841:
85:
1802:
666:. By fitting their voltage-clamp data, Hodgkin and Huxley were able to model how these equilibrium values and time constants varied with temperature and transmembrane voltage. The formulae are complex and depend exponentially on the voltage and temperature. For example, the time constant for sodium-channel activation probability
44:
illustrates how differently shaped action potentials can be generated on membranes with voltage-sensitive calcium channels and different types of sodium/potassium channels. The second type of mathematical model is a simplification of the first type; the goal is not to reproduce the experimental data,
1376:
Whereas the above models simulate the transmembrane voltage and current at a single patch of membrane, other mathematical models pertain to the voltages and currents in the ionic solution surrounding the neuron. Such models are helpful in interpreting data from extracellular electrodes, which were
1359:
The simplest models of the action potential are the "flush and fill" models (also called "integrate-and-fire" models), in which the input signal is summed (the "fill" phase) until it reaches a threshold, firing a pulse and resetting the summation to zero (the "flush" phase). All of these models are
481:
To fit their data accurately, Hodgkin and Huxley assumed that each type of ion channel had multiple "gates", so that the channel was open only if all the gates were open and closed otherwise. They also assumed that the probability of a gate being open was independent of the other gates being open;
35:
squid exemplifies such models. Although qualitatively correct, the H-H model does not describe every type of excitable membrane accurately, since it considers only two ions (sodium and potassium), each with only one type of voltage-sensitive channel. However, other ions such as
1495:
825:
is gradually increased; remarkably, the axon becomes stably quiescent again as the stimulating current is increased further still. A more general study of the types of qualitative behavior of axons predicted by the
Hodgkin–Huxley equations has also been carried out.
285:
1316:
69:
responsible for some automatic reflex actions. Such networks can generate a complex temporal pattern of action potentials that is used to coordinate muscular contractions, such as those involved in breathing or fast swimming to escape a predator.
451:
1043:
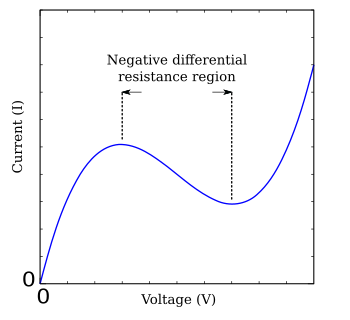
that has a region of negative slope in the middle, flanked by one maximum and one minimum (Figure FHN). A much-studied simple case of the FitzHugh–Nagumo model is the
Bonhoeffer-van der Pol nerve model, which is described by the equations
1133:
781:
608:
45:
but to understand qualitatively the role of action potentials in neural circuits. For such a purpose, detailed physiological models may be unnecessarily complicated and may obscure the "forest for the trees". The
810:. No general solution of these equations has been discovered. A less ambitious but generally applicable method for studying such non-linear dynamical systems is to consider their behavior in the vicinity of a
1797:{\displaystyle \phi (\mathbf {x} )={\frac {1}{4\pi \sigma _{\mathrm {outside} }}}\oint _{\mathrm {membrane} }{\frac {\partial }{\partial n}}{\frac {1}{\left|\mathbf {x} -{\boldsymbol {\xi }}\right|}}\leftdS}
24:
have been developed, which fall into two basic types. The first type seeks to model the experimental data quantitatively, i.e., to reproduce the measurements of current and voltage exactly. The renowned
1344:. True to the barnacle's physiology, the Morris–Lecar model replaces the voltage-gated sodium current of the Hodgkin–Huxley model with a voltage-dependent calcium current. There is no inactivation (no
160:
123:
of four types of ions. The two conductances on the left, for potassium (K) and sodium (Na), are shown with arrows to indicate that they can vary with the applied voltage, corresponding to the
1425:
966:
1030:
61:, which is coordinated by a burst of action potentials; entrainment can also be observed in individual neurons. Both types of models may be used to understand the behavior of small
1827:
1185:
1196:
357:
2532:
Sato S, Fukai H, Nomura T, Doi S (2005). "Bifurcation
Analysis of the Hodgkin–Huxley Equations". In Reeke GN, Poznanski RR, Lindsay KA, Rosenberg JR, Sporns O (eds.).
2223:
1980:
3150:"Simple capacitor-switch model of excitatory and inhibitory neuron with all parts biologically explained allows input fire pattern dependent chaotic oscillations"
1377:
common prior to the invention of the glass pipette electrode that allowed intracellular recording. The extracellular medium may be modeled as a normal isotropic
482:
this assumption was later validated for the inactivation gate. Hodgkin and Huxley modeled the voltage-sensitive potassium channel as having four gates; letting
491:
denote the probability of a single such gate being open, the probability of the whole channel being open is the product of four such probabilities, i.e.,
893:
Because of the complexity of the
Hodgkin–Huxley equations, various simplifications have been developed that exhibit qualitatively similar behavior. The
1348:
variable) and the calcium current equilibrates instantaneously, so that again, there are only two time-dependent variables: the transmembrane voltage
901:, the FHN model has only two independent variables, but exhibits a similar stability behavior to the full Hodgkin–Huxley equations. The equations are
1050:
680:
311:
are currents conveyed through the local sodium channels, potassium channels, and "leakage" channels (a catch-all), respectively. The initial term
139:
developed a set of equations to fit their experimental voltage-clamp data on the axonal membrane. The model assumes that the membrane capacitance
533:
3340:
3105:
2573:
2541:
2376:
2253:
2207:
1845:
the corresponding values just outside the membrane. Thus, given these σ and φ values on the membrane, the extracellular potential φ(
319:
853:
3359:
787:
502:. Similarly, the probability of the voltage-sensitive sodium channel was modeled to have three similar gates of probability
2400:
280:{\displaystyle C{\frac {dV}{dt}}=I_{\mathrm {tot} }=I_{\mathrm {ext} }+I_{\mathrm {Na} }+I_{\mathrm {K} }+I_{\mathrm {L} }}
3121:
Keener JP, Hoppensteadt FC, Rinzel J (1981). "Integrate-and-fire models of nerve membrane response to oscillatory input".
1190:
where the coefficient ε is assumed to be small. These equations can be combined into a second-order differential equation
1880:
1336:
A hybrid of the
Hodgkin–Huxley and FitzHugh–Nagumo models was developed by Morris and Lecar in 1981, and applied to the
2981:, van der Mark J (1929). "The heartbeat considered as a relaxation oscillation, and an electrical model of the heart".
