2101:
2797:
511:, resulting in stronger thermal stratification and overall lower average water column temperatures, which can eventually affect the onset of ice cover. Water quality can also be influenced by the runoff of salt from roads and sidewalks, which often creates a benthic saline layer that interferes with vertical mixing of surface waters. Further, the saline layer can prevent dissolved oxygen from reaching the bottom sediments, decreasing phosphorus recycling and affecting microbial communities.
31:
2823:
2811:
357:
547:. When these asynchronies in predator and prey populations occur year after year due to changes in stratification, populations may take years to rebound to their “normal” consistency. Combined with typically warmer lake temperatures associated with stratification patterns brought on by climate change, variable prey populations from year-to-year can be detrimental to cold water fish species.
2429:
523:(e.g. Great Bear Lake). Globally, lake stratification appears to be more stable with deeper and steeper thermoclines, and average lake temperature as a main determinant in the stratification response to changing temperatures. Further, surface warming rates are much greater than bottom warming rates, again indicating stronger thermal stratification across lakes.
403:
mixing events, such as storms or large river discharge, can break down stratification. Weather conditions induce a more rapid response in larger, shallower lakes, so these lakes are more dynamic and less understood. However, mixing regimes that are known to exist in large, shallow lakes are mostly diurnal, and the stratification is easily disturbed.
341:, and changes to weather patterns have been shown to alter the timing and intensity of stratification in lakes around the globe. Rising air temperatures have the same effect on lake bodies as a physical shift in geographic location, with tropical zones being particularly sensitive. These changes can further alter the fish,
408:
stratification to become disrupted affects the rate of transport and consumption of nutrients, in turn affecting the presence of algal growth. Stratification and mixing regimes in Earth’s largest lakes are also poorly understood, yet changes in thermal distributions, such as the rising temperatures found over time in
464:
In temperate latitudes, many lakes that become stratified during the summer months de-stratify during cooler windier weather with surface mixing by wind being a significant driver in this process. This is often referred to as "autumn turn-over". The mixing of the hypolimnium into the mixed water body
360:
Typical mixing pattern for many lakes, caused by the fact that water is less dense at temperatures other than 4 °C or 39 °F (the temperature where water is most dense). Lake stratification is stable in summer and winter, becoming unstable in spring and fall when the surface waters cross the
539:. Fluctuations in stratification consistency can accelerate deoxygenation of lakes, nutrient mineralization, and phosphorus release, having significant consequences for phytoplankton species. Furthermore, these changes in phytoplankton species composition and abundance can lead to adverse effects on
415:
Recent research suggests that seasonally ice-covered dimictic lakes may be described as "cryostratified" or "cryomictic" according to their wintertime stratification regimes. Cryostratified lakes exhibit inverse stratification near the ice surface and have depth-averaged temperatures near 4°C, while
394:
Heat is transported very slowly between the mixed layers of a stratified lake, where the diffusion of heat just one vertical meter takes about a month. The interaction between the atmosphere and lakes depends on how solar radiation is distributed, which is why water turbulence, mainly caused by wind
502:
Every lake has a set mixing regime that is influenced by lake morphometry and environmental conditions. However, changes to human influences in the form of land use change, increases in temperatures, and changes to weather patterns have been shown to alter the timing and intensity of stratification
402:
The lake mixing regime (e.g. polymictic, dimictic, meromictic) describes the yearly patterns of lake stratification that occur in most years. However, short-term events can influence lake stratification as well. Heat waves can cause periods of stratification in otherwise mixed, shallow lakes, while
526:
Changes to stratification patterns can also alter the community composition of lake ecosystems. In shallow lakes, temperature increases can alter the diatom community; while in deep lakes, the change is reflected in the deep chlorophyll layer taxa. Changes in mixing patterns and increased nutrient
407:
in China is an example of a large, shallow, diurnal lake, where even though the depth does not reach more than 3 metres (9.8 ft), the lake’s water turbidity is still dynamic enough to stratify and de-stratify due to the absorption of solar radiation mostly in the upper layer. The tendency for
514:
On a global scale, rising temperatures and changing weather patterns can also affect stratification in lakes. Rising air temperatures have the same effect on lake bodies as a physical shift in geographic location, with tropical zones being particularly sensitive. The intensity and scope of impact
489:
managers, the spatial distribution of fish within a lake is often adversely affected by thermal stratification and in some cases may indirectly cause large die-offs of recreationally important fish. One commonly used tool to reduce the severity of these lake management problems is to eliminate or
419:
Circulation processes during mixing periods cause the movement of oxygen and other dissolved nutrients, distributing them throughout the body of water. In lakes where benthic organisms are prominent, the respiration and consumption of these bottom-feeders may outweigh the mixing properties of
506:
There are a number of ways in which changes in human land use influence lake stratification and consequently water conditions. Urban expansion has led to the construction of roads and houses close to previously isolated lakes, sometimes causing increased runoff and pollution. The addition of
370:
The thermal stratification of lakes refers to a change in the temperature at different depths in the lake, and is due to the density of water varying with temperature. Cold water is denser than warm water and the epilimnion generally consists of water that is not as dense as the water in the
476:
Many types of aeration equipment have been used to thermally de-stratify lakes, particularly lakes subject to low oxygen or undesirable algal blooms. In fact, natural resource and environmental managers are often challenged by problems caused by lake and pond thermal stratification.
