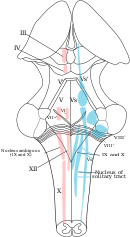347:. Ventilation was monitored both before and after lesions to the pneumatic center region and after subsequent bilateral vagotomy. Cats with pontine lesions had a prolonged inhalation duration. In cats, after anaesthesia and vagotomy, pontine transaction has been described as evoking a long sustained inspiratory discharges interrupted by short expiratory pauses. In rats on the other hand, after anaesthesia, vagotomy and pontine transaction, this breathing pattern was not observed, either in vivo or in vitro. These results suggest interspecies differences between rat and cat in the pontine influences on the medullary respiratory center.
42:
360:(IOS) signal of the inspiratory ramp provided by the pneumotaxic center. It controls the intensity of breathing, giving positive impulses to the neurons involved with inhalation. The apneustic center is inhibited by pulmonary stretch receptors and also by the pneumotaxic center. It also discharges an inhibitory impulse to the pneumotaxic center.
186:
374:
Breathing is the repetitive process of bringing air into the lungs and taking waste products out. The oxygen brought in from the air is a constant, on-going need of an organism to maintain life. This need is still there during sleep so that the functioning of this process has to be automatic and be
335:
that are constant in duration and interval. When a faster rate of breathing is needed the pneumotaxic center signals the dorsal respiratory group to speed up. When longer breaths are needed the bursts of activity are elongated. All the information that the body uses to help respiration happens in
193:
The dorsal respiratory group (DRG) has the most fundamental role in the control of respiration, initiating inspiration (inhalation). The DRG is a collection of neurons forming an elongated mass that extends most of the length of the dorsal medulla. They are near to the
106:, two in the medulla and one in the pons. In the medulla they are the dorsal respiratory group, and the ventral respiratory group. In the pons, the pontine respiratory group includes two areas known as the pneumotaxic center and the apneustic center.
379:. The in-breath is followed by the out-breath, giving the respiratory cycle of inhalation and exhalation. There are three phases of the respiratory cycle: inspiration, post-inspiration or passive expiration, and late or active expiration.
271:
The VRG contains both inspiratory and expiratory neurons. The ventral respiratory group of neurons are active in forceful breathing and inactive during quiet, restful respirations. The VRG sends inhibitory impulses to the apneustic center.
355:
The apneustic center of the lower pons appears to promote inhalation by constant stimulation of the neurons in the medulla oblongata. The apneustic center sends signals to the dorsal group in the medulla to delay the 'switch off, the
213:. Other important neurons are found in the adjacent areas including the reticular substance of the medulla. The solitary nucleus is the end-point for sensory information arriving from the pontine respiratory group, and from two
176:
is made up of two areas – the pneumotaxic center and the apneustic center. The dorsal and ventral medullary groups control the basic rhythm of respiration. The groups are paired with one on each side of the brainstem.
1113:
Shannon, Roger; Baekey, David M.; Morris, Kendall F.; Nuding, Sarah C.; Segers, Lauren S.; Lindsey, Bruce G. (2004). "Pontine respiratory group neuron discharge is altered during fictive cough in the decerebrate cat".
256:(expiratory) area of respiratory control. This area is in the ventrolateral part of the medulla, about 5 mm anterior and lateral to the dorsal respiratory group. The neurons involved include those in the
308:
to the apneustic center (which produces abnormal breathing during inhalation), cyclically inhibiting inhalation. The pneumotaxic center is responsible for limiting inspiration, providing an
1976:
1172:
894:
Monteau, R.; Errchidi, S.; Gauthier, P.; Hilaire, G.; Rega, P. (1989). "Pneumotaxic centre and apneustic breathing: Interspecies differences between rat and cat".
460:, to produce faster and deeper breaths. Normally at therapeutic doses, this effect is not noticeable, but may be evident when respiration is already compromised.
2359:
189:
Solitary tract nucleus in the dorsal respiratory group and nucleus ambiguous of the ventral respiratory group shown in their positions on the medulla oblongata.
2202:
2036:
2011:
639:
Betts, J. Gordon; Young, Kelly A.; Wise, James A.; Johnson, Eddie; Poe, Brandon; Kruse, Dean H.; Korol, Oksana; Johnson, Jody E.; Womble, Mark (2022-04-20).
386:. The respiratory rate is set in the respiratory center by the dorsal respiratory group, in the medulla, and these neurons are mostly concentrated in the
284:
in the pons, the pontine respiratory group (PRG) includes the pneumotaxic and apneustic centers. These have connections between them, and from both to the
2016:
241:. Thus, the dorsal respiratory group is seen as an integrating center that gives the ventral respiratory group output to modify the breathing rhythm.
1538:
409:. When the metabolic need for oxygen increases, inspiration becomes more forceful and the neurons in the ventral group are activated to bring about
249:
The VRG maintains a constant breathing rhythm by stimulating the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles to contract, resulting in inspiration.
2645:
691:
Song, G; Poon, CS (15 November 2004). "Functional and structural models of pontine modulation of mechanoreceptor and chemoreceptor reflexes".
