1869:
924:
panel of genes being expressed. NRL expression leads to the rod fate. NR2E3 further restricts cells to the rod fate by repressing cone genes. RORbeta is needed for both rod and cone development. TRbeta2 mediates the M cone fate. If any of the previously mentioned factors' functions are ablated, the default photoreceptor is a S cone. These events take place at different time periods for different species and include a complex pattern of activities that bring about a spectrum of phenotypes. If these regulatory networks are disrupted,
1868:
746:, and one PDE will cleave many cGMPs. This amplification means that even the absorption of one photon will affect membrane potential and signal to the brain that light is in the visual field. This is the main feature that differentiates rod photoreceptors from cone photoreceptors. Rods are extremely sensitive and have the capacity of registering a single photon of light, unlike cones. On the other hand, cones are known to have very fast kinetics in terms of rate of amplification of phototransduction, unlike rods.
422:
993:
down patients with rare diseases wiping out classic rod and cone photoreceptor function but preserving ganglion cell function. Despite having no rods or cones the patients continued to exhibit circadian photoentrainment, circadian behavioural patterns, melanopsin suppression, and pupil reactions, with peak spectral sensitivities to environmental and experimental light matching that for the melanopsin photopigment. Their brains could also associate vision with light of this frequency.
916:
rod or M cone generation. L cones are present in primates, however there is not much known for their developmental program due to use of rodents in research. There are five steps to developing photoreceptors: proliferation of multi-potent retinal progenitor cells (RPCs); restriction of competence of RPCs; cell fate specification; photoreceptor gene expression; and lastly axonal growth, synapse formation and outer segment growth.
204:
485:
47:
257:
1707:
223:(see graph). For example, the peak wavelength of the S-cone's spectral sensitivity is approximately 420 nm (nanometers, a measure of wavelength), so it is more likely to absorb a photon at 420 nm than at any other wavelength. Light of a longer wavelength can also produce the same response from an S-cone, but it would have to be brighter to do so.
413:
248:
230:, a photoreceptor's output signal is proportional only to the number of photons absorbed. The photoreceptors can not measure the wavelength of light that it absorbs and therefore does not detect color on its own. Rather, it is the ratios of responses of the three types of cone cells that can estimate wavelength, and therefore enable
726:
the classic (rod or cone) photoreceptor is depolarized in the dark, which means many sodium ions are flowing into the cell. Thus, the random opening or closing of sodium channels will not affect the membrane potential of the cell; only the closing of a large number of channels, through absorption of
992:
ipRGCs were only definitively detected ipRGCs in humans during landmark experiments in 2007 on rodless, coneless humans. As had been found in other mammals, the identity of the non-rod non-cone photoreceptor in humans was found to be a ganglion cell in the inner retina. The researchers had tracked
915:
The key events mediating rod versus S cone versus M cone differentiation are induced by several transcription factors, including RORbeta, OTX2, NRL, CRX, NR2E3 and TRbeta2. The S cone fate represents the default photoreceptor program; however, differential transcriptional activity can bring about
1904:
1:posterior segment 2:ora serrata 3:ciliary muscle 4:ciliary zonules 5:Schlemm's canal 6:pupil 7:anterior chamber 8:cornea 9:iris 10:lens cortex 11:lens nucleus 12:ciliary process 13:conjunctiva 14:inferior oblique muscule 15:inferior rectus muscule 16:medial rectus muscle 17:retinal arteries and
1001:
Rod and cone photoreceptors are common to almost all vertebrates. The pineal and parapineal glands are photoreceptive in non-mammalian vertebrates, but not in mammals. Birds have photoactive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)-contacting neurons within the paraventricular organ that respond to light in the
988:
sight and brightness detection. Classic photoreceptors (rods and cones) also feed into the novel visual system, which may constribute to color constancy. ipRGCs could be instrumental in understanding many diseases including major causes of blindness worldwide like glaucoma, a disease that affects
923:
signaling maintains progenitor cycling. Photoreceptor precursors come about through inhibition of Notch signaling and increased activity of various factors including achaete-scute homologue 1. OTX2 activity commits cells to the photoreceptor fate. CRX further defines the photoreceptor specific
666:
The rod and cone photoreceptors signal their absorption of photons via a decrease in the release of the neurotransmitter glutamate to bipolar cells at its axon terminal. Since the photoreceptor is depolarized in the dark, a high amount of glutamate is being released to bipolar cells in the dark.
187:(bright conditions), but the processes in each that supports phototransduction is similar. The intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells were discovered during the 1990s. These cells are thought not to contribute to sight directly, but have a role in the entrainment of the
697:
In essence, this property allows for one population of bipolar cells that gets excited by light and another population that gets inhibited by it, even though all photoreceptors show the same response to light. This complexity becomes both important and necessary for
502:, the mechanism by which the energy of a photon signals a mechanism in the cell that leads to its electrical polarization. This polarization ultimately leads to either the transmittance or inhibition of a neural signal that will be fed to the brain via the
453:, the area where ganglion cell fibers are collected into the optic nerve and leave the eye. The distribution of cone classes (L, M, S) are also nonhomogenous, with no S-cones in the fovea, and the ratio of L-cones to M-cones differing between individuals.
722:(in this case, light) reduces the cell's response or firing rate, different from most other sensory systems in which a stimulus increases the cell's response or firing rate. This difference has important functional consequences:
571:
A decrease in the intracellular calcium concentration means that less glutamate is released via calcium-induced exocytosis to the bipolar cell (see below). (The decreased calcium level slows the release of the neurotransmitter
567:
This change in the cell's membrane potential causes voltage-gated calcium channels to close. This leads to a decrease in the influx of calcium ions into the cell and thus the intracellular calcium ion concentration
379:. The function of the photoreceptor cell is to convert the light information of the photon into a form of information communicable to the nervous system and readily usable to the organism: This conversion is called
587:
ATP provided by the inner segment powers the sodium-potassium pump. This pump is necessary to reset the initial state of the outer segment by taking the sodium ions that are entering the cell and pumping them back
416:
Illustration of the distribution of cone cells in the fovea of an individual with normal color vision (left), and a color blind (protanopic) retina. Note that the center of the fovea holds very few blue-sensitive
1905:
veins 18:optic disc 19:dura mater 20:central retinal artery 21:central retinal vein 22:optic nerve 23:vorticose vein 24:bulbar sheath 25:macula 26:fovea 27:sclera 28:choroid 29:superior rectus muscle 30:retina
727:
a photon, will affect it and signal that light is in the visual field. This system may have less noise relative to sensory transduction schema that increase rate of neural firing in response to stimulus, like
556:
The net concentration of intracellular cGMP is reduced (due to its conversion to 5' GMP via PDE), resulting in the closure of cyclic nucleotide-gated Na ion channels located in the photoreceptor outer segment
605:
when not stimulated. This means that glutamate is released continuously when the cell is unstimulated, and stimulus causes release to stop. In the dark, cells have a relatively high concentration of
613:. These channels are nonspecific, allowing movement of both sodium and calcium ions when open. The movement of these positively charged ions into the cell (driven by their respective
2148:
946:
168:
941:
1616:
678:
Every rod or cone photoreceptor releases the same neurotransmitter, glutamate. However, the effect of glutamate differs in the bipolar cells, depending upon the type of
1888:
100:
690:, the bipolar cell will depolarize (and therefore will hyperpolarize with light as less glutamate is released). On the other hand, binding of glutamate to a
1885:
1886:
1090:
Foster, R.G.; Provencio, I.; Hudson, D.; Fiske, S.; Grip, W.; Menaker, M. (1991). "Circadian photoreception in the retinally degenerate mouse (rd/rd)".
