1249:. As long as core countries maintain scarcities of their goods, they can select customers from semi-periphery and periphery countries that are competing over them. When excess supply occurs, the core countries are the ones competing over a smaller market. This competition allows semi-peripheral nations to select from among core countries rather than vice versa when making decisions about commodity purchases, manufacturing investments, and sales of goods, shifting the balance of power to the semi-periphery. While in general there is a power shift from core to semi-periphery in times of economic struggles, there are few examples of semi-peripheral countries transitioning to core status. To accomplish this, semi-peripheral nations must not only take advantage of weaker core countries but must also exploit any existing advantages over other semi-peripheral nations. How well they exploit these advantages determines their arrangement within the semi-periphery class.
940:. The rapid development of industry triggered several reactions. Many European states explored new territories in addition to their original colonial holdings for new markets to exploit. The European world system continued to expand and include more regions, as it absorbed the Indian Ocean economic system through the acquisition of colonies by Britain, France, Spain, and Portugal, among others. Previously isolated regions, like much of the American interior zone, joined newly independent South American countries in becoming part of the periphery. By the nineteenth century, Asia and Africa had also entered the world system as peripheral regions. This development of Africa and Asia as peripheral continents allowed for new cores like the United States and Germany to improve their core status, rising higher within the world system.
969:
while old cores such as Spain and
Portugal faded to the semi-periphery. The growth of the power of the common man led to an expansion of thought concerning democracy, communism, and revolution, which pervaded the weaker semi-peripheral nations overcome with civil distress. In some cases, this led to the weakening of the nations, such as the violent revolution in France. This contributed to the adoption of totalitarian leaders, as seen in Germany and France. The major factors contributing to world war were the conflicts and power struggles taking place between the three classes of nations in the global system. Nations considered part of the semi-periphery felt oppressed by the stronger, larger core nations.
978:
957:
1778:
1125:
2170:
1737:
1358:
1650:
660:. A need for an in between category became quickly apparent, leading to the establishment of the semi-periphery category for societies that have moved away from the periphery but have not become core. In other words, the category describes societies that remain dependent, and to some extent underdeveloped, despite having achieved significant levels of industrialization. Semi-peripheral countries are tied into dynamic world systems that focus on the reliance of poor nations upon the wealthy, a concept known as the
705:
While these advances separate the semi-periphery from the periphery, they lack the power and the economic dominance of core nations and still have a lot of un-managed poverty, placing them beneath the core. Semi-peripheral countries are important contributors to the world economy because of the above reasons and because they tend to have above average land mass, meaning that they are host to an above average market. A primary example is China, a country with not only a large area but with a large population.
740:. This was the first time in history that the peripheries and semi-peripheries of the world became connected and involved in the trade of the world, both with cores and with each other. Through a lucrative trade system, including heavy taxing of goods traveling through their borders, they were able to maintain a steady stream of wealth, becoming the driving forces of economic change throughout this time period. In addition, a heavy emphasis on defense and border security, particularly among the
1088:
1173:. The new leading powers are mostly non-European (United States, Canada, Japan). Outside of these developed countries are countries (see list below) that are considered semi-periphery and are both dominant and dominated within economic, political, and social realms. These middle powers are a combination of nations that have emerged as a result of the fragmentation of the Soviet Union and nations that have risen because of their possession of resources in high demand, like oil in
2317:
1611:
913:
1763:
861:
2477:
2304:
2029:
2016:
1544:
551:
2291:
2042:
1962:
1923:
1570:
2462:
2278:
2211:
2183:
2144:
2109:
1856:
1685:
1637:
1557:
1425:
1332:
785:
2423:
1990:
1724:
1531:
1477:
2516:
2490:
2410:
2395:
2122:
2096:
2081:
2003:
1936:
1830:
1804:
1698:
1672:
1598:
1384:
1319:
994:
2503:
2449:
2436:
2343:
2263:
2237:
2068:
1949:
1910:
1884:
1817:
1624:
1505:
1490:
1438:
1397:
1258:
2369:
2250:
1791:
1371:
20:
2382:
2224:
1869:
1750:
1451:
2356:
2157:
1975:
1711:
1518:
1345:
844:. Despite these advances in influence and entrepreneurship, Genoa and Venice suffered from the crippling effects of the Black Plague, as much of the rest of Europe had before them. Venice was able to survive due to its connection with the Southern trade route, though her strength was much reduced by the middle of the fifteenth century. Genoa never fully recovered from the
623:. Semi-periphery countries have organizational characteristics of both core countries and periphery countries and are often geographically located between core and peripheral regions as well as between two or more competing core regions. Semi-periphery regions play a major role in mediating economic, political, and social activities that link core and peripheral areas.
2196:
2055:
1897:
1843:
1583:
1464:
1412:
719:
1234:, high wages, and diversified production while periphery countries have less technology, low profits, low wages, and less diversified production. Semi-periphery countries fall in the middle of these spectra, and their unique political and social structure place them in a position where they can best take advantage of economic downturns.
1245:, which combine to create a shift in surplus and power to the semi-periphery. Semi-periphery regions take advantage of the situation by expanding control of their home markets and the surrounding periphery countries at the expense of core countries. The underlying reason for this shift in power lies in the basic economic principle of
899:
to
Atlantic control left by the decline of Italian powers like Genoa and Venice. Much like the core European powers, Spain and Portugal had strong navies and expansive colonial domains, which they exploited for their natural resources and cheap labor. Rather than using the increased wealth to develop strong domestic
878:, gained the most from the world economy. Their ascension from previous peripheral and semi-peripheral status to the core was driven by the development of strong central government and military power, the combination of which made possible control of international commerce and exploitation of colonial possessions.
764:. Through their positions within the world trade system, semi-peripheries in the Middle East became crucially important in connecting the cities of Chinese and Indian cores with the fledgling cities of Europe, as well as serving as key points between other, more major core cities in the region, such as
1225:
to integrate into the world economy and establish local dominance. Outside of these strategies is that of self-reliance, a basic theory that as some countries grow, others will decline. Many countries in Africa and South
America have exhibited the qualities of a sub-imperial or semi-industrial power.
1164:
In today's global hierarchy, some states are transitioning upward while others are moving downward in terms of status and influence. Former colonial powers no longer exercise control over an international domain and are instead mostly relegated to their core; for example, former
European world powers
968:
represented both the core and the semi-periphery, as Europe dominated 80% of the world's market share. Much of the rest of the world was a diverse periphery, though Japan was a notable exception. As expansionism continued, new core nations emerged, such as the
Britain, Germany, and the United States,
868:
In a push to ensure stable economic growth, Europe turned to a capitalistic economy in the fifteenth and early sixteenth centuries to replace the failed feudal system. Modern capitalism allowed for economies to extend beyond geographical and political boundaries, leading to the formation of the first
664:. The term semi-periphery has been applied to countries that existed as early as in the thirteenth century. In theory, the creation of a semi-periphery category has added sociological and historical layers to previous developmental theories—yet it still has similar, inherently capitalist foundations.
