41:
688:
family of proteins. Structurally, pannexins and connexins are very similar, consisting of 4 transmembrane domains, 2 extracellular and 1 intracellular loop, along with intracellular N- and C-terminal tails. Despite this shared topology, the protein families do not share enough sequence similarity to
638:
Pannexins can form nonjunctional transmembrane channels for transport of molecules of less than 1000 Da. These hemichannels can be present in plasma, endoplasmic resticulum (ER) and Golgi membranes. They transport Ca, ATP,
744:
Truncating mutations in pannexin 1 have been shown to promote breast and colon cancer metastasis to the lungs by allowing cancer cells to survive mechanical stretch in the microcirculation through the release of ATP.
643:
and other small molecules and can form hemichannels with greater ease than connexin subunits. Pannexin 1 and pannexin 2 underlie channel function in neurons and contribute to ischemic brain damage.
669:. According to one of the hypotheses, pannexins also may participate in pathological reactions, including the neural damage after ischemia and subsequent cell death.
748:
Pannexins may be involved in the process of tumor development. Particularly, PANX2 expression levels predict post diagnosis survival for patients with glial tumors.
130:
1205:
Abascal F, Zardoya R (July 2012). "LRRC8 proteins share a common ancestor with pannexins, and may form hexameric channels involved in cell-cell communication".
484:
347:
210:
603:(from Greek 'παν' — all, and from Latin 'nexus' — connection) are a family of vertebrate proteins identified by their homology to the invertebrate
665:, hippocampal plasticity, and propagation of calcium waves. Calcium waves are supported by glial cells, which help maintain and modulate neuronal
1497:
1492:
1472:
615:
connecting the intracellular and extracellular space, allowing the passage of ions and small molecules between these compartments (such as
104:
99:
1502:
508:
371:
234:
496:
359:
222:
489:
352:
215:
700:
116:
22:
657:
Hypothetical roles of pannexins in the nervous system include participating in sensory processing, synchronization between
650:
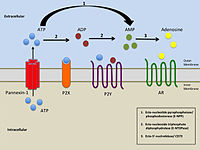
purinergic receptor. Activation of the pannexin channel through binding of ATP to P2X7 receptor leads to the release of
123:
1113:
Bao L, Locovei S, Dahl G (August 2004). "Pannexin membrane channels are mechanosensitive conduits for ATP".
646:
Pannexin 1 has been shown to be involved in early stages of innate immunity through an interaction with the
640:
616:
501:
93:
364:
227:
554:
417:
280:
57:
30:
1007:"Pannexin-1 mediates large pore formation and interleukin-1beta release by the ATP-gated P2X7 receptor"
1067:
959:
796:
63:
1240:
1187:
1138:
928:
822:
712:
1468:
1438:
1389:
1340:
1291:
1260:"The cryo-EM structure of a pannexin 1 reveals unique motifs for ion selection and inhibition"
1232:
1179:
1130:
1095:
1054:
Bargiotas P, Krenz A, Hormuzdi SG, Ridder DA, Herb A, Barakat W, et al. (December 2011).
1036:
987:
946:
Bargiotas P, Krenz A, Hormuzdi SG, Ridder DA, Herb A, Barakat W, et al. (December 2011).
920:
871:
814:
728:
718:
611:
in invertebrates, the pannexins have been shown to predominantly exist as large transmembrane
78:
1428:
1420:
1379:
1371:
1330:
1322:
1281:
1271:
1222:
1214:
1169:
1122:
1085:
1075:
1026:
1018:
977:
967:
910:
902:
861:
853:
804:
620:
558:
549:
412:
275:
73:
662:
578:
441:
421:
304:
284:
1358:
Furlow PW, Zhang S, Soong TD, Halberg N, Goodarzi H, Mangrum C, et al. (July 2015).
1071:
963:
915:
890:
800:
1433:
1408:
1384:
1359:
1335:
1310:
1286:
1259:
1090:
1055:
1031:
1006:
982:
947:
866:
857:
841:
809:
784:
40:
1486:
1360:"Mechanosensitive pannexin-1 channels mediate microvascular metastatic cell survival"
608:
1244:
1191:
1142:
932:
826:
696:
766:
does not affect channels formed by connexins, but it inhibits pannexin-1 channels.