606:
1891:
2457:
553:
PDE then catalyzes the hydrolysis of cGMP to 5' GMP. This is the second amplification step, where a single PDE hydrolyses about 1000 cGMP molecules.
1900:
610:
372:. Three different classes of photopsins in the cones react to different ranges of light frequency, a selectivity that allows the visual system to
1887:
219:
expressed in that cell. Humans have three classes of cones (L, M, S) that each differ in spectral sensitivity and 'prefer' photons of different
1892:
429:
Most vertebrate photoreceptors are located in the retina. The distribution of rods and cones (and classes thereof) in the retina is called the
1872:
1748:
1317:
1878:
1717:
390:. These cells are involved in various reflexive responses of the brain and body to the presence of (day)light, such as the regulation of
468:, have a tremendous number of rods in their retinae. Other vertebrates will also have a different number of cone classes, ranging from
989:
ganglion cells, and the study of the receptor offered potential as a new avenue to explore in trying to find treatments for blindness.
1721:
659:) transmit to the bipolar cells, which transmit then to the retinal ganglion cells. Retinal ganglion cell axons collectively form the
1348:
437:
has approximately 6 million cones and 120 million rods. At the "center" of the retina (the point directly behind the lens) lies the
1689:
1664:
1393:
1186:
1199:
Richardson, T.M. (1969). "Cytoplasmic and ciliary connections between the inner and outer segments of mammalian visual receptors".
1883:
539:, and activates it. This is the first amplification step – each photoactivated opsin triggers activation of about 100 transducins.
3081:
3011:
107:
1599:
1080:"eye, human." Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Ultimate Reference Suite. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica, 2010.
3076:
3006:
2621:
1876:
1580:
1895:
1894:
1624:
31:
1875:
1711:
984:
of the receptor is between 460 and 482 nm. However, they may also contribute to a rudimentary visual pathway enabling
2696:
1874:
95:
1014:
are different in both their morphological organization and their underlying biochemical pathways. This article describes
3286:
2691:
2679:
2450:
2394:
2339:
2307:
2144:
1047:
771:
1882:
2731:
2669:
2292:
2261:
2253:
1933:
598:
561:
1893:
1884:
1881:
1522:"Short-wavelength light sensitivity of circadian, pupillary, and visual awareness in humans lacking an outer retina"
3276:
2726:
2088:
2078:
1057:
1032:
1003:
1890:
1889:
3236:
3086:
3021:
2649:
1873:
1741:
499:
141:
3016:
2742:
1896:
1770:
1027:
687:
614:
493:
227:
137:
70:
1282:
694:
results in a hyperpolarization, so this bipolar cell will depolarize to light as less glutamate is released.
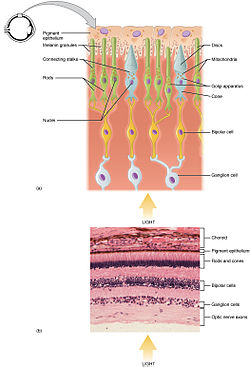
282:; they both have the same basic structure. Closest to the visual field (and farthest from the brain) is the
2715:
2443:
2083:
2039:
1897:
920:
679:
560:
As a result, sodium ions can no longer enter the cell, and the photoreceptor outer segment membrane becomes
521:
511:
3183:
2710:
2474:
2223:
2116:
1847:
977:
581:
315:
441:(or fovea centralis), which contains only cone cells; and is the region capable of producing the highest
3041:
3031:
2966:
2399:
2204:
2128:
2066:
2054:
2009:
950:
806:
719:
691:
456:
The number and ratio of rods to cones varies among species, dependent on whether an animal is primarily
346:
319:
216:
145:
1899:
961:, a light-sensitive protein. Therefore they constitute a third class of photoreceptors, in addition to
449:. Across the rest of the retina, rods and cones are intermingled. No photoreceptors are found at the
425:
Distribution of rods and cones along a line passing through the fovea and the blind spot of a human eye
368:. In cone cells, there are different types of opsins that combine with retinal to form pigments called
326:(and farthest from the field of view) is the outer segment, the part of the photoreceptor that absorbs
1880:
506:. The steps that apply to the phototransductuion pathway from vertebrate rod/cone photoreceptors are:
3166:
3063:
2993:
2819:
2674:
2389:
1734:
1533:
981:
929:
925:
728:
212:
129:
1898:
421:
171:. The two classic photoreceptor cells are rods and cones, each contributing information used by the
3206:
3051:
3046:
2581:
2514:
2414:
2120:
2071:
2059:
2049:
2004:
1938:
1901:
1852:
1799:
667:
Absorption of a photon will hyperpolarize the photoreceptor and therefore result in the release of
624:
Unstimulated (in the dark), cyclic-nucleotide gated channels in the outer segment are open because
450:
380:
373:
1879:
3281:
3211:
3142:
3111:
3101:
3096:
3091:
3036:
2812:
2722:
2576:
2384:
2164:
2160:
2156:
1827:
1448:
1411:"Transcriptional Regulation of Photoreceptor Development and Homeostasis in the Mammalian Retina"
1115:
446:
153:
1943:
1794:
398:
and other non-visual responses to light. Melanopsin functionally resembles invertebrate opsins.
1597:
Normal
Responses To Non-visual Effects Of Light Retained By Blind Humans Lacking Rods And Cones
3226:
3216:
3201:
3106:
2971:
2752:
2704:
2509:
2504:
2424:
2140:
2044:
1961:
1877:
1832:
1758:
1685:
1681:
1675:
1660:
1559:
1497:
1440:
1389:
1313:
1265:
1216:
1182:
1164:
1107:
703:
636:
547:
176:
3193:
3156:
3151:
2499:
2409:
2347:
2184:
1837:
1789:
1549:
1541:
1487:
1479:
1430:
1422:
1255:
1247:
1208:
1154:
1146:
1099:
699:
640:
524:
inside the protein from the cis-form to the trans-form, causing the retinal to change shape.
