104:
514:, the effective tax rate of income tax directly paid may differ from the effective economic incidence. When all taxes paid to local, state, and federal government are included, low, middle, and high income groups pay a similar share of their income to government. The article, using 2011 estimates of total income received versus total taxes paid, reported that the lowest 20% in income paid 2.1% of total taxes while receiving 3.4% of income. The middle 20% paid 10.3% of taxes while getting 11.4% of the income, and the top 1%, those with yearly incomes averaging $ 1,371,000, paid 21.6% of taxes while getting 21% of total income. Across eight income groups whose data were reported, the largest difference between total taxes paid and total income received was just 1.7 percentage points.
96:
708:
631:
serve as direct individual premiums for direct individual benefits, most do not include these taxes in the calculation of the progressive nature of federal taxes, just as they do not include similar private automobile, homeowners, and life insurance policy premiums. Another factor is that the social benefits themselves are paid in a progressive nature; individuals with lower lifetime average wages receive a larger benefit (as a percentage of their lifetime average wage income) than do individuals with higher lifetime average wages. However, if one were to expand the tax distribution example to include social security insurance taxes:
128:
technically correct, there are certain unintuitive outcomes; based on the Before-Tax Income metric, an individual with severe health issues that subsists purely on
Government Transfers may be considered part of the top one percent of income earners if his healthcare costs exceed the minimum threshold. Based on the data provided by the CBO, the resulting Net Tax liability as compared to income is presented in the accompanying charts. As of 2010, the bottom 99% by Market Income taken as a group had a negative Net Federal Tax burden, while the top 1 percent by Market Income paid in the aggregate 101% of Net Federal Taxes.
112:
share), Corporate Income Taxes, Excises Taxes, Estate and Gift Taxes, Customs Duties and
Miscellaneous Receipts. According to the Congressional Budget Office (CBO), the median taxpayer in the United States has had an effective overall federal tax burden that has declined from 19.14% of Before-Tax Income in 1979 to 11.20% of Before-Tax Income as of 2010. When simply comparing Market Income to After Tax Income, due to Government Transfers the Net Federal Tax burden of the median taxpayer has declined from 13.94% in 1979 to -8.76% in 2010 - this metric became negative for the first time in 2008.
759:
59:(the rate applied to the last bit of income) in the United States and United Kingdom exceeded 90%. As recently as the late 1970s, the top marginal tax rate in the U.S. was 70%. In the words of Piketty and Saez, "... the progressivity of the U.S. federal tax system at the top of the income distribution has declined dramatically since the 1960s". They continue, "... the most dramatic changes in federal tax system progressivity almost always take place within the top 1 percent of income earners, with relatively small changes occurring below the top percentile."
124:
direct cash assistance such as from Social
Security, unemployment insurance, Supplemental Security Income, Temporary Assistance for Needy Families veterans' programs, workers' compensation, and state and local government assistance programs. Such transfers also include the value of in-kind benefits: Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program vouchers (popularly known as food stamps); school lunches and breakfasts; housing assistance; and energy assistance and benefits provided by Medicare, Medicaid, and the Children's Health Insurance Program.
28:
20:
76:
491:
683:. All income earned up to a point, adjusted annually for inflation ($ 106,800 for the year 2010) is taxed at 7.65% (consisting of the 6.2% Social Security tax and the 1.45% Medicare tax) on the employee with an additional 7.65% in tax incurred by the employer. The annual limitation amount is sometimes called the "Social Security tax wage base amount" or "Contribution and Benefit Base." Above the annual limit amount, only the 1.45% Medicare tax is imposed.
88:
751:
691:
income individuals in terms of the "effective tax rate", the lower income individuals also receive a proportionately higher share of Social
Security benefits than do some higher income individuals, since the lower income individuals will receive a much higher income replacement percentage in retirement than higher income individuals affected by the Social Security tax wage base cap.
