544:
568:
556:
42:
532:, which might mediate the role of the PAG in maternal love. The lateral orbitofrontal cortex is activated by pleasant visual, tactile, and olfactory stimuli. Its response depends on pleasantness rather than on intensity of stimulation. Here, its activity is likely to reflect one aspect of the pleasant emotions associated with motherly love.
580:
62:
441:
Notably, the anterior cingulate cortex is thought to be responsible for emotional responses to pain, including perceived social or emotional pain. Reducing nociceptive signaling to this area not only reduces overall pain signaling, but appears to also reduce sensitivity to pain. Furthermore,
450:
Dorsal PAG neurons are activated during various defensive behaviors. Stimulation of the dorsal and lateral aspects of the PAG can provoke defensive responses characterised by freezing immobility, running, jumping,
1439:
422:
from these incoming first-order neurons and, in turn, inhibits the activation of the second-order neuron that is responsible for transmitting the pain signal up the spinothalamic tract to the
980:
965:
802:
683:
Silva, Carlos; McNaughton, Neil (2019-02-17). "Are periaqueductal grey and dorsal raphe the foundation of appetitive and aversive control? A comprehensive review".
269:
1591:
1367:
579:
1077:
426:(VPL) of the thalamus. The nociceptive signal is thus inhibited before reaching the cortical areas that interpret the signal as pain, such as the
543:
1019:
245:
567:
555:
786:
1391:
1300:
396:
276:
1374:
1362:
1416:
1331:
1283:
423:
135:
388:
264:
1396:
1586:
1459:
599:
1288:
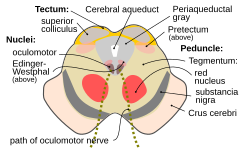
1070:
816:
Eisenberger NI, Lieberman MD, Williams KD (October 2003). "Does rejection hurt? An FMRI study of social exclusion".
585:
349:
1484:
427:
313:
behavior and behavioural responses to threatening stimuli. PAG is also the primary control center for descending
1467:
459:. In contrast, stimulation of the caudal ventrolateral PAG can result in an immobile, relaxed posture known as
306:
203:
1449:
1181:
1408:
1063:
467:
364:
252:
240:
1598:
1541:
1531:
1354:
1305:
959:
408:
145:
88:
442:
activation of mu-opioid receptors has been shown to provide an "analgesic" effect for emotional pain.
434:
and is supported by the fact that electrical stimulation of the PAG results in immediate and profound
1536:
1477:
1106:
825:
626:"The midbrain periaqueductal gray as an integrative and interoceptive neural structure for breathing"
529:
341:
220:
169:
164:
75:
734:
Basbaum AI, Fields HL (November 1978). "Endogenous pain control mechanisms: review and hypothesis".
1526:
1326:
1295:
1131:
1126:
1119:
1114:
431:
345:
122:
47:
344:, and also contains descending autonomic tracts. The ascending pain and temperature fibers of the
1379:
1244:
1215:
1011:
849:
796:
759:
716:
404:
392:
470:
freezing, whereas lesions of the dorsal aspect can reduce innate defensive behavior, virtually "
438:. The periaqueductal gray is also activated by viewing distressing images associated with pain.
1627:
1444:
1384:
1321:
1276:
1233:
1223:
1197:
1176:
1003:
947:
898:
841:
782:
751:
708:
700:
665:
657:
501:
329:
155:
130:
80:
1557:
1521:
1271:
995:
937:
929:
888:
880:
833:
743:
692:
647:
637:
353:
151:
126:
112:
98:
93:
51:
918:"Periaqueductal Gray Neuronal Activities Underlie Different Aspects of Defensive Behaviors"
1570:
1095:
17:
1046:
411:, respectively, on the axons of incoming C and A-delta fibers carrying pain signals from
829:
1151:
942:
917:
893:
868:
400:
159:
869:"Opioid modulation of resting-state anterior cingulate cortex functional connectivity"
1632:
1621:
1565:
1513:
999:
517:
357:
1015:
853:
763:
720:
696:
642:
625:
624:
Faull, Olivia K.; Subramanian, Hari H.; Ezra, Martyn; Pattinson, Kyle T. S. (2019).
1509:
1472:
1253:
1161:
933:
505:
456:
384:
140:
208:
1553:
1434:
1345:
1143:
521:
460:
452:
419:
325:
233:
103:
54:. Periaqueductal gray is the gray area just peripheral to the cerebral aqueduct.
