863:
they are almost vertical, and in the lower part they are nearly horizontal. In the lumbar region they are nearly horizontal. The spinous processes are separated by considerable intervals in the lumbar region, by narrower intervals in the neck, and are closely approximated in the middle of the thoracic region. Occasionally one of these processes deviates a little from the median line — which can sometimes be indicative of a fracture or a displacement of the spine. On either side of the spinous processes is the vertebral groove formed by the laminae in the cervical and lumbar regions, where it is shallow, and by the laminae and transverse processes in the thoracic region, where it is deep and broad; these grooves lodge the deep muscles of the back. Lateral to the spinous processes are the articular processes, and still more laterally the transverse processes. In the thoracic region, the transverse processes stand backward, on a plane considerably behind that of the same processes in the cervical and lumbar regions. In the cervical region, the transverse processes are placed in front of the articular processes, lateral to the pedicles and between the intervertebral foramina. In the thoracic region they are posterior to the pedicles, intervertebral foramina, and articular processes. In the lumbar region they are in front of the articular processes, but behind the intervertebral foramina.
59:
1633:. The shape of the vertebral body does, however, vary somewhat between different groups. In mammals, such as humans, it typically has flat upper and lower surfaces, while in reptiles the anterior surface commonly has a concave socket into which the expanded convex face of the next vertebral body fits. Even these patterns are only generalisations, however, and there may be variation in form of the vertebrae along the length of the spine even within a single species. Some unusual variations include the saddle-shaped sockets between the cervical vertebrae of birds and the presence of a narrow hollow canal running down the centre of the vertebral bodies of
413:
1336:
1257:
1112:
446:
1741:
347:(Top to bottom or head to pelvis). The number of those in the cervical region, however, is only rarely changed, while that in the coccygeal region varies most. Excluding rare deviations, the total number of vertebrae ranges from 32 to 35. In about 10% of people, both the total number of pre-sacral vertebrae and the number of vertebrae in individual parts of the spine can vary. The most frequent deviations are: 11 (rarely 13) thoracic vertebrae, 4 or 6 lumbar vertebrae, 3 or 5 coccygeal vertebrae (rarely up to 7).
957:
process termed resegmentation. Disruption of the somitogenesis process in humans results in diseases such as congenital scoliosis. So far, the human homologues of three genes associated to the mouse segmentation clock, (MESP2, DLL3 and LFNG), have been shown to be mutated in cases of congenital scoliosis, suggesting that the mechanisms involved in vertebral segmentation are conserved across vertebrates. In humans the first four somites are incorporated in the base of the
2149:
1543:
872:
articulation with the heads of the ribs. More posteriorly are the intervertebral foramina, formed by the juxtaposition of the vertebral notches, oval in shape, smallest in the cervical and upper part of the thoracic regions and gradually increasing in size to the last lumbar. They transmit the special spinal nerves and are situated between the transverse processes in the cervical region and in front of them, in the thoracic and lumbar regions.
420:
47:
806:
1026:
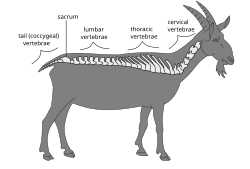
463:, which correspond to the curvatures of the vertebral column. The articulating vertebrae are named according to their region of the spine. Vertebrae in these regions are essentially alike, with minor variation. These regions are called the cervical spine, thoracic spine, lumbar spine, sacrum, and coccyx. There are seven cervical vertebrae, twelve thoracic vertebrae, and five lumbar vertebrae.
479:
1595:, the vertebrae consist of two cartilaginous tubes. The upper tube is formed from the vertebral arches, but also includes additional cartilaginous structures filling in the gaps between the vertebrae, and so enclosing the spinal cord in an essentially continuous sheath. The lower tube surrounds the notochord, and has a complex structure, often including multiple layers of
1711:, which are hollow depressions on the lateral portions of the vertebrae, perforated to create an entrance into the air chambers within the vertebrae, which served to decrease the weight of these bones without sacrificing strength. These pleurocoels were filled with air sacs, which would have further decreased weight. In
767:. These curves increase the vertebral column's strength, flexibility, and ability to absorb shock, stabilising the body in upright position. When the load on the spine is increased, the curvatures increase in depth (become more curved) to accommodate the extra weight. They then spring back when the weight is removed.
1383:
The general structure of vertebrae in other animals is largely the same as in humans. Individual vertebrae are composed of a centrum (body), arches protruding from the top and bottom of the centrum, and various processes projecting from the centrum and/or arches. An arch extending from the top of the
956:
which will form the skin of the back. Sclerotomes become subdivided into an anterior and a posterior compartment. This subdivision plays a key role in the definitive patterning of vertebrae that form when the posterior part of one somite fuses to the anterior part of the consecutive somite during a
813:
The lumbar curve is more marked in the female than in the male; it begins at the middle of the last thoracic vertebra, and ends at the sacrovertebral angle. It is convex anteriorly, the convexity of the lower three vertebrae being much greater than that of the upper two. This curve is described as a
466:
The number of vertebrae in a region can vary but overall the number remains the same. The number of those in the cervical region, however, is only rarely changed. The vertebrae of the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spines are independent bones and generally quite similar. The vertebrae of the sacrum
1094:
follows the different curves of the column; it is large and triangular in those parts of the column that enjoy the greatest freedom of movement, such as the cervical and lumbar regions, and is small and rounded in the thoracic region, where motion is more limited. The spinal cord terminates in the
871:
The sides of the vertebral column are separated from the posterior surface by the articular processes in the cervical and thoracic regions and by the transverse processes in the lumbar region. In the thoracic region, the sides of the bodies of the vertebrae are marked in the back by the facets for
862:
From behind, the vertebral column presents in the median line the spinous processes. In the cervical region (with the exception of the second and seventh vertebrae), these are short, horizontal, and bifid. In the upper part of the thoracic region they are directed obliquely downward; in the middle
853:
When viewed from in front, the width of the bodies of the vertebrae is seen to increase from the second cervical to the first thoracic; there is then a slight diminution in the next three vertebrae. Below this, there is again a gradual and progressive increase in width as low as the sacrovertebral
1666:
In birds, there is a variable number of cervical vertebrae, which often form the only truly flexible part of the spine. The thoracic vertebrae are partially fused, providing a solid brace for the wings during flight. The sacral vertebrae are fused with the lumbar vertebrae, and some thoracic and
1509:
are called thoracic vertebrae, while those without ribs are called lumbar vertebrae. The sacral vertebrae are those in the pelvic region, and range from one in amphibians, to two in most birds and modern reptiles, or up to three to five in mammals. When multiple sacral vertebrae are fused into a
1400:
with long tails. The vertebral processes can either give the structure rigidity, help them articulate with ribs, or serve as muscle attachment points. Common types are transverse process, diapophyses, parapophyses, and zygapophyses (both the cranial zygapophyses and the caudal zygapophyses). The
1644:
Reptiles often retain the primitive intercentra, which are present as small crescent-shaped bony elements lying between the bodies of adjacent vertebrae; similar structures are often found in the caudal vertebrae of mammals. In the tail, these are attached to chevron-shaped bones called
1227:
Scalloping vertebrae is the increase in the concavity of the posterior vertebral body. It can be seen on lateral X-ray and sagittal views of CT and MRI scans. Its concavity is due to the increased pressure exerting on the vertebrae due to a mass. Internal spinal mass such as spinal
786:
1688:
are among the few exceptions), followed by around twenty or so further vertebrae, divided between the thoracic and lumbar forms, depending on the number of ribs. There are generally three to five vertebrae with the sacrum, and anything up to fifty caudal vertebrae.
1440:-shaped articular surfaces. This type of configuration is seen in turtles that retract their necks, and birds, because it permits extensive lateral and vertical flexion motion without stretching the nerve cord too extensively or wringing it about its long axis.
1563:
consist of three discrete bony elements. The vertebral arch surrounds the spinal cord, and is of broadly similar form to that found in most other vertebrates. Just beneath the arch lies a small plate-like pleurocentrum, which protects the upper surface of the
797:
The thoracic curve, concave forward, begins at the middle of the second and ends at the middle of the twelfth thoracic vertebra. Its most prominent point behind corresponds to the spinous process of the seventh thoracic vertebra. This curve is known as a
840:, and are developed after birth. The cervical curve forms when the infant is able to hold up its head (at three or four months) and sit upright (at nine months). The lumbar curve forms later from twelve to eighteen months, when the child begins to walk.
1223:
that causes changes in its function, either temporary or permanent. Spinal cord injuries can be divided into categories: complete transection, hemisection, central spinal cord lesions, posterior spinal cord lesions, and anterior spinal cord lesions.
1011:
The primary curves (thoracic and sacral curvatures) form during fetal development. The secondary curves develop after birth. The cervical curvature forms as a result of lifting the head and the lumbar curvature forms as a result of walking.
318:
The number of vertebrae in a region can vary but overall the number remains the same. In a human vertebral column, there are normally 33 vertebrae. The upper 24 pre-sacral vertebrae are articulating and separated from each other by
1715:
dinosaurs, the largest known land vertebrates, pleurocoels and air sacs may have reduced the animal's weight by over a ton in some instances, a handy evolutionary adaption in animals that grew to over 30 metres in length. In many
1572:, but in the evolutionary line that led to reptiles (and hence, also to mammals and birds), the intercentrum became partially or wholly replaced by an enlarged pleurocentrum, which in turn became the bony vertebral body. In most
1609:. Even the arches are discontinuous, consisting of separate pieces of arch-shaped cartilage around the spinal cord in most parts of the body, changing to long strips of cartilage above and below in the tail region.
