190:
255:. The AI node of the salience network has been observed to be hyperactive in anxiety disorders, which is thought to reflect predictions of aversive bodily states leading to worrisome thoughts and anxious behaviors. In schizophrenia, both structural and functional abnormalities have been observed, thought to reflect excessive salience being ascribed to internally generated stimuli. In individuals with autism, the relative salience of social stimuli, such as face, eyes, and gaze, may be diminished, leading to poor social skills.
20:
271:) has generally been equated with the salience network, but it may represent a distinct but adjacent network or a part of the SN. The CO may involve more dorsal areas, while the SN involves more ventral and rostral areas of the anterior insula and medial frontal cortex containing von Economo neurons. The CO is sometimes also referred to as the
75:
stimuli, as well as in recruiting relevant functional networks. Together with its interconnected brain networks, the SN contributes to a variety of complex functions, including communication, social behavior, and self-awareness through the integration of sensory, emotional, and cognitive information.
226:
is transmitted "bottom-up" from sensory regions, a "top-down" signal localized to the AI and dACC occurs before a widespread evoked potential that corresponds to attentional shifting. It has also been hypothesized that the AI receives multimodal sensory input and the ACC and the associated
310:
that responds to unexpected salient stimuli. Some have defined it as a larger, bilateral network that is a combination of the SN and CO, while others have described it as a part of the salience network involving the more dorsal anterior insular cortex.
201:
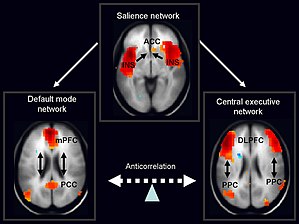
While the function of the salience network is not exactly known, it has been implicated in the detection and integration of emotional and sensory stimuli, as well as in modulating the switch between the internally directed cognition of the
141:
The subcortical nodes have yet to be structurally linked to the AI and dACC, however both seed-based and resting-state studies have observed intrinsic connectivity of the cortical nodes, with subcortical nodes consisting of the
1234:
178:
733:
Downar, J.; Crawley, A. P.; Mikulis, D. J.; Davis, K. D. (2000). "A multimodal cortical network for the detection of changes in the sensory environment".
1159:
Touroutoglou, Alexandra; Bliss-Moreau, Eliza; Zhang, Jiahe; Mantini, Dante; Vanduffel, Wim; Dickerson, Bradford C.; Barrett, Lisa
Feldman (2016-05-15).
581:
Menon V. (2015) Salience
Network. In: Arthur W. Toga, editor. Brain Mapping: An Encyclopedic Reference, vol. 2, pp. 597-611. Academic Press: Elsevier.
1285:
668:
1098:
215:
1397:
1392:
1330:
240:
80:
1335:
1320:
530:"Cortico-Striatal-Thalamic Loop Circuits of the Salience Network: A Central Pathway in Psychiatric Disease and Treatment"
582:
302:), has also been equated with the SN. The VAN is commonly defined as a right-hemisphere-dominant network involving the
1227:
1220:
363:"A critical role for the right fronto-insular cortex in switching between central-executive and default-mode networks"
1325:
1312:
56:
1428:
207:
135:
111:
68:
28:
1254:
303:
194:
131:
95:
197:
networks enables dynamic control of attention in relation to top-down goals and bottom-up sensory stimulation.
1402:
1280:
819:
Menon, V (October 2011). "Large-scale brain networks and psychopathology: a unifying triple network model".
248:
72:
114:(dACC). The node in the AI corresponds with the dorsal-anterior division distinguished in meta-analyses of
776:
Uddin, Lucina Q. (19 November 2014). "Salience processing and insular cortical function and dysfunction".
336:
252:
189:
170:
1099:"Cortical networks involved in visual awareness independent of visual attention - Supporting Information"
926:"Domain-general signals in the cingulo-opercular network for visuospatial attention and episodic memory"
924:
Sestieri, Carlo; Corbetta, Maurizio; Spadone, Sara; Romani, Gian Luca; Shulman, Gordon L. (March 2014).
115:
1371:
994:
374:
341:
331:
203:
88:
24:
1340:
235:
Dysfunction in the salience network have been observed in various psychiatric disorders, including
223:
174:
123:
1366:
1289:
844:
801:
758:
91:
84:
1361:
1198:
1180:
1141:
1123:
1079:
1061:
1022:
963:
945:
906:
888:
836:
793:
750:
715:
664:
636:
618:
561:
507:
453:
402:
211:
146:
143:
1097:
Webb, Taylor W.; Igelström, Kajsa M.; Schurger, Aaron; Graziano, Michael S. A. (2016-11-29).