2966:, van der Mark J (1928). "The heartbeat considered as a relaxation oscillation, and an electrical model of the heart".
1397:
1365:
54:
3288:
Mauro A (1960). "Properties of thin generators pertaining to electrophysiological potentials in volume conductors".
3369:
894:
835:
46:
811:
124:
66:
62:
2269:
Hanson, F.E.; Case, J.F.; Buck, E.; Buck, J. (1971). "Synchrony and Flash
Entrainment in a New Guinea Firefly".
79:
26:
1870:
907:
41:
974:
1447:
1333:
circuits that realize the FHN and van der Pol models of the action potential have been developed by Keener.
2589:
Sabah NH, Spangler RA (1970). "Repetitive response of the
Hodgkin-Huxley model for the squid giant axon".
2143:"A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve"
1810:
1459:
1322:
1141:
872:
326:
120:
2478:"Destruction of the sodium conductance inactivation by a specific protease in perfused nerve fibres from
1356:. The bursting, entrainment and other mathematical properties of this model have been studied in detail.
1311:{\displaystyle C{\frac {d^{2}V}{dt^{2}}}+\epsilon \left(V^{2}-1\right){\frac {dV}{dt}}+{\frac {V}{L}}=0.}
3148:
Cejnar, Pavel; Vyšata, Oldřich; Kukal, Jaromír; Beránek, Martin; Vališ, Martin; Procházka, Aleš (2020).
2978:
2963:
2948:
1974:
1361:
1330:
879:
50:
1487:
844:
Figure FHN: To mimick the action potential, the FitzHugh–Nagumo model and its relatives use a function
2855:
FitzHugh R (1969). "Mathematical models of axcitation and propagation in nerve". In HP Schwann (ed.).
814:. This analysis shows that the Hodgkin–Huxley system undergoes a transition from stable quiescence to
3161:
3048:
2921:
2776:
2598:
2278:
1885:
1875:
791:
446:{\displaystyle I_{\mathrm {K} }=g_{\mathrm {K} }\left(V-E_{\mathrm {K} }\right)p_{\mathrm {open,K} }}
2820:
Nagumo J, Arimoto S, Yoshizawa S (1962). "An active pulse transmission line simulating nerve axon".
840:
106:
represent the current through, and the voltage across, a small patch of membrane, respectively. The
3364:
325:
The model further assumes that a given ion channel is either fully open or closed; if closed, its
3308:
Woodbury JW (1965). "Chapter 3: Potentials in a volume conductor". In TC Ruch; HD Patton (eds.).
3017:
2937:
2837:
2745:
2345:
2302:
2217:
2134:
2085:
2036:
1987:
1920:
1475:
132:
3219:
2421:
The Book of GENESIS: Exploring
Realistic Neural Models with the GEneral NEural SImulation System
1996:"Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo"
1933:"Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo"
3336:
3258:
3223:
3189:
3101:
3074:
2901:
2802:
2737:
2709:
2614:
2569:
2557:
2537:
2511:
2465:
2372:
2337:
2294:
2249:
2203:
2172:
2123:
2074:
2025:
1962:
340:
of the channel being open, and the difference in voltage from that ion's equilibrium voltage,
2413:
40:
may be important and there is a great diversity of channels for all ions. As an example, the
3297:
3250:
3179:
3169:
3130:
3064:
3056:
3009:
2929:
2891:
2883:
2829:
2792:
2784:
2729:
2699:
2691:
2660:
2638:
2606:
2501:
2493:
2455:
2447:
2329:
2286:
2162:
2154:
2113:
2105:
2064:
2056:
2015:
2007:
1952:
1944:
1326:
21:
2568:(2nd printing, revised and corrected ed.). New York: Springer Verlag. pp. 12–16.
3000:
Keener JP (1983). "Analogue circuitry for the van der Pol and FitzHugh-Nagumo equations".
1439:
333:. Hence, the net current through an ion channel depends on two variables: the probability
17:
2094:"The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon of Loligo"
3165:
3052:
2925:
2780:
2602:
2282:
3212:
3184:
3149:
3092:
Rinzel J, Ermentrout GB (1989). "Analysis of Neural
Excitability and Oscillations". In
3069:
3036:
2896:
2871:
2797:
2764:
2720:
Kepler TB, Abbott LF, Marder E (1992). "Reduction of conductance-based neuron models".
2704:
2679:
2506:
2477:
2460:
2435:
2167:
2142:
2118:
2093:
2069:
2044:
2020:
1995:
1957:
1932:
1890:
1471:
1467:
1463:
1443:
1382:
3060:
2788:
3353:
3329:
3093:
2664:
2610:
2561:
2436:"Destruction of Sodium Conductance Inactivation in Squid Axons Perfused with Pronase"
2396:
2364:
2195:
2191:
2138:
2089:
2040:
1991:
1924:
525:
467:= 0) when the transmembrane voltage equals the equilibrium voltage of that ion (when
136:
3241:
Ling G, Gerard RW (1949). "The normal membrane potential of frog sartorius fibers".
3021:
2941:
2841:
2349:
2306:
88:
Equivalent electrical circuit for the
Hodgkin–Huxley model of the action potential.
2749:
2497:
2158:
2109:
2060:
2011:
1948:
1928:
1895:
898:
1389:
865:
457:
2320:
Guttman R, Feldman L, Jacobsson E (1980). "Frequency entrainment of squid axon".
2290:
1378:
3174:
2833:
2643:
2626:
2534:
Modeling in the Neurosciences: From Biological Systems to Neuromimetic Robotics
1128:{\displaystyle C{\frac {dV}{dt}}=I-\epsilon \left({\frac {V^{3}}{3}}-V\right),}
776:{\displaystyle {\frac {1}{\tau _{h}}}=0.07e^{-V/20}+{\frac {1}{1+e^{3-V/10}}}.}
3013:
1385:
84:
3301:
3100:. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Bradford Book, The MIT Press. pp. 135–169.
2371:. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Bradford Book, The MIT Press. pp. 171–194.
3262:
3254:
3193:
2905:
2806:
2765:"Impulses and Physiological States in Theoretical Models of Nerve Membrane"
2713:
2566:
Nonlinear Oscillations, Dynamical Systems and Bifurcations of Vector Fields
2298:
2202:. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Bradford Book, The MIT Press. pp. 97–133.
