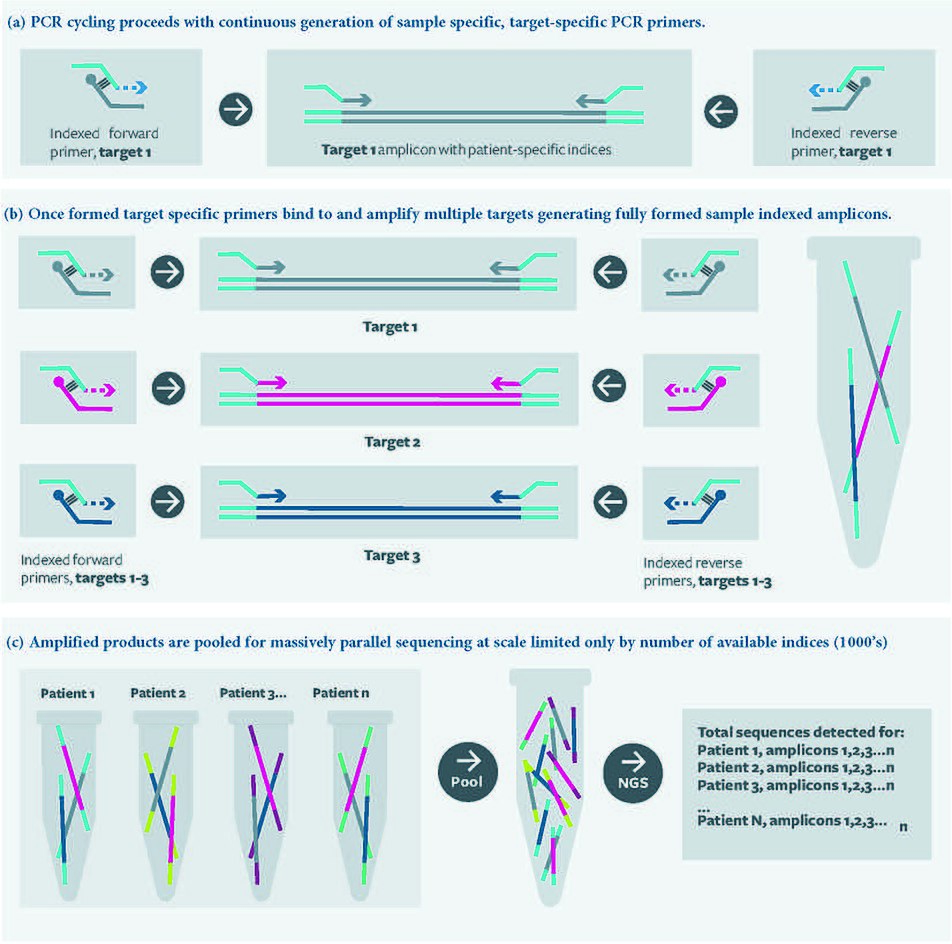
125:(NGS) laboratories where a single target specific probe pair can be used with a whole library of universal primers. This benefit is used with NGS applications to apply sample specific indexes independently to each end of the amplicon construct. A Laboratory employing this approach would only require a single set of index primers, which can be used with all target specific probes compatible with that index set. This significantly reduces the number and length of oligonucleotides required by the laboratory compared to using full length pre-synthesised indexed target specific primers.
77:. The oligonucleotides interact with each other in pairs; one oligonucleotide probe and one universal primer (containing functional domains of choice), which hybridize with each other at their 3’ ends. Once hybridized, the universal primer can be extended, using the oligonucleotide probe as the template, to yield fully formed, target specific primers, which are then available to amplify the template in subsequent rounds of thermal cycling as per a standard PCR reaction.
88:
80:
The oligonucleotide probe may also be blocked at the 3’ end preventing equivalent extension of the probe, but this is not essential. The probe is not consumed; it is available to act as a template for the universal primer to be ‘converted’ into target specific primer throughout successive PCR cycles.