652:
486:
412:
399:). When activated, these interneurons release either enkephalin or dynorphin (
376:
318:
310:
215:
884:
704:
661:
257:
1050:
837:
493:
435:
380:
379:-releasing neurons that project to the raphe nuclei in the brainstem. 5-HT (
333:
107:
67:
1007:
951:
902:
845:
712:
669:
41:
1055:
747:
1087:
755:
525:
337:
227:
867:
Gorka SM, Fitzgerald DA, de Wit H, Angstadt M, Phan KL (December 2014).
375:
Stimulation of the periaqueductal gray matter of the midbrain activates
282:
604:
549:
Schematic representation of the chief ganglionic categories (I to V).
497:
490:
482:
471:
61:
1047:
Stained brain slice images which include the "Periaqueductal gray"
391:
of the spinal cord where it forms excitatory connections with the
191:
777:
Jenkins, Dacher
Keltner, Keith Oatley, Jennifer M. (2013-01-29).
418:
The activation of the mu-opioid receptor inhibits the release of
463:, whereas its inhibition leads to increased locomotor activity.
314:
1059:
573:
Transverse section of mid-brain at level of superior colliculi.
561:
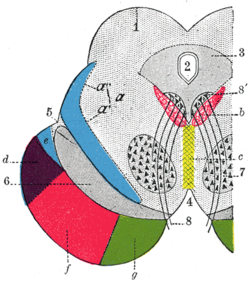
Transverse section of mid-brain at level of inferior colliculi.
1440:
Rostral interstitial nucleus of medial longitudinal fasciculus
466:
Lesions of the caudal ventrolateral PAG can greatly reduce
588:
section of human mid-brain showing periaqueductal gray
981:"The neural correlates of maternal and romantic love"
504:) via a pathway from the ventromedial nucleus of the
1579:
1552:
1508:
1501:
1458:
1407:
1353:
1344:
1314:
1261:
1252:
1243:
1232:
1214:
1190:
1169:
1160:
1142:
1105:
1094:
263:
251:
239:
226:
214:
202:
190:
185:
180:
34:
528:receptors, and it has direct connections with the
305:, is a brain region that plays a critical role in
516:The PAG may be specifically involved in human
352:(so-named because the fibers originate in the
1071:
8:
964:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
801:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
363:This region has been used as the target for
1505:
1350:
1258:
1249:
1240:
1166:
1102:
1078:
1064:
1056:
979:Andreas Bartels; Semir Zeki (March 2004).
60:
40:
941:
892:
651:
641:
27:Nucleus surrounding the cerebral aqueduct
616:
539:
430:. This is sometimes referred to as the
957:
794:
781:(3rd ed.). Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley.
630:Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews
455:, and increases in blood pressure and
280:
31:
520:. The PAG contains a high density of
321:-producing cells that suppress pain.
7:
348:send information to the PAG via the
25:
356:and terminate in the PAG, in the
1301:Anterior trigeminothalamic tract
1000:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.11.003
578:
566:
554:
542:
277:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
115:, with 8', its nucleus of origin
916:Deng H, Xiao X, Wang Z (2016).
697:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2019.02.001
643:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.12.020
395:located in Laminae II (aka the
367:in patients with chronic pain.
324:The periaqueductal gray is the
1417:Rostromedial tegmental nucleus
934:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4425-15.2016
424:ventral posterolateral nucleus
136:Medial longitudinal fasciculus
1:
478:Role in reproductive behavior
1587:Superior cerebellar peduncle
1460:Midbrain reticular formation
600:Rostral ventromedial medulla
415:activated in the periphery.