1568:, and below that, a larger arch-shaped intercentrum to protect the lower border. Both of these structures are embedded within a single cylindrical mass of cartilage. A similar arrangement was found in the primitive
1275:
is an exaggerated kyphotic (convex) curvature of the thoracic region in the sagittal plane, also called hyperkyphosis. This produces the so-called "humpback" or "dowager's hump", a condition commonly resulting from
1724:
dinosaurs, the caudal vertebrae were reinforced by ossified tendons. The presence of three or more sacral vertebrae, in association with the hip bones, is one of the defining characteristics of dinosaurs. The
931:
and continues until all somites are formed. Their number varies between species: there are 42 to 44 somites in the human embryo and around 52 in the chick embryo. The somites are spheres, formed from the
219:
There are around 50,000 species of animals that have a vertebral column. The human spine is one of the most-studied examples, as the general structure of human vertebrae is fairly typical (
1198:
is a narrowing of the spinal canal which can occur in any region of the spine though less commonly in the thoracic region. The stenosis can constrict the spinal canal giving rise to a
948:, which give rise to some of the bone of the skull, the vertebrae and ribs, migrate, leaving the remainder of the somite now termed a dermamyotome behind. This then splits to give the
2268:
O'Rahilly R, Müller F (2003). "Somites, spinal
Ganglia, and centra. Enumeration and interrelationships in staged human embryos, and implications for neural tube defects".
936:
that lies at the sides of the neural tube and they contain the precursors of spinal bone, the vertebrae ribs and some of the skull, as well as muscle, ligaments and skin.
1916:
4025:
2163:
Betts, J Gordon; Desaix, Peter; Johnson, Eddie; Johnson, Jody E; Korol, Oksana; Kruse, Dean; Poe, Brandon; Wise, James; Womble, Mark D; Young, Kelly A (May 14, 2023).
961:
of the skull and the next 33 somites will form the vertebrae, ribs, muscles, ligaments and skin. The remaining posterior somites degenerate. During the fourth week of
2471:
Kouwenhoven, Jan-Willem; Vincken, Koen L.; Bartels, Lambertus W.; Castelein, Rene M. (2006). "Analysis of preexistent vertebral rotation in the normal spine".
1420:
vertebra have centra with both ends concave. This shape is common in fish, where most motion is limited. Amphicoelous centra often are integrated with a full
1291:
1673:, which is thus of greater relative length than the sacrum of mammals. In living birds, the remaining caudal vertebrae are fused into a further bone, the
1447:(breed) can have one less vertebrae and pair of ribs. This anomaly disappears in foals that are the product of an Arabian and another breed of horse.
3748:
2767:
1580:, these two structures are fused with, and embedded within, a solid piece of bone superficially resembling the vertebral body of mammals. In living
2075:"Variation in Global Spinal Sagittal Parameters in Asymptomatic Adults with 11 Thoracic Vertebrae, four Lumbar Vertebrae, and six Lumbar Vertebrae"
1432:
vertebrae are the opposite, possessing anterior convexity and posterior concavity. They are found in salamanders, and in some non-avian dinosaurs.
3602:
3311:
2900:
1514:
is a similar fused structure found in birds that is composed of the sacral, lumbar, and some of the thoracic and caudal vertebra, as well as the
654:
above and below each vertebra, articulating with those of the adjacent vertebrae and are joined by a thin portion of the neural arch called the
4463:
2890:
1766:
1584:, there is simply a cylindrical piece of bone below the vertebral arch, with no trace of the separate elements present in the early tetrapods.
1177:
1005:
1455:
Vertebrae are defined by their location in the vertebral column. Cervical vertebrae are those in the neck area. With the exception of the two
58:
3533:
3404:
2355:
2252:
2172:
2131:
1949:
1891:
1863:
1827:
1800:
2586:
2221:
4018:
1613:
lack a true vertebral column, and are therefore not properly considered vertebrates, but a few tiny neural arches are present in the tail.
1409:, the pleurocentrum and the intercentrum are separate ossifications. Fused elements, however, classify a vertebra as having holospondyly.
1481:), all mammals have seven cervical vertebrae. In other vertebrates, the number of cervical vertebrae can range from a single vertebra in
3713:
3671:
2609:
1680:
Aside from the tail, the number of vertebrae in mammals is generally fairly constant. There are almost always seven cervical vertebrae (
2628:
2716:
2691:
1000:
The notochord disappears in the sclerotome (vertebral body) segments but persists in the region of the intervertebral discs as the
778:
and ends at the middle of the second thoracic vertebra; it is the least marked of all the curves. This inward curve is known as a
880:
There are different ligaments involved in the holding together of the vertebrae in the column, and in the column's movement. The
460:
239:
4011:
3398:
2049:
1908:
1199:
885:
359:
1416:, like those in mammals. These flat ends of the centra are especially good at supporting and distributing compressive forces.
3379:
1659:
of fish. The number of vertebrae in the spines of reptiles is highly variable, and may be several hundred in some species of
881:
355:
1833:
927:
are rhythmically added to the posterior of the embryo. Somite formation begins around the third week when the embryo begins
1366:
and also as vertical reference points to describe the locations of other parts of human anatomy, such as the positions of
1300:, lateral curvature, is the most common abnormal curvature, occurring in 0.5% of the population. It is more common among
4478:
3741:
2979:
2880:
2818:
2760:
1128:
1068:
605:
503:
1335:
664:
between the vertebrae. Underneath each pedicle is a small hole (enclosed by the pedicle of the vertebral below) called
4468:
3304:
1938:
Watson, Charles; Paxinos, George; Kayalioglu, Gulgun, eds. (2008). "Chapter 1 - The
Organization of the Spinal Cord".
3259:
2153:
1974:"A neglected point in surgical treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: Variations in the number of vertebrae"
1076:
1308:
of the two sides of one or more vertebrae, so that they do not fuse properly. It can also be caused by pulmonary
1147:
3982:
3073:
3044:
2813:
1651:, which attach below the base of the spine, and help to support the musculature. These latter bones are probably
1056:
941:
601:
303:
1256:
4483:
4473:
3516:
3511:
3494:
3489:
3484:
3068:
3061:
3056:
2516:"Opposite asymmetries of face and trunk and of kissing and hugging, as predicted by the axial twist hypothesis"
566:
387:
3806:
1729:
is a structure on the posterior part of a dinosaur's skull that articulates with the first cervical vertebra.
1412:
A vertebra can also be described in terms of the shape of the ends of the centrum. Centra with flat ends are
624:, the latter also being known as the neural spine. The transverse and spinous processes and their associated
3734:
3607:
3479:
3474:
3469:
3464:
3459:
3454:
3449:
3444:
3439:
3414:
3371:
3366:
3361:
3356:
3351:
3346:
3341:
3336:
2972:
2920:
2753:
209:
2610:"Why do almost all mammals have seven cervical vertebrae? Developmental constraints, Hox genes, and cancer"
1740:
1170:, also known as a pars defect, is a defect or fracture at the pars interarticularis of the vertebral arch.
636:. The spinous processes of the cervical and lumbar regions can be felt through the skin, and are important
235:. The shape of the vertebral body does, however, vary somewhat between different groups of living species.
3987:
3845:
3297:
2915:
2835:
1754:
1173:
1052:
977:. This column of tissue has a segmented appearance, with alternating areas of dense and less dense areas.
953:
916:
665:
412:
299:
94:
31:
4488:
3992:
3676:
3647:
3642:
3637:
3632:
3627:
3573:
3568:
3563:
3558:
3553:
3419:
2967:
2962:
2910:
896:
extends the length of the spine running along the back of the spinous processes, from the sacrum to the
893:
889:
656:
431:
is an area of the skin that sends sensory messages to a specific spinal nerve (right). The effects of a
379:
375:
1286:
is an exaggerated lordotic (concave) curvature of the lumbar region in the sagittal plane, is known as
2579:"Sticking Their Necks out for Evolution: Why Sloths and Manatees Have Unusually Long (or Short) Necks"
1428:
vertebrae are anteriorly concave and posteriorly convex. They are found in frogs and modern reptiles.
1111:
3090:
2845:
1287:
949:
673:
633:
3969:
3085:
3080:
2850:
2735:
1939:
1359:
1181:
994:
962:
920:
828:
The thoracic and sacral kyphotic curves are termed primary curves, because they are present in the
745:
Thoracolumbar spine (or region or division): the combined region of the thoracic vertebrae and the
707:
523:
428:
320:
181:
445:
3506:
3409:
3274:
3236:
3216:
3027:
3007:
2949:
2939:
2885:
2872:
2578:
2496:
2293:
1652:
1606:
1305:
1216:
897:
740:
736:
689:
683:
617:
499:
432:
391:
340:
336:
220:
178:
163:
3977:
2217:
888:
extend the length of the vertebral column along the front and back of the vertebral bodies. The
751:
Lumbosacral spine (or region or division): the combined region of the lumbar vertebrae and the
3893:
3867:
3590:
3264:
3049:
3032:
3002:
2830:
2712:
2687:
2632:
2547:
2488:
2453:
2402:
2351:
2321:
2285:
2248:
2168:
2127:
2104:
2011:
1993:
1945:
1887:
1859:
1823:
1796:
1726:
1527:
1348:
1344:
1153:
1080:
933:
900:
641:
613:
609:
554:
538:
367:
283:
275:
263:
2640:
467:
and coccyx are usually fused and unable to move independently. Two special vertebrae are the
4156:
3862:
3772:
3701:
2989:
2895:
2803:
2624:
2537:
2527:
2480:
2443:
2433:
2392:
2384:
2277:
2094:
2086:
2001:
1985:
1701:
consists of the cervical (neck), dorsal (back), sacral (hips), and caudal (tail) vertebrae.