514:
in the disc membrane of the outer segment absorbs a photon, changing the configuration of a
395:
391:
287:
192:
188:
386:
The opsin found in the intrinsically photosensitive ganglion cells of the retina is called
2961:
2930:
2925:
2807:
2802:
2626:
2322:
2281:
2277:
2199:
1603:
1385:
1379:
1356:
1309:
1303:
1052:
976:
the ipRGCs contribute to non-image-forming functions like circadian rhythms, behavior and
846:
840:
824:
818:
797:
790:
532:
527:
This results in a series of unstable intermediates, the last of which binds stronger to a
438:
184:
180:
1726:
1537:
1435:
140:. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (visible
3251:
3221:
3178:
2998:
2956:
2934:
2854:
2737:
2561:
2466:
2327:
2317:
2302:
2297:
1994:
1986:
1966:
1842:
1817:
1656:
1650:
1554:
1521:
1492:
1467:
1260:
1235:
1159:
1134:
1042:
1037:
954:
893:
886:
707:
602:
457:
407:
339:
307:
299:
203:
30:
This article is about cellular photoreceptors. For other types of photoreceptors, see
3270:
2900:
2885:
2566:
2352:
2287:
2124:
1596:
1212:
1062:
683:
442:
311:
172:
484:
3146:
3068:
2981:
2862:
2792:
2571:
2494:
2312:
2136:
1971:
1953:
1452:
1150:
1119:
577:
473:
295:
231:
46:
1251:
88:
75:
3161:
2976:
2880:
2838:
2770:
2765:
2586:
2524:
2519:
2489:
2404:
2273:
2230:
2168:
2132:
766:
738:
there is a lot of amplification in two stages of classic phototransduction: one
672:
660:
518:
503:
469:
220:
159:
There are currently three known types of photoreceptor cells in mammalian eyes:
1483:
3231:
2920:
2797:
2760:
2218:
1976:
1545:
966:
958:
743:
625:
536:
387:
17:
617:) depolarizes the membrane, and leads to the release of the neurotransmitter
207:
Normalized human photoreceptor absorbances for different wavelengths of light
144:) into signals that can stimulate biological processes. To be more specific,
3246:
2780:
2631:
2604:
2596:
2194:
2189:
2108:
1762:
985:
962:
756:
732:
618:
573:
528:
488:
The absorption of light leads to an isomeric change in the retinal molecule.
465:
461:
369:
365:
303:
291:
275:
164:
56:
1563:
1501:
1444:
1269:
869:
Stacks of membrane-enclosed disks are unattached to cell membrane directly
1706:
1220:
1168:
1111:
256:
2910:
2895:
2890:
2614:
2609:
2536:
2531:
2112:
760:
271:
160:
82:
52:
412:
59:, which are two of the three types of photosensitive cells in the retina
3173:
3134:
2364:
2265:
2209:
1925:
1103:
1011:
739:
515:
360:
355:
247:
1181:
Human
Physiology and Mechanisms of Disease by Arthur C. Guyton (1992)
113:
2833:
2788:
2553:
2359:
2269:
2023:
1809:
1781:
1007:
629:
543:
434:
306:. Farther back still is the inner segment, a specialized part of the
279:
149:
133:
1426:
1410:
718:
Phototransduction in rods and cones is somewhat unusual in that the
856:
Fast response to light, can perceive more rapid changes in stimuli
597:
Unlike most sensory receptor cells, photoreceptors actually become
1999:
1015:
973:
483:
376:
350:
335:
331:
327:
323:
202:
2435:
1617:"Scientists document light-sensitive birds eye within bird brain"
864:
Have less pigment than rods, require more light to detect images
3026:
2872:
1913:
628:(cGMP) is bound to them. Hence, positively charged ions (namely
283:
2439:
1730:
1680:(2nd ed.). Englewood Cliffs, N.J: Prentice Hall. pp.
861:
Have more pigment than cones, so can detect lower light levels
564:, due to the charge inside the membrane becoming more negative.
632:
338:, the molecule that absorbs photons, as well as voltage-gated
639:
in other nerve cells is usually −65 mV). This depolarization
1867:
1409:
Swaroop, Anand; Douglas Kim; Douglas
Forrest (August 2010).
635:) enter the photoreceptor, depolarizing it to about −40 mV (
1236:"Cilia in the CNS: The quiet organelle claims center stage"
953:, unlike other retinal ganglion cells, are intrinsically
812:
Not very light sensitive; sensitive only to direct light
314:. The chief function of the inner segment is to provide
278:
photoreceptors are found on the outermost layer of the
1468:"Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells"
1378:
Kandel, E. R.; Schwartz, J.H.; Jessell, T.M. (2000).
1135:"Visual pigments of rods and cones in a human retina"
1002:
absence of input from the eyes or neurotransmitters.
877:
About 120 million rods distributed around the retina
3192:
3133:
3126:
3062:
2992:
2949:
2909:
2871:
2853:
2846:
2832:
2779:
2751:
2657:
2648:
2595:
2552:
2545:
2482:
2473:
2377:
2338:
2252:
2243:
2177:
2097:
2032:
2022:
1985:
1952:
1924:
1912:
1808:
1780:
1769:
1515:
1513:
1511:
947:
Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells
169:
intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells
94:
81:
69:
64:
39:
942:Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cell
211:Each photoreceptor absorbs light according to its
880:About 6 million cones distributed in each retina
183:(dim conditions) whereas cones primarily mediate
1384:(4th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. pp.
853:Slow response to light, stimuli added over time
498:The path of a visual signal is described by the
1871:
1649:Campbell, Neil A. & Reece, Jane B. (2002).
1583:. New Scientist, 26 December 2007, issue 2635.
834:High visual acuity; better spatial resolution
2451:
1742:
1655:. San Francisco: Benjamin Cummings. pp.
1297:
1295:
1293:
1291:
765:Comparison of human rod and cone cells, from
8:
1133:Bowmaker J.K. & Dartnall H.J.A. (1980).
3130:
2850:
2843:
2654:
2549:
2479:
2458:
2444:
2436:
2249:
2029:
1921:
1777:
1749:
1735:
1727:
364:. In rod cells, these together are called
265:Anatomy of rods and cones varies slightly.
215:(absorptance), which is determined by the
45:
1553:
1491:
1434:
1259:
1158:
777:
420:
411:
1308:. New York: Worth Publishers. pp.