898:
In between the core and periphery was the semi-periphery, which constituted both previous core regions that had declined, like Italy, Spain and
Portugal, and peripheries that had improved their position, like southern Germany and southern France. Spain and Portugal had taken advantage of the opening
796:
met severe economic difficulties in the fourteenth and early fifteenth centuries. This decline in development was caused by a combination of the decline in agricultural production, the shrinking economy that had already hit its peak within the current feudal structure, and the devastating effects of
626:
These regions allow for the possibility of innovative technology, reforms in social and organizational structure, and dominance over peripheral nations. These changes can lead to a semi-periphery country being promoted to a core nation. Semi-periphery is, however, more than a description, as it also
704:
In terms of their contribution to industry and economy, the contemporary semi-peripheral states are semi-industrialized. Semi-peripheral countries are major exporters of minerals and agricultural goods. They are often focused in the manufacturing and exportation of industrial goods and commodities.
1196:
and Saudi Arabia, can utilize the strategy of seizing the chance. The strategy of promotion by invitation can be utilized by countries willing to be open to foreign governmental and regional administrative centers. Examples of past countries to utilize this strategy are the capitalist regimes in
881:
At the other end of the spectrum was the periphery, marked by lack of central government, exportation of raw materials to the core, and exploitive labor practices. In this time period, especially toward the end of the 17th century, South
America and parts of North America stood out as peripheral
943:
Throughout this time period was a constant shift within core regions from a combination of agriculture and industry to solely industrial enterprise. In this period, England was the leader in industrial and agricultural production, though by 1900, only ten percent of
England's populace worked in
630:
World-systems theory describes the semi-periphery as a key structural element in the world economy. The semi-periphery plays a vital role comparative to that of the role that Spain and
Portugal played in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries as intermediate trading groups within the European
903:
sectors, as other
Western European powers did, Spain and Portugal used imported gold and silver to obtain manufactured goods from the core countries, relegating them to semi-periphery instead of core status. So, while they had control over several peripheral regions and exploited them, a
691:
Semi-peripheral nations are a necessary structural element in a world-trade system, since such nations can serve to alleviate the political pressures that the core can exert upon the periphery and the political unrest that the periphery can direct back at the core. On the other hand, the
894:
of these regions controlled commerce and became wealthy through the new world economy, leading to their rise in power above the government. Even in periods of upheaval, local aristocrats were able to rely on core European powers to assist in keeping control over the economic system.
634:
Today, the semi-periphery is generally industrialized. Semi-peripheral countries contribute to the manufacturing and exportation of a variety of goods. They are marked by above average land mass, as exemplified by Argentina, China, India, Brazil, Mexico, Indonesia, and
695:
The semi-periphery exists because it needs to divide the economic power between the core and the periphery. Semi-periphery, referred to as the middle class by Wallerstein, is what makes the capitalist world function because it is much like the sociological
904:
characteristic of a core region, these countries failed to develop the quality manufacturing industries and the access to international banking that further defined core countries, leaving them a step below in the world system at semi-periphery status.
873:
that determined countries' relationships and placement within the categories of the world system: core, semi-periphery, periphery, and external. The core regions, most notably the countries of Northwestern Europe like England, France, and the
688:. They also serve as a political buffer zone in that while they are exploited, they are also the exploiters. These areas have either been core regions in the past or formerly-peripheral areas that have since advanced in the world economy.
23:
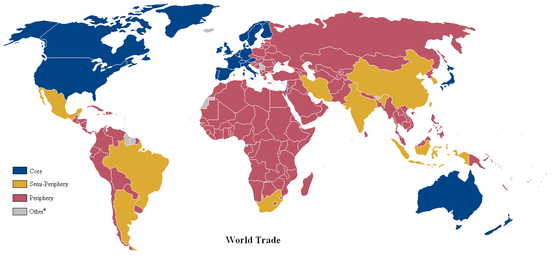
A world map of countries by trading status, late 20th century, using the world system differentiation into core countries (blue), semi-periphery countries (yellow) and periphery countries (red). Based on the list in Dunn, Kawana, Brewer
817:, the Middle East, and the other Mediterranean powers to maintain their growth despite the economic failures of their European trade partners. Genoa and Venice had influence beyond their trade channels. Both were instrumental in the
1066:
nations, who fell under the Soviet Union as bloc countries. Japan also fell back into semi-periphery, along with the industrializing China and India, until their recent upswing in influence. Change also came to North America, where
944:
agriculture, demonstrating the shift to industry not only in England but across the core stratum. The dramatic shift to industry extended beyond the core by the end of this time period, as core regions encouraged the development of
1229:
Wallerstein examines the role of semi-periphery countries during a period of economic downturn. To redefine core and periphery countries in an economic sense, core countries are characterized by advanced technology, high
700:
theory, where norms, customs, traditions, and institutions act as "organs" that work toward the proper functioning of the "body" as a whole. Without these industrializing countries, change will never reach the periphery.
1301:
where instability makes reform too dangerous to attempt. It has been within semi-peripheral nations where democratic reforms like the expansion of suffrage and the institution of the secret ballot have been implemented.
928:
and other industries. The merchant class further consolidated its power by extending control over internal markets and the prices of finished goods. The result was the development of the necessary capital to
651:
Semi-peripheral countries offer their citizens relatively diverse economic opportunities but also have extreme gaps between the rich and poor. World-system theorists originally used only two categories:
2334:(2005), who notes that this list is composed of countries that "have been consistently classified into a single one of the three zones of the world economy over the entire 28-year study period".
1265:
The semi-peripheral nations of the world have played an important role to world trade and interaction since early periods of globalized trade. This "middle ground" between the very powerful
579:
315:
1054:
This trend known to continued throughout the century, with Germany, Russia, and Japan also taking seats at the core. At the end of World War II however, Germany quickly fell to the
852:
trade route left the western Mediterranean and the Atlantic open to Portugal and Spain, who were already better positioned geographically to control Atlantic trade routes.
864:
Subsequent to taking over Portugal's empire (in blue) from 1580 to 1640, these were areas of the world that at one time were territories (in red) of the Spanish Empire.