1620:
Woolway, R. Iestyn; Sharma, Sapna; Weyhenmeyer, Gesa A.; Debolskiy, Andrey; Golub, Malgorzata; Mercado-Bettín, Daniel; Perroud, Marjorie; Stepanenko, Victor; Tan, Zeli; Grant, Luke; Ladwig, Robert; Mesman, Jorrit; Moore, Tadhg N.; Shatwell, Tom; Vanderkelen, Inne (2021-04-19).
534:
In northern temperate lakes, as climate change continues to cause increased variability in weather patterns as well as the timing of ice-on and ice-off dates, subsequent changes in stratification patterns from year to year can also have impacts across multiple
420:
strongly stratified lakes, resulting in zones of extremely low near-bottom oxygen and nutrient concentrations. This can be harmful to benthic organisms such as shellfish, which in the worst cases can wipe out entire populations. The accumulation of dissolved
395:
stress, can greatly increase the efficiency of heat transfer. In shallow lakes, stratification into epilimnion, metalimnion, and hypolimnion often does not occur, as wind or cooling causes regular mixing throughout the year. These lakes are called
57:
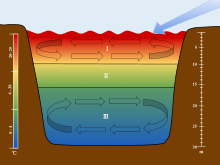
The scales are used to associate each section of the stratification to their corresponding depths and temperatures. The arrow is used to show the movement of wind over the surface of the water which initiates the turnover in the epilimnion and the
465:
of the lake recirculates nutrients, particularly phosphorus compounds, trapped in the hypolimnion during the warm weather. It also poses a risk of oxygen sag as a long established hypolimnion can be anoxic or very low in
503:
in lakes around the globe. These changes can further alter the fish, zooplankton, and phytoplankton community composition, in addition to creating gradients that alter the availability of dissolved oxygen and nutrients.
472:
Lake mixing regimes can shift in response to increasing air temperatures. Some dimictic lakes can turn into monomictic lakes, while some monomictic lakes might become meromictic, as a consequence of rising temperatures.
612:
Kraemer, Benjamin M.; Anneville, Orlane; Chandra, Sudeep; Dix, Margaret; Kuusisto, Esko; Livingstone, David M.; Rimmer, Alon; Schladow, S. Geoffrey; Silow, Eugene; Sitoki, Lewis M.; Tamatamah, Rashid (2015-06-28).
950:
Yang, Bernard; Wells, Mathew G.; McMeans, Bailey C.; Dugan, Hilary A.; Rusak, James A.; Weyhenmeyer, Gesa A.; Brentrup, Jennifer A.; Hrycik, Allison R.; Laas, Alo; Pilla, Rachel M.; Austin, Jay A. (2021-02-16).
1481:
Heiskanen, Jouni J.; Mammarella, Ivan; Ojala, Anne; Stepanenko, Victor; Erkkilä, Kukka-Maaria; Miettinen, Heli; Sandström, Heidi; Eugster, Werner; Leppäranta, Matti; Järvinen, Heikki; Vesala, Timo (2015).
1205:
Yang, Bernard; Wells, Mathew G.; McMeans, Bailey C.; Dugan, Hilary A.; Rusak, James A.; Weyhenmeyer, Gesa A.; Brentrup, Jennifer A.; Hrycik, Allison R.; Laas, Alo; Pilla, Rachel M.; Austin, Jay A. (2021).
1149:
Yang, Bernard; Wells, Mathew G.; McMeans, Bailey C.; Dugan, Hilary A.; Rusak, James A.; Weyhenmeyer, Gesa A.; Brentrup, Jennifer A.; Hrycik, Allison R.; Laas, Alo; Pilla, Rachel M.; Austin, Jay A. (2021).
2260:
2752:
1092:
Anderson, Eric J.; Stow, Craig A.; Gronewold, Andrew D.; Mason, Lacey A.; McCormick, Michael J.; Qian, Song S.; Ruberg, Steven A.; Beadle, Kyle; Constant, Stephen A.; Hawley, Nathan (2021-03-16).
375:
regions where lake water warms up and cools through the seasons, a cyclical pattern of overturn occurs that is repeated from year to year as the cold dense water at the top of the lake sinks (see
485:
may limit the recreational use of lakes and the commercial use of lake water. With severe thermal stratification in a lake, the quality of drinking water also can be adversely affected. For
923:
Wilhelm, Susann; Adrian, RITA (4 October 2007). "Impact of summer warming on the thermal characteristics of a polymictic lake and consequences for oxygen, nutrients and phytoplankton".
2255:
294:
399:. There is not a fixed depth that separates polymictic and stratifying lakes, as apart from depth, this is also influenced by turbidity, lake surface area, and climate.
2100:
2285:
1777:
2125:
287:
2275:
796:
1055:"Simulation and exploration of the mechanisms underlying the spatiotemporal distribution of surface mixed layer depth in a large shallow lake"
834:
671:
1580:"Earlier ice breakup induces changepoint responses in duration and variability of spring mixing and summer stratification in dimictic lakes"
2290:
2388:
2250:
280:
615:"Morphometry and average temperature affect lake stratification responses to climate change: LAKE STRATIFICATION RESPONSES TO CLIMATE"
376:
2280:
1416:
Lackey, Robert T. (June 1972). "Response of physical and chemical parameters to eliminating thermal stratification in a reservoir".