48:, as rates of tax generally increase as taxable income increases, at least with respect to individuals that earn wage income. As a group, the lowest earning workers, especially those with dependents, pay no income taxes and may actually receive a small subsidy from the federal government (from child credits and the
690:
When an individual's Social
Security benefit is calculated, income in excess of each year's Social Security Tax wage base amount is disregarded for purposes of the calculation of future benefits. Although some lower income individuals pay a proportionately higher share of payroll taxes than do higher
615:
To make the two tax rates realize an equal savings or discount from taking the maximum allowable deductions, the higher income tax bracket would have to have an effective tax rate of ~24.35% (31%-24.35%/31% = 21.4% or the same discount as the lower tax bracket) instead of 23%. This would necessitate
311:
that limits deductions and sets a flat tax rate of 26% to 28% with the higher rate commencing at $ 175,000 in income. There are also deduction phaseouts starting at $ 112,500 for single filers. The net effect is increased progressivity that completely limits deductions for state and local taxes and
123:
of people with smaller incomes, as they shift the incidence disproportionately to those with higher incomes. The data is presented in two forms, based on Market Income and based on Before-Tax Income. Before-Tax Income is defined as Market Income plus
Government Transfers. Government Transfers include
548:
include payments to doctors, premiums for medical insurance, prescription drugs and insulin expenses, state taxes paid, property taxes, and charitable contributions. In those two scenarios, assuming no other income, the tax calculations would be as follows for a single taxpayer with no dependents in
536:
payments, has significantly reduced the tax burden on income generated from savings and investing. An argument is often made that these types of income are not generally received by low-income taxpayers, and so this sort of "tax break" is anti-progressive. Further clouding the issue of progressivity
127:
While the CBO report does combine transfers to one's income for purposes of calculating Before-Tax Income, it does not net out
Government Transfers from one's tax liability for purposes of calculating rates based on Market Income. While presentation of income strata based on Before-Tax Income may be
611:
This would appear to be highly progressive - the person with the higher taxable income pays tax at twice the rate. However, if you divide the tax by the amount of gross income (i.e., before deductions), the effective rates are 11% and 23%: the higher income person's rate is still twice as high, but
299:
Additional brackets of 28%, 33%, 35% and 39.6% apply to higher levels of income. So, if a person has $ 50,000 of taxable income, his next dollar of income earned will be taxed at 25% - this is referred to as "being in the 25% tax bracket," or more formally as having a marginal rate of 25%. However,
111:
As of 2010, there were 118.7 million taxpaying households in the United States. The median marginal federal income tax rate is 15%. In addition, there are numerous other federal taxes and transfers that affect one's net tax burden, including federal payroll taxes (both employer share and employees
630:
Discussions of income tax progressivity often do not factor the payroll taxes (FICA - social security and medicare taxes), which have a "ceiling". This is because these insurance benefits are directly determined by individual contributions over that individual's lifetime. Thus, since payroll taxes
300:
the tax on $ 50,000 of taxable income figures to $ 9,058. This being 18% of $ 50,000, the taxpayer is referred to as having an effective tax rate of 18%. Starting in 2013, high-income households will also pay an additional
Medicare surcharge of 0.9% on earned income and 3.8% on investment income.
1027:
produced a similar breakdown for 1991 to 2004. Its computation of comprehensive household income consisted of both market-based income and the net value of government transfer payments, the latter are not part of the CBO's definition. In this report the top quintile earned 41.5% and paid 48.8% of
741:
The
Congressional Budget Office computes household taxes as the sum of income tax, payroll tax, corporate income tax, and excise taxes. It attributes corporate taxes to households "according to their share of capital income" and apportions excise taxes "according to their consumption of the taxed
295:
Progressivity in the income tax is accomplished mainly by establishing tax "brackets" - branches of income that are taxed at progressively higher rates. For example, for tax year 2006 an unmarried person with no dependents will pay 10% tax on the first $ 7,550 of taxable income. The next $ 23,100
737:
In addition to the income tax and payroll tax, computations of the tax burden of each segment of the population usually contain estimates of taxes that people do not pay by themselves directly. An example is the corporate income tax, which may be thought of as indirectly taxing the corporation's
725:
measured after taxes. Taxes became less progressive (i.e., they reduced income inequality relatively less) measured from 1979 to 2011. The tax policies of the mid-1980s were the least progressive period since 1979. Government transfer payments contributed more to reducing inequality than taxes.
135:
rate, the net wealth (not only income but also including real estate, cars, house, stocks, etc.) distribution of the United States does almost coincide with the share of income tax - the top 1% pay 36.9% of federal tax (wealth 32.7%), the top 5% pay 57.1% (wealth 57.2%), top 10% pay 68% (wealth
686:
In terms of the effective rate, this means that a worker earning $ 20,000 for 2010 pays at an effective rate of 7.65% (i.e., $ 20,000 x 7.65% = $ 1,530.00), while a worker earning $ 200,000 pays at an effective rate of only about 4.76% (i.e., the 7.65% rate is multiplied by $ 106,800, not by $
694:
If the higher income individuals want to receive an income replacement percentage in retirement that is similar to the income replacement percentage that lower income individuals receive from Social
Security, higher income individuals must achieve this through other means such as
62:
Progressivity, then, is a complex topic which does not lend itself to simple analyses. Given the "flattening" of tax burden that occurred in the early 1980s, many commentators note that the general structure of the U.S. tax system has begun to resemble a partial
612:
his deductions drive down the effective rate more quickly ((14%-11%)/14% = a 21.4% effective tax rate savings or discount at the low income bracket; (31%-23%)/31% = a 29% effective tax rate savings or discount at the higher income tax bracket).