681:
1258:
Michalski K, Syrjanen JL, Henze E, Kumpf J, Furukawa H, Kawate T (February 2020).
1126:
181:
842:"What is hidden in the pannexin treasure trove: the sneak peek and the guesswork"
525:
388:
251:
169:
658:
612:
588:
451:
314:
1424:
1060:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
952:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
1326:
1174:
1157:
906:
763:
751:
666:
532:
395:
258:
1462:
1022:
783:
Panchin Y, Kelmanson I, Matz M, Lukyanov K, Usman N, Lukyanov S (June 2000).
1080:
972:
627:
1442:
1393:
1344:
1295:
1236:
1218:
1183:
1134:
1099:
1040:
991:
924:
875:
818:
759:
726:) has been solved. It forms a heptameric disc. The human version (
685:
604:
537:
400:
263:
164:
1276:
1227:
840:
Litvin O, Tiunova A, Connell-Alberts Y, Panchin Y, Baranova A (2006).
732:
722:
704:
520:
383:
246:
1375:
647:
755:
693:
672:
Pannexin 1 channels are pathways for release of ATP from cells.
651:
513:
376:
239:
176:
45:
Simplified illustration of extracellular purinergic signalling
1311:"Cryo-EM structure of human heptameric Pannexin 1 channel"
1409:"Probenecid, a gout remedy, inhibits pannexin 1 channels"
1309:
Qu R, Dong L, Zhang J, Yu X, Wang L, Zhu S (March 2020).
785:"A ubiquitous family of putative gap junction molecules"
758:, allows for discrimination between channels formed by
1158:"Pannexin: to gap or not to gap, is that a question?"
684:
in vertebrates, including humans, are formed by the
584:
574:
569:
548:
543:
531:
519:
507:
495:
483:
475:
470:
465:
447:
437:
432:
411:
406:
394:
382:
370:
358:
346:
338:
333:
328:
310:
300:
295:
274:
269:
257:
245:
233:
221:
209:
201:
196:
191:
175:
163:
155:
150:
145:
1407:Silverman W, Locovei S, Dahl G (September 2008).
1056:"Pannexins in ischemia-induced neurodegeneration"
948:"Pannexins in ischemia-induced neurodegeneration"
1413:American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology
754:, a well-established drug for the treatment of
891:"Pannexins and gap junction protein diversity"
607:. While innexins are responsible for forming
124:
8:
889:Shestopalov VI, Panchin Y (February 2008).
1005:Pelegrin P, Surprenant A (November 2006).
846:Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine
566:
429:
292:
131:
117:
17:
1432:
1383:
1334:
1285:
1275:
1226:
1173:
1089:
1079:
1030:
981:
971:
914:
865:
808:
775:
626:Three pannexins have been described in
86:
50:
29:
1461:Andrew L Harris, Darren Locke (2009).
462:
325:
188:
142:
7:
895:Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences
1467:. New York: Springer. p. 574.
689:confidently infer common ancestry.
858:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2006.tb00424.x
707:may also be related to pannexins.
14:
716:(western clawed frog) pannexin (
39:
1156:Dahl G, Locovei S (July 2006).
1:
1127:10.1016/j.febslet.2004.07.009
810:10.1016/S0960-9822(00)00576-5
703:-forming LRRC8 proteins like
1498:Genes on human chromosome 22
1493:Genes on human chromosome 11
1519:
1503:Integral membrane proteins
1425:10.1152/ajpcell.00227.2008
630:: Panx1, Panx2 and Panx3.
1327:10.1038/s41422-020-0298-5
1175:10.1080/15216540600794526
907:10.1007/s00018-007-7200-1
676:Relationship to connexins
565:
428:
291:
1023:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601378
692:The N-terminal portion (
1081:10.1073/pnas.1018262108
973:10.1073/pnas.1018262108
94:Nucleoside transporters
1219:10.1002/bies.201100173
740:Clinical significance
736:) is similar.