2176:
2127:
2078:
2029:
1966:
351:. For example, the current through the potassium channel may be written as
3078:
2741:
2618:
2469:
2341:
603:{\displaystyle {\frac {dm}{dt}}=-{\frac {m-m_{\mathrm {eq} }}{\tau _{m}}}}
2695:
2651:
Evans JW, Feroe J (1977). "Local stability theory of the nerve impulse".
2515:
2451:
1341:
864:
plot). For comparison, a normal resistor would have a positive slope, by
815:
2887:
1462:. Maxwell's equations can be reduced to a relatively simple problem of
2933:
2733:
2333:
58:
37:
1325:
equation has stimulated much research in the mathematics of nonlinear
1337:
31:
3134:
2045:"The components of membrane conductance in the giant axon of Loligo"
1807:
where the integration is over the complete surface of the membrane;
1466:, since the ionic concentrations change too slowly (compared to the
2872:"ACTIVATION OF PASSIVE IRON AS A MODEL FOR THE EXCITATION OF NERVE"
115:
represents the capacitance of the membrane patch, whereas the four
1837:
are the conductivity and potential just within the membrane, and σ
839:
83:
2363:
Getting PA (1989). "Reconstruction of Small Neural Networks". In
786:
In summary, the Hodgkin–Huxley equations are complex, non-linear
329:
is zero, whereas if open, its conductance is some constant value
3227:
2194:, Adams PR (1989). "Multiple Channels and Calcium Dynamics". In
506:
and a fourth gate, associated with inactivation, of probability
2680:"Thresholds and Plateaus in the Hodgkin-Huxley Nerve Equations"
897:
is a typical example of such a simplified system. Based on the
318:
represents the current arriving from external sources, such as
670:
varies as 3 with the Celsius temperature θ, and with voltage
644:
probability will always roughly equal its equilibrium value
3037:"Voltage oscillations in the barnacle giant muscle fiber"
2536:(2nd ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press. pp. 459–478.
49:
is typical of this class, which is often studied for its
3276:
Lorente de No R (1947). "A Study of Nerve Physiology".
3098:
Methods in Neuronal Modeling: From Synapses to Networks
2369:
Methods in Neuronal Modeling: From Synapses to Networks
2200:
Methods in Neuronal Modeling: From Synapses to Networks
57:
in nature, for example in the synchronized lighting of
524:. The probabilities for each gate are assumed to obey
1813:
1498:
1400:
1199:
1144:
1053:
977:
910:
683:
536:
360:
163:
2912:
Bonhoeffer KF (1953). "Modelle der Nervenerregung".
2239:
2237:
2235:
2233:
3328:
3211:
3002:IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics
2397:http://www.els.net/elsonline/figpage/I0000206.html
1821:
1796:
1419:
1310:
1179:
1127:
1024:
960:
775:
602:
445:
279:
2627:"Nerve axon equations. I. Linear approximations"
1420:{\displaystyle \mathbf {j} =\sigma \mathbf {E} }
3335:. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University.
3205:
3203:
2391:Hooper, Scott L. "Central Pattern Generators."
322:from the dendrites or a scientist's electrode.
1915:
1913:
1911:
2246:An introduction to the mathematics of neurons
1861:can be calculated from this potential field.
1381:; in such solutions, the current follows the
147:changes with the total transmembrane current
143:is constant; thus, the transmembrane voltage
8:
2527:
2525:
2423:. New York: Springer Verlag. pp. 29–49.
2399:(2 of 2) Online: Accessed 27 November 2007
2222:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
1979:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
2434:Armstrong CM, Bezanilla F, Rojas E (1973).
3218:. New York: John Wiley and Sons. pp.
634:changes on a time-scale more slowly than τ
3331:From Clocks to Chaos: The Rhythms of Life
3183:
3173:
3068:
2895:
2796:
2703:
2642:
2505:
2459:
2248:. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
2166:
2117:
2068:
2019:
1956:
1814:
1812:
1775:
1750:
1749:
1723:
1722:
1707:
1679:
1678:
1649:
1648:
1627:
1619:
1609:
1594:
1566:
1565:
1533:
1532:
1516:
1505:
1497:
1412:
1401:
1399:
1292:
1269:
1252:
1228:
1210:
1203:
1198:
1148:
1143:
1100:
1094:
1057:
1052:
981:
976:
961:{\displaystyle C{\frac {dV}{dt}}=I-g(V),}
914:
909:
757:
747:
731:
718:
711:
693:
684:
682:
592:
577:
576:
563:
537:
535:
421:
420:
404:
403:
381:
380:
366:
365:
359:
270:
269:
255:
254:
237:
236:
216:
215:
195:
194:
167:
162:
1025:{\displaystyle L{\frac {dI}{dt}}=E-V-RI}
818:oscillations as the stimulating current
2859:. New York: McGraw-Hill. pp. 1–85.
1907:
1815:
1776:
1708:
1628:
460:. By definition, no net current flows (
2951:(1926). "On relaxation-oscillations".
2215:
1972:
3278:Stud. Rockefeller Inst. Med. Research
1849:) can be calculated for any position
1388:, according to the continuum form of
1372:Extracellular potentials and currents
20:, several mathematical models of the
7:
1822:{\displaystyle {\boldsymbol {\xi }}}
1180:{\displaystyle L{\frac {dI}{dt}}=-V}
626:depend on the instantaneous voltage
3123:SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics
1458:, which in turn may be found using
1446:, respectively, and where σ is the
1352:and the potassium gate probability
3312:. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders Co.
1766:
1763:
1760:
1757:
1754:
1751:
1739:
1736:
1733:
1730:
1727:
1724:
1698:
1695:
1692:
1689:
1686:
1683:
1680:
1668:
1665:
1662:
1659:
1656:
1653:
1650:
1600:
1596:
1588:
1585:
1582:
1579:
1576:
1573:
1570:
1567:
1552:
1549:
1546:
1543:
1540:
1537:
1534:
620:and the relaxation time constant τ
581:
578:
437:
431:
428:
425:
422:
405:
382:
367:
320:excitatory postsynaptic potentials
271:
256:
241:
238:
223:
220:
217:
202:
199:
196:
14:
613:where both the equilibrium value
1829:is a position on the membrane, σ
1620:
1506:
1413:
1402:
854:negative differential resistance
2419:. In Bower J, Beeman D (eds.).
