26:
506:(DRG) located in the medulla. Increased input from the pneumotaxic center decreases the duration and increases the frequency of bursts of activity in the DRG, producing shorter and more frequent inhalations. The apneustic center delays the end of a burst in the DRG, extending periods of inhalation.
473:
generated in the pontine tegmentum. They can be observed in mammals to precede the onset of REM sleep, and continue throughout its course. After periods of memory training, P-wave density increases during subsequent sleep periods in rats. This may be an indication of a link between
366:
of the ear, while the superior salivary nucleus controls the secretion of saliva and tears through parasympathetic innervation of structures including the lacrimal gland and the mucosal glands of the nose, palate, and pharynx. The facial
311:
Thanks to the number of different nuclei located within the pontine tegmentum, it is a region associated with a range of functions including sensory and motor functions (due to the cranial nuclei and fiber tracts), control of
382:, is located within the pons. The vestibular nuclei process information from the ear canals regarding the orientation and acceleration of the head. The remaining nuclei are located within the medulla.
437:. Recent research has discovered that the PPN is involved in the planning of movement, and that different networks of neurons in the PPN are switched on during real and imagined movement.
389:, which process auditory input from the cochlea, lie on the border of the pons and the medulla. Some of the fibers from the cochlear nerve cross over in the pontine tegmentum, forming the
303:, which are located further caudally in the brainstem. The dorsal respiratory group are connected to the pneumotaxic and apneustic centres of the pontine tegmentum.
1056:
124:
899:
332:
of the trigeminal nerve represents touch and position information of the head and face, but not the neck or back of the head, which are innervated by the
283:. Nearby important structures include the cranial nerve nuclei of the oculomotor (3rd) and trochlear (4th) nerve nuclei, which are located in the
1342:
324:
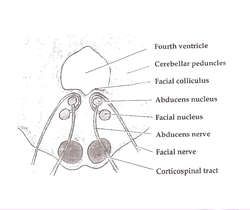
The pontine tegmentum contains nuclei of several cranial nerves and consequently has a role in several groups of sensory and motor processes.
100:
1337:
433:. While once thought important to the initiation of movement, recent research suggests a role in providing sensory feedback to the
1327:
1137:
938:
371:, which carries taste information from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue, is located caudal to the pontine tegmentum in the medulla.
131:
1128:
1048:
1332:
998:
960:
847:
407:
260:
204:
1013:
119:
316:
and levels of arousal and vigilance (due to the ascending cholinergic systems), and some aspects of respiratory control.
1196:
1008:
986:
456:
359:
165:
1191:
1092:
965:
375:
1277:
819:
358:
of the facial nerve are located within the pontine tegmentum. The facial motor nucleus serve motor control of the
1146:
1141:
1114:
1080:
1061:
991:
499:
444:. In animal studies, lesions of the pontine tegmentum greatly reduce or even eliminate REM sleep. Injection of a
355:
252:
196:
1203:
1166:
1118:
889:
503:
403:
300:
256:
200:
169:
58:
1186:
1075:
955:
933:
248:
577:
Woolf, NJ; Butcher, LL (2011). "Cholinergic systems mediate action from movement to higher consciousness".
336:. Pain and temperature information is also not represented within the principle nucleus, but rather in the
1282:
884:
107:
95:
1377:
1272:
1029:
1003:
232:
776:
Braun, AR; Balkin, TJ; Carson, RE; Varga, M; Baldwin, P; Selbie, S; Belenky, P; Herscovitch, P (1997).
25:
1354:
1225:
1123:
928:
459:
studies seem to indicate that there is a correlation between blood flow in the pontine tegmentum and
351:
192:
75:
1322:
1267:
1181:
272:
1176:
840:
707:
676:
602:
559:
491:
470:
280:
276:
268:
264:
220:
216:
212:
208:
1087:
950:
904:
799:
758:
699:
654:
594:
551:
534:
Alheid, GF; Milsom, WK; McCrimmon, DR (2004). "Pontine influences on breathing: an overview".