1188:
1172:
1131:
1113:
1069:
1053:
1012:
1002:
953:
937:
896:
880:
828:
785:
742:
705:
697:
626:
610:
551:
541:
497:
489:
443:
433:
392:
382:
236:
166:
154:
322:) be used as a standard anatomical name for the network that includes the SN, CO, and VAN.
94:
analysis. The functional connectivity has been linked with structural connectivity through
1387:
210:. Evidence that the salience network mediates a switch between the DMN and CEN comes from
127:
998:
983:"Spontaneous neuronal activity distinguishes human dorsal and ventral attention systems"
686:"Dorsal and ventral attention systems: distinct neural circuits but collaborative roles"
378:
173:. The salience network is also distinguished by distinct cellular components, including
1423:
1193:
1160:
1136:
1074:
1041:
1017:
982:
958:
925:
901:
868:
710:
685:
631:
598:
556:
529:
502:
477:
448:
421:
397:
362:
307:
107:
64:
1417:
1345:
1297:
1259:
1176:
583:
https://med.stanford.edu/content/dam/sm/scsnl/documents/Menon_Salience_Network_15.pdf
244:
1042:"Asymmetric development of dorsal and ventral attention networks in the human brain"
848:
1302:
1264:
805:
762:
422:"Bridging disparate symptoms of schizophrenia: a triple network dysfunction theory"
420:
Nekovarova, Tereza; Fajnerova, Iveta; Horacek, Jiri; Spaniel, Filip (30 May 2014).
219:
162:
19:
16:
Large-scale brain network involved in detecting and attending to relevant stimuli
478:"Saliency, switching, attention and control: a network model of insula function"
119:
60:
832:
614:
1243:
1057:
493:
1184:
1127:
1065:
949:
892:
701:
622:
599:"Towards a Universal Taxonomy of Macro-scale Functional Human Brain Networks"
546:
438:
1118:
1007:
981:
Fox, M.D.; Corbetta, M.; Snyder, A.Z.; Vincent, J.L.; Raichle, M.E. (2006).
387:
1202:
1145:
1083:
1026:
967:
910:
840:
797:
754:
719:
640:
565:
511:
457:
406:
941:
158:
884:
150:
1212:
597:
Uddin, Lucina Q.; Yeo, B. T. Thomas; Spreng, R. Nathan (2019-11-01).
789:
23:
The salience network is theorized to mediate switching between the
746:
1216:
118:
related neuroimaging studies. The AI and dACC are linked via a
592:
590:
98:, which reveals white matter tracts between the AI and dACC.
867:
Gratton, Caterina; Sun, Haoxin; Petersen, Steven E. (2018).
361:
Sridharan, D.; Levitin, D. J.; Menon, V. (22 August 2008).
218:. The timing of electrophysiological responses during the
126:. Other regions of the network may include the inferior
222:
is consistent with interaction, as after the initial
1380:
1354:
1311:
1273:
1040:Farrant, Kristafor; Uddin, Lucina Q. (2015-02-12).
227:dorsomedial prefrontal cortex sends motor output.
106:The salience network is primarily anchored at the
71:(dACC). It is involved in detecting and filtering
1161:"A Ventral Salience Network in the Macaque Brain"
1106:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
367:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
193:Interaction between the ventral (salience) and
1228:
206:and the externally directed cognition of the
181:circuits contribute to the salience network.
8:
684:Vossel, S; Geng, JJ; Fink, GR (April 2014).
471:
469:
467:
1235:
1221:
1213:
1192:
1135:
1117:
1073:
1016:
1006:
957:
900:
709:
630:
555:
545:
528:Peters, SK; Dunlop, K; Downar, J (2016).
501:
447:
437:
396:
386:
523:
521:
188:
18:
654:
652:
650:
353:
862:
860:
858:
7:
1046:Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience
577:
575:
426:Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience
314:In 2019, Uddin et al. proposed that
79:The network is detectable through
63:that is primarily composed of the
43:), also known anatomically as the
14:
1336:Dorsal frontoparietal (Attention)
930:Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience
534:Frontiers in Systems Neuroscience
476:Menon, V; Uddin, LQ (June 2010).