788:ordinary differential equations
2591:Journal of Theoretical Biology
2498:10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011608
2159:10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764
2110:10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004719
2061:10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004718
2012:10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717
1949:10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717
1853:; in turn, the electric field
1780:
1772:
1712:
1704:
1510:
1502:
952:
946:
125:voltage-sensitive ion channels
1:
3061:10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84782-0
2789:10.1016/S0006-3495(61)86902-6
1482:) at any extracellular point
1438:are vectors representing the
1039:is a function of the voltage
3210:Stevens, Charles F. (1966).
2665:10.1016/0025-5564(77)90076-1
2611:10.1016/0022-5193(70)90017-2
2412:Nelson ME, Rinzel J (1994).
2291:10.1126/science.174.4005.161
1881:Models of neural computation
794:: the transmembrane voltage
3327:Glass L, Mackey MC (1988).
655:changes more quickly, then
3386:
3175:10.1038/s41598-020-63834-7
3035:Morris C, Lecar H (1981).
2834:10.1109/JRPROC.1962.288235
2644:10.1512/iumj.1972.21.21071
2414:"The Hodgkin–Huxley Model"
833:
154:according to the equation
77:
67:central pattern generators
63:biological neural networks
3310:Physiology and Biophysics
3214:Neurophysiology: A Primer
3014:10.1109/TSMC.1983.6313098
856:(a negative slope on the
3302:10.1152/jn.1960.23.2.132
2476:Rojas E, Rudy B (1976).
2244:Hoppensteadt FC (1986).
1871:Biological neuron models
798:, and the probabilities
630:across the membrane. If
42:cardiac action potential
456:which is equivalent to
3255:10.1002/jcp.1030340304
3243:J. Cell. Comp. Physiol
2968:Philosophical Magazine
2953:Philosophical Magazine
2870:Bonhoeffer KF (1948).
2857:Biological Engineering
2822:Proceedings of the IRE
2722:Biological Cybernetics
1823:
1798:
1474:to be important. The
1421:
1360:capable of exhibiting
1312:
1181:
1129:
1026:
962:
890:
777:
604:
447:
281:
128:
3360:Mathematical modeling
2631:Indiana Univ. Math. J
2000:Journal of Physiology
1937:Journal of Physiology
1824:
1799:
1422:
1313:
1182:
1130:
1027:
963:
895:FitzHugh–Nagumo model
843:
836:FitzHugh–Nagumo model
830:FitzHugh–Nagumo model
792:independent variables
778:
605:
448:
282:
87:
47:FitzHugh–Nagumo model
29:of the axon from the
2983:Arch. Neerl. Physiol
2696:10.1085/jgp.43.5.867
2452:10.1085/jgp.62.4.375
1886:Saltatory conduction
1876:GHK current equation
1857:and current density
1811:
1496:
1486:can be solved using
1398:
1368:in nervous systems.
1197:
1142:
1051:
975:
908:
681:
534:
526:first-order kinetics
358:
161:
80:Hodgkin–Huxley model
74:Hodgkin–Huxley model
51:entrainment behavior
27:Hodgkin–Huxley model
3166:2020NatSR..10.7353C
3053:1981BpJ....35..193M
3041:Biophysical Journal
2926:1953NW.....40..301B
2914:Naturwissenschaften
2888:10.1085/jgp.32.1.69
2781:1961BpJ.....1..445F
2769:Biophysical Journal
2763:FitzHugh R (1961).
2678:FitzHugh R (1960).
2603:1970JThBi..29..155S
2367:and I Segev (ed.).
2283:1971Sci...174..161H
1460:Maxwell's equations
3154:Scientific Reports
2934:10.1007/BF00632438
2734:10.1007/BF00197717
2334:10.1007/BF01869347
1819:
1794:
1488:Green's identities
1476:electric potential
1454:can be found from
1417:
1308:
1177:
1125:
1022:
958:
891:
878:is the inverse of
773:
600:
443:
277:
133:Alan Lloyd Hodgkin
129:
3370:Action potentials
3342:978-0-691-08496-1
3107:978-0-262-11133-1
3096:, I Segev (ed.).
2828:(10): 2061–2070.
2625:Evans JW (1972).
2575:978-0-387-90819-9
2543:978-0-415-32868-5
2378:978-0-262-11133-1
2277:(4005): 161–164.
2255:978-0-521-31574-6
2209:978-0-262-11133-1
2198:, I Segev (ed.).
1637:
1607:
1559:
1366:commonly observed
1327:dynamical systems
1300:
1287:
1235:
1166:
1109:
1075:
999:
932:
768:
699:
598:
555:
185:
55:commonly observed
53:. Entrainment is
3377:
3346:
3334:
3314:
3313:
3305:
3285:
3273:
3267:
3266:
3238:
3232:
3231:
3217:
3207:
3198:
3197:
3187:
3177:
3145:
3139:
3138:
3118:
3112:
3111:
3089:
3083:
3082:
3072:
3032:
3026:
3025:
3008:(5): 1010–1014.