1569:
1542:
1185:
1096:
1084:
1048:
1001:
752:
746:
701:
695:
519:
371:
363:
344:
185:
335:. The articulating vertebrae are named according to their region of the spine. There are 7
3937:
3905:
3688:
3521:
3431:
3390:
3385:
3328:
3241:
3231:
2905:
2855:
2823:
2157:
2148:
1406:
1367:
1363:
1355:
1195:
904:
661:
637:
621:
534:
507:
468:
383:
279:
271:
267:
4174:
821:
The sacral curve begins at the sacrovertebral articulation, and ends at the point of the
785:
4493:
4431:
4341:
4289:
4146:
3910:
3898:
3757:
3181:
2932:
2927:
2808:
2542:
2515:
2484:
2448:
2421:
2397:
2372:
2099:
2074:
2006:
1746:
1588:
1573:
1547:
1358:, with reference points are taken from the middle of the vertebral body. This provides
1323:
1265:
1245:
1161:
1157:
981:
958:
775:
771:
578:
531:
511:
487:
472:
287:
166:
128:
46:
4457:
4366:
4356:
3959:
3942:
3888:
3825:
3659:
3619:
3585:
3545:
3269:
3251:
3226:
3208:
3186:
3164:
3100:
3039:
1973:
1771:
1761:
1647:
1596:
1560:
1515:
1444:
1402:
1167:
937:
436:
290:
in humans that can affect both the bony vertebrae and the intervertebral discs, with
2297:
2037:
1176:, more commonly called a "slipped disc", is the result of a tear in the outer ring (
805:
4351:
3852:
3320:
3095:
2957:
2862:
2679:
2500:
1554:
1497:
1317:
1277:
1241:
1124:
1100:
1091:
1072:
1064:
1044:
928:
669:
584:
574:
562:
542:
307:
213:
205:
189:
155:
143:
1401:
centrum of the vertebra can be classified based on the fusion of its elements. In
1131:
in which there is a defective closure of the vertebral arch. Sometimes the spinal
731:
For some medical purposes, adjacent vertebral regions may be considered together:
1817:
1312:(partial or complete deflation of one or more lobes of the lungs) as observed in
4436:
4361:
4262:
4124:
4109:
3883:
3840:
3811:
3196:
3191:
3176:
2312:
1989:
1605:
have vertebral arches, but nothing resembling the vertebral bodies found in all
1385:
1309:
1229:
1220:
1060:
1038:
1030:
1025:
984:. Development of the appropriate shapes of the vertebral bodies is regulated by
980:
As the sclerotome develops, it condenses further eventually developing into the
970:
651:
648:
550:
546:
201:
197:
193:
854:
angle. From this point there is a rapid diminution, to the apex of the coccyx.
188:
is a notochord remnant). The dorsal portion of the vertebral column houses the
17:
4406:
4279:
4230:
4104:
4056:
4048:
4042:
4034:
3947:
3159:
2740:
2388:
1736:
1707:
1702:
1493:
1477:
1237:
1233:
1210:
993:
The less dense tissue that separates the sclerotome segments develop into the
966:
945:
764:
726:
722:
478:
132:
1997:
1518:. Caudal vertebrae compose the tail, and the final few can be fused into the
4378:
4257:
4094:
3932:
3924:
3790:
3221:
3154:
1717:
1674:
1669:
1621:
The general structure of human vertebrae is fairly typical of that found in
1581:
1565:
1523:
1519:
1511:
1482:
1461:
1421:
1297:
974:
558:
295:
170:
147:
139:
2636:
2551:
2492:
2457:
2406:
2325:
2289:
2247:(Pbk. ed.). Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. p. 45.
2108:
2015:
1501:. The dorsal vertebrae range from the bottom of the neck to the top of the
1354:
Individual vertebrae of the human vertebral column can be felt and used as
1260:
Diagram showing normal curvature of the vertebrae from childhood to teenage
1164:
with respect to the adjacent vertebra to a degree less than a dislocation.
419:
2629:
10.1002/(SICI)1097-010X(19990415)285:1<19::AID-JEZ3>3.0.CO;2-Z
735:
Cervicothoracic spine (or region or division): the combined region of the
4386:
4306:
4141:
4074:
4003:
3952:
3857:
3785:
3780:
3141:
2788:
1721:
1712:
1698:
1467:
1283:
1272:
1132:
986:
815:
799:
779:
770:
The upper cervical spine has a curve, convex forward, that begins at the
625:
570:
403:
351:
291:
174:
159:
151:
2438:
1043:
The vertebral column surrounds the spinal cord which travels within the
4321:
4267:
4213:
4203:
4089:
2532:
1685:
1638:
1626:
1610:
1602:
1577:
1490:
1472:
1393:
1135:
and also the spinal cord can protrude through this, and this is called
924:
495:
251:
228:
2281:
1139:. Where the condition does not involve this protrusion it is known as
944:
acting in cells of the paraxial mesoderm. Soon after their formation,
825:; its concavity is directed downward and forward as a kyphotic curve.
459:
The vertebrae in the human vertebral column is divided into different
100:
4336:
4311:
4252:
4245:
4240:
4235:
4179:
4119:
4099:
3132:
3112:
3019:
2745:
2090:
1622:
1502:
1437:
1397:
1313:
1301:
1206:
1189:
822:
594:
590:
328:
324:
255:
247:
224:
135:
2711:(Second ed.). Oxford: Blackwell Publishing. pp. 299–300.
2686:. Philadelphia, PA: Holt-Saunders International. pp. 161–170.
553:. Because the vertebral column will outgrow the spinal cord during
453:
Spinal nerves exit the spinal cord between each pair of vertebrae.
4416:
4396:
4346:
4326:
4316:
4272:
4218:
4208:
4194:
4151:
4079:
2780:
1793:
Functional anatomy of the vertebrates: an evolutionary perspective
1681:
1660:
1634:
1592:
1541:
1531:
1456:
1388:
is found underneath the centrum in the caudal (tail) vertebrae of
1340:
1255:
1024:
829:
804:
790:
784:
774:(second cervical vertebra) at the apex of the odontoid process or
82:
3726:
4421:
4411:
4401:
4331:
4184:
4166:
4084:
4069:
4064:
3289:
2776:
1630:
1486:
1389:
629:
259:
243:
238:
Individual vertebrae are named according to their corresponding
232:
64:
4007:
3730:
3293:
2749:
1143:. Sometimes all of the vertebral arches may remain incomplete.
4426:
4391:
4298:
4136:
4131:
4114:
3149:
2038:"Numerical vertebral variations in the human adult and embryo"
1656:
1506:
1268:
or dorsopathy and includes the following abnormal curvatures:
940:
and the subsequent distribution of somites is controlled by a
892:
connect the adjoining spinous processes of the vertebrae. The
763:
The vertebral column is curved in several places, a result of
527:
2202:
Palastanga N, Soames RW (2012). Churchill
Livingstone (ed.).
2311:
Peabody, Tucker; Black, Asa C.; Das, Joe M. (8 April 2023).
1858:. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. p. 17.
1290:
and also as "swayback". Temporary lordosis is common during
1150:, which is the fusion of any two of the cervical vertebrae.
1705:
dinosaur vertebrae sometimes possess features known as
1264:
Excessive or abnormal spinal curvature is classed as a
1055:
that supplies nerves and receives information from the
354:
extending the length of the column, which include the
323:, and the lower nine are fused in adults, five in the
30:"Spine (anatomy)" redirects here. For other uses, see
1822:. Benjamin-Cummings Publishing Company. p. 333.
1184:, which lets some of the soft gel-like material, the
2420:
Baig MN, Byrne F, Devitt A, McCabe JP (April 2018).
660:. The orientation of the facet joints restricts the
4377:
4297:
4288:
4193:
4165:
4055:
4041:
3968:
3923:
3876:
3833:
3824:
3799:
3771:
3764:
3687:
3618:
3544:
3430:
3327:
3250:
3207:
3140:
3131:
3111:
3018:
2988:
2948:
2871:
2796:
2787:
2167:. Houston: OpenStax CNX. 7.3 The Vertebral Column.
573:-like bundle of spinal nerves descriptively called
81:
76:
71:
39:
2371:Patel R, Appannagari A, Whang PG (December 2008).
2350:(32nd ed.). Elsevier Saunders. p. 1748.
2204:Anatomy and Human Movement: Structure and Function
1667:caudal vertebrae, to form a single structure, the
600:The vertebral arch is formed by a ventral pair of
1984:(34). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: e4682.
526:) and provides articulations and anchorages for
1886:. New York: Crown Publishers, Inc. p. 34.
1510:single structure, it is called the sacrum. The
1362:that can be used to guide procedures such as a
1115:3D Medical Animation still shot of Spina Bifida
2243:Drake RL, Gray H, Mitchell AW, Vogl W (2005).
1877:
1875:
1854:Drake RL, Vogl W, Mitchell AW, Gray H (2005).
1156:is the forward displacement of a vertebra and
1079:to the body, with nerves emerging forming the
647:The four articular processes for two pairs of
486:A typical vertebra consists of two parts: the
4019:
3742:
3305:
2761:
2073:Ying-zhao, Yan; et al. (February 2022).