216:transcranial magnetic stimulation
1331:Lateral frontoparietal (Control)
1177:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.02.029
112:dorsal anterior cingulate cortex
69:dorsal anterior cingulate cortex
1398:Psychophysiological Interaction
1393:Dynamic functional connectivity
1321:Medial frontoparietal (Default)
1274:Data acquisition and processing
663:. Elsevier. pp. 597–611.
482:Brain Structure & Function
288:ventral frontoparietal network
241:post-traumatic stress disorder
179:Cortico-striatal-thalamic loop
81:independent component analysis
1:
1326:Midcingulo-insular (Salience)
821:Trends in Cognitive Sciences
224:mismatch negativity response
869:"Control networks and hubs"
778:Nature Reviews Neuroscience
1447:
833:10.1016/j.tics.2011.08.003
659:Menon, V; Toga, A (2015).
615:10.1007/s10548-019-00744-6
316:midcingulo-insular network
212:Granger causality analysis
45:midcingulo-insular network
1341:Pericentral (Somatomotor)
1250:
1058:10.1016/j.dcn.2015.02.001
494:10.1007/s00429-010-0262-0
280:ventral attention network
265:cingulo-opercular network
208:central executive network
136:lateral prefrontal cortex
53:ventral attention network
29:central executive network
1255:Human Connectome Project
702:10.1177/1073858413494269
547:10.3389/fnsys.2016.00104
439:10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00171
304:temporoparietal junction
296:ventral attention system
132:temporoparietal junction
96:diffusion tensor imaging
1403:Dynamic causal modeling
1355:Functional modes/states
1281:Functional neuroimaging
1119:10.1073/pnas.1611505113
1008:10.1073/pnas.0604187103
388:10.1073/pnas.0800005105
273:cingulo-insular network
249:frontotemporal dementia
92:functional connectivity
337:Frontoparietal network
214:and studies utilizing
198:
171:ventral tegmental area
32:
286:), also known as the
231:Clinical significance
192:
116:task-positive network
22:
942:10.1162/jocn_a_00504
342:Bottom-up processing
332:Default mode network
204:default mode network
25:default mode network
1381:Analytic strategies
1313:Functional networks
1112:(48): 13923–13928.
999:2006PNAS..10310046F
993:(26): 10046–10051.
735:Nature Neuroscience
379:2008PNAS..10512569S
373:(34): 12569–12574.
253:Alzheimer's disease
175:von Economo neurons
124:uncinate fasciculus
87:images, as well as
57:large scale network
1367:Resting state fMRI
1346:Occipital (Visual)
1298:Diffusion-weighted
1244:Human connectomics
885:10.1111/psyp.13032
690:The Neuroscientist
199:
157:, the dorsomedial
120:white matter tract
85:resting state fMRI
33:
1411:
1410:
1372:Naturalistic fMRI
670:978-0-12-397316-0
237:anxiety disorders
147:extended amygdala
1436:
1429:Neural circuitry
1237:
1230:
1223:
1214:
1207:
1206:
1196:
1156:
1150:
1149:
1139:
1121:
1103:
1094:
1088:
1087:
1077:
1037:
1031:
1030:
1020:
1010:
978:
972:
971:
961:
921:
915:
914:
904:
873:Psychophysiology
864:
853:
852:
816:
810:
809:
773:
767:
766:
730:
724:
723:
713:
681:
675:
674:
661:Salience Network
656:
645:
644:
634:
603:Brain Topography
594:
585:
579:
570:
569:
559:
549:
525:
516:
515:
505:
473:
462:
461:
451:
441:
417:
411:
410:
400:
390:
358:
306:and the ventral
195:dorsal attention
177:in the AI/dACC.
167:substantia nigra
155:ventral striatum
37:salience network
1446:
1445:
1439:
1438:
1437:
1435:
1434:
1433:
1414:
1413:
1412:
1407:
1388:Network science
1376:
1350:
1307:
1269:
1246:
1241:
1211:
1210:
1158:
1157:
1153:
1101:
1096:
1095:
1091:
1039:
1038:
1034:
980:
979:
975:
923:
922:
918:
866:
865:
856:
827:(10): 483–506.
818:
817:
813:
790:10.1038/nrn3857
775:
774:
770:
732:
731:
727:
683:
682:
678:
671:
658:
657:
648:
596:
595:
588:
580:
573:
527:
526:
519:
488:(5–6): 655–67.