2997:
2991:
2990:
2975:
2960:
2945:
2909:
2899:
2867:
2861:
2860:
2852:
2846:
2845:
2817:
2811:
2810:
2800:
2760:
2754:
2753:
2717:
2707:
2675:
2669:
2668:
2648:
2646:
2622:
2586:
2580:
2579:
2554:
2548:
2547:
2529:
2520:
2519:
2509:
2473:
2463:
2431:
2425:
2424:
2418:
2409:
2403:
2389:
2383:
2382:
2360:
2354:
2353:
2317:
2311:
2310:
2266:
2260:
2259:
2241:
2228:
2227:
2221:
2213:
2187:
2181:
2180:
2170:
2131:
2121:
2082:
2072:
2033:
2023:
1984:
1978:
1970:
1960:
1917:
1828:
1826:
1825:
1820:
1818:
1803:
1801:
1800:
1795:
1787:
1783:
1779:
1771:
1770:
1769:
1744:
1743:
1742:
1711:
1703:
1702:
1701:
1673:
1672:
1671:
1638:
1636:
1632:
1631:
1623:
1610:
1608:
1606:
1595:
1593:
1592:
1591:
1560:
1558:
1557:
1556:
1555:
1517:
1509:
1472:magnetic effects
1426:
1424:
1423:
1418:
1416:
1405:
1317:
1315:
1314:
1309:
1301:
1293:
1288:
1286:
1278:
1270:
1268:
1264:
1257:
1256:
1236:
1234:
1233:
1232:
1219:
1215:
1214:
1204:
1186:
1184:
1183:
1178:
1167:
1165:
1157:
1149:
1134:
1132:
1131:
1126:
1121:
1117:
1110:
1105:
1104:
1095:
1076:
1074:
1066:
1058:
1031:
1029:
1028:
1023:
1000:
998:
990:
982:
967:
965:
964:
959:
933:
931:
923:
915:
782:
780:
779:
774:
769:
767:
766:
765:
761:
732:
727:
726:
722:
700:
698:
697:
685:
659:will lag behind
609:
607:
606:
601:
599:
597:
596:
587:
586:
585:
584:
564:
556:
554:
546:
538:
452:
450:
449:
444:
442:
441:
440:
415:
411:
410:
409:
408:
387:
386:
385:
372:
371:
370:
286:
284:
283:
278:
276:
275:
274:
261:
260:
259:
246:
245:
244:
228:
227:
226:
207:
206:
205:
186:
184:
176:
168:
119:s represent the
22:action potential
3385:
3384:
3380:
3379:
3378:
3376:
3375:
3374:
3350:
3349:
3343:
3326:
3323:
3321:Further reading
3318:
3317:
3307:
3306:
3290:J. Neurophysiol
3287:
3286:
3275:
3274:
3270:
3240:
3239:
3235:
3209:
3208:
3201:
3147:
3146:
3142:
3135:10.1137/0141042
3120:
3119:
3115:
3108:
3091:
3090:
3086:
3034:
3033:
3029:
2999:
2998:
2994:
2977:
2976:
2962:
2961:
2947:
2946:
2920:(11): 301–311.
2911:
2910:
2876:J. Gen. Physiol
2869:
2868:
2864:
2854:
2853:
2849:
2819:
2818:
2814:
2762:
2761:
2757:
2719:
2718:
2684:J. Gen. Physiol
2677:
2676:
2672:
2650:
2649:
2624:
2623:
2588:
2587:
2583:
2576:
2556:
2555:
2551:
2544:
2531:
2530:
2523:
2475:
2474:
2440:J. Gen. Physiol
2433:
2432:
2428:
2416:
2411:
2410:
2406:
2390:
2386:
2379:
2362:
2361:
2357:
2319:
2318:
2314:
2268:
2267:
2263:
2256:
2243:
2242:
2231:
2214:
2210:
2189:
2188:
2184:
2133:
2132:
2084:
2083:
2035:
2034:
1986:
1985:
1971:
1919:
1918:
1909:
1904:
1867:
1844:
1840:
1836:
1832:
1809:
1808:
1745:
1718:
1674:
1644:
1643:
1639:
1618:
1614:
1599:
1561:
1528:
1521:
1494:
1493:
1440:current density
1396:
1395:
1374:
1279:
1271:
1248:
1247:
1243:
1224:
1220:
1206:
1205:
1195:
1194:
1158:
1150:
1140:
1139:
1096:
1093:
1089:
1067:
1059:
1049:
1048:
991:
983:
973:
972:
924:
916:
906:
905:
838:
832:
824:
743:
736:
707:
689:
679:
678:
665:
650:
639:
625:
619:
588:
572:
565:
547:
539:
532:
531:
516:
497:
490:
477:
466:
416:
399:
392:
388:
376:
361:
356:
355:
350:
339:
317:
310:
303:
296:
265:
250:
232:
211:
190:
177:
169:
159:
158:
153:
114:
105:
96:
82:
76:
18:neurophysiology
12:
11:
5:
3383:
3381:
3373:
3372:
3367:
3362:
3352:
3351:
3348:
3347:
3341:
3322:
3319:
3316:
3315:
3296:(2): 132–143.
3268:
3249:(3): 383–396.
3233:
3199:
3140:
3129:(3): 503–517.
3113:
3106:
3084:
3047:(1): 193–213.
3027:
2992:
2862:
2847:
2812:
2775:(6): 445–466.
2755:
2728:(5): 381–387.
2690:(5): 867–896.
2670:
2659:(1–2): 23–50.
2637:(9): 877–885.
2597:(2): 155–171.
2581:
2574:
2558:Guckenheimer J
2549:
2542:
2521:
2492:(2): 501–531.
2446:(4): 375–391.
2426:
2404:
2384:
2377:
2355:
2322:J. Membr. Biol
2312:
2261:
2254:
2229:
2208:
2182:
2153:(4): 500–544.
2104:(4): 497–506.
2055:(4): 473–496.
2006:(4): 449–472.
1943:(4): 424–448.