738:
customers (through higher prices) or its owners (through lower dividends or profits). Another example is excise taxes, e.g. on gasoline, which may be paid from throughout the economy without recording individual contributions.
1028:
total taxes. The fourth quintile earned 21.0% and paid 22.4%. The third quintile earned 15.4% and paid 14.8%. The second quintile earned 12.2% and paid 9.6%. The lowest quintile earned 9.8% and paid 4.3% of total taxes.
31:
As of 2010, 68.8% of Federal individual tax receipts including payroll taxes, were paid by the top 20% of taxpayers by income group. The top 1% paid 24.2% whereas the bottom 20% paid 0.4% due to deductions and the
797:
The second quintile earned 8.4%. It paid a net -0.3% of income taxes, meaning in aggregate this quintile received slightly more back in income tax credits than it paid in income taxes. It paid 4.4% of all federal
498:
While the top marginal tax rate on ordinary income is 35 percent, average rates that a household in the upper income bracket pays is less. Much of the earnings of those in the top income bracket come from
699:, IRAs, defined benefit pension plans, personal savings, etc. As a percentage of income, some higher income individuals receive less from Social Security than do lower income individuals.
510:
The effective tax rate paid by an individual in the upper income bracket is highly dependent on the ratio of income they earn from capital gains, interest and dividends. As discussed in a
147:
system (FICA), a 12.4% Social Security tax on wages up to $ 117,000 (for 2013) and a 2.9% Medicare tax (a 15.3% total tax that is often split between employee and employer) is called a
507:
of 15.3%, which are paid by the employer and employee, individuals in the upper income bracket pay on average an effective rate not much different than that of other income brackets.
55:"Progressivity" as it pertains to tax is usually defined as meaning that the higher a person's level of income, the higher a tax rate that person pays. In the mid-twentieth century,
1556:: 10 (avg. adjusted gross income = $ 57, 311, 000 avg. tax amount/ 16.6% avg tax rate = $ 344, 831, 528), pp. 2–3 (7.85% interest + 7.11% dividends + 66.29% capital gains = 81.25%)
687:
200,000, resulting in a tax of $ 8,170.20, plus the $ 1,351.40 tax, at 1.45%, on the remaining $ 93,200, for a total tax of $ 9,521.60, which is about 4.7608% of $ 200,000).
151:
on income with no standard deduction or personal exemptions but in effect is forced savings which return to the payer in the form of retirement benefits and health care. The
303:
The US federal tax system also includes deductions for state and local taxes for lower income households which mitigates what are sometimes regressive taxes, particularly
23:
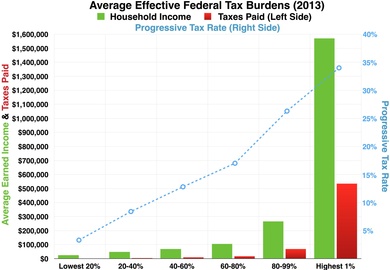
Based on CBO Estimates, under 2013 tax law the top 1% will be paying the highest average tax rates since 1979, while other income groups will remain at historic lows.
103:
742:
good or service." The CBO report shows each part of the taxes (income, payroll, corporate and excise) separately in addition to showing the totals we report here.
95:
1698:
1405:
763:
1281:
707:
625:
144:
1480:
1206:
1615:
1297:
716:
523:
152:
1441:
163:
544:
available to him, whereas a taxpayer with $ 200,000 of wage income might easily have $ 50,000 or more of "itemized" deductions. Allowable
1672:
Who Pays Taxes and Who Receives Government Spending? An Analysis of Federal, State and Local Tax and Spending Distributions, 1991-2004
1322:
770:
The Congressional Budget Office breaks down the 2007 share of the tax burden according to each segment of the population as follows:
79:
U.S. federal income (individual and corporate) and payroll tax rates by income percentile and component as projected for 2014 by the
304:
616:
an additional income tax of $ 1,975 from the higher tax bracket ($ 200,000*24.35% = $ 48,700), or an extra 0.99% in this model.
774:
The highest quintile in total earned 55.9% of all income. It paid 86.0% of federal income taxes and 68.9% of all federal taxes
672:
290:
41:
711:
CBO chart illustrating the percent reduction in income inequality due to Federal taxes and income transfers from 1979 to 2011.
