167:
it does in a fully developed adult. A doctor will assess the burns and calculate the total area of the child's body that is covered in the burn and from there will determine the course of treatment depending on the extent of the burns. Depending on the TBSA the patient may be transferred to a specialist burn unit for specialized care, however often patients that are transferred to these units have had their TBSA overestimated in the hospital that they presented too and perhaps did not require the referral. Depending on the TBSA the management of the patient will differ, for example an adult burn <10% TBSA is classified as a minor burn however in a young patient a minor burn is classified as <5% TBSA and for moderate burns in adults is classified as 10-20% TBSA and in a child is 5-10% TBSA. All child burns which are >10% TBSA are referred to specialized center to management.
204:
191:
change dressings that are covering the burn as it is too difficult to do this successfully due to the pain associated with this. Depending on the anatomical location of the burn, at a later stage after the burn has healed and there are no signs of infection the patient may be offered surgery to release the burn so that their movement is not restricted.
190:
Patients with severe burns may be treated with surgery to remove the burnt area and at a later stage be offered skin graft over the area, this is made difficult in patients with a large TBSA as they have limited areas where grafts could be taken. In child with severe burns, surgery is often needed to
166:
To determine the management strategy of any burn, it is essential that the Total Burn Area is calculated. This differs from an adult to a child as the total body surface area is divided up differently for a child and for an adult- mainly as a child's head takes up a larger percentage of the TBSA than
199:
It is important to remember that some child burns are not accidental and health care workers need to observe for suspicious injuries in children. Non-accidental child burns are more common in low income households, families with a single parent or young parents. Social services may also be contacted
178:
is often used-4 times the weight of the patient (kg) times the total burn surface area (TBSA). Once this has been calculated, half of this volume is to be given to the patient in the first 8 hours from the time the burn occurred (adjusted if the patient presents later to hospital) and the remaining
173:
is an initial management step of all major burns, with the objective to replace the fluid that has been lost due to the burn and to re-establish the normal fluid level in the child, without overloading with fluid. To determine how much fluid to give the
134:
These burns are often described as painless as the nerve endings have been burned so they can no longer transmit pain along their axon. These burns are white in appearance as the capillaries have been damaged, the skin is leathery.
179:
volume to be given over the next 16 hours, therefore the total volume is given over 24 hours. The fluid is given to ensure that there is enough volume flowing around the body so tissues are not starved of
228:
Hashemi, Sayed Saeed; Sharhani, Asaad; Lotfi, Bahare; Ahmadi-Juibari, Toraj; Shaahmadi, Zahra; Aghaei, Abbas (2017). "A Systematic Review on the
Epidemiology of Pediatric Burn in Iran".
76:
but a small percentage are serious and need to be transferred to specialist burn centers, where a multidisciplinary team of specially trained doctors, including
56:
is an injury to the skin or underlying tissue in person under the age of 18, and is globally the most common type of pediatric injury. Burns can be caused my
158:
More burns are reported in under 15-year-old boys than girls and more burns are recorded in children living in urban areas than rural areas.
438:
Face, Stephen; Dalton, Sarah (2017-06-15). "Consistency of total body surface area assessment in severe burns: Implications for practice".
147:, where the child is exposed to hot liquids e.g. spilling hot water or a hot bath. neglected children's are also a risk factors for burns
187:
However, the
Parkland Formula has often underestimated the needs of children in this case, especially those with inhalation injuries.
568:
498:
279:
Sheridan, Robert L.; Remensnyder, John P.; Schnitzer, Jay J.; Schulz, John T.; Ryan, Colleen M.; Tompkins, Ronald G. (2000-03-01).
203:
592:
200:
when the burn injury is thought not to be deliberate but perhaps due to inadequate supervision of the child.
612:
586:
471:
261:
65:
40:
574:
564:
542:
504:
494:
463:
455:
410:
369:
351:
310:
302:
253:
245:
170:
35:
106:
Depending on the type of burn that has occurred, there will be different signs and symptoms.
534:
525:
Levitt, Andrew (1983). "The
Parkland formula in patients with burns and inhalation injury".
447:
418:
402:
359:
341:
292:
237:
175:
44:
617:
364:
329:
131:
81:
73:
538:
423:
390:
606:
475:
84:
can care for the child. Mortality rates at centers like this at are recorded at 3%.
265:
241:
406:
297:
280:
69:
578:
546:
508:
459:
414:
355:
346:
306:
249:
451:
110:
467:
373:
328:
Bhananker, Sanjay M.; Ramaiah, Ramesh; Krishnamoorthy, Vijay (2012-09-01).
314:
257:
184:
144:
126:
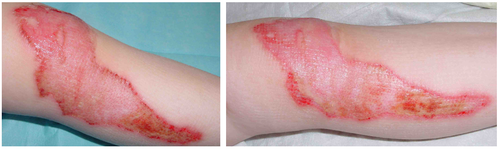
A full thickness burn has damaged the epidermis and the entire dermis,
121:
77:
180:
117:
202:
127:
116:
A partial thickness burn has damaged the epidermis and underlying
61:
57:
334:
International
Journal of Critical Illness and Injury Science
493:(2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
281:"Current Expectations for Survival in Pediatric Burns"
155:
There are several risk factors for pediatric burns;
34:
26:
21:
489:Mahadevan, Swaminatha V.; Garmel, Gus. M. (2011).
391:"ABC of burns: pathophysiology and types of burns"
207:WIRA-Wiki-GH-009-Burn-wound-improvement-with-wIRA
143:Up to 70% of children's burns are as a result of
285:Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine
491:An introduction to clinical emergency medicine
8:
561:Handbook of burns. Volume 1, Acute burn care
18:
563:. Jeschke, Marc G. Wien: Springer. 2012.
