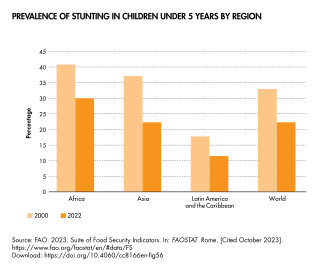208:
246:
interventions.The three main causes of stunting in South Asia, and probably in most developing countries, are poor feeding practices, poor maternal nutrition, and poor sanitation. A recent risk assessment analysis for 137 developing countries found that the leading risk factors for stunting were fetal growth restriction (birth weight <10th centile) followed by unimproved sanitation and diarrhea. It was estimated that 22% of stunting cases were attributable to environmental factors while 14% were attributable to child nutrition. In addition, looking at trends from 1970 to 2012 for 116 countries, women’s education, gender equality and finally quantity and quality of foods available at the country level have been instrumental in reducing stunting rates, while income growth and governance have played facilitating roles.
225:
705:
since then, with the 2019 rate (28.8 percent) only marginally lower than that of 2008. Researchers attribute the problem to micronutrient deficiencies brought on by poverty, maternal under-education, food insecurity, and poor environmental conditions. To address stunting and other health and food security issues, the
Philippine Plan of Action for Nutrition (PPAN) was established as an umbrella initiative to meet health and nutrition targets in the country by 2028. Since 2015, there has been a decline in stunting across all age groups, from infants to teenagers, with the most significant improvement observed among 5 to 10-year-olds, dropping from 31.2 percent in 2015 to 19.7 percent in 2021.
217:
126:
569:
prevalence of stunting, and is due to the high rates of population growth. The data therefore indicate that the rate of reduction of stunting in Africa has not been able to counterbalance the increased number of growing children that fall into the trap of malnutrition, due to population growth in the region. This is also true in
Oceania, unlike Asia and Latin America and the Caribbean where substantial absolute reductions in the number of stunted children have been observed (for example, Asia reduced its number of stunted children from 133 million to 88 million between 2000 and 2015).
207:
62:
557:
in 2016. The decline is happening, but it is uneven geographically, it is unequal among different groups in society, and prevalence of stunting remains at unacceptably high numbers. Too many children who are not able to fulfill their genetic physical and cognitive developmental potential. A research paper published in
January 2020, which mapped stunting, wasting and underweight in children in low- and middle-income countries, predicted that only five countries would meet global targets for reducing malnutrition by 2025 in all second administrative subdivisions.
612:
concurrently, due to increased wealth and the persistence of significant inequalities. The challenges these countries face are particularly difficult as they require intervening on two levels on what has come to be called “double burden of malnutrition”. As an example, in India 30% of children under 5 years of age are stunted, and 20% are overweight. Neglecting these nutritional problems is not an option anymore if countries are to escape poverty traps and provide opportunities to their people to live fulfilling productive lives without stunting.
608:
such series, investigators define the importance of the 1000 day and identify child malnutrition as being responsible for one third of all child deaths worldwide. This finding is key in that it points at malnutrition as a key determinant of child mortality that is often overlooked. When a child dies of pneumonia, malaria or diarrhea (some of the causes of child mortality in the world), it may well be that malnutrition is a key contributing factor that prevents the body from successfully fighting the infection and recovering from these diseases.
678:
component. The strategy was multisectoral in that it involved the health, education, water, sanitation and hygiene, agriculture and housing sectors and stakeholders. It was led by the
Government and the Prime Minister himself, and included non-governmental partners at both central, regional and community level. After the strategy was implemented, stunting went from 22.9% to 17.9% (2005–2010), with very significant improvements in rural areas where it had been more difficult to reduce stunting rates in the past.
627:, with its 194 member states, convened to discuss global issues of maternal, infant and young child nutrition, and developed a plan with 6 targets for 2025. The first of such targets aims to reduce by 40% the number of children who are stunted in the world, by 2025. This would correspond to 100 million stunted children in 2025. At the current reduction rate, the predicted number in 2025 will be 127 million, indicating the need to scale-up and intensify efforts if the global community is to reach its goals.
748:
260:
over six months old. Breastfeeding in long time with inadequate complementary feeding leads to growth failure due to insufficient nutrients which are essential for childhood development. The relationship between undernutrition and prolonged duration of breastfeeding is mostly observed among children from poor households and whose parents are uneducated as they are more likely to continue breast-feeding without meeting minimum dietary diversity requirement.
561:
larger improvements than Africa, which needs to address this issue with much more effort if it is to win the battle against a problem that has been crippling its development for decades. Of these regions, Latin
America and the Caribbean are on track to achieve global targets set with global initiatives such as the United Nations Millennium Development Goals and the World Health Assembly targets (see following section on global targets).
643:(SDGs) to be achieved by 2030. SDG 2 aims to “End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition, and promote sustainable agriculture”. Sub-goal 2.2. aims to “by 2030 end all forms of malnutrition, including achieving by 2025 the internationally agreed targets on stunting and wasting in children under five years of age, and address the nutritional needs of adolescent girls, pregnant and lactating women, and older persons”.
462:-series on maternal and child nutrition estimated that the impact of all existing interventions designed to improve nutrition and prevent related diseases in mothers and children, could reduce stunting at 3 years by merely 36%. Hence, factors explaining the shortfall in observed associations between child feeding practices and nutrient intake and linear growth, have increasingly been the focus of scientific interest.
660:
1990 to 4.8% in 2008. The successful reduction in child malnutrition in Brazil can be attributed to strong political commitment that led to improvements in the water and sanitation system, increased female schooling, scale-up of quality maternal and child health services, increased economic power at family level (including successful cash transfer programs), and improvements in food security throughout the country.
565:
In Asia, the highest rate is observed in South Asia at 34.4%. South-East Asia is at 26.3%. Pacific
Islands also display a high rate at 38.2%. Central and South America are respectively at 15.6 and 9.9%. South Asia, given its very high population at over 1 billion and high prevalence rate of stunting, is the region currently hosting the highest absolute number of children with stunting (60 million plus).
687:
that the country hosts almost half of all stunted children under 5 in the world. This was achieved through integrated community-based programs that were designed by a central advisory body that promoted multisectoral collaboration, provided advice to policy-makers on evidence-based solutions, and advocated for the key role of the 1000 days (pregnancy and first two years of life).
1919:
511:
as the country's food security landscape. Interventions to keep adolescent girls in school can be effective at delaying marriage with subsequent nutritional benefits for both women and babies. Regulating milk substitutes is also very important to ensure that as many mothers as possible breastfeed their babies, unless a clear contraindication is present.
651:
launched at the UN General
Assembly of 2010 and it calls for country-led multi-sectoral strategies to address child malnutrition by scaling-up evidence-based interventions in both nutrition specific and sensitive areas. As of 2016, 50 countries have joined the SUN Movement with strategies that are aligned with international frameworks of action.
4145:
122:(WHO) is for the "height-for-age" value to be less than two standard deviations of the median of WHO Child Growth Standards. Stunted growth is usually associated with poverty, unsanitary environmental conditions, maternal undernutrition, frequent illness, and/or inappropriate feeding practice and care during early years of life.
475:
phase of the 1000 days of pregnancy and first two years of life. An example of this are attempts to control anemia in women of reproductive age. A well-nourished mother is the first step of stunting prevention, decreasing chances of the baby being born of low birth-weight, which is the first risk factor for future malnutrition.
631:
investment of $ 18 for every dollar spent thanks to its impact on economic productivity. Despite the evidence in favor of investing in the reduction of stunting, current investments are too low at about $ 2.9 billion per year, with $ 1.6 billion coming from
Governments, $ 0.2 billion from donors, and $ 1.1 paid by individuals.
496:
should be prioritized. The same should be done for risk factors such as anemia, maternal under-nutrition, food insecurity, low birth-weight, breastfeeding practices etc. By collecting more detailed information, it is easier to ensure that policy interventions really address the root causes of stunting.
659:
Brazil displayed a remarkable reduction in the rates of child stunting under age 5, from 37% in 1974, to 7.1% in 2007. This happened in association with impressive social and economic development that reduced the numbers of
Brazilians living in extreme poverty (less than $ 1.25 per day) from 25.6% in
564:
Sub-regional stunting rates are as follows: In Africa, the highest rates are observed in East Africa (37.5%). All other Sub-Saharan sub-regions also have high rates, with 32.1% in West Africa, 31.2% in
Central Africa, and 28.4% in Southern Africa. North Africa is at 18%, and the Middle East at 16.2%.
527:
UNICEF has estimated that: "Globally, more than one quarter (26 per cent) of children under 5 years of age were stunted in 2011 – roughly 165 million children worldwide." and "In sub-Saharan Africa, 40 per cent of children under 5 years of age are stunted; in South Asia, 39 per cent are stunted." The
482:
After birth, in terms of interventions for the child, early initiation of breastfeeding, together with exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months, are pillars of stunting prevention. Introducing proper complementary feeding after 6 months of age together with breastfeeding until age 2 is the next
331:
is proposed as an immediate causal factor of childhood stunting. This is an asymptomatic small intestinal disorder characterized by chronic gut inflammation, reduced absorptive surface area, and disruption of intestinal barrier function. This small bowel disorder is attributable to sustained exposure
281:
Maternal undernutrition increases the risk of stunting at 2 years age. Based on data from 19 birth cohorts from LMICs, 20% of stunting is attributed to being born small-for-gestational-age (SGA). Further, estimated stunting at 2 years attributed to fetal growth restriction and preterm birth in 2011
560:
Over the period 2000–2015, Asia reduced its stunting prevalence from 38 to 24%, Africa from 38 to 32%, and Latin America and the Caribbean from 18 to 11%. This equates to a relative reduction of 36, 17 and 39% respectively, indicating that Asia and Latin America and the Caribbean have displayed much
556:
and stunting. No statistics are currently available for these combined conditions. Stunting has been on the decline for the past 15 years, but this decline has been too slow. As a comparison, there were 255 million stunted children in 1990, 224 in 1995, 198 in 2000, 182 in 2005, 169 in 2010, and 156
506:
Designing and implementing policies promoting proper breastfeeding and complementary feeding practice (focusing on diet diversity for both macro and micronutrients). This can ensure optimal infant nutrition as well as protection from infections that can weaken the child's body. Labor policy ensuring
457:
to improve complementary feeding may achieve behavioral change but have no or small effects on growth. Further, studies on the effect of micronutrient fortification, increased availability of key nutrients or increased energy density of complementary foods on stunting also show heterogenous results.