1359:
1915:
1770:
1683:"A perspective on the ecological and evolutionary consequences of phenological variability in lake ice on north-temperate lakes"
2742:
383:
the lake water turns over during the spring and the fall. This process occurs more slowly in deeper water and as a result, a
314:
to form separate and distinct thermal layers during warm weather. Typically stratified lakes show three distinct layers: the
693:
Edlund, Mark; Almendinger, James; Fang, Xing; Hobbs, Joy; VanderMeulen, David; Key, Rebecca; Engstrom, Daniel (2017-09-07).
2762:
2747:
1870:
2757:
1763:
515:
depends on location and lake morphometry, but in some cases can be so extreme as to require a reclassification from
2065:
531:
and abundance, while decreased nutrient availability can be detrimental for benthic communities and fish habitat.
2373:
2267:
1454:
Lackey, Robert T.; Holmes, Donald W. (July 1972). "Evaluation of Two
Methods of Aeration to Prevent Winterkill".
1737:
2826:
2619:
2614:
1910:
1467:
2527:
2338:
2232:
1960:
1950:
743:
Novotny Eric V.; Stefan Heinz G. (2012-12-01). "Road Salt Impact on Lake
Stratification and Water Quality".
566:
2353:
2343:
2045:
2030:
561:
416:
cryomictic lakes have no under-ice thermocline and have depth-averaged winter temperatures closer to 0°C.
412:’s deep waters, have the ability to significantly alter the largest freshwater ecosystems on the planet.
1681:
Feiner, Zachary S.; Dugan, Hilary A.; Lottig, Noah R.; Sass, Greg G.; Gerrish, Gretchen A. (2022-09-01).
2772:
2699:
2499:
2474:
2449:
2333:
2080:
1860:
773:
571:
540:
1207:
1151:
1094:"Seasonal overturn and stratification changes drive deep-water warming in one of Earth's largest lakes"
1262:
695:"Effects of Climate Change on Lake Thermal Structure and Biotic Response in Northern Wilderness Lakes"
2507:
2469:
1800:
1495:
1425:
1387:
1316:
1301:
1219:
1163:
964:
868:
481:
have been directly associated with thermal gradients, stagnation, and ice cover. Excessive growth of
814:
2729:
2383:
2192:
1920:
1880:
528:
1378:
Lackey, Robert T. (February 1972). "A technique for eliminating thermal stratification in lakes".
2852:
2649:
2644:
2512:
2454:
2348:
2197:
2115:
2000:
1980:
1890:
1833:
1579:
1521:
1332:
1261:
Wiles, Philip J.; van Duren, Luca A.; Häse, Clivia; Larsen, Jens; Simpson, John H. (2006-04-01).
1243:
1187:
988:
2659:
2634:
2537:
2484:
2403:
2070:
2035:
1975:
1935:
1905:
1875:
1786:
1741:
1702:
1660:
1642:
1599:
1560:
1513:
1355:
1282:
1235:
1179:
1131:
1113:
1074:
1035:
1027:
980:
830:
716:
667:
372:
322:(or metalimnion), the middle layer, whose depth may change throughout the day; and the colder
263:
2767:
2459:
2363:
2315:
2227:
2120:
2060:
1818:
1733:
1694:
1650:
1634:
1591:
1552:
1540:
1503:
1463:
1433:
1395:
1324:
1274:
1227:
1171:
1121:
1105:
1066:
1019:
972:
932:
905:
876:
822:
752:
706:
626:
350:
952:
896:
Lewis Jr., William M. (October 1983). "A Revised
Classification of Lakes Based on Mixing".
756:
2737:
2704:
2565:
2517:
2393:
2368:
2177:
2130:
2055:
1900:
1885:
1721:
656:
556:
516:
449:
396:
334:
236:
223:
201:
190:
30:
1350:
Cooke, G. Dennis; Welch, Eugene B.; Peterson, Spencer; Nichols, Stanley A., eds. (2005).
792:
371:
hypolimnion. However, the temperature of maximum density for freshwater is 4 °C. In
1682:
1499:
1429:
1391:
1320:
1223:
1167:
968:
872:
349:
community composition, in addition to creating gradients that alter the availability of
2847:
2601:
2555:
2550:
2522:
2489:
2358:
2217:
2145:
2135:
1985:
1930:
1848:
1843:
1838:
1655:
1622:
1437:
1399:
1126:
1093:
614:
491:
421:
338:
268:
100:
657:"Impact of Climate Change on Sensitivity of Lake Stratification: A Global Perspective"
452:, a very large quantity of carbon dioxide can quickly leave the lake and displace the
17:
2841:
2815:
2709:
2674:
2575:
2570:
2545:
2075:
2040:
2015:
1865:
1828:
1525:
1336:
1247:
1191:
992:
936:
826:
581:
536:
520:
508:
494:. Aeration has met with some success, although it has rarely proved to be a panacea.