511:
801:
The lowest quintile earned 4.0% of all income and received a net -3.0% income tax credits. It paid 1.0% of all federal taxes.
758:
762:
Proposed tax plan payment rates by income group as a percentage of income, including mandatory health insurance, of four
115:
The CBO report in 2013 shows the share of federal taxes paid by taxpayers of various income levels. The data shows the
1655:
1599:
1531:
27:
1648:
296:(i.e. taxable income over $ 7,550, up to $ 30,650) is taxed at 15%. The next $ 43,550 of income is taxed at 25%.
503:, interest and dividends, which are taxed at 15 percent. Also because only income up to $ 106,800 is subject to
19:
676:
49:
33:
75:
1458:
1409:
308:
1298:"T13-0174 - Average Effective Federal Tax Rates by Filing Status; by Expanded Cash Income Percentile, 2014"
1703:
1551:"The 400 Individual Income Tax Returns Reporting the Highest Adjusted Gross Incomes Each Year, 1992-2008"
1569:
1277:
791:
The fourth quintile earned 19.3% of income. It paid 12.7% of income taxes and 16.5 of all federal taxes.
139:
Other taxes in the United States have a less progressive structure or a regressive structure, and legal
794:
The third quintile earned 13.1% of income. It paid 4.6% of income taxes and 9.2% of all federal taxes.
1649:"Average Federal Tax Rates for All Households, by Comprehensive Household Income Quintile, 1979-2007"
1595:
1358:
734:
These tables show the share of taxes, and effective tax rate, for each quintile of household income.
1301:
1236:
777:
The top 1% earned 19.4% of all income. It paid 39.5% of income taxes and 28.1% of all federal taxes
545:
132:
1334:
786:
The next 10% earned 13.9% of income. It paid 13.3% of income taxes and 13.9% of all federal taxes.
490:
1485:
1259:
1211:
780:
The next 4% earned 12.9% of income. It paid 21.5%. of income taxes and 16.2% of all federal taxes
541:
783:
The next 5% earned 9.7% of income. It paid 11.7% of income taxes and 10.7% of all federal taxes
1437:
722:
167:
87:
80:
56:
1251:
1582:
1285:
116:
107:
CBO Data Shares of Market Income and Net Federal Taxes, By Income Group, 2010 - 99% and 1%
64:
45:
1679:
1432:
1232:
1024:
750:
148:
671:
Some lower income individuals pay a proportionately higher share of payroll taxes for
537:
is that far more deductions and tax credits are available to higher-income taxpayers.
1692:
504:
500:
140:
120:
1263:
529:
1550:
1505:
119:
structure of the U.S. federal income tax system on individuals that reduces the
1359:"A Rolling Tide: Changes in the Distribution of Wealth in the U.S., 1989-2001"
1670:
166:
has concluded that the combined federal, state, and local government average
99:
CBO Data Shares of Market Income and Net Federal Taxes, By Income Group, 2010
1513:
1509:
533:
159:
of U.S. taxpayers pay more in payroll taxes than they do in income taxes.
1631:
1611:
143:
loopholes change the overall tax burden distribution. For example, the
1255:
36:. With 2013 tax law changes, the top 1% will pay an even larger share.
1383:
721:
According to the CBO, U.S. federal tax policies substantially reduce
696:
754:
Total tax rates by income percentile in the United States, 1950-2018
1184:
312:
certain other credits for individuals earning more than $ 306,300.
757:
749:
706:
489:
102:
94:
86:
74:
1384:"Studies Shed New Light on Effects of Administration's Tax Cuts"
1185:"The Distribution of Household Income and Federal Taxes, 2010"
1632:"The Distribution of Household Income and Federal Taxes 2011"
1526:
1524:
1522:
1634:. Congressional Budget Office, US Government. November 2014.
528:
In recent years, a reduction in the tax rates applicable to
540:
A taxpayer with $ 40,000 of wage income may only have the
1335:"Effective Marginal Tax Rates on Labor Income, Table 2"
679:
than do some higher income individuals in terms of the
1187:. The US Congressional Budget Office (CBO). 2013-12-04
319:
179:
Breakdown of Income and Income Taxes Paid by Category
177:
1626:
1624:
1612:
Top Ten Facts on Social Security's 70th Anniversary
136:69.8%), and the bottom 50% pay 3.3% (wealth 2.8%).
1669:Chamberlain, Andrew; Prante, Gerald (March 2007),
337:Income from Capital Gains, Interest and Dividends
131:If the federal taxation rate is compared with the
1481:"Tax Code May Be the Most Progressive Since 1979"
1300:. Tax Policy Center. Jul 25, 2013. Archived from
1207:"Tax Code May Be the Most Progressive Since 1979"
1237:"How Progressive is the US Federal Tax System?"