1289:Vestibulo-oculomotor fibers
496:. It also plays a role in
432:gate control theory of pain
197:substantia grisea centralis
66:Transverse section through
1649:
485:of the PAG are excited by
446:Role in defensive behavior
401:endogenous opioid peptides
365:brain-stimulating implants
350:spinomesencephalic pathway
18:Periaqueductal grey matter
1485:Reticulotegmental nucleus
1425:
512:Role in maternal behavior
500:copulatory behavior (see
275:
59:
39:
1468:dorsal tegmental nucleus
1397:Edinger–Westphal nucleus
885:10.1177/0269881114548436
685:Progress in Neurobiology
1450:Interpeduncular nucleus
1182:Central tegmental tract
838:10.1126/science.1089134
393:inhibitory interneurons
1409:Ventral tegmental area
779:Understanding emotions
409:kappa opioid receptors
125:(in blue) with a' the
1599:Interpeduncular fossa
1542:Temporopontine fibers
1306:Dentatothalamic tract
748:10.1002/ana.410040511
397:substantia gelatinosa
340:. It projects to the
301:), also known as the
146:Temporopontine fibers
89:Interpeduncular space
1537:Frontopontine fibers
1532:Corticopontine tract
1107:Corpora quadrigemina
530:orbitofrontal cortex
383:) released from the
342:nucleus raphe magnus
170:Frontopontine fibers
165:Cerebrospinal fibers
154:, which runs to the
85:Central gray stratum
76:Corpora quadrigemina
1527:Corticobulbar tract
1522:Corticospinal tract
1430:Periaqueductal gray
1327:Rubro-olivary tract
1296:Spinothalamic tract
1262:Sensory / ascending
1170:Sensory / ascending
1127:Superior colliculus
1115:Inferior colliculus
830:2003Sci...302..290E
653:20.500.11850/317617
346:spinothalamic tract
328:located around the
317:modulation. It has
295:periaqueductal gray
48:superior colliculus
35:Periaqueductal gray
1380:Oculomotor nucleus
1315:Motor / descending
1191:Motor / descending
873:J. Psychopharmacol
428:anterior cingulate
1615:
1614:
1611:
1610:
1607:
1606:
1497:
1496:
1493:
1492:
1445:Parabrachial area
1385:Trochlear nucleus
1340:
1339:
1322:Rubrospinal tract
1224:Cerebral aqueduct
1210:
1209:
1206:
1205:
1198:Tectospinal tract
1177:Spinotectal tract
1132:Superior brachium
1120:Inferior brachium
1051:BrainMaps project
536:Additional images
518:maternal behavior
502:lordosis behavior
403:), which bind to
371:Role in analgesia
330:cerebral aqueduct
291:
290:
286:
156:lentiform nucleus
131:lateral lemniscus
81:Cerebral aqueduct
16:(Redirected from
1640:
1558:Substantia nigra
1506:
1351:
1259:
1250:
1241:
1167:
1103:
1080:
1073:
1066:
1057:
1034:
1033:
1031:
1030:
1024:
1018:. Archived from
994:(3): 1155–1166.
985:
976:
970:
969:
963:
955:
945:
913:
907:
906:
896:
864:
858:
857:
813:
807:
806:
800:
792:
774:
768:
767:
731:
725:
724:
680:
674:
673:
655:
645:
621:
582:
570:
558:
546:
387:descends to the
283:edit on Wikidata
152:medial lemniscus
127:medial lemniscus
113:Oculomotor nerve
99:Substantia nigra
94:Sulcus lateralis
64:
52:oculomotor nerve
50:showing path of
46:Section through
44:
32:
21:
1648:
1647:
1643:
1642:
1641:
1639:
1638:
1637:
1618:
1617:
1616:
1603:
1575:
1571:Pars reticulata
1548:
1489:
1454:
1421:
1403:
1336:
1310:
1236:
1228:
1202:
1186:
1156:
1138:
1098:
1090:
1086:Anatomy of the
1084:
1043:
1038:
1037:
1028:
1026:
1022:
983:
978:
977:
973:
956:
915:
914:
910:
879:(12): 1115–24.
866:
865:
861:
824:(5643): 290–2.
815:
814:
810:
793:
789:
776:
775:
771:
733:
732:
728:
682:
681:
677:
623:
622:
618:
613:
596:
589:
583:
574:
571:
562:
559:
550:
547:
538:
514:
480:
448:
373:
287:
176:
175:
174:
118:
55:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1646:
1644:
1636:
1635:
1630:
1620:
1619:
1613:
1612:
1609:
1608:
1605:
1604:
1602:
1601:
1596:
1595:
1594:
1583:
1581:
1577:
1576:
1574:
1573:
1568:
1562:
1560:
1550:
1549:
1547:
1546:
1545:
1544:
1539:
1529:
1524:
1518:
1516:
1503:
1499:
1498:
1495:
1494:
1491:
1490:
1488:
1487:
1482:
1481:
1480:
1470:
1464:
1462:
1456:
1455:
1453:
1452:
1447:
1442:
1437:
1432:
1426:
1423:
1422:
1420:
1419:
1413:
1411:
1405:
1404:
1402:
1401:
1400:
1399:
1389:
1388:
1387:
1382:
1372:
1371:
1370:
1359:
1357:
1355:cranial nuclei
1348:
1342:
1341:
1338:
1337:
1335:
1334:
1332:Descending MLF
1329:
1324:
1318:
1316:
1312:
1311:
1309:
1308:
1303:
1298:
1293:
1292:
1291:
1281:
1280:
1279:
1274:
1265:
1263:
1256:
1247:
1238:
1230:
1229:
1227:
1226:
1220:
1218:
1212:
1211:
1208:
1207:
1204:
1203:
1201:
1200:
1194:
1192:
1188:
1187:
1185:
1184:
1179:
1173:
1171:
1164:
1158:
1157:
1155:
1154:
1152:Pretectal area
1148:
1146:
1140:
1139:
1137:
1136:
1135:
1134:
1124:
1123:
1122:
1111:
1109:
1100:
1092:
1091:
1085:
1083:
1082:
1075:
1068:
1060:
1054:
1053:
1042:
1041:External links
1039:
1036:
1035:
971:
928:(29): 7580–8.
