1375:), ATPase gene gain and loss as well as horizontal transfer occurred seldom in contrast to most other bacterial phyla. Some families (i.e., Kdp-type ATPases) underwent far less horizontal gene transfer than other prokaryotic families, possibly due to their multisubunit characteristics. Functional motifs are better conserved across family lines than across organismal lines, and these motifs can be family specific, facilitating functional predictions. In some cases, gene fusion events created P-type ATPases covalently linked to regulatory catalytic enzymes. In one family (FUPA Family 24), a type I ATPase gene (N-terminal) is fused to a type II ATPase gene (C-terminal) with retention of function only for the latter. Genome minimalization led to preferential loss of P-type ATPase genes. Chan et al. (2010) suggested that in prokaryotes and some unicellular eukaryotes, the primary function of P-type ATPases is protection from extreme environmental stress conditions. The classification of P-type ATPases of unknown function into phylogenetic families provides guides for future molecular biological studies.
757:), invariant residues in helixes 6, 7 and 8 form two transmembrane metal binding sites (TM-MBSs). These bind Cu with high affinity in a trigonal planar geometry. The cytoplasmic Cu chaperone CopZ transfers the metal directly to the TM-MBSs; however, loading both of the TM-MBSs requires binding of nucleotides to the enzyme. In agreement with the classical transport mechanism of P-type ATPases, occupancy of both transmembrane sites by cytoplasmic Cu is a requirement for enzyme phosphorylation and subsequent transport into the periplasmic or extracellular milieu. Transport studies have shown that most Cu-ATPases drive cytoplasmic Cu efflux, albeit with quite different transport rates in tune with their various physiological roles. Archetypical Cu-efflux pumps responsible for Cu tolerance, like the
737:), has been studied. CopZ interacted with and delivered the metal to the N-terminal metal binding domain(s) of CopA (MBDs). Cu-loaded MBDs, acting as metal donors, were unable to activate CopA or a truncated CopA lacking MBDs. Conversely, Cu-loaded CopZ activated the CopA ATPase and CopA constructs in which MBDs were rendered unable to bind Cu. Furthermore, under nonturnover conditions, CopZ transferred Cu to the TM-MBS of a CopA lacking MBDs altogether. Thus, MBDs may serve a regulatory function without participating directly in metal transport, and the chaperone delivers Cu directly to transmembrane transport sites of Cu-ATPases. Wu et al. (2008) have determined structures of two constructs of the Cu (CopA) pump from
1206:. Ten transmembrane helices and three cytoplasmic domains define the functional unit of ATP-coupled proton transport across the plasma membrane, and the structure is locked in a functional state not previously observed in P-type ATPases. The transmembrane domain reveals a large cavity, which is likely to be filled with water, located near the middle of the membrane plane where it is lined by conserved hydrophilic and charged residues. Proton transport against a high membrane potential is readily explained by this structural arrangement.
5096:
446:(M1-M10), with the binding sites for transported ligand(s) located near the midpoint of the bilayer. While most subfamilies have 10 transmembrane helices, there are some notable exceptions. The P1A ATPases are predicted to have 7, and the large subfamily of heavy metal pumps P1B) is predicted to have 8 transmembrane helices. P5 ATPases appear to have a total of 12 transmembrane helices.
516:
of the transported ligand(s) in the transmembrane binding sites, and it is pivot in transposing the energy from the hydrolysis of ATP in the cytoplasmic domains to the vectorial transport of cations in the transmembrane domain. The A domain dephosphorylates the P domain as part of the reaction cycle using a highly conserved TGES motif located at one end of the jellyroll.
398:
function. Additional subunits that lack catalytic activity are present in the ATPase complexes of P1A, P2A, P2C and P4 ATPases. E.g. the catalytic alpha subunit of Na/K-ATPase consists of two additional subunits, beta and gamma, involved in trafficking, folding, and regulation of these pumps. The first P-type ATPase to be crystallized was
21:
862:(M1-M10), with the two Ca-binding sites located near the midpoint of the bilayer. The binding sites are formed by side-chains and backbone carbonyls from M4, M5, M6, and M8. M4 is unwound in this region due to a conserved proline (P308). This unwinding of M4 is recognised as a key structural feature of P-type ATPases.
761:
CopA, have turnover rates ten times higher than those involved in cuproprotein assembly (or alternative functions). This explains the incapability of the latter group to significantly contribute to the metal efflux required for survival in high copper environments. Structural and mechanistic details
632:
analysis of 159 sequences made in 1998 by
Axelsen and Palmgren suggested that P-type ATPases can be divided into five subfamilies (types; designated as P1-P5), based strictly on a conserved sequence kernel excluding the highly variable N and C terminal regions. Chan et al. (2010) also analyzed P-type
912:
state, the reaction cycle begins as the enzyme releases 1-3 protons from the cation-ligating residues, in exchange for cytoplasmic Ca-ions. This leads to assembly of the phosphorylation site between the ATP-bound N domain and the P domain, while the A domain directs the occlusion of the bound Ca. In
515:
The A domain serves as a built-in protein phosphatase that functions to dephosphorylate the phosphorylated P domain. The A domain is the smallest of the three cytoplasmic domains. It consists of a distorted jellyroll structure and two short helices. It is the actuator domain modulating the occlusion
397:
P-type ATPases have a single catalytic subunit of 70 - 140 kDa. The catalytic subunit hydrolyzes ATP, contains the aspartyl phosphorylation site and binding sites for the transported ligand(s) and catalyzes ion transport. Various subfamilies of P-type ATPases also need additional subunits for proper
2914:
Di Fonzo, A; Chien, H. F; Socal, M; Giraudo, S; Tassorelli, C; Iliceto, G; Fabbrini, G; Marconi, R; Fincati, E; Abbruzzese, G; Marini, P; Squitieri, F; Horstink, M. W; Montagna, P; Libera, A. D; Stocchi, F; Goldwurm, S; Ferreira, J. J; Meco, G; Martignoni, E; Lopiano, L; Jardim, L. B; Oostra, B. A;
1341:
Chan et al., (2010) conducted an equivalent but more extensive analysis of the P-type ATPase
Superfamily in Prokaryotes and compared them with those from Eukaryotes. While some families are represented in both types of organisms, others are found only in one of the other type. The primary functions
506:
The N domain serves as a built-in protein kinase that functions to phosphorylate the P domain. The N domain is inserted between the two segments of the P domain, and is formed of a seven-strand antiparallel β-sheet between two helix bundles. This domain contains the ATP-binding pocket, pointing out
462:
The P domain contains the canonical aspartic acid residue phosphorylated (in a conserved DKTGT motif; the 'D' is the one letter abbreviation of the amino acid aspartate) during the reaction cycle. It is composed of two parts widely separated in sequence. These two parts assemble into a seven-strand
929:
P state. During this transition, the transmembrane Ca-binding residues are forced apart, destroying the high-affinity binding site. This is in agreement with the general model form substrate translocation, showing that energy in primary transport is not used to bind the substrate but to release it
745:
of tubular crystals, which revealed the overall architecture and domain organization of the molecule. They localized its N-terminal MBD within the cytoplasmic domains that use ATP hydrolysis to drive the transport cycle and built a pseudoatomic model by fitting existing crystallographic structures
945:
Xu et al. proposed how Ca binding induces conformational changes in TMS 4 and 5 in the membrane domain (M) that in turn induce rotation of the phosphorylation domain (P). The nucleotide binding (N) and β-sheet (β) domains are highly mobile, with N flexibly linked to P, and β flexibly linked to M.
2870:
Ramirez, A; Heimbach, A; Gründemann, J; Stiller, B; Hampshire, D; Cid, L. P; Goebel, I; Mubaidin, A. F; Wriekat, A. L; Roeper, J; Al-Din, A; Hillmer, A. M; Karsak, M; Liss, B; Woods, C. G; Behrens, M. I; Kubisch, C (2006). "Hereditary parkinsonism with dementia is caused by mutations in ATP13A2,
449:
Common for all P-type ATPases is a core of 6 transmembrane-spanning segments (also called the 'transport (T) domain'; M1-M6 in SERCA), that harbors the binding sites for the translocated ligand(s). The ligand(s) enter through a half-channel to the binding site and leave on the other side of the
453:
Varying among P-type ATPase is the additional number of transmembrane-spanning segments (also called the 'support (S) domain', which between subfamilies ranges from 2 to 6. Extra transmembrane-segments likely provides structural support for the T domain and can also have specialized functions.
1118:
has been determined with two rubidium ions bound in an occluded state in the transmembrane part of the α-subunit. Several of the residues forming the cavity for rubidium/potassium occlusion in the Na/K-ATPase are homologous to those binding calcium in the Ca-ATPase of the sarco(endo)plasmic
987:
dephosphorylation and suggest a direct participation of the side chains of the TGES loop in the control and facilitation of the insertion of the loop in the catalytic site. The interactions of the TGES loop furthermore seem to facilitate its disengagement from the catalytic site during the
933:
As the Ca dissociate to the luminal side, the cation binding sites are neutralised by proton binding, which makes a closure of the transmembrane segments favourable. This closure is coupled to a downward rotation of the A domain and a movement of the P domain, which then leads to the
619:
ATP hydrolysis occurs in the cytoplasmic headpiece at the interface between domain N and P. Two Mg-ion sites form part of the active site. ATP hydrolysis is tightly coupled to translocation of the transported ligand(s) through the membrane, more than 40 Å away, by the A domain.
924:
This then allows the A domain to rotate toward the phosphorylation site, making a firm association with both the P and the N domains. This movement of the A domain exerts a downward push on M3-M4 and a drag on M1-M2, forcing the pump to open at the luminal side and forming the
1070:
to autoinhibitory built-in domains situated at either the carboxy-terminal (animals) or amino-terminal (plants) end of the pump protein. In the cell, they are situated in the plasma membrane (animals and plants) and the internal membranes (plants).
596:, it has low affinity of the exported substrate and high affinity for the imported substrate. Four major enzyme states form the cornerstones in the reaction cycle. Several additional reaction intermediates occur interposed. These are termed E
1350:
Many P-type ATPase families are found exclusively in prokaryotes (e.g. Kdp-type K uptake ATPases (type III) and all prokaryotic functionally uncharacterized P-type ATPase (FUPA) families), while others are restricted to eukaryotes (e.g.
941:
The P domain is dephosphorylated by the A domain, and the cycle completes when the phosphate is released from the enzyme, stimulated by the newly bound ATP, while a cytoplasmic pathway opens to exchange the protons for two new Ca ions.
921:~P state becomes formed through a kinase reaction, where the P domain becomes phosphorylated, producing ADP. The cleavage of the β-phosphodiester bond releases the gamma-phosphate from ADP and unleashes the N domain from the P domain.
2538:
Morth, J. Preben; Pedersen, Bjørn P.; Toustrup-Jensen, Mads S.; Sørensen, Thomas L.-M.; Petersen, Janne; Andersen, Jens Peter; Vilsen, Bente; Nissen, Poul (2007-12-13). "Crystal structure of the sodium-potassium pump".