1103:
1080:
843:
595:
538:
1165:
164:
The respiratory center is divided into three major groups, two in the medulla and one in the pons. The two groups in the medulla are the
2640:
1609:
1464:
2068:
1659:
1051:
675:
623:
563:
513:
331:
The pneumotaxic center regulates the amount of air that can be taken into the body in each breath. The dorsal respiratory group has
988:"Microcircuits in respiratory rhythm generation: commonalities with other rhythm generating networks and evolutionary perspectives"
2630:
2440:
2241:
2431:
2351:
2073:
1981:
1158:
1528:
109:
The respiratory center is responsible for generating and maintaining the rhythm of respiration, and also of adjusting this in
2635:
2301:
2263:
2150:
1916:
1911:
1901:
1896:
859:
Gautier, H; Bertrand, F (1975). "Respiratory effects of pneumatic center lesions and subsequent vagotomy in chronic cats".
640:
2316:
1774:
1255:
665:
2499:
2311:
2289:
2088:
2041:
1837:
1377:
2494:
2395:
2268:
1779:
1742:
1547:
1496:
1347:
402:
304:. The pneumotaxic center controls both the rate and the pattern of breathing. The pneumotaxic center is considered an
2685:
2580:
1732:
1501:
2449:
2444:
2417:
2383:
2364:
2294:
2083:
2078:
1832:
1827:
1809:
1737:
1409:
1340:
1321:
369:
226:
1352:
2506:
2469:
2421:
2192:
1993:
1715:
1485:
1316:
1210:
376:
336:
the pneumotaxic center. If this was damaged or in any way harmed it would make breathing almost impossible.
57:
1847:
265:
2489:
2378:
2258:
2236:
1518:
1387:
328:. Absence of the center results in an increase in depth of respiration and a decrease in respiratory rate.
41:
2585:
2187:
2117:
2110:
2100:
1335:
1282:
1272:
1181:
469:
332:
305:
222:
153:
69:
2575:
2332:
2306:
1937:
1686:
1652:
1523:
1459:
252:
In the medulla, the ventral respiratory group (VRG) consists of four groups of neurons that make up the
736:"Cytoarchitecture of Pneumotaxic Integration of Respiratory and Nonrespiratory Information in the Rat"
2657:
2528:
2426:
2231:
2105:
1578:
1433:
1397:
1232:
1227:
2625:
2570:
2484:
2063:
2031:
1971:
1942:
1891:
1881:
1764:
1260:
442:
414:
410:
301:
297:
146:
2680:
2479:
2143:
1588:
1583:
1563:
1421:
1297:
1139:
919:
716:
398:
129:
in order to regulate the rate and depth of breathing. Input is stimulated by altered levels of
2390:
2253:
2207:
2171:
1842:
1727:
1722:
1669:
1626:
1542:
1508:
1310:
1265:
1247:
1131:
1099:
1076:
1047:
1017:
968:
911:
876:
839:
816:
767:
708:
671:
619:
591:
559:
534:
509:
281:
142:
91:
2565:
2474:
2435:
2373:
2248:
1886:
1769:
1705:
1645:
1443:
1392:
1302:
1217:
1123:
1007:
999:
958:
950:
903:
868:
806:
798:
757:
747:
700:
387:
383:
325:
313:
285:
257:
238:
210:
203:
118:
2511:
2197:
1804:
1799:
1621:
1469:
1438:
1039:
145:
and anxiety from the hypothalamus, and also by signals from the cerebral cortex to give a
122:
339:
One study on this subject was on anaesthetized paralyzed cats before and after bilateral
943:
Philosophical
Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences
2603:
2546:
2226:
1710:
1567:
1557:
1414:
1372:
1237:
1012:
987:
963:
938:
811:
786:
762:
735:
406:
214:
134:
114:
2690:
2674:
2136:
2026:
2021:
1573:
1329:
1242:
907:
872:
397:. Quiet breathing only requires the activity of the dorsal group which activates the
317:
195:
923:
720:
296:
The pneumotaxic center is located in the upper part of the pons. Its nuclei are the
152:
Injury to respiratory groups can cause various breathing disorders that may require
2652:
2556:
2280:
2217:
2095:
1988:
1863:
1513:
1382:
1364:
1222:
1143:
752:
474:
434:
430:
426:
321:
230:
126:
939:"Pontine respiratory activity involved in inspiratory/expiratory phase transition"
17:
62:
2538:
2328:
2055:
1677:
1552:
457:
343:. Ventilation was monitored in awake and anaesthetized cats breathing air or CO
261:
218:
199:
110:
1127:
1003:
704:
1614:
1533:
1428:
1205:
1200:
479:
253:
113:
response to physiological changes. The respiratory center receives input from
393:
The basic rhythm of respiration is that of quiet, restful breathing known as
1490:
99:
1135:
1021:
972:
954:
820:
771:
712:
915:
880:
1637:
1150:
1095:
802:
590:(12th ed.). Philadelphia, Pa.: Saunders/Elsevier. pp. 505–510.