1906:
1905:
1903:
1900:
1899:
1898:
1893:
1891:Bioelectronics
1888:
1883:
1878:
1873:
1866:
1863:
1842:
1838:
1834:
1830:
1817:
1805:
1804:
1793:
1790:
1786:
1782:
1778:
1774:
1768:
1765:
1762:
1759:
1756:
1753:
1748:
1741:
1738:
1735:
1732:
1729:
1726:
1721:
1717:
1714:
1710:
1706:
1700:
1697:
1694:
1691:
1688:
1685:
1682:
1677:
1670:
1667:
1664:
1661:
1658:
1655:
1652:
1647:
1642:
1635:
1630:
1626:
1622:
1617:
1613:
1605:
1602:
1598:
1590:
1587:
1584:
1581:
1578:
1575:
1572:
1569:
1564:
1554:
1551:
1548:
1545:
1542:
1539:
1536:
1531:
1527:
1524:
1520:
1515:
1512:
1508:
1504:
1501:
1468:speed of light
1464:electrostatics
1444:electric field
1428:
1427:
1415:
1411:
1408:
1404:
1379:ionic solution
1373:
1370:
1319:
1318:
1307:
1304:
1299:
1296:
1291:
1285:
1282:
1277:
1274:
1267:
1263:
1260:
1255:
1251:
1246:
1242:
1239:
1231:
1227:
1223:
1218:
1213:
1209:
1202:
1188:
1187:
1176:
1173:
1170:
1164:
1161:
1156:
1153:
1147:
1136:
1135:
1124:
1120:
1116:
1113:
1108:
1103:
1099:
1092:
1088:
1085:
1082:
1079:
1073:
1070:
1065:
1062:
1056:
1033:
1032:
1021:
1018:
1015:
1012:
1009:
1006:
1003:
997:
994:
989:
986:
980:
969:
968:
957:
954:
951:
948:
945:
942:
939:
936:
930:
927:
922:
919:
913:
834:Main article:
831:
828:
822:
784:
783:
772:
764:
760:
756:
753:
750:
746:
742:
739:
735:
730:
725:
721:
717:
714:
710:
706:
703:
696:
692:
688:
663:
651:; however, if
648:
635:
621:
617:
611:
610:
595:
591:
583:
580:
575:
571:
568:
562:
559:
553:
550:
545:
542:
514:
495:
486:
475:
464:
454:
453:
439:
436:
433:
430:
427:
424:
419:
414:
407:
402:
398:
395:
391:
384:
379:
375:
369:
364:
348:
337:
315:
308:
301:
294:
288:
287:
273:
268:
264:
258:
253:
249:
243:
240:
235:
231:
225:
222:
219:
214:
210:
204:
201:
198:
193:
189:
183:
180:
175:
172:
166:
151:
110:
101:
92:
78:Main article:
75:
72:
65:, such as the
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3382:
3371:
3368:
3366:
3363:
3361:
3358:
3357:
3355:
3344:
3338:
3333:
3332:
3325:
3324:
3320:
3311:
3303:
3299:
3295:
3291:
3283:
3279:
3272:
3269:
3264:
3260:
3256:
3252:
3248:
3244:
3237:
3234:
3229:
3225:
3221:
3216:
3215:
3206:
3204:
3200:
3195:
3191:
3186:
3181:
3176:
3171:
3167:
3163:
3159:
3155:
3151:
3144:
3141:
3136:
3132:
3128:
3124:
3117:
3114:
3109:
3103:
3099:
3095:
3088:
3085:
3080:
3076:
3071:
3066:
3062:
3058:
3054:
3050:
3046:
3042:
3038:
3031:
3028:
3023:
3019:
3015:
3011:
3007:
3003:
2996:
2993:
2988:
2984:
2980:
2979:van der Pol B
2973:
2969:
2965:
2964:van der Pol B
2958:
2954:
2950:
2949:van der Pol B
2943:
2939:
2935:
2931:
2927:
2923:
2919:
2915:
2907:
2903:
2898:
2893:
2889:
2885:
2881:
2877:
2873:
2866:
2863:
2858:
2851:
2848:
2843:
2839:
2835:
2831:
2827:
2823:
2816:
2813:
2808:
2804:
2799:
2794:
2790:
2786:
2782:
2778:
2774:
2770:
2766:
2759:
2756:
2751:
2747:
2743:
2739:
2735:
2731:
2727:
2723:
2715:
2711:
2706:
2701:
2697:
2693:
2689:
2685:
2681:
2674:
2671:
2666:
2662:
2658:
2654:
2645:
2640:
2636:
2632:
2628:
2620:
2616:
2612:
2608:
2604:
2600:
2596:
2592:
2585:
2582:
2577:
2571:
2567:
2563:
2559:
2553:
2550:
2545:
2539:
2535:
2528:
2526:
2522:
2517:
2513:
2508:
2503:
2499:
2495:
2491:
2487:
2483:
2481:
2471:
2467:
2462:
2457:
2453:
2449:
2445:
2441:
2437:
2430:
2427:
2422:
2415:
2408:
2405:
2401:
2398:
2394:
2393:Embryonic ELS
2388:
2385:
2380:
2374:
2370:
2366:
2359:
2356:
2351:
2347:
2343:
2339:
2335:
2331:
2327:
2323:
2316:
2313:
2308:
2304:
2300:
2296:
2292:
2288:
2284:
2280:
2276:
2272:
2265:
2262:
2257:
2251:
2247:
2240:
2238:
2236:
2234:
2230:
2225:
2219:
2211:
2205:
2201:
2197:
2193:
2186:
2183:
2178:
2174:
2169:
2164:
2160:
2156:
2152:
2148:
2144:
2140:
2136:
2129:
2125:
2120:
2115:
2111:
2107:
2103:
2099:
2095:
2091:
2087:
2080:
2076:
2071:
2066:
2062:
2058:
2054:
2050:
2046:
2042:
2038:
2031:
2027:
2022:
2017:
2013:
2009:
2005:
2001:
1997:
1993:
1989:
1982:
1976:
1968:
1964:
1959:
1954:
1950:
1946:
1942:
1938:
1934:
1930:
1926:
1922:
1916:
1914:
1912:
1908:
1901:
1897:
1894:
1892:
1889:
1887:
1884:
1882:
1879:
1877:
1874:
1872:
1869:
1868:
1864:
1862:
1860:
1856:
1852:
1848:
1791:
1788:
1784:
1746:
1719:
1715:
1675:
1645:
1640:
1633:
1624:
1615:
1611:
1603:
1562:
1529:
1525:
1522:
1518:
1513:
1499:
1492:
1491:
1490:
1489:
1485:
1481:
1477:
1473:
1469:
1465:
1461:
1457:
1453:
1449:
1445:
1441:
1437:
1433:
1409:
1406:
1394:
1393:
1392:
1391:
1387:
1384:
1380:
1371:
1369:
1367:
1363:
1357:
1355:
1351:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1334:
1332:
1328:
1324:
1305:
1302:
1297:
1294:
1289:
1283:
1280:
1275:
1272:
1265:
1261:
1258:
1253:
1249:
1244:
1240:
1237:
1229:
1225:
1221:
1216:
1211:
1207:
1200:
1193:
1192:
1191:
1174:
1171:
1168:
1162:
1159:
1154:
1151:
1145:
1138:
1137:
1122:
1118:
1114:
1111:
1106:
1101:
1097:
1090:
1086:
1083:
1080:
1077:
1071:
1068:
1063:
1060:
1054:
1047:
1046:
1045:
1042:
1038:
1019:
1016:
1013:
1010:
1007:
1004:
1001:
995:
992:
987:
984:
978:
971:
970:
955:
949:
943:
940:
937:
934:
928:
925:
920:
917:
911:
904:
903:
902:
900:
896:
888:
884:
881:
877:
874:
870:
867:
863:
859:
855:
851:
847:
842:
837:
829:
827:
821:
817:
813:
809:
805:
801:
797:
793:
789:
770:
762:
758:
754:
751:
748:
744:
740:
737:
733:
728:
723:
719:
715:
712:
708:
704:
701:
694:
690:
686:
677:
676:
675:
673:
669:
662:
658:
654:
647:
643:
638:
633:
629:
624:
616:
593:
589:
573:
569:
566:
560:
557:
551:
548:
543:
540:
530:
529:
528:
527:
523:
520:
513:
509:
505:
501:
494:
489:
485:
479:
474:
470:
463:
459:
434:
417:
412:
400:
396:
393:
389:
377:
373:
362:
354:
353:
352:
347:
343:
336:
332:
328:
323:
321:
314:
307:
300:
293:
266:
262:
251:
247:
233:
229:
212:
208:
191:
187:
181:
178:
173:
170:
164:
157:
156:
155:
150:
146:
142:
138:
137:Andrew Huxley
134:
126:
122:
118:
113:
109:
104:
100:
95:
91:
86:
81:
73:
71:
68:
64:
60:
56:
52:
48:
43:
39:
34:
33:
28:
23:
19:
3330:
3309:
3293:
3289:
3281:
3277:
3271:
3246:
3242:
3236:
3213:
3157:
3153:
3143:
3126:
3122:
3116:
3097:
3087:
3044:
3040:
3030:
3005:
3001:
2995:
2986:
2982:
2971:
2967:
2956:
2952:
2917:
2913:
2882:(1): 69–91.