2240:
Meng, Dan; Bruschweiler-Li, Lei; Zhang, Fengli; Brüschweiler, Rafael (2015-08-18). "Modulation and
Functional Role of the Orientations of the N- and P-Domains of Cu+ -Transporting ATPase along the Ion Transport Cycle".
532:, which, in the presence of Ca, activates P2B ATPases by neutralizing the terminal constraint. The P3A plasma membrane proton pumps have a C-terminal regulatory domain, which, when unphosphorylated, inhibits pumping.
857:
section with two Ca-binding sites. The cytoplasmic section consists of three cytoplasmic domains, designated the P, N, and A domains, containing over half the mass of the protein. The transmembrane section has ten
429:
section with binding sites for the transported ligand(s). The cytoplasmic section consists of three cytoplasmic domains, designated the P, N, and A domains, containing over half the mass of the protein.
528:
that have been found to be involved in regulation. The P2B Ca ATPases have autoinbitory domains in their amino-terminal (plants) or carboxy-terminal (animals) regions, which contain binding sites for
637:
analysis grouped the proteins independent of the organism from which they are isolated and showed that the diversification of the P-type ATPase family occurred prior to the separation of
544:
to drive transport. They form a high-energy aspartyl-phosphoanhydride intermediate in the reaction cycle, and they interconvert between at least two different conformations, denoted by E
717:
binding to transmembrane metal-binding sites (TM-MBS) in Cu-ATPases is required for enzyme phosphorylation and subsequent transport. However, Cu does not access Cu-ATPases in a free (
816:(also referred to as SERCA). These pumps have two Ca ion binding sites and are often regulated by inhibitory accessory proteins having a single trans-membrane spanning segment (e.g.
770:
P2 ATPases (or Type II ATPases) are split into four groups. Topological type II ATPases (specific for Na,K, H Ca, Mg and phospholipids) predominate in eukaryotes (approx. twofold).
1123:
of the α-subunit is contained within a pocket between transmembrane helices and seems to be a novel regulatory element controlling sodium affinity, possibly influenced by the
3923:
2961:
Chan, Henry; Babayan, Vartan; Blyumin, Elya; Gandhi, Charmy; Hak, Kunal; Harake, Danielle; Kumar, Kris; Lee, Perry; Li, Tze T. (2010-01-01). "The p-type ATPase superfamily".
969:
states. Anthonisen et al. (2006) characterized the kinetics of the partial reaction steps of the transport cycle and the binding of the phosphoryl analogs BeF, AlF, MgF, and
657:
P1 ATPases (or Type I ATPases) consists of the transition/heavy metal ATPases. Topological type I (heavy metal) P-type ATPases predominate in prokaryotes (approx. tenfold).
973:
in mutants with alterations to conserved TGES loop residues. The data provide functional evidence supporting a role of Glu in activating the water molecule involved in the
946:
Modeling of the fungal H ATPase, based on the structures of the Ca pump, suggested a comparable 70º rotation of N relative to P to deliver ATP to the phosphorylation site.
1342:
of prokaryotic P-type ATPases appear to be protection from environmental stress conditions. Only about half of the P-type ATPase families are functionally characterized.
1312:
provides a representative list of members of the P-ATPase superfamily, which as of early 2016 consisting of 20 families. Members of the P-ATPase superfamily are found in
840:(also referred to as SPCA). These pumps have a single Ca ion binding site and are located in secretory vesicles (animals) or the vacuolar membrane (fungi). (TC# 3.A.3.2)
2675:
Pedersen, Bjørn P.; Buch-Pedersen, Morten J.; Preben Morth, J.; Palmgren, Michael G.; Nissen, Poul (2007-12-13). "Crystal structure of the plasma membrane proton pump".
2006:
Chan, Henry; Babayan, Vartan; Blyumin, Elya; Gandhi, Charmy; Hak, Kunal; Harake, Danielle; Kumar, Kris; Lee, Perry; Li, Tze T. (2010). "The P-Type ATPase
Superfamily".
183:
633:
ATPases in all major prokaryotic phyla for which complete genome sequence data were available and compared the results with those for eukaryotic P-type ATPases. The
127:
115:
470:
The folding pattern and the locations of the critical amino acids for phosphorylation in P-type ATPases has the haloacid dehalogenase fold characteristic of the
2915:
Barbosa, E. R; Italian
Parkinson Genetics Network; Bonifati, V (2007). "ATP13A2 missense mutations in juvenile parkinsonism and young onset Parkinson disease".
3717:
560:
notation stems from the initial studies on this family of enzymes made on the Na/K-ATPase, where the sodium form and the potassium form are referred to as E
524:
Some members of the P-type ATPase family have additional regulatory (R) domains fused to the pump. Heavy metal P1B pumps can have several N- and C-terminal
930:
again from the buried counter ions. At the same time the N domain becomes exposed to the cytosol, ready for ATP exchange at the nucleotide-binding site.
1938:
4616:
1300:
P5B ATPases (or Type VB) are found in the lysosomal membrane of animals. Mutations in these pumps are linked to a variety of neurological diseases.
3916:
4146:
2781:"Intracellular targeting signals and lipid specificity determinants of the ALA/ALIS P4-ATPase complex reside in the catalytic ALA alpha-subunit"
1733:
Toyoshima C, Nakasako M, Nomura H, Ogawa H (June 2000). "Crystal structure of the calcium pump of sarcoplasmic reticulum at 2.6 A resolution".
83:
4115:
3482:
1416:
837:
791:
3847:
1308:
In addition to the subfamilies of P-type ATPases listed above, several prokaryotic families of unknown function have been identified. The
5121:
3096:
2301:
Xu, Chen; Rice, William J.; He, Wanzhong; Stokes, David L. (2002-02-08). "A structural model for the catalytic cycle of Ca(2+)-ATPase".
3478:
3909:
669:). They are atypical P-type ATPases because, unlike other P-type ATPases, they function as part of a heterotetrameric complex (called
471:
4815:
1166:
P2D ATPases (or Type IID) include a small number of Na (and K) exporting ATPases found in fungi and mosses. (Fungal K transporters;
3710:
3071:
746:
into the cryoelectron microscopy maps for CopA. The results also similarly suggested a Cu-dependent regulatory role for the MBD.
2284:
913:
this occluded state, the Ca ions are buried in a proteinaceous environment with no access to either side of the membrane. The Ca
4706:
1883:
Olesen C, Picard M, Winther AM, et al. (December 2007). "The structural basis of calcium transport by the calcium pump".
4701:
3049:
474:, as predicted by sequence homology. The HAD superfamily functions on the common theme of an aspartate ester formation by an
4971:
203:
4723:
3867:
1363:, but rarely between most eukaryotic kingdoms, and even more rarely between eukaryotes and prokaryotes. In some bacterial
313:, absorption of nutrient in the intestine and other physiological processes. Prominent examples of P-type ATPases are the
5086:
2734:
Lenoir G, Williamson P, Holthuis JC (December 2007). "On the origin of lipid asymmetry: the flip side of ion transport".
4771:
4088:
1430:
1072:
1063:
1045:
5126:
4693:
3703:
2829:
2118:"Mechanism of Cu+-transporting ATPases: soluble Cu+ chaperones directly transfer Cu+ to transmembrane transport sites"
2779:
Lopez-Marques RL, Poulsen LR, Hanisch S, Meffert K, Buch-Pedersen MJ, Jakobsen MK, Pomorski TG, Palmgren MG (2010).
1599:
1199:
1193:
1187:
326:
3815:
3080:
1829:
Sørensen TL, Møller JV, Nissen P (June 2004). "Phosphoryl transfer and calcium ion occlusion in the calcium pump".
4956:
1671:
Pedersen PL, Carafoli E (1987). "Ion motive ATPases. I. Ubiquity, properties, and significance to cell function".
5072:
5059:
5046:
5033:
5020:
5007:
4994:
4752:
4293:
4191:
4016:
4012:
3989:
3962:
3949:
3936:
3685:
3445:
3440:
2598:
2524:
1589:
1490:
1104:
1094:
318:
4966:
1698:
SKOU JC (February 1957). "The influence of some cations on an adenosine triphosphatase from peripheral nerves".
4920:
4863:
4307:
4002:
3967:
3940:
3810:
1356:
1259:
897:
742:
2058:"Bioinformatic Characterization of P-Type ATPases Encoded Within the Fully Sequenced Genomes of 26 Eukaryotes"
286:
Most members of this transporter superfamily catalyze cation uptake and/or efflux, however one subfamily, the
267:(ATP). In addition, they all appear to interconvert between at least two different conformations, denoted by E
191:
2613:
2353:
382:
isolated in 1957. The Na/K-ATPase was only the first member of a large and still-growing protein family (see
4868:
4677:
4640:
3979:
1982:
1594:
1203:
372:
4407:
4047:
3538:
1220:
P3B ATPases (or Type IIIB) are presumed Mg-ATPases found in eubacteria and plants. Fungal H transporters (
885:
825:
694:
682:
541:
264:
592:, the pump has high affinity for the exported substrate and low affinity for the imported substrate. In E
4889:
4808:
4537:
4445:
3777:
3762:
1332:
1283:
859:
843:
Crystal structures of
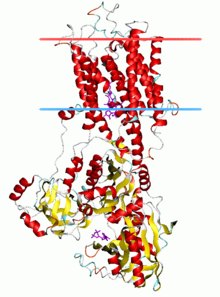
Sarcoplasimc/endoplasmic reticulum ATP driven calcium pumps can be found in RCSB.
829:
491:
443:
403:
4961:
877:
showing that Ca binding induces major changes in all three cytoplasmic domains relative to each other.
187:
3064:
2684:
2625:
2548:
2365:
2129:
1950:
1892:
1838:
1742:
649:. This underlines the significance of this protein family for cell survival under stress conditions.
96:
3573:
386:
5131:
4925:
4742:
3736:
1255:
722:
379:
139:
711:). They are key elements for metal resistance and metal homeostasis in a wide range of organisms.
