586:
585:
549:
543:
542:
516:
505:
504:
478:
465:
464:
444:
408:Theory of change
345:theory of change
336:racial disparity
188:
108:Program planning
59:
56:
50:
27:
19:
1435:
1434:
1430:
1429:
1428:
1426:
1425:
1424:
1405:
1404:
1403:
1391:(4m): 353–361.
1382:
1368:
1355:
1348:
1337:
1332:
1303:
1282:
1261:
1248:
1225:
1204:
1191:
1187:
1185:Further reading
1182:
1181:
1166:
1153:
1152:
1148:
1099:
1098:
1094:
1087:
1070:
1069:
1065:
1052:
1042:
1038:
1017:
1016:
1012:
997:
984:
983:
979:
971:
964:
963:
959:
952:
931:
930:
923:
908:
895:
894:
890:
875:
862:
861:
857:
842:
829:
828:
821:
809:
808:
801:
765:
764:
760:
728:
723:
722:
718:
697:
685:
673:
672:
668:
660:
653:
652:
648:
594:
593:
589:
566:10.1002/jrsm.32
551:
550:
546:
539:
519:"Logic Model".
518:
517:
508:
501:
480:
479:
468:
446:
445:
441:
436:
418:Critical theory
404:
378:
353:
313:
255:
249:
183:
178:
166:social programs
147:
110:
105:
96:
60:
54:
51:
41:
28:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1433:
1431:
1423:
1422:
1417:
1407:
1406:
1402:
1401:
1380:
1366:
1353:
1330:
1301:
1280:
1270:(3): 251–257.
1259:
1246:
1236:(1–2): 17–32.
1223:
1213:(1): 103–117.
1202:
1188:
1186:
1183:
1180:
1179:
1164:
1146:
1092:
1085:
1063:
1036:
1010:
995:
977:
957:
950:
921:
906:
888:
873:
855:
840:
819:
799:
758:
716:
683:
666:
646:
587:
544:
537:
506:
499:
466:
455:(4): 493–503.
438:
437:
435:
432:
431:
430:
425:
420:
415:
410:
403:
400:
399:
398:
395:
392:
389:
386:
377:
374:
366:not-for-profit
352:
349:
312:
309:
297:implementation
293:
292:
285:
278:
251:Main article:
248:
245:
238:
237:
234:
231:
228:
224:
223:
218:
213:
208:
202:
201:
198:
195:
192:
182:
179:
177:
174:
146:
143:
138:think backward
134:
133:
130:
127:
124:
121:
118:
109:
106:
104:
101:
95:
92:
62:
61:
31:
29:
22:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1432:
1421:
1418:
1416:
1413:
1412:
1410:
1398:
1394:
1390:
1386:
1381:
1377:
1372:
1367:
1363:
1359:
1354:
1347:
1343:
1336:
1331:
1327:
1323:
1319:
1315:
1311:
1307:
1302:
1298:
1294:
1290:
1286:
1281:
1277:
1273:
1269:
1265:
1260:
1256:
1252:
1247:
1243:
1239:
1235:
1231:
1230:
1224:
1220:
1216:
1212:
1208:
1203:
1199:
1195:
1190:
1189:
1184:
1175:
1171:
1167:
1161:
1157:
1150:
1147:
1143:
1139:
1135:
1130:
1125:
1120:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1103:
1096:
1093:
1088:
1086:9780132921930
1082:
1077:
1076:
1067:
1064:
1059:
1047:
1039:
1033:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1014:
1011:
1006:
1002:
998:
992:
988:
981:
978:
970:
969:
961:
958:
953:
951:9780199975839
947:
943:
939:
935:
928:
926:
922:
917:
913:
909:
903:
899:
892:
889:
884:
880:
876:
870:
866:
859:
856:
851:
847:
843:
837:
833:
826:
824:
820:
815:
814:
806:
804:
800:
795:
791:
786:
781:
777:
773:
769:
762:
759:
754:
750:
746:
742:
739:(1): 110–33.