1059:within the body. The spinal cord consists of
1004:. The nucleus pulposus and the fibers of the
8:
1795:. Harcourt College Publishers. p. 277.
1146:Another, though rare, congenital disease is
704:(pelvis region): 5 (fused) vertebrae (S1–S5)
2377:Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine
2188:
2186:
2184:
1384:centrum is called a neural arch, while the
919:pattern of the spine is established during
569:) end of the spinal canal is occupied by a
162:has been replaced by a segmented series of
138:. The vertebral column is the defining and
4294:
4026:
4012:
4004:
3830:
3768:
3749:
3735:
3727:
3312:
3298:
3290:
3137:
2793:
2768:
2754:
2746:
2059:– via Biodiversity Heritage Library.
1326:, a combination of kyphosis and scoliosis.
809:Lateral lumbar X-ray of a 34-year-old male
266:, features on vertebrae (particularly the
57:
51:The human vertebral column and its regions
45:
2541:
2531:
2447:
2437:
2396:
2098:
2005:
1909:"Numerical Variation in Vertebral Column"
1641:, containing a remnant of the notochord.
1047:, formed from a central hole within each
692:(chest/upper back): 12 vertebrae (T1–T12)
439:(left). S1-S5 are part of the os sacrum.
2741:VIRTUAL Spine – online learning resource
2348:Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary
1334:
1110:
628:serve as important attachment sites for
561:the spinal cord often ends at the upper
541:, the series of which align to form the
477:
3603:Posterior branches of the lumbar nerves
1783:
1677:, for attachment of the tail feathers.
903:. From there it is continuous with the
679:From top to bottom, the vertebrae are:
2709:Introduction to the Study of Dinosaurs
1767:Neuromechanics of idiopathic scoliosis
1546:A vertebra (diameter 5 mm) of a small
1396:, some birds, some dinosaurs and some
98:
36:
3534:Posterior branches of thoracic nerves
3405:Posterior branches of cervical nerves
2674:
2672:
2670:
2668:
2666:
2664:
2662:
2660:
2085:(2). John Wiley & Sons: 341–348.
2068:
2066:
1819:Biology: A Guide to the Natural World
1339:Surface projections of organs of the
969:shift their position to surround the
832:. The cervical and lumbar curves are
597:are fused without a central foramen.
196:formed by alignment of the vertebral
7:
2422:"Signs of Nature in Spine Radiology"
710:(tailbone): 4 (3–5, fused) vertebrae
565:(at around L1/L2 level), the lower (
3714:Posterior branch of coccygeal nerve
3672:Posterior branches of sacral nerves
2617:The Journal of Experimental Zoology
2320:. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls.
1505:. Dorsal vertebrae attached to the
1160:is a posterior displacement of one
1071:. Adjacent to each vertebra emerge
668:, which transmit the corresponding
27:Bony structure found in vertebrates
2589:from the original on 26 April 2019
2485:10.1097/01.brs.0000219938.14686.b3
1919:from the original on July 11, 2020
1907:Bergman RA, Afifi AK, Miyauchi R.
1882:Gray H, Pick TP, Howden R (1977).
25:
3517:Thoraco-abdominal nerves – T7–T11
2224:from the original on 13 July 2018
1051:. The spinal cord is part of the
1008:make up the intervertebral disc.
698:(lower back): 5 vertebrae (L1–L5)
142:characteristic of the vertebrate
2152: This article incorporates
2147:
1739:
952:which will form the muscles and
886:posterior longitudinal ligaments
444:
418:
411:
360:posterior longitudinal ligaments
286:. There are also many different
2052:from the original on 2021-04-10
1836:from the original on 2023-01-24
1033:nested in the vertebral column.
632:and paraspinal muscles and the
200:that encloses and protects the
2314:Anatomy, Back, Vertebral Canal
537:. Together, these enclose the
435:depend on the level along the
407:
1:
4464:Bones of the vertebral column
1555:Fish anatomy § Vertebrae
1248:causes vertebrae scalloping.
362:at the front and back of the
310:being recognizable examples.
3970:Intervertebral disc disorder
2980:Uncinate process of vertebra
2881:Uncinate process of vertebra
2514:de Lussanet, M.H.E. (2019).
2126:. McGraw-Hill. p. 565.
1972:Hu, Zongshan (August 2016).
1075:. The spinal nerves provide
676:that exit the spinal canal.
504:standard anatomical position
2245:Gray's anatomy for students
1990:10.1097/MD.0000000000004682
1856:Gray's anatomy for students
1791:Liem KF, Walker WF (2001).
686:(neck): 7 vertebrae (C1–C7)
475:, on which the head rests.
4510:
3260:Superior thoracic aperture
1752:
1552:
1077:sympathetic nervous supply
1067:and a central cavity, the
1036:
720:
715:Combined vertebral regions
401:
127:, is the core part of the
29:
3983:Degenerative disc disease
3074:posterior sacral foramina
2389:10.1007/s12178-008-9028-1
1057:peripheral nervous system
942:clock and wavefront model
452:
443:
426:
388:intertransverse ligaments
223:) of that found in other
93:
56:
44:
3062:anterior sacral foramina
2165:Anatomy & Physiology
2124:Anatomy & Physiology
1697:The vertebral column in
3512:Intercostobrachial – T2
1379:Variations in vertebrae
1209:(tailbone) is known as
765:human bipedal evolution
506:) and withstands axial
210:intervertebral foramina
4035:Human regional anatomy
3988:Spinal disc herniation
3846:Ankylosing spondylitis
3608:Superior cluneal L1–L3
3415:Greater occipital – C2
2836:Intervertebral foramen
2608:Galis F (April 1999).
2218:"interspinal ligament"
2036:Bardeen, C.R. (1904).
1755:anatomical terminology
1550:
1522:in birds, or into the
1351:
1261:
1174:Spinal disc herniation
1116:
1053:central nervous system
1034:
890:interspinous ligaments
810:
794:
793:of a 57-year-old male.
666:intervertebral foramen
483:
380:supraspinous ligaments
300:ankylosing spondylitis
95:Anatomical terminology
63:Vertebral column of a
32:Spine (disambiguation)
3993:Facet joint arthrosis
3807:Scheuermann's disease
3677:Medial cluneal nerves
2682:, Parsons TS (1977).
2192:Gray's Anatomy (1918)
2042:Anatomischer Anzeiger
1545:
1338:
1259:
1148:Klippel–Feil syndrome
1114:
1107:Clinical significance
1028:
894:supraspinous ligament
808:
788:
721:Further information:
657:pars interarticularis
634:thoracolumbar fasciae
608:, and supports seven
604:and a dorsal pair of
482:Anatomy of a vertebra
481:
3420:Third occipital – C3
3091:Lateral sacral crest
2736:Spinal Term Glossary
2270:Cells Tissues Organs
2156:available under the
1485:to as many as 25 in
1405:, bones such as the
1360:anatomical landmarks
1331:Anatomical landmarks
1304:and may result from
1288:lumbar hyperlordosis
1200:neurological deficit
1141:spina bifida occulta
1137:spina bifida cystica
995:intervertebral discs
674:dorsal root ganglion
392:transverse processes
321:intervertebral discs
182:intervertebral discs
115:, also known as the
4479:Bones of the thorax
3086:Medial sacral crest
3081:Median sacral crest
2684:The Vertebrate Body
2439:10.7759/cureus.2456
2346:Dorland WA (2012).
2220:. Merriam-Webster.
2079:Orthopaedic Surgery
1538:Fish and amphibians
1182:intervertebral disc
1129:congenital disorder
350:There are numerous
88:columna vertebralis
4469:Vertebrate anatomy
3275:Infrasternal angle
3237:Xiphisternal joint
3217:Suprasternal notch
2950:Thoracic vertebrae
2940:Vertebra prominens
2901:Posterior tubercle
2886:Transverse foramen
2873:Cervical vertebrae
2707:Martin AJ (2006).
2533:10.7717/peerj.7096
2122:Saladin K (2012).
1753:This article uses
1607:higher vertebrates
1589:cartilaginous fish
1561:lobe-finned fishes
1551:
1451:Regional vertebrae
1352:
1262:
1217:Spinal cord injury
1117:
1035:
811:
795:
741:thoracic vertebrae
737:cervical vertebrae
549:that contains the
484:
433:spinal cord injury
341:thoracic vertebrae
337:cervical vertebrae
304:degenerative discs
276:medical procedures
212:to innervate each
179:fibrocartilaginous
158:rod) found in all
4451:
4450:
4447:
4446:
4001:
4000:
3919:
3918:
3894:Spondylolisthesis
3820:
3819:
3724:
3723:
3591:Lumbosacral trunk
3410:Suboccipital – C1
3287:
3286:
3283:
3282:
3265:Intercostal space
3127:
3126:
3050:sacral tuberosity
3033:sacral promontory
2891:Anterior tubercle
2831:Vertebral foramen
2797:General structure
2585:. Science Daily.
2479:(13): 1467–1472.
2357:978-1-4160-6257-8
2282:10.1159/000068948
2254:978-0-443-06612-2
2174:978-1-947172-04-3
2133:978-0-07-337825-1
1951:978-0-12-374247-6
1944:. ScienceDirect.
