331:
44:
35:
553:
599:
424:. In 1973, PR toxin was first partially characterized by isolating moldy corn on which the fungi had grown. Although its lethal dose was determined shortly after the isolation of the chemical, details of its toxic effects were not fully clarified until 1982 in a study with mice, rats, anesthetized cats and preparations of isolated rat
456:. The aldehyde group on C-12 is directly involved in the biological activity as removal leads to inactivation of the compound. The two epoxide groups do not play an important role, as removal showed no difference in activity. When exposed to air, PR toxin may decompose. How and why this happens, is however not known.
648:
The PR toxin dysfunctions the transcriptional process in the liver. RNA polymerases I & II, the two main RNA polymerase systems in the liver, are affected by the toxin. The toxin needs no further enzymatic conversion to exert its effects on these systems. The liver seems to be the most influenced
717:
In conclusion, the tissue cells and blood vessels were directly damaged by PR toxin. This caused leakage of fluid resulting among other things in edema of the lungs and ascites fluid. Also, the damage on the blood vessels resulted in increased capillary permeability. This increased permeability lead
644:
Multiple experiments have shown the different effects of PR toxin: it can cause damage to the liver and kidney, can induce carcinogenicity, and can in vivo inhibit DNA replication, protein synthesis, and transcription. Most experiments on the effect of the PR toxin focus on the inhibition of protein
580:
wasn't the determining factor, the inhibition was not decreased by increasing the amount of polysomes. The increase of pH 5 enzymes on the other hand, had a significant inhibitory effect. A higher concentration of pH 5 enzymes made the inhibitory effect less effective. These findings proved that the
657:
The toxicity of PR toxin was measured both intraperitoneally as well as orally. The first determined median lethal dose of pure PR toxin intraperitoneal in weanling rats was 11 mg/kg. The oral median lethal dose was 115 mg/kg. The same study reported that ten minutes after an oral dose of
635:
The process did not alter the uptake of amino acids in the liver, but the translational process was exclusively affected. The toxic effect of this toxin is as expected close with the fact that the process of protein synthesis is inhibited. However the real toxic effect could be that some required
572:
The PR toxin caused an inhibition of the incorporation of amino acids. These results show that the toxin was responsible for altering the translating process. Together with some earlier experiments it has been proved that the PR toxin was indeed active on the cell metabolism. Another interesting
706:
The effects were different for the different ways PR toxin was taken up. When the median lethal dose was ingested orally, the pathology was described as swollen-gas filled stomach and intestines as well as edema and congestion in the lungs. The kidney showed degenerative changes as well as
537:
685:
An acute human study has yet to be done, so no LD50 test results or doses are known yet. However, there is one case report from 1982 in which toxic effects are described on a human. This person was working in a factory in which the blue cheese was produced. The mold of
702:
Studies of the effects on animals were done on mice, rats, anesthetized cats and preparations of isolated rat auricle. Toxic effects in mice and rats included abdominal writhing, decrease of motor activity and respiration rate, weakness of the hind legs and ataxia.
589:
When the PR toxin was directly administered to rats, protein synthesis in the liver was not as high as it normally would be. This in vivo administration showed that the isolated cells from the rat's liver had a much lower transcriptional capacity.
154:
690:
was inhaled by this person and she developed hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Because of this lung inflammation, the person experienced among other things coughing, dyspnea, reduced lung volumes and
714:
fluid and edema of the lungs and scrotum. While intravenous injection showed, for the same animals, large volumes of pleural and pericardial volumes as well as lung edema.
543:
Eremofortin C has been isolated from microbial sources and found to be in a spontaneous equilibrium between an open-chain hydroxy–ketone structure and a
1185:
370:
354:
InChI=1S/C17H20O6/c1-8-12(21-9(2)19)14-13(22-14)10-5-11(20)17(6-15(8,10)3)16(4,7-18)23-17/h5,7-8,12-14H,6H2,1-4H3/t8-,12+,13-,14+,15+,16+,17-/m0/s1
694:. Antibodies against the mold were found afterwards in serum and lavage fluid. However, the LD50 values have not yet been determined.