450:
438:
340:
102:. The respiratory center is made up of three major respiratory groups of
75:
2128:
641:"22.3 The Process of Breathing - Anatomy and Physiology 2e | OpenStax"
1195:
986:
Ramirez, JM; Dashevskiy, T; Marlin, IA; Baertsch, N (December 2016).
446:
394:
130:
103:
225:. The solitary nucleus sends signals to the respiratory center from
185:
184:
2160:
1592:
1291:
234:
95:
46:
Respiratory groups in the respiratory center and their influence
2132:
1641:
1154:
202:, and just behind the ventral group. They set and maintain the
533:(3rd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. p. 332.
1044:
138:
1075:(6th ed.). McGraw-Hill Professional. pp. 193–4.
664:
Koeppen, Bruce M.; Stanton, Bruce A. (18 January 2017).
425:
Depression of the respiratory center can be caused by:
2616:
2596:
2555:
2537:
2524:
2462:
2406:
2340:
2327:
2279:
2216:
2180:
2167:
2054:
2004:
1964:
1957:
1927:
1871:
1862:
1818:
1792:
1753:
1694:
1685:
1676:
1602:
1478:
1452:
1363:
1281:
1188:
156:, and is usually associated with a poor prognosis.
56:
51:
34:
1042:. In Brunton LL, Chabner BA, Knollmann BC (eds.).
529:Pocock, Gillian; Richards, Christopher D. (2006).
556:Anatomy Physiology The Unity of Form and Function
937:Mörschel, M; Dutschmann, M (12 September 2009).
734:Song, Gang; Yu, Yunguo; Poon, Chi-Sang (2006).
618:(3rd ed.). McGraw-Hill. pp. 646–647.
588:Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology
2144:
1653:
1166:
1046:(12th ed.). New York, USA: McGraw-Hill.
531:Human physiology : the basis of medicine
8:
456:The respiratory center can be stimulated by
417:is termed dyspnea – the opposite of eupnea.
1033:
1031:
787:"Pontine mechanisms of respiratory control"
558:. McGraw-Hill Education. pp. 868–871.
508:(13th. ed.). Wiley. pp. 906–909.
2534:
2337:
2177:
2151:
2137:
2129:
1961:
1868:
1691:
1682:
1660:
1646:
1638:
1173:
1159:
1151:
405:. Exhalation is passive and relies on the
40:
1912:Descending dorsal longitudinal fasciculus
1116:Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology
1011:
962:
810:
761:
751:
693:Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology
609:
607:
581:
579:
577:
575:
499:
497:
495:
1897:Ascending dorsal longitudinal fasciculus
1040:"Miscellaneous Sympathomimetic Agonists"
785:Dutschmann, M; Dick, TE (October 2012).
390:that extends the length of the medulla.
491:
382:The number of cycles per minute is the
209:Most of the neurons are located in the
506:Principles of anatomy & physiology
233:, and other types of receptors in the
73:
31:
441:. A depression can also be caused by
260:, the nucleus retroambiguus, and the
7:
1539:oxygen–hemoglobin dissociation curve
27:Brain region controlling respiration
143:hormonal changes relating to stress
1465:hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction
1094:(3rd ed.). Philadelphia, PA:
504:Tortora, G; Derrickson, B (2011).
25:
1038:Westfall DP, Westfall TC (2010).
667:Berne and Levy Physiology E-Book
992:Current Opinion in Neurobiology
2302:Medial longitudinal fasciculus
2264:Medial longitudinal fasciculus
1917:Medial longitudinal fasciculus
1902:Medial longitudinal fasciculus
753:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3029-05.2006
312:(IOS). It limits the burst of
1:
2317:Lateral vestibulospinal tract
1775:Dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve
1071:Levitzky, Michael G. (2002).
320:, effectively decreasing the
211:nucleus of the solitary tract
2500:Lateral parabrachial nucleus
2312:Medial vestibulospinal tract
2290:Inferior cerebellar peduncle
2042:Inferior cerebellar peduncle
1838:Rostral ventromedial medulla
908:10.1016/0304-3940(89)90465-5
873:10.1016/0034-5687(75)90073-0
834:Dutschmann, Mathias (2011).
670:. Elsevier Health Sciences.
403:external intercostal muscles
2495:Medial parabrachial nucleus
2269:Vestibulo-oculomotor fibers
1780:Inferior salivatory nucleus
1497:Ventilation/perfusion ratio
1348:pulmonary stretch receptors
1090:Costanzo, Linda S. (2006).
407:elastic recoil of the lungs
333:rhythmic bursts of activity
302:medial parabrachial nucleus
2707:
1833:Arcuate nucleus of medulla
1529:alveolar–arterial gradient
1128:10.1016/j.resp.2004.05.002
1004:10.1016/j.conb.2016.08.003
705:10.1016/j.resp.2004.05.009
367:
2450:Inferior salivary nucleus
2445:Superior salivary nucleus
2295:Vestibulocerebellar tract
1828:Ventral respiratory group
1810:Accessory cuneate nucleus
1410:respiratory minute volume
1322:ventral respiratory group
838:. : John Wiley and Sons.