829:, in the late thirteenth century. The Byzantine Empire took advantage of its strategic position along various trade routes and the decline of Western Europe to rise to
210:
1188:
identifies three ways by which countries can emerge from the periphery into the semi-periphery. Countries with a large market and room for industrial growth, like
572:
1177:. While these nations are by no means on the level of the stated world powers, they are able to exert influence over the weaker nations of the impoverished
245:
142:
1015:
275:
639:. More land mass typically means an increased market size and share. Semi-peripheral nations are not all large though, as smaller countries such as
293:
40:
801:
epidemic. The regression of Western Europe into the semi-periphery and periphery allowed for the rise of the trading powers of Italy, most notably
565:
309:
260:
250:
205:
1293:, originate in the semi-periphery. He notes that innovations in democracy came from the semi-periphery rather than the more established, stable
890:
for export to Europe, a distinctive characteristic of the new capitalism, as goods were no longer produced solely for internal consumption. The
100:
736:
This era of human history found the semi-periphery concentrated in the area stretching from the Middle East to China, including India and the
692:
semi-periphery can find itself excluded from the region's politics, as it lies just outside the bounds of political arena of the core states.
298:
672:
The semi periphery is needed to stabilize the world system, as it facilitates interaction and provides a connection between the low-income
265:
152:
60:
680:
by adding another step in the world system hierarchy. As the middle ground, semi-peripheral countries display characteristics of both the
1277:, the semi-periphery areas around Europe's Mediterranean Coast facilitated trade between the peripheries of the more manufacturing based
948:
in peripheral and semi-peripheral zones to further develop those markets and create demand for newly developed machines and other goods.
230:
67:
3248:
982:
3268:
3207:
3184:
3161:
3135:
3074:
3039:
3007:
2981:
1041:
135:
848:
and its defeat at the hands of Venice in the late fourteenth century. The decline of Genoa and the shift in Venice's focus to the
756:. Because of its position along a convenient route through the Indian Ocean, India established its role as a "hinge" between the
1783:
535:
870:
225:
117:
3253:
1019:
31:
977:
3263:
3243:
1079:. On the other side of the Pacific, Australia was also developing, helping to secure an Allied Victory in World War II.
956:
219:
3115:
Social Cohesion, Sustainable Development and Turkey's Accession to the European Union: Implications from a Global Model
3152:
The Modern World-System: Capitalist Agriculture and the Origins of the European World-Economy in the Sixteenth Century
1114:
920:
The development of trade between Europe, the Americas, and the East generated massive profits for a relatively small
3258:
240:
1124:
200:
3084:
1286:
1004:
912:
697:
167:
87:
924:
elite in the European colonial powers. These merchants were able to utilize their profits to take control of
1108:
1023:
1008:
172:
112:
72:
47:
2991:
3096:
Shaw, Timothy M. "The Semiperiphery in Africa and South America: Subimperialism and Semiindustrialism".
627:
serves as a position within the world hierarchy in which social and economic change can be interpreted.
82:
2937:
1058:
along with war-ravaged France. As the rest of Europe struggled to rebuild itself, it also fell to the
3145:
1185:
1068:
593:
486:
436:
421:
338:
333:
215:
147:
122:
1663:
The following are semi-periphery countries from an updated version of essays by Wallerstein (1997).
1270:
1087:
916:
As the Industrial Revolution developed British manufactured output surged ahead of other economies.
685:
673:
653:
616:
376:
348:
2876:
1218:
2545:
1238:
1231:
1076:
451:
371:
1184:
Other terms used to describe semi-periphery countries include sub-imperial and semi-industrial.
821:
through their provisions of troops, transport vessels, and naval ships. Genoa also assisted the
792:
Following increases in population and commerce in Western Europe in the thirteenth century, the
2949:
1128:
World map indicating the category of Human Development Index by country (based on 2014 update)
860:
3203:
3180:
3157:
3131:
3101:
3070:
3035:
3003:
2999:
2977:
2888:
2540:
2331:
1222:
937:
753:
661:
605:
162:
157:
107:
2965:
1063:
822:
456:
411:
396:
270:
254:
195:
77:
2877:"INSIDE THE BRIC: ANALYSIS OF THE SEMIPERIPHERAL NATURE OF BRAZIL, RUSSIA, INDIA AND CHINA"
809:. These Italian city-states took advantage of their established trade connections with the
555:
501:
471:
461:
446:
3196:
3173:
3028:
3127:
3063:
2970:
2535:
1768:
1266:
1170:
1118:
1059:
1055:
830:
826:
681:
677:
657:
620:
481:
441:
426:
391:
550:
3237:
3150:
3058:
2135:
The following are semi-periphery countries according to Dunn, Kawana, Brewer (2000).
1274:
945:
930:
900:
887:
837:
810:
793:
737:
496:
476:
431:
416:
401:
343:
3089:
Where and When was Democracy Invented. Comparative Studies in Society & History
2550:
2482:
2309:
2034:
2021:
1549:
1178:
1174:
882:
zones under the control and capitalistic exploitation of core countries in Europe.
798:
726:
491:
406:
303:
235:
2996:
Rise and Demise: Comparing World-Systems The Semi Periphery: The Seedbed of Change
788:
The Black Death rapidly spread along the major European sea and land trade routes.
2296:
2047:
1967:
1928:
1575:
1298:
1294:
993:
925:
891:
875:
845:
784:
506:
381:
353:
177:
1273:
allowed those two zones to interact with greater ease. For example, during the
1257:
1192:, South Africa, and Mexico, and countries with valuable energy resources, like
1169:, Africa, or Asia, but rather have consolidated their power in the form of the
2467:
841:
609:
511:
466:
386:
19:
3105:
2892:
1289:, also notes that political developments, particularly in the advancement of
2283:
2216:
2188:
2149:
2114:
1861:
1690:
1642:
1562:
1430:
1337:
1310:
The following are semi-periphery countries according to Wallerstein (1976).
1290:
1282:
1072:
749:
723:
643:, Poland, and Greece can be described to exist within the semi-periphery.
2428:
1995:
1729:
1536:
1482:
1278:
1246:
1166:
921:
818:
814:
3051:
Modern History Sourcebook: Summary of Wallerstein on World System Theory
2933:
2864:
2521:
2495:
2415:
2400:
2127:
2101:
2086:
2008:
1941:
1835:
1809:
1703:
1677:
1603:
1389:
1324:
1214:
1206:
849:
765:
741:
730:
718:
612:
2508:
2454:
2441:
2361:
2348:
2322:
2268:
2242:
2162:
2073:
1980:
1954:
1915:
1889:
1822:
1716:
1629:
1616:
1523:
1510:
1495:
1443:
1402:
1350:
1242:
1189:
883:
806:
640:
2881:
Austral: Brazilian Journal of Strategy & International Relations
840:
government and institutions that are viewed as precursors to modern
752:
also played a role, as seen in India's development of an impressive
3230:
Windows on Humanity by Conrad Phillip KOTTAK. Chapter 17, page 390.