422:
363:
345:
296:
217:
584:
7:
520:
518:
385:
383:
223:
221:
230:Journal of Burn Care & Research
109:A superficial burn has damaged the
14:
120:, and is red, painful and often
92:There are three types of burns;
113:, and this appears as redness.
440:Emergency Medicine Australasia
1:
539:10.1016/s0196-0644(83)80675-1
527:Annals of Emergency Medicine
242:10.1097/bcr.0000000000000524
72:. Most burns do not require
401:(7458): 148.3. 2004-07-15.
634:
407:10.1136/bmj.329.7458.148-b
298:10.1001/archpedi.154.3.245
330:"Pediatric burn injuries"
347:10.4103/2229-5151.100889
452:10.1111/1742-6723.12806
591:: CS1 maint: others (
208:
99:Partial thickness burn
206:
171:Fluid resuscitation
102:Full thickness burn
209:
88:Signs and symptoms
74:hospital admission
41:Emergency medicine
82:anesthesiologists
50:
49:
30:Burns in children
16:Medical condition
625:
597:
596:
590:
582:
557:
551:
550:
522:
513:
512:
486:
480:
479:
435:
429:
428:
426:
387:
378:
377:
367:
349:
325:
319:
318:
300:
276:
270:
269:
236:(6): e944–e951.
225:
176:Parkland formula
132:skin appendages.
96:Superficial burn
19:
633:
632:
628:
627:
626:
624:
623:
622:
603:
602:
601:
600:
583:
571:
559:
558:
554:
524:
523:
516:
501:
488:
487:
483:
437:
436:
432:
389:
388:
381:
327:
326:
322:
278:
277:
273:
227:
226:
219:
214:
197:
164:
153:
141:
90:
45:plastic surgery
17:
12:
11:
5:
631:
629:
621:
620:
615:
605:
604:
599:
598:
569:
552:
514:
499:
481:
446:(4): 429–432.
430:
379:
320:
271:
216:
215:
213:
210:
196:
193:
163:
160:
152:
149:
140:
137:
104:
103:
100:
97:
89:
86:
54:pediatric burn
48:
47:
38:
32:
31:
28:
24:
23:
22:Pediatric burn
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
630:
619:
616:
614:
611:
610:
608:
594:
588:
580:
576:
572:
570:9783709103487
566:
562:
556:
553:
548:
544:
540:
536:
532:
528:
521:
519:
515:
510:
506:
502:
500:9780521747769
496:
492:
485:
482:
477:
473:
469:
465:
461:
457:
453:
449:
445:
441:
434:
431:
425:
420:
416:
412:
408:
404:
400:
396:
392:
386:
384:
380:
375:
371:
366:
361:
357:
353:
348:
343:
340:(3): 128–34.
339:
335:
331:
324:
321:
316:
312:
308:
304:
299:
294:
290:
286:
282:
275:
272:
267:
263:
259:
255:
251:
247:
243:
239:
235:
231:
224:
222:
218:
211:
205:
201:
194:
192:
188:
186:
182:
177:
172:
168:
161:
159:
156:
150:
148:
146:
138:
136:
133:
129:
124:
123:
119:
114:
112:
107:
101:
98:
95:
94:
93:
87:
85:
83:
79:
75:
71:
67:
63:
59:
55:
46:
42:
39:
37:
33:
29:
25:
20:
560:
555:
530:
526:
490:
484:
443:
439:
433:
398:
394:
337:
333:
323:
291:(3): 245–9.
288:
284:
274:
233:
229:
198:
189:
169:
165:
157:
154:
142:
125:
115:
108:
105:
91:
53:
51:
27:Other names
613:Pediatrics
607:Categories
533:(8): 525.
212:References
195:Management
185:nutrients.
70:irritation
587:cite book
579:808634197
547:0196-0644
509:665137591
460:1742-6731
415:0959-8138
356:2229-5151
307:1072-4710
250:1559-047X
162:Treatment
111:epidermis
36:Specialty
476:13732426
468:28620921
374:23181206
315:10710021
258:28328658
122:blisters
78:surgeons
66:chemical
365:3500004
266:3661230
577:
567:
545:
507:
497:
474:
466:
458:
424:478267
421:
413:
372:
362:
354:
313:
305:
264:
256:
248:
181:oxygen
145:scalds
128:nerves
118:dermis
618:Burns
472:S2CID
262:S2CID
151:Risks
139:Cause
593:link
575:OCLC
565:ISBN
543:ISSN
505:OCLC
495:ISBN
464:PMID
456:ISSN
411:ISSN
370:PMID
352:ISSN
311:PMID
303:ISSN
254:PMID
246:ISSN
130:and
80:and
62:cold
58:heat
535:doi
448:doi
419:PMC
403:doi
399:329
395:BMJ
360:PMC
342:doi
293:doi
289:154
238:doi
183:or
68:or
609::
589:}}
585:{{
573:.
541:.
531:12
529:.
517:^
503:.
470:.
462:.
454:.
444:29
442:.
417:.
409:.
397:.
393:.
382:^
368:.
358:.
350:.
336:.
332:.
309:.
301:.
287:.
283:.
260:.
252:.
244:.
234:38
232:.
220:^
64:,
60:,
52:A
43:,
595:)
581:.
549:.
537::
511:.
478:.
450::
427:.
405::
376:.
344::
338:2
317:.
295::
268:.
240::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.