4858:
4757:
4323:
3901:
3756:
3726:
2994:
2940:
2896:
2716:
2657:
2580:
2454:
2397:
2334:
2031:
1974:
1916:
1862:
1766:
1251:
1124:
1066:
that transport Ca. These pumps have a single Ca ion binding site and are regulated by binding of
952:
Crystal structures have shown that the conserved TGES loop of the Ca-ATPase is isolated in the Ca
407:
812:
that transport Ca. P2A ATPases are split into two groups. Members of the first group are called
576:
schema has been proven to work, but there exist more than two major conformational states. The E
5116:
3997:
3744:
3035:
2986:
2978:
2932:
2888:
2852:
2810:
2761:
2708:
2700:
2649:
2641:
2572:
2564:
2506:
2498:
2446:
2438:
2389:
2381:
2326:
2318:
2266:
2258:
2222:
2204:
2165:
2147:
2095:
2077:
2023:
1966:
1908:
1854:
1819:
1801:
1758:
1715:
1653:
1359:
has occurred frequently among bacteria and archaea, which have similar distributions of these
1325:
1132:
1010:
178:
3672:
3667:
3652:
3340:
2417:"The dimeric form of Ca2+-ATPase is involved in Ca2+ transport in the sarcoplasmic reticulum"
1797:
1577:
1573:
1561:
670:
4904:
4899:
4873:
4801:
4387:
4333:
4315:
4181:
4171:
4125:
3787:
3752:
3636:
3630:
3625:
3603:
3593:
3583:
3550:
3432:
3427:
3417:
3198:
3138:
3025:
2970:
2924:
2880:
2844:
2800:
2792:
2751:
2743:
2692:
2633:
2556:
2488:
2428:
2373:
2310:
2250:
2212:
2196:
2155:
2137:
2085:
2069:
2015:
1958:
1900:
1846:
1793:
1750:
1707:
1680:
1645:
1547:
1543:
1539:
1523:
1515:
1507:
1484:
1476:
1424:
1215:
306:
252:
4200:
3614:
3454:
3449:
1531:
1270:
P5 ATPases (or Type V ATPases) have unknown specificity. This large group is found only in
170:
4951:
4935:
4848:
4734:
4623:
4437:
4137:
3957:
3562:
3388:
3084:
3057:
1649:
1452:
1202:
is best characterized in plants and yeast. It maintains the level of intracellular pH and
1115:
1100:
1088:
893:
314:
256:
2688:
2629:
2552:
2369:
2133:
1954:
1896:
1842:
1746:
5100:
4989:
4930:
4057:
3486:
3470:
2928:
2805:
2780:
2217:
2184:
2160:
2117:
2090:
2057:
1372:
1057:
874:
809:
803:
376:
310:
25:
2477:"Mutational analysis of the conserved TGES loop of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase"
734:
120:
5110:
4894:
4853:
4601:
3888:
3842:
3566:
1711:
1684:
1247:
854:
817:
754:
730:
464:
426:
295:
88:
2944:
2661:
2401:
2185:"Structure of a copper pump suggests a regulatory role for its metal-binding domain"
1978:
1866:
1630:
949:
One report suggests that this sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca ATPase is homodimeric.
673:), where the actual K transport is mediated by another subcomponent of the complex.
52:
4843:
4586:
4559:
4488:
4481:
4464:
4459:
4433:
3872:
3852:
3105:
3092:
2998:
2900:
2720:
2584:
2035:
1920:
1770:
1368:
1309:
1225:
1221:
1167:
1108:
1076:
1051:
797:
708:
704:
666:
634:
629:
483:
475:
291:
166:
2614:"Structure, Mechanism, and Regulation of the Neurospora Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase"
2475:
Anthonisen, Anne Nyholm; Clausen, Johannes D.; Andersen, Jens Peter (2006-10-20).
2458:
2354:"Structure, mechanism, and regulation of the Neurospora plasma membrane H+-ATPase"
2338:
144:
132:
3030:
3013:
2848:
280:
108:
64:
5067:
5002:
4838:
4682:
3862:
3857:
3834:
3772:
2254:
889:
850:
422:
299:
5095:
2747:
2122:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
4667:
4356:
3882:
3805:
3014:"Sodium or potassium efflux ATPase: A fungal, bryophyte, and protozoal ATPase"
2200:
2073:
1271:
1120:
1067:
821:
700:
638:
529:
525:
383:
244:
2982:
2704:
2645:
2568:
2502:
2442:
2385:
2322:
2262:
2208:
2151:
2081:
5041:
5015:
4373:
3932:
3800:
3795:
2796:
2637:
2377:
2142:
1850:
1383:
Human genes encoding P-type ATPases or P-type ATPase-like proteins include:
1335:
membranes. In prokaryotes, they are localized to the cytoplasmic membranes.
1321:
901:
646:
260:
3039:
2990:
2936:
2892:
2856:
2814:
2765:
2712:
2653:
2576:
2510:
2493:
2476:
2450:
2393:
2330:
2314:
2270:
2226:
2169:
2099:
2027:
1912:
1858:
1805:
1762:
1719:
1657:
1970:
1784:
Stokes DL, Green NM (2003). "Structure and function of the calcium pump".
1282:
P5A ATPases (or Type VA) are involved in regulation of homeostasis in the
92:
3546:
3345:
3335:
3330:
3315:
3310:
3305:
3295:
3290:
3285:
3275:
3270:
3260:
3255:
3250:
3245:
3226:
3218:
3114:
2828:
Sørensen DM, Holen HW, Holemans T, Vangheluwe P, Palmgren MG (May 2014).
1609:
1503:
1352:
1313:
1243:
1237:
970:
287:
236:
232:
59:
2696:
2560:
1904:
1008:
Crystal
Structures of Calcium ATPase are available in RCSB and include:
4778:
4747:
4525:
4520:
4279:
4269:
4244:
4239:
3974:
3825:
3767:
3662:
3657:
3325:
3320:
3300:
3280:
3265:
3240:
3235:
3230:
2433:
2416:
1962:
1939:"Evolution of substrate specificities in the P-type ATPase superfamily"
1569:
1565:
1317:
1295:
718:
642:
363:
where the ligand can be either a metal ion or a phospholipid molecule.
240:
76:
71:
2974:
2756:
2019:
1823:
1328:
is usually in accordance with specificity for the transported ion(s).
1154:
1148:
1142:
1136:
1032:
1026:
1020:
1014:
5054:
4824:
4655:
4297:
4274:
4264:
4234:
4229:
4224:
4219:
4176:
4166:
4161:
4156:
4151:
4120:
4108:
4103:
4098:
4093:
4081:
4076:
4071:
4020:
3695:
3646:
3641:
3620:
3598:
3588:
3525:
3520:
3515:
3510:
3505:
3500:
3495:
3490:
3462:
3422:
3412:
3407:
3402:
3397:
3392:
3362:
3352:
3188:
3168:
3163:
3158:
3153:
3133:
3123:
3088:
1754:
1555:
1551:
1535:
1519:
1511:
1497:
1480:
1472:
1468:
1464:
1460:
1456:
1446:
1442:
1438:
1434:
1420:
1410:
1406:
1402:
1364:
1360:
785:
585:
411:
248:
198:
20:
2884:
938:-P* occluded state. Meanwhile, the N domain exchanges ADP for ATP.
283:) which, as of early 2016, includes 20 different protein families.
5028:
4711:
4650:
4633:
4628:
4476:
4454:
4420:
4415:
4400:
4378:
4366:
4361:
4351:
4346:
4341:
4066:
4042:
3609:
3533:
3474:
3208:
3203:
3193:
3183:
3178:
3173:
3148:
3143:
3128:
1604:
1527:
1398:
1392:
1388:
881:
846:
833:
813:
779:
762:
of copper-transporting P-type ATPase functionhave been described.
714:
699:
P1B ATPases (or Type IB ATPases) are involved in transport of the
688:
463:
parallel β-sheet with eight short associated a-helices, forming a
415:
399:
322:
1114:
The X-ray crystal structure at 3.5 Å resolution of the pig renal
4716:
4672:
4660:
4645:
4611:
4606:
4591:
4574:
4569:
4564:
4552:
4547:
4542:
4532:
4508:
4503:
4498:
4493:
4395:
3577:
2612:
Kühlbrandt, Werner; Zeelen, Johan; Dietrich, Jens (2002-09-06).
2352:
Kühlbrandt, Werner; Zeelen, Johan; Dietrich, Jens (2002-09-06).
2183:
Wu, Chen-Chou; Rice, William J.; Stokes, David L. (2008-06-01).
160:
103:
47:
4797:
3905:
3699:
3053:
1338:
P-type ATPases from 26 eukaryotic species were analyzed later.
4766:
4762:
836:
is a type IIA pump. The second group of P2A ATPases is called
1178:
P3 ATPases (or Type III ATPases) are split into two groups.
255:
named based upon their ability to catalyze auto- (or self-)
2116:
González-Guerrero, Manuel; Argüello, José M. (2008-04-22).
1331:
In eukaryotes, they are present in the plasma membranes or
4793:
490:
is clearly observed in the solved structure of SERCA with
1083:
P2C ATPases (sodium/potassium and proton/potassium pumps)
421:
The catalytic subunit of P-type ATPases is composed of a
418:
is representative for the superfamily of P-type ATPases.
3012:
Rodríguez-Navarro, Alonso; Benito, Begoña (2010-10-01).
2830:"Towards defining the substrate of orphan P5A-ATPases"
1130:
Crystal
Structures are available in RCSB and include:
1099:
P2C ATPases (or Type IIC) include the closely related
5084:
2415:
Ushimaru, Makoto; Fukushima, Yoshihiro (2008-09-15).
414:. It is generally acknowledged that the structure of
962:
state but becomes inserted in the catalytic site in
4980:
4944:
4913:
4882:
4831:
4732:
4691:
4431:
4305:
4292:
4257:
4209:
4190:
4136:
4056:
4035:
4028:
4011:
3988:
3948:
3881:
3833:
3824:
3786:
3743:
3377:
3361:
3217:
3113:
3104:
2963:
Journal of
Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology
2056:Thever, Mark D.; Jr, Milton H. Saier (2009-06-23).
2008:
Journal of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology
665:
P1A ATPases (or Type IA) are involved in K import (
197:
177:
159:
154:
138:
126:
114:
102:
82:
70:
58:
46:
38:
33:
3018:Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes
568:, respectively, in the "Post-Albers scheme". The E
263:residue within the pump and their energy source,
900:, and to countertransport 1-3 protons into the
540:All P-type ATPases use the energy derived from
337:The generalized reaction for P-type ATPases is
305:In humans, P-type ATPases serve as a basis for
1196:from prokaryotes, protists, plants and fungi.
231:, are a large group of evolutionarily related
4809:
3917:
3711:
3065:
8:
2871:encoding a lysosomal type 5 P-type ATPase".
584:notation highlights the selectivity of the
371:The first P-type ATPase discovered was the
4816:
4802:
4794:
4302:
4032:
4025:
3924:
3910:
3902:
3830:
3735:Mechanisms for chemical transport through
3718:
3704:
3696:
3110:
3072:
3058:
3050:
151:
19:
3461:3.A.3.1.4: H/K transporting, nongastric:
3029:
2804:
2755:
2492:
2432:
2216:
2159:
2141:
2089:
1932:
1930:
733:), to the corresponding Cu-ATPase, CopA (
298:to maintain the asymmetric nature of the
1937:Axelsen KB, Palmgren MG (January 1998).
1878:
1876:
1798:10.1146/annurev.biophys.32.110601.142433
1274:and is further divided into two groups.