554:Saladin, Kenneth (2012).
370:Central pattern generator
276:Pontine respiratory group
245:Ventral respiratory group
227:peripheral chemoreceptors
174:pontine respiratory group
170:ventral respiratory group
68:
39:
2507:Superior olivary nucleus
2470:Pedunculopontine nucleus
2422:Trigeminal motor nucleus
2242:Ventral trigeminal tract
2193:Superior medullary velum
1994:Inferior olivary nucleus
1716:Dorsal respiratory group
1317:dorsal respiratory group
1211:obligate nasal breathing
836:Comprehensive Physiology
791:Comprehensive Physiology
377:autonomic nervous system
181:Dorsal respiratory group
166:dorsal respiratory group
2490:Subparabrachial nucleus
2259:Central tegmental tract
2237:Dorsal trigeminal tract
2012:Posterior median sulcus
1977:Anterior median fissure
1519:pulmonary gas pressures
740:Journal of Neuroscience
298:subparabrachial nucleus
2586:Pontocerebellar fibers
2188:Cerebellopontine angle
2118:Perihypoglossal nuclei
1273:mechanical ventilation
1182:Respiratory physiology
955:10.1098/rstb.2009.0074
861:Respiration Physiology
470:Control of respiration
358:inspiratory off switch
310:inspiratory off-switch
223:glossopharyngeal nerve
190:
154:mechanical ventilation
70:Anatomical terminology
2576:Corticopontine fibers
2307:Vestibulospinal tract
2017:Posterolateral sulcus
1938:Olivocerebellar tract
1848:Pre-Bötzinger complex
1524:alveolar gas equation
1460:pulmonary circulation
421:Clinical significance
368:Further information:
266:pre-Bötzinger complex
188:
2427:Facial motor nucleus
2232:Trigeminal lemniscus
1982:Anterolateral sulcus
1579:respiratory quotient
1434:body plethysmography
1353:Hering–Breuer reflex
1228:pulmonary surfactant
1073:Pulmonary Physiology
896:Neuroscience Letters
803:10.1002/cphy.c100015
2626:Reticular formation
2571:Corticobulbar tract
2566:Corticospinal tract
2485:Parabrachial nuclei
2064:Reticular formation
2032:Hypoglossal trigone
1943:Rubro-olivary tract
1892:Juxtarestiform body
1882:Sensory decussation
1765:Hypoglossal nucleus
1422:Lung function tests
1256:hyperresponsiveness
614:Saladin, K (2011).
586:Hall, John (2011).
415:Shortness of breath
411:forceful exhalation
324:and regulating the
204:rate of respiration
172:. In the pons, the
2617:Other grey: Raphe/
2559:: Motor/descending
2480:Pneumotaxic center
2463:Grey: Other nuclei
1934:Descending tracts
1589:diffusion capacity
1584:arterial blood gas
1564:carbonic anhydrase
1298:pneumotaxic center
364:Respiratory rhythm
292:Pneumotaxic center
237:in particular the
191:
160:Respiratory groups
90:is located in the
88:respiratory center
35:Respiratory center
18:Respiratory rhythm
2686:Medulla oblongata
2668:
2667:
2612:
2611:
2520:
2519:
2458:
2457:
2391:Vestibular nuclei
2254:Lateral lemniscus
2208:Facial colliculus
2126:
2125:
2050:
2049:
1953:
1952:
1858:
1857:
1843:Botzinger complex
1788:
1787:
1728:Vestibular nuclei
1723:Gustatory nucleus
1635:
1634:
1543:Oxygen saturation
1509:zones of the lung
1248:airway resistance
1105:978-1-4160-2320-3
1082:978-0-07-138765-1
949:(1529): 2517–26.
845:978-0-470-65071-4
597:978-1-4160-4574-8
540:978-0-19-856878-0
314:action potentials
282:pontine tegmentum
239:stretch receptors
147:conscious control
92:medulla oblongata
84:
83:
79:
16:(Redirected from
2698:
2535:
2475:Apneustic center
2436:Abducens nucleus
2411:
2374:Cochlear nucleus
2345:
2338:
2249:Medial lemniscus
2178:
2153:
2146:
2139:
2130:
1962:
1887:Medial lemniscus
1869:
1770:Nucleus ambiguus
1758:
1706:Solitary nucleus
1699:
1692:
1683:
1662:
1655:
1648:
1639:
1444:nitrogen washout
1303:apneustic center
1218:respiratory rate
1175:
1168:
1161:
1152:
1147:
1109:
1086:
1058:
1057:
1035:
1026:
1025:
1015:
983:
977:
976:
966:
934:
928:
927:
891:
885:
884:
856:
850:
849:
831:
825:
824:
814:
782:
776:
775:
765:
755:
731:
725:
724:
688:
682:
681:
661:
655:
654:
652:
651:
636:
630:
629:
611:
602:
601:
583:
570:
569:
551:
545:
544:
526:
520:
519:
501:
388:solitary nucleus
384:respiratory rate
351:Apneustic center
326:respiratory rate
286:solitary nucleus
258:nucleus ambiguus
149:of respiration.