307:. Higher income households are subject to the
1678:, Tax Foundation Working Paper, vol. 1,
8:
1643:
1641:
170:for most workers to be about 40% of income.
1382:Kamin, David; Shapiro, Isaac (2004-09-13).
1179:
1177:
1175:
1430:Friedman, Milton; Friedman, Rose (1980).
1386:. Center on Budget and Policy Priorities
1030:
809:
764:2020 United States presidential election
633:
551:
26:
18:
1171:
1016:
1013:
1010:
1007:
1004:
996:
993:
990:
987:
984:
976:
973:
970:
967:
964:
956:
953:
950:
947:
944:
876:
870:
864:
858:
852:
626:Federal Insurance Contributions Act tax
1616:Center on Budget and Policy Priorities
1578:
1567:
717:Income inequality in the United States
524:Capital gains tax in the United States
494:Progressive taxes in the United States
334:Effective Income and Payroll Tax Rate
153:Center on Budget and Policy Priorities
7:
164:National Bureau of Economic Research
1268:quote from p. 22 in the conclusion.
1036:(1991 to 2004 Tax Foundation data)
321:Average Effective Income Tax Rates
1459:"Where Do You Rank as a Taxpayer?"
14:
1357:Kennickell, Arthur (March 2003).
323:for Different Income Groups 2007
1699:United States federal income tax
1457:McCormally, Kevin (2010-12-18).
1244:Journal of Economic Perspectives
42:United States federal income tax
1596:Is Social Security Progressive?
1364:. United States Federal Reserve
291:Income tax in the United States
806:Tax burden by household income
1:
1324:, Congressional Budget Office
1041:(incl. government transfers)
1532:"Effective Income Tax Rates"
1479:Lowrey, Annie (2013-01-04).
1205:Lowrey, Annie (2013-01-04).
746:Tax burden by income bracket
664:
661:
604:
601:
331:Average Income Before Taxes
282:
279:
268:
265:
254:
251:
240:
237:
226:
223:
212:
209:
1656:Congressional Budget Office
1600:Congressional Budget Office
1408:. MSN Money. Archived from
1404:Burns, Scott (2007-02-21).
703:Effect on income inequality
653:
650:
642:
639:
593:
590:
582:
579:
571:
568:
560:
557:
512:Wall Street Journal article
91:CBO Median Income Tax Rates
1720:
1549:Internal Revenue Service.
1284:February 26, 2007, at the
1235:; Saez, E. (Winter 2007).
1059:(incl. Fed, State, Local)
1054:(incl. Fed, State, Local)
1049:State and Local Tax Share
714:
623:
521:
316:Effective income tax rates
288:
276:
273:
262:
259:
248:
245:
234:
231:
220:
217:
206:
203:
1618:. Retrieved July 23, 2008
1602:, retrieved July 23, 2008
1406:"Your real tax rate: 40%"
839:
834:
829:
824:
819:
659:Rate paid on gross income
481:
461:
413:
336:
333:
330:
1046:(incl. Social Security)
327:
50:Earned Income Tax Credit
34:Earned income tax credit
309:Alternative Minimum Tax
1577:Cite journal requires
767:
755:
712:
495:
483:*Adjusted Gross Income
108:
100:
92:
84:
37:
24:
1280:, Tax Policy Center
761:
753:
715:Further information:
710:
542:"standard" deductions
493:
106:
98:
90:
78:
30:
22:
16:Overview of tax rates
566:Allowable deductions
1304:on 11 December 2014
827:Federal Income Tax
637:Social security tax
546:itemized deductions
518:Capital gains taxes
324:
180:
133:wealth distribution
1536:The New York Times
1512:(individuals) and
1486:The New York Times
1256:10.1257/jep.21.1.3
1212:The New York Times
842:All Federal Taxes
837:All Federal Taxes
768:
756:
713:
681:effective tax rate
496:
320:
178:
109:
101:
93:
85:
57:marginal tax rates
38:
25:
1614:by Jason Furman,
1443:978-0-15-633460-0
1163:
1162:
1044:Federal Tax Share
1021:
1020:
723:income inequality
669:
668:
609:
608:
488:
487:
484:
287:
286:
168:marginal tax rate
81:Tax Policy Center
1711:
1683:
1682:
1677:
1666:
1660:
1659:
1653:
1645:
1636:
1635:
1628:
1619:
1609:
1603:
1593:
1587:
1586:
1580:
1575:
1573:
1565:
1563:
1561:
1555:
1546:
1540:
1539:
1528:
1517:
1503:
1497:
1496:
1494:
1493:
1476:
1470:
1469:
1467:
1466:
1454:
1448:
1447:
1427:
1421:
1420:
1418:
1417:
1401:
1395:
1394:
1392:
1391:
1379:
1373:
1372:
1370:
1369:
1363:
1354:
1348:
1347:
1345:
1344:
1339:
1331:
1325:
1320:
1314:
1313:
1311:
1309:
1294:
1288:
1275:
1269:
1267:
1241:
1229:
1223:
1222:
1220:
1219:
1202:
1196:
1195:
1193:
1192:
1181:
1031:
817:(2007 CBO data)
813:Household Income
810:
634:
552:
482:
325:
199:Income Tax Paid
181:
71:Tax distribution
40:In general, the
1719:
1718:
1714:
1713:
1712:
1710:
1709:
1708:
1689:
1688:
1687:
1686:
1675:
1668:
1667:
1663:
1651:
1647:
1646:
1639:
1630:
1629:
1622:
1610:
1606:
1594:
1590:
1576:
1566:
1559:
1557:
1553:
1548:
1547:
1543:
1530:
1529:
1520:
1516:(corporations).