1073:
663:, via which they project to the brain.
330:. Outer segments are actually modified
1591:
1589:
1575:
1573:
464:. Certain owls, such as the nocturnal
111:
36:
1581:Blind people 'see' sunrise and sunset
932:or other visual deficits may result.
872:Disks are attached to outer membrane
800:(vision under high light conditions)
175:to form an image of the environment,
7:
793:(vision under low light conditions)
607:cyclic guanosine 3'-5' monophosphate
601:when stimulated; and conversely are
152:, triggering a change in the cell's
1337:(7 ed.). Thomson and Wadswoth.
1092:Journal of Comparative Physiology A
542:Each transducin then activates the
1722:Neuroscience Information Framework
25:
1355:. World Owl Trust. Archived from
949:(ipRGCs) are a subset (≈1–3%) of
751:Difference between rods and cones
576:, which excites the postsynaptic
1705:
1234:Louvi, A.; Grove, E. A. (2011).
742:will activate many molecules of
643:is often known as dark current.
255:
246:
108:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
2622:Oligodendrocyte progenitor cell
1718:NIF Search – Photoreceptor Cell
809:; sensitive to scattered light
334:that contain disks filled with
1520:Zaidi FH, et al. (2007).
1466:Do MT, Yau KW (October 2010).
1151:10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013097
675:terminal to the bipolar cell.
32:Photoreceptor (disambiguation)
1:
686:. When glutamate binds to an
2395:Optical coherence tomography
2149:Photosensitive ganglion cell
1623:. Birds News. Archived from
1381:Principles of Neural Science
1333:Goldstein, E. Bruce (2007).
1302:Schacter, Daniel L. (2011).
1252:10.1016/j.neuron.2011.03.002
1213:10.1016/0042-6989(69)90010-8
1048:Photosensitive ganglion cell
936:Ganglion cell photoreceptors
772:Principles of Neural Science
302:, which contains the cell's
27:Type of neuroepithelial cell
2732:Postganglionic nerve fibers
2145:Giant retina ganglion cells
1934:Capillary lamina of choroid
1415:Nature Reviews Neuroscience
1004:Invertebrate photoreceptors
286:terminal, which releases a
3303:
2727:Preganglionic nerve fibers
2089:Retinal pigment epithelium
2079:External limiting membrane
1484:10.1152/physrev.00013.2010
1033:G protein-coupled receptor
939:
754:
491:
405:
322:. Finally, closest to the
29:
3237:Olfactory receptor neuron
2901:Neurofibril/neurofilament
1865:
1546:10.1016/j.cub.2007.11.034
1305:Psychology Second Edition
901:Confer achromatic vision
500:phototransduction cascade
179:. Rods primarily mediate
142:electromagnetic radiation
128:is a specialized type of
106:
44:
1335:Sensation and Perception
1028:Visual phototransduction
997:Non-human photoreceptors
615:electrochemical gradient
494:Visual phototransduction
228:principle of univariance
138:visual phototransduction
51:Functional parts of the
2084:Layer of rods and cones
2040:Inner limiting membrane
1674:Freeman, Scott (2002).
957:due to the presence of
611:cGMP-gated ion channels
512:Vertebrate visual opsin
226:In accordance with the
3184:Neuromuscular junction
3047:III or Aδ or fast pain
1906:
978:pupillary light reflex
951:retinal ganglion cells
489:
426:
418:
298:. Farther back is the
217:photoreceptor proteins
208:
146:photoreceptor proteins
2400:Eye care professional
2205:Foveal avascular zone
2067:Outer plexiform layer
2055:Inner plexiform layer
2010:Iris sphincter muscle
1903:
1472:Physiological Reviews
1349:"Owl Eye Information"
1283:Foundations of Vision
1006:in organisms such as
692:metabotropic receptor
487:
424:
415:
347:photoreceptor protein
320:sodium-potassium pump
206:
3202:Meissner's corpuscle
3167:Postsynaptic density
3064:Efferent nerve fiber
3052:IV or C or slow pain
2994:Afferent nerve fiber
2820:Satellite glial cell
2420:Physiological Optics
2390:Ocular immune system
2129:Retina ganglion cell
1714:at Wikimedia Commons
1595:Medical News Today.
982:spectral sensitivity
930:macular degeneration
926:retinitis pigmentosa
904:Confer color vision
651:The photoreceptors (
609:(cGMP), which opens
213:spectral sensitivity
130:neuroepithelial cell
3287:Photoreceptor cells
3207:Merkel nerve ending
2244:Anatomical regions
2105:Photoreceptor cells
2072:Outer nuclear layer
2060:Inner nuclear layer
2050:Ganglion cell layer
2005:Iris dilator muscle
1800:Trabecular meshwork
1712:Photoreceptor cells
1606:. 14 December 2007.
1538:2007CBio...17.2122Z
1359:on 16 February 2018
688:ionotropic receptor
381:signal transduction
148:in the cell absorb
136:that is capable of
3242:Photoreceptor cell
3212:Pacinian corpuscle
3143:Electrical synapse
3097:Lower motor neuron
3092:Upper motor neuron
2813:Internodal segment
2753:Connective tissues
2723:Autonomic ganglion
1907:
1677:Biological Science
1602:2009-02-06 at the
1285:, Brian A. Wandell
1104:10.1007/BF00198171
896:pigment in humans
831:Low visual acuity
490:
427:
419:
209:
154:membrane potential
126:photoreceptor cell
101:85613 86740, 85613
40:Photoreceptor cell
3277:Human eye anatomy
3264:
3263:
3260:
3259:
3227:Free nerve ending
3194:Sensory receptors
3122:
3121:
3037:Ib or Golgi or Aα
2945:
2944:
2828:
2827:
2705:Ramus communicans
2644:
2643:
2640:
2639:
2510:Commissural fiber
2505:Association fiber
2500:Projection fibers
2433:
2432:
2425:Visual perception
2373:
2372:
2340:Posterior segment
2308:Posterior chamber
2239:
2238:
2141:Bistratified cell
2045:Nerve fiber layer
2018:
2017:
1962:Ciliary processes
1863:
1862:
1710:Media related to
1319:978-1-4292-3719-2
908:
907:
682:imbedded in that
671:glutamate at the
637:resting potential
593:Hyperpolarization
548:phosphodiesterase
392:circadian rhythms
318:(energy) for the
122:
121:
117:
16:(Redirected from
3294:
3157:Synaptic vesicle
3152:Chemical synapse
3131:
2851:
2844:
2655:
2550:
2480:
2460:
2453:
2446:
2437:
2410:Refractive error
2348:Vitreous chamber
2293:Anterior chamber
2254:Anterior segment
2250:
2030:
1939:Bruch's membrane
1922:
1914:Uvea / vascular
1870:
1790:Episcleral layer
1778:
1751:
1744:
1737:
1728:
1709:
1695:
1670:
1637:
1636:
1634:
1632:
1613:
1607:
1593:
1584:
1577:
1568:
1567:
1557:
1517:
1506:
1505:
1495:
1463:
1457:
1456:
1438:
1406:
1400:
1399:
1375:
1369:
1368:
1366:
1364:
1345:
1339:
1338:
1330:
1324:
1323:
1299:
1286:
1280:
1274:
1273:
1263:
1246:(6): 1046–1060.