271:
analysis. The technique has also been proven as a useful and powerful tool in the identification of the causative infectious pathogen in patients suspected of having a bacterial infection, in this setting it has been shown to provide a significant increase in the number of clinical samples in which
91:
Representation of a typical multiplex RC-PCR for generating amplicon libraries for downstream analysis by
Illumina next generation sequencing. Multiple targets are amplified and dual indexed in a single closed tube reaction. Target specific primer generation occurs in the first and subsequent rounds
116:
RC-PCR provides significant advantages over other methods of amplicon library preparation methods. Most significantly it is a single closed tube reaction, this eliminates cross contamination associated with other two-step PCR approaches as well as utilising less reagent and requiring less labour to
475:
Donovan-Banfield, I’ah; Penrice-Randal, Rebekah; Goldswain, Hannah; Rzeszutek, Aleksandra M.; Pilgrim, Jack; Bullock, Katie; Saunders, Geoffrey; Northey, Josh; Dong, Xiaofeng; Ryan, Yan; Reynolds, Helen; Tetlow, Michelle; Walker, Lauren E.; FitzGerald, Richard; Hale, Colin (2022-11-26).
439:
Wolters, Femke; Coolen, Jordy P. M.; Tostmann, Alma; Groningen, Lenneke F. J. van; Bleeker-Rovers, Chantal P.; Tan, Edward C. T. H.; Geest-Blankert, Nannet van der; Hautvast, Jeannine L. A.; Hopman, Joost; Wertheim, Heiman F. L.; Rahamat-Langendoen, Janette C. (2020-10-29).
242:
In May 2019 the
Intellectual property was licensed to Nimagen B.V. to develop, manufacture and market kits exploiting the technology. Currently commercially available kits employing the technology include those for Human identification and more recently for the
272:
a potentially clinically relevant pathogen is identified compared to the commonly used 16S Sanger method. It has also been shown to provide similar advantages over traditional methods in the deconvolution of microbial communities in environmental samples.
251:
virus for variant identification, tracking and treatment response. In August 2022 Nimagen officially launched a range of products employing the RC-PCR technology for human forensics applications under the trademark IDseek®.
288:
Mattocks, Christopher; Ward, Daniel; Mackay, Deborah (2021-03-05). "RT-RC-PCR: a novel and highly scalable next-generation sequencing method for simultaneous detection of SARS-COV-2 and typing variants of concern".
120:
The technique also provides the significant advantage of the flexibility of appending any desired sequence or functional domain of choice to either end of any amplicon. This is currently most advantageous in modern
182:
Single ended RC-PCR – This variation of the method is used when only one complementary universal primer probe pair is provided in the reaction to generate one target specific primer. The other target specific
73:
In RC-PCR, no target specific primers are present in the reaction mixture. Instead target specific primers are formed as the reaction proceeds. A typical reaction employing the approach requires four
541:
Moorlag, Simone J. C. F. M.; Coolen, Jordy P. M.; van den Bosch, Bart; Jin, Elisabeth Hui-Mei; Buil, Jochem B.; Wertheim, Heiman F. L.; Melchers, Willem J. G. (2023-05-25). Luethy, Paul M. (ed.).
54:
Representation of the interaction of the universal primer and RC probe to generate functional target specific primer. Universal primer hybridises to the RC probe and is extended by the
543:"Targeting the 16S rRNA Gene by Reverse Complement PCR Next-Generation Sequencing: Specific and Sensitive Detection and Identification of Microbes Directly in Clinical Samples"
268:
34:(NGS). The technique permits both the amplification and the ability to append sequences or functional domains of choice independently to either end of the generated
128:
The generation of the target specific primer in the reaction as it progresses also leads to more balanced reaction components. Concentrations of target specific
51:
590:
Leontidou, Kleopatra; Abad-Recio, Ion L.; Rubel, Verena; Filker, Sabine; Däumer, Martin; Thielen, Alexander; Lanzén, Anders; Stoeck, Thorsten (2023-11-16).
204:
Following the invention of RC-PCR in 2013 the technique was clinically validated and employed diagnostically for a range of both inherited diseases such as
592:"Simultaneous analysis of seven <scp>16S rRNA</scp> hypervariable gene regions increases efficiency in marine bacterial diversity detection"
392:"Reverse complement-PCR, an innovative and effective method for multiplexing forensically relevant single nucleotide polymorphism marker systems"
255:
The RC-PCR approach is becoming more widely used for human health and several CE IVD kits are available for human clinical diagnostics including
105:
676:
179:
template, the formation of tailed target specific primers and the amplification of the desired targets in a single closed tube reaction.
63:
132:
are more aligned with target molecule concentration thereby reducing the potential of both off target priming and primer dimerisation.