436:
of a child's life, from pregnancy to the child's second birthday, in order to reduce the prevalence of stunting. The first 1000 days in a child's life are a crucial "window of opportunity" because the brain develops rapidly, laying the foundation for future cognitive and social ability. Furthermore,
194:
and stroke. At societal level, stunted individuals do not fulfill their physical and cognitive developmental potential and will not be able to contribute maximally to society. Stunting can therefore limit economic development and productivity, and it has been estimated that it can affect a country's
668:
Nearly one-third of the children under five years of age are stunted in Bangladesh and 9% are severely stunted. The country is on track in reducing the prevalence of stunted growth. If the current trend continues, the prevalence would be 21% in 2025, while the target is 27%. Maternal undernutrition
593:
has investigated links between lack of sanitation and stunting in Vietnam and Lao PDR. An example is in Vietnam where the lack of sanitation in rural villages in mountainous regions of Vietnam led to five-year-old children being 3.7 cm shorter than healthy children living in villages with good
547:
As of 2015, it was estimated that there were 156 million stunted children under 5 in the world, 90% of them living in low and low-middle income countries. 56% of these were in Asia, and 37% in Africa. It is possible that some of these children concurrently had other forms of malnutrition, including
510:
Introducing interventions addressing social and other health determinants of stunting, such as poor sanitation and access to drinking water, early marriages, intestinal parasite infections, malaria and other childhood preventable disease (referred to as “nutrition-sensitive interventions”), as well
478:
Balanced protein–energy supplementation in pregnancy seem to improve birth weight of children, with greater effects in undernourished women. Meanwhile, micronutrient supplements and lipid based nutrient supplements (LNS) (providing both macro-and micronutrients) during pregnancy have shown mixed
198:
Stunting is highly prevalent in low- and middle income countries (LMICs) and has severe consequences including increased risk of infections, mortality and loss of human capital. The global prevalence of stunting decreased from 33% to 23% between 2000 and 2016. Meanwhile, 37% of children in South
686:
The State of Maharashtra in Central-Western India has been able to produce an impressive reduction in stunting rates in children under 2 years of age from 44% to 22.8% in the 2005–2012 period. This is particularly remarkable given the immense challenges India has faced to address malnutrition, and
650:
The "Scaling Up Nutrition Movement (SUN)" movement is the main network of governments, non-governmental and international organizations, donors, private companies and academic institutions working together in pursuit of improved global nutrition and a world without hunger and malnutrition. It was
495:
Improvement in nutrition surveillance activities to identify rates and trends of stunting and other forms of malnutrition within countries. This should be done with an equity perspective, as it is likely that stunting rates will vary greatly between different population groups. The most vulnerable
259:
is recommended for the first six months of life and complementary feeding of nutritious food alongside breastfeeding for children aged six months to 2-years-old. Prolonged exclusive breastfeeding is associated with undernutrition because breast milk alone is nutritionally insufficient for children
173:
The impact of stunting on child development has been established in multiple studies. If a child is stunted at age 2 they will have higher risk of poor cognitive and educational achievement in life, with subsequent socio-economic and inter-generational consequences. Multi-country studies have also
704:
In the Philippines, one in three children below five years old is stunted. Even though the country's economic growth has steadily increased by 4% annually, almost a third of Filipino children have stunted growth. The prevalence of stunting declined during the early 2000s but has remained the same
607:
has published two comprehensive series on maternal and child nutrition, in 2008 and 2013. The series review the epidemiology of global malnutrition and analyze the state of the evidence for cost-effective interventions that should be scaled-up to achieve impact and global targets. In the first of
465:
Recent works showed promise that intervention with egg may improve linear growth in children. Comprehensive intervention package containing eggs also found to be effective in improving linear growth in children. However, the effect of egg intervention may not persist for longer period. Therefore,
366:
for shortness and not because of inadequate nutrition. However, if substantially more than 5% of an identified child population have height for age that is less than the fifth percentile on the reference curve, then the population is said to have a higher-than-expected prevalence of stunting, and
133:
As of 2020, an estimated 149 million children under 5 years of age, are stunted worldwide. More than 85% of the world's stunted children live in Africa and Asia. Once established, stunting and its effects typically become permanent. Stunted children may never regain the height lost as a result of
611:
In the follow-up series in 2013, the focus on undernutrition is expanded to the increasing burden of obesity in both high, middle and low income countries. Several countries with high levels of child stunting and undernutrition are starting to display worrisome increasing trends of child obesity
502:
Designing and implementing policies promoting nutritional and health well-being of mothers and women of reproductive age. The main focus should be on the 1000 days of pregnancy and first two years of life, but the pre-conception period should not be neglected as it can play a significant role in
474:
Ensuring proper nutrition of pregnant and lactating mothers is essential. Achieving so by helping women of reproductive age be in good nutritional status at conception is an excellent preventive measure. A focus on the pre-conception period has recently been introduced as a complement to the key
361:
As an indicator of nutritional status, comparisons of children's measurements with growth reference curves may be used differently for populations of children than for individual children. The fact that an individual child falls below the fifth percentile for height for age on a growth reference
677:
After a decade (1995–2005) in which stunting rates stagnated in the country, Peru designed and implemented a national strategy against child malnutrition called crecer ("grow"), which complemented a social development conditional cash-transfer program called juntos, which included a nutritional
572:
The reduction in stunting is closely linked to poverty reduction and the will and ability of governments to set up solid multisectoral approaches to reduce chronic malnutrition. Low income countries are the only group with more stunted children today than in the year 2000. Conversely, all other
294:
practices. The ingestion of high quantities of fecal bacteria by young children through putting soiled fingers or household items in the mouth leads to intestinal infections. This affect children's nutritional status by diminishing appetite, reducing nutrient absorption, and increasing nutrient
630:
The World Bank estimates that the extra cost to achieve the reduction goal will be $ 8.50 yearly per stunted child, for a total of $ 49.6 Billion for the next decade. Stunting has been shown to be one of the most cost-effective global health problems to invest in, with an estimated return on
568:
Looking at absolute numbers of children under 5 affected by stunting, it is obvious why current efforts and reductions are insufficient. The absolute number of stunted children has increased in Africa from 50.4 to 58.5 million in the time 2000–2015. This is despite the reduction in percentage
277:
predisposes the fetus to poor growth leading to intrauterine growth retardation, which is strongly associated with low birth weight and size. Women who are underweight or anemic during pregnancy, are more likely to have stunted children which perpetuates the inter-generational transmission of
268:
Poor maternal nutrition during pregnancy and breastfeeding can lead to stunted growth of their children. Proper nutrition for mothers during the prenatal and postnatal period is important for ensuring healthy birth weight and for healthy childhood growth. Prenatal causes of child stunting are
523:
According to the World Health organisation if less than 20% of the population is affected by stunting, this is regarded as "low prevalence" in terms of public health significance. Values of 40% or more are regarded as very high prevalence, and values in between as medium to high
245:
Almost all stunting occurs within the 1,000-day period that spans from conception to a child's second birthday, which constitutes a window of opportunity for growth promotion. The recognition of pre-natal factors underlines the inter-generational aspects of growth, and the need for early
254:
Inadequate complementary child feeding and a general lack of vital nutrients beside pure caloric intake is one cause for stunted growth. Children need to be fed diets which meet the minimum requirements in terms of frequency and diversity in order to prevent undernutrition. Exclusive
669:
and increased pathogen load in the intestine are the major risk factors of stunting in Bangladeshi children. Daily supplementation with egg, cow milk, and micronutrient powder found to be effective in improving linear growth of children in a community-based trial in Bangladesh.
458:
It is estimated that education interventions, if optimally designed and implemented, could reduce stunting by 0.6 z-scores while food-based interventions could reduce stunting by 0.5 z-scores, which is moderate compared to the average global growth deficit. Finally, the
646:
The global community has recognized more and more the critical importance of stunting during the past decade. Investments to address it have increased but remain far from being sufficient to solve it and unleash the human potential that remains trapped in malnutrition.
695:
In Nepal, short maternal stature, low maternal education, poor access to health services and poverty are strong determinants for stunting. However, in Nepal, stunting has decreased from 57% in 2001 to 36% in 2016, with lower prevalence in urban than in rural settings.
3466:
Dewey KG, Mridha MK, Matias SL, Arnold CD, Cummins JR, Khan MS, Maalouf-Manasseh Z, Siddiqui Z, Ullah MB, Vosti SA (April 2017). "Lipid-based nutrient supplementation in the first 1000 d improves child growth in Bangladesh: a cluster-randomized effectiveness trial".
3522:"Supplementation of Maternal Diets during Pregnancy and for 6 Months Postpartum and Infant Diets Thereafter with Small-Quantity Lipid-Based Nutrient Supplements Does Not Promote Child Growth by 18 Months of Age in Rural Malawi: A Randomized Controlled Trial"
4005:
Kim R, Mejía-Guevara I, Corsi DJ, Aguayo VM, Subramanian SV (August 2017). "Relative importance of 13 correlates of child stunting in South Asia: Insights from nationally representative data from Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India, Nepal, and Pakistan".
2858:"Combining Intensive Counseling by Frontline Workers with a Nationwide Mass Media Campaign Has Large Differential Impacts on Complementary Feeding Practices but Not on Child Growth: Results of a Cluster-Randomized Program Evaluation in Bangladesh"
437:
it is also the time when young children are the most at risk of infections that lead to diarrhoea. It is the time when they stop breast feeding (weaning process), begin to crawl, put things in their mouths and become exposed to faecal matter from
3381:
Huybregts L, Roberfroid D, Lanou H, Menten J, Meda N, Van Camp J, Kolsteren P (December 2009). "Prenatal food supplementation fortified with multiple micronutrients increases birth length: a randomized controlled trial in rural Burkina Faso".
4288:
306:
Research on a global level has found that the proportion of stunting that could be attributed to five or more episodes of diarrhoea before two years of age was 25%. Since diarrhoea is closely linked with water, sanitation and hygiene
340:
causing linear growth failure is unclear, but it is hypothesized that chronic inflammatory state and impaired absorption associated with this condition may inhibit bone growth and affect the linear growth during early years of life.
3827:
174:
suggested that stunting is associated with reductions in schooling, decreased economic productivity and poverty. Stunted children also display higher risk of developing chronic non-communicable conditions such as diabetes and
282:
was 33% in all developing countries and 41% in South Asia. Restricted pre- and postnatal growth are in turn important determinants of short adult height, increasing the likelihood of the next generation also being stunted.
357:
of the reference population in height for age are defined as stunted, regardless of the reason. The lower than fifth percentile corresponds to less than two standard deviations of the WHO Child Growth Standards median.
479:
effects on birth weight and -length. Similarly, studies supplementing LNS to mothers during pregnancy and lactation and their children during the complementary feeding period show heterogeneous results for stunting.
1787:"Interventions to Improve Intake of Complementary Foods by Infants 6 to 12 Months of Age in Developing Countries: Impact on Growth and on the Prevalence of Malnutrition and Potential Contribution to Child Survival"
211:
The prevalence of child stunting generally increases as cities become smaller and moving away from urban centres while child wasting and overweight are lower and exhibit less evident trends across the rural-urbann
182:, that can produce metabolic imbalances if the individual is exposed to excessive or poor quality diets as an adult. This can lead to higher risk of developing other related non-communicable diseases such as
278:
stunting. Children born with low birthweight are more at risk of stunting. However, the effect of prenatal undernutrition can be addressed during the postnatal period through proper child feeding practices.
2514:
Ngure FM, Reid BM, Humphrey JH, Mbuya MN, Pelto G, Stoltzfus RJ (January 2014). "Water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH), environmental enteropathy, nutrition, and early child development: making the links".
242:. However, this is not uncontradicted. Recent evidence stresses that stunting may not be taken as a synonym of malnutrition, but as the natural condition of human height in non-Westernized societies.
2566:
Millward DJ (June 2017). "Nutrition, infection and stunting: the roles of deficiencies of individual nutrients and foods, and of inflammation, as determinants of reduced linear growth of children".
178:
as adults. If a stunted child undergoes substantial weight gain after age 2, there is a higher chance of becoming obese. This is believed to be caused by metabolic changes produced by chronic
1455:
Black RE, Victora CG, Walker SP, Bhutta ZA, Christian P, de Onis M, et al. (August 2013). "Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries".
1132:
Black RE, Allen LH, Bhutta ZA, Caulfield LE, de Onis M, Ezzati M, et al. (January 2008). "Maternal and child undernutrition: global and regional exposures and health consequences".
539:
found that in 2019 22.5 percent of children under the age of five were stunted, 9.2 percent were wasted, and 9.9 percent were overweight across several Arab and North African countries.
405:"). Without provision of toilets, prevention of tropical intestinal diseases, which may affect almost all children in the developing world and lead to stunting will not be possible.
2701:
514:
Broadly speaking, effective policies to reduce stunting require multisectoral approaches, strong political commitment, community involvement and integrated service delivery.
3047:
Bhutta ZA, Ahmed T, Black RE, Cousens S, Dewey K, Giugliani E, et al. (February 2008). "What works? Interventions for maternal and child undernutrition and survival".
3652:
NENA Regional Network on Nutrition-sensitive Food System. Empowering women and ensuring gender equality in agri-food systems to achieve better nutrition − Technical brief
3236:"A comprehensive intervention package improves the linear growth of children under 2-years-old in rural Bangladesh: a community-based cluster randomized controlled trial"
166:
Women of shorter stature have a greater risk for complications during child birth due to their smaller pelvis, and are at risk of delivering a baby with low birth weight
2907:"Social Franchising and a Nationwide Mass Media Campaign Increased the Prevalence of Adequate Complementary Feeding in Vietnam: A Cluster-Randomized Program Evaluation"
4351:
577:
and malnutrition, whereby malnourished children are not able to maximally contribute to economic development as adults, and poverty increases chances of malnutrition.
4185:
Ulep, Valerie; Uy, Jhanna; Casas, Lyle Daryll D.; Capanzana, Mario V.; Nkoroi, Alice; Galera Jr., Rene Gerard; Carpio, Maria Evelyn; Tan, Frederich (February 2023).
3752:"Investing in the Next Generation - Children grow taller, and smarter, in rural, mountainous villages of Lao PDR where all community members use improved sanitation"
5021:
3841:
573:
countries (high-income, upper-middle income, lower-middle income) have achieved reductions in the numbers of stunted children. This sadly perpetuates a vicious
639:
In 2015, the United Nations and its member states agreed on a new sustainable development agenda to promote prosperity and reduce poverty, putting forward 17
594:
access to sanitation. This difference in height is irreversible and matters a great deal for a child's cognitive development and future productive potential.
466:
intervention programs should consider egg intervention for a longer period with emphasis on overall diet quality and improvement of environmental conditions.
425:
Three of these determinants should receive attention in particular: access to sanitation, and diversity of calorie sources from food supplies. A study by the
4971:
2678:
1547:
Victora CG, de Onis M, Hallal PC, Blössner M, Shrimpton R (March 2010). "Worldwide timing of growth faltering: revisiting implications for interventions".
499:
Political will to develop and implement national targets and strategies in line with evidence-based international guidelines as well as contextual factors.