738:
734:
727:
720:
717:
712:
708:
702:
694:
690:
686:
680:
676:
670:
667:
659:
658:
650:
647:
642:
638:
633:
628:
623:
618:
614:
610:
606:
602:
598:
591:
588:
583:
579:
575:
571:
567:
563:
559:
555:
548:
545:
540:
534:
530:
526:
522:
515:
513:
511:
507:
502:
496:
492:
488:
484:
477:
475:
473:
471:
467:
462:
458:
454:
450:
443:
440:
433:
429:
426:
424:
421:
419:
416:
414:
411:
409:
406:
405:
401:
396:
393:
390:
387:
383:
382:
381:
376:Disadvantages
375:
373:
371:
367:
363:
358:
350:
348:
346:
342:
337:
332:
330:
326:
317:
310:
308:
306:
302:
298:
290:
286:
283:
279:
276:
273:
272:
271:
268:
259:
254:
246:
244:
225:
222:
217:
212:
207:
203:
199:
196:
193:
190:
189:
186:
180:
175:
173:
169:
167:
163:
158:
156:
152:
144:
142:
139:
131:
128:
125:
122:
119:
116:
115:
114:
107:
102:
100:
93:
91:
89:
83:
80:
76:
68:
58:
55:February 2010
48:
44:
39:
35:
32:This article
30:
26:
21:
20:
1388:
1384:
1375:
1361:
1346:the original
1341:
1312:(2): 47–65.
1309:
1305:
1291:(1): 65–72.
1288:
1284:
1267:
1263:
1254:
1250:
1233:
1227:
1210:
1206:
1197:
1155:
1149:
1141:
1109:
1105:
1095:
1074:
1066:
1019:
1013:
986:
980:
967:
960:
933:
897:
891:
864:
858:
831:
812:
775:
771:
761:
736:
732:
719:
674:
669:
656:
649:
604:
600:
590:
560:(1): 33–42.
557:
553:
547:
520:
482:
452:
448:
442:
379:
354:
333:
322:
294:
288:
281:
274:
264:
241:
220:
215:
210:
205:
184:
170:
159:
148:
137:
135:
111:
97:
84:
75:Logic models
74:
73:
52:
43:You can help
33:
1257:(1): 24–41.
1054:|work=
413:Backcasting
287:Finally, a
194:Activities
1409:Categories
778:(2): A60.
434:References
351:Advantages
305:efficiency
151:government
145:Evaluation
1326:141946096
1174:791492618
1056:ignored (
1046:cite book
883:660161852
850:914256995
701:cite book
693:905371520
162:education
47:talk page
1138:29043247
1005:52706526
794:18341795
753:61673390
641:26575182
601:PLOS ONE
582:34282960
574:26061598
402:See also
197:Outputs
1378:. 2006.
1129:5632356
1112:: 256.
785:2396971
632:4648510
609:Bibcode
364:. For
191:Inputs
155:budgets
1324:
1172:
1162:
1136:
1126:
1083:
1034:
1003:
993:
948:
916:712569
914:
904:
881:
871:
848:
838:
792:
782:
751:
691:
681:
639:
629:
580:
572:
535:
497:
385:model.
362:profit
301:impact
45:. The
1349:(PDF)
1338:(PDF)
1322:S2CID
972:(PDF)
749:S2CID
729:(PDF)
661:(PDF)
578:S2CID
1362:RAND
1170:OCLC
1160:ISBN
1134:PMID
1081:ISBN
1058:help
1032:ISBN
1001:OCLC
991:ISBN
946:ISBN
912:OCLC
902:ISBN
879:OCLC
869:ISBN
846:OCLC
836:ISBN
790:PMID
711:link
707:link
689:OCLC
679:ISBN
637:PMID
570:PMID
533:ISBN
495:ISBN
303:and
265:The
1393:doi
1314:doi
1293:doi
1272:doi
1238:doi
1215:doi
1124:PMC
1114:doi
1024:doi
938:doi
780:PMC
741:doi
627:PMC
617:doi
562:doi
525:doi
487:doi
457:doi
368:or
164:or
1411::
1389:24
1387:.
1374:.
1360:.
1340:.
1320:.
1310:33
1308:.
1289:22
1287:.
1268:20
1266:.
1255:23
1253:.
1234:17
1232:.
1211:33
1209:.
1196:.
1168:.
1140:.
1132:.
1122:.
1108:.
1104:.
1050::
1048:}}
1044:{{
1030:.
999:.
944:.
936:.
924:^
910:.
877:.
844:.
822:^
802:^
788:.
774:.
770:.
747:.
737:40
735:.
731:.
703:}}
699:{{
687:.
635:.
625:.
615:.
605:10
603:.
599:.
576:.
568:.
556:.
531:.
509:^
493:.
469:^
453:23
451:.
307:.
299:,
1399:.
1395::
1364:.
1328:.
1316::
1299:.
1295::
1278:.
1274::
1244:.
1240::
1221:.
1217::
1200:.
1176:.
1116::
1110:5
1089:.
1060:)
1040:.
1026::
1007:.
954:.
940::
918:.
885:.
852:.
796:.
776:5
755:.
743::
713:)
695:.
643:.
619::
611::
584:.
564::
558:2
541:.
527::
503:.
489::
463:.
459::
57:)
53:(
40:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.