1893:978-0-517-65293-0
1865:978-0-8089-2306-0
1829:978-0-321-61655-5
1802:978-0-03-022369-3
1727:occipital condyle
1617:Other vertebrates
1574:ray-finned fishes
1559:The vertebrae of
1345:transpyloric line
1219:is damage to the
1188:, bulge out in a
1154:Spondylolisthesis
1085:splanchnic nerves
1081:sympathetic trunk
934:paraxial mesoderm
901:cervical vertebra
858:Posterior surface
789:A thoracic spine
642:clinical medicine
638:surface landmarks
555:child development
539:vertebral foramen
457:
456:
384:spinous processes
368:ligamentum flavum
284:spinal anesthesia
272:surface landmarks
270:) can be used as
264:clinical medicine
109:
108:
104:
16:(Redirected from
4501:
4295:
4226:Vertebral column
4028:
4021:
4014:
4005:
3877:non inflammatory
3863:Spondylodiscitis
3831:
3773:Spinal curvature
3769:
3751:
3744:
3737:
3728:
3702:Coccygeal plexus
3314:
3307:
3300:
3291:
3138:
2990:Lumbar vertebrae
2896:Carotid tubercle
2794:
2770:
2763:
2756:
2747:
2723:
2722:
2704:
2698:
2697:
2676:
2655:
2654:
2652:
2651:
2645:
2639:. Archived from
2614:
2605:
2599:
2598:
2596:
2594:
2575:
2569:
2562:
2556:
2555:
2545:
2535:
2511:
2505:
2504:
2468:
2462:
2461:
2451:
2441:
2417:
2411:
2410:
2400:
2368:
2362:
2361:
2343:
2337:
2336:
2334:
2332:
2319:
2308:
2302:
2301:
2265:
2259:
2258:
2240:
2234:
2233:
2231:
2229:
2214:
2208:
2207:
2199:
2193:
2190:
2179:
2178:
2151:
2144:
2138:
2137:
2119:
2113:
2112:
2102:
2091:10.1111/os.13185
2070:
2061:
2060:
2058:
2057:
2033:
2027:
2026:
2024:
2022:
2009:
1969:
1963:
1962:
1960:
1958:
1935:
1929:
1928:
1926:
1924:
1904:
1898:
1897:
1879:
1870:
1869:
1851:
1845:
1844:
1842:
1841:
1816:Krogh D (2010).
1813:
1807:
1806:
1788:
1749:
1744:
1743:
1576:, including all
1526:or tail bone in
1186:nucleus pulposus
1097:conus medullaris
1002:nucleus pulposus
867:Lateral surfaces
849:Anterior surface
753:sacral vertebrae
747:lumbar vertebrae
535:skeletal muscles
448:
422:
415:
408:
364:vertebral bodies
345:lumbar vertebrae
327:and four in the
280:lumbar punctures
208:exiting via the
113:vertebral column
101:edit on Wikidata
61:
49:
40:Vertebral column
37:
21:
4509:
4508:
4504:
4503:
4502:
4500:
4499:
4498:
4484:Irregular bones
4474:Skeletal system
4454:
4453:
4452:
4443:
4373:
4284:
4189:
4161:
4051:
4037:
4032:
4002:
3997:
3978:Schmorl's nodes
3964:
3938:Upper back pain
3915:
3906:Spinal stenosis
3872:
3816:
3795:
3760:
3755:
3725:
3720:
3683:
3614:
3540:
3522:Subcostal – T12
3426:
3391:Brachial plexus
3386:Cervical plexus
3323:
3318:
3288:
3279:
3246:
3242:Xiphoid process
3232:Body of sternum
3203:
3123:
3107:
3045:Lateral surface
3014:
2984:
2944:
2867:
2783:
2774:
2732:
2727:
2726:
2719:
2706:
2705:
2701:
2694:
2678:
2677:
2658:
2649:
2647:
2643:
2612:
2607:
2606:
2602:
2592:
2590:
2577:
2576:
2572:
2563:
2559:
2513:
2512:
2508:
2470:
2469:
2465:
2419:
2418:
2414:
2370:
2369:
2365:
2358:
2345:
2344:
2340:
2330:
2328:
2317:
2310:
2309:
2305:
2267:
2266:
2262:
2255:
2242:
2241:
2237:
2227:
2225:
2216:
2215:
2211:
2201:
2200:
2196:
2191:
2182:
2175:
2162:
2145:
2141:
2134:
2121:
2120:
2116:
2072:
2071:
2064:
2055:
2053:
2035:
2034:
2030:
2020:
2018:
1971:
1970:
1966:
1956:
1954:
1952:
1941:The Spinal Cord
1937:
1936:
1932:
1922:
1920:
1906:
1905:
1901:
1894:
1881:
1880:
1873:
1866:
1853:
1852:
1848:
1839:
1837:
1830:
1815:
1814:
1810:
1803:
1790:
1789:
1785:
1780:
1758:
1745:
1738:
1735:
1695:
1619:
1570:Labyrinthodonts
1557:
1548:ray-finned fish
1540:
1453:
1443:In horses, the
1436:vertebrae have
1407:spinous process
1381:
1376:
1364:lumbar puncture
1356:surface anatomy
1333:
1254:
1196:Spinal stenosis
1178:anulus fibrosus
1122:
1109:
1041:
1023:
1018:
1006:anulus fibrosus
913:
905:nuchal ligament
878:
846:
761:
729:
717:
662:range of motion
514:(also known as
508:structural load
406:
400:
370:in deep to the
316:
288:spinal diseases
268:spinous process
192:, an elongated
186:center of which
177:, separated by
169:(or sometimes,
167:irregular bones
105:
67:
52:
35:
28:
23:
22:
18:Spine (anatomy)
15:
12:
11:
5:
4507:
4505:
4497:
4496:
4491:
4486:
4481:
4476:
4471:
4466:
4456:
4455:
4449:
4448:
4445:
4444:
4442:
4441:
4440:
4439:
4434:
4429:
4424:
4419:
4409:
4404:
4399:
4394:
4389:
4383:
4381:
4375:
4374:
4372:
4371:
4370:
4369:
4364:
4359:
4354:
4349:
4344:
4339:
4329:
4324:
4319:
4314:
4309:
4303:
4301:
4292:
4286:
4285:
4283:
4282:
4277:
4276:
4275:
4270:
4265:
4255:
4250:
4249:
4248:
4243:
4233:
4228:
4223:
4222:
4221:
4216:
4211:
4200:
4198:
4191:
4190:
4188:
4187:
4182:
4177:
4171:
4169:
4163:
4162:
4160:
4159:
4154:
4149:
4144:
4139:
4134:
4129:
4128:
4127:
4122:
4117:
4112:
4107:
4102:
4097:
4092:
4087:
4082:
4077:
4067:
4061:
4059:
4053:
4052:
4047:
4045:
4039:
4038:
4033:
4031:
4030:
4023:
4016:
4008:
3999:
3998:
3996:
3995:
3990:
3985:
3980:
3974:
3972:
3966:
3965:
3963:
3962:
3957:
3956:
3955:
3950:
3940:
3935:
3929:
3927:
3921:
3920:
3917:
3916:
3914:
3913:
3911:Facet syndrome
3908:
3903:
3902:
3901:
3899:Retrolisthesis
3891:
3886:
3880:
3878:
3874:
3873:
3871:
3870:
3868:Pott's disease
3865:
3860:
3855:
3850:
3849:
3848:
3837:
3835:
3828:
3822:
3821:
3818:
3817:
3815:
3814:
3809:
3803:
3801:
3797:
3796:
3794:
3793:
3788:
3783:
3777:
3775:
3766:
3762:
3761:
3758:Spinal disease
3756:
3754:
3753:
3746:
3739:
3731:
3722:
3721:
3719:
3718:
3717:
3716:
3706:
3705:
3704:
3693:
3691:
3685:
3684:
3682:
3681:
3680:
3679:
3674:
3664:
3663:
3662:
3651:
3650:
3645:
3640:
3635:
3630:
3624:
3622:
3616:
3615:
3613:
3612:
3611:
3610:
3605:
3595:
3594:
3593:
3588:
3577:
3576:
3571:
3566:
3561:
3556:
3550:
3548:
3542:
3541:
3539:
3538:
3537:
3536:
3526:
3525:
3524:
3519:
3514:
3509:
3498:
3497:
3492:
3487:
3482:
3477:
3472:
3467:
3462:
3457:
3452:
3447:
3442:
3436:
3434:
3428:
3427:
3425:
3424:
3423:
3422:
3417:
3412:
3407:
3395:
3394:
3393:
3388:
3375:
3374:
3369:
3364:
3359:
3354:
3349:
3344:
3339:
3333:
3331:
3325:
3324:
3319:
3317:
3316:
3309:
3302:
3294:
3285:
3284:
3281:
3280:
3278:
3277:
3272:
3267:
3262:
3256:
3254:
3248:
3247:
3245:
3244:
3239:
3234:
3229:
3224:
3219:
3213:
3211:
3205:
3204:
3202:
3201:
3200:
3199:
3194:
3189:
3184:
3179:
3169:
3168:
3167:
3162:
3157:
3146:
3144:
3135:
3129:
3128:
3125:
3124:
3122:
3121:
3117:
3115:
3109:
3108:
3106:
3105:
3104:
3103:
3093:
3088:
3083:
3078:
3077:
3076:
3069:Dorsal surface
3066:
3065:
3064:
3057:Pelvic surface
3054:
3053:
3052:
3042:
3037:
3036:
3035:
3024:
3022:
3016:
3015:
3013:
3012:
3011:
3010:
3005:
2994:
2992:
2986:
2985:
2983:
2982:
2977:
2976:
2975:
2970:
2965:
2954:
2952:
2946:
2945:
2943:
2942:
2937:
2936:
2935:
2925:
2924:
2923:
2921:posterior arch
2918:
2913:
2903:
2898:
2893:
2888:
2883:
2877:
2875:
2869:
2868:
2866:
2865:
2860:
2859:
2858:
2853:
2848:
2838:
2833:
2828:
2827:
2826:
2821:
2816:
2806:
2800:
2798:
2791:
2785:
2784:
2775:
2773:
2772:
2765:
2758:
2750:
2744:
2743:
2738:
2731:
2730:External links
2728:
2725:
2724:
2717:
2699:
2692:
2656:
2600:
2570:
2557:
2506:
2463:
2412:
2383:(3–4): 223–6.