409:
380:
346:
330:
212:
89:
78:
881:
856:
2810:
2801:
2580:
2560:
2464:
2202:
2085:
2005:
1965:
1955:
1925:
1484:"Effects of water clarity on lake stratification and lake-atmosphere heat exchange"
576:
247:
111:
1278:
356:
333:
and environmental conditions. However, changes to human influences in the form of
387:
may form. If the stratification of water lasts for extended periods, the lake is
2714:
2689:
2684:
2654:
2437:
2413:
2378:
2187:
2090:
2010:
1970:
1823:
1008:"Temporal and spatial characteristics of potential energy anomaly in Lake Taihu"
433:
384:
342:
323:
319:
157:
146:
52:
45:
1638:
1109:
2694:
2629:
2418:
2398:
2182:
2155:
1940:
1853:
1328:
1070:
1023:
404:
388:
315:
135:
38:
1745:
1706:
1646:
1603:
1564:
1517:
1286:
1239:
1183:
1117:
1078:
1031:
984:
720:
2719:
2624:
2408:
2172:
2165:
2140:
2050:
1698:
1054:
1007:
486:
478:
441:
429:
2428:
1664:
1302:"Worldwide alteration of lake mixing regimes in response to climate change"
1263:"Stratification and mixing in the Limfjorden in relation to mussel culture"
1135:
1039:
664:
Water
Resources Management in the Face of Climatic/Hydrologic Uncertainties
448:) is potentially dangerous because if one of these lakes is triggered into
1722:"Empirical Links between Thermal Habitat, Fish Growth, and Climate Change"
2669:
2479:
2025:
2020:
1945:
1508:
1483:
1231:
1175:
976:
631:
482:
437:
2679:
2639:
2609:
2587:
2207:
1995:
1895:
544:
1595:
2664:
1990:
1755:
711:
694:
466:
453:
445:
425:
1556:
909:
355:
29:
1623:"Phenological shifts in lake stratification under climate change"
857:"Generalized scaling of seasonal thermal stratification in lakes"
2160:
311:
2313:
1797:
1759:
456:
needed for life by people and animals in the surrounding area.
2222:
2212:
1300:
Woolway, R. Iestyn; Merchant, Christopher J. (18 March 2019).
329:
Every lake has a set mixing regime that is influenced by lake
1541:"Changes in climate and weather extremes in the 21st century"
768:
766:
787:
785:
783:
655:
Meyer, Gabriela K.; Masliev, Ilya; Somlyódy, László (1996),
1738:
10.1577/1548-8659(1999)128<0656:ELBTHF>2.0.CO;2
1006:
Zhao, Qiaohua; Ren, Yan; Wang, Julian X. L. (2018-08-01).
1468:
10.1577/1548-8640(1972)34[175:EOTMOA]2.0.CO;2
1411:
1409:
1373:
1371:
1053:
Zhao, Qiaohua; Sun, Jihua; Zhu, Guangwei (2012-11-01).
1354:(Third ed.). Boca Raton: CRC Press. p. 616.
1720:
King, J. R.; Shuter, B. J.; Zimmerman, A. P. (1999).
2728:
2600:
2536:
2498:
2436:
2326:
2243:
2108:
1811:
1449:
1447:
1418:
Journal of the
American Water Resources Association
1380:
Journal of the
American Water Resources Association
1208:"A New Thermal Categorization of Ice-Covered Lakes"
1152:"A New Thermal Categorization of Ice-Covered Lakes"
953:"A New Thermal Categorization of Ice-Covered Lakes"
34:Lakes are stratified into three separate sections:
1687:Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences
1352:Restoration and Management of Lakes and Reservoirs
898:Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences
27:Separation of water in a lake into distinct layers
1578:Pilla, Rachel M.; Williamson, Craig E. (2022).
1726:Transactions of the American Fisheries Society
2061:Stable isotope analysis in aquatic ecosystems
1771:
288:
8:
1488:Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres
1012:Environmental Science and Pollution Research
507:particulate matter to lake bodies can lower
2126:Freshwater environmental quality parameters
855:Kirillin, G.; Shatwell, T. (October 2016).
2442:
2323:
2310:
1808:
1794:
1778:
1764:
1756:
666:, Springer Netherlands, pp. 225–270,
295:
281:
61:
1654:
1507:
1125:
880:
710:
630:
527:availability can also affect zooplankton
797:Georgia Department of Natural Resources
593:
255:
176:
119:
64:
1676:
1674:
1615:
1613:
815:"Density Stratification and Stability"
490:lessen thermal stratification through
326:, extending to the floor of the lake.
318:, comprising the top warm layer; the
7:
808:
806:
776:. Water on the Web. October 7, 2015.
738:
736:
734:
732:
730:
688:
686:
684:
682:
650:
648:
646:
644:
642:
607:
605:
603:
601:
599:
597:
2389:Oceanic physical-biological process
2251:List of freshwater ecoregions (WWF)
1438:10.1111/j.1752-1688.1972.tb05181.x
1400:10.1111/j.1752-1688.1972.tb05092.x
813:Boehrer, B.; Schultze, M. (2009),
757:10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0000590
377:stable and unstable stratification
25:
2822:
2821:
2809:
2795:
2427:
2099:
1916:Colored dissolved organic matter
1059:Advances in Atmospheric Sciences
937:10.1111/j.1365-2427.2007.01887.x
827:10.1016/b978-012370626-3.00077-6
745:Journal of Hydraulic Engineering
2261:Latin America and the Caribbean
882:10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.08.008
2743:Ecological values of mangroves
2286:North Pacific Subtropical Gyre
1456:The Progressive Fish-Culturist
821:, Elsevier, pp. 583–593,
1:
1279:10.1016/j.jmarsys.2005.09.009
819:Encyclopedia of Inland Waters
424:in three meromictic lakes in
2763:Marine conservation activism
2748:Fisheries and climate change
1539:Rummukainen, Markku (2012).