2879:
2875:
2865:
2856:
2850:
2825:
2821:
2815:
2772:
2768:
2758:
2725:
2721:
2687:
2683:
2673:
2656:
2653:Math. Biosci
2652:
2634:
2630:
2594:
2590:
2584:
2565:
2552:
2533:
2489:
2485:
2479:
2443:
2439:
2429:
2420:
2407:
2392:
2387:
2368:
2358:
2325:
2321:
2315:
2274:
2270:
2264:
2245:
2199:
2185:
2150:
2146:
2101:
2097:
2052:
2048:
2003:
1999:
1975:cite journal
1940:
1936:
1896:Cable theory
1858:
1854:
1850:
1846:
1806:
1483:
1479:
1455:
1451:
1448:conductivity
1435:
1431:
1429:
1375:
1358:
1353:
1349:
1345:
1335:
1320:
1189:
1040:
1036:
1034:
899:tunnel diode
892:
886:
882:
875:
871:, where the
868:
861:
857:
849:
845:
819:
807:
803:
799:
795:
785:
671:
667:
660:
656:
652:
645:
641:
636:
631:
627:
622:
614:
612:
521:
518:
511:
507:
503:
499:
492:
487:
483:
480:
472:
468:
461:
455:
345:
341:
334:
330:
324:
312:
305:
298:
291:
289:
148:
144:
140:
130:
121:conductances
116:
111:
107:
102:
98:
93:
89:
30:
15:
3284:: Chap. 16.
3160:(1): 7353.
2328:(1): 9–18.
2190:Yamada WM,
1386:field lines
1364:, which is
1362:entrainment
1323:van der Pol
873:conductance
812:fixed point
327:conductance
3365:Capacitors
3354:Categories
2989:: 418–443.
2974:: 763–775.
2959:: 978–992.
2486:J. Physiol
2135:Hodgkin AL
2086:Hodgkin AL
2037:Hodgkin AL
1988:Hodgkin AL
1921:Hodgkin AL
1902:References
880:resistance
2218:cite book
2147:J Physiol
2139:Huxley AF
2098:J Physiol
2090:Huxley AF
2049:J Physiol
2041:Huxley AF
1992:Huxley AF
1925:Huxley AF
1816:ξ
1777:ξ
1747:ϕ
1720:σ
1716:−
1709:ξ
1676:ϕ
1646:σ
1629:ξ
1625:−
1601:∂
1597:∂
1563:∮
1530:σ
1526:π
1500:ϕ
1450:. Thus,
1410:σ
1390:Ohm's Law
1342:barnacles
1340:fiber of
1259:−
1241:ϵ
1172:−
1112:−
1087:ϵ
1084:−
1014:−
1008:−
941:−
866:Ohm's law
752:−
713:−
691:τ
590:τ
570:−
561:−
458:Ohm's law
397:−
59:fireflies
3263:15410483
3228:66015872
3194:32355185
3022:20077648
2942:19149460
2906:18885679
2842:51648050
2807:19431309
2714:13823315
2564:(1986).
2562:Holmes P
2350:10775478
2307:41760422
2299:17742039
2177:12991237
2141:(1952).
2128:14946715
2092:(1952).
2079:14946714
2043:(1952).
2030:14946713
1994:(1952).
1967:14946713
1931:(1952).
1865:See also
1383:electric
816:bursting
790:in four
515:open, Na
510:; thus,
344:−
131:In 1952
3185:7192907
3162:Bibcode
3094:C. Koch
3079:7260316
3070:1327511
3049:Bibcode
2922:Bibcode
2897:2213747
2798:1366333
2777:Bibcode
2750:6789007
2742:1562643
2705:2195039
2619:5500466
2599:Bibcode
2507:1307656
2470:4755846
2461:2226121
2395:(1999)
2342:7441721
2279:Bibcode
2271:Science
2196:C. Koch
2168:1392413
2119:1392212
2070:1392209
2021:1392213
1958:1392213
1843:outside
1839:outside
852:) with
496:open, K
38:calcium
3339:
3261:
3226:
3222:–173.
3192:
3182:
3104:
3077:
3067:
3020:
2940:
2904:
2894:
2840:
2805:
2795:
2748:
2740:
2712:
2702:
2617:
2572:
2540:
2516:994046
2514:
2504:
2480:Loligo
2468:
2458:
2375:
2365:C Koch
2348:
2340:
2305:
2297:
2252:
2206:
2192:Koch C
2175:
2165:
2126:
2116:
2077:
2067:
2028:
2018:
1965:
1955:
1929:Katz B
1835:inside
1831:inside
1470:) for
1430:where
1338:muscle
1331:Op-amp
1035:where
869:I = GV
640:, the
304:, and
290:where
32:Loligo
3018:S2CID
2938:S2CID
2838:S2CID
2746:S2CID
2417:(PDF)
2346:S2CID
2303:S2CID
1841:and φ
1833:and φ
1321:This
3337:ISBN
3259:PMID
3224:LCCN
3190:PMID
3102:ISBN
3075:PMID
2902:PMID
2803:PMID
2738:PMID
2710:PMID
2615:PMID
2570:ISBN
2538:ISBN
2512:PMID
2466:PMID
2373:ISBN
2338:PMID
2295:PMID
2250:ISBN
2224:link
2204:ISBN
2173:PMID
2124:PMID
2075:PMID
2026:PMID
1981:link
1963:PMID
1442:and
1434:and
1037:g(V)
860:vs.