2363:
2356:
2338:
2303:
2260:
2253:
2235:
2209:
2194:
2180:
2173:
2139:
2132:
2114:
2062:
2028:
1964:
1950:
1930:
1913:Anatomy Atlase
1899:
1892:
1884:Gray's Anatomy
1871:
1864:
1846:
1828:
1808:
1801:
1782:
1781:
1779:
1776:
1775:
1774:
1769:
1764:
1751:
1750:
1747:Anatomy portal
1734:
1731:
1694:
1691:
1618:
1615:
1539:
1536:
1452:
1449:
1430:Opisthocoelous
1380:
1377:
1375:
1372:
1332:
1329:
1328:
1327:
1324:Kyphoscoliosis
1321:
1306:unequal growth
1295:
1281:
1266:spinal disease
1253:
1250:
1246:achondroplasia
1162:vertebral body
1158:retrolisthesis
1121:
1118:
1108:
1105:
1037:Main article:
1022:
1019:
1017:
1014:
982:vertebral body
959:occipital bone
912:
909:
877:
874:
869:
868:
860:
859:
851:
850:
845:
842:
760:
757:
756:
755:
749:
743:
716:
713:
712:
711:
705:
699:
693:
690:Thoracic spine
687:
684:Cervical spine
512:vertebral arch
488:vertebral body
455:
454:
450:
449:
441:
440:
424:
423:
416:
402:Main article:
399:
396:
315:
312:
129:axial skeleton
107:
106:
97:
91:
90:
85:
79:
78:
74:
73:
69:
68:
62:
54:
53:
50:
42:
41:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4506:
4495:
4492:
4490:
4487:
4485:
4482:
4480:
4477:
4475:
4472:
4470:
4467:
4465:
4462:
4461:
4459:
4438:
4435:
4433:
4430:
4428:
4425:
4423:
4420:
4418:
4415:
4414:
4413:
4410:
4408:
4405:
4403:
4400:
4398:
4395:
4393:
4390:
4388:
4385:
4384:
4382:
4380:
4376:
4368:
4365:
4363:
4360:
4358:
4355:
4353:
4350:
4348:
4345:
4343:
4340:
4338:
4335:
4334:
4333:
4330:
4328:
4325:
4323:
4320:
4318:
4315:
4313:
4310:
4308:
4305:
4304:
4302:
4300:
4296:
4293:
4291:
4287:
4281:
4278:
4274:
4271:
4269:
4266:
4264:
4261:
4260:
4259:
4256:
4254:
4251:
4247:
4244:
4242:
4239:
4238:
4237:
4234:
4232:
4229:
4227:
4224:
4220:
4217:
4215:
4212:
4210:
4207:
4206:
4205:
4202:
4201:
4199:
4196:
4192:
4186:
4183:
4181:
4178:
4176:
4173:
4172:
4170:
4168:
4164:
4158:
4155:
4153:
4150:
4148:
4145:
4143:
4140:
4138:
4135:
4133:
4130:
4126:
4123:
4121:
4118:
4116:
4113:
4111:
4108:
4106:
4103:
4101:
4098:
4096:
4093:
4091:
4088:
4086:
4083:
4081:
4078:
4076:
4073:
4072:
4071:
4068:
4066:
4063:
4062:
4060:
4058:
4054:
4050:
4046:
4044:
4040:
4036:
4029:
4024:
4022:
4017:
4015:
4010:
4009:
4006:
3994:
3991:
3989:
3986:
3984:
3981:
3979:
3976:
3975:
3973:
3971:
3967:
3961:
3960:Radiculopathy
3958:
3954:
3951:
3949:
3946:
3945:
3944:
3943:Low back pain
3941:
3939:
3936:
3934:
3931:
3930:
3928:
3926:
3922:
3912:
3909:
3907:
3904:
3900:
3897:
3896:
3895:
3892:
3890:
3889:Spondylolysis
3887:
3885:
3882:
3881:
3879:
3875:
3869:
3866:
3864:
3861:
3859:
3856:
3854:
3851:
3847:
3844:
3843:
3842:
3839:
3838:
3836:
3832:
3829:
3827:
3826:Spondylopathy
3823:
3813:
3810:
3808:
3805:
3804:
3802:
3798:
3792:
3789:
3787:
3784:
3782:
3779:
3778:
3776:
3774:
3770:
3767:
3763:
3759:
3752:
3747:
3745:
3740:
3738:
3733:
3732:
3729:
3715:
3712:
3711:
3710:
3707:
3703:
3700:
3699:
3698:
3695:
3694:
3692:
3690:
3686:
3678:
3675:
3673:
3670:
3669:
3668:
3665:
3661:
3660:Sacral plexus
3658:
3657:
3656:
3653:
3652:
3649:
3646:
3644:
3641:
3639:
3636:
3634:
3631:
3629:
3626:
3625:
3623:
3621:
3617:
3609:
3606:
3604:
3601:
3600:
3599:
3596:
3592:
3589:
3587:
3586:Lumbar plexus
3584:
3583:
3582:
3579:
3578:
3575:
3572:
3570:
3567:
3565:
3562:
3560:
3557:
3555:
3552:
3551:
3549:
3547:
3543:
3535:
3532:
3531:
3530:
3527:
3523:
3520:
3518:
3515:
3513:
3510:
3508:
3505:
3504:
3503:
3500:
3499:
3496:
3493:
3491:
3488:
3486:
3483:
3481:
3478:
3476:
3473:
3471:
3468:
3466:
3463:
3461:
3458:
3456:
3453:
3451:
3448:
3446:
3443:
3441:
3438:
3437:
3435:
3433:
3429:
3421:
3418:
3416:
3413:
3411:
3408:
3406:
3403:
3402:
3401:
3400:
3396:
3392:
3389:
3387:
3384:
3383:
3382:
3381:
3377:
3376:
3373:
3370:
3368:
3365:
3363:
3360:
3358:
3355:
3353:
3350:
3348:
3345:
3343:
3340:
3338:
3335:
3334:
3332:
3330:
3326:
3322:
3321:Spinal nerves
3315:
3310:
3308:
3303:
3301:
3296:
3295:
3292:
3276:
3273:
3271:
3270:Costal margin
3268:
3266:
3263:
3261:
3258:
3257:
3255:
3253:
3252:Thoracic cage
3249:
3243:
3240:
3238:
3235:
3233:
3230:
3228:
3227:Sternal angle
3225:
3223:
3220:
3218:
3215:
3214:
3212:
3210:
3206:
3198:
3195:
3193:
3190:
3188:
3187:costal groove
3185:
3183:
3180:
3178:
3175:
3174:
3173:
3170:
3166:
3165:floating ribs
3163:
3161:
3158:
3156:
3153:
3152:
3151:
3148:
3147:
3145:
3143:
3139:
3136:
3134:
3130:
3119:
3118:
3116:
3114:
3110:
3102:
3101:sacral hiatus
3099:
3098:
3097:
3094:
3092:
3089:
3087:
3084:
3082:
3079:
3075:
3072:
3071:
3070:
3067:
3063:
3060:
3059:
3058:
3055:
3051:
3048:
3047:
3046:
3043:
3041:
3040:Ala of sacrum
3038:
3034:
3031:
3030:
3029:
3026:
3025:
3023:
3021:
3017:
3009:
3006:
3004:
3001:
3000:
2999:
2996:
2995:
2993:
2991:
2987:
2981:
2978:
2974:
2971:
2969:
2966:
2964:
2961:
2960:
2959:
2958:Costal facets
2956:
2955:
2953:
2951:
2947:
2941:
2938:
2934:
2931:
2930:
2929:
2926:
2922:
2919:
2917:
2916:anterior arch
2914:
2912:
2909:
2908:
2907:
2904:
2902:
2899:
2897:
2894:
2892:
2889:
2887:
2884:
2882:
2879:
2878:
2876:
2874:
2870:
2864:
2861:
2857:
2854:
2852:
2849:
2847:
2844:
2843:
2842:
2839:
2837:
2834:
2832:
2829:
2825:
2822:
2820:
2817:
2815:
2812:
2811:
2810:
2807:
2805:
2802:
2801:
2799:
2795:
2792:
2790:
2786:
2782:
2778:
2771:
2766:
2764:
2759:
2757:
2752:
2751:
2748:
2742:
2739:
2737:
2734:
2733:
2729:
2720:
2718:1-4051-3413-5
2714:
2710:
2703:
2700:
2695:
2693:0-03-910284-X
2689:
2685:
2681:
2675:
2673:
2671:
2669:
2667:
2665:
2663:
2661:
2657:
2646:on 2004-11-10
2642:
2638:
2634:
2630:
2626:
2622:
2618:
2611:
2604:
2601:
2588:
2584:
2580:
2574:
2571:
2567:
2561:
2558:
2553:
2549:
2544:
2539:
2534:
2529:
2525:
2521:
2517:
2510:
2507:
2502:
2498:
2494:
2490:
2486:
2482:
2478:
2474:
2467:
2464:
2459:
2455:
2450:
2445:
2440:
2435:
2431:
2427:
2423:
2416:
2413:
2408:
2404:
2399:
2394:
2390:
2386:
2382:
2378:
2374:
2367:
2364:
2359:
2353:
2349:
2342:
2339:
2327:
2323:
2316:
2315:
2307:
2304:
2299:
2295:
2291:
2287:
2283:
2279:
2275:
2271:
2264:
2261:
2256:
2250:
2246:
2239:
2236:
2223:
2219:
2213:
2210:
2205:
2198:
2195:
2189:
2187:
2185:
2181:
2176:
2170:
2166:
2161:
2159:
2155:
2150:
2143:
2140:
2135:
2129:
2125:
2118:
2115:
2110:
2106:
2101:
2096:
2092:
2088:
2084:
2080:
2076:
2069:
2067:
2063:
2051:
2047:
2043:
2039:
2032:
2029:
2017:
2013:
2008:
2003:
1999:
1995:
1991:
1987:
1983:
1979:
1975:
1968:
1965:
1953:
1947:
1943:
1942:
1934:
1931:
1918:
1914:
1910:
1903:
1900:
1895:
1889:
1885:
1878:
1876:
1872:
1867:
1861:
1857:
1850:
1847:
1835:
1831:
1825:
1821:
1820:
1812:
1809:
1804:
1798:
1794:
1787:
1784:
1777:
1773:
1772:Neutral spine
1770:
1768:
1765:
1763:
1762:Low back pain
1760:
1759:
1756:
1748:
1742:
1737:
1732:
1730:
1728:
1723:
1719:
1714:
1710:
1709:
1704:
1700:
1692:
1690:
1687:
1683:
1678:
1676:
1672:
1671:
1664:
1662:
1658:
1654:
1650:
1649:
1648:haemal arches
1642:
1640:
1636:
1632:
1628:
1624:
1616:
1614:
1612:
1608:
1604:
1600:
1598:
1597:calcification
1594:
1590:
1585:
1583:
1579:
1575:
1571:
1567:
1562:
1556:
1549:
1544:
1537:
1535:
1533:
1529:
1525:
1521:
1517:
1516:pelvic girdle
1513:
1508:
1504:
1500:
1499:
1495:
1492:
1489:or 76 in the
1488:
1484:
1480:
1479:
1474:
1470:
1469:
1464:
1463:
1458:
1450:
1448:
1446:
1441:
1439:
1435:
1434:Heterocoelous
1431:
1427:
1423:
1419:
1415:
1410:
1408:
1404:
1403:temnospondyls
1399:
1395:
1391:
1387:
1378:
1374:Other animals
1373:
1371:
1369:
1365:
1361:
1357:
1350:
1346:
1342:
1337:
1330:
1325:
1322:
1319:
1315:
1311:
1307:
1303:
1299:
1296:
1293:
1289:
1285:
1282:
1279:
1274:
1271:
1270:
1269:
1267:
1258:
1251:
1249:
1247:
1243:
1239:
1235:
1231:
1225:
1222:
1218:
1214:
1212:
1208:
1203:
1201:
1197:
1193:
1191:
1187:
1183:
1179:
1175:
1171:
1169:
1168:Spondylolysis
1165:
1163:
1159:
1155:
1151:
1149:
1144:
1142:
1138:
1134:
1130:
1126:
1119:
1113:
1106:
1104:
1102:
1098:
1093:
1088:
1086:
1082:
1078:
1074:
1073:spinal nerves
1070:
1069:central canal
1066:
1062:
1058:
1054:
1050:
1046:
1040:
1032:
1027:
1020:
1015:
1013:
1009:
1007:
1003:
998:
996:
991:
989:
988:
983:
978:
976:
972:
968:
964:
963:embryogenesis
960:
955:
951:
947:
943:
939:
938:Somitogenesis
935:
930:
926:
922:
921:embryogenesis
918:
915:The striking
910:
908:
906:
902:
899:
895:
891:
887:
883:
875:
873:
866:
865:
864:
857:
856:
855:
848:
847:
843:
841:
839:
835:
831:
826:
824:
819:
817:
807:
803:
801:
792:
787:
783:
781:
777:
773:
768:
766:
758:
754:
750:
748:
744:
742:
738:
734:
733:
732:
728:
724:
719:
714:
709:
706:
703:
700:
697:
694:
691:
688:
685:
682:
681:
680:
677:
675:
671:
667:
663:
659:
658:
653:
650:
645:
643:
639:
635:
631:
627:
623:
619:
615:
611:
607:
603:
598:
596:
592:
588:
586:
580:
576:
572:
568:
564:
560:
556:
552:
548:
544:
540:
536:
533:
529:
525:
521:
517:
513:
509:
505:
501:
497:
493:
489:
480:
476:
474:
470:
464:
462:
451:
447:
442:
438:
437:spinal column
434:
430:
425:
421:
417:
414:
410:
409:
405:
397:
395:
393:
389:
385:
381:
377:
373:
369:
365:
361:
357:
353:
348:
346:
342:
338:
334:
330:
326:
322:
313:
311:
309:
305:
301:
297:
293:
289:
285:
281:
277:
273:
269:
265:
261:
257:
253:
249:
245:
241:
236:
234:
230:
226:
222:
217:
215:
214:body segments
211:
207:
206:spinal nerves
203:
199:
198:neural arches
195:
191:
187:
183:
180:
176:
172:
168:
165:
161:
157:
153:
149:
145:
141:
137:
134:
130:
126:
122:
118:
117:spinal column
114:
102:
96:
92:
89:
86:
84:
80:
75:
70:
66:
60:
55:
48:
43:
38:
33:
19:
4489:Back anatomy
4225:
4175:Adam's apple
3853:Sacroiliitis
3834:inflammatory
3708:
3696:
3666:
3654:
3597:
3580:
3528:
3501:
3397:
3378:
3171:
3096:Sacral canal
2997:
2911:lateral mass
2863:Spinal canal
2840:
2708:
2702:
2683:
2648:. Retrieved
2641:the original
2623:(1): 19–26.
2620:
2616:
2603:
2591:. Retrieved
2583:May 6th 2011
2582:
2573:
2565:
2560:
2523:
2519:
2509:
2476:
2472:
2466:
2432:(4): e2456.
2429:
2425:
2415:
2380:
2376:
2373:"Coccydynia"
2366:
2347:
2341:
2329:. Retrieved
2313:
2306:
2276:(2): 75–92.
2273:
2269:
2263:
2244:
2238:
2226:. Retrieved
2212:
2203:
2197:
2164:
2146:
2142:
2123:
2117:
2082:
2078:
2054:. Retrieved
2045:
2041:
2031:
2019:. Retrieved
1981:
1977:
1967:
1955:. Retrieved
1940:
1933:
1921:. Retrieved
1912:
1902:
1883:
1855:
1849:
1838:. Retrieved
1818:
1811:
1792:
1786:
1706:
1696:
1679:
1668:
1665:
1657:ventral ribs
1646:
1643:
1620:
1601:
1586:
1558:
1498:Elasmosaurus
1496:
1476:
1466:
1460:
1454:
1442:
1433:
1429:
1425:
1418:Amphicoelous
1417:
1413:
1411:
1382:
1353:
1318:pneumothorax
1278:osteoporosis
1263:
1242:neurofibroma
1226:
1215:
1205:Pain at the
1204:
1194:
1172:
1166:
1152:
1145:
1140:
1136:
1125:Spina bifida
1123:
1101:cauda equina
1092:spinal canal
1089:
1065:white matter
1045:spinal canal
1042:
1010:
999:
992:
985:
979:
929:gastrulation
914:
879:
870:
861:
852:
837:
834:compensatory
833:
827:
820:
812:
796:
769:
762:
730:
718:
696:Lumbar spine
678:
670:spinal nerve
655:
652:facet joints
646:
599:
585:horse's tail
582:
575:cauda equina
563:lumbar spine
543:spinal canal
518:), which is
515:
494:), which is
491:
485:
465:
461:body regions
458:
390:between the
376:interspinous
349:
332:
317:
308:spina bifida
237:
218:
190:spinal canal
156:glycoprotein
150:(an elastic
146:, where the
144:endoskeleton
124:
120:
116:
112:
110:
87:
3884:Spondylosis
3841:Spondylitis
3812:Torticollis
3507:Intercostal
2568:, pp. 27–28
2566:The Arabian
2331:24 November
2048:: 497–519.
1708:pleurocoels
1703:Saurischian
1528:chimpanzees
1386:haemal arch
1347:is seen at
1310:atelectasis
1230:astrocytoma
1221:spinal cord
1039:Spinal cord
1031:spinal cord
1021:Spinal cord
971:spinal cord
967:sclerotomes
946:sclerotomes
911:Development
589:), and the
551:spinal cord
547:body cavity
516:neural arch
510:; and the
240:body region
202:spinal cord
164:mineralized
77:Identifiers
4458:Categories
4342:Fingernail
3948:Coccydynia
3160:false ribs
3008:mammillary
2973:transverse
2846:transverse
2650:2012-01-04
2318:(Internet)
2228:29 January
2056:2021-04-10
2021:1 November
1957:1 November
1840:2015-06-27
1778:References
1653:homologous
1591:, such as
1582:amphibians
1553:See also:
1494:plesiosaur
1483:amphibians
1478:Trichechus
1471:) and the
1426:Procoelous
1238:schwannoma
1234:ependymoma
1211:coccydynia
954:dermatomes
727:Human neck
723:Human back
618:transverse
577:(from
386:, and the
221:homologous
171:cartilages
133:vertebrate
4258:Genitalia
3933:Neck pain
3925:Back pain
3791:Scoliosis
3765:Deforming
3709:posterior
3689:Coccygeal
3667:posterior
3598:posterior
3529:posterior
3399:posterior
3222:Manubrium
3155:true ribs
3003:accessory
2998:Processes
2851:articular
2841:Processes
2789:Vertebrae
2564:Edwards,
2526:: e7096.