573:
finding is the decreased activity of respiratory control and oxidative phosphorylation in the (isolated) mitochondria of the liver .
345:
840:"PR Toxin - Biosynthesis, Genetic Regulation, Toxicological Potential, Prevention and Control Measures: Overview and Challenges"
615:
564:
Different experiments have shown the effects of the PR toxin on liver cells in culture (in vitro) and in the liver (in vivo).
395:
288:
524:
309:
512:
718:
to a decrease in blood volume and direct damage to the vital organs including lungs, kidneys, liver and heart.
951:
Moreau, Serge; Cacan, Monique; Lablache-Combier, Alain (1997). "Eremofortin C, a new metabolite obtained from
488:
523:
analog of PR toxin (incorrectly illustrated in the following diagram), which is then further oxidized by a
484:
480:
420:
212:
1047:
901:
70:
56:
1048:"Biochemical effects of PR toxin on rat liver mitochondrial respiration and oxidative phosphorylation"
917:
476:
326:
1165:
120:
496:
172:
1175:
1170:
1141:
1102:
1067:
1028:
972:
933:
871:
810:
773:
508:
425:
43:
1180:
1133:
1094:
1059:
1018:
964:
925:
861:
851:
802:
763:
755:
232:
34:
552:
297:
130:
520:
330:
658:
160 mg/kg, the animals experienced breathing problems that eventually led to death.
921:
866:
839:
581:
PR toxin was not altering the polysomes but in some way dysfunctions the pH 5 enzymes.
483:. Aristolochene then gains an alcohol, a ketone, and an additional alkene, mediated by
389:
192:
768:
739:
536:
1159:
1137:
1063:
1023:
1002:
929:
806:
472:
468:
1085:
Campbell, J.A.; et al. (1983). "Cheese worker's hypersensitivity pneumonitis".
516:
504:
277:
759:
1098:
500:
465:
1120:
Chen, F.C.; et al. (1982). "Acute toxicity of PR toxin, a mycotoxin from
791:
Chen, F.C.; et al. (1982). "Acute toxicity of PR toxin, a mycotoxin from
223:
856:
902:"Mechanism of the inhibition of transcription by pr toxin, a mycotoxin from
691:
415:
875:
1145:
1106:
1071:
814:
777:
710:
If PR toxin was injected intraperitoneally, cats, mice and rats developed
1032:
976:
937:
577:
528:
445:
968:
17:
711:
492:
453:
437:
264:
544:
203:
388:
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their
252:
449:
183:
153:
143:
243:
1003:"Inhibition of protein synthesis by PR toxin, a mycotoxin from
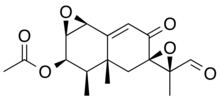
64:)-8,12-Dioxo-1β,2β:7,11-diepoxy-7α-eremophil-9-en-3β-yl acetate
592:
103:)-3′-Formyl-3,3′,3a-trimethyl-6-oxo-1a,2,3a,4,6,7b-hexahydro-3
740:"Isolation and Partial Characterization of a Mycotoxin from
503:
sidechain, again by P450 monooxygenase, and addition of the
314:
436:
PR toxin contains multiple functional groups, including
955:cultures and from biotransformation of PR toxin".
171:
667:- LD50 test, intraperitoneal route: 11.6
276:
129:
733:
731:
519:on the side-chain to eremofortin C, the
499:gives eremofortin B. Epoxidation of the
8:
535:
378:C1(2(O2)C3=CC(=O)4(C13C)(O4)(C)C=O)OC(=O)C
329:
231:
26:
1022:
865:
855:
767:
636:proteins aren't made in a proper amount.