888:is used to transport 2 Ca-ions from the
814:sarco/endoplasmatic reticulum Ca-ATPases
5091:
1621:
1605:Sarco/endoplasmatic reticulum Ca-ATPase
1192:P3A ATPases (or Type IIIA) contain the
865:Structures are available for both the E
824:. In the cell, they are located in the
472:haloacid dehalogenase (HAD) superfamily
450:membrane through another half-channel.
1355:and all 13 eukaryotic FUPA families).
808:P2A ATPases (or Type IIA ATPases) are
703:: Cu, Ag, Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb and Co (TC#s
507:toward the solvent near the P-domain.
311:secretion and absorption in the kidney
15:
2956:
2954:
2470:
2468:
2296:
2294:
2111:
2109:
2051:
2049:
2047:
2045:
1650:10.1146/annurev.biophys.093008.131331
7:
3848:Non-specific, adsorptive pinocytosis
2001:
1999:
1242:P4 ATPases (or Type IV ATPases) are
277:P-type ATPase (P-ATPase) Superfamily
2481:The Journal of Biological Chemistry
1310:Transporter Classification Database
1304:Further phylogenetic classification
1232:P4 ATPases (phospholipid flippases)
1075:(PMCA) of animals is a P2B ATPase (
2929:10.1212/01.wnl.0000260963.08711.08
235:and lipid pumps that are found in
14:
3106:F-, V-, and A-type ATPase (3.A.2)
5094:
329:(H-ATPase) of plants and fungi.
275:. P-type ATPases fall under the
3122:H transporting, mitochondrial:
677:P1B ATPases (heavy metal pumps)
1786:Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct
1673:Trends in Biochemical Sciences
1629:Palmgren MG, Nissen P (2011).
1062:P2B (or Type IIB ATPases) are
1:
3868:Receptor-mediated endocytosis
1496:P2C: H/K ATPase, nongastric:
1246:involved in the transport of
1210:P3B ATPases (magnesium pumps)
792:Secretory Pathway Ca²⁺ ATPase
661:P1A ATPases (potassium pumps)
502:Nucleotide binding (N) domain
259:(hence P) of a key conserved
155:Available protein structures:
3031:10.1016/j.bbamem.2010.07.009
2849:10.1016/j.bbagen.2014.05.008
2303:Journal of Molecular Biology
1712:10.1016/0006-3002(57)90343-8
1685:10.1016/0968-0004(87)90071-5
838:secretory pathway Ca-ATPases
404:sarco(endo)plasmic reticulum
4694:Protein-synthesizing GTPase
2255:10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00420
2062:Journal of Membrane Biology
1417:secretory pathway Ca-ATPase
1046:Plasma membrane Ca2+ ATPase
1040:P2B ATPases (calcium pumps)
774:P2A ATPases (calcium pumps)
526:heavy metal-binding domains
438:The transmembrane section (
327:plasma membrane proton pump
5148:
5122:Integral membrane proteins
3816:Secondary active transport
3532:3.A.3.5: Cu transporting:
3081:Membrane transport protein
2748:10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.09.008
1489:P2C: H/K ATPase, gastric:
1293:
1235:
1213:
1185:
1182:P3A ATPases (proton pumps)
1162:P2D ATPases (sodium pumps)
1092:
1086:
1055:
1049:
1043:
801:
795:
789:
783:
777:
692:
686:
680:
458:Phosphorylation (P) domain
333:General transport reaction
294:) is involved in flipping
4972:Michaelis–Menten kinetics
4753:Guanylate-binding protein
3937:acid anhydride hydrolases
3733:
3681:
3227:H transporting, lysosomal
2201:10.1016/j.str.2008.02.025
2074:10.1007/s00232-009-9176-2
1194:plasma membrane H-ATPases
1188:Plasma membrane H+-ATPase
1095:Hydrogen potassium ATPase
1073:Plasma membrane Ca-ATPase
721:) form but is bound to a
309:, relaxation of muscles,
150:
18:
4864:Diffusion-limited enzyme
4308:Heterotrimeric G protein
4003:Phosphoadenylylsulfatase
3811:Primary active transport
1600:Plasma membrane H-ATPase
1357:Horizontal gene transfer
1346:Horizontal Gene Transfer
1260:phosphatidylethanolamine
1200:Plasma membrane H-ATPase
898:sarcoplasmatic reticulum
729:Cu-chaperone, CopZ (see
725:. The delivery of Cu by
3980:Thiamine-triphosphatase
2797:10.1091/mbc.E09-08-0656
2638:10.1126/science.1072574
2421:The Biochemical Journal
2378:10.1126/science.1072574
2143:10.1073/pnas.0711446105
1851:10.1126/science.1099366
1204:transmembrane potential
1158:, among others.
1036:, among others.
743:cryoelectron microscopy
2837:Biochim. Biophys. Acta
2494:10.1074/jbc.M605194200
2315:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5330
1700:Biochim. Biophys. Acta
1353:phospholipid flippases
751:Archaeoglobus fulgidus
739:Archaeoglobus fulgidus
727:Archaeoglobus fulgidus
695:Wilson disease protein
265:adenosine triphosphate
4957:Eadie–Hofstee diagram
4890:Allosteric regulation
4735:Polymerization motors
4446:Rho family of GTPases
3763:Facilitated diffusion
1333:endoplasmic reticular
1284:endoplasmic reticulum
860:transmembrane helices
683:Zn2+-exporting ATPase
520:Regulatory (R) domain
444:transmembrane helices
387:Prosite motif PS00154
319:proton-potassium pump
315:sodium-potassium pump
251:are α-helical bundle
4967:Lineweaver–Burk plot
3737:biological membranes
1324:. Clustering on the
1107:from animal cells. (
442:) typically has ten
348:(in) + ATP → nLigand
325:(Ca-ATPase) and the
253:primary transporters
4743:dynamin superfamily
3635:Class VI, type 11:
2736:Curr Opin Chem Biol
2697:10.1038/nature06417
2689:2007Natur.450.1111P
2683:(7172): 1111–1114.
2630:2002Sci...297.1692K
2624:(5587): 1692–1696.
2561:10.1038/nature06419
2553:2007Natur.450.1043M
2547:(7172): 1043–1049.
2487:(42): 31572–31582.
2370:2002Sci...297.1692K
2364:(5587): 1692–1696.
2134:2008PNAS..105.5992G
1955:1998JMolE..46...84A
1905:10.1038/nature06418
1897:2007Natur.450.1036O
1843:2004Sci...304.1672S
1747:2000Natur.405..647T
1256:phosphatidylcholine
904:. Starting in the E
511:Actuator (A) domain
380:Jens Christian Skou
317:(Na/K-ATPase), the
5127:Transport proteins
4926:Enzyme superfamily
4859:Enzyme promiscuity
3757:mediated transport
3727:Membrane transport
3619:Class V, type 10:
3608:Class II, type 9:
2434:10.1042/BJ20071701
1963:10.1007/PL00006286
1638:Annu. Rev. Biophys
1252:phosphatidylserine
1125:membrane potential
408:fast twitch muscle
321:(H/K-ATPase), the
5082:
5081:
4791:
4790:
4787:
4786:
4288:
4287:
4253:
4252:
3998:Adenylylsulfatase
3899:
3898:
3895:
3894:
3745:Passive transport
3693:
3692:
3582:Class I, type 8:
3389:Na/K transporting
3373:
3372:
3024:(10): 1841–1853.
2975:10.1159/000319588
2249:(32): 5095–5102.
2128:(16): 5992–5997.
2020:10.1159/000319588
1891:(7172): 1036–42.
1326:phylogenetic tree
849:is composed of a
723:chaperone protein
213:
212:
209:
208:
204:structure summary
5139:
5099:
5098:
5090:
4962:Hanes–Woolf plot
4905:Enzyme activator
4900:Enzyme inhibitor
4874:Enzyme catalysis
4818:
4811:
4804:
4795:
4303:
4033:
4026:
3926:
3919:
3912:
3903:
3831:
3788:Active transport
3753:Simple diffusion
3720:
3713:
3706:
3697:
3686:ATPase disorders
3557:Other/ungrouped:
3111:
3074:
3067:
3060:
3051:
3044:
3043:
3033:
3009:
3003:
3002:
2958:
2949:
2948:
2911:
2905:
2904:
2867:
2861:
2860:
2834:
2825:
2819:
2818:
2808:
2776:
2770:
2769:
2759:
2731:
2725:
2724:
2672:
2666:
2665:
2609:
2603:
2602:
2595:
2589:
2588:
2535:
2529:
2528:
2521:
2515:
2514:
2496:
2472:
2463:
2462:
2436:
2412:
2406:
2405:
2349:
2343:
2342:
2298:
2289:
2288:
2281:
2275:
2274:
2237:
2231:
2230:
2220:
2180:
2174:
2173:
2163:
2145:
2113:
2104:
2103:
2093:
2053:
2040:
2039:
2003:
1994:
1993:
1991:
1990:
1981:. Archived from
1934:
1925:
1924:
1880:
1871:
1870:
1837:(5677): 1672–5.
1826:
1816:
1810:
1809:
1781:
1775:
1774:
1755:10.1038/35015017
1741:(6787): 647–55.
1730:
1724:
1723:
1695:
1689:
1688:
1668:
1662:
1661:
1635:
1631:"P-type ATPases"
1626:
1387:P1B: Cu ATPase:
1216:Magnesium-ATPase
1157:
1151:
1145:
1139:
1121:carboxy terminus
1035:
1029:
1023:
1017:
759:Escherichia coli
701:soft Lewis acids
482:mechanism. This
434:Membrane section
219:, also known as
152:
23:
16:
5147:
5146:
5142:
5141:
5140:
5138:
5137:
5136:
5107:
5106:
5105:
5093:
5085:
5083:
5078:
4990:Oxidoreductases
4976:
4952:Enzyme kinetics
4940:
4936:List of enzymes
4909:
4878:
4849:Catalytic triad
4827:
4822:
4792:
4783:
4728:
4687:
4438:Ras superfamily
4427:
4411:
4391:
4337:
4327:
4319:
4284:
4249:
4205:
4186:
4132:
4089:Plasma membrane
4052:
4007:
3984:
3958:Pyrophosphatase
3944:
3930:
3900:
3891:
3877:
3820:
3782:
3739:
3729:
3724:
3694:
3689:
3677:
3574:Mg transporting
3487:Ca transporting
3369:
3368:found in Archea
3357:
3213:
3100:
3078:
3048:
3047:
3011:
3010:
3006:
2960:
2959:
2952:
2923:(19): 1557–62.
2913:
2912:
2908:
2879:(10): 1184–91.