515:
430:
379:
177:
1262:
1171:
1132:
1070:
945:
789:
748:
738:
691:
644:
636:
586:
543:
495:
386:
368:
363:
344:
337:
329:
236:
185:
173:
1208:
894:
434:
296:
677:"Imagined gait modulates neuronal network dynamics in the human pedunculopontine nucleus"
1300:
1243:
923:
753:
726:
649:
624:
390:
288:
240:
181:
1382:
1371:
833:
426:
778:"Regional cerebral blood flow throughout the sleep-wake cycle. An H2(15)O PET study"
563:
1349:
1253:
977:
914:
606:
333:
292:
244:
711:
623:
Tsang, EW; Hamani, C; Moro, E; Mazzella, F; Poon, YY; Lozano, AM; Chen, R (2010).
640:
625:"Involvement of the human pedunculopontine nucleus region in voluntary movements"
63:
1235:
1025:
445:
172:. The pontine tegmentum is all the material dorsal from the basilar pons to the
88:
794:
777:
547:
590:
70:
743:
112:
466:
460:
452:
441:
418:
161:
762:
703:
658:
598:
555:
803:
479:
422:
402:
The pontine tegmentum contains two predominately cholinergic nuclei, the
284:
82:
725:
Mena-Segovia, Juan; Bolam, J. Paul; Martinez-Gonzalez, Cristina (2011).
137:
448:
414:
825:
455:), into the pontine tegmentum produces a state of REM sleep in cats.
251:
and their associated fibre tracts. The dorsal pons also contains the
695:
475:
313:
46:
857:
157:
829:
30:
Brainstem -- tegmentum not labeled, but is visible near center
727:"Topographical Organization of the Pedunculopontine Nucleus"
440:
It is also implicated in the generation and maintenance of
340:, which is caudal to the pontine tegmentum in the medulla.
291:
are located within the basilar pons. Also nearby are the
255:, the mesopontine cholinergic system comprising the
1313:
1293:
1252:
1234:
1221:
1159:
1103:
1037:
1024:
976:
913:
877:
864:
118:
106:
94:
81:
69:
57:
45:
40:
35:
18:
502:that provide antagonistic control signals to the
413:The PPN is involved in many functions, including
347:controls abduction (outward rotation) of the eye.
398:Functions of the mesopontine cholinergic system
393:, which is thought to help sound localisation.
841:
410:, which project widely throughout the brain.
8:
670:
668:
822:at the University of Michigan Health System
1231:
1034:
874:
848:
834:
826:
24:
793:
752:
742:
648:
536:Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology
299:, nuclei of cranial nerves 9-12, and the
675:Tattersall, T. L.; et al. (2014).
618:
616:
526:
176:. Along with the dorsal surface of the
135:
15:
320:Functions of the cranial nerve nuclei
7:
429:, and voluntary limb movements and
14:
486:Function of the respiratory group
490:The two respiratory areas – the
168:or ventral pons is known as the
132:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
231:The pontine tegmentum contains
999:Medial longitudinal fasciculus
961:Medial longitudinal fasciculus
408:laterodorsal tegmental nucleus
261:laterodorsal tegmental nucleus
205:laterodorsal tegmental nucleus
1:
1014:Lateral vestibulospinal tract
469:) or P-waves in rodents, are
191:Its contents include several
1197:Lateral parabrachial nucleus
1009:Medial vestibulospinal tract
987:Inferior cerebellar peduncle
641:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181f25b35
360:muscles of facial expression
233:nuclei of the cranial nerves
156:, is the dorsal part of the
1192:Medial parabrachial nucleus
966:Vestibulo-oculomotor fibers
376:superior vestibular nucleus
267:of the dorsal pons are the
1399:
579:Behavioural Brain Research
548:10.1016/j.resp.2004.06.016
1147:Inferior salivary nucleus
1142:Superior salivary nucleus
992:Vestibulocerebellar tract
731:Frontiers in Neuroanatomy
591:10.1016/j.bbr.2009.12.046
500:pontine respiratory group
385:The two divisions of the
356:superior salivary nucleus
338:spinal trigeminal nucleus