869:
worldwide economic system. At the base of this world system was an
3227:. York, Pennsylvania: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2004., pg. 412.
2374:
2255:
2201:
2175:
2060:
1902:
1848:
1796:
1742:
1655:
1588:
1469:
1417:
1376:
1363:
1256:
1210:
1202:
1198:
1123:
976:
960:
A ration party of the Royal Irish Rifles in a communication trench
955:
802:
769:
745:
717:
2387:
2229:
1874:
1755:
1456:
1193:
965:
773:
761:
757:
636:
1297:, where profit discourages great reform, or the extremely poor
987:
1101: Emerging and developing economies (not least developed)
836:
During this time period, Genoa and Venice developed forms of
3175:
Semi-Peripheral Countries and The Contemporary World Crisis
936:
This era was defined by the transition from agriculture to
2972:
Before European Hegemony: the world system a.d. 1250-1350
3223:
Kaplan, David H.; Wheeler, James O.; Holloway, James O.
2932:, American Sociological Review, 2000 February, Vol. 65
2950:
The Country-Level Income Structure of the World-Economy
2875:
Morales Ruvalcaba, Daniel Efrén (11 September 2013).
1165:
do not exert influence over colonial outposts in the
2330:
And this is the semi-periphery listing according to
1237:
These economic downturns occur because of increased
2741:
Chirot, Daniel, and Thomas D. Hall. 1982. 8:81-106.
3195:
3172:
3149:
3062:
3027:
2969:
1281:and the cores of India and China. John Markoff, a
886:and indigenous workers in these regions developed
16:Industrializing countries in world-systems theory
3019:World-System Theory Annual Review of Sociology
3202:. New York City: Cambridge University Press.
2952:. Journal of World-Systems Research 11:29-55.
573:
8:
3034:. New York City: Harcourt Brace Jovanovich.
2825:
2823:
2821:
2819:
2817:
2815:
2813:
2811:
1022:. Unsourced material may be challenged and
3124:The Regional Reography of the World-System
2906:
2904:
2902:
2801:
2799:
2797:
2795:
2793:
2791:
2789:
2787:
2785:
2783:
2781:
2779:
2777:
2775:
2773:
2771:
2769:
2767:
2663:
2661:
2659:
2657:
2655:
2653:
580:
566:
27:
2765:
2763:
2761:
2759:
2757:
2755:
2753:
2751:
2749:
2747:
2667:Wallerstein 1974 Vol.3, No.4., pp 461-483
2651:
2649:
2647:
2645:
2643:
2641:
2639:
2637:
2635:
2633:
2623:
2593:
2591:
2589:
2587:
2585:
1107: Emerging and developing economies (
1042:Learn how and when to remove this message
744:, allowed them to be fairly impenetrable
276:Chinese school of international relations
3017:Chirot, Daniel; Hall, Thomas D. (1982).
2855:
2675:
2673:
2621:
2619:
2617:
2615:
2613:
2611:
2609:
2607:
2605:
2603:
2336:
2137:
1665:
1312:
1086:
911:
859:
783:
18:
2853:
2851:
2849:
2847:
2845:
2843:
2841:
2839:
2837:
2835:
2571:
2569:
2567:
2565:
2561:
30:
3030:Social Change in the Twentieth Century
2728:
2726:
2724:
2722:
2720:
2718:
2716:
2714:
825:when it helped recapture the capital,
3098:The Review of Black Political Economy
2861:The Review of Black Political Economy
2712:
2710:
2708:
2706:
2704:
2702:
2700:
2698:
2696:
2694:
7:
1020:adding citations to reliable sources
1071:led to the rise of countries like
532:
14:
3179:. New York City: Academic Press.
3156:. New York City: Academic Press.
2994:; Hall, Thomas D (7 March 1997).
1306:Lists of semi-periphery countries
2514:
2501:
2488:
2475:
2460:
2447:
2434:
2421:
2408:
2393:
2380:
2367:
2354:
2341:
2315:
2302:
2289:
2276:
2261:
2248:
2235:
2222:
2209:
2194:
2181:
2168:
2155:
2142:
2120:
2107:
2094:
2079:
2066:
2053:
2040:
2027:
2014:
2001:
1988:
1973:
1960:
1947:
1934:
1921:
1908:
1895:
1882:
1867:
1854:
1841:
1828:
1815:
1802:
1789:
1784:Democratic Republic of the Congo
1776:
1761:
1748:
1735:
1722:
1709:
1696:
1683:
1670:
1648:
1635:
1622:
1609:
1596:
1581:
1568:
1555:
1542:
1529:
1516:
1503:
1488:
1475:
1462:
1449:
1436:
1423:
1410:
1395:
1382:
1369:
1356:
1343:
1330:
1317:
992:
549:
3069:. New York City: Random House.
981:Burned-out buildings after the
871:international division of labor
833:status until its fall in 1453.
600:(sometimes referred to as just
226:International political economy
118:Uneven and combined development
3194:Wallerstein, Immanuel (1979).
3171:Wallerstein, Immanuel (1974).
2938:Appendix with the country list
2930:Trade Globalization since 1795
2575:Chase-Dunn and Thomas D. Hall.
1269:and the backwaters of the far
32:International relations theory
1:
2627:Wallerstein 1976, pp. 229-233
1062:, with the exception of many
615:which are positioned between
3198:The Capitalist World Economy
2948:Salvatore J. Babones. 2005.
220:liberal intergovernmentalism
2919:Wallerstein 1997 pp. 95-119
3285:
2910:Markoff, John. 1999-1041:4
933:the European core states.
241:Hegemonic stability theory
3249:International development
1275:13th-century world system
201:Critical security studies
3269:Sociological terminology
1287:University of Pittsburgh
1095: Advanced economies
698:structural functionalism
598:semi-periphery countries
168:Territorial peace theory
88:Liberal institutionalism
3026:Chirot, Daniel (1977).
2992:Chase-Dunn, Christopher
2597:Terlouw 1992 pg 136-145
1113:Classifications by the
709:History and development
536:International relations
173:Democratic peace theory
113:Theories of imperialism
73:Democratic peace theory
48:Feminist constructivism
3122:Terlouw, Kees (1992).
3049:Halsall, Paul (1997).
2976:. New York City: OUP.
2928:Dunn, Kawana, Brewer,
2805:Halsall 1997, pp.14-19
1262:
1221:. These countries use
1161:
1158: Data unavailable
1121:
985:
961:
917:
865:
789:
733:
25:
3254:Development economics
3146:Wallerstein, Immanuel
2829:Hobsbawn, Eric. 1987.
