69:. Malachite green is applied to the slide, which can penetrate the tough walls of the endospores, staining them green. After five minutes, the slide is removed from the steam, and the paper towel is removed. After cooling, the slide is rinsed with water for thirty seconds. The slide is then stained with diluted safranin for two minutes, which stains most other microorganic bodies red or pink. The slide is then rinsed again, and blotted dry with
20:
158:
52:
Endospores cannot be stained by normal staining procedures because their walls are practically impermeable to all chemicals. The
Schaeffer- Fulton endospore stain uses heat to drive the primary stain(malachite green) into the endospore. After cooling, the slide is decolorized with water and
199:
223:
192:
238:
185:
65:. The slide is then suspended over a water bath with some sort of porus paper over it, so that the slide is
228:
124:
233:
41:
by staining any present endospores green, and any other bacterial bodies red. The primary stain is
89:
77:
218:
88:
The procedure was designed by Alice B. Schaeffer and MacDonald Fulton, two microbiologists at
25:
42:
19:
169:
70:
212:
105:
62:
165:
38:
66:
46:
157:
61:
Using an aseptic technique, bacteria are placed on a slide and
29:
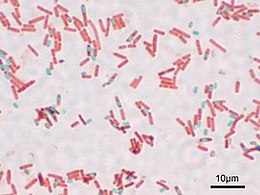
showing endospores as green and the vegetative cell as red
92:, during the 1930s. The procedure also goes by the name
173:
96:, referring to two bacteriologists during the 1900s.
76:After drying, the slide can then be viewed under a
134:
132:
193:
49:, which dyes any other bacterial bodies red.
8:
200:
186:
18:
117:
7:
154:
152:
140:Laboratory Exercises in Microbiology
37:is a technique designed to isolate
14:
125:Definition:Schaeffer-Fulton Stain
156:
53:counterstained with safranin.
1:
142:, page 58. McGraw Hill, 2002.
16:Endospore isolation technique
172:. You can help Knowledge by
255:
151:
45:, and the counterstain is
23:A stained preparation of
224:Microbiology techniques
168:-related article is a
35:Schaeffer–Fulton stain
30:
138:Harley and Prescott:
22:
94:Wirtz-Conklin method
239:Microbiology stubs
90:Middlebury College
31:
181:
180:
26:Bacillus subtilis
246:
202:
195:
188:
160:
153:
143:
136:
127:
122:
78:light microscope
254:
253:
249:
248:
247:
245:
244:
243:
209:
208:
207:
206:
149:
147:
146:
137:
130:
123:
119:
114:
102:
86:
59:
43:malachite green
17:
12:
11:
5:
252:
250:
242:
241:
236:
231:
226:
221:
211:
210:
205:
204:
197:
190:
182:
179:
178:
161:
145:
144:
128:
116:
115:
113:
110:
109:
108:
101:
98:
85:
82:
71:bibulous paper
58:
55:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
251:
240:
237:
235:
232:
230:
227:
225:
222:
220:
217:
216:
214:
203:
198:
196:
191:
189:
184:
183:
177:
175:
171:
167:
162:
159:
155:
150:
141:
135:
133:
129:
126:
121:
118:
111:
107:
106:Moeller stain
104:
103:
99:
97:
95:
91:
83:
81:
79:
74:
72:
68:
64:
56:
54:
50:
48:
44:
40:
36:
28:
27:
21:
229:Bacteriology
174:expanding it
166:microbiology
163:
148:
139:
120:
93:
87:
75:
60:
51:
34:
32:
24:
234:Microscopy
213:Categories
112:References
63:heat fixed
39:endospores
57:Procedure
219:Staining
100:See also
47:safranin
84:History
67:steamed
164:This
170:stub
33:The
215::
131:^
80:.
73:.
201:e
194:t
187:v
176:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.