1218:"Associations of suboptimal growth with all-cause and cause-specific mortality in children under five years: a pooled analysis of ten prospective studies"
528:
four countries with the highest prevalence are Timor-Leste, Burundi, Niger and Madagascar where more than half of children under 5 years old are stunted.
1177:"The effect of multiple anthropometric deficits on child mortality: meta-analysis of individual data in 10 prospective studies from developing countries"
453:
shows only small benefits for linear growth and results from studies supplementing lipid based nutrient supplements (LNS) to children are inconclusive.
1035:
3774:"Nutritional interventions for preventing stunting in children (birth to 59 months) living in urban slums in low- and middle-income countries (LMIC)"
332:
to intestinal pathogens caused by faecal contamination of food and water. Recent evidence confirmed a causal relationship between stunted growth and
2398:
2374:"Under-nutrition and water, sanitation and hygiene - Water, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) play a fundamental role in improving nutritional outcomes"
3953:"Childhood stunting in relation to the pre- and postnatal environment during the first 2 years of life: The MAL-ED longitudinal birth cohort study"
408:
Studies have looked at ranking the underlying determinants in terms of their potency in reducing child stunting and found in the order of potency:
224:
1644:"Risk Factors for Childhood Stunting in 137 Developing Countries: A Comparative Risk Assessment Analysis at Global, Regional, and Country Levels"
729:
4167:
216:
4698:
3668:
3615:
3577:
150:
Stunted growth in children has the following public health impacts apart from the obvious impact of shorter stature of the person affected:
4469:
4344:
4244:
3599:
Near East and North Africa Regional Overview of Food Security and Nutrition 2020. Enhancing resilience of food systems in the Arab States
2768:"Linear growth increased in young children in an urban slum of Haiti: a randomized controlled trial of a lipid-based nutrient supplement"
5014:
4725:
4637:
362:
curve may reflect normal variation in growth within a population: the individual child may be short simply because both parents carried
336:
in children. Several studies are also underway to examine the link between this condition and stunted growth. The exact pathogenesis of
2817:"Provision of 10-40 g/d Lipid-Based Nutrient Supplements from 6 to 18 Months of Age Does Not Prevent Linear Growth Faltering in Malawi"
429:
has stressed that: "The first two should be prioritized because they have strong impacts yet are farthest below their desired levels".
125:
1828:"Determinants of suboptimal complementary feeding practices among children aged 6-23 months in four anglophone West African countries"
311:), this is a good indicator for the connection between WASH and stunted growth. To what extent improvements in drinking water safety,
3185:"Daily Supplementation With Egg, Cow Milk, and Multiple Micronutrients Increases Linear Growth of Young Children with Short Stature"
532:
3567:
426:
5096:
5038:
5324:
5292:
4404:
4337:
3674:
382:
applying several nutritional modifications or changes in a population on a large scale which have a high benefit and a low cost
3751:
3629:
157:
Delayed neurocognitive development and therefore poorer school performance and later on reduced productivity in the work force
5007:
1984:"Risk of childhood undernutrition related to small-for-gestational age and preterm birth in low- and middle-income countries"
615:
Nutritional interventions such as dietary supplementation and nutritional education have the potential to decrease stunting.
3726:
4399:
640:
450:
3849:
2766:
Iannotti LL, Dulience SJ, Green J, Joseph S, François J, Anténor ML, Lesorogol C, Mounce J, Nickerson NM (January 2014).
5101:
4582:
4479:
586:
3891:. National Institute of Population Research and Training (NIPORT). Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. October 2020.
5371:
4885:
809:
134:
stunting, and most children will never gain the corresponding body weight. Living in an environment where many people
2959:"Systematic review of the efficacy and effectiveness of complementary feeding interventions in developing countries"
393:
To prevent stunting, it is not just a matter of providing better nutrition but also access to clean water, improved
199:
Asia are stunted, and due to a large population size, the region bears about 40% of the global burden of stunting.
4577:
1324:
734:
239:
233:
98:, is defined as impaired growth and development manifested by low height-for-age. It is a primary manifestation of
3425:
Adu-Afarwuah S, Lartey A, Okronipa H, Ashorn P, Zeilani M, Peerson JM, Arimond M, Vosti S, Dewey KG (April 2015).
2686:
61:
5453:
4956:
4572:
4439:
1736:"Prevalence and determinants of stunting in a conflict-ridden border region in Armenia - a cross-sectional study"
350:
337:
333:
328:
119:
5394:
4966:
4489:
2702:"The first 1,000 days of a child's life are the most important to their development - and our economic success"
3884:
1042:
5106:
4484:
1036:"World Health Assembly Global Nutrition Targets 2025: Stunting Policy Brief, World Health Organization 2014"
319:
practices contribute to reduce stunting depends on the how bad these practices were prior to interventions.
238:
In many publications, the causes for stunting are considered very similar if not the same as the causes for
187:
169:
Stunted growth can be passed to the next generation, known as the "intergenerational cycle of malnutrition"
5184:
4715:
4187:"The Determinants of the Socioeconomic Inequality and the Trajectory of Child Stunting in the Philippines"
3904:"Nutrition and Food Security in Bangladesh: Achievements, Challenges, and Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic"
220:
Children living in unsanitary conditions in an urban slum in India, at risk of diarrhea and stunted growth
3291:
Iannotti LL, Chapnick M, Nicholas J, Gallegos-Riofrio CA, Moreno P, Douglas K, et al. (April 2020).
5448:
5344:
5277:
5145:
4474:
4168:"Undernutrition in the Philippines – Scale Scope and Opportunities for Nutrition Policy and Programming"
917:
How much international variation in child height can sanitation explain? - Policy research working paper
624:
4245:"The Philippines renews its commitment to nutrition with updated action plan - Philippines | ReliefWeb"
3131:
Iannotti LL, Lutter CK, Stewart CP, Gallegos Riofrío CA, Malo C, Reinhart G, et al. (July 2017).
2631:
Humphrey JH (September 2009). "Child undernutrition, tropical enteropathy, toilets, and handwashing".
5255:
5249:
5241:
5226:
5207:
4693:
4632:
4532:
4506:
3247:
2524:
2467:"Can water, sanitation and hygiene help eliminate stunting? Current evidence and policy implications"
1229:
872:
1111:
5458:
5361:
5349:
5339:
4961:
4946:
4098:"Maternal and Child Nutrition in Nepal: Examining drivers of progress from the mid- 1990s to 2010s"
3828:
Integrated Safeguards Data Sheet (Appraisal Stage)-Guangxi Laibin Water Environment Project-P126817
3427:"Lipid-based nutrient supplement increases the birth size of infants of primiparous women in Ghana"
714:
379:
a kind of environment where political commitment can thrive (also called an "enabling environment")
1982:
Christian P, Lee SE, Donahue Angel M, Adair LS, Arifeen SE, Ashorn P, et al. (October 2013).
1175:
McDonald CM, Olofin I, Flaxman S, Fawzi WW, Spiegelman D, Caulfield LE, et al. (April 2013).
5412:
5269:
5068:
4454:
4146:"Risk factors of stunting during the complementary feeding period 6-23 months in the Philippines"
3621:
3502:
3407:
3162:
3072:
2656:
2591:
2548:
2351:
2201:
1964:
1621:
1572:
1529:
1480:
1434:
1157:
191:
756:
747:
2609:
1078:
5384:
5379:
5334:
5329:
5171:
5158:
4780:
4668:
4647:
4607:
4429:
4166:
Mbuya, Nkosinathi V; Demombynes, Gabriel; Piza, Sharon Faye A.; Adona, Ann Jillian V. (2021).
4075:
4023:
3984:
3933:
3803:
3664:
3611:
3573:
3543:
3494:
3448:
3399:
3363:
3322:
3273:
3216:
3154:
3113:
3064:
3029:
2988:
2936:
2887:
2838:
2797:
2748:
2648:
2583:
2540:
2496:
2447:
2343:
2322:"Pathophysiology of environmental enteric dysfunction and its impact on oral vaccine efficacy"
2302:
2253:
2193:
2152:
2103:
2054:
2013:
1956:
1908:
1857:
1808:
1767:
1675:
1613:
1564:
1521:
1472:
1426:
1391:
1306:
1257:
1198:
1149:
960:
898:
719:
389:, and a supportive health environment through increasing access to safe water and sanitation).
115:
74:
5297:
5212:
4562:
4537:
4224:
4216:
4186:
4109:
4065:
4057:
4015:
3974:
3964:
3923:
3915:
3793:
3785:
3656:
3603:
3533:
3484:
3476:
3438:
3391:
3353:
3312:
3304:
3263:
3255:
3206:
3196:
3144:
3103:
3056:
3019:
2978:
2970:
2926:
2918:
2877:
2869:
2828:
2787:
2779:
2738:
2640:
2575:
2532:
2486:
2478:
2437:
2429:
2333:
2292:
2284:
2243:
2235:
2183:
2142:
2134:
2093:
2085:
2044:
2003:
1995:
1948:
1898:
1888:
1847:
1839:
1798:
1757:
1747:
1711:
1665:
1655:
1603:
1556:
1511:
1464:
1418:
1409:
Scheffler C, Hermanussen M (May 2022). "Stunting is the natural condition of human height".
1381:
1296:
1288:
1247:
1237:
1188:
1141:
950:
942:
888:
880:
574:
303:) which are both linked to poor sanitation have been shown to contribute to child stunting.
1275:
Victora CG, Adair L, Fall C, Hallal PC, Martorell R, Richter L, Sachdev HS (January 2008).
228:
Child next to open sewer in slum in Kampala, Uganda, at risk of diarrhea and stunted growth
5319:
5314:
4986:
4936:
4865:
4840:
4810:
4720:
4627:
4567:
3342:"Maternal nutrition and birth outcomes: effect of balanced protein-energy supplementation"
2373:
916:
438:
433:
274:
135:
1642:
Danaei G, Andrews KG, Sudfeld CR, Fink G, McCoy DC, Peet E, et al. (November 2016).
3251:
2905:
Rawat R, Nguyen PH, Tran LM, Hajeebhoy N, Nguyen HV, Baker J, et al. (April 2017).
2727:"Do multiple micronutrient interventions improve child health, growth, and development?"
2528:
2033:"Associations between prenatal and postnatal growth and adult body size and composition"
1233:
876:
5354:
4976:
4860:
4800:
4464:
4459:
4449:
4444:
4409:
4070:
4045:
3979:
3952:
3928:
3903:
3798:
3773:
3317:
3292:
3268:
3235:
3183:
Mahfuz M, Alam MA, Das S, Fahim SM, Hossain MS, Petri WA, et al. (February 2020).
2983:
2958:
2931:
2906:
2882:
2857:
2856:
Menon P, Nguyen PH, Saha KK, Khaled A, Sanghvi T, Baker J, et al. (October 2016).
2792:
2767:
2491:
2466:
2442:
2417:
2297:
2272:
2248:
2223:
2147:
2122:
2121:
Walker CL, Rudan I, Liu L, Nair H, Theodoratou E, Bhutta ZA, et al. (April 2013).
2098:
2073:
2008:
1983:
1903:
1876:
1852:
1827:
1762:
1735:
1670:
1643:
1301:
1276:
1252:
1217:
955:
931:"Early and Long-term Consequences of Nutritional Stunting: From Childhood to Adulthood"
930:
893:
860:
270:
31:
3902:
Fahim SM, Hossain MS, Sen S, Das S, Hosssain M, Ahmed T, et al. (December 2021).
3583:
3234:
Ara G, Sanin KI, Khanam M, Sarker MS, Tofail F, Nahar B, et al. (December 2022).
3060:
2815:
Maleta KM, Phuka J, Alho L, Cheung YB, Dewey KG, Ashorn U, et al. (August 2015).
2644:
2172:"Environmental Enteric Dysfunction and Growth Failure/Stunting in Global Child Health"
2138:
1468:
1292:
1145:
1030:
1028:
1026:
1024:
1022:
1020:
1018:
1016:
1014:
1012:
1010:
1008:
1006:
1004:
1002:
1000:
998:
996:
994:
5442:
5389:
5287:
4981:
4951:
4931:
4790:
4765:
4688:
4602:
4592:
4587:
4501:
4394:
3625:
3358:
3341:
3133:"Eggs in Early Complementary Feeding and Child Growth: A Randomized Controlled Trial"
2974:
2595:
2355:
1968:
1608:
1591:
1438:
992:
990:
988:
986:
984:
982:
980:
978:
976:
974:
752:
724:
432:
The goal of UN agencies, governments and NGO is now to optimise nutrition during the
386:
349:
Growth stunting is identified by comparing measurements of children's heights to the
300:
256:
107:
35:
4019:
3520:
Ashorn P, Alho L, Ashorn U, Cheung YB, Dewey KG, Gondwe A, et al. (June 2015).
3506:
3411:
3166:
3076:
2660:
2552:
2416:
Chen RY, Kung VL, Das S, Hossain MS, Hibberd MC, Guruge J, et al. (July 2020).