1231:
1225:
1224:
1196:
1190:
1179:
1173:
1172:
1162:
1130:
1124:
1123:
1087:
1081:
1078:
1018:photoreceptors.
845:Concentrated in
778:
582:horizontal cells
396:pupillary reflex
358:molecule called
288:neurotransmitter
259:
250:
199:Photosensitivity
193:pupillary reflex
189:circadian rhythm
114:edit on Wikidata
49:
37:
21:
3302:
3301:
3297:
3296:
3295:
3293:
3292:
3291:
3267:
3266:
3265:
3256:
3188:
3118:
3067:
3058:
3042:II or Aβ and Aγ
2997:
2988:
2941:
2931:Apical dendrite
2926:Dendritic spine
2905:
2867:
2837:
2824:
2808:Node of Ranvier
2803:Myelin incisure
2775:
2747:
2636:
2627:Oligodendrocyte
2610:Ependymal cells
2591:
2541:
2469:
2464:
2434:
2429:
2369:
2334:
2323:Capsule of lens
2278:Lacrimal system
2245:
2235:
2195:Parafoveal area
2190:Perifoveal area
2173:
2117:Horizontal cell
2093:
2014:
1981:
1948:
1944:Sattler's layer
1915:
1908:
1902:
1859:
1804:
1795:Schlemm's canal
1773:
1765:
1757:Anatomy of the
1755:
1702:
1692:
1673:
1667:
1648:
1645:
1640:
1630:
1628:
1615:
1614:
1610:
1604:Wayback Machine
1594:
1587:
1578:
1571:
1526:Current Biology
1519:
1518:
1509:
1465:
1464:
1460:
1427:10.1038/nrn2880
1408:
1407:
1403:
1396:
1377:
1376:
1372:
1362:
1360:
1347:
1346:
1342:
1332:
1331:
1327:
1320:
1301:
1300:
1289:
1281:
1277:
1233:
1232:
1228:
1201:Vision Research
1198:
1197:
1193:
1180:
1176:
1132:
1131:
1127:
1089:
1088:
1084:
1079:
1075:
1071:
1053:Horizontal cell
1024:
999:
944:
938:
913:
892:Three types of
839:Not present in
825:legal blindness
819:night blindness
798:photopic vision
791:scotopic vision
763:
755:Main articles:
753:
716:
700:detecting color
684:cell's membrane
649:
595:
496:
482:
410:
404:
345:The membranous
340:sodium channels
269:
268:
267:
266:
262:
261:
260:
252:
251:
240:
201:
185:photopic vision
181:scotopic vision
118:
60:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
3300:
3298:
3290:
3289:
3284:
3279:
3269:
3268:
3262:
3261:
3258:
3257:
3255:
3254:
3252:Taste receptor
3249:
3244:
3239:
3234:
3229:
3224:
3222:Muscle spindle
3219:
3217:Ruffini ending
3214:
3209:
3204:
3198:
3196:
3190:
3189:
3187:
3186:
3181:
3179:Ribbon synapse
3176:
3171:
3170:
3169:
3164:
3159:
3149:
3139:
3137:
3128:
3124:
3123:
3120:
3119:
3117:
3116:
3115:
3114:
3109:
3104:
3094:
3089:
3084:
3079:
3073:
3071:
3060:
3059:
3057:
3056:
3055:
3054:
3049:
3044:
3039:
3034:
3024:
3019:
3014:
3009:
3003:
3001:
2999:Sensory neuron
2990:
2989:
2987:
2986:
2985:
2984:
2974:
2969:
2967:Pseudounipolar
2964:
2959:
2953:
2951:
2947:
2946:
2943:
2942:
2940:
2939:
2938:
2937:
2935:Basal dendrite
2928:
2923:
2915:
2913:
2907:
2906:
2904:
2903:
2898:
2893:
2888:
2886:Axon terminals
2883:
2877:
2875:
2869:
2868:
2866:
2865:
2859:
2857:
2848:
2841:
2830:
2829:
2826:
2825:
2823:
2822:
2817:
2816:
2815:
2810:
2805:
2800:
2785:
2783:
2777:
2776:
2774:
2773:
2768:
2763:
2757:
2755:
2749:
2748:
2746:
2745:
2740:
2738:Nerve fascicle
2735:
2729:
2720:
2719:
2718:
2713:
2701:
2700:
2699:
2694:
2684:
2683:
2682:
2677:
2672:
2661:
2659:
2652:
2646:
2645:
2642:
2641:
2638:
2637:
2635:
2634:
2629:
2624:
2619:
2618:
2617:
2607:
2601:
2599:
2593:
2592:
2590:
2589:
2584:
2579:
2574:
2569:
2564:
2558:
2556:
2547:
2543:
2542:
2540:
2539:
2534:
2529:
2528:
2527:
2522:
2517:
2512:
2507:
2502:
2492:
2486:
2484:
2477:
2471:
2470:
2467:Nervous tissue
2465:
2463:
2462:
2455:
2448:
2440:
2431:
2430:
2428:
2427:
2422:
2417:
2412:
2407:
2402:
2397:
2392:
2387:
2381:
2379:
2375:
2374:
2371:
2370:
2368:
2367:
2362:
2357:
2356:
2355:
2344:
2342:
2336:
2335:
2333:
2332:
2331:
2330:
2328:Zonule of Zinn
2325:
2315:
2310:
2305:
2300:
2298:Aqueous humour
2295:
2290:
2285:
2258:
2256:
2247:
2241:
2240:
2237:
2236:
2234:
2233:
2228:
2227:
2226:
2216:
2215:
2214:
2213:
2212:
2207:
2197:
2192:
2181:
2179:
2175:
2174:
2172:
2171:
2101:
2099:
2095:
2094:
2092:
2091:
2086:
2081:
2075:
2074:
2069:
2063:
2062:
2057:
2052:
2047:
2042:
2036:
2034:
2027:
2020:
2019:
2016:
2015:
2013:
2012:
2007:
2002:
1997:
1991:
1989:
1983:
1982:
1980:
1979:
1974:
1969:
1967:Ciliary muscle
1964:
1958:
1956:
1950:
1949:
1947:
1946:
1941:
1936:
1930:
1928:
1919:
1910:
1909:
1866:
1864:
1861:
1860:
1858:
1857:
1856:
1855:
1850:
1845:
1840:
1835:
1830:
1820:
1814:
1812:
1806:
1805:
1803:
1802:
1797:
1792:
1786:
1784:
1775:
1767:
1766:
1756:
1754:
1753:
1746:
1739:
1731:
1725:
1724:
1715:
1701:
1700:External links
1698:
1697:
1696:
1690:
1671:
1665:
1644:
1641:
1639:
1638:
1627:on 2 July 2017
1608:
1585:
1569:
1532:(24): 2122–8.