119:mechanoreceptors
76:edit on Wikidata
44:
32:
21:
2706:
2705:
2701:
2700:
2699:
2697:
2696:
2695:
2671:
2670:
2669:
2664:
2618:
2608:
2592:
2551:
2526:
2516:
2512:Locus coeruleus
2454:
2407:
2402:
2341:
2323:
2275:
2212:
2203:Medial eminence
2198:Sulcus limitans
2169:
2163:
2159:Anatomy of the
2157:
2127:
2122:
2069:Gigantocellular
2046:
2037:Medial eminence
2000:
1949:
1923:
1854:
1814:
1805:Cuneate nucleus
1800:Gracile nucleus
1784:
1754:
1749:
1695:
1672:
1668:Anatomy of the
1666:
1636:
1631:
1622:oxygen toxicity
1598:
1486:ventilation (V)
1474:
1470:pulmonary shunt
1448:
1439:peak flow meter
1359:
1277:
1184:
1179:
1112:
1106:
1098:. p. 224.
1089:
1083:
1070:
1067:
1065:Further reading
1062:
1061:
1054:
1037:
1036:
1029:
985:
984:
980:
936:
935:
931:
893:
892:
888:
858:
857:
853:
846:
833:
832:
828:
784:
783:
779:
733:
732:
728:
699:(2–3): 281–92.
690:
689:
685:
678:
663:
662:
658:
649:
647:
638:
637:
633:
626:
613:
612:
605:
598:
585:
584:
573:
566:
553:
552:
548:
541:
528:
527:
523:
516:
503:
502:
493:
488:
466:
423:
372:
366:
353:
346:
294:
278:
247:
183:
162:
123:cerebral cortex
80:
47:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2704:
2702:
2694:
2693:
2688:
2683:
2673:
2672:
2666:
2665:
2663:
2662:
2661:
2660:
2650:
2649:
2648:
2643:
2638:
2633:
2622:
2620:
2614:
2613:
2610:
2609:
2607:
2606:
2604:Basilar sulcus
2600:
2598:
2594:
2593:
2591:
2590:
2589:
2588:
2578:
2573:
2568:
2562:
2560:
2553:
2552:
2550:
2549:
2547:Pontine nuclei
2543:
2541:
2532:
2522:
2521:
2518:
2517:
2515:
2514:
2509:
2504:
2503:
2502:
2497:
2492:
2482:
2477:
2472:
2466:
2464:
2460:
2459:
2456:
2455:
2453:
2452:
2447:
2438:
2429:
2424:
2414:
2412:
2404:
2403:
2401:
2400:
2399:
2398:
2388:
2387:
2386:
2381:
2371:
2370:
2369:
2368:
2367:
2362:
2348:
2346:
2335:
2333:Cranial nuclei
2325:
2324:
2322:
2321:
2320:
2319:
2314:
2309:
2299:
2298:
2297:
2286:
2284:
2277:
2276:
2274:
2273:
2272:
2271:
2261:
2256:
2251:
2246:
2245:
2244:
2239:
2229:
2227:Trapezoid body
2223:
2221:
2214:
2213:
2211:
2210:
2205:
2200:
2195:
2190:
2184:
2182:
2175:
2165:
2164:
2158:
2156:
2155:
2148:
2141:
2133:
2124:
2123:
2121:
2120:
2115:
2114:
2113:
2108:
2103:
2093:
2092:
2091:
2086:
2081:
2076:
2071:
2060:
2058:
2052:
2051:
2048:
2047:
2045:
2044:
2039:
2034:
2029:
2024:
2019:
2014:
2008:
2006:
2002:
2001:
1999:
1998:
1997:
1996:
1986:
1985:
1984:
1979:
1968:
1966:
1959:
1955:
1954:
1951:
1950:
1948:
1947:
1946:
1945:
1940:
1931:
1929:
1925:
1924:
1922:
1921:
1920:
1919:
1914:
1906:
1905:
1904:
1899:
1894:
1889:
1884:
1875:
1873:
1866:
1860:
1859:
1856:
1855:
1853:
1852:
1851:
1850:
1845:
1840:
1835:
1830:
1822:
1820:
1816:
1815:
1813:
1812:
1807:
1802:
1796:
1794:
1790:
1789:
1786:
1785:
1783:
1782:
1777:
1772:
1767:
1761:
1759:
1751:
1750:
1748:
1747:
1746:
1745:
1740:
1735:
1725:
1720:
1719:
1718:
1713:
1702:
1700:
1689:
1687:Cranial nuclei
1680:
1674:
1673:
1667:
1665:
1664:
1657:
1650:
1642:
1633:
1632:
1630:
1629:
1624:
1619:
1618:
1617:
1606:
1604:
1600:
1599:
1597:
1596:
1586:
1581:
1576:
1571:
1568:chloride shift
1561:
1558:Haldane effect
1555:
1550:
1545:
1536:
1531:
1526:
1521:
1516:
1511:
1506:
1505:
1504:
1499:
1488:
1482:
1480:
1476:
1475:
1473:
1472:
1467:
1462:
1456:
1454:
1450:
1449:
1447:
1446:
1441:
1436:
1431:
1426:
1424:
1418:
1417:
1415:FEV1/FVC ratio
1412:
1407:
1405:
1401:
1400:
1395:
1390:
1385:
1380:
1375:
1369:
1367:
1361:
1360:
1358:
1357:
1356:
1355:
1345:
1344:
1343:
1338:
1330:chemoreceptors
1326:
1325:
1324:
1319:
1307:
1306:
1305:
1300:
1287:
1285:
1279:
1278:
1276:
1275:
1270:
1269:
1268:
1263:
1258:
1250:
1245:
1240:
1238:elastic recoil
1235:
1230:
1225:
1220:
1215:
1214:
1213:
1208:
1203:
1192:
1190:
1186:
1185:
1180:
1178:
1177:
1170:
1163:
1155:
1149:
1148:
1110:
1104:
1087:
1081:
1066:
1063:
1060:
1059:
1052:
1027:
978:
929:
886:
851:
844:
826:
797:(4): 2443–69.