641:inositol triphosphate
87:Membrane transporters
58:Purinergic signalling
32:Purinergic signalling
1364:Nature Cell Biology
1277:10.7554/eLife.54670
1072:2011PNAS..10820772B
964:2011PNAS..10820772B
801:2000CBio...10.R473P
710:The structure of a
1464:Connexins, A Guide
713:Xenopus tropicalis
1474:978-1-934115-46-6
598:
597:
594:
593:
461:
460:
457:
456:
324:
323:
320:
319:
187:
186:
141:
140:
74:Ectonucleotidases
1510:
1478:
1447:
1446:
1436:
1404:
1398:
1397:
1387:
1355:
1349:
1348:
1338:
1306:
1300:
1299:
1289:
1279:
1255:
1249:
1248:
1230:
1202:
1196:
1195:
1177:
1153:
1147:
1146:
1110:
1104:
1103:
1093:
1083:
1051:
1045:
1044:
1034:
1011:The EMBO Journal
1002:
996:
995:
985:
975:
943:
937:
936:
918:
886:
880:
879:
869:
837:
831:
830:
812:
780:
735:
725:
621:sulforhodamine B
567:
463:
430:
326:
293:
189:
143:
133:
126:
119:
43:
33:
18:
1518:
1517:
1513:
1512:
1511:
1509:
1508:
1507:
1483:
1482:
1481:
1475:
1460:
1456:
1454:Further reading
1451:
1450:
1406:
1405:
1401:
1376:10.1038/ncb3194
1357:
1356:
1352:
1308:
1307:
1303:
1257:
1256:
1252:
1204:
1203:
1199:
1155:
1154:
1150:
1112:
1111:
1107:
1066:(51): 20772–7.
1053:
1052:
1048:
1017:(21): 5071–82.
1004:
1003:
999:
958:(51): 20772–7.
945:
944:
940:
888:
887:
883:
839:
838:
834:
789:Current Biology
782:
781:
777:
772:
762:and pannexins.
742:
727:
717:
678:
636:
137:
46:
31:
12:
11:
5:
1516:
1514:
1506:
1505:
1500:
1495:
1485:
1484:
1480:
1479:
1473:
1457:
1455:
1452:
1449:
1448:
1399:
1350:
1321:(5): 446–448.
1301:
1250:
1197:
1148:
1105:
1046:
997:
938:
881:
832:
795:(13): R473-4.
774:
773:
771:
768:
741:
738:
680:Intercellular
677:
674:
652:interleukin-1β
635:
632:
596:
595:
592:
591:
586:
582:
581:
576:
572:
571:
563:
562:
552:
546:
545:
541:
540:
535:
529:
528:
523:
517:
516:
511:
505:
504:
499:
493:
492:
487:
481:
480:
477:
473:
472:
468:
467:
459:
458:
455:
454:
449:
445:
444:
439:
435:
434:
426:
425:
415:
409:
408:
404:
403:
398:
392:
391:
386:
380:
379:
374:
368:
367:
362:
356:
355:
350:
344:
343:
340:
336:
335:
331:
330:
322:
321:
318:
317:
312:
308:
307:
302:
298:
297:
289:
288:
278:
272:
271:
267:
266:
261:
255:
254:
249:
243:
242:
237:
231:
230:
225:
219:
218:
213:
207:
206:
203:
199:
198:
194:
193:
185:
184:
179:
173:
172:
167:
161:
160:
157:
153:
152:
148:
147:
139:
138:
136:
135:
128:
121:
113:
110:
109:
108:
107:
102:
89:
88:
84:
83:
82:
81:
76:
71:
66:
53:
52:
48:
47:
44:
36:
35:
27:
26:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1515:
1504:
1501:
1499:
1496:
1494:
1491:
1490:
1488:
1476:
1470:
1466:
1465:
1459:
1458:
1453:
1444:
1440:
1435:
1430:
1426:
1422:
1419:(3): C761-7.
1418:
1414:
1410:
1403:
1400:
1395:
1391:
1386:
1381:
1377:
1373:
1370:(7): 943–52.