475:
474:
465:
419:
418:
414:
360:
359:
355:
350:
328:
261:
233:
187:
128:parietal cortex
108:anterior insula
104:
65:anterior insula
17:
12:
11:
5:
1444:
1443:
1440:
1432:
1431:
1426:
1416:
1415:
1409:
1408:
1406:
1405:
1400:
1395:
1390:
1384:
1382:
1378:
1377:
1375:
1374:
1369:
1364:
1358:
1356:
1352:
1351:
1349:
1348:
1343:
1338:
1333:
1328:
1323:
1317:
1315:
1309:
1308:
1306:
1305:
1300:
1295:
1283:
1277:
1275:
1271:
1270:
1268:
1267:
1262:
1257:
1251:
1248:
1247:
1242:
1240:
1239:
1232:
1225:
1217:
1209:
1208:
1151:
1089:
1032:
973:
936:(3): 551–568.
916:
854:
811:
768:
741:(3): 277–283.
725:
676:
669:
646:
609:(6): 926–942.
586:
571:
517:
463:
412:
352:
351:
349:
346:
345:
344:
339:
334:
327:
324:
308:frontal cortex
260:
257:
232:
229:
186:
183:
103:
100:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1442:
1441:
1430:
1427:
1425:
1422:
1421:
1419:
1404:
1401:
1399:
1396:
1394:
1391:
1389:
1386:
1385:
1383:
1379:
1373:
1370:
1368:
1365:
1363:
1360:
1359:
1357:
1353:
1347:
1344:
1342:
1339:
1337:
1334:
1332:
1329:
1327:
1324:
1322:
1319:
1318:
1316:
1314:
1310:
1304:
1301:
1299:
1296:
1293:
1292:
1287:
1286:BOLD-weighted
1284:
1282:
1279:
1278:
1276:
1272:
1266:
1263:
1261:
1260:Brain mapping
1258:
1256:
1253:
1252:
1249:
1245:
1238:
1233:
1231:
1226:
1224:
1219:
1218:
1215:
1204:
1200:
1195:
1190:
1186:
1182:
1178:
1174:
1170:
1166:
1162:
1155:
1152:
1147:
1143:
1138:
1133:
1129:
1125:
1120:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1100:
1093:
1090:
1085:
1081:
1076:
1071:
1067:
1063:
1059:
1055:
1051:
1047:
1043:
1036:
1033:
1028:
1024:
1019:
1014:
1009:
1004:
1000:
996:
992:
988:
984:
977:
974:
969:
965:
960:
955:
951:
947:
943:
939:
935:
931:
927:
920:
917:
912:
908:
903:
898:
894:
890:
886:
882:
879:(3): e13032.
878:
874:
870:
863:
861:
859:
855:
850:
846:
842:
838:
834:
830:
826:
822:
815:
812:
807:
803:
799:
795:
791:
787:
783:
779:
772:
769:
764:
760:
756:
752:
748:
747:10.1038/72991
744:
740:
736:
729:
726:
721:
717:
712:
707:
703:
699:
695:
691:
687:
680:
677:
672:
666:
662:
655:
653:
651:
647:
642:
638:
633:
628:
624:
620:
616:
612:
608:
604:
600:
593:
591:
587:
584:
578:
576:
572:
567:
563:
558:
553:
548:
543:
539:
535:
531:
524:
522:
518:
513:
509:
504:
499:
495:
491:
487:
483:
479:
472:
470:
468:
464:
459:
455:
450:
445:
440:
435:
431:
427:
423:
416:
413:
408:
404:
399:
394:
389:
384:
380:
376:
372:
368:
364:
357:
354:
347:
343:
340:
338:
335:
333:
330:
329:
325:
323:
321:
317:
312:
309:
305:
301:
297:
293:
289:
285:
281:
276:
274:
270:
266:
258:
256:
254:
250:
246:
245:schizophrenia
242:
238:
230:
228:
225:
221:
217:
213:
209:
205:
196:
191:
184:
182:
180:
176:
172:
168:
164:
160:
156:
152:
148:
145:
144:sublenticular
139:
137:
133:
129:
125:
121:
117:
113:
109:
101:
99:
97:
93:
90:
86:
82:
77:
74:
70:
66:
62:
58:
54:
50:
46:
42:
38:
30:
26:
21:
1303:Tractography
1290:
1265:Neuroimaging
1168:
1164:
1154:
1109:
1105:
1092:
1049:
1045:
1035:
990:
986:
976:
933:
929:
919:
876:
872:
824:
820:
814:
784:(1): 55–61.