2158:CC BY 4.0
1998:1536-5964
1718:hadrosaur
1699:dinosaurs
1693:Dinosaurs
1675:pygostyle
1670:synsacrum
1655:with the
1611:Hagfishes
1566:notochord
1524:coccygeal
1520:pygostyle
1512:synsacrum
1462:Choloepus
1422:notochord
1298:Scoliosis
1292:pregnancy
1252:Curvature
1180:) of the
987:HOX genes
975:notochord
917:segmented
876:Ligaments
838:secondary
626:ligaments
614:articular
610:processes
559:adulthood
524:posterior
502:, in the
429:dermatome
398:Vertebrae
352:ligaments
314:Structure
296:scoliosis
274:to guide
175:vertebrae
173:) called
160:chordates
154:-wrapped
148:notochord
140:eponymous
4387:Buttocks
4307:Shoulder
4142:Mandible
4075:Forehead
3953:Sciatica
3858:Discitis
3786:Lordosis
3781:Kyphosis
3697:anterior
3655:anterior
3581:anterior
3502:anterior
3432:Thoracic
3380:anterior
3329:Cervical
3182:tubercle
3142:Rib cage
2968:inferior
2963:superior
2680:Romer AS
2637:10327647
2587:Archived
2552:31211022
2493:16741456
2458:29888160
2407:19468909
2326:32491519
2298:84983794
2290:12649586
2222:Archived
2160:license.
2109:34935276
2050:Archived
2016:27559975
1978:Medicine
1923:June 11,
1917:Archived
1834:Archived
1733:See also
1722:theropod
1713:sauropod
1686:manatees
1639:tuataras
1627:reptiles
1603:Lampreys
1578:teleosts
1475:genus, (
1468:Bradypus
1459:genera (
1414:acoelous
1394:reptiles
1284:Lordosis
1273:Kyphosis
1133:meninges
1083:and the
1049:vertebra
1016:Function
973:and the
950:myotomes
882:anterior
844:Surfaces
816:lordotic
800:kyphotic
780:lordotic
739:and the
620:and one
602:pedicles
571:ponytail
500:anterior
404:Vertebra
382:between
356:anterior
333:tailbone
292:kyphosis
278:such as
229:reptiles
152:collagen
125:backbone
4432:Toenail
4322:Forearm
4268:Scrotum
4214:Midriff
4204:Abdomen
4197:(Trunk)
4147:Occiput
4090:Eyebrow
3209:Sternum
2856:spinous
2814:pedicle
2779:of the
2593:25 July
2543:6557252
2501:2401041
2449:5991933
2398:2682410
2100:8867438
2007:5400342
1623:mammals
1491:extinct
1473:manatee
1445:Arabian
1398:mammals
1392:, most
1302:females
1120:Disease
925:somites
898:seventh
818:curve.
802:curve.
782:curve.
622:spinous
612:, four
606:laminae
496:ventral
492:centrum
372:laminae
252:abdomen
225:mammals
204:, with
136:animals
72:Details
4367:Little
4357:Middle
4337:Finger
4312:Axilla
4253:Pelvis
4246:Nipple
4241:Breast
4236:Thorax
4180:Throat
4157:Temple
4120:Tongue
4100:Eyelid
3620:Sacral
3546:Lumbar
3133:Thorax
3113:Coccyx
3020:Sacrum
2819:lamina
2715:
2690:
2635:
2550:
2540:
2499:
2491:
2456:
2446:
2426:Cureus
2405:
2395:
2354:
2324:
2296:
2288:
2251:
2171:
2130:
2107:
2097:
2014:
2004:
1996:
1948:
1890:
1862:
1826:
1799:
1682:sloths
1635:geckos
1629:, and
1593:sharks
1532:humans
1503:pelvis
1438:saddle
1368:organs
1343:. The
1314:asthma
1244:, and
1207:coccyx
1190:hernia
965:, the
823:coccyx
708:Coccyx
702:Sacrum
616:, two
595:coccyx
591:sacrum
567:caudal
520:dorsal
374:, the
366:, the
343:and 5
329:coccyx
325:sacrum
262:). In
256:pelvis
248:thorax
194:cavity
4494:Spine
4417:Ankle
4397:Thigh
4352:Index
4347:Thumb
4327:Wrist
4317:Elbow
4290:Limbs
4273:Vulva
4263:Penis
4219:Navel
4209:Waist
4195:Torso
4152:Scalp
4125:Tooth
4110:Mouth
4080:Cheek
3800:Other
3177:angle
3172:Parts
2906:Atlas
2824:notch
2781:torso
2777:Bones
2644:(PDF)
2613:(PDF)
2520:PeerJ
2497:S2CID
2473:Spine
2294:S2CID
1661:snake
1631:birds
1530:(and
1487:swans
1457:sloth
1341:torso
1127:is a
923:when
836:, or
830:fetus
791:X-ray
759:Shape
649:plane
581:
579:Latin
557:, by
469:atlas
339:, 12
331:, or
233:birds
184:(the
121:spine
99:[
83:Latin
4437:Sole
4422:Heel
4412:Foot
4407:Calf
4402:Knee
4362:Ring
4332:Hand
4280:Anus
4231:Back
4185:Nape
4167:Neck
4105:Nose
4085:Chin
4070:Face
4065:Hair
4057:Head
4049:Skin
4043:Body
3197:head
3192:neck
3150:Ribs
3120:none
3028:Base
2933:dens
2928:Axis
2809:Arch
2804:Body
2713:ISBN
2688:ISBN
2633:PMID
2595:2013
2548:PMID
2489:PMID
2454:PMID
2403:PMID
2352:ISBN
2333:2023
2322:PMID
2286:PMID
2249:ISBN
2230:2016
2169:ISBN
2154:text
2128:ISBN
2105:PMID
2023:2023
2012:PMID
1994:ISSN
1959:2023
1946:ISBN
1925:2020
1888:ISBN
1860:ISBN
1824:ISBN
1797:ISBN
1720:and
1684:and
1637:and
1507:ribs
1465:and
1390:fish
1099:and
1090:The
1063:and
1061:grey
1029:The
884:and
776:dens
772:axis
725:and
672:and
630:back
593:and
545:, a
532:core
530:and
528:ribs
522:(or
498:(or
490:(or
473:axis
471:and
378:and
358:and
306:and
282:and
260:tail
244:neck
231:and
111:The
65:goat
4427:Toe
4392:Hip
4379:Leg
4299:Arm
4137:Jaw
4132:Ear
4115:Lip
4095:Eye
3495:T12
3490:T11
3485:T10
2625:doi
2621:285
2538:PMC
2528:doi
2481:doi
2444:PMC
2434:doi
2393:PMC
2385:doi
2278:doi
2274:173
2095:PMC
2087:doi
2002:PMC
1986:doi
1587:In
1534:).
1316:or
640:in
258:or
131:in
123:or
4460::
3648:S5
3643:S4
3638:S3
3633:S2
3628:S1
3574:L5
3569:L4
3564:L3
3559:L2
3554:L1
3480:T9
3475:T8
3470:T7
3465:T6
3460:T5
3455:T4
3450:T3
3445:T2
3440:T1
3372:C8
3367:C7
3362:C6
3357:C5
3352:C4
3347:C3
3342:C2
3337:C1
2659:^
2631:.
2619:.
2615:.
2581:.
2546:.
2536:.
2522:.
2518:.
2495:.
2487:.
2477:31
2475:.
2452:.
2442:.
2430:10
2428:.
2424:.
2401:.
2391:.
2379:.
2375:.
2292:.
2284:.
2272:.
2183:^
2103:.
2093:.
2083:14
2081:.
2077:.
2065:^
2046:25
2044:.
2040:.
2010:.
2000:.
1992:.
1982:95
1980:.
1976:.
1915:.
1911:.
1874:^
1832:.
1663:.
1625:,
1599:.
1424:.
1370:.
1349:L1
1240:,
1236:,
1232:,
1213:.
1202:.
1192:.
1103:.
1087:.
997:.
990:.
907:.
644:.
427:A
394:.
302:,
298:,
254:,
250:,
246:,
227:,
216:.
119:,
4027:e
4020:t
4013:v
3750:e
3743:t
3736:v
3313:e
3306:t
3299:v
2769:e
2762:t
2755:v
2721:.
2696:.
2653:.
2627::
2597:.
2554:.
2530::
2524:7
2503:.
2483::
2460:.
2436::
2409:.
2387::
2381:1
2360:.
2335:.
2300:.
2280::
2257:.
2232:.
2206:.
2177:.
2136:.
2111:.
2089::
2025:.
1988::
1961:.
1927:.
1896:.
1868:.
1843:.
1805:.
1757:.
1320:.
1294:.
1280:.
587:"
583:"
294:/
242:(
103:]
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.