330:principal sensory nucleus
269:pontine respiratory group
253:reticulotegmental nucleus
209:pontine respiratory group
197:reticulotegmental nucleus
130:
23:
1204:Superior olivary nucleus
1167:Pedunculopontine nucleus
1119:Trigeminal motor nucleus
939:Ventral trigeminal tract
890:Superior medullary velum
795:10.1093/brain/120.7.1173
744:10.3389/fnana.2011.00022
504:dorsal respiratory group
404:pedunculopontine nucleus
301:dorsal respiratory group
257:pedunculopontine nucleus
201:pedunculopontine nucleus
170:basilar part of the pons
1187:Subparabrachial nucleus
956:Central tegmental tract
934:Dorsal trigeminal tract
249:vestibulocochlear (8th)
180:, it forms part of the
1283:Pontocerebellar fibers
885:Cerebellopontine angle
1273:Corticopontine fibers
1004:Vestibulospinal tract
207:. It also houses the
1124:Facial motor nucleus
929:Trigeminal lemniscus
352:facial motor nucleus
193:cranial nerve nuclei
1323:Reticular formation
1268:Corticobulbar tract
1263:Corticospinal tract
1182:Parabrachial nuclei
820:Atlas image: n2a3p2
684:Nature Neuroscience
273:parabrachial nuclei
215:which includes the
184:– the floor of the
160:located within the
1314:Other grey: Raphe/
1256:: Motor/descending
1177:Pneumotaxic center
1160:Grey: Other nuclei
492:pneumotaxic center
277:pneumotaxic centre
265:respiratory center
217:pneumotaxic centre
213:respiratory center
1365:
1364:
1309:
1308:
1217:
1216:
1155:
1154:
1088:Vestibular nuclei
951:Lateral lemniscus
905:Facial colliculus
516:Facial colliculus
380:vestibular nuclei
178:medulla oblongata
150:pontine tegmentum
146:
145:
141:
19:Pontine tegmentum
1390:
1232:
1172:Apneustic center
1133:Abducens nucleus
1108:
1071:Cochlear nucleus
1042:
1035:
946:Medial lemniscus
875:
850:
843:
836:
827:
808:
807:
797:
788:(7): 1173–1197.
773:
767:
766:
756:
746:
722:
716:
715:
681:
672:
663:
662:
652:
620:
611:
610:
574:
568:
567:
542:(2–3): 105–114.
531:
496:apneustic center
465:Pontine waves, (
387:cochlear nucleus
369:solitary nucleus
364:stapedius muscle
345:abducens nucleus
281:apneustic centre
237:trigeminal (5th)
221:apneustic centre
186:fourth ventricle
174:fourth ventricle
138:edit on Wikidata
52:tegmentum pontis
28:
16:
1398:
1397:
1393:
1392:
1391:
1389:
1388:
1387:
1368:
1367:
1366:
1361:
1315:
1305:
1289:
1248:
1223:
1213:
1209:Locus coeruleus
1151:
1104:
1099:
1038:
1020:
972:
909:
900:Medial eminence
895:Sulcus limitans
866:
860:
856:Anatomy of the
854:
816:
811:
775:
774:
770:
724:
723:
719:
696:10.1038/nn.3642
679:
674:
673:
666:
622:
621:
614:
576:
575:
571:
533:
532:
528:
524:
512:
488:
435:cerebral cortex
400:
334:cervical nerves
322:
314:stages of sleep
309:
297:locus coeruleus
229:
142:
31:
12:
11:
5:
1396:
1394:
1386:
1385:
1380:
1370:
1369:
1363:
1362:
1360:
1359:
1358:
1357:
1347:
1346:
1345:
1340:
1335:
1330:
1319:
1317:
1311:
1310:
1307:
1306:
1304:
1303:
1301:Basilar sulcus
1297:
1295:
1291:
1290:
1288:
1287:
1286:
1285:
1275:
1270:
1265:
1259:
1257:
1250:
1249:
1247:
1246:
1244:Pontine nuclei
1240:
1238:
1229:
1219:
1218:
1215:
1214:
1212:
1211:
1206:
1201:
1200:
1199:
1194:
1189:
1179:
1174:
1169:
1163:
1161:
1157:
1156:
1153:
1152:
1150:
1149:
1144:
1135:
1126:
1121:
1111:
1109:
1101:
1100:
1098:
1097:
1096:
1095:
1085:
1084:
1083:
1078:
1068:
1067:
1066:
1065:
1064:
1059:
1045:
1043:
1032:
1030:Cranial nuclei
1022:
1021:
1019:
1018:
1017:
1016:
1011:
1006:
996:
995:
994:
983:
981:
974:
973:
971:
970:
969:
968:
958:
953:
948:
943:
942:
941:
936:
926:
924:Trapezoid body
920:
918:
911:
910:
908:
907:
902:
897:
892:
887:
881:
879:
872:
862:
861:
855:
853:
852:
845:
838:
830:
824:
823:
815:
814:External links
812:
810:
809:
768:
717:
690:(3): 449–454.