781:
777:
771:
738:
734:
728:
696:(2): 150–9.
693:
689:
679:
660:
606:
602:
537:
533:
485:
481:
429:
425:
415:
370:
366:
356:
319:
315:
313:
299:
295:
291:
287:
283:
279:
277:
272:
268:
264:
262:
259:Nomenclature
234:
220:oddball task
200:
163:hypothalamus
140:
105:
78:
52:
48:
44:
40:
36:
34:
1171:: 190–197.
1052:: 165–174.
61:human brain
1418:Categories
1165:NeuroImage
348:References
165:, and the
122:along the
89:seed based
1362:Task fMRI
1291:task-free
1185:1053-8119
1128:0027-8424
1066:1878-9293
950:0898-929X
893:1469-8986
623:1573-6792
110:(AI) and
67:(AI) and
1203:26899785
1146:27849616
1084:25797238
1027:16788060
968:24144246
911:29193146
849:26653572
841:21908230
798:25406711
755:10700261
720:23835449
641:31707621
566:28082874
512:20512370
458:24910597
407:18723676
326:See also
185:Function
159:thalamus
130:, right
1194:4851897
1137:5137756
1075:4396619
1018:1480402
995:Bibcode
959:3947512
902:5811327
806:7786680
763:8807081
711:4107817
632:7325607
557:5187454
540:: 104.
503:2899886
449:4038855
432:: 171.
398:2527952
375:Bibcode
151:putamen
102:Anatomy
73:salient
59:of the
55:, is a
1201:
1191:
1183:
1144:
1134:
1126:
1082:
1072:
1064:
1025:
1015:
966:
956:
948:
909:
899:
891:
847:
839:
804:
796:
761:
753:
718:
708:
667:
639:
629:
621:
564:
554:
510:
500:
456:
446:
405:
395:
251:, and
153:, the
149:, the
134:, and
1424:Brain
1102:(PDF)
845:S2CID
802:S2CID
759:S2CID
320:M-CIN
294:) or
51:) or
49:M-CIN
1199:PMID
1181:ISSN
1142:PMID
1124:ISSN
1080:PMID
1062:ISSN
1023:PMID
987:PNAS
964:PMID
946:ISSN
907:PMID
889:ISSN
837:PMID
794:PMID
751:PMID
716:PMID
665:ISBN
637:PMID
619:ISSN
562:PMID
508:PMID
454:PMID
403:PMID
278:The
263:The
35:The
27:and
1189:PMC
1173:doi
1169:132
1132:PMC
1114:doi
1110:113
1070:PMC
1054:doi
1013:PMC
1003:doi
991:103
954:PMC
938:doi
897:PMC
881:doi
829:doi
786:doi
743:doi
706:PMC
698:doi
627:PMC
611:doi
552:PMC
542:doi
498:PMC
490:doi
486:214
444:PMC
434:doi
393:PMC
383:doi
371:105
300:VAS
292:VFN
284:VAN
83:of
1420::
1197:.
1187:.
1179:.
1167:.
1163:.
1140:.
1130:.
1122:.
1108:.
1104:.
1078:.
1068:.
1060:.
1050:12
1048:.
1044:.
1021:.
1011:.
1001:.
989:.
985:.
962:.
952:.
944:.
934:26
932:.
928:.
905:.
895:.
887:.
877:55
875:.
871:.
857:^
843:.
835:.
825:15
823:.
800:.
792:.
782:16
780:.
757:.
749:.
737:.
714:.
704:.
694:20
692:.
688:.
649:^
635:.
625:.
617:.
607:32
605:.
601:.
589:^
574:^
560:.
550:.
538:10
536:.
532:.
520:^
506:.
496:.
484:.
480:.
466:^
452:.
442:.
428:.
424:.
401:.
391:.
381:.
369:.
365:.
275:.
269:CO
247:,
243:,
239:,
161:,
138:.
41:SN
1294:)
1288:(
1236:e
1229:t
1222:v
1205:.
1175::
1148:.
1116::
1086:.
1056::
1029:.
1005::
997::
970:.
940::
913:.
883::
851:.
831::
808:.
788::
765:.
745::
739:3
722:.
700::
673:.
643:.
613::
568:.
544::
514:.
492::
460:.
436::
430:8
409:.
385::
377::
318:(
298:(
290:(
282:(
267:(
169:/
47:(
39:(
31:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.