608:needs attention from an expert in Biology
296:
664:- LDLo test, via oral route: 115
1052:Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics
838:Dubey, M.K.; et al. (2019-03-29).
727:
679:- LD50 test, intraperitoneal: 2
676:- LD50 test, via oral route: 72
645:synthesis and impairment of the liver.
464:PR toxin is derived from the 15-carbon
375:
350:
325:
107:-spirooxirene-5,2′-oxiran]-2-yl acetate
1087:American Review of Respiratory Disease
618:may be able to help recruit an expert.
738:Wei, R.D.; et al. (1973-01-25).
670:- LD50 test, intravenous: 8.2
357:Key: GSPFUBNBRPVALJ-VIEAGMIOSA-N
211:
191:
7:
1001:Moulé, Y; et al. (1978-04-15).
996:
994:
992:
990:
988:
986:
895:
893:
891:
889:
887:
885:
833:
831:
829:
827:
1186:Heterocyclic compounds with 3 rings
682:- LD50 test, intravenous: 2
267:
251:
25:
748:American Society for Microbiology
525:short-chain alcohol dehydrogenase
1046:Aujard, C.; et al. (1979).
612:poor wording, meaning not clear.
597:
551:
42:
33:
910:Chemico-Biological Interactions
900:Moule, Y.; et al. (1976).
392:(at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
1:
1138:10.1016/0041-0101(82)90006-x
1064:10.1016/0003-9861(84)90420-x
1024:10.1016/0014-5793(78)80207-5
930:10.1016/0009-2797(76)90101-0
807:10.1016/0041-0101(82)90006-x
760:10.1128/am.25.1.111-114.1973
673:Acute Mouse studies (mg/kg)
511:gives eremofortin A. A
1099:10.1164/arrd.1983.127.4.495
610:. The specific problem is:
1202:
793:Penicillium roqueforti'".
661:Acute Rat studies (mg/kg)
513:short-chain oxidoreductase
408:Penicillin Roquefort toxin
844:Frontiers in Pharmacology
576:Apparently the amount of
386:
366:
341:
113:
69:
55:
50:
41:
32:
857:10.3389/fphar.2018.00288
491:. Addition of the fused-
479:catalyzed by the enzyme
432:Structure and reactivity
649:organ by the PR toxin.
418:produced by the fungus
1122:Penicillium roqueforti
1005:Penicillium roqueforti
953:Penicillium roqueforti
904:Penicillium roqueforti
742:Penicillium roqueforti
688:Penicillium roqueforti
489:quinone oxidoreductase
481:aristolochene synthase
450:α,β-unsaturated ketone
421:Penicillium roqueforti
485:hydroxysterol oxidase
71:Systematic IUPAC name
477:farnesyl diphosphate
969:10.1021/jo00435a023
922:1976CBI....14..207M
640:Mechanism of action
616:WikiProject Biology
29:
698:Effects on animals
497:P450 monooxygenase
452:(-C=C-CO) and two
396:Infobox references
27:
963:(15): 2632–2634.
633:
632:
509:acetyltransferase
404:Chemical compound
402:
401:
310:CompTox Dashboard
155:Interactive image
16:(Redirected from
1193:
1150:
1149:
1117:
1111:
1110:
1082:
1076:
1075:
1043:
1037:
1036:
1026:
998:
981:
980:
948:
942:
941:
916:(3–4): 207–216.