1508:. Also see IRS
1504:
1500:
1491:
1489:
1478:
1477:
1473:
1464:
1462:
1456:
1455:
1451:
1444:
1429:
1428:
1424:
1415:
1413:
1403:
1402:
1398:
1389:
1387:
1381:
1380:
1376:
1367:
1365:
1361:
1356:
1355:
1351:
1342:
1340:
1337:
1333:
1332:
1328:
1321:
1317:
1307:
1305:
1296:
1295:
1291:
1286:Wayback Machine
1278:Consumption tax
1276:
1272:
1239:
1231:
1230:
1226:
1217:
1215:
1204:
1203:
1199:
1190:
1188:
1183:
1182:
1173:
1168:
1058:
1053:
1052:Total Tax Share
1045:
1040:
1035:
841:
836:
831:
826:
821:
816:
814:
808:
748:
732:
719:
705:
673:Social Security
628:
622:
526:
520:
322:
318:
293:
277:Under $ 36,055
235:Over $ 125,195
221:Over $ 175,817
207:Over $ 464,682
198:
193:
185:
176:
117:progressive tax
73:
65:consumption tax
17:
12:
11:
5:
1717:
1715:
1707:
1706:
1701:
1691:
1690:
1685:
1684:
1680:Tax Foundation
1661:
1637:
1620:
1604:
1588:
1579:|journal=
1541:
1518:
1498:
1471:
1449:
1442:
1433:Free to choose
1422:
1396:
1374:
1349:
1326:
1315:
1289:
1270:
1224:
1197:
1170:
1169:
1167:
1164:
1161:
1160:
1157:
1154:
1151:
1148:
1145:
1141:
1140:
1137:
1134:
1131:
1128:
1125:
1121:
1120:
1117:
1114:
1111:
1108:
1105:
1101:
1100:
1097:
1094:
1091:
1088:
1085:
1081:
1080:
1077:
1074:
1071:
1068:
1065:
1061:
1060:
1057:Total Tax Rate
1055:
1050:
1047:
1042:
1037:
1025:Tax Foundation
1019:
1018:
1015:
1012:
1009:
1006:
1003:
999:
998:
995:
992:
989:
986:
983:
979:
978:
975:
972:
969:
966:
963:
959:
958:
955:
952:
949:
946:
943:
939:
938:
935:
932:
929:
926:
923:
919:
918:
915:
912:
909:
906:
903:
899:
898:
895:
892:
889:
886:
883:
879:
878:
875:
872:
869:
866:
863:
860:
857:
854:
851:
848:
844:
843:
840:Tax Rate incl.