1369:
1365:
1361:
1354:
1351:
1346:
1342:
1337:
1332:
1328:
1324:
1320:
1316:
1315:Cell Research
1312:
1305:
1302:
1297:
1293:
1288:
1283:
1278:
1273:
1269:
1265:
1261:
1254:
1251:
1246:
1242:
1238:
1234:
1229:
1224:
1220:
1216:
1213:(7): 551–60.
1212:
1208:
1201:
1198:
1193:
1189:
1185:
1181:
1176:
1171:
1168:(7): 409–19.
1167:
1163:
1159:
1152:
1149:
1144:
1140:
1136:
1132:
1128:
1124:
1121:(1–3): 65–8.
1120:
1116:
1109:
1106:
1101:
1097:
1092:
1087:
1082:
1077:
1073:
1069:
1065:
1061:
1057:
1050:
1047:
1042:
1038:
1033:
1028:
1024:
1020:
1016:
1012:
1008:
1001:
998:
993:
989:
984:
979:
974:
969:
965:
961:
957:
953:
949:
942:
939:
934:
930:
926:
922:
917:
912:
908:
904:
901:(3): 376–94.
900:
896:
892:
885:
882:
877:
873:
868:
863:
859:
855:
852:(3): 613–34.
851:
847:
843:
836:
833:
828:
824:
820:
816:
811:
806:
802:
798:
794:
790:
786:
779:
776:
769:
767:
765:
761:
757:
753:
749:
746:
739:
737:
734:
730:
724:
720:
715:
714:
708:
706:
702:
698:
695:
690:
687:
683:
682:gap junctions
675:
673:
670:
668:
664:
660:
655:
653:
649:
644:
642:
633:
631:
629:
624:
622:
618:
614:
610:
609:gap junctions
606:
602:
590:
587:
583:
580:
577:
573:
568:
564:
561:
560:
556:
553:
551:
547:
542:
539:
536:
534:
530:
527:
524:
522:
518:
515:
512:
510:
506:
503:
500:
498:
494:
491:
488:
486:
482:
478:
474:
469:
464:
453:
450:
446:
443:
440:
436:
431:
427:
424:
423:
419:
416:
414:
410:
405:
402:
399:
397:
393:
390:
387:
385:
381:
378:
375:
373:
369:
366:
363:
361:
357:
354:
351:
349:
345:
341:
337:
332:
327:
316:
313:
309:
306:
303:
299:
294:
290:
287:
286:
282:
279:
277:
273:
268:
265:
262:
260:
256:
253:
250:
248:
244:
241:
238:
236:
232:
229:
226:
224:
220:
217:
214:
212:
208:
204:
200:
195:
190:
183:
180:
178:
174:
171:
168:
166:
162:
158:
154:
149:
144:
134:
129:
127:
122:
120:
115:
114:
112:
111:
106:
105:Equilibrative
103:
101:
100:Concentrative
98:
97:
96:
95:
91:
90:
85:
80:
77:
75:
72:
70:
67:
65:
62:
61:
60:
59:
55:
54:
49:
42:
38:
37:
34:
28:
24:
20:
19:
16:
1463:
1416:
1412:
1402:
1367:
1363:
1353:
1318:
1314:
1304:
1267:
1263:
1253:
1228:10261/124027
1210:
1206:
1200:
1165:
1161:
1151:
1118:
1115:FEBS Letters
1114:
1108:
1063:
1059:
1049:
1014:
1010:
1000:
955:
951:
941:
898:
894:
884:
849:
845:
835:
792:
788:
778:
750:
747:
743:
711:
709:
691:
679:
671:
656:
645:
637:
625:
600:
599:
557:
420:
283:
92:
68:
56:
15:
659:hippocampus
579:Swiss-model
471:Identifiers
442:Swiss-model
334:Identifiers
305:Swiss-model
197:Identifiers
151:Identifiers
1487:Categories
1270:: e54670.