1212:Geophysical Research Letters
1156:Geophysical Research Letters
957:Geophysical Research Letters
793:"Lake Lanier Turnover Facts"
619:Geophysical Research Letters
2758:Human impact on marine life
2635:Davidson Seamount § Ecology
1871:Aquatic population dynamics
2869:
1639:10.1038/s41467-021-22657-4
1584:Limnology and Oceanography
1110:10.1038/s41467-021-21971-1
2789:
2445:
2425:
2374:Marine primary production
2322:
2309:
2268:List of marine ecoregions
2097:
1807:
1793:
1329:10.1038/s41561-019-0322-x
1267:Journal of Marine Systems
1071:10.1007/s00376-012-1262-1
1024:10.1007/s11356-018-2204-y
2620:Coastal biogeomorphology
2615:Marine coastal ecosystem
774:"Density Stratification"
498:Anthropogenic influences
339:increases in temperature
2528:Paradox of the plankton
2339:Diel vertical migration
2233:Freshwater swamp forest
1951:GIS and aquatic science
1799:General components and
1699:10.1139/cjfas-2021-0221
2354:Large marine ecosystem
2046:Shoaling and schooling
562:Stratification (water)
362:
59:
18:Thermal stratification
2773:Marine protected area
2700:Salt pannes and pools
2475:Marine larval ecology
2450:Census of Marine Life
2334:Deep scattering layer
2291:San Francisco Estuary
2256:Africa and Madagascar
2081:Underwater camouflage
1861:Aquatic biomonitoring
1801:freshwater ecosystems
1627:Nature Communications
1098:Nature Communications
861:Earth-Science Reviews
572:Freshwater ecosystems
359:
33:
2508:Marine bacteriophage
2470:Marine invertebrates
1545:WIREs Climate Change
1509:10.1002/2014JD022938
1232:10.1029/2020GL091374
1218:(3): e2020GL091374.
1176:10.1029/2020GL091374
1162:(3): e2020GL091374.
977:10.1029/2020GL091374
632:10.1002/2015GL064097
2384:Ocean fertilization
2193:Trophic state index
2151:Lake stratification
1881:Aquatic respiration
1500:2015JGRD..120.7412H
1430:1972JAWRA...8..589L
1392:1972JAWRA...8...46L
1321:2019NatGe..12..271W
1224:2021GeoRL..4891374Y
1168:2021GeoRL..4891374Y
1018:(24): 24316–24325.
969:2021GeoRL..4891374Y
873:2016ESRv..161..179K
529:species composition
379:). For example, in
310:is the tendency of
308:Lake stratification
121:Lake stratification
2650:Intertidal wetland
2645:Intertidal ecology
2513:Marine prokaryotes
2455:Deep-sea community
2349:Iron fertilization
2272:Specific examples
2198:Upland and lowland
2116:Freshwater biology
1981:Microbial food web
1891:Aquatic toxicology
1834:Aquatic adaptation
1787:Aquatic ecosystems
925:Freshwater Biology
363:
264:Aquatic ecosystems
60:
2835:
2834:
2816:Oceans portal
2785:
2784:
2781:
2780:
2660:Hydrothermal vent
2596:
2595:
2485:Seashore wildlife
2316:Marine ecosystems
2305:
2304:
2301:
2300:
2071:Thermal pollution
2036:Ramsar Convention
1976:Microbial ecology
1936:Fisheries science
1876:Aquatic predation
1596:10.1002/lno.11888
1494:(15): 7412–7428.
1309:Nature Geoscience
904:(10): 1779–1787.
836:978-0-12-370626-3
751:(12): 1069–1080.
673:978-94-010-6577-1
625:(12): 4981–4988.
460:De-stratification
305:
304:
16:(Redirected from
2860:
2825:
2824:
2818:
2814:
2813:
2804:
2802:Lakes portal
2800:
2799:
2798:
2768:Marine pollution
2460:Deep-water coral
2443:
2431:
2364:Marine chemistry
2324:
2311:
2228:Freshwater marsh
2121:Freshwater biome
2103:
1819:Acoustic ecology
1809:
1795:
1780:
1773:
1766:
1757:
1750:
1749:
1717:
1711:
1710:
1693:(9): 1590–1604.
1678:
1669:
1668:
1658:
1617:
1608:
1607:
1575:
1569:
1568:
1536:
1530:
1529:
1511:
1478:
1472:
1471:
1451:
1442:
1441:
1413:
1404:
1403:
1375:
1366:
1365:
1347:
1341:
1340:
1306:
1297:
1291:
1290:
1258:
1252:
1251:
1202:
1196:
1195:
1146:
1140:
1139:
1129:
1089:
1083:
1082:
1065:(6): 1360–1373.