2732:Janet Abu-Lughod 1989
2577:The Seedbed of Change
1260:
1223:dependent development
1127:
1090:
980:
959:
915:
863:
787:
721:
316:Inter-paradigm debate
83:Republican liberalism
22:
3264:World systems theory
1186:Immanuel Wallerstein
1069:American imperialism
1016:improve this section
676:and the high-income
594:world-systems theory
487:Immanuel Wallerstein
437:Peter J. Katzenstein
422:Samuel P. Huntington
339:Historical sociology
334:International ethics
216:Intergovernmentalism
148:Neoclassical realism
123:World-systems theory
3244:Imperialism studies
654:periphery countries
647:Sociological theory
556:Politics portal
377:Zbigniew Brzezinski
349:State cartel theory
3002:: Westview Press.
2546:Developing country
1263:
1162:
1122:
1077:Dominican Republic
986:
983:bombing of Hamburg
962:
918:
866:
790:
734:
602:the semi-periphery
452:Stephen D. Krasner
26:
3259:Political economy
3065:The Age of Empire
3000:Boulder, Colorado
2966:Abu-Lughod, Janet
2859:Shaw, Timothy M.
2541:Dependency theory
2527:
2526:
2328:
2327:
2133:
2132:
1661:
1660:
1052:
1051:
1044:
938:industrialization
754:maritime industry
674:peripheral states
662:dependency theory
631:colonial empire.
590:
589:
246:Copenhagen School
163:Defensive realism
158:Offensive realism
143:Classical realism
108:Dependency theory
3276:
3213:
3201:
3190:
3178:
3167:
3155:
3141:
3118:
3109:
3092:
3080:
3068:
3054:
3045:
3033:
3022:
3013:
2987:
2975:
2953:
2946:
2940:
2926:
2920:
2917:
2911:
2908:
2897:
2896:
2872:
2866:
2857:
2830:
2827:
2806:
2803:
2742:
2739:
2733:
2730:
2689:
2686:
2680:
2677:
2668:
2665:
2628:
2625:
2598:
2595:
2580:
2579:.Chapter 5 of C.
2573:
2520:
2518:
2517:
2507:
2505:
2504:
2494:
2492:
2491:
2481:
2479:
2478:
2466:
2464:
2463:
2453:
2451:
2450:
2440:
2438:
2437:
2427:
2425:
2424:
2414:
2412:
2411:
2399:
2397:
2396:
2386:
2384:
2383:
2373:
2371:
2370:
2360:
2358:
2357:
2347:
2345:
2344:
2337:
2321:
2319:
2318:
2308:
2306:
2305:
2295:
2293:
2292:
2282:
2280:
2279:
2267:
2265:
2264:
2254:
2252:
2251:
2241:
2239:
2238:
2228:
2226:
2225:
2215:
2213:
2212:
2200:
2198:
2197:
2187:
2185:
2184:
2174:
2172:
2171:
2161:
2159:
2158:
2148:
2146:
2145:
2138:
2126:
2124:
2123:
2113:
2111:
2110:
2100:
2098:
2097:
2085:
2083:
2082:
2072:
2070:
2069:
2059:
2057:
2056:
2046:
2044:
2043:
2033:
2031:
2030:
2020:
2018:
2017:
2007:
2005:
2004:
1994:
1992:
1991:
1979:
1977:
1976:
1966:
1964:
1963:
1953:
1951:
1950:
1940:
1938:
1937:
1927:
1925:
1924:
1914:
1912:
1911:
1901:
1899:
1898:
1888:
1886:
1885:
1873:
1871:
1870:
1860:
1858:
1857:
1847:
1845:
1844:
1834:
1832:
1831:
1821:
1819:
1818:
1808:
1806:
1805:
1795:
1793:
1792:
1782:
1780:
1779:
1767:
1765:
1764:
1754:
1752:
1751:
1741:
1739:
1738:
1728:
1726:
1725:
1715:
1713:
1712:
1702:
1700:
1699:
1689:
1687:
1686:
1676:
1674:
1673:
1666:
1654:
1652:
1651:
1641:
1639:
1638:
1628:
1626:
1625:
1615:
1613:
1612:
1602:
1600:
1599:
1587:
1585:
1584:
1574:
1572:
1571:
1561:
1559:
1558:
1548:
1546:
1545:
1535:
1533:
1532:
1522:
1520:
1519:
1509:
1507:
1506:
1494:
1492:
1491:
1481:
1479:
1478:
1468:
1466:
1465:
1455:
1453:
1452:
1442:
1440:
1439:
1429:
1427:
1426:
1416:
1414:
1413:
1401:
1399:
1398:
1388:
1386:
1385:
1375:
1373:
1372:
1362:
1360:
1359:
1349:
1347:
1346:
1336:
1334:
1333:
1323:
1321:
1320:
1313:
1157:
1151:
1145:
1139:
1133:
1106:
1100:
1094:
1064:Eastern European
1047:
1040:
1036:
1033:
1027:
996:
988:
823:Byzantine Empire
582:
575:
568:
554:
553:
534:
457:John Mearsheimer
412:Martha Finnemore
397:Michael W. Doyle
328:Other approaches
271:Intercommunalism
255:neofunctionalism
196:Neo-Gramscianism
78:Capitalist peace
28:
3284:
3283:
3279:
3278:
3277:
3275:
3274:
3273:
3234:
3233:
3225:Urban Geography
3220:
3218:Further reading
3210:
3193:
3187:
3170:
3164:
3144:
3138:
3121:
3112:
3095:
3083:
3077:
3057:
3048:
3042:
3025:
3016:
3010:
2990:
2984:
2964:
2961:
2956:
2947:
2943:
2927:
2923:
2918:
2914:
2909:
2900:
2874:
2873:
2869:
2863:: pp. 341-358.