908:
859:
808:
787:
769:
726:
675:
615:
614:
612:
609:
608:
607:
602:
595:
592:
591:
590:
584:
577:
575:
572:
565:
563:
560:
553:
551:
548:
541:
537:
534:
513:
510:
479:
476:
474:" the animal.
447:
444:
372:
369:
360:or midbrain).
289:
288:
279:
273:
272:
267:
261:
260:
255:
249:
248:
243:
237:
236:
231:
224:
223:
218:
212:
211:
206:
200:
199:
194:
188:
187:
183:
182:
178:
177:
173:
172:
167:
162:
148:
143:
138:
133:
119:
117:
116:
110:
101:
96:
91:
86:
83:
78:
72:
71:
65:
57:
56:
45:
37:
36:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1645:
1634:
1631:
1629:
1626:
1625:
1623:
1600:
1597:
1593:
1590:
1589:
1588:
1585:
1584:
1582:
1578:
1572:
1569:
1567:
1566:Pars compacta
1564:
1563:
1561:
1559:
1555:
1551:
1543:
1540:
1538:
1535:
1534:
1533:
1530:
1528:
1525:
1523:
1520:
1519:
1517:
1515:
1514:Cerebral crus
1511:
1507:
1504:
1500:
1486:
1483:
1479:
1476:
1475:
1474:
1471:
1469:
1466:
1465:
1463:
1461:
1457:
1451:
1448:
1446:
1443:
1441:
1438:
1436:
1433:
1431:
1428:
1427:
1424:
1418:
1415:
1414:
1412:
1410:
1406:
1398:
1395:
1394:
1393:
1390:
1386:
1383:
1381:
1378:
1377:
1376:
1373:
1369:
1368:Mesencephalic
1366:
1365:
1364:
1361:
1360:
1358:
1356:
1352:
1349:
1347:
1343:
1333:
1330:
1328:
1325:
1323:
1320:
1319:
1317:
1313:
1307:
1304:
1302:
1299:
1297:
1294:
1290:
1287:
1286:
1285:
1284:Ascending MLF
1282:
1278:
1275:
1273:
1270:
1269:
1267:
1266:
1264:
1260:
1257:
1255:
1251:
1248:
1246:
1242:
1239:
1235:
1231:
1225:
1222:
1221:
1219:
1217:
1213:
1199:
1196:
1195:
1193:
1189:
1183:
1180:
1178:
1175:
1174:
1172:
1168:
1165:
1163:
1159:
1153:
1150:
1149:
1147:
1145:
1141:
1133:
1130:
1129:
1128:
1125:
1121:
1118:
1117:
1116:
1113:
1112:
1110:
1108:
1104:
1101:
1097:
1093:
1089:
1081:
1076:
1074:
1069:
1067:
1062:
1061:
1058:
1052:
1048:
1045:
1044:
1040:
1025:on 2017-08-29
1021:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1005:
1001:
997:
993:
989:
982:
975:
972:
967:
961:
953:
949:
944:
939:
935:
931:
927:
923:
919:
912:
909:
904:
900:
895:
890:
886:
882:
878:
874:
870:
863:
860:
855:
851:
847:
843:
839:
835:
831:
827:
823:
819:
812:
809:
804:
798:
790:
788:9781118147436
784:
780:
773:
770:
765:
761:
757:
753:
749:
745:
742:(5): 451–62.