664:
612:
569:
525:
523:
520:
519:
518:
511:
508:
487:
484:
406:(PPN) and the
399:
396:
395:
394:
391:trapezoid body
383:
378:, one of four
372:
348:
341:
321:
318:
308:
305:
289:pontine nuclei
241:abducens (6th)
228:
225:
182:rhomboid fossa
144:
143:
134:
128:
127:
122:
116:
115:
110:
104:
103:
98:
92:
91:
86:
79:
78:
73:
67:
66:
61:
55:
54:
49:
43:
42:
38:
37:
33:
32:
29:
21:
20:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1395:
1384:
1381:
1379:
1376:
1375:
1373:
1356:
1353:
1352:
1351:
1348:
1344:
1341:
1339:
1336:
1334:
1331:
1329:
1326:
1325:
1324:
1321:
1320:
1318:
1312:
1302:
1299:
1298:
1296:
1292:
1284:
1281:
1280:
1279:
1276:
1274:
1271:
1269:
1266:
1264:
1261:
1260:
1258:
1255:
1251:
1245:
1242:
1241:
1239:
1237:
1233:
1230:
1227:
1220:
1210:
1207:
1205:
1202:
1198:
1195:
1193:
1190:
1188:
1185:
1184:
1183:
1180:
1178:
1175:
1173:
1170:
1168:
1165:
1164:
1162:
1158:
1148:
1145:
1143:
1139:
1136:
1134:
1130:
1127:
1125:
1122:
1120:
1116:
1113:
1112:
1110:
1107:
1102:
1094:
1091:
1090:
1089:
1086:
1082:
1079:
1077:
1074:
1073:
1072:
1069:
1063:
1060:
1058:
1055:
1054:
1052:
1051:
1050:
1047:
1046:
1044:
1041:
1036:
1033:
1031:
1027:
1023:
1015:
1012:
1010:
1007:
1005:
1002:
1001:
1000:
997:
993:
990:
989:
988:
985:
984:
982:
979:
975:
967:
964:
963:
962:
959:
957:
954:
952:
949:
947:
944:
940:
937:
935:
932:
931:
930:
927:
925:
922:
921:
919:
916:
912:
906:
903:
901:
898:
896:
893:
891:
888:
886:
883:
882:
880:
876:
873:
870:
863:
859:
851:
846:
844:
839:
837:
832:
831:
828:
821:
818:
817:
813:
805:
801:
796:
791:
787:
783:
779:
772:
769:
764:
760:
755:
750:
745:
740:
736:
732:
728:
721:
718:
713:
709:
705:
701:
697:
693:
689:
685:
678:
671:
669:
665:
660:
656:
651:
646:
642:
638:
635:(11): 950–9.
634:
630:
626:
619:
617:
613:
608:
604:
600:
596:
592:
588:
585:(2): 488–98.
