185:
96:
215:. The Barnwell and the Clive locations are operated by EnergySolutions, the Richland location is operated by U.S. Ecology, and the Andrews County location is operated by Waste Control Specialists. Barnwell, Richland, and Andrews County accept Classes A through C of low-level waste, whereas Clive only accepts Class A LLW. The DOE has dozens of LLW sites under management. The largest of these exist at DOE Reservations around the country (e.g. the
36:
246:, reproduced in the table below. These are not all the isotopes disposed of at these facilities, just the ones that are of most concern for the long-term monitoring of the sites. Waste is divided into three classes, A through C, where A is the least radioactive and C is the most radioactive. Class A LLW is able to be deposited near the surface, whereas Classes B and C LLW have to be buried progressively deeper.
154:, then it has a special status as mixed low-level waste (MLLW) and must satisfy treatment, storage, and disposal regulations both as LLW and as hazardous waste. While the bulk of LLW is not highly radioactive, the definition of LLW does not include references to its activity, and some LLW may be quite radioactive, as in the case of radioactive sources used in industry and medicine.
165:. This waste typically consists of contaminated protective shoe covers and clothing, wiping rags, mops, filters, reactor water treatment residues, equipments and tools, luminous dials, medical tubes, swabs, injection needles, syringes, and laboratory animal carcasses and tissues. The radioactivity can range from just above
249:
In 10 C.F.R. § 20.2002, the NRC reserves the right to grant a free release of radioactive waste. The overall activity of such a disposal cannot exceed 1 mrem/yr and the NRC regards requests on a case-by-case basis. Low-level waste passing such strict regulations is then disposed of in a landfill with
176:(IAEA) provides recommendations. Some countries, such as France, specify categories for long-lived low- and intermediate-level waste. U.S. regulations do not define the category of intermediate-level waste.
195:
Depending on who "owns" the waste, its handling and disposal is regulated differently. All nuclear facilities, whether they are a utility or a disposal site, have to comply with
733:
Jorge L. Contreras, "In the
Village Square: Risk Misperception and Decisionmaking in the Regulation of Low-Level Radioactive Waste", 19 Ecology Law Quarterly 481 (1992) (
676:
46:
650:
622:
582:
250:
other garbage. Items allowed to be disposed of in this way include glow-in-the-dark watches (radium) and smoke detectors (americium).
173:
80:
169:
found in nature to very highly radioactive in certain cases such as parts from inside the reactor vessel in a nuclear power plant.
560:(TRU). These require different disposal pathways. TRU wastes from the U.S. nuclear weapons complex is currently disposed at the
687:
228:
243:
232:
196:
189:
561:
184:
62:
568:, though other sites also are being considered for on-site disposal of particularly difficult to manage TRU wastes.
762:
577:
236:
158:
711:
200:
123:
212:
139:
172:
The definition of low-level waste is set by the nuclear regulators of individual countries, though the
565:
204:
166:
58:
556:
nuclides with a half life greater than 5 years; any more than 100 nCi, and it must be classified as
95:
220:
592:
542:
131:
633:
597:
587:
557:
162:
143:
135:
538:
224:
127:
242:
Classes of wastes are detailed in 10 C.F.R. § 61.55 Waste
Classification, enforced by the
147:
623:"Classification of Radioactive Waste : a Safety Guide. Safety Series No. 111-G-1.1"
483:
756:
550:
504:
451:
119:
356:
260:
216:
747:
553:
486:
208:
17:
520:
467:
435:
373:
419:
390:
325:
308:
275:
142:. In essence, it is a definition by exclusion, and LLW is that category of
161:
with radioactive material or have become radioactive through exposure to
291:
199:(NRC) regulations. The four low-level waste facilities in the U.S. are
138:(TRU), or certain byproduct materials known as 11e(2) wastes, such as
734:
546:
183:
94:
712:
151:
146:
that do not fit into the other categories. If LLW is mixed with
27:
Nuclear waste that does not fit into the categorical definitions
677:"New Federal Waste Facility Opens with Ribbon Cutting Ceremony"
29:
45:
deal primarily with the United States and do not represent a
122:
that does not fit into the categorical definitions for
54:
651:"Disposal of Commercial Low-Level Radioactive Waste"
252:
730:. New York: Taylor & Francis, 2002. Second ed.