2873:Nature Genetics
2869:
2868:
2864:
2832:
2827:
2826:
2822:
2778:
2777:
2773:
2733:
2732:
2728:
2674:
2673:
2669:
2611:
2610:
2606:
2597:
2596:
2592:
2537:
2536:
2532:
2523:
2522:
2518:
2474:
2473:
2466:
2414:
2413:
2409:
2351:
2350:
2346:
2300:
2299:
2292:
2283:
2282:
2278:
2239:
2238:
2234:
2182:
2181:
2177:
2115:
2114:
2107:
2055:
2054:
2043:
2005:
2004:
1997:
1988:
1986:
1936:
1935:
1928:
1882:
1881:
1874:
1828:
1818:
1817:
1813:
1783:
1782:
1778:
1732:
1731:
1727:
1697:
1696:
1692:
1670:
1669:
1665:
1633:
1628:
1627:
1623:
1618:
1586:
1399:SERCA Ca ATPase
1381:
1348:
1306:
1298:
1292:
1280:
1268:
1240:
1234:
1218:
1212:
1190:
1184:
1176:
1164:
1153:
1147:
1141:
1131:
1119:reticulum. The
1097:
1091:
1085:
1060:
1054:
1048:
1042:
1031:
1025:
1019:
1009:
1004:
998:
994:
986:
979:
968:
961:
955:
937:
928:
920:
916:
911:
907:
880:In the case of
872:
868:
806:
800:
794:
788:
782:
776:
768:
697:
691:
685:
679:
663:
655:
626:
615:
611:
607:
603:
599:
595:
591:
583:
579:
575:
571:
567:
563:
559:
555:
551:
547:
538:
522:
513:
504:
497:
487:
479:
460:
436:
395:
369:
359:
356:(out) + ADP + P
355:
351:
347:
344:(out) + mLigand
343:
335:
274:
270:
257:phosphorylation
228:
224:
116:OPM superfamily
29:
12:
11:
5:
5145:
5143:
5135:
5134:
5129:
5124:
5119:
5109:
5108:
5104:
5103:
5080:
5079:
5077:
5076:
5063:
5050:
5037:
5024:
5011:
4998:
4984:
4982:
4978:
4977:
4975:
4974:
4969:
4964:
4959:
4954:
4948:
4946:
4942:
4941:
4939:
4938:
4933:
4928:
4923:
4917:
4915:
4914:Classification
4911:
4910:
4908:
4907:
4902:
4897:
4892:
4886:
4884:
4880:
4879:
4877:
4876:
4871:
4866:
4861:
4856:
4851:
4846:
4841:
4835:
4833:
4829:
4828:
4823:
4821:
4820:
4813:
4806:
4798:
4789:
4788:
4785:
4784:
4782:
4781:
4776:
4775:
4774:
4769:
4760:
4755:
4750:
4739:
4737:
4730:
4729:
4727:
4726:
4721:
4720:
4719:
4714:
4709:
4698:
4696:
4689:
4688:
4686:
4685:
4680:
4675:
4670:
4665:
4664:
4663:
4658:
4653:
4648:
4638:
4637:
4636:
4631:
4621:
4620:
4619:
4614:
4609:
4597:
4596:
4595:
4594:
4589:
4579:
4578:
4577:
4572:
4567:
4557:
4556:
4555:
4550:
4545:
4535:
4530:
4529:
4528:
4523:
4513:
4512:
4511:
4506:
4501:
4496:
4486:
4485:
4484:
4479:
4469:
4468:
4467:
4462:
4457:
4442:
4440:
4429:
4428:
4426:
4425:
4424:
4423:
4418:
4409:
4405:
4404:
4403:
4398:
4389:
4385:
4384:
4383:
4382:
4381:
4371:
4370:
4369:
4364:
4354:
4349:
4344:
4335:
4331:
4330:
4329:
4325:
4317:
4312:
4310:
4300:
4290:
4289:
4286:
4285:
4283:
4282:
4277:
4272:
4267:
4261:
4259:
4255:
4254:
4251:
4250:
4248:
4247:
4242:
4237:
4232:
4227:
4222:
4216:
4214:
4207:
4206:
4204:
4203:
4197:
4195:
4188:
4187:
4185:
4184:
4179:
4174:
4169:
4164:
4159:
4154:
4149:
4143:
4141:
4134:
4133:
4131:
4130:
4129:
4128:
4123:
4113:
4112:
4111:
4106:
4101:
4096:
4086:
4085:
4084:
4079:
4074:
4063:
4061:
4054:
4053:
4051:
4050:
4045:
4039:
4037:
4036:Cu++ (3.6.3.4)
4030:
4023:
4009:
4008:
4006:
4005:
4000:
3994:
3992:
3986:
3985:
3983:
3982:
3977:
3972:
3971:
3970:
3965:
3954:
3952:
3946:
3945:
3931:
3929:
3928:
3921:
3914:
3906:
3897:
3896:
3893:
3892:
3887:
3885:
3879:
3878:
3876:
3875:
3870:
3865:
3860:
3855:
3850:
3845:
3839:
3837:
3828:
3822:
3821:
3819:
3818:
3813:
3808:
3803:
3798:
3792:
3790:
3784:
3783:
3781:
3780:
3775:
3770:
3765:
3760:
3749:
3747:
3741:
3740:
3734:
3731:
3730:
3725:
3723:
3722:
3715:
3708:
3700:
3691:
3690:
3682:
3679:
3678:
3676:
3675:
3670:
3665:
3660:
3655:
3649:
3644:
3639:
3633:
3628:
3623:
3617:
3612:
3606:
3601:
3596:
3591:
3586:
3580:
3570:
3569:
3559:
3558:
3554:
3553:
3542:
3541:
3536:
3529:
3528:
3523:
3518:
3513:
3508:
3503:
3498:
3493:
3466:
3465:
3458:
3457:
3452:
3446:H/K exchanging
3443:
3436:
3435:
3430:
3425:
3420:
3415:
3410:
3405:
3400:
3395:
3384:
3382:
3375:
3374:
3371:
3370:
3367:
3365:
3359:
3358:
3356:
3355:
3349:
3348:
3343:
3338:
3333:
3328:
3323:
3318:
3313:
3308:
3303:
3298:
3293:
3288:
3283:
3278:
3273:
3268:
3263:
3258:
3253:
3248:
3243:
3238:
3233:
3223:
3221:
3215:
3214:
3212:
3211:
3206:
3201:
3196:
3191:
3186:
3181:
3176:
3171:
3166:
3161:
3156:
3151:
3146:
3141:
3136:
3131:
3126:
3119:
3117:
3108:
3102:
3101:
3079:
3077:
3076:
3069:
3062:
3054:
3046:
3045:
3004:
2969:(1–2): 5–104.
2950:
2906:
2885:10.1038/ng1884
2862:
2820:
2791:(5): 791–801.
2771:
2726:
2667:
2604:
2590:
2530:
2516:
2464:
2427:(3): 357–361.
2407:
2344:
2309:(1): 201–211.
2290:
2276:
2232:
2195:(6): 976–985.
2175:
2105:
2068:(3): 115–130.
2041:
2014:(1–2): 5–104.
1995:
1926:
1872:
1811:
1776:
1725:
1706:(2): 394–401.
1690:
1663:
1620:
1619:
1617:
1614:
1613:
1612:
1607:
1602:
1597:
1592:
1585:
1582:
1581:
1580:
1558:
1500:
1494:
1487:
1449:
1427:
1413:
1395:
1380:
1377:
1373:Fusobacteriota
1347:
1344:
1305:
1302:
1294:Main article:
1291:
1288:
1279:
1276:
1267:
1264:
1236:Main article:
1233:
1230:
1214:Main article:
1211:
1208:
1186:Main article:
1183:
1180:
1175:
1172:
1163:
1160:
1093:Main article:
1087:Main article:
1084:
1081:
1058:Calcium ATPase
1056:Main article:
1050:Main article:
1044:Main article:
1041:
1038:
1002:
996:
992:
984:
977:
966:
959:
953:
935:
926:
918:
914:
909:
905:
884:, energy from
873:states of the
870:
866:
853:section and a
804:Calcium ATPase
802:Main article:
796:Main article:
790:Main article:
784:Main article:
778:Main article:
775:
772:
767:
764:
735:TC# 3.A.3.5.30
693:Main article:
687:Main article:
681:Main article:
678:
675:
662:
659:
654:
651:
625:
624:Classification
622:
613:
609:
605:
601:
597:
593:
589:
581:
577:
573:
569:
565:
561:
557:
553:
549:
545:
537:
534:
521:
518:
512:
509:
503:
500:
495:
485:
477:
459:
456:
435:
432:
425:section and a
394:
391:
377:Nobel laureate
368:
365:
357:
353:
352:(in) + mLigand
349:
345:
341:
334:
331:
307:nerve impulses
272:
268:
226:
222:
217:P-type ATPases
211:
210:
207:
206:
201:
195:
194:
181:
175:
174:
164:
157:
156:
148:
147:
142:
136:
135:
130:
124:
123:
118:
112:
111:
106:
100:
99:
86:
80:
79:
74:
68:
67:
62:
56:
55:
50:
44:
43:
40:
36:
35:
31:
30:
26:Calcium ATPase
24:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
5144:
5133:
5130:
5128:
5125:
5123:
5120:
5118:
5115:
5114:
5112:
5102:
5097:
5092:
5088:
5074:
5070:
5069:
5064:
5061:
5057:
5056:
5051:
5048:
5044:
5043:
5038:
5035:
5031:
5030:
5025:
5022:
5018:
5017:
5012:
5009:
5005:
5004:
4999:
4996:
4992:
4991:
4986:
4985:
4983:
4979:
4973:
4970:
4968:
4965:
4963:
4960:
4958:
4955:
4953:
4950:
4949:
4947:
4943:
4937:
4934:
4932:
4931:Enzyme family
4929:
4927:
4924:
4922:
4919:
4918:
4916:
4912:
4906:
4903:
4901:
4898:
4896:
4895:Cooperativity
4893:
4891:
4888:
4887:
4885:
4881:
4875:
4872:
4870:
4867:
4865:
4862:
4860:
4857:
4855:
4854:Oxyanion hole
4852:
4850:
4847:
4845:
4842:
4840:
4837:
4836:
4834:
4830:
4826:
4819:
4814:
4812:
4807:
4805:
4800:
4799:
4796:
4780:
4777:
4773:
4770:
4768:
4764:
4761:
4759:
4756:
4754:
4751:
4749:
4746:
4745:
4744:
4741:
4740:
4738:
4736:
4731:
4725:
4722:
4718:
4715:
4713:
4710:
4708:
4705:
4704:
4703:
4700:
4699:
4697:
4695:
4690:
4684:
4681:
4679:
4676:
4674:
4671:
4669:
4666:
4662:
4659:
4657:
4654:
4652:
4649:
4647:
4644:
4643:
4642:
4639:
4635:
4632:
4630:
4627:
4626:
4625:
4622:
4618:
4615:
4613:
4610:
4608:
4605:
4604:
4603:
4599:
4598:
4593:
4590:
4588:
4585:
4584:
4583:
4580:
4576:
4573:
4571:
4568:
4566:
4563:
4562:
4561:
4558:
4554:
4551:
4549:
4546:
4544:
4541:
4540:
4539:
4536:
4534:
4531:
4527:
4524:
4522:
4519:
4518:
4517:
4514:
4510:
4507:
4505:
4502:
4500:
4497:
4495:
4492:
4491:
4490:
4487:
4483:
4480:
4478:
4475:
4474:
4473:
4470:
4466:
4463:
4461:
4458:
4456:
4453:
4452:
4451:
4447:
4444:
4443:
4441:
4439:
4435:
4430:
4422:
4419:
4417:
4414:
4413:
4412:
4406:
4402:
4399:
4397:
4394:
4393:
4392:
4386:
4380:
4377:
4376:
4375:
4372:
4368:
4365:
4363:
4360:
4359:
4358:
4355:
4353:
4350:
4348:
4345:
4343:
4340:
4339:
4338:
4332:
4328:
4322:
4321:
4320:
4314:
4313:
4311:
4309:
4304:
4301:
4299:
4295:
4291:
4281:
4278:
4276:
4273:
4271:
4268:
4266:
4263:
4262:
4260:
4256:
4246:
4243:
4241:
4238:
4236:
4233:
4231:
4228:
4226:
4223:
4221:
4218:
4217:
4215:
4213:
4212:P-type ATPase
4208:
4202:
4199:
4198:
4196:
4193:
4189:
4183:
4180:
4178:
4175:
4173:
4170:
4168:
4165:
4163:
4160:
4158:
4155:
4153:
4150:
4148:
4145:
4144:
4142:
4139:
4135:
4127:
4124:
4122:
4119:
4118:
4117:
4114:
4110:
4107:
4105:
4102:
4100:
4097:
4095:
4092:
4091:
4090:
4087:
4083:
4080:
4078:
4075:
4073:
4070:
4069:
4068:
4065:
4064:
4062:
4059:
4055:
4049:
4046:
4044:
4041:
4040:
4038:
4034:
4031:
4027:
4024:
4022:
4018:
4014:
4010:
4004:
4001:
3999:
3996:
3995:
3993:
3991:
3987:
3981:
3978:
3976:
3973:
3969:
3966:
3964:
3961:
3960:
3959:
3956:
3955:
3953:
3951:
3947:
3942:
3938:
3934:
3927:
3922:
3920:
3915:
3913:
3908:
3907:
3904:
3890:
3889:Degranulation
3886:
3884:
3880:
3874:
3871:
3869:
3866:
3864:
3861:
3859:
3856:
3854:
3851:
3849:
3846:
3844:
3843:Efferocytosis
3841:
3840:
3838:
3836:
3832:
3829:
3827:
3823:
3817:
3814:
3812:
3809:
3807:
3804:
3802:
3799:
3797:
3794:
3793:
3791:
3789:
3785:
3779:
3776:
3774:
3771:
3769:
3766:
3764:
3761:
3758:
3754:
3751:
3750:
3748:
3746:
3742:
3738:
3732:
3728:
3721:
3716:
3714:
3709:
3707:
3702:
3701:
3698:
3688:
3687:
3680:
3674:
3671:
3669:
3666:
3664:
3661:
3659:
3656:
3654:
3650:
3648:
3645:
3643:
3640:
3638:
3634:
3632:
3629:
3627:
3624:
3622:
3618:
3616:
3613:
3611:
3607:
3605:
3602:
3600:
3597:
3595:
3592:
3590:
3587:
3585:
3581:
3579:
3575:
3572:
3571:
3568:
3564:
3561:
3560:
3556:
3555:
3552:
3548:
3544:
3543:
3540:
3537:
3535:
3531:
3530:
3527:
3524:
3522:
3519:
3517:
3514:
3512:
3509:
3507:
3504:
3502:
3499:
3497:
3494:
3492:
3488:
3484:
3480:
3476:
3472:
3468:
3467:
3464:
3460:
3459:
3456:
3453:
3451:
3447:
3444:
3442:
3438:
3437:
3434:
3431:
3429:
3426:
3424:
3421:
3419:
3416:
3414:
3411:
3409:
3406:
3404:
3401:
3399:
3396:
3394:
3390:
3386:
3385:
3383:
3380:
3379:P-type ATPase
3376:
3366:
3364:
3360:
3354:
3351:
3350:
3347:
3344:
3342:
3339:
3337:
3334:
3332:
3329:
3327:
3324:
3322:
3319:
3317:
3314:
3312:
3309:
3307:
3304:
3302:
3299:
3297:
3294:
3292:
3289:
3287:
3284:
3282:
3279:
3277:
3274:
3272:
3269:
3267:
3264:
3262:
3259:
3257:
3254:
3252:
3249:
3247:
3244:
3242:
3239:
3237:
3234:
3232:
3228:
3225:
3224:
3222:
3220:
3216:
3210:
3207:
3205:
3202:
3200:
3197:
3195:
3192:
3190:
3187:
3185:
3182:
3180:
3177:
3175:
3172:
3170:
3167:
3165:
3162:
3160:
3157:
3155:
3152:
3150:
3147:
3145:
3142:
3140:
3137:
3135:
3132:
3130:
3127:
3125:
3121:
3120:
3118:
3116:
3112:
3109:
3107:
3103:
3098:
3094:
3090:
3086:
3082:
3075:
3070:
3068:
3063:
3061:
3056:
3055:
3052:
3041:
3037:
3032:
3027:
3023:
3019:
3015:
3008:
3005:
3000:
2996:
2992:
2988:
2984:
2980:
2976:
2972:
2968:
2964:
2957:
2955:
2951:
2946:
2942:
2938:
2934:
2930:
2926:
2922:
2918:
2910:
2907:
2902:
2898:
2894:
2890:
2886:
2882:
2878:
2874:
2866:
2863:
2858:
2854:
2850:
2846:
2843:(3): 524–35.
2842:
2838:
2831:
2824:
2821:
2816:
2812:
2807:
2802:
2798:
2794:
2790:
2786:
2785:Mol Biol Cell
2782:
2775:
2772:
2767:
2763:
2758:
2753:
2749:
2745:
2742:(6): 654–61.
2741:
2737:
2730:
2727:
2722:
2718:
2714:
2710:
2706:
2702:
2698:
2694:
2690:
2686:
2682:
2678:
2671:
2668:
2663:
2659:
2655:
2651:
2647:
2643:
2639:
2635:
2631:
2627:
2623:
2619:
2615:
2608:
2605:
2600:
2594:
2591:
2586:
2582:
2578:
2574:
2570:
2566:
2562:
2558:
2554:
2550:
2546:
2542:
2534:
2531:
2526:
2520:
2517:
2512:
2508:
2504:
2500:
2495:
2490:
2486:
2482:
2478:
2471:
2469:
2465:
2460:
2456:
2452:
2448:
2444:
2440:
2435:
2430:
2426:
2422:
2418:
2411:
2408:
2403:
2399:
2395:
2391:
2387:
2383:
2379:
2375:
2371:
2367:
2363:
2359:
2355:
2348:
2345:
2340:
2336:
2332:
2328:
2324:
2320:
2316:
2312:
2308:
2304:
2297:
2295:
2291:
2286:
2280:
2277:
2272:
2268:
2264:
2260:
2256:
2252:
2248:
2244:
2236:
2233:
2228:
2224:
2219:
2214:
2210:
2206:
2202:
2198:
2194:
2190:
2186:
2179:
2176:
2171:
2167:
2162:
2157:
2153:
2149:
2144:
2139:
2135:
2131:
2127:
2123:
2119:
2112:
2110:
2106:
2101:
2097:
2092:
2087:
2083:
2079:
2075:
2071:
2067:
2063:
2059:
2052:
2050:
2048:
2046:
2042:
2037:
2033:
2029:
2025:
2021:
2017:
2013:
2009:
2002:
2000:
1996:
1985:on 2000-09-15
1984:
1980:
1976:
1972:
1968:
1964:
1960:
1956:
1952:
1949:(1): 84–101.
1948:
1944:
1940:
1933:
1931:
1927:
1922:
1918:
1914:
1910:
1906:
1902:
1898:
1894:
1890:
1886:
1879:
1877:
1873:
1868:
1864:
1860:
1856:
1852:
1848:
1844:
1840:
1836:
1832:
1825:
1821:
1815:
1812:
1807:
1803:
1799:
1795:
1791:
1787:
1780:
1777:
1772:
1768:
1764:
1760:
1756:
1752:
1748:
1744:
1740:
1736:
1729:
1726:
1721:
1717:
1713:
1709:
1705:
1701:
1694:
1691:
1686:
1682:
1678:
1674:
1667:
1664:
1659:
1655:
1651:
1647:
1643:
1639:
1632:
1625:
1622:
1615:
1611:
1608:
1606:
1603:
1601:
1598:
1596:
1593:
1591:
1588:
1587:
1583:
1579:
1575:
1571:
1567:
1563:
1559:
1557:
1553:
1549:
1545:
1541:
1537:
1533:
1529:
1525:
1521:
1517:
1513:
1509:
1505:
1501:
1499:
1495:
1492:
1488:
1486:
1482:
1478:
1474:
1470:
1466:
1462:
1458:
1454:
1450:
1448:
1444:
1440:
1436:
1432:
1428:
1426:
1422:
1418:
1414:
1412:
1408:
1404:
1400:
1396:
1394:
1390:
1386:
1385:
1384:
1378:
1376:
1374:
1370:
1366:
1362:
1358:
1354:
1345:
1343:
1339:
1336:
1334:
1329:
1327:
1323:
1319:
1315:
1311:
1303:
1301:
1297:
1289:
1287:
1285:
1277:
1275:
1273:
1265:
1263:
1261:
1257:
1253:
1249:
1248:phospholipids
1245:
1239:
1231:
1229:
1227:
1223:
1217:
1209:
1207:
1205:
1201:
1197:
1195:
1189:
1181:
1179:
1173:
1171:
1169:
1161:
1159:
1156:
1150:
1144:
1138:
1134:
1128:
1126:
1122:
1117:
1112:
1110:
1106:
1102:
1096:
1090:
1089:Na+/K+-ATPase
1082:
1080:
1078:
1074:
1069:
1065:
1059:
1053:
1047:
1039:
1037:
1034:
1028:
1022:
1016:
1012:
1006:
1001:
991:
983:
976:
972:
965:
958:
950:
947:
943:
939:
931:
922:
903:
899:
895:
891:
887:
883:
878:
876:
863:
861:
856:
855:transmembrane
852:
848:
844:
841:
839:
835:
831:
830:endoplasmatic
827:
823:
819:
818:phospholamban
815:
811:
805:
799:
793:
787:
781:
773:
771:
765:
763:
760:
756:
755:TC# 3.A.3.5.7
752:
747:
744:
740:
736:
732:
731:TC# 3.A.3.5.7
728:
724:
720:
716:
712:
710:
706:
702:
696:
690:
684:
676:
674:
672:
668:
660:
658:
652:
650:
648:
644:
640:
636:
631:
623:
621:
617:
587:
543:
535:
533:
531:
527:
519:
517:
510:
508:
501:
499:
493:
489:
481:
473:
468:
466:
465:Rossmann fold
457:
455:
451:
447:
445:
441:
433:
431:
428:
427:transmembrane
424:
419:
417:
413:
409:
406:Ca-ATPase of
405:
401:
392:
390:
388:
385:
381:
378:
374:
366:
364:
361:
338:
332:
330:
328:
324:
320:
316:
312:
308:
303:
301:
297:
296:phospholipids
293:
289:
284:
282:
278:
266:
262:
258:
254:
250:
246:
242:
238:
234:
230:
218:
205:
202:
200:
196:
193:
189:
185:
182:
180:
176:
172:
168:
165:
162:
158:
153:
149:
146:
143:
141:
137:
134:
131:
129:
125:
122:
119:
117:
113:
110:
107:
105:
101:
98:
94:
90:
87:
85:
81:
78:
75:
73:
69:
66:
63:
61:
57:
54:
51:
49:
45:
41:
37:
32:
28:, E2-Pi state
27:
22:
17:
5068:Translocases
5065:
5052:
5039:
5026:
5013:
5003:Transferases
5000:
4987:
4844:Binding site
4581:
4515:
4471:
4449:
4434:Small GTPase
4211:
4048:Wilson/ATP7B
4043:Menkes/ATP7A
3873:Transcytosis
3853:Phagocytosis
3683:
3378:
3093:ATP synthase
3021:
3017:
3007:
2966:
2962:
2920:
2916:
2909:
2876:
2872:
2865:
2840:
2836:
2823:
2788:
2784:
2774:
2739:
2735:
2729:
2680:
2676:
2670:
2621:
2617:
2607:
2593:
2544:
2540:
2533:
2519:
2484:
2480:
2424:
2420:
2410:
2361:
2357:
2347:
2306:
2302:
2279:
2246:
2243:Biochemistry
2242:
2235:
2192:
2188:
2178:
2125:
2121:
2065:
2061:
2011:
2007:
1987:. Retrieved
1983:the original
1946:
1943:J. Mol. Evol
1942:
1888:
1884:
1834:
1830:
1814:
1789:
1785:
1779:
1738:
1734:
1728:
1703:
1699:
1693:
1676:
1672:
1666:
1641:
1637:
1624:
1595:Na/ K-ATPase
1382:
1369:Bacteroidota
1349:
1340:
1337:
1330:
1307:
1299:
1281:
1269:
1241:
1219:
1198:
1191:
1177:
1165:
1129:
1113:
1098:
1061:
1052:Calcium pump
1007:
1005:transition.