2858:
2833:
2828:
2809:
2804:
2745:
2740:
2736:
2731:
2692:
2687:
2683:
2678:
2671:
2666:
2631:
2626:
2601:
2596:
2583:
2574:
2563:
2559:
2532:
2515:
2513:
2502:
2500:
2489:
2487:
2476:
2474:
2461:
2459:
2448:
2446:
2435:
2433:
2422:
2420:
2409:
2407:
2394:
2392:
2381:
2379:
2368:
2366:
2355:
2353:
2342:
2340:
2316:
2314:
2303:
2301:
2290:
2288:
2277:
2275:
2262:
2260:
2249:
2247:
2236:
2234:
2223:
2221:
2210:
2208:
2195:
2193:
2182:
2180:
2169:
2167:
2156:
2154:
2143:
2141:
2121:
2119:
2108:
2106:
2095:
2093:
2080:
2078:
2067:
2065:
2054:
2052:
2041:
2039:
2028:
2026:
2015:
2013:
2002:
2000:
1989:
1987:
1974:
1972:
1961:
1959:
1948:
1946:
1935:
1933:
1922:
1920:
1909:
1907:
1896:
1894:
1883:
1881:
1868:
1866:
1855:
1853:
1842:
1840:
1829:
1827:
1816:
1814:
1803:
1801:
1790:
1788:
1777:
1775:
1762:
1760:
1749:
1747:
1736:
1734:
1723:
1721:
1710:
1708:
1697:
1695:
1684:
1682:
1671:
1669:
1649:
1647:
1636:
1634:
1623:
1621:
1610:
1608:
1597:
1595:
1582:
1580:
1569:
1567:
1556:
1554:
1543:
1541:
1530:
1528:
1517:
1515:
1504:
1502:
1489:
1487:
1476:
1474:
1463:
1461:
1450:
1448:
1437:
1435:
1424:
1422:
1411:
1409:
1396:
1394:
1383:
1381:
1370:
1368:
1357:
1355:
1344:
1342:
1331:
1329:
1318:
1316:
1308:
1279:Northern Europe
1255:
1160:
1159:
1155:
1153:
1149:
1147:
1143:
1141:
1137:
1135:
1134: Very High
1131:
1112:
1109:least developed
1104:
1102:
1098:
1096:
1092:
1085:
1048:
1037:
1031:
1028:
1013:
997:
975:
954:
910:
858:
782:
716:
711:
670:
649:
606:industrializing
586:
548:
543:
542:
541:
540:
539:
538:
531:
525:
517:
516:
502:Alexander Wendt
472:Kathryn Sikkink
462:Hans Morgenthau
447:Henry Kissinger
372:Michael Barnett
367:
359:
358:
329:
321:
320:
289:
288:Classifications
281:
280:
266:Postcolonialism
206:Critical theory
191:
183:
182:
138:
128:
127:
103:
93:
92:
63:
53:
52:
43:
17:
12:
11:
5:
3282:
3280:
3272:
3271:
3266:
3261:
3256:
3251:
3246:
3236:
3235:
3232:
3231:
3228:
3219:
3216:
3215:
3214:
3208:
3191:
3185:
3168:
3162:
3142:
3136:
3119:
3110:
3093:
3081:
3075:
3059:Hobsbawn, Eric
3055:
3046:
3040:
3023:
3014:
3008:
2988:
2982:
2960:
2957:
2955:
2954:
2941:
2921:
2912:
2898:
2883:(in Spanish).
2867:
2831:
2807:
2743:
2734:
2690:
2681:
2669:
2629:
2599:
2581:
2560:
2558:
2555:
2554:
2553:
2548:
2543:
2538:
2536:Core-periphery
2531:
2528:
2525:
2524:
2511:
2498:
2485:
2471:
2470:
2457:
2444:
2431:
2418:
2404:
2403:
2390:
2377:
2364:
2351:
2326:
2325:
2312:
2299:
2286:
2272:
2271:
2258:
2245:
2232:
2219:
2205:
2204:
2191:
2178:
2165:
2152:
2131:
2130:
2117:
2104:
2090:
2089:
2076:
2063:
2050:
2037:
2024:
2011:
1998:
1984:
1983:
1970:
1957:
1944:
1931:
1918:
1905:
1892:
1878:
1877:
1864:
1851:
1838:
1825:
1812:
1799:
1786:
1772:
1771:
1769:Czech Republic
1758:
1745:
1732:
1719:
1706:
1693:
1680:
1659:
1658:
1645:
1632:
1619:
1606:
1592:
1591:
1578:
1565:
1552:
1539:
1526:
1513:
1499:
1498:
1485:
1472:
1459:
1446:
1433:
1420:
1406:
1405:
1392:
1379:
1366:
1353:
1340:
1327:
1307:
1304:
1254:
1251:
1241:and decreased
1171:European Union
1154:
1148:
1142:
1136:
1130:
1129:
1103:
1097:
1091:
1084:
1081:
1060:semi-periphery
1056:semi-periphery
1050:
1049:
1000:
998:
991:
974:
971:
953:
950:
909:
906:
857:
854:
827:Constantinople
781:
778:
715:
712:
710:
707:
669:
666:
658:core countries
648:
645:
621:core countries
588:
587:
585:
584:
577:
570:
562:
559:
558:
545:
544:
530:
529:
528:
527:
526:
523:
522:
519:
518:
515:
514:
509:
504:
499:
494:
489:
484:
482:J. Ann Tickner
479:
474:
469:
464:
459:
454:
449:
444:
442:Robert Keohane
439:
434:
429:
427:John Ikenberry
424:
419:
414:
409:
404:
399:
394:
392:Daniel Deudney
389:
384:
379:
374:
368:
365:
364:
361:
360:
357:
356:
351:
346:
341:
336:
330:
327:
326:
323:
322:
319:
318:
313:
306:
301:
296:
294:Postpositivism
290:
287:
286:
283:
282:
279:
278:
273:
268:
263:
258:
248:
243:
238:
233:
228:
223:
213:
211:English School
208:
203:
198:
192:
190:Other theories
189:
188:
185:
184:
181:
180:
175:
170:
165:
160:
155:
150:
145:
139:
134:
133:
130:
129:
126:
125:
120:
115:
110:
104:
99:
98:
95:
94:
91:
90:
85:
80:
75:
70:
64:
59:
58:
55:
54:
51:
50:
44:
41:Constructivism
39:
38:
35:
34:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3281:
3270:
3267:
3265:
3262:
3260:
3257:
3255:
3252:
3250:
3247:
3245:
3242:
3241:
3239:
3229:
3226:
3222:
3221:
3217:
3211:
3209:0-521-29358-8
3205:
3200:
3199:
3192:
3188:
3186:0-521-29358-8
3182:
3177:
3176:
3169:
3165:
3163:0-12-785920-9
3159:
3154:
3153:
3147:
3143:
3139:
3137:90-6266-091-6
3133:
3129:
3125:
3120:
3116:
3111:
3107:
3103:
3099:
3094:
3090:
3086:
3085:Markoff, John
3082:
3078:
3076:0-679-72175-4
3072:
3067:
3066:
3060:
3056:
3052:
3047:
3043:
3041:0-15-581420-6
3037:
3032:
3031:
3024:
3020:
3015:
3011:
3009:0-8133-1006-7
3005:
3001:
2997:
2993:
2989:
2985:
2983:0-19-506774-6
2979:
2974:
2973:
2967:
2963:
2962:
2958:
2951:
2945:
2942:
2939:
2935:
2931:
2925:
2922:
2916:
2913:
2907:
2905:
2903:
2899:
2894:
2890:
2886:
2882:
2878:
2871:
2868:
2865:
2862:
2856:
2854:
2852:
2850:
2848:
2846:
2844:
2842:
2840:
2838:
2836:
2832:
2826:
2824:
2822:
2820:
2818:
2816:
2814:
2812:
2808:
2802:
2800:
2798:
2796:
2794:
2792:
2790:
2788:
2786:
2784:
2782:
2780:
2778:
2776:
2774:
2772:
2770:
2768:
2766:
2764:
2762:
2760:
2758:
2756:
2754:
2752:
2750:
2748:
2744:
2738:
2735:
2729:
2727:
2725:
2723:
2721:
2719:
2717:
2715:
2713:
2711:
2709:
2707:
2705:
2703:
2701:
2699:
2697:
2695:
2691:
2685:
2682:
2679:Chirot. 1977.