1050:
1044:
1043:
1003:
997:
996:
947:
941:
940:
920:
914:
913:
893:
887:
886:
884:
852:
846:
845:
844:
843:
810:
801:
800:
789:
778:
777:
770:
761:
760:
740:
725:
724:
714:
712:10.3390/w9090678
690:
677:
676:
661:
652:
637:
636:
634:
609:
541:fish recruitment
351:dissolved oxygen
297:
290:
283:
246:
244:
235:
233:
222:
220:
211:
209:
200:
198:
189:
187:
169:Destratification
167:
165:
156:
154:
145:
143:
134:
132:
110:
108:
99:
97:
88:
86:
77:
75:
62:
21:
2868:
2867:
2863:
2862:
2861:
2859:
2858:
2857:
2838:
2837:
2836:
2831:
2808:
2807:
2796:
2794:
2793:
2777:
2738:Coral bleaching
2724:
2705:Seagrass meadow
2602:Marine habitats
2592:
2566:Coral reef fish
2532:
2518:Marine protists
2494:
2432:
2423:
2394:Ocean turbidity
2369:Marine food web
2318:
2297:
2239:
2178:River ecosystem
2131:Freshwater fish
2104:
2095:
1901:Bioluminescence
1886:Aquatic science
1803:
1789:
1784:
1754:
1753:
1719:
1718:
1714:
1680:
1679:
1672:
1619:
1618:
1611:
1577:
1576:
1572:
1557:10.1002/wcc.160
1538:
1537:
1533:
1480:
1479:
1475:
1453:
1452:
1445:
1415:
1414:
1407:
1377:
1376:
1369:
1362:
1349:
1348:
1344:
1304:
1299:
1298:
1294:
1260:
1259:
1255:
1204:
1203:
1199:
1148:
1147:
1143:
1091:
1090:
1086:
1052:
1051:
1047:
1005:
1004:
1000:
949:
948:
944:
922:
921:
917:
910:10.1139/f83-207
895:
894:
890:
854:
853:
849:
841:
839:
837:
812:
811:
804:
791:
790:
781:
772:
771:
764:
742:
741:
728:
692:
691:
680:
674:
659:
654:
653:
640:
611:
610:
595:
590:
557:Aquatic Science
553:
500:
462:
450:limnic eruption
368:
335:land use change
301:
242:
241:
237:Meromictic lake
231:
230:
224:Polymictic lake
218:
217:
207:
206:
202:Monomictic lake
196:
195:
191:Holomictic lake
185:
184:
163:
162:
152:
151:
141:
140:
130:
129:
106:
105:
95:
94:
84:
83:
73:
72:
56:
49:
42:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2866:
2864:
2856:
2855:
2850:
2840:
2839:
2833:
2832:
2830:
2829:
2819:
2805:
2790:
2787:
2786:
2783:
2782:
2779:
2778:
2776:
2775:
2770:
2765:
2760:
2755:
2750:
2745:
2740:
2734:
2732:
2726:
2725:
2723:
2722:
2717:
2712:
2707:
2702:
2697:
2692:
2687:
2682:
2677:
2672:
2667:
2662:
2657:
2652:
2647:
2642:
2637:
2632:
2627:
2622:
2617:
2612:
2606:
2604:
2598:
2597:
2594:
2593:
2591:
2590:
2585:
2584:
2583:
2578:
2573:
2568:
2563:
2556:Saltwater fish
2553:
2551:Marine reptile
2548:
2542:
2540:
2534:
2533:
2531:
2530:
2525:
2523:Marine viruses
2520:
2515:
2510:
2504:
2502:
2500:Microorganisms
2496:
2495:
2493:
2492:
2490:Wild fisheries
2487:
2482:
2477:
2472:
2467:
2462:
2457:
2452:
2446:
2440:
2434:
2433:
2426:
2424:
2422:
2421:
2416:
2411:
2406:
2404:Thorson's rule
2401:
2396:
2391:
2386:
2381:
2376:
2371:
2366:
2361:
2359:Marine biology
2356:
2351:
2346:
2341:
2336:
2330:
2328:
2320:
2319:
2314:
2307:
2306:
2303:
2302:
2299:
2298:
2296:
2295:
2294:
2293:
2288:
2283:
2278:
2270:
2265:
2264:
2263:
2258:
2247:
2245:
2241:
2240:
2238:
2237:
2236:
2235:
2230:
2225:
2220:
2218:Brackish marsh
2215:
2205:
2200:
2195:
2190:
2185:
2180:
2175:
2170:
2169:
2168:
2158:
2153:
2148:
2146:Lake ecosystem
2143:
2138:
2136:Hyporheic zone
2133:
2128:
2123:
2118:
2112:
2110:
2106:
2105:
2098:
2096:
2094:
2093:
2088:
2083:
2078:
2073:
2068:
2063:
2058:
2053:
2048:
2043:
2038:
2033:
2028:
2023:
2018:
2013:
2008:
2003:
1998:
1993:
1988:
1986:Microbial loop
1983:
1978:
1973:
1968:
1963:
1958:
1953:
1948:
1943:
1938:
1933:
1931:Eutrophication
1928:
1923:
1918:
1913:
1911:Cascade effect
1908:
1903:
1898:
1893:
1888:
1883:
1878:
1873:
1868:
1863:
1858:
1857:
1856:
1851:
1846:
1839:Aquatic animal
1836:
1831:
1826:
1821:
1815:
1813:
1805:
1804:
1798:
1791:
1790:
1785:
1783:
1782:
1775:
1768:
1760:
1752:
1751:
1732:(4): 656–665.
1712:
1670:
1609:
1570:
1551:(2): 115–129.
1531:
1473:
1462:(3): 175–178.
1443:
1424:(3): 589–599.
1405:
1367:
1360:
1342:
1315:(4): 271–276.
