81:
97:
241:
221:
205:
327:
298:
146:
31:
313:
due to their greater buoyancy, eventually breaking through and rising towards the surface. This salt is impermeable, and when it crosses a layer of permeable rock, in which hydrocarbons are migrating, it blocks the pathway in much the same manner as a fault trap. This is one of the reasons why there
181:
trap is formed by the movement of permeable and impermeable layers of rock along a fault plane. The permeable reservoir rock faults such that it is adjacent to an impermeable rock, preventing hydrocarbons from further migration. In some cases, there can be an impermeable substance along the fault
169:(the highest point where hydrocarbons can escape the anticline). This type of trap is by far the most significant to the hydrocarbon industry. Anticline traps are usually long oval domes of land that can often be seen by looking at a geological map or by flying over the land.
280:
In a stratigraphic trap, the geometry allowing the accumulation of hydrocarbons is of sedimentary origin and has not undergone any tectonic deformation. Such traps can be found in clinoforms, in a pinching-out sedimentary structure, under an
62:. Traps can be of two types: stratigraphic or structural. Structural traps are the most important type of trap as they represent the majority of the world's discovered petroleum resources.
345:, the initial reservoir geometry is the one of a fault-controlled structural trap, but the caprock is generally made by the draping sedimentation of mudstones during the
479:
517:
395:
463:
129:
A structural trap is a type of geological trap that forms as a result of changes in the structure of the subsurface, due to
162:
165:
rock present in this dome shape, then hydrocarbons can accumulate at the crest until the anticline is filled to the
549:
521:
399:
342:
335:
315:
358:
59:
473:
363:
80:
459:
39:
382:
183:
178:
130:
264:
134:
113:
444:
Gluyas, J. & Swarbrick, R. (2004) Petroleum
Geoscience. Publ. Blackwell Publishing
421:
240:
96:
543:
346:
310:
282:
211:
326:
220:
204:
17:
493:
272:
260:
121:
103:
55:
227:
182:
surface (such as clay) that also acts to prevent migration. This is known as
306:
286:
247:
154:
87:
51:
385:& Allen J.R. (1990) Basin Analysis. pp 373. Publ. Blackwell Publishing
331:
268:
231:
117:
27:
Geological structure allowing accumulation of hydrocarbons in a reservoir
341:
Hybrid traps are the combination of two types of traps. In the case of
158:
47:
250:
161:
have been pushed into forming a domed shape. If there is a layer of
325:
296:
144:
29:
318:, despite the many technical challenges that accompany it.
46:
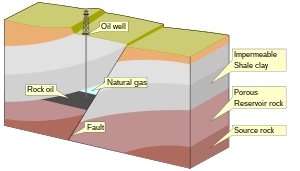
is a geological structure affecting the reservoir rock and
458:(2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 351.
297:
145:
30:
285:or in a structure created by the creep of an
137:, gravitational, and compactional processes.
8:
478:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
309:trap, masses of salt are pushed up through
314:is significant focus on subsurface salt
454:Sheriff, R. E., Geldart, L. P. (1995).