2676:
2674:
2670:
2664:
2662:
2660:
2658:
2656:
2654:
2652:
2650:
2648:
2646:
2644:
2642:
2640:
2638:
2636:
2634:
2630:
2624:
2622:
2620:
2618:
2616:
2614:
2612:
2610:
2608:
2606:
2604:
2600:
2594:
2592:
2590:
2588:
2586:
2582:
2578:
2572:
2570:
2568:
2566:
2562:
2556:
2552:
2549:
2547:
2544:
2542:
2539:
2537:
2534:
2533:
2529:
2523:
2512:
2510:
2499:
2497:
2486:
2484:
2473:
2472:
2469:
2458:
2456:
2445:
2443:
2432:
2430:
2419:
2417:
2406:
2405:
2402:
2391:
2389:
2378:
2376:
2365:
2363:
2352:
2350:
2339:
2338:
2335:
2333:
2324:
2313:
2311:
2300:
2298:
2287:
2285:
2274:
2273:
2270:
2259:
2257:
2246:
2244:
2233:
2231:
2220:
2218:
2207:
2206:
2203:
2192:
2190:
2179:
2177:
2166:
2164:
2153:
2151:
2140:
2139:
2136:
2129:
2118:
2116:
2105:
2103:
2092:
2091:
2088:
2077:
2075:
2064:
2062:
2051:
2049:
2038:
2036:
2025:
2023:
2012:
2010:
1999:
1997:
1986:
1985:
1982:
1971:
1969:
1958:
1956:
1945:
1943:
1932:
1930:
1919:
1917:
1906:
1904:
1893:
1891:
1880:
1879:
1876:
1865:
1863:
1852:
1850:
1839:
1837:
1826:
1824:
1813:
1811:
1800:
1798:
1787:
1785:
1774:
1773:
1770:
1759:
1757:
1746:
1744:
1733:
1731:
1720:
1718:
1707:
1705:
1694:
1692:
1681:
1679:
1668:
1667:
1664:
1657:
1646:
1644:
1633:
1631:
1620:
1618:
1607:
1605:
1594:
1593:
1590:
1579:
1577:
1566:
1564:
1553:
1551:
1540:
1538:
1527:
1525:
1514:
1512:
1501:
1500:
1497:
1486:
1484:
1473:
1471:
1460:
1458:
1447:
1445:
1434:
1432:
1421:
1419:
1408:
1407:
1404:
1393:
1391:
1380:
1378:
1367:
1365:
1354:
1352:
1341:
1339:
1328:
1326:
1315:
1314:
1311:
1305:
1303:
1300:
1296:
1292:
1288:
1284:
1280:
1276:
1272:
1268:
1259:
1252:
1250:
1248:
1244:
1240:
1235:
1233:
1227:
1224:
1220:
1219:Côte d'Ivoire
1216:
1212:
1208:
1204:
1200:
1195:
1191:
1187:
1182:
1180:
1176:
1172:
1168:
1126:
1120:
1116:
1110:
1089:
1082:
1080:
1078:
1074:
1070:
1065:
1061:
1057:
1046:
1043:
1035:
1025:
1021:
1017:
1011:
1010:
1006:
1001:This section
999:
995:
990:
989:
984:
979:
972:
970:
967:
958:
951:
949:
947:
946:manufacturing
941:
939:
934:
932:
931:industrialize
927:
923:
914:
907:
905:
902:
901:manufacturing
896:
893:
889:
888:raw materials
885:
879:
877:
872:
862:
855:
853:
851:
847:
843:
839:
838:laissez-faire
834:
832:
828:
824:
820:
816:
812:
811:Mongol Empire
808:
804:
800:
795:
794:feudal system
786:
779:
777:
775:
771:
767:
763:
759:
755:
751:
747:
743:
739:
738:Mongol Empire
732:
728:
725:
720:
713:
708:
706:
702:
699:
693:
689:
687:
683:
679:
675:
667:
665:
663:
659:
655:
646:
644:
642:
638:
632:
628:
624:
622:
618:
617:the periphery
614:
611:
607:
603:
599:
595:
583:
578:
576:
571:
569:
564:
563:
561:
560:
557:
552:
547:
546:
537:
533:
521:
520:
513:
510:
508:
505:
503:
500:
498:
497:Kenneth Waltz
495:
493:
490:
488:
485:
483:
480:
478:
477:Susan Strange
475:
473:
470:
468:
465:
463:
460:
458:
455:
453:
450:
448:
445:
443:
440:
438:
435:
433:
432:Robert Jervis
430:
428:
425:
423:
420:
418:
417:Robert Gilpin
415:
413:
410:
408:
405:
403:
402:Cynthia Enloe
400:
398:
395:
393:
390:
388:
385:
383:
380:
378:
375:
373:
370:
369:
363:
362:
355:
352:
350:
347:
345:
344:Regime theory
342:
340:
337:
335:
332:
331:
325:
324:
317:
314:
311:
310:Great Debates
307:
305:
302:
300:
297:
295:
292:
291:
285:
284:
277:
274:
272:
269:
267:
264:
262:
261:Postmodernism
259:
256:
252:
251:Functionalism
249:
247:
244:
242:
239:
237:
234:
232:
229:
227:
224:
221:
217:
214:
212:
209:
207:
204:
202:
199:
197:
194:
193:
187:
186:
179:
176:
174:
171:
169:
166:
164:
161:
159:
156:
154:
151:
149:
146:
144:
141:
140:
137:
132:
131:
124:
121:
119:
116:
114:
111:
109:
106:
105:
102:
97:
96:
89:
86:
84:
81:
79:
76:
74:
71:
69:
66:
65:
62:
57:
56:
49:
46:
45:
42:
37:
36:
33:
29:
21:
3224:
3197:
3174:
3151:
3123:
3114:
3097:
3088:
3064:
3050:
3029:
3018:
2995:
2971:
2944:
2929:
2924:
2915:
2884:
2880:
2870:
2860:
2737:
2684:
2576:
2551:Second World
2483:South Africa
2329:
2310:South Africa
2134:
2035:South Africa
2022:Saudi Arabia
1662:
1550:Saudi Arabia
1309:
1295:core nations
1264:
1261:A ballot box
1236:
1228:
1197:Africa like
1183:
1179:Fourth World
1175:Saudi Arabia
1163:
1146: Medium
1053:
1038:
1029:
1014:Please help
1002:
963:
942:
935:
919:
897:
880:
867:
835:
799:Black Plague
791:
735:
727:trade routes
714:13th century
703:
694:
690:
671:
650:
633:
629:
625:
601:
597:
591:
492:Stephen Walt
407:James Fearon
304:Reflectivism
236:Green theory
3113:Tausch, A.