2205:
1625:
1576:
1484:
1277:"Maternal and child undernutrition: consequences for adult health and human capital"
1216:
Olofin I, McDonald CM, Ezzati M, Flaxman S, Black RE, Fawzi WW, et al. (2013).
5307:
5282:
5236:
5030:
4820:
4815:
4795:
4775:
4761:
4705:
4552:
4434:
4384:
3789:
3650:
2089:
1716:
1699:
1533:
1161:
183:
179:
99:
3008:"Worldwide timing of growth faltering: implications for nutritional interventions"
2170:
Owino V, Ahmed T, Freemark M, Kelly P, Loy A, Manary M, Loechl C (December 2016).
1500:"Global dietary patterns and diets in childhood: implications for health outcomes"
1353:
Stop Stunting in South Asia. A common Narrative on Marternal and Child Nutrition.
3969:
1952:
1734:
A Balalian A, Simonyan H, Hekimian K, Deckelbaum RJ, Sargsyan A (December 2017).
1700:"Reducing Child Undernutrition: Past Drivers and Priorities for the Post-MDG Era"
1660:
1242:
929:
De Sanctis V, Soliman A, Alaaraj N, Ahmed S, Alyafei F, Hamed N (February 2021).
772:
118:
brought on by a malnourished mother. The definition of stunting according to the
5427:
5417:
5302:
5058:
5048:
4926:
4921:
4895:
4785:
4770:
4751:
4710:
4678:
4673:
4511:
4389:
4144:
Guirindola, Mildred; Goyena, Eva; Maniego, Ma. Lynell Valdeabella (April 2021).
3006:
Shrimpton R, Victora CG, de Onis M, Lima RC, Blössner M, Clugston G (May 2001).
316:
3259:
3108:
3091:
1923:
1803:
1786:
919:. The World Bank, Sustainable Development Network, Water and Sanitation Program
832:
5119:
5077:
4905:
4850:
4845:
4835:
4830:
4683:
4557:
4419:
4414:
4370:
4114:
4097:
3569:
Improving child nutrition : the achievable imperative for global progress
2579:
2338:
2321:
2273:"Environmental Enteric Dysfunction: A Case Definition for Intervention Trials"
1939:
Akhtar S (October 2016). "Malnutrition in South Asia-A Critical Reappraisal".
1877:"Stunting, Wasting and Underweight in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Systematic Review"
1752:
1386:
1369:
884:
603:
590:
553:
459:
449:
Previous interventions to reduce stunting have shown modest effects. Multiple
394:
354:
291:
139:
79:
3919:
2049:
2032:
1826:
Issaka AI, Agho KE, Page AN, Burns PL, Stevens GJ, Dibley MJ (October 2015).
1812:
946:
142:, is an important cause of stunted growth in children, for example in India.
102:(or more precisely chronic undernutrition) and recurrent infections, such as
4890:
4756:
4735:
4617:
4542:
4494:
4424:
4379:
4297:
3480:
3443:
3426:
3395:
3293:"Egg intervention effect on linear growth no longer present after two years"
3132:
2783:
2239:
1193:
1176:
454:
111:
4220:
4079:
4027:
3988:
3937:
3807:
3721:
3719:
3717:
3715:
3713:
3711:
3547:
3498:
3452:
3403:
3367:
3326:
3277:
3220:
3158:
3149:
3117:
3068:
3033:
3024:
3007:
2992:
2940:
2891:
2842:
2801:
2752:
2652:
2587:
2544:
2500:
2451:
2347:
2306:
2257:
2197:
2188:
2171:
2156:
2107:
2058:
2017:
1960:
1912:
1893:
1861:
1771:
1679:
1617:
1568:
1560:
1525:
1476:
1430:
1395:
1332:
United Nations Children's Fund; World Health Organization; World Bank Group
1310:
1261:
1202:
1153:
964:
902:
859:
Local Burden of Disease Child Growth Failure Collaborators (January 2020).
507:
mothers have the chance to breastfeed should be considered where necessary.
290:
There is most likely a link between children's linear growth and household
3709:
3707:
3705:
3703:
3701:
3699:
3697:
3695:
3693:
3691:
3538:
3521:
2922:
2873:
2833:
2816:
2743:
2726:
2433:
2288:
5422:
5132:
5091:
5053:
4941:
4880:
4870:
4805:
4642:
4622:
4547:
4329:
4323:
3090:
McKay S, Gaudier E, Campbell DI, Prentice AM, Albers R (September 2010).
2418:"Duodenal Microbiota in Stunted Undernourished Children with Enteropathy"
1999:
491:
In summary, key policy interventions for the prevention of stunting are:
296:
103:
4280:
3201:
3184:
1875:
Akombi BJ, Agho KE, Hall JJ, Wali N, Renzaho AM, Merom D (August 2017).
5231:
4900:
4875:
4652:
4314:, regional conference on nutrition in South Asia (website slow to load)
4229:
2536:
2382:
A successful global effort to tackle under-nutrition must include WASH.
1918:
1422:
549:
175:
17:
4061:
3489:
3308:
3211:
3178:
3176:
3092:"Environmental enteropathy: new targets for nutritional interventions"
2482:
2399:
Reframing Undernutrition: Faecally-Transmitted Infections and the 5 As
2031:
Li H, Stein AD, Barnhart HX, Ramakrishnan U, Martorell R (June 2003).
1843:
1516:
1499:
1106:
1104:
1102:
1100:
1098:
1096:
1094:
1092:
1073:
1071:
1069:
1067:
1065:
1063:
1061:
1059:
1057:
1055:
861:"Mapping child growth failure across low- and middle-income countries"
129:
Prevalence of stunting in children under 5 years by region (2020-2022)
5220:
4825:
4612:
4597:
4360:
4292:
4208:
4207:
Capanzana, Mario V.; Demombynes, Gabriel; Gubbins, Paul (June 2020).
3867:"Working together in the fight against malnutrition in all its forms"
3660:
3607:
398:
312:
353:
2006 growth reference population: children who fall below the fifth
3597:
4730:
3866:
3734:
UNICEF / WHO / World Bank Group Joint Child Malnutrition Estimates
1357:(Report). Kathmandu, Nepal: United Nation's Children's fund. 2015.
223:
215:
4172:
International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/ World Bank
1922:
Material was copied from this source, which is available under a
1881:
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health
1592:"Intergenerational influences on child growth and undernutrition"
4516:
402:
363:
308:
5003:
4999:
4333:
2320:
Marie C, Ali A, Chandwe K, Petri WA, Kelly P (September 2018).
1368:
Scheffler C, Hermanussen M, Bogin B, et al. (March 2020).
4317:
833:"The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2022"
412:
percent of dietary energy from non-staples (greatest impact)
206:
4311:
2405:(Report). Brighton: Institute of Development Studies (IDS).
3772:
Goudet SM, Bogin BA, Madise NJ, Griffiths PL (June 2019).
3572:. United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), New York, USA.
2222:
Budge S, Parker AH, Hutchings PT, Garbutt C (April 2019).
3861:
3859:
2725:
Ramakrishnan U, Goldenberg T, Allen LH (November 2011).
4096:
Cunningham KH, Singh A, Karmacharya C, Rana PR (2017).
755: by Marianne Sandsmark Morseth available under the
4209:"Why Are So Many Children Stunted in the Philippines?"
2224:"Environmental enteric dysfunction and child stunting"
1924:
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License
367:
malnutrition is generally the first cause considered.
4133:(Report). Kathmandu, Nepal: Ministry of Health. 2017.
2277:
The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene
401:) and hand washing at critical times (summarised as "
4270:
2123:"Global burden of childhood pneumonia and diarrhoea"
69:
World map in 2016: Share of children who are stunted
5405:
5370:
5268:
5199:
5076:
5067:
5037:
4914:
4744:
4661:
4525:
4368:
4274:
2672:
2670:
2610:"The Lancet series on Maternal and Child Nutrition"
1785:Caulfield LE, Huffman SL, Piwoz EG (January 1999).
73:
51:
46:
4091:
4089:
3885:"Bangladesh Demographic and Health Survey 2017-18"
2679:"How to better link WASH and nutrition programmes"
1729:
1727:
114:and even before birth, due to malnutrition during
375:Three main things are needed to reduce stunting:
4046:"Stunting in Nepal: looking back, looking ahead"
2367:
2365:
537:Regional Overview of Food Security and Nutrition
4324:Visualizing child growth failure from 2000-2017
4044:Devkota MD, Adhikari RK, Upreti SR (May 2016).
4039:
4037:
3745:
3743:
2217:
2215:
2074:"The stunting syndrome in developing countries"
810:"Nutrition Landscape Information System (NLiS)"
3842:"United Nations Sustainable Development Goals"
3821:
3819:
3817:
3561:
3559:
3557:
2271:Denno DM, Tarr PI, Nataro JP (December 2017).
1941:Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition
1934:
1932:
1637:
1635:
854:
852:
5015:
4855:(American 'crib' and 'cradle', British 'cot')
4345:
3951:MAL-ED Network Investigators (October 2017).
2952:
2950:
2072:Prendergast AJ, Humphrey JH (November 2014).
1693:
1691:
1689:
1450:
1448:
1127:
1125:
8:
4194:Philippine Institute for Development Studies
154:Greater risk for illness and premature death
4000:
3998:
3778:The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
2392:
2390:
1370:"Stunting is not a synonym of malnutrition"
385:a strong foundation that can drive change (
5073:
5022:
5008:
5000:
4352:
4338:
4330:
4271:
4129:Nepal demographic and health survey 2016.
3469:The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
3431:The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
3384:The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
2772:The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
2517:Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences
2078:Paediatrics and International Child Health
2037:The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
1181:The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
415:access to sanitation and women's education
43:
34:. For causes other than malnutrition, see
4228:
4113:
4069:
3978:
3968:
3927:
3797:
3727:"Levels and trends in child malnutrition"
3537:
3488:
3442:
3357:
3316:
3267:
3210:
3200:
3148:
3107:
3023:
2982:
2930:
2881:
2832:
2791:
2742:
2683:Concern Worldwide Technical Briefing Note
2490:
2441:
2337:
2296:
2247:
2187:
2146:
2097:
2048:
2007:
1902:
1892:
1851:
1802:
1761:
1751:
1715:
1669:
1659:
1607:
1515:
1385:
1325:"Levels and trends in child malnutrition"
1300:
1251:
1241:
1192:
954:
892:
445:Dietary interventions to improve stunting
3750:Quattri M, Smets S, Inthavong V (2014).
503:ensuring the fetus and baby's nutrition.
124:
27:Reduced growth rate in human development
3830:(Report). The World Bank. pp. 1–9.
2957:Dewey KG, Adu-Afarwuah S (April 2008).
764:
4233:– via Open Knowledge Repository.
730:Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition
30:For stunting of growth in plants, see
3346:Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology
1988:International Journal of Epidemiology
1596:Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology
1590:Martorell R, Zongrone A (July 2012).
1355:UNICEF Regional Office for South Asia
804:
802:
800:
798:
796:
794:
792:
7:
4470:Infant respiratory distress syndrome
2465:Cumming O, Cairncross S (May 2016).
1504:Annals of Nutrition & Metabolism
4155:: 134–137 – via ResearchGate.
2422:The New England Journal of Medicine
2397:Chambers R, von Medeazza G (2014).
1112:"Maternal and child undernutrition"
3908:The Journal of Infectious Diseases
3759:WSP (Water and Sanitation Program)
25:
4131:Ministry of Health; New ERA; ICF.
3848:. 1 December 2014. Archived from
2677:Flachenberg F, Kopplow R (2014).
1698:Smith LC, Haddad L (April 2015).
441:and environmental enteropathies.
3359:10.1111/j.1365-3016.2012.01308.x
3340:Imdad A, Bhutta ZA (July 2012).
2975:10.1111/j.1740-8709.2007.00124.x
1917:
1609:10.1111/j.1365-3016.2012.01298.x
751: This article incorporates
746:
535:'s Near East and North Africa −
427:Institute of Development Studies
421:per capita dietary energy supply
299:and intestinal worm infections (
60:
4405:Breastfeeding and mental health
4020:10.1016/j.socscimed.2017.06.017
3677:from the original on 2022-12-17
3632:from the original on 2023-01-15
1116:Series from the Lancet journals
1083:Series from the Lancet journals
4153:Malaysian Journal of Nutrition
4050:Maternal & Child Nutrition
3790:10.1002/14651858.CD011695.pub2
3297:Maternal & Child Nutrition
2963:Maternal & Child Nutrition
2471:Maternal & Child Nutrition
2090:10.1179/2046905514Y.0000000158
1832:Maternal & Child Nutrition
1717:10.1016/j.worlddev.2014.11.014
1079:"Maternal and child nutrition"
470:Pregnant and lactating mothers
295:losses.The diseases recurrent
55:Stunting, nutritional stunting
1:
4400:Breastfeeding and medications
4213:Policy Research Working paper
4008:Social Science & Medicine
3061:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61693-6
2645:10.1016/s0140-6736(09)60950-8
2139:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60222-6
1469:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60937-X
1293:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61692-4
1146:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61690-0
641:Sustainable Development Goals
635:Sustainable Development Goals
451:micronutrient supplementation
4962:Neonatal withdrawal syndrome
4583:Infant cognitive development
4480:Neonatal intensive care unit
3970:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002408
1953:10.1080/10408398.2013.832143
1661:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002164
1243:10.1371/journal.pone.0064636
587:Water and Sanitation Program
5097:Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome
4886:Supplemental nursing system
4326:, interactive visualization
3914:(Supplement_7): S901–S909.