838:
833:
828:
823:
818:
807:
804:
803:
802:
799:
795:
792:
789:
788:
787:
784:
781:
778:
747:
744:
731:
728:
704:
701:
667:
666:
663:
660:
656:
655:
652:
649:
645:
644:
641:
638:
624:Main article:
621:
618:
607:
606:
603:
600:
599:Statutory rate
596:
595:
592:
589:
585:
584:
581:
578:
577:Taxable income
574:
573:
570:
567:
563:
562:
559:
556:
522:Main article:
519:
516:
486:
485:
480:
477:
476:
473:
470:
467:
463:
462:
460:
457:
456:
453:
450:
447:
443:
442:
439:
436:
433:
429:
428:
425:
422:
419:
415:
414:
412:
409:
408:
405:
402:
399:
395:
394:
391:
388:
385:
381:
380:
377:
374:
371:
367:
366:
363:
360:
357:
353:
352:
349:
346:
343:
339:
338:
335:
332:
329:
317:
314:
305:property taxes
289:Main article:
285:
284:
281:
278:
275:
271:
270:
267:
264:
263:Over $ 36,055
261:
257:
256:
253:
250:
249:Over $ 73,354
247:
243:
242:
239:
236:
233:
229:
228:
225:
222:
219:
215:
214:
211:
208:
205:
201:
200:
197:Percentage of
195:
192:Percentage of
190:
187:
175:
172:
149:regressive tax
72:
69:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1716:
1705:
1704:Tax incidence
1702:
1700:
1697:
1696:
1694:
1681:
1674:
1673:
1665:
1662:
1657:
1650:
1644:
1642:
1638:
1633:
1627:
1625:
1621:
1617:
1613:
1608:
1605:
1601:
1597:
1592:
1589:
1584:
1571:
1552:
1545:
1542:
1538:. 2012-01-17.
1537:
1533:
1527:
1525:
1523:
1519:
1515:
1511:
1507:
1502:
1499:
1488:
1487:
1482:
1475:
1472:
1460:
1453:
1450:
1445:
1439:
1435:
1434:
1426:
1423:
1412:on 2011-07-14
1411:
1407:
1400:
1397:
1385:
1378:
1375:
1360:
1353:
1350:
1336:
1330:
1327:
1323:
1319:
1316:
1303:
1299:
1293:
1290:
1287:
1283:
1279:
1274:
1271:
1265:
1261:
1257:
1253:
1249:
1245:
1238:
1234:
1228:
1225:
1214:
1213:
1208:
1201:
1198:
1186:
1180:
1178:
1176:
1172:
1165:
1158:
1155:
1152:
1149:
1146:
1143:
1142:
1138:
1135:
1132:
1129:
1126:
1123:
1122:
1118:
1115:
1112:
1109:
1106:
1103:
1102:
1098:
1095:
1092:
1089:
1086:
1083:
1082:
1078:
1075:
1072:
1069:
1066:
1063:
1062:
1056:
1051:
1048:
1043:
1038:
1033:
1032:
1029:
1026:
1001:
1000:
981:
980:
961:
960:
941:
940:
936:
933:
930:
927:
924:
921:
920:
916:
913:
910:
907:
904:
901:
900:
896:
893:
890:
887:
884:
881:
880:
873:
867:
861:
855:
849:
846:
845:
812:
811:
805:
800:
796:
793:
790:
785:
782:
779:
776:
775:
773:
772:
771:
765:
760:
752:
745:
743:
739:
735:
729:
727:
724:
718:
709:
702:
700:
698:
692:
688:
684:
682:
678:
674:
658:
657:
647:
646:
636:
635:
632:
627:
619:
617:
613:
598:
597:
587:
586:
576:
575:
565:
564:
554:
553:
550:
547:
543:
538:
535:
532:and received
531:
530:capital gains
525:
517:
515:
513:
508:
506:
505:payroll taxes
502:
501:capital gains
492:
479:
478:
474:
471:
469:$ 344,831,528
468:
465:
464:
459:
458:
454:
451:
448:
445:
444:
440:
437:
434:
431:
430:
426:
423:
420:
417:
416:
411:
410:
406:
403:
400:
397:
396:
392:
389:
386:
383:
382:
378:
375:
372:
369:
368:
364:
361:
358:
355:
354:
350:
347:
344:
341:
340:
326:
315:
313:
310:
306:
301:
297:
292:
272:
258:
244:
230:
216:
202:
196:
191:
188:
183:
182:
173:
171:
169:
165:
160:
158:
157:three-fourths
154:
150:
146:
142:
141:tax avoidance
137:
134:
129:
125:
122:
121:tax incidence
118:
113:
105:
97:
89:
82:
77:
70:
68:
66:
60:
58:
53:
51:
47:
43:
35:
29:
21:
1671:
1664:
1607:
1591:
1570:cite journal
1558:. Retrieved
1544:
1535:
1501:
1490:. Retrieved
1484:
1474:
1463:. Retrieved
1452:
1436:. Harcourt.
1431:
1425:
1414:. Retrieved
1410:the original
1399:
1388:. Retrieved
1377:
1366:. Retrieved
1352:
1341:. Retrieved
1329:
1318:
1306:. Retrieved
1302:the original
1292:
1273:
1247:
1243:
1227:
1216:. Retrieved
1210:
1200:
1189:. Retrieved
1022:
830:Tax Rate for
769:
740:
736:
733:
720:
693:
689:
685:
680:
670:
629:
614:
610:
539:
527:
509:
497:
302:
298:
294:
174:Income taxes
161:
156:
155:states that
138:
130:
126:
114:
110:
61:
54:
39:
1560:29 February
1461:. Kiplinger
1250:(1): 3–24.