1507:
1478:(4): 1547–81.
1458:
1421:(8): 563–576.
1401:
1394:
1370:
1340:
1325:
1318:
1287:
1275:
1226:
1207:(7): 727–731.
1191:
1174:
1125:
1082:
1072:
1070:
1067:
1066:
1065:
1060:
1055:
1050:
1045:
1043:Photosensitive
1040:
1038:Sensory system
1035:
1030:
1023:
1020:
998:
995:
955:photosensitive
940:Main article:
937:
934:
912:
909:
906:
905:
902:
898:
897:
894:photosensitive
890:
887:photosensitive
882:
881:
878:
874:
873:
870:
866:
865:
862:
858:
857:
854:
850:
849:
843:
836:
835:
832:
828:
827:
821:
814:
813:
810:
802:
801:
794:
786:
785:
782:
752:
749:
748:
747:
736:
715:
712:
648:
645:
599:hyperpolarized
594:
591:
590:
589:
585:
569:
565:
562:hyperpolarized
558:
554:
551:
546:cGMP-specific
540:
525:
492:Main article:
481:
478:
431:retinal mosaic
408:Retinal mosaic
406:Main article:
403:
402:Retinal mosaic
400:
264:
263:
254:
253:
245:
244:
243:
242:
241:
239:
236:
200:
197:
120:
119:
110:
104:
103:
98:
92:
91:
86:
79:
78:
73:
67:
66:
62:
61:
50:
42:
41:
26:
24:
18:Photoreception
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3299:
3288:
3285:
3283:
3280:
3278:
3275:
3274:
3272:
3253:
3250:
3248:
3245:
3243:
3240:
3238:
3235:
3233:
3230:
3228:
3225:
3223:
3220:
3218:
3215:
3213:
3210:
3208:
3205:
3203:
3200:
3199:
3197:
3195:
3191:
3185:
3182:
3180:
3177:
3175:
3172:
3168:
3165:
3163:
3160:
3158:
3155:
3154:
3153:
3150:
3148:
3144:
3141:
3140:
3138:
3136:
3132:
3129:
3125:
3113:
3112:γ motorneuron
3110:
3108:
3107:β motorneuron
3105:
3103:
3102:α motorneuron
3100:
3099:
3098:
3095:
3093:
3090:
3088:
3085:
3083:
3080:
3078:
3075:
3074:
3072:
3070:
3065:
3061:
3053:
3050:
3048:
3045:
3043:
3040:
3038:
3035:
3033:
3030:
3029:
3028:
3025:
3023:
3020:
3018:
3015:
3013:
3010:
3008:
3005:
3004:
3002:
3000:
2995:
2991:
2983:
2980:
2979:
2978:
2975:
2973:
2970:
2968:
2965:
2963:
2960:
2958:
2955:
2954:
2952:
2948:
2936:
2932:
2929:
2927:
2924:
2922:
2919:
2918:
2917:
2916:
2914:
2912:
2908:
2902:
2899:
2897:
2894:
2892:
2889:
2887:
2884:
2882:
2879:
2878:
2876:
2874:
2870:
2864:
2861:
2860:
2858:
2856:
2852:
2849:
2845:
2842:
2840:
2835:
2831:
2821:
2818:
2814:
2811:
2809:
2806:
2804:
2801:
2799:
2796:
2795:
2794:
2790:
2787:
2786:
2784:
2782:
2778:
2772:
2769:
2767:
2764:
2762:
2759:
2758:
2756:
2754:
2750:
2744:
2741:
2739:
2736:
2733:
2730:
2728:
2724:
2721:
2717:
2714:
2712:
2709:
2708:
2707:
2706:
2702:
2698:
2695:
2693:
2690:
2689:
2688:
2685:
2681:
2678:
2676:
2673:
2671:
2668:
2667:
2666:
2663:
2662:
2660:
2656:
2653:
2651:
2647:
2633:
2630:
2628:
2625:
2623:
2620:
2616:
2613:
2612:
2611:
2608:
2606:
2603:
2602:
2600:
2598:
2594:
2588:
2585:
2583:
2580:
2578:
2575:
2573:
2570:
2568:
2565:
2563:
2560:
2559:
2557:
2555:
2551:
2548:
2544:
2538:
2535:
2533:
2530:
2526:
2523:
2521:
2518:
2516:
2513:
2511:
2508:
2506:
2503:
2501:
2498:
2497:
2496:
2493:
2491:
2488:
2487:
2485:
2481:
2478:
2476:
2472:
2468:
2461:
2456:
2454:
2449:
2447:
2442:
2441:
2438:
2426:
2423:
2421:
2418:
2416:
2415:Accommodation
2413:
2411:
2408:
2406:
2403:
2401:
2398:
2396:
2393:
2391:
2388:
2386:
2383:
2382:
2380:
2376:
2366:
2363:
2361:
2358:
2354:
2353:Vitreous body
2351:
2350:
2349:
2346:
2345:
2343:
2341:
2337:
2329:
2326:
2324:
2321:
2320:
2319:
2316:
2314:
2311:
2309:
2306:
2304:
2301:
2299:
2296:
2294:
2291:
2289:
2288:Fibrous tunic
2286:
2283:
2279:
2275:
2271:
2267:
2263:
2260:
2259:
2257:
2255:
2251:
2248:
2242:
2232:
2229:
2225:
2222:
2221:
2220:
2217:
2211:
2208:
2206:
2203:
2202:
2201:
2198:
2196:
2193:
2191:
2188:
2187:
2186:
2183:
2182:
2180:
2176:
2170:
2166:
2162:
2158:
2154:
2150:
2146:
2142:
2138:
2134:
2130:
2126:
2125:Amacrine cell
2122:
2118:
2114:
2110:
2106:
2103:
2102:
2100:
2096:
2090:
2087:
2085:
2082:
2080:
2077:
2076:
2073:
2070:
2068:
2065:
2064:
2061:
2058:
2056:
2053:
2051:
2048:
2046:
2043:
2041:
2038:
2037:
2035:
2031:
2028:
2025:
2021:
2011:
2008:
2006:
2003:
2001:
1998:
1996:
1993:
1992:
1990:
1988:
1984:
1978:
1975:
1973:
1970:
1968:
1965:
1963:
1960:
1959:
1957:
1955:
1951:
1945:
1942:
1940:
1937:
1935:
1932:
1931:
1929:
1927:
1923:
1920:
1917:
1911:
1854:
1851:
1849:
1846:
1844:
1841:
1839:
1836:
1834:
1831:
1829:
1826:
1825:
1824:
1821:
1819:
1816:
1815:
1813:
1811:
1807:
1801:
1798:
1796:
1793:
1791:
1788:
1787:
1785:
1783:
1779:
1776:
1772:
1771:Fibrous tunic
1768:
1764:
1760:
1752:
1747:
1745:
1740:
1738:
1733:
1732:
1729:
1723:
1719:
1716:
1713:
1708:
1704:
1703:
1699:
1693:
1691:0-13-140941-7
1687:
1683:
1679:
1678:
1672:
1668:
1666:0-8053-6624-5
1662:
1658:
1654:
1653:
1647:
1646:
1642:
1626:
1622:
1621:birdsnews.com
1618:
1612:
1609:
1605:
1601:
1598:
1592:
1590:
1586:
1582:
1576:
1574:
1570:
1565:
1561:
1556:
1551:
1547:
1543:
1539:
1535:
1531:
1527:
1523:
1516:
1514:
1512:
1508:
1503:
1499:
1494:
1489:
1485:
1481:
1477:
1473:
1469:
1462:
1459:
1454:
1450:
1446:
1442:
1437:
1432:
1428:
1424:
1420:
1416:
1412:
1405:
1402:
1397:
1395:0-8385-7701-6
1391:
1387:
1383:
1382:
1374:
1371:
1358:
1354:
1350:
1344:
1341:
1336:
1329:
1326:
1321:
1315:
1311:
1307:
1306:
1298:
1296:
1294:
1292:
1288:
1284:
1279:
1276:
1271:
1267:
1262:
1257:
1253:
1249:
1245:
1241:
1237:
1230:
1227:
1222:
1218:
1214:
1210:
1206:
1202:
1195:
1192:
1188:
1187:0-7216-3299-8
1184:
1178:
1175:
1170:
1166:
1161:
1156:
1152:
1148:
1144:
1140:
1136:
1129:
1126:
1121:
1117:
1113:
1109:
1105:
1101:
1097:
1093:
1086:
1083:
1077:
1074:
1068:
1064:
1063:Amacrine cell
1061:
1059:
1056:
1054:
1051:
1049:
1046:
1044:
1041:
1039:
1036:
1034:
1031:
1029:
1026:
1025:
1021:
1019:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1005:
996:
994:
990:
987:
983:
979:
975:
970:
968:
964:
960:
956:
952:
948:
943:
935:
933:
931:
927:
922:
917:
910:
903:
900:
899:
895:
891:
888:
884:
883:
879:
876:
875:
871:
868:
867:
863:
860:
859:
855:
852:
851:
848:
844:
842:
838:
837:
833:
830:
829:
826:
822:
820:
816:
815:
811:
808:
804:
803:
799:
795:
792:
788:
787:
783:
780:
779:
776:
774:
773:
768:
762:
758:
750:
745:
741:
737:
734:
730:
725:
724:
723:
721:
713:
711:
709:
705:
701:
695:
693:
689:
685:
681:
676:
674:
670:
664:
662:
658:
654:
647:Bipolar cells
646:
644:
642:
638:
634:
631:
627:
622:
620:
616:
612:
608:
604:
600:
592:
586:
583:
579:
578:bipolar cells
575:
570:
566:
563:
559:
555:
552:
549:
545:
541:
538:
534:
530:
526:
523:
520:
517:
513:
509:
508:
507:
505:
501:
495:
486:
479:
477:
475:
474:pentachromats
471:
467:
463:
459:
454:
452:
448:
444:
443:visual acuity
440:
436:
433:. Each human
432:
423:
414:
409:
401:
399:
397:
393:
389:
384:
382:
378:
375:
371:
367:
363:
362:
357:
353:
352:
348:
343:
341:
337:
333:
329:
325:
321:
317:
313:
309:
305:
301:
297:
296:bipolar cells
293:
289:
285:
281:
277:
273:
258:
249:
237:
235:
233:
229:
224:
222:
218:
214:
205:
198:
196:
194:
190:
186:
182:
178:
174:
173:visual system
170:
166:
162:
157:
155:
151:
147:
143:
139:
135:
132:found in the
131:
127:
115:
109:
105:
102:
99:
97:
93:
90:
87:
84:
80:
77:
74:
72:
68:
63:
58:
54:
48:
43:
38:
33:
19:
3241:
3147:Gap junction
3069:Motor neuron
2863:Axon hillock
2839:nerve fibers
2793:Schwann cell
2703:
2686:
2664:
2582:Medium spiny
2495:White matter
2483:Tissue Types
2419:
2313:Ciliary body
2153:Diencephalon
2152:
2137:Parasol cell
2121:Bipolar cell
2104:
1972:Pars plicata
1954:Ciliary body
1822:
1676:
1651:
1643:Bibliography
1629:. Retrieved
1625:the original
1620:
1611:
1529:
1525:
1475:
1471:
1461:
1418:
1414:
1404:
1380:
1373:
1361:. Retrieved
1357:the original
1352:
1343:
1334:
1328:
1304:
1278:
1243:
1239:
1229:
1204:
1200:
1194:
1177:
1142:
1138:
1128:
1098:(1): 39–50.
1095:
1091:
1085:
1076:
1058:Bipolar cell
1000:
991:
971:
945:
918:
914:
885:One type of
823:Loss causes
817:Loss causes
770:
764:
717:
696:
677:
668:
665:
656:
652:
650:
623:
596:
497:
470:monochromats
455:
430:
428:
385:
359:
349:
344:
312:mitochondria
270:
232:color vision
225:
210:
158:
125:
123:
89:sao226523927
3162:Active zone
3127:Termination
2977:Interneuron
2881:Telodendron
2789:Myelination
2771:Endoneurium
2766:Perineurium
2587:Interneuron
2577:Von Economo
2525:Decussation
2520:Nerve tract
2490:Grey matter
2405:Eye disease
2385:Keratocytes
2274:Conjunctiva
2231:Ora serrata
2169:Muller glia
2133:Midget cell
1853:Endothelium
1843:Dua's layer
1579:Coghlan A.