2372:Velleman Y, Pugh I (2013).
1791:Food and Nutrition Bulletin
5475:
4638:Prenatal development table
4578:Irritant diaper dermatitis
3260:10.1038/s41598-022-26269-w
3109:10.1016/j.inhe.2010.07.006
2568:Nutrition Research Reviews
2380:. UK: WaterAid and Share.
1804:10.1177/156482659902000203
735:Undernutrition in children
234:Undernutrition in children
231:
160:Reduced cognitive capacity
29:
5102:Wernicke's encephalopathy
4957:Prenatal cocaine exposure
4745:Infant care and equipment
4662:Socialization and Culture
4573:Infant visual development
4440:Infant and toddler safety
4115:10.1016/j.gfs.2017.02.001
2612:. The Lancet. 6 June 2013
2580:10.1017/S0954422416000238
2339:10.1038/s41385-018-0036-1
1753:10.1186/s40795-017-0204-9
1387:10.1038/s41430-019-0439-4
885:10.1038/s41586-019-1878-8
455:Educational interventions
351:World Health Organization
338:environmental enteropathy
334:environmental enteropathy
329:environmental enteropathy
323:Environmental enteropathy
269:associated with maternal
120:World Health Organization
68:
59:
4967:Parental child abduction
4490:Oral rehydration therapy
3526:The Journal of Nutrition
3189:The Journal of Nutrition
2911:The Journal of Nutrition
2862:The Journal of Nutrition
2821:The Journal of Nutrition
2731:The Journal of Nutrition
947:10.23750/abm.v92i1.11346
240:malnutrition in children
4972:Parental responsibility
4485:Newborn care and safety
3481:10.3945/ajcn.116.147942
3444:10.3945/ajcn.114.091546
3396:10.3945/ajcn.2009.28253
2784:10.3945/ajcn.113.063883
1194:10.3945/ajcn.112.047639
4716:Grandparent visitation
4221:10.1596/1813-9450-9294
3920:10.1093/infdis/jiab473
3871:scalingupnutrition.org
3150:10.1542/peds.2016-3459
3025:10.1542/peds.107.5.e75
2189:10.1542/peds.2016-0641
2050:10.1093/ajcn/77.6.1498
1894:10.3390/ijerph14080863
1561:10.1542/peds.2009-1519
229:
221:
213:
188:coronary heart disease
163:Future risk of obesity
130:
5278:Electrolyte imbalance
5146:Pyridoxine deficiency
5120:Riboflavin deficiency
4475:Infant sleep training
3826:Procee P (May 2013).
3539:10.3945/jn.114.207225
2923:10.3945/jn.116.243907
2874:10.3945/jn.116.232314
2834:10.3945/jn.114.208181
2744:10.3945/jn.111.146845
2700:Lake A (2017-01-14).
2434:10.1056/NEJMoa1916004
2403:IDS Working Paper 450
2289:10.4269/ajtmh.17-0183
2240:10.1093/nutrit/nuy068
1048:on September 9, 2014.
625:World Health Assembly
327:The condition termed
232:Further information:
227:
219:
210:
128:
96:linear growth failure
5256:Vitamin K deficiency
5250:Vitamin E deficiency
5227:Vitamin D deficiency
5208:Vitamin A deficiency
5107:Korsakoff's syndrome
4633:Prenatal development
4533:Attachment parenting
4507:Shaken baby syndrome
4102:Global Food Security
3655:. Cairo: FAO. 2023.
3602:. Cairo: FAO. 2021.
3096:International Health
2706:World Economic Forum
531:The 2020 edition of
487:Policy interventions
418:access to safe water
136:defecate in the open
4947:Infant ear piercing
3352:(Suppl 1): 178–90.
3252:2022NatSR..1221962A
2639:(9694): 1032–1035.
2529:2014NYASA1308..118N
2477:(Suppl 1): 91–105.
2133:(9875): 1405–1416.
1602:(Suppl 1): 302–14.
1234:2013PLoSO...864636O
915:Spears, D. (2013).
877:2020Natur.577..231L
831:nina (2022-07-06).
715:Compensatory growth
682:India (Maharashtra)
5270:Mineral deficiency
5069:Vitamin deficiency
4455:Infant food safety
4056:(Suppl 1): 257–9.
3852:on 4 January 2017.
3761:. USA: World Bank.
3240:Scientific Reports
2969:(Suppl 1): 24–85.
2537:10.1111/nyas.12330
2326:Mucosal Immunology
2000:10.1093/ije/dyt109
1838:(Suppl 1): 14–30.
1510:(Suppl 1): 29–37.
1423:10.1002/ajhb.23693
552:and stunting, and
264:Maternal nutrition
230:
222:
214:
192:metabolic syndrome
131:
5436:
5435:
5385:Failure to thrive
5380:Delayed milestone
5264:
5263:
5242:Harrison's groove
5172:Folate deficiency
5159:Biotin deficiency
4997:
4996:
4857:
4694:Children's rights
4608:Object permanence
4430:Failure to thrive
4320:, program website
4307:
4306:
4062:10.1111/mcn.12286
3670:978-92-5-137438-2
3617:978-92-5-134471-2
3579:978-92-806-4686-3
3309:10.1111/mcn.12925
3202:10.1093/jn/nxz253
3055:(9610): 417–440.
2868:(10): 2075–2084.
2483:10.1111/mcn.12258
2228:Nutrition Reviews
1947:(14): 2320–2330.
1844:10.1111/mcn.12194
1704:World Development
1517:10.1159/000346185
1498:Allen LH (2012).
1463:(9890): 427–451.
1287:(9609): 340–357.
1140:(9608): 243–260.
871:(7789): 231–234.
720:Failure to thrive
250:Feeding practices
116:fetal development
85:
84:
41:Medical condition
16:(Redirected from
5466:
5454:Growth disorders
5074:
5024:
5017:
5010:
5001:
4853:
4538:Baby-led weaning
4354:
4347:
4340:
4331:
4318:Alive and Thrive
4272:
4260:
4259:
4257:
4256:
4241:
4235:
4234:
4232:
4204:
4198:
4197:
4191:
4182:
4176:
4175:
4163:
4157:
4156:
4150:
4141:
4135:
4134:
4126:
4120:
4119:
4117:
4093:
4084:
4083:
4073:
4041:
4032:
4031:
4002:
3993:
3992:
3982:
3972:
3963:(10): e1002408.
3948:
3942:
3941:
3931:
3899:
3893:
3892:
3881:
3875:
3874:
3863:
3854:
3853:
3838:
3832:
3831:
3823:
3812:
3811:
3801:
3769:
3763:
3762:
3756:
3747:
3738:
3737:
3731:
3723:
3686:
3685:
3683:
3682:
3661:10.4060/cc3657en
3647:
3641:
3640:
3638:
3637:
3608:10.4060/cb4902en
3594:
3588:
3587:
3586:on May 13, 2013.
3582:. Archived from
3563:
3552:
3551:
3541:
3532:(6): 1345–1353.
3517:
3511:
3510:
3492:
3463:
3457:
3456:
3446:
3422:
3416:
3415:
3378:
3372:
3371:
3361:
3337:
3331:
3330:
3320:
3288:
3282:
3281:
3271:
3231:
3225:
3224:
3214:
3204:
3180:
3171:
3170:
3152:
3143:(1): e20163459.
3128:
3122:
3121:
3111:
3087:
3081:
3080:
3044:
3038:
3037:
3027:
3003:
2997:
2996:
2986:
2954:
2945:
2944:
2934:
2902:
2896:
2895:
2885:
2853:
2847:
2846:
2836:
2827:(8): 1909–1915.
2812:
2806:
2805:
2795:
2763:
2757:
2756:
2746:
2722:
2716:
2715:
2713:
2712:
2697:
2691:
2690:
2685:. Archived from
2674:
2665:
2664:
2628:
2622:
2621:
2619:
2617:
2606:
2600:
2599:
2563:
2557:
2556:
2511:
2505:
2504:
2494:
2462:
2456:
2455:
2445:
2413:
2407:
2406:
2394:
2385:
2384:
2369:
2360:
2359:
2341:
2332:(5): 1290–1298.
2317:
2311:
2310:
2300:
2283:(6): 1643–1646.
2268:
2262:
2261:
2251:
2219:
2210:
2209:
2191:
2182:(6): e20160641.
2167:
2161:
2160:
2150:
2118:
2112:
2111:
2101:
2069:
2063:
2062:
2052:
2028:
2022:
2021:
2011:
1994:(5): 1340–1355.
1979:
1973:
1972:
1936:
1927:
1921:
1916:
1906:
1896:
1872:
1866:
1865:
1855:
1823:
1817:
1816:
1806:
1782:
1776:
1775:
1765:
1755:
1731:
1722:
1721:
1719:
1695:
1684:
1683:
1673:
1663:
1654:(11): e1002164.
1639:
1630:
1629:
1611:
1587:
1581:
1580:
1544:
1538:
1537:
1519:
1495:
1489:
1488:
1452:
1443:
1442:
1406:
1400:
1399:
1389:
1365:
1359:
1358:
1350:
1344:
1343:
1341:
1339:
1329:
1321:
1315:
1314:
1304:
1272:
1266:
1265:
1255:
1245:
1213:
1207:
1206:
1196:
1172:
1166:
1165:
1129:
1120:
1119:
1108:
1087:
1086:
1075:
1050:
1049:
1047:
1041:. Archived from
1040:
1032:
969:
968:
958:
926:
920:
913:
907:
906:
896:
856:
847:
846:
844:
843:
828:
822:
821:
819:
817:
806:
787:
786:
784:
783:
769:
750:
575:cycle of poverty
90:, also known as
64:
44:
21:
5474:
5473:
5469:
5468:
5467:
5465:
5464:
5463:
5439:
5438:
5437:
5432:
5401:
5366:
5260:
5195:
5188:
5181:
5168:
5155:
5142:
5129:
5116:
5088:
5063:
5040:
5033:
5028:
4998:
4993:
4987:Paternity fraud
4937:Closed adoption
4910:
4866:Infant clothing
4841:Haberman Feeder
4811:Car seat safety
4740:
4721:Infant swimming
4699:UN Child rights
4657:
4568:Gestational age
4521:
4364:
4358:
4308:
4303:
4302:
4283:
4269:
4264:
4263:
4254:
4252:
4243:
4242:
4238:
4206:
4205:
4201:
4189:
4184:
4183:
4179:
4165:
4164:
4160:
4148:
4143:
4142:
4138:
4128:
4127:
4123:
4095:
4094:
4087:
4043:
4042:
4035:
4004:
4003:
3996:
3950:
3949:
3945:
3901:
3900:
3896:
3889:The DHS Program
3883:
3882:
3878:
3865:
3864:
3857:
3840:
3839:
3835:
3825:
3824:
3815:
3784:(6): CD011695.
3771:
3770:
3766:
3754:
3749:
3748:
3741:
3729:
3725:
3724:
3689:
3680:
3678:
3671:
3649:
3648:
3644:
3635:
3633:
3618:
3596:
3595:
3591:
3580:
3566:UNICEF (2013).
3565:
3564:
3555:
3519:
3518:
3514:
3465:
3464:
3460:
3424:
3423:
3419:
3390:(6): 1593–600.
3380:
3379:
3375:
3339:
3338:
3334:
3290:
3289:
3285:
3233:
3232:
3228:
3182:
3181:
3174:
3130:
3129:
3125:
3089:
3088:
3084:
3046:
3045:
3041:
3005:
3004:
3000:
2956:
2955:
2948:
2904:
2903:
2899:
2855:
2854:
2850:
2814:
2813:
2809:
2765:
2764:
2760:
2737:(11): 2066–75.
2724:
2723:
2719:
2710:
2708:
2699:
2698:
2694:
2676:
2675:
2668:
2630:
2629:
2625:
2615:
2613:
2608:
2607:
2603:
2565:
2564:
2560:
2513:
2512:
2508:
2464:
2463:
2459:
2415:
2414:
2410:
2396:
2395:
2388:
2371:
2370:
2363:
2319:
2318:
2314:
2270:
2269:
2265:
2221:
2220:
2213:
2169:
2168:
2164:
2120:
2119:
2115:
2071:
2070:
2066:
2043:(6): 1498–505.