897:
880:
879:
869:
859:
835:
822:
819:
788:
782:
781:
771:
735:
628:
625:
619:
601:
600:
593:
555:
539:
334:
333:
318:
316:
300:
280:
269:
255:
235:
215:
195:
175:
157:
133:
46:
37:
30:
21:
1201:
1200:
1196:
1195:
1194:
1192:
1191:
1190:
1156:
1155:
1154:
1153:
1119:
1118:
1114:
1084:
1083:
1079:
1045:
1044:
1040:
1000:
999:
984:
950:
949:
945:
899:
898:
883:
837:
836:
825:
790:
789:
785:
737:
736:
729:
724:
700:
655:
642:
629:
623:
620:
614:
606:This paragraph
602:
598:
587:
570:
562:
521:primary alcohol
462:
443:
434:
405:
398:
393:
382:
379:
374:
373:
362:
359:
358:
355:
349:
348:
337:
319:
312:
303:
283:
270:
258:
238:
218:
198:
178:
160:
147:
136:
123:
109:
108:
65:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1199:
1197:
1189:
1188:
1183:
1178:
1173:
1168:
1158:
1157:
1152:
1151:
1132:(2): 433–441.
1112:
1093:(4): 495–496.
1077:
1058:(2): 400–411.
1038:
1017:(2): 313–323.
982:
943:
881:
823:
801:(2): 433–441.
783:
754:(1): 111–114.
726:
725:
723:
720:
699:
696:
654:
651:
641:
638:
631:
630:
605:
603:
596:
586:
583:
569:
566:
561:
558:
557:
556:
541:
540:
475:produced from
461:
458:
441:
433:
430:
403:
400:
399:
394:
390:standard state
387:
384:
383:
381:
380:
377:
369:
368:
367:
364:
363:
361:
360:
356:
353:
352:
344:
343:
342:
339:
338:
336:
335:
327:DTXSID40971740
322:
320:
308:
305:
304:
302:
301:
293:
291:
285:
284:
282:
281:
273:
271:
263:
260:
259:
257:
256:
248:
246:
240:
239:
237:
236:
228:
226:
220:
219:
217:
216:
208:
206:
200:
199:
197:
196:
188:
186:
180:
179:
177:
176:
168:
166:
162:
161:
159:
158:
150:
148:
141:
138:
137:
135:
134:
126:
124:
119:
116:
115:
111:
110:
74:
73:
67:
66:
59:
53:
52:
48:
47:
39:
38:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1198:
1187:
1184:
1182:
1179:
1177:
1174:
1172:
1169:
1167:
1164:
1163:
1161:
1147:
1143:
1139:
1135:
1131:
1127:
1123:
1116:
1113:
1108:
1104:
1100:
1096:
1092:
1088:
1081:
1078:
1073:
1069:
1065:
1061:
1057:
1053:
1049:
1042:
1039:
1034:
1030:
1025:
1020:
1016:
1012:
1008:
1006:
997:
995:
993:
991:
989:
987:
983:
978:
974:
970:
966:
962:
958:
954:
947:
944:
939:
935:
931:
927:
923:
919:
915:
911:
907:
905:
896:
894:
892:
890:
888:
886:
882:
877:
873:
868:
863:
858:
853:
849:
845:
841:
834:
832:
830:
828:
824:
821:
818:
816:
812:
808:
804:
800:
794:
787:
784:
779:
775:
770:
765:
761:
757:
753:
749:
745:
743:
734:
732:
728:
721:
719:
715:
713:
708:
704:
697:
695:
693:
689:
683:
680:
677:
674:
671:
668:
665:
662:
659:
652:
650:
646:
639:
637:
627:
617:
613:
609:
604:
595:
594:
591:
584:
582:
579:
574:
567:
565:
559:
554:
550:
549:
548:
546:
538:
534:
533:
532:
530:
526:
522:
518:
514:
510:
506:
502:
498:
494:
490:
486:
482:
478:
474:
473:sesquiterpene
470:
469:aristolochene
467:
459:
457:
455:
451:
447:
439:
431:
429:
427:
423:
422:
417:
413:
409:
397:
391:
385:
376:
372:
365:
351:
347:
340:
332:
328:
324:
323:
321:
311:
307:
306:
299:
295:
294:
292:
290:
287:
286:
279:
275:
274:
272:
266:
262:
261:
254:
250:
249:
247:
245:
242:
241:
234:
230:
229:
227:
225:
222:
221:
214:
213:ChEMBL4176158
210:
209:
207:
205:
202:
201:
194:
190:
189:
187:
185:
182:
181:
174:
170:
169:
167:
164:
163:
156:
152:
151:
149:
145:
140:
139:
132:
128:
127:
125:
122:
118:
117:
112:
106:
102:
98:
94:
90:
86:
82:
78:
72:
68:
63:
58:
54:
49:
45:
40:
36:
31:
19:
1129:
1125:
1121:
1115:
1090:
1086:
1080:
1055:
1051:
1041:
1014:
1011:FEBS Letters
1010:
1004:
960:
957:J. Org. Chem
956:
952:
946:
913:
909:
903:
847:
843:
820:
798:
796:
792:
786:
751:
747:
741:
716:
709:
707:hemorrhage.