999:
989:
981:
974:
963:
956:
951:
948:
944:
940:
932:
923:
892:side to the
879:
864:
845:
842:
826:sarcoplasmic
807:
798:Calcium pump
769:
758:
750:
748:
738:
726:
713:
698:
664:
656:
635:phylogenetic
630:phylogenetic
627:
618:
539:
523:
514:
505:
469:
461:
452:
448:
439:
437:
420:
396:
370:
362:
339:
336:
323:calcium pump
304:
285:
276:
220:
216:
214:
42:E1-E2_ATPase
4839:Active site
4758:Mitofusin-1
4733:3.6.5.5-6:
4702:Prokaryotic
3863:Potocytosis
3858:Pinocytosis
3835:Endocytosis
3545:3.A.3.8.8:
3439:3.A.3.1.2:
3387:3.A.3.1.1:
1590:H/ K-ATPase
1453:Na/K ATPase
1379:Human genes
1290:P5B ATPases
1278:P5A ATPases
1226:TC# 3.A.3.4
1222:TC# 3.A.3.3
1168:TC# 3.A.3.9
1116:Na/K-ATPase
1109:TC# 3.A.3.1
1105:H/K ATPases
1077:TC# 3.A.3.2
890:cytoplasmic
851:cytoplasmic
832:reticulum.
667:TC# 3.A.3.7
423:cytoplasmic
410:from adult
373:Na/K-ATPase
300:biomembrane
292:TC# 3.A.3.8
128:OPM protein
34:Identifiers
5132:Physiology
5111:Categories
5042:Isomerases
5016:Hydrolases
4883:Regulation
4724:Eukaryotic
4357:Transducin
4194:(3.6.3.10)
3933:Hydrolases
3883:Exocytosis
3806:Antiporter
3219:H (V-type)
3115:H (F-type)
3097:TC 3A2-3A3
2757:1874/26974
2599:"Rcsb Pdb"
2525:"Rcsb Pdb"
2285:"Rcsb Pdb"
1989:2009-06-10
1792:: 445–68.
1679:: 146–50.
1644:: 243–66.
1616:References
1322:eukaryotes
1272:eukaryotes
1266:P5 ATPases
1250:, such as
1224:) and Mg (
1174:P3 ATPases
1068:calmodulin
1064:Ca ATPases
822:sarcolipin
810:Ca ATPases
766:P2 ATPases
653:P1 ATPases
639:eubacteria
608:-P*, and E
530:calmodulin
488:2 reaction
480:2 reaction
384:Swiss-Prot
245:eukaryotes
167:structures
140:Membranome
4921:EC number
4692:3.6.5.3:
4432:3.6.5.2:
4374:Gustducin
4306:3.6.5.1:
4140:(3.6.3.9)
4060:(3.6.3.8)
3963:Inorganic
3801:Symporter
3796:Uniporter
3684:see also
3651:type 13:
3469:3.A.3.2:
3085:ion pumps
2983:1660-2412
2917:Neurology
2705:0028-0836
2646:0036-8075
2569:1476-4687
2503:0021-9258
2443:1470-8728
2386:1095-9203
2323:0022-2836
2263:1520-4995
2209:0969-2126
2189:Structure
2152:1091-6490
2082:0022-2631
1827:;
1431:Ca ATPase
1244:flippases
1152:,
1146:,
1140:,
1030:,
1024:,
1018:,
902:cytoplasm
875:Ca ATPase
647:eucaryota
536:Mechanism
393:Structure
367:Discovery
288:flippases
281:TC# 3.A.3
261:aspartate
247:. P-type
77:PDOC00139
65:IPR008250
5117:EC 3.6.3
4945:Kinetics
4869:Cofactor
4832:Activity
3968:Thiamine
3778:Carriers
3773:Channels
3755:(or non-
3547:flippase
3363:A-ATPase
3346:ATP6V0E1
3336:ATP6V0D2
3331:ATP6V0D1
3316:ATP6V0A4
3311:ATP6V0A2
3306:ATP6V0A1
3296:ATP6V1G3
3291:ATP6V1G2
3286:ATP6V1G1
3276:ATP6V1E2
3271:ATP6V1E1
3261:ATP6V1C2
3256:ATP6V1C1
3251:ATP6V1B2
3246:ATP6V1B1
3040:20650263
2991:20962537
2945:24070567
2937:17485642
2893:16964263
2857:24836520
2815:20053675
2766:17981493
2713:18075595
2662:16320388
2654:12169656
2577:18075585
2511:16893884
2451:18471093
2402:16320388
2394:12169656
2331:11829513
2271:26196187
2227:18547529
2170:18417453
2100:19548020
2028:20962537
1979:10238525
1913:18075584
1867:30576015
1859:15192230
1806:12598367
1763:10864315
1720:13412736
1658:21351879
1610:V-ATPase
1584:See also
1504:Flippase
1314:bacteria
1238:Flippase
971:vanadate
719:hydrated
494:plus AlF
440:M domain
375:, which
237:bacteria
184:RCSB PDB
60:InterPro
5101:Biology
5055:Ligases
4825:Enzymes
4779:Tubulin
4748:Dynamin
4600:other:
4280:Katanin
4270:Kinesin
4245:ATP13A3
4240:ATP13A2
3975:Apyrase
3826:Cytosis
3768:Osmosis
3673:ATP13A5
3668:ATP13A4
3663:ATP13A3
3658:ATP13A2
3653:ATP13A1
3381:(3.A.3)
3341:ATP6V0E
3326:ATP6V0C
3321:ATP6V0B
3301:ATP6V1H
3281:ATP6V1F
3266:ATP6V1D
3241:ATP6V1A
3236:ATP6AP2
3231:ATP6AP1
3089:ATPases
2999:7316282
2901:6502952
2806:2828965
2721:4413142
2685:Bibcode
2626:Bibcode
2618:Science
2585:4344526
2549:Bibcode
2366:Bibcode
2358:Science
2218:2705936
2161:2329688
2130:Bibcode
2091:2709905
2036:7316282
1971:9419228
1951:Bibcode
1921:4323780
1893:Bibcode
1839:Bibcode
1831:Science
1771:4316039
1743:Bibcode
1578:ATP13A5
1574:ATP13A4
1570:ATP13A3
1566:ATP13A2
1562:ATP13A1
1361:enzymes
1318:archaea
1296:ATP13A2
896:of the
882:SERCA1a
847:SERCA1a
834:SERCA1a
749:In the
709:3.A.3.6
705:3.A.3.5
671:KdpFABC
643:archaea
552:. The E
416:SERCA1a
400:SERCA1a
340:nLigand
249:ATPases
241:archaea
229:ATPases
72:PROSITE
53:PF00122
5087:Portal
5029:Lyases
4656:ARL13B
4516:RhoBTB
4410:α12/13
4298:GTPase
4275:Myosin
4265:Dynein
4235:ATP12A
4230:ATP11B
4225:ATP10A
4220:ATP8B1
4210:Other
4182:ATP1B4
4177:ATP1B3
4172:ATP1B2
4167:ATP1B1
4162:ATP1A4
4157:ATP1A3
4152:ATP1A2
4147:ATP1A1
4138:Na+/K+
4126:ATP2C2
4121:ATP2C1
4109:ATP2B4
4104:ATP2B3
4099:ATP2B2
4094:ATP2B1
4082:ATP2A3
4077:ATP2A2
4072:ATP2A1
4021:ATPase
3647:ATP11C
3642:ATP11B
3637:ATP11A
3631:ATP10D
3626:ATP10B
3621:ATP10A
3604:ATP8B4
3599:ATP8B3
3594:ATP8B2
3589:ATP8B1
3584:ATP8A1
3551:ATP8A2
3526:ATP2C1
3521:ATP2B4
3516:ATP2B3
3511:ATP2B2
3506:ATP2B1
3501:ATP2A3
3496:ATP2A2
3491:ATP2A1
3463:ATP12A
3433:ATP1G1
3428:ATP1B4
3423:ATP1B3
3418:ATP1B2
3413:ATP1B1
3408:ATP1A4
3403:ATP1A3
3398:ATP1A2
3393:ATP1A1
3353:TCIRG1
3199:ATP5L2
3189:ATP5J2
3169:ATP5G3
3164:ATP5G2
3159:ATP5G1
3154:ATP5F1
3139:ATP5C2
3134:ATP5C1
3124:ATP5A1
3038:
2997:
2989:
2981:
2943:
2935:
2899:
2891:
2855:
2813:
2803:
2764:
2719:
2711:
2703:
2677:Nature
2660:
2652:
2644:
2583:
2575:
2567:
2541:Nature
2509:
2501:
2459:698714
2457:
2449:
2441:
2400:
2392:
2384:
2339:596014
2337:
2329:
2321:
2269:
2261:
2225:
2215:
2207:
2168:
2158:
2150:
2098:
2088:
2080:
2034:
2026:
1977:
1969:
1919:
1911:
1885:Nature
1865:
1857:
1804:
1769:
1761:
1735:Nature
1718:
1656:
1556:ATP11C
1552:ATP11B
1548:ATP11A
1544:ATP10D
1540:ATP10B
1536:ATP10A
1524:ATP8B4
1520:ATP8B3
1516:ATP8B2
1512:ATP8B1
1508:ATP8A1
1498:ATP12A
1485:ATP1B4
1481:ATP1B3
1477:ATP1B2
1473:ATP1B1
1469:ATP1A4
1465:ATP1A3
1461:ATP1A2
1457:ATP1A1
1447:ATP2B4
1443:ATP2B3
1439:ATP2B2
1435:ATP2B1
1425:ATP2C2
1421:ATP2C1
1411:ATP2A3
1407:ATP2A2
1403:ATP2A1
1367:(e.g.