806:and
705:0.07
338:open
135:and
97:and
3298:doi
3282:132
3251:doi
3220:161
3180:PMC
3170:doi
3131:doi
3065:PMC
3057:doi
3010:doi
2930:doi
2892:PMC
2884:doi
2830:doi
2793:PMC
2785:doi
2730:doi
2700:PMC
2692:doi
2661:doi
2639:doi
2607:doi
2502:PMC
2494:doi
2490:262
2456:PMC
2448:doi
2330:doi
2287:doi
2275:174
2163:PMC
2155:doi
2151:117
2114:PMC
2106:doi
2102:116
2065:PMC
2057:doi
2053:116
2016:PMC
2008:doi
2004:116
1953:PMC
1945:doi
1941:116
885:=1/
823:ext
674:as
478:).
316:ext
152:tot
16:In
3356::
3294:23
3292:.
3280:.
3257:.
3247:34
3245:.
3202:^
3188:.
3178:.
3168:.
3158:10
3156:.
3152:.
3127:41
3125:.
3073:.
3063:.
3055:.
3045:35
3043:.
3039:.
3016:.
3006:13
3004:.
2987:14
2985:.
2970:.
2955:.
2936:.
2928:.
2918:40
2916:.
2900:.
2890:.
2880:32
2878:.
2874:.
2836:.
2826:50
2824:.
2801:.
2791:.
2783:.
2771:.
2767:.
2744:.
2736:.
2726:66
2724:.
2708:.
2698:.
2688:43
2686:.
2682:.
2657:37
2655:.
2635:21
2633:.
2629:.
2613:.
2605:.
2595:29
2593:.
2560:,
2524:^
2510:.
2500:.
2488:.
2484:.
2464:.
2454:.
2444:62
2442:.
2438:.
2344:.
2336:.
2326:56
2324:.
2301:.
2293:.
2285:.
2273:.
2232:^
2220:}}
2216:{{
2171:.
2161:.
2149:.
2145:.
2137:,
2122:.
2112:.
2100:.
2096:.
2088:,
2073:.
2063:.
2051:.
2047:.
2039:,
2024:.
2014:.
2002:.
1998:.
1990:,
1977:}}
1973:{{
1961:.
1951:.
1939:.
1935:.
1927:,
1923:,
1910:^
1478:φ(
1329:.
1306:0.
802:,
763:10
724:20
664:eq
649:eq
618:eq
517:=
498:=
471:=
349:eq
297:,
295:Na
117:g'
3345:.
3304:.
3300::
3265:.
3253::
3230:.
3196:.
3172::
3164::
3137:.
3133::
3110:.
3081:.
3059::
3051::
3024:.
3012::
2972:6
2957:2
2944:.
2932::
2924::
2908:.
2886::
2844:.
2832::
2809:.
2787::
2779::
2773:1
2752:.
2732::
2716:.
2694::
2667:.
2663::
2647:.
2641::
2621:.
2609::
2601::
2578:.
2546:.
2518:.
2496::
2482:"
2472:.
2450::
2402:.
2381:.
2352:.
2332::
2309:.
2289::
2281::
2258:.
2226:)
2212:.
2179:.
2157::
2130:.
2108::
2081:.
2059::
2032:.
2010::
1983:)
1969:.
1947::
1859:j
1855:E
1851:x
1847:x
1792:S
1789:d
1785:]
1781:)
1773:(
1767:e
1764:d
1761:i
1758:s
1755:n
1752:i
1740:e
1737:d
1734:i
1731:s
1728:n
1725:i
1713:)
1705:(
1699:e
1696:d
1693:i
1690:s
1687:t
1684:u
1681:o
1669:e
1666:d
1663:i
1660:s
1657:t
1654:u
1651:o
1641:[
1634:|
1621:x
1616:|
1612:1
1604:n
1589:e
1586:n
1583:a
1580:r
1577:b
1574:m
1571:e
1568:m
1553:e
1550:d
1547:i
1544:s
1541:t
1538:u
1535:o
1523:4
1519:1
1514:=
1511:)
1507:x
1503:(
1484:x
1480:x
1456:E
1452:j
1436:E
1432:j
1414:E
1407:=
1403:j
1354:n
1350:V
1346:h
1303:=
1298:L
1295:V
1290:+
1284:t
1281:d
1276:V
1273:d
1266:)
1262:1
1254:2
1250:V
1245:(
1238:+
1230:2
1226:t
1222:d
1217:V
1212:2
1208:d
1201:C
1175:V
1169:=
1163:t
1160:d
1155:I
1152:d
1146:L
1123:,
1119:)
1115:V
1107:3
1102:3
1098:V
1091:(
1081:I
1078:=
1072:t
1069:d
1064:V
1061:d
1055:C
1041:V
1020:I
1017:R
1011:V
1005:E
1002:=
996:t
993:d
988:I
985:d
979:L
956:,
953:)
950:V
947:(
944:g
938:I
935:=
929:t
926:d
921:V
918:d
912:C
889:.
887:R
883:G
876:G
862:V
858:I
850:V
848:(
846:g
820:I
808:n
804:h
800:m
796:V
771:.
759:/
755:V
749:3
745:e
741:+
738:1
734:1
729:+
720:/
716:V
709:e
702:=
695:h
687:1
672:V
668:h
661:m
657:m
653:V
646:m
642:m
637:m
632:V
628:V
623:m
615:m
594:m
582:q
579:e
574:m
567:m
558:=
552:t
549:d
544:m
541:d
522:h
519:m
512:p
508:h
504:m
500:n
493:p
488:n
484:p
476:K
473:E
469:V
465:K
462:I
438:K
435:,
432:n
429:e
426:p
423:o
418:p
413:)
406:K
401:E
394:V
390:(
383:K
378:g
374:=
368:K
363:I
346:V
342:V
335:p
331:g
313:I
309:L
306:I
302:K
299:I
292:I
272:L
267:I
263:+
257:K
252:I
248:+
242:a
239:N
234:I
230:+
224:t
221:x
218:e
213:I
209:=
203:t
200:o
197:t
192:I
188:=
182:t
179:d
174:V
171:d
165:C
149:I
145:V
141:C
127:.
112:m
108:C
103:m
99:V
94:m
90:I
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.