705:
701:
687:
684:
681:
678:
675:
672:
669:
666:
663:
660:
656:
647:
643:
634:
621:
611:
607:
588:
575:
571:
563:
542:
527:to give the
517:methyl group
505:acetyl group
463:
435:
419:
411:
407:
406:
114:Identifiers
104:
100:
96:
92:
88:
84:
80:
76:
61:
515:oxidizes a
501:isopropenyl
466:hydrocarbon
1166:Mycotoxins
1160:Categories
722:References
624:March 2024
560:Metabolism
495:oxygen by
298:F9W0X88AFM
224:ChemSpider
193:CHEBI:7883
142:3D model (
131:56299-00-4
121:CAS Number
57:IUPAC name
692:hypoxemia
578:polysomes
460:Synthesis
416:mycotoxin
28:PR toxin
1176:Acetates
1171:Epoxides
876:29651243
653:Toxicity
568:In vitro
529:aldehyde
454:epoxides
448:(-CHO),
446:aldehyde
426:auricles
412:PR toxin
18:PR-toxin
1181:Ketones
1146:7080052
1126:Toxicon
1107:6838056
1072:6324685
918:Bibcode
867:5885497
850:: 288.
815:7080052
795:Toxicon
778:4687064
712:ascites
585:In vivo
493:epoxide
444:COO-),
438:acetoxy
414:) is a
265:PubChem
1144:
1105:
1070:
1033:648640
1031:
977:874620
975:
938:182392
936:
874:
864:
813:
776:
769:380745
766:
547:form.
545:lactol
507:by an
371:SMILES
278:440907
253:C06079
233:389737
204:ChEMBL
173:B01991
165:3DMet
51:Names
346:InChI
184:ChEBI
144:JSmol
1142:PMID
1103:PMID
1068:PMID
1029:PMID
973:PMID
934:PMID
872:PMID
811:PMID
774:PMID
487:and
471:, a
289:UNII
244:KEGG
1134:doi
1124:".
1095:doi
1091:127
1060:doi
1056:230
1019:doi
965:doi
926:doi
862:PMC
852:doi
803:doi
764:PMC
756:doi
440:(CH
315:EPA
268:CID
99:,7b
95:,3a
91:,3′
83:,2′
75:(1a
60:(11
1162::
1140:.
1130:20
1128:.
1101:.
1089:.
1066:.
1054:.
1050:.
1027:.
1015:88
1013:.
1009:.
985:^
971:.
961:42
959:.
932:.
924:.
914:14
912:.
908:.
884:^
870:.
860:.
846:.
842:.
826:^
809:.
799:20
797:.
772:.
762:.
752:25
750:.
746:.
730:^
531:.
428:.
87:,3
79:,2
1148:.
1136::
1109:.
1097::
1074:.
1062::
1035:.
1021::
1007:"
979:.
967::
940:.
928::
920::
906:"
878:.
854::
848:9
817:.
805::
780:.
758::
744:"
626:)
622:(
442:3
410:(
317:)
313:(
146:)
105:H
101:S
97:R
93:S
89:R
85:R
81:R
77:R
62:S
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.