1292:
1273:(1): 129–143.
1253:
1197:
1141:
1084:
1045:
998:
942:
915:
888:
847:
835:
802:
779:
762:
726:
678:
672:
638:
592:
591:
589:
586:
585:
584:
579:
574:
569:
564:
559:
552:
549:
537:trophic levels
499:
496:
492:water aeration
461:
458:
422:carbon dioxide
381:dimictic lakes
367:
364:
353:and nutrients.
303:
302:
300:
299:
292:
285:
277:
274:
273:
272:
271:
269:Wild fisheries
266:
258:
257:
253:
252:
251:
250:
239:
228:
227:
226:
215:
204:
179:
178:
174:
173:
172:
171:
160:
149:
138:
124:
123:
117:
116:
115:
114:
103:
101:Profundal zone
92:
81:
67:
66:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2865:
2854:
2851:
2849:
2846:
2845:
2843:
2828:
2820:
2817:
2812:
2806:
2803:
2792:
2791:
2788:
2774:
2771:
2769:
2766:
2764:
2761:
2759:
2756:
2754:
2751:
2749:
2746:
2744:
2741:
2739:
2736:
2735:
2733:
2731:
2727:
2721:
2718:
2716:
2713:
2711:
2710:Sponge ground
2708:
2706:
2703:
2701:
2698:
2696:
2693:
2691:
2688:
2686:
2683:
2681:
2678:
2676:
2675:Marine biomes
2673:
2671:
2668:
2666:
2663:
2661:
2658:
2656:
2653:
2651:
2648:
2646:
2643:
2641:
2638:
2636:
2633:
2631:
2628:
2626:
2623:
2621:
2618:
2616:
2613:
2611:
2608:
2607:
2605:
2603:
2599:
2589:
2586:
2582:
2579:
2577:
2576:Demersal fish
2574:
2572:
2571:Deep-sea fish
2569:
2567:
2564:
2562:
2559:
2558:
2557:
2554:
2552:
2549:
2547:
2546:Marine mammal
2544:
2543:
2541:
2539:
2535:
2529:
2526:
2524:
2521:
2519:
2516:
2514:
2511:
2509:
2506:
2505:
2503:
2501:
2497:
2491:
2488:
2486:
2483:
2481:
2478:
2476:
2473:
2471:
2468:
2466:
2463:
2461:
2458:
2456:
2453:
2451:
2448:
2447:
2444:
2441:
2439:
2435:
2430:
2420:
2417:
2415:
2412:
2410:
2407:
2405:
2402:
2400:
2397:
2395:
2392:
2390:
2387:
2385:
2382:
2380:
2377:
2375:
2372:
2370:
2367:
2365:
2362:
2360:
2357:
2355:
2352:
2350:
2347:
2345:
2342:
2340:
2337:
2335:
2332:
2331:
2329:
2325:
2321:
2317:
2312:
2308:
2292:
2289:
2287:
2284:
2282:
2279:
2277:
2274:
2273:
2271:
2269:
2266:
2262:
2259:
2257:
2254:
2253:
2252:
2249:
2248:
2246:
2242:
2234:
2231:
2229:
2226:
2224:
2221:
2219:
2216:
2214:
2211:
2210:
2209:
2206:
2204:
2201:
2199:
2196:
2194:
2191:
2189:
2186:
2184:
2181:
2179:
2176:
2174:
2171:
2167:
2164:
2163:
2162:
2159:
2157:
2154:
2152:
2149:
2147:
2144:
2142:
2139:
2137:
2134:
2132:
2129:
2127:
2124:
2122:
2119:
2117:
2114:
2113:
2111:
2107:
2102:
2092:
2089:
2087:
2084:
2082:
2079:
2077:
2076:Trophic level
2074:
2072:
2069:
2067:
2064:
2062:
2059:
2057:
2054:
2052:
2049:
2047:
2044:
2042:
2041:Sediment trap
2039:
2037:
2034:
2032:
2029:
2027:
2024:
2022:
2019:
2017:
2016:Phytoplankton
2014:
2012:
2009:
2007:
2004:
2002:
1999:
1997:
1994:
1992:
1989:
1987:
1984:
1982:
1979:
1977:
1974:
1972:
1969:
1967:
1964:
1962:
1959:
1957:
1954:
1952:
1949:
1947:
1944:
1942:
1939:
1937:
1934:
1932:
1929:
1927:
1924:
1922:
1919:
1917:
1914:
1912:
1909:
1907:
1904:
1902:
1899:
1897:
1894:
1892:
1889:
1887:
1884:
1882:
1879:
1877:
1874:
1872:
1869:
1867:
1866:Aquatic plant
1864:
1862:
1859:
1855:
1852:
1850:
1847:
1845:
1842:
1841:
1840:
1837:
1835:
1832:
1830:
1829:Anoxic waters
1827:
1825:
1822:
1820:
1817:
1816:
1814:
1810:
1806:
1802:
1796:
1792:
1788:
1781:
1776:
1774:
1769:
1767:
1762:
1761:
1758:
1747:
1743:
1739:
1735:
1731:
1727:
1723:
1716:
1713:
1708:
1704:
1700:
1696:
1692:
1688:
1684:
1677:
1675:
1671:
1666:
1662:
1657:
1652:
1648:
1644:
1640:
1636:
1632:
1628:
1624:
1616:
1614:
1610:
1605:
1601:
1597:
1593:
1589:
1585:
1581:
1574:
1571:
1566:
1562:
1558:
1554:
1550:
1546:
1542:
1535:
1532:
1527:
1523:
1519:
1515:
1510:
1505:
1501:
1497:
1493:
1489:
1485:
1477:
1474:
1469:
1465:
1461:
1457:
1450:
1448:
1444:
1439:
1435:
1431:
1427:
1423:
1419:
1412:
1410:
1406:
1401:
1397:
1393:
1389:
1385:
1381:
1374:
1372:
1368:
1363:
1361:9781566706254
1357:
1353:
1346:
1343:
1338:
1334:
1330:
1326:
1322:
1318:
1314:
1310:
1303:
1296:
1293:
1288:
1284:
1280:
1276:
1272:
1268:
1264:
1257:
1254:
1249:
1245:
1241:
1237:
1233:
1229:
1225:
1221:
1217:
1213:
1209:
1201:
1198:
1193:
1189:
1185:
1181:
1177:
1173:
1169:
1165:
1161:
1157:
1153:
1145:
1142:
1137:
1133:
1128:
1123:
1119:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1103:
1099:
1095:
1088:
1085:
1080:
1076:
1072:
1068:
1064:
1060:
1056:
1049:
1046:
1041:
1037:
1033:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1002:
999:
994:
990:
986:
982:
978:
974:
970:
966:
963:(3): e91374.