661:
681:
646:
671:
478:"Characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 genomic variation in response to molnupiravir treatment in the AGILE Phase IIa clinical trial"
335:
Kieser, Rachel E.; Buś, Magdalena M.; King, Jonathan L.; van der Vliet, Walter; Theelen, Joop; Budowle, Bruce (January 2020).
686:
442:"Novel SARS-CoV-2 Whole-genome sequencing technique using Reverse Complement PCR enables fast and accurate outbreak analysis"
39:
81:
This generation of target specific primer occurs in parallel with standard PCR amplification under standard PCR conditions.
390:
Bus, Magdalena M; de Jong, Erik AC; King, Jonathan L; der Vliet, Walter van; Theelen, Joop; Budowle, Bruce (2021-08-05).
310:
92:
with target amplification and amplicon generation occurring in the second and subsequent rounds of thermal cycling.
696:
217:
122:
31:
228:
UK. More recently work has been undertaken to utilise the technology in the fight against the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.
188:
184:
168:
164:
142:
129:
59:
192:
109:
23:
50:
337:"Reverse Complement PCR: A novel one-step PCR system for typing highly degraded DNA for human identification"
244:
221:
641:
38:
in a single closed tube reaction. RC-PCR was invented in 2013 by Daniel Ward and
Christopher Mattocks at
172:
161:
157:
108:
Diagrammatic representation of relative reaction components of a RC-PCR reaction compared to a standard
489:
290:
691:
666:
457:
372:
295:
621:
613:
572:
523:
505:
441:
421:
413:
364:
356:
213:
87:
148:
RT-RC-PCR – This modification is used when the template material supplied in the reaction is
145:
probe sets are present in the reaction mixture to amplify two or more targets simultaneously.
603:
562:
554:
513:
497:
449:
403:
348:
104:
74:
542:
239:
applications have been filed in other jurisdictions worldwide and are currently pending.
493:
518:
477:
55:
655:
461:
376:
256:
209:
205:
352:
501:
558:
453:
248:
617:
576:
509:
417:
360:
608:
591:
336:
225:
625:
527:
425:
368:
408:
391:
35:
567:
236:
232:
171:
and
Reverse complement probes of the method. This approach permits
264:
86:
311:"NimaGen Licenses PCR Tech From Salisbury NHS Foundation Trust"
26:(PCR). It is primarily used to generate amplicon libraries for
260:
176:
153:
149:
27:
235:
application was filed in the UK in 2015 and awarded in 2020.
156:. In this modification the reaction mixture also contains
66:
sequence of the desired target specific primer sequence.
224:in the Wessex Regional Genetics Laboratory (WRGL),
62:. The 5 prime portion of the RC probe contains the
141:Multiplex RC-PCR – where two or more universal
16:Modification of the polymerase chain reaction
8:
20:Reverse complement polymerase chain reaction
607:
566:
517:
407:
294:
341:Forensic Science International. Genetics
103:
49:
280:
7:
647:WIPO patent filing information page
22:(RC-PCR) is a modification of the
14:
40:Salisbury NHS Foundation Trust
1:
296:10.1101/2021.03.02.21252704v1
216:acquired disorders including
187:is provided as a traditional
677:Molecular biology techniques
353:10.1016/j.fsigen.2019.102201
218:Myeloproliferative neoplasms
58:generating target specific
713:
596:Environmental Microbiology
502:10.1038/s41467-022-34839-9
123:next generation sequencing
32:next generation sequencing
662:Polymerase chain reaction
559:10.1128/spectrum.04483-22
454:10.1101/2020.10.29.360578
167:as well as the universal
24:polymerase chain reaction
682:DNA profiling techniques
609:10.1111/1462-2920.16530
245:whole genome sequencing
672:DNA sequencing methods
222:Acute myeloid leukemia
113:
93:
67:
687:Laboratory techniques
547:Microbiology Spectrum
482:Nature Communications
448:: 2020.10.29.360578.
409:10.2144/btn-2021-0031
173:reverse transcription
162:reverse transcription
158:reverse transcriptase
107:
90:
53:
402:(3): btn–2021–0031.
553:(3). David Gaston.
494:2022NatCo..13.7284D
697:British inventions
114:
94:
68:
64:reverse complement
602:(12): 3484–3501.