375:
157:is an area of the subsurface where the
471:
246:Stratigraphic trap associated with an
7:
54:system allowing the accumulation of
25:
396:"Petroleum Research Institution"
239:
219:
203:
95:
79:
518:"Petroleum Research Institute"
1:
210:Stratigraphic trap under an
230:(reservoir rock) sealed in
566:
330:Hybrid trap formed by the
226:Stratigraphic trap in a
102:Structural trap along a
456:Exploration Seismology
338:
302:
150:
86:Structural trap in an
35:
329:
300:
148:
33:
524:on February 14, 2015
402:on February 14, 2015
359:Petroleum reservoir
364:Structural geology
339:
303:
197:Stratigraphic trap
190:Stratigraphic trap
151:
36:
18:Stratigraphic trap
550:Petroleum geology
422:"structural trap"
40:petroleum geology
16:(Redirected from
557:
534:
533:
531:
529:
520:. Archived from
514:
508:
507:
505:
504:
490:
484:
483:
477:
469:
451:
445:
442:
436:
435:
433:
432:
418:
412:
411:
409:
407:
398:. Archived from
392:
386:
380:
243:
223:
207:
99:
83:
73:Structural traps
66:Structural traps
21:
565:
564:
560:
559:
558:
556:
555:
554:
540:
539:
538:
537:
527:
525:
516:
515:
511:
502:
500:
498:Energy Glossary
492:
491:
487:
470:
466:
453:
452:
448:
443:
439:
430:
428:
426:Energy Glossary
420:
419:
415:
405:
403:
394:
393:
389:
381:
377:
372:
355:
324:
295:
278:
277:
276:
275:
256:
255:
254:
244:
236:
235:
224:
216:
215:
208:
199:
198:
192:
175:
149:Anticlinal trap
143:
141:Anticlinal trap
127:
126:
125:
124:
109:
108:
107:
100:
92:
91:
84:
75:
74:
68:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
563:
561:
553:
552:
542:
541:
536:
535:
509:
485:
464:
446:
437:
413:
387:
374:
373:
371:
368:
367:
366:
361:
354:
351:
323:
320:
301:Salt dome trap
294:
293:Salt dome trap
291:
265:reservoir rock
258:
257:
245:
238:
237:
225:
218:
217:
209:
202:
201:
200:
196:
195:
194:
193:
191:
188:
174:
171:
142:
139:
114:reservoir rock
111:
110:
101:
94:
93:
85:
78:
77:
76:
72:
71:
70:
69:
67:
64:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
562:
551:
548:
547:
545:
523:
519:
513:
510:
499:
495:
489:
486:
481:
475:
467:
465:0-521-46826-4
461:
457:
450:
447:
441:
438:
427:
423:
417:
414:
401:
397:
391:
388:
384:
379:
376:
369:
365:
362:
360:
357:
356:
352:
350:
348:
344:
343:tilted blocks
337:
336:tilted blocks
333:
328:
321:
319:
317:
312:
311:clastic rocks
308:
299:
292:
290:
288:
284:
274:
270:
266:
262:
252:
249:
242:
233:
229:
222:
213:
206:
189:
187:
185:
180:
172:
170:
168:
164:
160:
156:
147:
140:
138:
136:
132:
123:
119:
115:
105:
98:
89:
82:
65:
63:
61:
57:
53:
49:
45:
41:
32:
19:
526:. Retrieved
522:the original
512:
501:. Retrieved
497:
494:"Fault trap"
488:
455:
449:
440:
429:. Retrieved
425:
416:
404:. Retrieved
400:the original
390:
378:
347:oceanisation
340:
304:
283:unconformity
279:
273:hydrocarbons
212:unconformity
176:
166:
152:
128:
122:hydrocarbons
56:hydrocarbons
43:
37:
334:draping of
322:Hybrid trap
261:source rock
167:spill point
163:impermeable
104:fault plane
503:2023-01-27
431:2023-01-27
383:Allen P.A.
370:References
263:; yellow:
234:(caprock).
228:coral reef
184:clay smear
173:Fault trap
34:Fault trap
528:August 2,
474:cite book
406:August 2,
349:process.
307:salt dome
287:evaporite
267:; green:
248:evaporite
232:mudstones
155:anticline
116:; green:
88:anticline
60:reservoir
52:petroleum
544:Category
353:See also
332:mudstone
269:cap rock
135:diapiric
131:tectonic
118:cap rock
112:yellow:
316:imaging
271:; red:
253:(pink).
120:; red:
48:caprock
462:
259:blue:
251:diapir
159:strata
305:In a
179:fault
58:in a
50:of a
530:2019
480:link
460:ISBN
408:2019
44:trap
42:, a
153:An
38:In
546::
496:.
476:}}
472:{{
424:.
289:.
186:.
177:A
133:,
532:.
506:.
482:)
468:.
434:.
410:.
214:.
106:.
90:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.