1145:: 501–511.
911:Development
805:Very light
767:Eric Kandel
673:presynaptic
661:optic nerve
603:depolarized
519:Schiff base
504:optic nerve
445:or highest
354:contains a
221:wavelengths
65:Identifiers
3271:Categories
3232:Nociceptor
2972:Multipolar
2921:Nissl body
2798:Neurilemma
2761:Epineurium
2546:Cell Types
2246:of the eye
2219:Optic disc
1977:Pars plana
1848:Descemet's
1828:Epithelium
1139:J. Physiol
1069:References
967:cone cells
959:melanopsin
769:et al. in
744:transducin
714:Advantages
626:cyclic GMP
537:transducin
451:blind spot
447:resolution
388:melanopsin
370:photopsins
304:organelles
3282:Histology
3247:Hair cell
2781:Neuroglia
2743:Funiculus
2632:Microglia
2605:Astrocyte
2562:Pyramidal
2515:Lemniscus
2224:Optic cup
2109:Cone cell
1763:human eye
1657:1064–1067
986:conscious
807:sensitive
796:Used for
789:Used for
757:Cone cell
733:olfaction
619:glutamate
574:glutamate
557:membrane.
535:, called
529:G protein
480:Signaling
466:tawny owl
462:nocturnal
374:transduce
366:rhodopsin
300:cell body
292:glutamate
238:Histology
3032:Ia or Aα
2962:Unipolar
2911:Dendrite
2896:Axolemma
2891:Axoplasm
2675:Ganglion
2615:Tanycyte
2567:Purkinje
2554:Neuronal
2537:Meninges
2532:Neuropil
2113:Rod cell
1918:(middle)
1833:Bowman's
1720:via the
1600:Archived
1564:18082405
1502:20959623
1445:20648062
1436:11346175
1353:owls.org
1270:21435552
1022:See also
1012:molluscs
889:pigment
761:Rod cell
720:stimulus
704:contrast
680:receptor
533:membrane
522:cofactor
310:full of
191:and the
83:NeuroLex
3174:Autapse
3135:Synapse
2982:Renshaw
2957:Bipolar
2834:Neurons
2687:Ventral
2658:General
2572:Granule
2365:Choroid
2266:Eyebrow
2210:Foveola
2026:(inner)
1926:Choroid
1774:(outer)
1761:of the
1682:835–837
1652:Biology
1631:20 July
1555:2151130
1534:Bibcode
1493:4374737
1453:6034699
1386:507–513
1310:136–137
1261:3070490
1221:4979023
1169:7359434
1160:1279132
1120:1124159
1112:1941717
1008:insects
980:. Peak
740:pigment
710:, etc.
641:current
531:in the
516:retinal
458:diurnal
361:retinal
356:pigment
290:called
150:photons
76:D010786
3027:fibers
2665:Dorsal
2360:Retina
2270:Eyelid
2262:Adnexa
2185:Macula
2165:K cell
2161:M cell
2157:P cell
2033:Layers
2024:Retina
1995:Stroma
1838:Stroma
1823:layers
1818:Limbus
1810:Cornea
1782:Sclera
1688:
1663:
1562:
1552:
1500:
1490:
1451:
1443:
1433:
1392:
1316:
1268:
1258:
1240:Neuron
1219:
1189:p. 373
1185:
1167:
1157:
1118:
1110:
974:humans
919:Early
784:Cones
630:sodium
568:falls.
550:(PDE).
544:enzyme
435:retina
417:cones.
280:retina
167:, and
134:retina
2950:Types
2847:Parts
2716:White
2697:Ramus
2680:Ramus
2597:Glial
2378:Other
2282:Orbit
2200:Fovea
2178:Other
2115:) → (
2098:Cells
2000:Pupil
1916:tunic
1759:globe
1449:S2CID
1363:1 May
1116:S2CID
1016:human
921:Notch
847:fovea
841:fovea
781:Rods
729:touch
708:edges
657:cones
439:fovea
377:color
351:opsin
336:opsin
332:cilia
328:light
324:brain
177:sight
165:cones
112:[
57:cones
2873:Axon
2855:Soma
2711:Gray
2692:Root
2670:Root
2318:Lens
2303:Iris
2151:) →
2127:) →
2119:) →
1987:Iris
1686:ISBN
1661:ISBN
1633:2017
1560:PMID
1498:PMID
1441:PMID
1390:ISBN
1365:2017
1314:ISBN
1266:PMID
1217:PMID
1183:ISBN
1165:PMID
1108:PMID
1010:and
965:and
759:and
731:and
669:less
655:and
653:rods
633:ions
588:out.
580:and
510:The
308:cell
284:axon
276:cone
274:and
161:rods
71:MeSH
55:and
53:rods
3087:SVE
3082:GVE
3077:GSE
3022:SVA
3017:SSA
3012:GVA
3007:GSA
2650:PNS
2475:CNS
2123:→ (
1550:PMC
1542:doi
1488:PMC
1480:doi
1431:PMC
1423:doi
1256:PMC
1248:doi
1209:doi
1155:PMC
1147:doi
1143:298
1100:doi
1096:169
972:In
963:rod
472:to
460:or
316:ATP
294:to
272:Rod
96:FMA
3273::
2791::
2280:,
2276:,
2272:,
2268:,
2167:,
2163:,
2159:,
2155::
2147:,
2143:,
2139:,
2135:,
2111:,
1684:.
1659:.
1619:.
1588:^
1572:^
1558:.
1548:.
1540:.
1530:17
1528:.
1524:.
1510:^
1496:.
1486:.
1476:90
1474:.
1470:.
1447:.
1439:.
1429:.
1419:11
1417:.
1413:.
1388:.
1351:.
1312:.
1290:^
1264:.
1254:.
1244:69
1242:.
1238:.
1215:.
1203:.
1163:.
1153:.
1141:.
1137:.
1114:.
1106:.
1094:.
969:.
928:,
775:.
706:,
702:,
621:.
584:.)
476:.
394:,
383:.
342:.
234:.
195:.
163:,
156:.
124:A
85:ID
3145:/
3066:/
2996:/
2933:/
2836:/
2734:)
2725:(
2459:e
2452:t
2445:v
2284:)
2264:(
2131:(
2107:(
1750:e
1743:t
1736:v
1694:.
1669:.
1635:.
1566:.
1544::
1536::
1504:.
1482::
1455:.
1425::
1398:.
1367:.
1322:.
1272:.
1250::
1223:.
1211::
1205:9
1171:.
1149::
1122:.
1102::
735:.
116:]
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.