1162:IUBMB Life
770:References
764:Probenecid
752:Probenecid
667:metabolism
575:Structures
570:Search for
544:Other data
466:pannexin 3
438:Structures
433:Search for
407:Other data
329:pannexin 2
301:Structures
296:Search for
270:Other data
192:pannexin 1
79:Metabolism
1207:BioEssays
760:connexins
628:Chordates
601:Pannexins
526:NM_052959
485:NCBI gene
389:NM_052839
348:NCBI gene
252:NM_015368
211:NCBI gene
170:IPR039099
69:Pannexins
64:Receptors
1443:18596212
1394:26098574
1345:32203128
1296:32048993
1245:24648128
1237:22532330
1192:24038607
1184:16801216
1143:43459258
1135:15304325
1100:22147915
1041:17036048
992:22147915
933:23181471
925:17982731
916:11131650
876:16989724
827:20001454
819:10898987
686:connexin
634:Function
613:channels
605:innexins
589:InterPro
452:InterPro
315:InterPro
165:InterPro
159:Pannexin
146:Pannexin
51:Concepts
23:a series
21:Part of
1434:2544448
1385:5310712
1336:7196123
1287:7108861
1091:3251101
1068:Bibcode
1032:1630421
983:3251101
960:Bibcode
867:3933146
797:Bibcode
697:PF12534
585:Domains
555:Chr. 11
533:UniProt
448:Domains
418:Chr. 22
396:UniProt
311:Domains
285:q14-q21
281:Chr. 11
259:UniProt
1471:
1441:
1431:
1392:
1382:
1343:
1333:
1294:
1284:
1243:
1235:
1190:
1182:
1141:
1133:
1098:
1088:
1039:
1029:
990:
980:
931:
923:
913:
874:
864:
825:
817:
705:LRRC8A
663:cortex
538:Q96QZ0
521:RefSeq
514:608422
490:116337
476:Symbol
401:Q96RD6
384:RefSeq
377:608421
339:Symbol
264:Q96RD7
247:RefSeq
240:608420
202:Symbol
182:1.A.25
156:Symbol
1264:eLife
1241:S2CID
1188:S2CID
1139:S2CID
929:S2CID
823:S2CID
699:) of
559:q24.2
550:Locus
502:20573
479:PANX3
413:Locus
353:56666
342:PANX2
276:Locus
216:24145
205:PANX1
1469:ISBN
1439:PMID
1390:PMID
1341:PMID
1292:PMID
1233:PMID
1180:PMID
1131:PMID
1096:PMID
1037:PMID
988:PMID
921:PMID
872:PMID
815:PMID
756:gout
733:6M02
723:6VD7
701:VRAC
694:Pfam
661:and
648:P2X7
619:and
509:OMIM
497:HGNC
372:OMIM
365:8600
360:HGNC
235:OMIM
228:8599
223:HGNC
177:TCDB
1429:PMC
1421:doi
1417:295
1380:PMC
1372:doi
1331:PMC
1323:doi
1282:PMC
1272:doi
1223:hdl
1215:doi
1170:doi
1123:doi
1119:572
1086:PMC
1076:doi
1064:108
1027:PMC
1019:doi
978:PMC
968:doi
956:108
911:PMC
903:doi
862:PMC
854:doi
805:doi
729:PDB
719:PDB
623:).
617:ATP
422:q13
1489::
1437:.
1427:.
1415:.
1411:.
1388:.
1378:.
1368:17
1366:.
1362:.
1339:.
1329:.
1319:30
1317:.
1313:.
1290:.
1280:.
1266:.
1262:.
1239:.
1231:.
1221:.
1211:34
1209:.
1186:.
1178:.
1166:58
1164:.
1160:.
1137:.
1129:.
1117:.
1094:.
1084:.
1074:.
1062:.
1058:.
1035:.
1025:.
1015:25
1013:.
1009:.
986:.
976:.
966:.
954:.
950:.
927:.
919:.
909:.
899:65
897:.
893:.
870:.
860:.
850:10
848:.
844:.
821:.
813:.
803:.
793:10
791:.
787:.
731::
721::
654:.
25:on
1477:.
1445:.
1423::
1396:.
1374::
1347:.
1325::
1298:.
1274::
1268:9
1247:.
1225::
1217::
1194:.
1172::
1145:.
1125::
1102:.
1078::
1070::
1043:.
1021::
994:.
970::
962::
935:.
905::
878:.
856::
829:.
807::
799::
132:e
125:t
118:v
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.