2030:
2029:
2025:
1981:
1980:
1976:
1938:
1937:
1930:
1874:
1873:
1869:
1825:
1824:
1820:
1784:
1783:
1779:
1733:
1732:
1725:
1697:
1696:
1687:
1641:
1640:
1633:
1589:
1588:
1584:
1546:
1545:
1541:
1497:
1496:
1492:
1454:
1453:
1446:
1408:
1407:
1403:
1374:Eur J Clin Nutr
1367:
1366:
1362:
1352:
1351:
1347:
1337:
1335:
1327:
1323:
1322:
1318:
1274:
1273:
1269:
1215:
1214:
1210:
1174:
1173:
1169:
1131:
1130:
1123:
1118:. January 2008.
1110:
1109:
1090:
1077:
1076:
1053:
1045:
1038:
1034:
1033:
972:
941:(1): e2021168.
935:Acta Bio-Medica
928:
927:
923:
914:
910:
858:
857:
850:
841:
839:
830:
829:
825:
815:
813:
808:
807:
790:
781:
779:
771:
770:
766:
743:
711:
702:
693:
684:
675:
666:
657:
637:
621:
600:
598:Review articles
583:
545:
521:
489:
472:
447:
439:open defecation
434:first 1000 days
373:
347:
325:
288:
273:. Low maternal
266:
252:
236:
205:
148:
138:due to lack of
42:
39:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
5472:
5470:
5462:
5461:
5456:
5451:
5441:
5440:
5434:
5433:
5431:
5430:
5425:
5420:
5415:
5409:
5407:
5403:
5402:
5400:
5399:
5398:
5397:
5387:
5382:
5376:
5374:
5368:
5367:
5365:
5364:
5359:
5358:
5357:
5355:Keshan disease
5347:
5342:
5337:
5332:
5327:
5322:
5317:
5312:
5311:
5310:
5305:
5300:
5295:
5290:
5285:
5274:
5272:
5266:
5265:
5262:
5261:
5259:
5258:
5252:
5246:
5245:
5244:
5239:
5234:
5223:
5217:
5216:
5215:
5203:
5201:
5197:
5196:
5194:
5193:
5192:
5191:
5186:
5179:
5176:
5175:
5174:
5166:
5163:
5162:
5161:
5153:
5150:
5149:
5148:
5140:
5137:
5136:
5135:
5127:
5124:
5123:
5122:
5114:
5111:
5110:
5109:
5104:
5099:
5094:
5086:
5082:
5080:
5071:
5065:
5064:
5062:
5061:
5056:
5051:
5045:
5043:
5039:Protein-energy
5035:
5034:
5029:
5027:
5026:
5019:
5012:
5004:
4995:
4994:
4992:
4991:
4990:
4989:
4979:
4977:Parenting plan
4974:
4969:
4964:
4959:
4954:
4949:
4944:
4939:
4934:
4929:
4924:
4918:
4916:
4912:
4911:
4909:
4908:
4903:
4898:
4893:
4888:
4883:
4878:
4873:
4868:
4863:
4861:Infant carrier
4858:
4848:
4843:
4838:
4833:
4828:
4823:
4818:
4813:
4808:
4803:
4801:Baby transport
4798:
4793:
4788:
4783:
4778:
4773:
4768:
4759:
4754:
4748:
4746:
4742:
4741:
4739:
4738:
4733:
4728:
4723:
4718:
4713:
4708:
4703:
4702:
4701:
4691:
4686:
4681:
4676:
4671:
4665:
4663:
4659:
4658:
4656:
4655:
4650:
4645:
4640:
4635:
4630:
4625:
4620:
4615:
4610:
4605:
4600:
4595:
4590:
4585:
4580:
4575:
4570:
4565:
4560:
4555:
4550:
4545:
4540:
4535:
4529:
4527:
4523:
4522:
4520:
4519:
4514:
4509:
4504:
4499:
4498:
4497:
4487:
4482:
4477:
4472:
4467:
4465:Infant massage
4462:
4460:Infant formula
4457:
4452:
4450:Infant feeding
4447:
4445:Infant bathing
4442:
4437:
4432:
4427:
4422:
4417:
4412:
4410:Bottle feeding
4407:
4402:
4397:
4392:
4387:
4382:
4376:
4374:
4366:
4365:
4363:and their care
4359:
4357:
4356:
4349:
4342:
4334:
4328:
4327:
4321:
4315:
4305:
4304:
4301:
4300:
4284:
4279:
4278:
4276:
4275:Classification
4268:
4267:External links
4265:
4262:
4261:
4236:
4199:
4177:
4158:
4136:
4121:
4085:
4033:
3994:
3943:
3894:
3876:
3855:
3833:
3813:
3764:
3739:
3687:
3669:
3642:
3616:
3589:
3578:
3553:
3512:
3475:(4): 944–957.
3458:
3417:
3373:
3332:
3283:
3226:
3195:(2): 394–403.
3172:
3123:
3082:
3039:
2998:
2946:
2917:(4): 670–679.
2897:
2848:
2807:
2778:(1): 198–208.
2758:
2717:
2692:
2689:on 2015-12-28.
2666:
2623:
2601:
2558:
2523:(1): 118–128.
2506:
2457:
2428:(4): 321–333.
2408:
2386:
2361:
2312:
2263:
2234:(4): 240–253.
2211:
2162:
2113:
2064:
2023:
1974:
1928:
1867:
1818:
1797:(2): 183–200.
1777:
1723:
1685:
1631:
1582:
1555:(3): e473–80.
1539:
1490:
1444:
1401:
1380:(3): 377–386.
1360:
1345:
1316:
1267:
1208:
1187:(4): 896–901.
1167:
1121:
1088:
1051:
970:
921:
908:
848:
823:
788:
773:"Malnutrition"
763:
762:
742:
739:
738:
737:
732:
727:
722:
717:
710:
707:
701:
698:
692:
689:
683:
680:
674:
671:
665:
662:
656:
653:
636:
633:
620:
617:
599:
596:
582:
579:
544:
541:
520:
517:
516:
515:
512:
508:
504:
500:
497:
488:
485:
471:
468:
446:
443:
423:
422:
419:
416:
413:
391:
390:
383:
380:
372:
369:
346:
343:
324:
321:
287:
284:
271:undernutrition
265:
262:
251:
248:
204:
201:
195:GDP up to 3%.
171:
170:
167:
164:
161:
158:
155:
147:
146:Health effects
144:
88:Stunted growth
83:
82:
77:
71:
70:
66:
65:
57:
56:
53:
49:
48:
47:Stunted growth
40:
32:Stunt (botany)
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
5471:
5460:
5457:
5455:
5452:
5450:
5447:
5446:
5444:
5429:
5426:
5424:
5421:
5419:
5416:
5414:
5411:
5410:
5408:
5404:
5396:
5393:
5392:
5391:
5390:Short stature
5388:
5386:
5383:
5381:
5378:
5377:
5375:
5373:
5369:
5363:
5360:
5356:
5353:
5352:
5351:
5348:
5346:
5343:
5341:
5338:
5336:
5333:
5331:
5328:
5326:
5323:
5321:
5318:
5316:
5313:
5309:
5306:
5304:
5301:
5299:
5296:
5294:
5291:
5289:
5286:
5284:
5281:
5280:
5279:
5276:
5275:
5273:
5271:
5267:
5257:
5253:
5251:
5247:
5243:
5240:
5238:
5235:
5233:
5230:
5229:
5228:
5224:
5222:
5218:
5214:
5213:Bitot's spots
5211:
5210:
5209:
5205:
5204:
5202:
5198:
5190:
5183:
5182:
5177:
5173:
5170:
5169:
5164:
5160:
5157:
5156:
5151:
5147:
5144:
5143:
5138:
5134:
5131:
5130:
5125:
5121:
5118:
5117:
5112:
5108:
5105:
5103:
5100:
5098:
5095:
5093:
5090:
5089:
5084:
5083:
5081:
5079:
5075:
5072:
5070:
5066:
5060:
5057:
5055:
5052:
5050:
5047:
5046:
5044:
5042:
5036:
5032:
5025:
5020:
5018:
5013:
5011:
5006:
5005:
5002:
4988:
4985:
4984:
4983:
4980:
4978:
4975:
4973:
4970:
4968:
4965:
4963:
4960:
4958:
4955:
4953:
4952:Open adoption
4950:
4948:
4945:
4943:
4940:
4938:
4935:
4933:
4932:Child neglect
4930:
4928:
4925:
4923:
4920:
4919:
4917:
4913:
4907:
4904:
4902:
4899:
4897:
4894:
4892:
4889:
4887:
4884:
4882:
4879:
4877:
4874:
4872:
4869:
4867:
4864:
4862:
4859:
4856:
4852:
4849:
4847:
4844:
4842:
4839:
4837:
4834:
4832:
4829:
4827:
4824:
4822:
4819:
4817:
4814:
4812:
4809:
4807:
4804:
4802:
4799:
4797:
4794:
4792:
4789:
4787:
4784:
4782:
4779:
4777:
4774:
4772:
4769:
4767:
4766:Hidden camera
4763:
4760:
4758:
4755:
4753:
4750:
4749:
4747:
4743:
4737:
4734:
4732:
4729:
4727:
4724:
4722:
4719:
4717:
4714:
4712:
4709:
4707:
4704:
4700:
4697:
4696:
4695:
4692:
4690:
4689:Child custody
4687:
4685:
4682:
4680:
4677:
4675:
4672:
4670:
4667:
4666:
4664:
4660:
4654:
4651:
4649:
4646:
4644:
4641:
4639:
4636:
4634:
4631:
4629:
4626:
4624:
4621:
4619:
4616:
4614:
4611:
4609:
4606:
4604:
4603:Nursery rhyme
4601:
4599:
4596:
4594:
4593:Kangaroo care
4591:
4589:
4588:Infant crying
4586:
4584:
4581:
4579:
4576:
4574:
4571:
4569:
4566:
4564:
4561:
4559:
4556:
4554:
4551:
4549:
4546:
4544:
4541:
4539:
4536:
4534:
4531:
4530:
4528:
4524:
4518:
4515:
4513:
4510:
4508:
4505:
4503:
4502:Preterm birth
4500:
4496:
4493:
4492:
4491:
4488:
4486:
4483:
4481:
4478:
4476:
4473:
4471:
4468:
4466:
4463:
4461:
4458:
4456:
4453:
4451:
4448:
4446:
4443:
4441:
4438:
4436:
4433:
4431:
4428:
4426:
4423:
4421:
4418:
4416:
4413:
4411:
4408:
4406:
4403:
4401:
4398:
4396:
4395:Breastfeeding
4393:
4391:
4388:
4386:
4383:
4381:
4378:
4377:
4375:
4372:
4367:
4362:
4355:
4350:
4348:
4343:
4341:
4336:
4335:
4332:
4325:
4322:
4319:
4316:
4313:
4312:Stop stunting
4310:
4309:
4299:
4295:
4294:
4290:
4286:
4285:
4282:
4277:
4273:
4266:
4250:
4249:reliefweb.int
4246:
4240:
4237:
4231:
4226:
4222:
4218:
4214:
4210:
4203:
4200:
4195:
4188:
4181:
4178:
4173:
4169:
4162:
4159:
4154:
4147:
4140:
4137:
4132:
4125:
4122:
4116:
4111:
4107:
4103:
4099:
4092:
4090:
4086:
4081:
4077:
4072:
4067:
4063:
4059:
4055:
4051:
4047:
4040:
4038:
4034:
4029:
4025:
4021:
4017:
4013:
4009:
4001:
3999:
3995:
3990:
3986:
3981:
3976:
3971:
3966:
3962:
3958:
3957:PLOS Medicine
3954:
3947:
3944:
3939:
3935:
3930:
3925:
3921:
3917:
3913:
3909:
3905:
3898:
3895:
3890:
3886:
3880:
3877:
3872:
3868:
3862:
3860:
3856:
3851:
3847:
3843:
3837:
3834:
3829:
3822:
3820:
3818:
3814:
3809:
3805:
3800:
3795:
3791:
3787:
3783:
3779:
3775:
3768:
3765:
3760:
3753:
3746:
3744:
3740:
3735:
3728:
3722:
3720:
3718:
3716:
3714:
3712:
3710:
3708:
3706:
3704:
3702:
3700:
3698:
3696:
3694:
3692:
3688:
3676:
3672:
3666:
3662:
3658:
3654:
3653:
3646:
3643:
3631:
3627:
3623:
3619:
3613:
3609:
3605:
3601:
3600:
3593:
3590:
3585:
3581:
3575:
3571:
3570:
3562:
3560:
3558:
3554:
3549:
3545:
3540:
3535:
3531:
3527:
3523:
3516:
3513:
3508:
3504:
3500:
3496:
3491:
3486:
3482:
3478:
3474:
3470:
3462:
3459:
3454:
3450:
3445:
3440:
3437:(4): 835–46.