2297:South Korea
2048:South Korea
1968:North Korea
1929:New Zealand
1576:South Korea
1283:sociologist
926:agriculture
892:aristocracy
876:Netherlands
846:Black Death
748:obstacles.
678:core states
507:Yan Xuetong
382:Hedley Bull
354:Geopolitics
299:Rationalism
178:Realpolitik
3238:Categories
2959:References
2468:Seychelles
1140: High
973:1914–today
842:capitalism
610:capitalist
604:) are the
524:Categories
512:Qin Yaqing
467:Joseph Nye
387:E. H. Carr
153:Neorealism
61:Liberalism
3106:0034-6446
2893:2238-6912
2688:Tausch A.
2284:Singapore
2217:Indonesia
2189:Hong Kong
2150:Argentina
2115:Venezuela
1862:Indonesia
1691:Argentina
1643:Venezuela
1563:Singapore
1431:Indonesia
1338:Argentina
1299:periphery
1291:democracy
1271:periphery
1152: Low
1073:Guatemala
1032:June 2010
1003:does not
952:1875–1914
908:1700–1875
856:1450–1700
780:1300–1450
750:Geography
724:Silk Road
686:periphery
613:countries
608:, mostly
3148:(1976).
3130:: KNAG.
3087:(1999).
3061:(1987).
2968:(1989).
2530:See also
2429:Malaysia
1996:Portugal
1730:Bulgaria
1537:Portugal
1483:Malaysia
1247:scarcity
1167:Americas
1117:and the
1075:and the
922:merchant
819:Crusades
815:Far East
722:Ancient
684:and the
668:Function
366:Scholars
231:Feminism
68:Idealism
3128:Utrecht
2934:article
2522:Uruguay
2496:Tunisia
2416:Jamaica
2401:Hungary
2332:Babones
2128:Vietnam
2102:Uruguay
2087:Ukraine
2009:Romania
1942:Nigeria
1836:Hungary
1810:Finland
1704:Austria
1678:Algeria
1604:Nigeria
1390:Finland
1325:Algeria
1285:at the
1253:Effects
1232:profits
1215:Senegal
1207:Nigeria
1024:removed
1009:sources
850:Red Sea
766:Baghdad
742:Mongols
731:Eurasia
729:across
136:Realism
101:Marxism
24:(2000).
3206:
3183:
3160:
3134:
3104:
3073:
3038:
3006:
2980:
2891:
2519:
2509:Turkey
2506:
2493:
2480:
2465:
2455:Panama
2452:
2442:Mexico
2439:
2426:
2413:
2398:
2385:
2372:
2362:Brazil
2359:
2349:Belize
2346:
2323:Taiwan
2320:
2307:
2294:
2281:
2269:Mexico
2266:
2253:
2243:Israel
2240:
2227:
2214:
2199:
2186:
2173:
2163:Brazil
2160:
2147:
2125:
2112:
2099:
2084:
2074:Turkey
2071:
2058:
2045:
2032:
2019:
2006:
1993:
1981:Poland
1978:
1965:
1955:Norway
1952:
1939:
1926:
1916:Mexico
1913:
1900:
1890:Israel
1887:
1872:
1859:
1846:
1833:
1823:Greece
1820:
1807:
1794:
1781:
1766:
1753:
1740:
1727:
1717:Brazil
1714:
1701:
1688:
1675:
1653:
1640:
1630:Turkey
1627:
1617:Taiwan
1614:
1601:
1586:
1573:
1560:
1547:
1534:
1524:Poland
1521:
1511:Norway
1508:
1496:Mexico
1493:
1480:
1467:
1454:
1444:Israel
1441:
1428:
1415:
1403:Greece
1400:
1387:
1374:
1361:
1351:Brazil
1348:
1335:
1322:
1243:demand
1239:supply
1217:, and
1190:Brazil
1156:
1150:
1144:
1138:
1132:
1105:
1099:
1093:
884:Slaves
813:, the
807:Venice
772:, and
641:Israel
596:, the
2887:(4).
2557:Notes
2375:Chile
2256:Macau
2202:India
2176:China
2061:Spain
1903:Italy
1849:India
1797:Egypt
1743:China
1656:Zaire
1589:Spain
1470:Italy
1418:India
1377:Egypt
1364:China
1267:cores
1211:Zaire
1203:Kenya
1199:Egypt
1083:Today
803:Genoa
770:Cairo
746:trade
3204:ISBN
3181:ISBN
3158:ISBN
3132:ISBN
3102:ISSN
3071:ISBN
3036:ISBN
3004:ISBN
2978:ISBN
2889:ISSN
2388:Fiji
2230:Iran
1875:Iran
1756:Cuba
1457:Iran
1194:Iran
1007:any
1005:cite
966:West
964:The
831:core
805:and
797:the
774:Aden
762:West
760:and
758:East
682:core
656:and
637:Iran
619:and
1115:IMF
1018:by
592:In
3240::
3126:.
3100:.
2998:.
2936:,
2901:^
2879:.
2834:^
2810:^
2746:^
2693:^
2672:^
2632:^
2602:^
2584:^
2564:^
1213:,
1209:,
1205:,
1201:,
1181:.
1119:UN
776:.
768:,
3212:.
3189:.
3166:.
3140:.
3117:.
3108:.
3091:.
3079:.
3053:.
3044:.
3021:.
3012:.
2986:.
2895:.
2885:2
1111:)
1045:)
1039:(
1034:)
1030:(
1026:.
1012:.
581:e
574:t
567:v
312:"
308:"
257:)
253:(
222:)
218:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.