704:
642:RC-PCR animation
630:
629:
611:
587:
581:
580:
570:
538:
532:
531:
521:
472:
466:
465:
436:
430:
429:
411:
387:
381:
380:
332:
326:
325:
323:
322:
307:
301:
300:
298:
285:
191:as per standard
175:of the provided
75:oligonucleotides
712:
711:
707:
706:
705:
703:
702:
701:
652:
651:
638:
633:
589:
588:
584:
540:
539:
535:
474:
473:
469:
438:
437:
433:
389:
388:
384:
334:
333:
329:
320:
318:
309:
308:
304:
287:
286:
282:
278:
206:hemochromatosis
202:
138:
102:
96:
84:
70:
48:
17:
12:
11:
5:
710:
708:
700:
699:
694:
689:
684:
679:
674:
669:
664:
654:
653:
650:
649:
644:
637:
636:External links
634:
632:
631:
582:
533:
467:
431:
382:
327:
302:
279:
277:
274:
201:
198:
197:
196:
180:
146:
137:
134:
101:
98:
56:DNA polymerase
47:
44:
30:sequencing by
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
709:
698:
695:
693:
690:
688:
685:
683:
680:
678:
675:
673:
670:
668:
665:
663:
660:
659:
657:
648:
645:
643:
640:
639:
635:
627:
623:
619:
615:
610:
605:
601:
597:
593:
586:
583:
578:
574:
569:
564:
560:
556:
552:
548:
544:
537:
534:
529:
525:
520:
515:
511:
507:
503:
499:
495:
491:
487:
483:
479:
471:
468:
463:
459:
455:
451:
447:
443:
435:
432:
427:
423:
419:
415:
410:
405:
401:
397:
396:BioTechniques
393:
386:
383:
378:
374:
370:
366:
362:
358:
354:
350:
346:
342:
338:
331:
328:
316:
312:
306:
303:
297:
292:
284:
281:
275:
273:
270:
266:
262:
258:
253:
250:
246:
240:
238:
234:
229:
227:
223:
219:
215:
211:
210:thrombophilia
207:
199:
194:
190:
186:
181:
178:
174:
170:
166:
163:
159:
155:
151:
147:
144:
140:
139:
135:
133:
131:
126:
124:
118:
111:
106:
99:
97:
89:
85:
82:
78:
76:
71:
65:
61:
57:
52:
45:
43:
41:
37:
33:
29:
25:
21:
599:
595:
585:
550:
546:
536:
485:
481:
470:
445:
434:
399:
395:
385:
344:
340:
330:
319:. Retrieved
317:. 2019-01-14
314:
305:
283:
254:
241:
230:
203:
160:enzymes and
152:rather than
127:
119:
115:
95:
83:
79:
72:
69:
19:
18:
568:2066/294286
488:(1): 7284.
214:somatically
212:as well as
692:Amplifiers
667:SARS-CoV-2
656:Categories
347:: 102201.
321:2021-04-22
276:References
249:SARS-CoV-2
136:Variations
100:Advantages
46:Principles
618:1462-2912
577:2165-0497
510:2041-1723
462:226228646
418:0736-6205
377:208535138
361:1878-0326
315:Genomeweb
226:Salisbury
117:perform.
112:reaction.
36:amplicons
626:37974518
528:36435798
426:34350776
369:31786458
519:9701236
490:Bibcode
446:bioRxiv
291:medRxiv
247:of the
200:History
169:primers
165:primers
624:
616:
575:
526:
516:
508:
460:
424:
416:
375:
367:
359:
293:
237:Patent
233:patent
189:primer
185:primer
143:primer
130:primer
60:primer
42:, UK.
458:S2CID
373:S2CID
265:PALB2
622:PMID
614:ISSN
573:ISSN
524:PMID
506:ISSN
422:PMID
414:ISSN
365:PMID
357:ISSN
269:CFTR
267:and
261:TP53
257:BRCA
231:The
220:and
208:and
604:doi
563:hdl
555:doi
514:PMC
498:doi
450:doi
404:doi
349:doi
193:PCR
177:RNA
154:DNA
150:RNA
110:PCR
28:DNA
658::
620:.
612:.
600:25
598:.
594:.
571:.
561:.
551:11
549:.
545:.
522:.
512:.
504:.
496:.
486:13
484:.
480:.
456:.
444:.
420:.
412:.
400:71
398:.
394:.
371:.
363:.
355:.
345:44
343:.
339:.
313:.
263:,
259:,
628:.
606::
579:.
565::
557::
530:.
500::
492::
464:.
452::
428:.
406::
379:.
351::
324:.
299:.
195:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.