3436:
3432:
3428:
3421:
3418:
3413:
3409:
3405:
3401:
3397:
3393:
3389:
3385:
3377:
3374:
3369:
3365:
3360:
3355:
3351:
3347:
3343:
3336:
3333:
3328:
3324:
3319:
3314:
3310:
3306:
3303:(2): e12925.
3302:
3298:
3294:
3287:
3284:
3279:
3275:
3270:
3265:
3261:
3257:
3253:
3249:
3245:
3241:
3237:
3230:
3227:
3222:
3218:
3213:
3208:
3203:
3198:
3194:
3190:
3186:
3179:
3177:
3173:
3168:
3164:
3160:
3156:
3151:
3146:
3142:
3138:
3134:
3127:
3124:
3119:
3115:
3110:
3105:
3102:(3): 172–80.
3101:
3097:
3093:
3086:
3083:
3078:
3074:
3070:
3066:
3062:
3058:
3054:
3050:
3043:
3040:
3035:
3031:
3026:
3021:
3017:
3013:
3009:
3002:
2999:
2994:
2990:
2985:
2980:
2976:
2972:
2968:
2964:
2960:
2953:
2951:
2947:
2942:
2938:
2933:
2928:
2924:
2920:
2916:
2912:
2908:
2901:
2898:
2893:
2889:
2884:
2879:
2875:
2871:
2867:
2863:
2859:
2852:
2849:
2844:
2840:
2835:
2830:
2826:
2822:
2818:
2811:
2808:
2803:
2799:
2794:
2789:
2785:
2781:
2777:
2773:
2769:
2762:
2759:
2754:
2750:
2745:
2740:
2736:
2732:
2728:
2721:
2718:
2707:
2703:
2696:
2693:
2688:
2684:
2680:
2673:
2671:
2667:
2662:
2658:
2654:
2650:
2646:
2642:
2638:
2634:
2627:
2624:
2611:
2605:
2602:
2597:
2593:
2589:
2585:
2581:
2577:
2573:
2569:
2562:
2559:
2554:
2550:
2546:
2542:
2538:
2534:
2530:
2526:
2522:
2518:
2510:
2507:
2502:
2498:
2493:
2488:
2484:
2480:
2476:
2472:
2468:
2461:
2458:
2453:
2449:
2444:
2439:
2435:
2431:
2427:
2423:
2419:
2412:
2409:
2404:
2400:
2393:
2391:
2387:
2383:
2379:
2378:Briefing Note
2375:
2368:
2366:
2362:
2357:
2353:
2349:
2345:
2340:
2335:
2331:
2327:
2323:
2316:
2313:
2308:
2304:
2299:
2294:
2290:
2286:
2282:
2278:
2274:
2267:
2264:
2259:
2255:
2250:
2245:
2241:
2237:
2233:
2229:
2225:
2218:
2216:
2212:
2207:
2203:
2199:
2195:
2190:
2185:
2181:
2177:
2173:
2166:
2163:
2158:
2154:
2149:
2144:
2140:
2136:
2132:
2128:
2124:
2117:
2114:
2109:
2105:
2100:
2095:
2091:
2087:
2084:(4): 250–65.
2083:
2079:
2075:
2068:
2065:
2060:
2056:
2051:
2046:
2042:
2038:
2034:
2027:
2024:
2019:
2015:
2010:
2005:
2001:
1997:
1993:
1989:
1985:
1978:
1975:
1970:
1966:
1962:
1958:
1954:
1950:
1946:
1942:
1935:
1933:
1929:
1925:
1920:
1914:
1910:
1905:
1900:
1895:
1890:
1886:
1882:
1878:
1871:
1868:
1863:
1859:
1854:
1849:
1845:
1841:
1837:
1833:
1829:
1822:
1819:
1814:
1810:
1805:
1800:
1796:
1792:
1788:
1781:
1778:
1773:
1769:
1764:
1759:
1754:
1749:
1745:
1741:
1740:BMC Nutrition
1737:
1730:
1728:
1724:
1718:
1713:
1709:
1705:
1701:
1694:
1692:
1690:
1686:
1681:
1677:
1672:
1667:
1662:
1657:
1653:
1649:
1648:PLOS Medicine
1645:
1638:
1636:
1632:
1627:
1623:
1619:
1615:
1610:
1605:
1601:
1597:
1593:
1586:
1583:
1578:
1574:
1570:
1566:
1562:
1558:
1554:
1550:
1543:
1540:
1535:
1531:
1527:
1523:
1518:
1513:
1509:
1505:
1501:
1494:
1491:
1486:
1482:
1478:
1474:
1470:
1466:
1462:
1458:
1451:
1449:
1445:
1440:
1436:
1432:
1428:
1424:
1420:
1417:(5): e23693.
1416:
1412:
1411:Am J Hum Biol
1405:
1402:
1397:
1393:
1388:
1383:
1379:
1375:
1371:
1364:
1361:
1356:
1349:
1346:
1333:
1326:
1320:
1317:
1312:
1308:
1303:
1298:
1294:
1290:
1286:
1282:
1278:
1271:
1268:
1263:
1259:
1254:
1249:
1244:
1239:
1235:
1231:
1228:(5): e64636.
1227:
1223:
1219:
1212:
1209:
1204:
1200:
1195:
1190:
1186:
1182:
1178:
1171:
1168:
1163:
1159:
1155:
1151:
1147:
1143:
1139:
1135:
1128:
1126:
1122:
1117:
1113:
1107:
1105:
1103:
1101:
1099:
1097:
1095:
1093:
1089:
1084:
1080:
1074:
1072:
1070:
1068:
1066:
1064:
1062:
1060:
1058:
1056:
1052:
1044:
1037:
1031:
1029:
1027:
1025:
1023:
1021:
1019:
1017:
1015:
1013:
1011:
1009:
1007:
1005:
1003:
1001:
999:
997:
995:
993:
991:
989:
987:
985:
983:
981:
979:
977:
975:
971:
966:
962:
957:
952:
948:
944:
940:
936:
932:
925:
922:
918:
912:
909:
904:
900:
895:
890:
886:
882:
878:
874:
870:
866:
862:
855:
853:
849:
838:
834:
827:
824:
811:
805:
803:
801:
799:
797:
795:
793:
789:
778:
774:
768:
765:
761:
760:
758:
754:
749:
740:
736:
733:
731:
728:
726:
725:Food security
723:
721:
718:
716:
713:
712:
708:
706:
699:
697:
690:
688:
681:
679:
672:
670:
663:
661:
654:
652:
648:
644:
642:
634:
632:
628:
626:
618:
616:
613:
609:
606:
605:
597:
595:
592:
588:
580:
578:
576:
570:
566:
562:
558:
555:
551:
542:
540:
538:
534:
529:
525:
518:
513:
509:
505:
501:
498:
494:
493:
492:
486:
484:
480:
476:
469:
467:
463:
461:
456:
452:
444:
442:
440:
435:
430:
428:
420:
417:
414:
411:
410:
409:
406:
404:
400:
396:
388:
387:food security
384:
381:
378:
377:
376:
370:
368:
365:
359:
356:
352:
344:
342:
339:
335:
330:
322:
320:
318:
315:use and good
314:
310:
304:
302:
301:helminthiasis
298:
293:
285:
283:
279:
276:
272:
263:
261:
258:
257:breastfeeding
249:
247:
243:
241:
235:
226:
218:
209:
202:
200:
196:
193:
189:
185:
181:
177:
168:
165:
162:
159:
156:
153:
152:
151:
145:
143:
141:
137:
127:
123:
121:
117:
113:
109:
108:helminthiasis
105:
101:
97:
93:
89:
81:
78:
76:
72:
67:
63:
58:
54:
50:
45:
37:
36:Short stature
33:
19:
5449:Malnutrition
5237:Osteomalacia
5041:malnutrition
5031:Malnutrition
4915:Other topics
4854:
4821:Cradle board
4816:Cloth diaper
4776:Baby shampoo
4762:Baby monitor
4752:Baby bouncer
4706:Circumcision
4553:Birth defect
4435:Immunization
4385:Birth weight
4287:
4253:. Retrieved
4251:. 2023-09-26
4248:
4239:
4212:
4202:
4193:
4180:
4171:
4161:
4152:
4139:
4130:
4124:
4105:
4101:
4053:
4049:
4011:
4007:
3960:
3956:
3946:
3911:
3907:
3897:
3888:
3879:
3870:
3850:the original
3845:
3836:
3781:
3777:
3767:
3758:
3733:
3679:. Retrieved
3651:
3645:
3634:. Retrieved
3598:
3592:
3584:the original
3568:
3529:
3525:
3515:
3472:
3468:
3461:
3434:
3430:
3420:
3387:
3383:
3376:
3349:
3345:
3335:
3300:
3296:
3286:
3246:(1): 21962.
3243:
3239:
3229:
3192:
3188:
3140:
3136:
3126:
3099:
3095:
3085:
3052:
3048:
3042:
3015:
3011:
3001:
2966:
2962:
2914:
2910:
2900:
2865:
2861:
2851:
2824:
2820:
2810:
2775:
2771:
2761:
2734:
2730:
2720:
2709:. Retrieved
2705:
2695:
2687:the original
2682:
2636:
2632:
2626:
2614:. Retrieved
2604:
2574:(1): 50–72.
2571:
2567:
2561:
2520:
2516:
2509:
2474:
2470:
2460:
2425:
2421:
2411:
2402:
2381:
2377:
2329:
2325:
2315:
2280:
2276:
2266:
2231:
2227:
2179:
2175:
2165:
2130:
2126:
2116:
2081:
2077:
2067:
2040:
2036:
2026:
1991:
1987:
1977:
1944:
1940:
1884:
1880:
1870:
1835:
1831:
1821:
1794:
1790:
1780:
1743:
1739:
1707:
1703:
1651:
1647:
1599:
1595:
1585:
1552:
1548:
1542:
1507:
1503:
1493:
1460:
1456:
1414:
1410:
1404:
1377:
1373:
1363:
1354:
1348:
1336:. Retrieved
1331:
1319:
1284:
1280:
1270:
1225:
1221:
1211:
1184:
1180:
1170:
1137:
1133:
1115:
1085:. June 2013.
1082:
1043:the original
938:
934:
924:
911:
868:
864:
840:. Retrieved
836:
826:
814:. Retrieved
780:. Retrieved
776:
767:
757:CC BY-SA 3.0
745:
744:
703:
694:
685:
676:
667:
658:
649:
645:
638:
629:
622:
614:
610:
602:
601:
584:
571:
567:
563:
559:
546:
536:
530:
526:
524:prevalence.
522:
519:Epidemiology
490:
481:
477:
473:
464:
448:
431:
424:
407:
392:
374:
360:
348:
326:
305:
289:
280:
267:
253:
244:
237:
197:
184:hypertension
180:malnutrition
172:
149:
132:
100:malnutrition
95:
91:
87:
86:
5428:Underweight
5418:Weight loss
5059:Catabolysis
5049:Kwashiorkor
4927:Babywearing
4922:Baby shower
4896:Swim diaper
4786:Baby walker
4771:Baby powder
4711:Foster care
4679:Child abuse
4674:Babysitting
4526:Development
4512:Soy formula
4390:Breast pump
4230:10986/33989
4014:: 144–154.
3846:UN-DESA/DSD
1710:: 180–204.
837:UNICEF DATA
816:12 November
777:www.who.int
700:Philippines
317:handwashing
110:, in early
52:Other names
5459:Sanitation
5443:Categories
5395:Idiopathic
5345:Molybdenum
5189:deficiency
5078:B vitamins
4906:Travel cot
4851:Infant bed
4846:High chair
4836:Baby wipes
4831:Diaper bag
4796:Baby swing
4684:Child care
4669:Attachment
4558:Childbirth
4420:Cradle cap
4371:Pediatrics
4255:2024-04-22
3681:2023-01-15
3636:2023-01-15
3490:10361/8919
3212:2292/59199
3137:Pediatrics
3018:(5): E75.
3012:Pediatrics
2711:2021-09-11
2616:8 November
2176:Pediatrics
1887:(8): 863.
1549:Pediatrics
842:2023-02-15
782:2023-02-15
741:References
664:Bangladesh
604:The Lancet
591:World Bank
554:overweight
397:(hygienic
395:sanitation
371:Prevention
355:percentile
292:sanitation
286:Sanitation
212:continuum.
140:sanitation
80:Pediatrics
5325:Manganese
5303:Potassium
5298:Phosphate
5293:Magnesium
5185:Vitamin B
4982:Paternity
4891:Swaddling
4757:Baby gate
4736:Wet nurse
4726:Milk bank
4618:Parenting
4543:Baby talk
4495:Pedialyte
4425:Esotropia
4380:Baby food
4108:: 30–37.