741:
737:
730:
727:
722:
718:
714:
710:
706:
702:
698:
694:
690:
686:
679:
676:
671:
667:
663:
659:
654:
649:
644:
639:
635:
631:
627:
620:
617:
610:
606:
603:
601:
598:
597:
593:
587:
581:
576:
569:
564:
557:
552:
545:
540:
535:
533:
531:
527:
523:
519:
511:
509:
507:
503:
499:
495:
492:
488:
484:
477:
475:
473:
469:
464:
462:
458:
454:
445:
443:
439:
437:
433:
429:
425:
421:
416:
414:
410:
406:
402:
398:
394:
390:
386:
382:
378:
370:
368:
366:
361:
359:
358:mesencephalon
355:
351:
347:
343:
339:
335:
331:
327:
322:
320:
316:
312:
308:
304:
300:
296:
284:
278:
274:
271:
268:
266:
262:
259:
256:
254:
250:
247:
244:
242:
238:
235:
232:
229:
225:
222:
219:
217:
213:
210:
207:
205:
201:
198:
195:
193:
189:
184:
179:
171:
168:
166:
163:
161:
157:
153:
149:
147:
144:
142:
139:
137:
134:
132:
128:
124:
121:
120:
114:
111:
109:
105:
102:
100:
97:
95:
92:
90:
87:
84:
82:
79:
77:
74:
73:
69:
63:
58:
53:
49:
43:
38:
33:
30:
19:
1473:Raphe nuclei
1429:
1254:White matter
1162:White matter
1027:. Retrieved
1020:the original
991:
987:
974:
960:cite journal
925:
921:
911:
876:
872:
862:
821:
817:
811:
778:
772:
739:
735:
729:
688:
684:
678:
633:
629:
619:
515:
506:hypothalamus
481:
465:
457:muscle tonus
449:
440:
417:
385:raphe nuclei
374:
362:
323:
303:central gray
302:
298:
294:
292:
246:A14.1.06.321
196:
29:
1592:Decussation
1435:Red nucleus
1346:Grey matter
1144:Grey matter
736:Ann. Neurol
636:: 135–144.
522:vasopressin
468:conditioned
453:tachycardia
420:substance P
413:nociceptors
389:dorsal horn
332:within the
326:gray matter
234:birnlex_973
186:Identifiers
150:Portion of
129:and a" the
104:Red nucleus
1622:Categories
1029:2013-01-27
988:NeuroImage
922:J Neurosci
611:References
494:analgesics
487:endorphins
461:quiescence
377:enkephalin
319:enkephalin
309:function,
216:NeuroNames
1268:Lemnisci
1245:Tegmentum
1237:(Ventral)
797:cite book
705:1873-5118
691:: 33–72.
662:1873-7528
436:analgesia
381:serotonin
334:tegmentum
311:motivated
307:autonomic
123:Lemniscus
108:tegmentum
68:mid-brain
1628:Midbrain
1234:Peduncle
1099:(Dorsal)
1088:midbrain
1016:15237043
1008:15006682
952:27445137
903:25237122
854:21253445
846:14551436
764:72620829
721:73478335
713:30786258
670:30611797
594:See also
526:oxytocin
338:midbrain
228:NeuroLex
1580:Surface
1277:Lateral
1049:at the
943:6705556
894:5613932
826:Bibcode
818:Science
605:Emotion
489:and by
483:Neurons
336:of the
209:D010487
181:Details
1478:dorsal
1272:Medial
1096:Tectum
1014:
1006:
950:
940:
901:
891:
852:
844:
785:
762:
756:216303
754:
719:
711:
703:
668:
660:
498:female
491:opiate
472:taming
160:insula
1510:White
1023:(PDF)
1012:S2CID
984:(PDF)
850:S2CID
760:S2CID
717:S2CID
354:spine
281:[
270:83134
192:Latin
141:Raphé
1633:Pain
1554:Grey
1502:Base
1004:PMID
966:link
948:PMID
899:PMID
842:PMID
803:link
783:ISBN
752:PMID
709:PMID
701:ISSN
666:PMID
658:ISSN
524:and
407:and
315:pain
293:The
258:5909
241:TA98
221:1584
204:MeSH
158:and
1392:GVE
1375:GSE
1363:GSA
1216:CSF
996:doi
938:PMC
930:doi
889:PMC
881:doi
834:doi
822:302
744:doi
693:doi
689:177
648:hdl
638:doi
586:MRI
299:PAG
265:FMA
253:TA2
106:of
1624::
1556:/
1512:/
1010:.
1002:.
992:21
990:.
986:.
962:}}
958:{{
946:.
936:.
926:36
924:.
920:.
897:.
887:.
877:28
875:.
871:.
848:.
840:.
832:.
820:.
799:}}
795:{{
758:.
750:.
738:.
715:.
707:.
699:.
687:.
664:.
656:.
646:.
634:98
632:.
628:.
508:.
405:mu
230:ID
70:.
1079:e
1072:t
1065:v
1032:.
998::
968:)
954:.
932::
905:.
883::
856:.
836::
828::
805:)
791:.
766:.
746::
740:4
723:.
695::
672:.
650::
640::
297:(
285:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.