545:(SNF). C Class low level waste has a limit of 100
43:The examples and perspective in this article
8:
274:Total of all nuclides with less than 5-year
726:Fentiman, Audeen W. and James H. Saling.
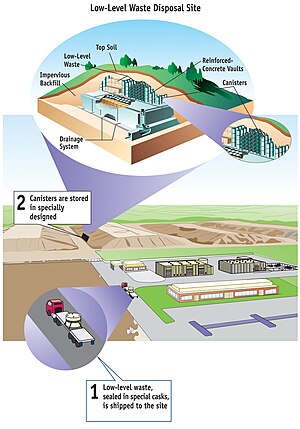
99:NRC graphic of a low-level waste facility
81:Learn how and when to remove this message
614:
491:with a half life greater than 5 years
269:Class C (Ci/m) (upper limit for LLW)
7:
632:. Vienna: IAEA. 1994. Archived from
157:LLW includes items that have become
583:Mixed waste (radioactive/hazardous)
188:Low-level waste storage pit at the
748:NRC description of low-level waste
174:International Atomic Energy Agency
25:
239:, to name the most significant).
537:LLW should not be confused with
34:
229:Los Alamos National Laboratory
1:
686:. 6 June 2013. Archived from
244:Nuclear Regulatory Commission
233:Oak Ridge National Laboratory
197:Nuclear Regulatory Commission
190:Nevada National Security Site
728:Radioactive Waste Management
562:Waste Isolation Pilot Plant
112:low-level radioactive waste
57:, discuss the issue on the
779:
578:Low Level Waste Repository
684:Waste Control Specialists
342:Ni-63 in activated metal
237:Idaho National Laboratory
655:Nuclear Energy Institute
438:(Nb) in activated metal
422:(Ni) in activated metal
406:C-14 in activated metal
201:Barnwell, South Carolina
124:intermediate-level waste
211:; and as of June 2013,
192:
100:
213:Andrews County, Texas
187:
140:uranium mill tailings
98:
566:Carlsbad, New Mexico
205:Richland, Washington
63:create a new article
55:improve this article
549:Curies per gram of
221:Savannah River Site
217:Hanford Reservation
721:General references
593:Spent nuclear fuel
543:spent nuclear fuel
193:
144:radioactive wastes
132:spent nuclear fuel
101:
763:Radioactive waste
630:RADWASS Programme
598:Transuranic waste
588:Radioactive waste
558:transuranic waste
535:
534:
167:background levels
163:neutron radiation
150:as classified by
136:transuranic waste
91:
90:
83:
65:, as appropriate.
16:(Redirected from
770:
714:
709:
703:
702:
700:
698:
692:
681:
673:
667:
666:
664:
662:
647:
641:
640:
638:
627:
619:
539:high-level waste
253:
225:Nevada Test Site
148:hazardous wastes
128:high-level waste
86:
79:
75:
72:
66:
38:
37:
30:
21:
778:
777:
773:
772:
771:
769:
768:
767:
753:
752:
744:
723:
718:
717:
710:
706:
696:
694:
690:
679:
675:
674:
670:
660:
658:
649:
648:
644:
639:on 15 May 2005.