3626:241502462
2596:206289300
2356:256559217
1969:205691877
1813:0379-5721
1439:243987638
623:The 2012
345:Diagnosis
112:childhood
75:Specialty
5423:Cachexia
5413:Anorexia
5362:Fluorine
5350:Selenium
5340:Chromium
5288:Chloride
5133:Pellagra
5092:Beriberi
5054:Marasmus
4942:Cry room
4881:Stroller
4871:Pacifier
4806:Bassinet
4781:Baby toy
4643:Teething
4623:Peekaboo
4563:Crawling
4548:Babbling
4369:Health (
4174:: 35–36.
4080:27187924
4028:28686964
3989:29069076
3938:34668556
3808:31204795
3675:Archived
3630:Archived
3548:25926413
3507:25969492
3499:28275125
3453:25833980
3412:10474629
3404:19812173
3368:22742610
3327:31849201
3278:36536016
3221:31665385
3167:24732575
3159:28588101
3118:24037697
3077:18345055
3069:18206226
3034:11331725
2993:18289157
2941:28179488
2892:27581575
2843:26063066
2802:24225356
2753:21956959
2661:13851530
2653:19766883
2588:28112064
2553:21280033
2545:24571214
2501:27187910
2452:32706533
2348:29988114
2307:29016294
2258:30753710
2206:19436395
2198:27940670
2157:23582727
2108:25310000
2059:12791630
2018:23920141
1961:25830938
1913:28788108
1862:26364789
1772:32153861
1680:27802277
1626:28533635
1618:22742617
1577:21204674
1569:20156903
1526:23343945
1485:12237910
1477:23746772
1431:34761833
1396:31142828
1311:18206223
1262:23734210
1222:PLOS ONE
1203:23426036
1154:18207566
965:33682846
903:31915393
759:license.
709:See also
619:Examples
581:Research
297:diarrhea
104:diarrhea
92:stunting
5406:General
5283:Calcium
5232:Rickets
4901:Teether
4876:Playpen
4653:Weaning
4648:Walking
4361:Infants
4071:5084730
3980:5656304
3929:8687095
3799:6572871
3736:. 2016.
3318:7083396
3269:9763408
3248:Bibcode
2984:6860813
2932:5368587
2883:5037872
2793:3862455
2525:Bibcode
2492:5084825
2443:7289524
2298:5805039
2249:6394759
2148:7159282
2099:4232245
2009:3816349
1904:5580567
1853:6860259
1763:7050870
1671:5089547
1534:8299631
1302:2258311
1253:3667136
1230:Bibcode
1162:3910132
956:7975963
894:7015855
873:Bibcode
589:of the
550:wasting
399:toilets
176:obesity
18:Stunted
5372:Growth
5335:Iodine
5330:Copper
5308:Sodium
5221:Scurvy
4826:Diaper
4613:Parent
4598:Mother
4078:
4068:
4026:
3987:
3977:
3936:
3926:
3806:
3796:
3667:
3624:
3614:
3576:
3546:
3505:
3497:
3451:
3410:
3402:
3366:
3325:
3315:
3276:
3266:
3219:
3165:
3157:
3116:
3075:
3067:
3049:Lancet
3032:
2991:
2981:
2939:
2929:
2890:
2880:
2841:
2800:
2790:
2751:
2659:
2651:
2633:Lancet
2594:
2586:
2551:
2543:
2499:
2489:
2450:
2440:
2354:
2346:
2305:
2295:
2256:
2246:
2204:
2196:
2155:
2145:
2127:Lancet
2106:
2096:
2057:
2016:
2006:
1967:
1959:
1911:
1901:
1860:
1850:
1811:
1770:
1760:
1746:: 85.
1678:
1668:
1624:
1616:
1575:
1567:
1532:
1524:
1483:
1475:
1457:Lancet
1437:
1429:
1394:
1338:12 May
1334:. 2017
1309:
1299:
1281:Lancet
1260:
1250:
1201:
1160:
1152:
1134:Lancet
963:
953:
901:
891:
865:Nature
655:Brazil
543:Trends
483:step.
460:Lancet
313:toilet
203:Causes
5200:Other
4731:Nanny
4415:Colic
4190:(PDF)
4149:(PDF)
3755:(PDF)
3730:(PDF)
3622:S2CID
3503:S2CID
3408:S2CID
3163:S2CID
3073:S2CID
2657:S2CID
2592:S2CID
2549:S2CID
2352:S2CID
2202:S2CID
1965:S2CID
1622:S2CID
1573:S2CID
1530:S2CID
1481:S2CID
1435:S2CID
1328:(PDF)
1158:S2CID
1046:(PDF)
1039:(PDF)
812:. WHO
691:Nepal
364:genes
5320:Zinc
5315:Iron
4628:Play
4517:SIDS
4076:PMID
4024:PMID
3985:PMID
3934:PMID
3804:PMID
3665:ISBN
3612:ISBN
3574:ISBN
3544:PMID
3495:PMID
3449:PMID
3400:PMID
3364:PMID
3323:PMID
3274:PMID
3217:PMID
3155:PMID
3114:PMID
3065:PMID
3030:PMID
2989:PMID
2937:PMID
2888:PMID
2839:PMID
2798:PMID
2749:PMID
2649:PMID
2618:2014
2584:PMID
2541:PMID
2521:1308
2497:PMID
2448:PMID
2344:PMID
2303:PMID
2254:PMID
2194:PMID
2153:PMID
2104:PMID
2055:PMID
2014:PMID
1957:PMID
1909:PMID
1858:PMID
1809:ISSN
1768:PMID
1676:PMID
1614:PMID
1565:PMID
1522:PMID
1473:PMID
1427:PMID
1392:PMID
1340:2017
1307:PMID
1258:PMID
1199:PMID
1150:PMID
961:PMID
899:PMID
818:2014
753:text
673:Peru
585:The
403:WASH
309:WASH
106:and
5254:K:
5248:E:
5225:D:
5219:C:
5206:A:
4791:Bib
4298:E45
4289:ICD
4225:hdl
4217:doi
4110:doi
4066:PMC
4058:doi
4016:doi
4012:187
3975:PMC
3965:doi
3924:PMC
3916:doi
3912:224
3794:PMC
3786:doi
3657:doi
3604:doi
3534:doi
3530:145
3485:hdl
3477:doi
3473:105
3439:doi
3435:101
3392:doi
3354:doi
3313:PMC
3305:doi
3264:PMC
3256:doi
3207:hdl
3197:doi
3193:150
3145:doi
3141:140
3104:doi
3057:doi
3053:371
3020:doi
3016:107
2979:PMC
2971:doi
2927:PMC
2919:doi
2915:147
2878:PMC
2870:doi
2866:146
2829:doi
2825:145
2788:PMC
2780:doi
2739:doi
2735:141
2641:doi
2637:374
2576:doi
2533:doi
2487:PMC
2479:doi
2438:PMC
2430:doi
2426:383
2334:doi
2293:PMC
2285:doi
2244:PMC
2236:doi
2184:doi
2180:138
2143:PMC
2135:doi
2131:381
2094:PMC
2086:doi
2045:doi
2004:PMC
1996:doi
1949:doi
1899:PMC
1889:doi
1848:PMC
1840:doi
1799:doi
1758:PMC
1748:doi
1712:doi
1666:PMC
1656:doi
1604:doi
1557:doi
1553:125
1512:doi
1465:doi
1461:382
1419:doi
1382:doi
1297:PMC
1289:doi
1285:371
1248:PMC
1238:doi
1189:doi
1142:doi
1138:371
951:PMC
943:doi
889:PMC
881:doi
869:577
533:FAO
275:BMI
94:or
5445::
5187:12
5180:12
4296::
4293:10
4247:.
4223:.
4215:.
4211:.
4192:.
4170:.
4151:.
4106:13
4104:.
4100:.
4088:^
4074:.
4064:.
4054:12
4052:.
4048:.
4036:^
4022:.
4010:.
3997:^
3983:.
3973:.
3961:14
3959:.
3955:.
3932:.
3922:.
3910:.
3906:.
3887:.
3869:.
3858:^
3844:.
3816:^
3802:.
3792:.
3780:.
3776:.
3757:.
3742:^
3732:.
3690:^
3673:.
3663:.
3628:.
3620:.
3610:.
3556:^
3542:.
3528:.
3524:.
3501:.
3493:.
3483:.
3471:.
3447:.
3433:.
3429:.
3406:.
3398:.
3388:90
3386:.
3362:.
3350:26
3348:.
3344:.
3321:.
3311:.
3301:16
3299:.
3295:.
3272:.
3262:.
3254:.
3244:12
3242:.
3238:.
3215:.
3205:.
3191:.
3187:.
3175:^
3161:.
3153:.
3139:.
3135:.
3112:.
3098:.
3094:.
3071:.
3063:.
3051:.
3028:.
3014:.
3010:.
2987:.
2977:.
2965:.
2961:.
2949:^
2935:.
2925:.
2913:.
2909:.
2886:.
2876:.
2864:.
2860:.
2837:.
2823:.
2819:.
2796:.
2786:.
2776:99
2774:.
2770:.
2747:.
2733:.
2729:.
2704:.
2681:.
2669:^
2655:.
2647:.
2635:.
2590:.
2582:.
2572:30
2570:.
2547:.
2539:.
2531:.
2519:.
2495:.
2485:.
2475:12
2473:.
2469:.
2446:.
2436:.
2424:.
2420:.
2401:.
2389:^
2376:.
2364:^
2350:.
2342:.
2330:11
2328:.
2324:.
2301:.
2291:.
2281:97
2279:.
2275:.
2252:.
2242:.
2232:77
2230:.
2226:.
2214:^
2200:.
2192:.
2178:.
2174:.
2151:.
2141:.
2129:.
2125:.
2102:.
2092:.
2082:34
2080:.
2076:.
2053:.
2041:77
2039:.
2035:.
2012:.
2002:.
1992:42
1990:.
1986:.
1963:.
1955:.
1945:56
1943:.
1931:^
1907:.
1897:.
1885:14
1883:.
1879:.
1856:.
1846:.
1836:11
1834:.
1830:.
1807:.
1795:20
1793:.
1789:.
1766:.
1756:.
1742:.
1738:.
1726:^
1708:68
1706:.
1702:.
1688:^
1674:.
1664:.
1652:13
1650:.
1646:.
1634:^
1620:.
1612:.
1600:26
1598:.
1594:.
1571:.
1563:.
1551:.
1528:.
1520:.
1508:61
1506:.
1502:.
1479:.
1471:.
1459:.
1447:^
1433:.
1425:.
1415:34
1413:.
1390:.
1378:74
1376:.
1372:.
1330:.
1305:.
1295:.
1283:.
1279:.
1256:.
1246:.
1236:.
1224:.
1220:.
1197:.
1185:97
1183:.
1179:.
1156:.
1148:.
1136:.
1124:^
1114:.
1091:^
1081:.
1054:^
973:^
959:.
949:.
939:92
937:.
933:.
897:.
887:.
879:.
867:.
863:.
851:^
835:.
791:^
775:.
190:,
186:,
5178:B
5167:9
5165:B
5154:7
5152:B
5141:6
5139:B
5128:3
5126:B
5115:2
5113:B
5087:1
5085:B
5023:e
5016:t
5009:v
4764:/
4373:)
4353:e
4346:t
4339:v
4291:-
4281:D
4258:.
4227::
4219::
4196:.
4118:.
4112::
4082:.
4060::
4030:.
4018::
3991:.
3967::
3940:.
3918::
3873:.
3810:.
3788::
3782:6
3684:.
3659::
3639:.
3606::
3550:.
3536::
3509:.
3487::
3479::
3455:.
3441::
3414:.
3394::
3370:.
3356::
3329:.
3307::
3280:.
3258::
3250::
3223:.
3209::
3199::
3169:.
3147::
3120:.
3106::
3100:2
3079:.
3059::
3036:.
3022::
2995:.
2973::
2967:4
2943:.
2921::
2894:.
2872::
2845:.
2831::
2804:.
2782::
2755:.
2741::
2714:.
2663:.
2643::
2620:.
2598:.
2578::
2555:.
2535::
2527::
2503:.
2481::
2454:.
2432::
2358:.
2336::
2309:.
2287::
2260:.
2238::
2208:.
2186::
2159:.
2137::
2110:.
2088::
2061:.
2047::
2020:.
1998::
1971:.
1951::
1926:.
1915:.
1891::
1864:.
1842::
1815:.
1801::
1774:.
1750::
1744:3
1720:.
1714::
1682:.
1658::
1628:.
1606::
1579:.
1559::
1536:.
1514::
1487:.
1467::
1441:.
1421::
1398:.
1384::
1342:.
1313:.
1291::
1264:.
1240::
1232::
1226:8
1205:.
1191::
1164:.
1144::
967:.
945::
905:.
883::
875::
845:.
820:.
785:.
307:(
38:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.