786:ATP2A1
753:CopA (
645:, and
588:. In E
586:enzyme
412:rabbit
243:, and
199:PDBsum
173:
163:
97:SUPFAM
39:Symbol
4981:Types
4712:EF-Tu
4651:SAR1B
4634:RAB27
4629:RAB23
4582:RhoDF
4472:RhoUV
4455:CDC42
4450:Cdc42
4436:>
4421:GNA13
4416:GNA12
4401:GNA11
4390:αq/11
4379:GNAT3
4367:GNAT2
4362:GNAT1
4352:GNAI3
4347:GNAI2
4342:GNAI1
4294:3.6.5
4258:3.6.4
4201:ATP4A
4192:H+/K+
4067:SERCA
4029:3.6.3
4013:3.6.3
3990:3.6.2
3950:3.6.1
3615:ATP9B
3610:ATP9A
3539:ATP7B
3534:ATP7A
3475:SERCA
3455:ATP4B
3450:ATP4A
3209:ATP5S
3204:ATP5O
3194:ATP5L
3184:ATP5J
3179:ATP5I
3174:ATP5H
3149:ATP5E
3144:ATP5D
3129:ATP5B
2995:S2CID
2941:S2CID
2897:S2CID
2833:(PDF)
2717:S2CID
2658:S2CID
2581:S2CID
2455:S2CID
2398:S2CID
2335:S2CID
2032:S2CID
1975:S2CID
1917:S2CID
1863:S2CID
1767:S2CID
1634:(PDF)
1532:ATP9B
1528:ATP9A
1491:ATP4A
1451:P2C:
1429:P2B:
1415:P2A:
1397:P2A:
1393:ATP7B
1389:ATP7A
1365:phyla
894:lumen
869:and E
780:SERCA
715:Metal
689:ATP7A
600:~P, E
564:and E
548:and E
271:and E
109:3.A.3
93:SCOPe
84:SCOP2
5073:list
5066:EC7
5060:list
5053:EC6
5047:list
5040:EC5
5034:list
5027:EC4
5021:list
5014:EC3
5008:list
5001:EC2
4995:list
4988:EC1
4772:OPA1
4765:and
4717:EF-G
4707:IF-2
4673:Rheb
4661:ARL6
4646:ARF6
4617:NRAS
4612:KRAS
4607:HRAS
4592:RhoD
4587:RhoF
4533:RhoH
4509:RhoG
4494:Rac1
4482:RhoV
4477:RhoU
4460:TC10
4396:GNAQ
4116:SPCA
3943:3.6)
3578:ATP3
3563:Na/K
3485:) /
3483:SPCA
3479:PMCA
3036:PMID
3022:1798
2987:PMID
2979:ISSN
2933:PMID
2889:PMID
2853:PMID
2841:1850
2811:PMID
2762:PMID
2709:PMID
2701:ISSN
2650:PMID
2642:ISSN
2573:PMID
2565:ISSN
2507:PMID
2499:ISSN
2447:PMID
2439:ISSN
2390:PMID
2382:ISSN
2327:PMID
2319:ISSN
2267:PMID
2259:ISSN
2223:PMID
2205:ISSN
2166:PMID
2148:ISSN
2096:PMID
2078:ISSN
2024:PMID
1967:PMID
1909:PMID
1855:PMID
1824:1T5T
1802:PMID
1759:PMID
1716:PMID
1654:PMID
1560:P5:
1502:P4:
1371:and
1320:and
1258:and
1155:3WGV
1149:3WGU
1143:4RET
1137:4RES
1103:and
1101:Na/K
1033:2M73
1027:2M7E
1021:2L1W
1015:4AQR
995:→ Ca
980:P →
820:and
707:and
604:P, E
402:, a
215:The
192:PDBj
188:PDBe
171:ECOD
161:Pfam
133:3b9b
104:TCDB
89:1su4
48:Pfam
4767:MX2
4763:MX1
4683:RGK
4678:Rap
4668:Ran
4641:Arf
4624:Rab
4602:Ras
4560:Rnd
4538:Rho
4489:Rac
4465:TCL
4326:olf
4058:Ca+
3441:H/K
3026:doi
2971:doi
2925:doi
2881:doi
2845:doi
2801:PMC
2793:doi
2752:hdl
2744:doi
2693:doi
2681:450
2634:doi
2622:297
2557:doi
2545:450
2489:doi
2485:281
2429:doi
2425:414
2374:doi
2362:297
2311:doi
2307:316
2251:doi
2213:PMC
2197:doi
2156:PMC
2138:doi
2126:105
2086:PMC
2070:doi
2066:229
2016:doi
1959:doi
1901:doi
1889:450
1847:doi
1835:304
1820:PDB
1794:doi
1751:doi
1739:405
1708:doi
1681:doi
1646:doi
1133:PDB
1011:PDB
886:ATP
828:or
741:by
542:ATP
492:ADP
389:).
290:, (
233:ion
179:PDB
145:224
5113::
4448::
4336:αi
4318:αs
4296::
4019::
3941:EC
3935::
3576::
3565:–
3549::
3489::
3481:,
3477:,
3471:Ca
3448::
3391::
3229::
3091:/
3087:,
3083::
3034:.
3020:.
3016:.
2993:.
2985:.
2977:.
2967:19
2965:.
2953:^
2939:.
2931:.
2921:68
2919:.
2895:.
2887:.
2877:38
2875:.
2851:.
2839:.
2835:.
2809:.
2799:.
2789:21
2787:.
2783:.
2760:.
2750:.
2740:11
2738:.
2715:.
2707:.
2699:.
2691:.
2679:.
2656:.
2648:.
2640:.
2632:.
2620:.
2616:.
2579:.
2571:.
2563:.
2555:.
2543:.
2505:.
2497:.
2483:.
2479:.
2467:^
2453:.
2445:.
2437:.
2423:.
2419:.
2396:.
2388:.
2380:.
2372:.
2360:.
2356:.
2333:.
2325:.
2317:.
2305:.
2293:^
2265:.
2257:.
2247:54
2245:.
2221:.
2211:.
2203:.
2193:16
2191:.
2187:.
2164:.
2154:.
2146:.
2136:.
2124:.
2120:.
2108:^
2094:.
2084:.
2076:.
2064:.
2060:.
2044:^
2030:.
2022:.
2012:19
2010:.
1998:^
1973:.
1965:.
1957:.
1947:46
1945:.
1941:.
1929:^
1915:.
1907:.
1899:.
1887:.
1875:^
1861:.
1853:.
1845:.
1833:.
1822::
1800:.
1790:32
1788:.
1765:.
1757:.
1749:.
1737:.
1714:.
1704:23
1702:.
1677:12
1675:.
1652:.
1642:40
1640:.
1636:.
1576:,
1572:,
1568:,
1564:,
1554:,
1550:,
1546:,
1542:,
1538:,
1534:,
1530:,
1526:,
1522:,
1518:,
1514:,
1510:,
1506::
1483:,
1479:,
1475:,
1471:,
1467:,
1463:,
1459:,
1455::
1445:,
1441:,
1437:,
1433::
1423:,
1419::
1409:,
1405:,
1401::
1391:,
1316:,
1286:.
1262:.
1254:,
1228:)
1170:)
1135::
1127:.
1111:)
1079:)
1013::
908:/E
641:,
628:A
616:.
612:/E
580:-E
572:-E
556:-E
498:.
467:.
360:.
302:.
239:,
225:-E
190:;
186:;
169:/
121:22
95:/
91:/
5089::
5075:)
5071:(
5062:)
5058:(
5049:)
5045:(
5036:)
5032:(
5023:)
5019:(
5010:)
5006:(
4997:)
4993:(
4817:e
4810:t
4803:v
4575:3
4570:2
4565:1
4553:C
4548:B
4543:A
4526:2
4521:1
4504:3
4499:2
4408:G
4388:G
4334:G
4324:G
4316:G
4017:4
4015:-
3939:(
3925:e
3918:t
3911:v
3759:)
3719:e
3712:t
3705:v
3567:H
3473:(
3099:)
3095:(
3073:e
3066:t
3059:v
3042:.
3028::
3001:.
2973::
2947:.
2927::
2903:.
2883::
2859:.
2847::
2817:.
2795::
2768:.
2754::
2746::
2723:.
2695::
2687::
2664:.
2636::
2628::
2601:.
2587:.
2559::
2551::
2527:.
2513:.
2491::
2461:.
2431::
2404:.
2376::
2368::
2341:.
2313::
2287:.
2273:.
2253::
2229:.
2199::
2172:.
2140::
2132::
2102:.
2072::
2038:.
2018::
1992:.
1961::
1953::
1923:.
1903::
1895::
1869:.
1849::
1841::
1808:.
1796::
1773:.
1753::
1745::
1722:.
1710::
1687:.
1683::
1660:.
1648::
1493:;
1003:1
1000:E
997:2
993:2
990:E
985:2
982:E
978:2
975:E
967:2
964:E
960:1
957:E
954:2
936:2
934:E
927:2
925:E
919:1
917:E
915:2
910:2
906:1
871:2
867:1
614:2
610:1
606:2
602:2
598:1
594:2
590:1
582:2
578:1
574:2
570:1
566:2
562:1
558:2
554:1
550:2
546:1
496:4
486:N
484:S
478:N
476:S
358:i
354:2
350:1
346:2
342:1
279:(
273:2
269:1
227:2
223:1
221:E
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.