636:
625:
621:
620:
616:
611:
606:
574:
490:
266:Class B (Ci/m)
182:
104:Low-level waste
87:
76:
70:
67:
52:
39:
35:
28:
23:
22:
18:Low level waste
15:
12:
11:
5:
776:
774:
766:
765:
755:
754:
751:
750:
743:
742:External links
740:
739:
738:
731:
722:
719:
716:
715:
704:
693:on 23 May 2014
668:
642:
613:
612:
610:
607:
605:
602:
601:
600:
595:
590:
585:
580:
573:
570:
551:alpha-emitting
533:
532:
529:
527:
524:
517:
516:
513:
511:
508:
501:
500:
497:
495:
492:
484:Alpha emitting
480:
479:
476:
474:
471:
464:
463:
460:
458:
455:
448:
447:
444:
442:
439:
432:
431:
428:
426:
423:
416:
415:
412:
410:
407:
403:
402:
399:
397:
394:
387:
386:
383:
380:
377:
370:
369:
366:
363:
360:
353:
352:
349:
346:
343:
339:
338:
335:
332:
329:
322:
321:
318:
315:
312:
305:
304:
301:
298:
295:
288:
287:
284:
281:
278:
271:
270:
267:
264:
257:
181:
178:
89:
88:
49:of the subject
47:worldwide view
42:
40:
33:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
775:
764:
761:
760:
758:
749:
746:
745:
741:
736:
732:
729:
725:
724:
720:
713:
708:
705:
689:
685:
678:
672:
669:
656:
652:
646:
643:
635:
631:
624:
618:
615:
608:
603:
599:
596:
594:
591:
589:
586:
584:
581:
579:
576:
575:
571:
569:
567:
563:
559:
555:
552:
548:
544:
540:
530:
528:
525:
522:
519:
518:
514:
512:
509:
506:
505:Plutonium-241
503:
502:
498:
496:
493:
488:
485:
482:
481:
477:
475:
472:
469:
466:
465:
461:
459:
456:
453:
452:Technetium-99
450:
449:
445:
443:
440:
437:
434:
433:
429:
427:
424:
421:
418:
417:
413:
411:
408:
405:
404:
400:
398:
395:
392:
389:
388:
384:
381:
378:
375:
372:
371:
367:
364:
361:
358:
355:
354:
350:
347:
344:
341:
340:
336:
333:
330:
327:
324:
323:
319:
316:
313:
310:
307:
306:
302:
299:
296:
293:
290:
289:
285:
282:
279:
277:
273:
272:
268:
265:
262:
258:
256:Radionuclide
255:
254:
251:
247:
245:
240:
238:
234:
230:
226:
222:
218:
214:
210:
206:
202:
198:
191:
186:
179:
177:
175:
170:
168:
164:
160:
155:
153:
149:
145:
141:
137:
133:
129:
125:
121:
120:nuclear waste
117:
113:
109:
105:
97:
93:
85:
82:
74:
71:December 2010
64:
60:
56:
50:
48:
41:
32:
31:
19:
727:
707:
695:. Retrieved
688:the original
683:
671:
659:. Retrieved
657:. April 2014
654:
645:
634:the original
629:
617:
564:(WIPP) near
536:
531:20000 nCi/g
357:Strontium-90
248:
241:
194:
171:
159:contaminated
156:
115:
111:
107:
103:
102:
92:
77:
68:
44:
554:transuranic
526:2000 nCi/g
515:3500 nCi/g
487:transuranic
209:Clive, Utah
604:References
521:Curium-242
510:350 nCi/g
499:100 nCi/g
468:Iodine-129
436:Niobium-94
374:Cesium-137
541:(HLW) or
494:10 nCi/g
420:Nickel-59
391:Carbon-14
326:Nickel-63
320:No limit
317:No limit
309:Cobalt-60
303:No limit
300:No limit
286:No limit
283:No limit
276:half life
259:Class A (
59:talk page
757:Category
572:See also
489:nuclides
180:Disposal
53:You may
292:Tritium
134:(SNF),
130:(HLW),
126:(ILW),
473:0.008
261:Curies
697:9 May
691:(PDF)
680:(PDF)
661:8 May
637:(PDF)
626:(PDF)
609:Notes
547:nano-
523:(Cm)
507:(Pu)
478:0.08
454:(Tc)
441:0.02
385:4600
376:(Cs)
368:7000
362:0.04
359:(Sr)
351:7000
328:(Ni)
311:(Co)
118:) is
110:) or
61:, or
735:SSRN
699:2015
663:2015
470:(I)
457:0.3
446:0.2
430:220
396:0.8
393:(C)
365:150
348:700
337:700
331:3.5
314:700
294:(H)
280:700
263:/m)
152:RCRA
116:LLRW
425:22
414:80
382:44
345:35
334:70
297:40
108:LLW
759::
682:.
653:.
628:.
462:3
409:8
401:8
379:1
235:,
231:,
227:,
223:,
219:,
207:;
203:;
737:)
701:.
665:.
114:(
106:(
84:)
78:(
73:)
69:(
51:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.