777:
726:
683:
676:
656:
631:
624:
603:
596:
571:
564:
546:
539:
521:
514:
490:
489:
487:
484:
483:
482:
477:
472:
465:
462:
422:
419:
365:
362:
352:
349:
344:
293:
290:
277:
274:
246:
243:
215:cranial nerves
182:
179:
161:
158:
135:carbon dioxide
115:chemoreceptors
82:
81:
72:
66:
65:
60:
54:
53:
49:
48:
45:
37:
36:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2703:
2692:
2689:
2687:
2684:
2682:
2679:
2678:
2676:
2659:
2656:
2655:
2654:
2651:
2647:
2644:
2642:
2639:
2637:
2634:
2632:
2629:
2628:
2627:
2624:
2623:
2621:
2615:
2605:
2602:
2601:
2599:
2595:
2587:
2584:
2583:
2582:
2579:
2577:
2574:
2572:
2569:
2567:
2564:
2563:
2561:
2558:
2554:
2548:
2545:
2544:
2542:
2540:
2536:
2533:
2530:
2523:
2513:
2510:
2508:
2505:
2501:
2498:
2496:
2493:
2491:
2488:
2487:
2486:
2483:
2481:
2478:
2476:
2473:
2471:
2468:
2467:
2465:
2461:
2451:
2448:
2446:
2442:
2439:
2437:
2433:
2430:
2428:
2425:
2423:
2419:
2416:
2415:
2413:
2410:
2405:
2397:
2394:
2393:
2392:
2389:
2385:
2382:
2380:
2377:
2376:
2375:
2372:
2366:
2363:
2361:
2358:
2357:
2355:
2354:
2353:
2350:
2349:
2347:
2344:
2339:
2336:
2334:
2330:
2326:
2318:
2315:
2313:
2310:
2308:
2305:
2304:
2303:
2300:
2296:
2293:
2292:
2291:
2288:
2287:
2285:
2282:
2278:
2270:
2267:
2266:
2265:
2262:
2260:
2257:
2255:
2252:
2250:
2247:
2243:
2240:
2238:
2235:
2234:
2233:
2230:
2228:
2225:
2224:
2222:
2219:
2215:
2209:
2206:
2204:
2201:
2199:
2196:
2194:
2191:
2189:
2186:
2185:
2183:
2179:
2176:
2173:
2166:
2162:
2154:
2149:
2147:
2142:
2140:
2135:
2134:
2131:
2119:
2116:
2112:
2109:
2107:
2104:
2102:
2099:
2098:
2097:
2094:
2090:
2087:
2085:
2082:
2080:
2077:
2075:
2074:Parvocellular
2072:
2070:
2067:
2066:
2065:
2062:
2061:
2059:
2057:
2053:
2043:
2040:
2038:
2035:
2033:
2030:
2028:
2027:Vagal trigone
2025:
2023:
2022:Area postrema
2020:
2018:
2015:
2013:
2010:
2009:
2007:
2003:
1995:
1992:
1991:
1990:
1987:
1983:
1980:
1978:
1975:
1974:
1973:
1970:
1969:
1967:
1963:
1960:
1956:
1944:
1941:
1939:
1936:
1935:
1933:
1932:
1930:
1926:
1918:
1915:
1913:
1910:
1909:
1907:
1903:
1900:
1898:
1895:
1893:
1890:
1888:
1885:
1883:
1880:
1879:
1877:
1876:
1874:
1870:
1867:
1865:
1861:
1849:
1846:
1844:
1841:
1839:
1836:
1834:
1831:
1829:
1826:
1825:
1824:
1823:
1821:
1817:
1811:
1808:
1806:
1803:
1801:
1798:
1797:
1795:
1791:
1781:
1778:
1776:
1773:
1771:
1768:
1766:
1763:
1762:
1760:
1757:
1752:
1744:
1741:
1739:
1736:
1734:
1731:
1730:
1729:
1726:
1724:
1721:
1717:
1714:
1712:
1709:
1708:
1707:
1704:
1703:
1701:
1698:
1693:
1690:
1688:
1684:
1681:
1679:
1675:
1671:
1663:
1658:
1656:
1651:
1649:
1644:
1643:
1640:
1628:
1625:
1623:
1620:
1616:
1613:
1612:
1611:
1610:high altitude
1608:
1607:
1605:
1603:Insufficiency
1601:
1594:
1590:
1587:
1585:
1582:
1580:
1577:
1575:
1574:oxyhemoglobin
1572:
1569:
1565:
1562:
1559:
1556:
1554:
1551:
1549:
1546:
1544:
1540:
1537:
1535:
1532:
1530:
1527:
1525:
1522:
1520:
1517:
1515:
1512:
1510:
1507:
1503:
1500:
1498:
1495:
1494:
1492:
1489:
1487:
1484:
1483:
1481:
1477:
1471:
1468:
1466:
1463:
1461:
1458:
1457:
1455:
1451:
1445:
1442:
1440:
1437:
1435:
1432:
1430:
1427:
1425:
1423:
1420:
1419:
1416:
1413:
1411:
1408:
1406:
1403:
1402:
1399:
1396:
1394:
1391:
1389:
1386:
1384:
1381:
1379:
1376:
1374:
1371:
1370:
1368:
1366:
1362:
1354:
1351:
1350:
1349:
1346:
1342:
1339:
1337:
1334:
1333:
1332:
1331:
1327:
1323:
1320:
1318:
1315:
1314:
1313:
1312:
1308:
1304:
1301:
1299:
1296:
1295:
1294:
1293:
1289:
1288:
1286:
1284:
1280:
1274:
1271:
1267:
1264:
1262:
1259:
1257:
1254:
1253:
1251:
1249:
1246:
1244:
1243:hysteresivity
1241:
1239:
1236:
1234:
1231:
1229:
1226:
1224:
1221:
1219:
1216:
1212:
1209:
1207:
1204:
1202:
1199:
1198:
1197:
1194:
1193:
1191:
1187:
1183:
1176:
1171:
1169:
1164:
1162:
1157:
1156:
1153:
1145:
1141:
1137:
1133:
1129:
1125:
1121:
1117:
1111:
1107:
1101:
1097:
1093:
1088:
1084:
1078:
1074:
1069:
1068:
1064:
1055:
1053:9780071624428
1049:
1045:
1041:
1034:
1032:
1028:
1023:
1019:
1014:
1009:
1005:
1001:
997:
993:
989:
982:
979:
974:
970:
965:
960:
956:
952:
948:
944:
940:
933:
930:
925:
921:
917:
913:
909:
905:
901:
897:
890:
887:
882:
878:
874:
870:
866:
862:
855:
852:
847:
841:
837:
830:
827:
822:
818:
813:
808:
804:
800:
796:
792:
788:
781:
778:
773:
769:
764:
759:
754:
749:
746:(1): 300–10.
745:
741:
737:
730:
727:
722:
718:
714:
710:
706:
702:
698:
694:
687:
684:
679:
677:9780323523400
673:
669:
668:
660:
657:
646:
642:
635:
632:
627:
625:9780071222075
621:
617:
616:Human anatomy
610:
608:
604:
599:
593:
589:
582:
580:
578:
576:
572:
567:
565:9780073378251
561:
557:
550:
547:
542:
536:
532:
525:
522:
517:
515:9780470646083
511:
507:
500:
498:
496:
492:
485:
481:
478:
476:
473:
471:
468:
467:
463:
461:
459:
454:
452:
448:
444:
440:
436:
432:
428:
420:
418:
416:
412:
408:
404:
400:
396:
391:
389:
385:
380:
378:
371:
363:
361:
359:
350:
348:
342:
337:
334:
329:
327:
323:
319:
318:phrenic nerve
315:
311:
307:
303:
299:
291:
289:
287:
283:
275:
273:
269:
267:
263:
259:
255:
250:
244:
242:
240:
236:
232:
231:baroreceptors
228:
224:
220:
216:
212:
207:
205:
201:
197:
196:central canal
187:
180:
178:
175:
171:
167:
159:
157:
155:
150:
148:
144:
140:
136:
132:
128:
124:
120:
116:
112:
107:
105:
101:
97:
93:
89:
77:
71:
67:
64:
61:
59:
55:
50:
43:
38:
33:
30:
19:
2653:Raphe nuclei
2408:
2342:
2096:Raphe nuclei
1864:White matter
1755:
1696:
1514:gas exchange
1479:Interactions
1404:calculations
1365:Lung volumes
1328:
1309:
1290:
1261:constriction
1223:respirometer
1122:(1): 43–54.
1119:
1115:
1091:
1072:
1043:
995:
991:
981:
946:
942:
932:
902:(3): 311–6.
899:
895:
889:
867:(1): 71–85.