1233:Piketty, T.
1014: 1.0%
1005: 4.0%
994: 4.4%
985: 8.4%
974: 9.2%
971: 3.3%
968: 4.6%
951: 6.2%
832:Income Tax
555:Wage income
449:$ 1,873,000
274:Bottom 50%
145:payroll tax
46:progressive
1693:Categories
1492:2014-02-03
1465:2010-06-18
1416:2008-03-13
1390:2006-07-23
1368:2007-09-19
1343:2010-07-27
1308:3 November
1218:2014-01-06
1191:2014-01-06
1166:References
1034:Percentile
815:Percentile
766:candidates
730:Breakdowns
620:FICA taxes
588:Income tax
561:$ 200,000
1514:Form 4626
1510:Form 6251
1506:26 USC 55
1064:80%–100%
822:Earnings
648:Total tax
534:dividends
435:$ 611,200
421:$ 394,500
401:$ 264,700
328:Quintile
189:2012 AGI
186:Category
1282:Archived
922:80%–89%
902:90%–94%
882:95%–98%
835:Share of
825:Share of
820:Share of
677:Medicare
643:$ 8,740
583:148,570
558:$ 40,000
466:Top 400
418:Top 10%
398:Highest
387:$ 94,100
373:$ 64,500
359:$ 42,500
345:$ 18,400
260:Top 50%
246:Top 25%
232:Top 10%
194:All AGI
67:regime.
1598:by the
1264:5160267
1124:20–39%
1104:40–59%
1084:60–79%
982:20–39%
962:40–59%
942:60–79%
847:Top 1%
697:401(k)s
654:55,465
640:$ 3,060
594:46,725
572:51,430
446:Top 1%
432:Top 5%
384:Fourth
370:Middle
356:Second
342:Lowest
218:Top 5%
204:Top 1%
184:Income
1440:
1262:
1159:13.0%
1144:0–19%
1139:23.2%
1133:12.2%
1127:12.2%
1119:28.2%
1116:14.8%
1113:16.3%
1110:14.1%
1107:15.4%
1099:31.3%
1096:22.4%
1093:22.7%
1090:22.2%
1087:21.0%
1079:34.5%
1076:48.8%
1073:41.4%
1070:52.8%
1067:41.5%
1039:Income
1011:−6.8%
1008:−3.0%
1002:0–19%
997:10.6%
991:−0.4%
988:−0.3%
977:14.3%
965:13.1%
957:17.4%
954:16.5%
948:12.7%
945:19.3%
934:13.9%
928:13.3%
925:13.9%
914:10.7%
908:11.7%
894:16.2%
888:21.5%
885:12.9%
877:25.1%
874:29.5%
871:68.9%
868:28.1%
865:23.2%
862:19.0%
859:86.0%
856:38.5%
853:55.9%
850:19.4%
798:taxes.
580:31,550
549:2006:
475:81.3%
455:43.4%
441:32.1%
427:26.7%
407:21.4%
1676:(PDF)
1652:(PDF)
1554:(PDF)
1362:(PDF)
1338:(PDF)
1260:S2CID
1240:(PDF)
1156:4.3%
1153:7.5%
1150:2.6%
1147:9.8%
1136:9.6%
1130:8.3%
1017:4.0%
905:9.7%
651:7,505
591:4,445
569:8,450
472:16.6%
452:20.6%
438:20.9%
424:20.7%
404:20.1%
393:3.7%
390:15.7%
379:2.5%
376:12.7%
365:1.6%
351:1.3%
1583:help
1562:2012
1438:ISBN
1310:2013
1023:The
675:and
665:28%
605:31%
362:9.1%
348:2.0%
280:11%
269:97%
266:89%
255:86%
252:69%
241:70%
238:48%
227:59%
224:37%
213:38%
210:22%
162:The
1252:doi
937:na
931:na
917:na
911:na
897:na
891:na
662:19%
602:14%
283:3%
52:).
44:is
1695::
1654:.
1640:^
1623:^
1574::
1572:}}
1568:{{
1534:.
1521:^
1483:.
1258:.
1248:21
1246:.
1242:.
1209:.
1174:^
1658:.
1585:)
1581:(
1564:.
1495:.
1468:.
1446:.
1419:.
1393:.
1371:.
1346:.
1312:.
1266:,
1254::
1221:.
1194:.
83:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.