584:
580:
573:
570:
565:
561:
557:
553:
549:
545:
541:
537:
530:
527:
521:
517:
514:
513:
509:
507:
505:
501:
497:
493:
485:
483:
481:
477:
472:
468:
463:
462:
458:
454:
450:
447:
443:
438:
436:
432:
428:
424:
420:
416:
411:
409:
405:
397:
392:
388:
384:
381:
377:
373:
370:
365:
361:
357:
353:
349:
346:
342:
339:
335:
331:
327:
326:
325:
319:
317:
315:
306:
304:
302:
298:
294:
290:
286:
282:
278:
274:
270:
266:
262:
258:
254:
250:
246:
242:
238:
234:
226:
224:
222:
218:
214:
210:
206:
202:
198:
194:
189:
187:
183:
179:
175:
171:
167:
163:
159:
155:
151:
139:
133:
129:
126:
123:
121:
117:
114:
111:
109:
105:
102:
99:
97:
93:
90:
87:
84:
80:
77:
74:
72:
68:
65:
62:
60:
56:
53:
50:
48:
44:
39:
34:
27:
22:
17:
1378:Neuroanatomy
1350:Raphe nuclei
1105:
1039:
868:
785:
781:
771:
734:
730:
720:
687:
683:
632:
628:
582:
578:
572:
539:
535:
529:
498:make up the
489:
464:
439:
412:
401:
323:
310:
293:raphe nuclei
245:facial (7th)
230:
190:
166:ventral part
153:
149:
147:
101:A14.1.05.301
51:
1053:Trigeminal
471:brain waves
446:cholinergic
154:dorsal pons
89:birnlex_923
41:Identifiers
1372:Categories
1343:Paramedian
522:References
431:locomotion
279:, and the
219:, and the
71:NeuroNames
1338:Tegmental
1316:reticular
1106:efferent:
1057:Principal
1040:afferent:
917:: Sensory
869:tegmentum
629:Neurology
467:PGO waves
461:REM sleep
453:carbachol
442:REM sleep
419:attention
263:. In the
162:brainstem
1222:Ventral/
1093:Superior
1081:Anterior
980:: Motor
763:21503154
704:24487235
659:20702790
599:20060422
564:32801207
556:15519548
510:See also
494:and the
480:learning
423:learning
362:and the
354:and the
307:Function
295:and the
285:midbrain
271:and the
259:and the
203:and the
83:NeuroLex
1294:Surface
878:Surface
865:Dorsal/
804:9236630
754:3074429
650:2942031
607:9768708
449:agonist
415:arousal
275:in the
227:Anatomy
211:of the
64:D065821
36:Details
1355:Median
1328:Caudal
1076:Dorsal
1062:Spinal
802:
761:
751:
737:: 22.
712:405368
710:
702:
657:
647:
605:
597:
562:
554:
451:(e.g.
427:reward
287:. The
247:, and
199:, the
195:, the
164:. The
1254:White
978:White
915:White
782:Brain
708:S2CID
680:(PDF)
603:S2CID
560:S2CID
476:sleep
152:, or
136:[
125:71108
47:Latin
1383:Pons
1333:Oral
1236:Grey
1226:base
1026:Grey
858:pons
800:PMID
759:PMID
700:PMID
655:PMID
595:PMID
552:PMID
478:and
374:The
350:The
343:The
328:The
158:pons
148:The
113:5929
96:TA98
59:MeSH
1278:MCP
1138:GVE
1129:GSE
1115:SVE
1049:GSA
790:doi
786:120
749:PMC
739:doi
692:doi
645:PMC
637:doi
587:doi
583:221
544:doi
540:143
457:PET
188:.
120:FMA
108:TA2
76:557
1374::
1140::
1131::
1117::
1028::
798:.
784:.
780:.
757:.
747:.
733:.
729:.
706:.
698:.
688:17
686:.
682:.
667:^
653:.
643:.
633:75
631:.
627:.
615:^
601:.
593:.
581:.
558:.
550:.
538:.
482:.
425:,
421:,
417:,
243:,
239:,
223:.
85:ID
1228:)
1224:(
871:)
867:(
849:e
842:t
835:v
806:.
792::
765:.
741::
735:5
714:.
694::
661:.
639::
609:.
589::
566:.
546::
235:(
140:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.