864:
860:
854:
835:
829:
794:
790:
780:
743:
739:
729:
696:
692:
686:
666:
659:
648:. Retrieved
645:openstax.org
644:
634:
615:
587:
555:
549:
530:
524:
505:
475:Cough center
455:
435:brain tumour
431:brain damage
427:brain trauma
424:
392:
381:
375:part of the
373:
357:
354:
338:
330:
322:tidal volume
309:
295:
279:
270:
262:interneurons
251:
248:
208:
192:
173:
169:
165:
163:
151:
127:hypothalamus
108:
87:
85:
29:
2356:Trigeminal
1678:Grey matter
1553:Bohr effect
1453:Circulation
1189:Respiration
458:amphetamine
219:vagus nerve
200:spinal cord
111:homeostatic
52:Identifiers
2675:Categories
2646:Paramedian
2089:Paramedian
1615:death zone
1534:hemoglobin
1429:spirometry
1388:dead space
1341:peripheral
1266:dilatation
1252:bronchial
1233:compliance
1206:exhalation
1201:inhalation
1092:Physiology
650:2024-03-20
486:References
480:Gag reflex
445:including
401:, and the
306:antagonist
254:exhalation
221:, and the
125:, and the
2681:Brainstem
2641:Tegmental
2619:reticular
2409:efferent:
2360:Principal
2343:afferent:
2220:: Sensory
2172:tegmentum
1756:efferent:
1697:afferent:
1491:Perfusion
998:: 53–61.
451:sedatives
399:diaphragm
100:brainstem
98:, in the
2525:Ventral/
2396:Superior
2384:Anterior
2283:: Motor
2111:Pallidus
2101:Obscurus
1878:Sensory
1743:Inferior
1502:V/Q scan
1136:15351303
1096:Elsevier
1022:27589601
973:19651653
924:42790256
821:23720253
772:16399700
721:38265906
713:15519561
464:See also
439:ischemia
341:vagotomy
300:and the
168:and the
139:blood pH
2597:Surface
2181:Surface
2168:Dorsal/
2084:Lateral
2079:Ventral
1972:Pyramid
1958:Surface
1928:Ventral
1819:Ventral
1733:Lateral
1670:medulla
1627:hypoxia
1548:2,3-BPG
1336:central
1311:medulla
1283:Control
1144:8425115
1013:5495096
964:2865127
916:2725956
881:1129551
812:4422496
763:6674322
447:opioids
316:in the
280:In the
264:in the
198:of the
104:neurons
63:D012125
2658:Median
2631:Caudal
2379:Dorsal
2365:Spinal
2106:Magnus
1908:Motor
1872:Dorsal
1793:Dorsal
1738:Medial
1196:breath
1142:
1134:
1102:
1079:
1050:
1020:
1010:
971:
961:
922:
914:
879:
842:
819:
809:
770:
760:
719:
711:
674:
622:
594:
562:
537:
512:
449:, and
395:eupnea
217:– the
137:, and
131:oxygen
121:, the
2557:White
2281:White
2218:White
1989:Olive
1965:Front
1711:tract
1140:S2CID
920:S2CID
717:S2CID
443:drugs
437:, or
235:lungs
141:, by
74:[
2691:Pons
2636:Oral
2539:Grey
2529:base
2329:Grey
2161:pons
2056:Grey
2005:Back
1593:DLCO
1493:(Q)
1292:pons
1132:PMID
1100:ISBN
1077:ISBN
1048:ISBN
1018:PMID
969:PMID
912:PMID
877:PMID
840:ISBN
817:PMID
768:PMID
709:PMID
672:ISBN
620:ISBN
592:ISBN
560:ISBN
535:ISBN
510:ISBN
433:, a
96:pons
94:and
86:The
58:MeSH
2581:MCP
2441:GVE
2432:GSE
2418:SVE
2352:GSA
1398:PEF
1378:FRC
1124:doi
1120:142
1008:PMC
1000:doi
959:PMC
951:doi
947:364
904:doi
869:doi
807:PMC
799:doi
758:PMC
748:doi
701:doi
697:143
2677::
2443::
2434::
2420::
2331::
1393:CC
1383:Vt
1373:VC
1138:.
1130:.
1118:.
1030:^
1016:.
1006:.
996:41
994:.
990:.
967:.
957:.
945:.
941:.
918:.
910:.
900:99
898:.
875:.
865:23
863:.
815:.
805:.
793:.
789:.
766:.
756:.
744:26
742:.
738:.
715:.
707:.
695:.
643:.
606:^
574:^
494:^
453:.
429:,
413:.
288:.
268:.
229:,
206:.
133:,
117:,
2531:)
2527:(
2174:)
2170:(
2152:e
2145:t
2138:v
1661:e
1654:t
1647:v
1595:)
1591:(
1570:)
1566:(
1560:)
1541:(
1174:e
1167:t
1160:v
1146:.
1126::
1108:.
1085:.
1056:.
1024:.
1002::
975:.
953::
926:.
906::
883:.
871::
848:.
823:.
801::
795:2
774:.
750::
723:.
703::
680:.
653:.
628:.
600:.
568:.
543:.
518:.
345:2
78:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.