962:
958:
954:
946:
943:
938:
934:
931:(2): 226–37.
930:
926:
919:
916:
911:
907:
903:
899:
892:
889:
883:
878:
874:
870:
866:
862:
858:
851:
848:
838:
832:
828:
824:
820:
816:
809:
807:
803:
798:
794:
788:
786:
784:
780:
775:
769:
767:
763:
758:
754:
750:
746:
739:
737:
735:
733:
731:
727:
722:
718:
713:
708:
704:
700:
696:
689:
687:
685:
683:
679:
675:
669:
665:
658:
651:
649:
647:
645:
643:
639:
633:
628:
624:
620:
616:
608:
606:
604:
602:
600:
598:
594:
587:
583:
582:Lake aeration
580:
578:
575:
573:
570:
568:
565:
563:
560:
558:
555:
554:
550:
548:
546:
542:
538:
532:
530:
524:
522:
518:
512:
510:
509:water clarity
504:
497:
495:
493:
488:
484:
480:
479:Fish die-offs
474:
470:
468:
459:
457:
455:
451:
447:
443:
439:
435:
431:
427:
423:
417:
413:
411:
410:Lake Michigan
406:
400:
398:
392:
390:
386:
382:
378:
374:
365:
358:
354:
352:
348:
347:phytoplankton
344:
340:
336:
332:
327:
325:
321:
317:
313:
309:
298:
293:
291:
286:
284:
279:
278:
276:
275:
270:
267:
265:
262:
261:
260:
259:
254:
249:
240:
238:
229:
225:
216:
214:
213:Dimictic lake
205:
203:
194:
193:
192:
183:
182:
181:
180:
175:
170:
161:
159:
150:
148:
139:
137:
128:
127:
126:
125:
122:
118:
113:
104:
102:
93:
91:
90:Limnetic zone
82:
80:
79:Littoral zone
71:
70:
69:
68:
63:
55:
54:
48:
47:
41:
40:
32:
19:
2730:Conservation
2581:Pelagic fish
2561:Coastal fish
2465:Marine fungi
2203:Water garden
2150:
2086:Water column
2031:Productivity
2006:Pelagic zone
1966:Macrobenthos
1956:Hydrobiology
1926:Ecohydrology
1729:
1725:
1715:
1690:
1686:
1630:
1626:
1587:
1583:
1573:
1548:
1544:
1534:
1491:
1487:
1476:
1459:
1455:
1421:
1417:
1386:(1): 46–49.
1383:
1379:
1351:
1345:
1312:
1308:
1295:
1270:
1266:
1256:
1215:
1211:
1200:
1159:
1155:
1144:
1101:
1097:
1087:
1062:
1058:
1048:
1015:
1011:
1001:
960:
956:
945:
928:
924:
918:
901:
897:
891:
864:
860:
850:
840:, retrieved
818:
748:
744:
702:
698:
663:
622:
618:
577:Water column
533:
525:
513:
505:
501:
475:
471:
463:
418:
414:
401:
393:
369:
328:
307:
306:
248:Amictic lake
168:
120:
112:Benthic zone
58:hypolimnion.
51:
44:
37:
2715:Sponge reef
2690:Rocky shore
2685:Oyster reef
2655:Kelp forest
2538:Vertebrates
2438:Marine life
2414:Viral shunt
2379:Marine snow
2281:Maharashtra
2188:Stream pool
2091:Zooplankton
2011:Photic zone
1971:Meiobenthos
1824:Algal bloom
1633:(1): 2318.
1104:(1): 1688.
867:: 179–190.
434:Lake Monoun
385:thermal bar
343:zooplankton
331:morphometry
324:hypolimnion
320:thermocline
158:Hypolimnion
147:Metalimnion
53:Hypolimnion
46:Metalimnion
2842:Categories
2695:Salt marsh
2630:Coral reef
2419:Whale fall
2399:Photophore
2276:Everglades
2244:Ecoregions
2183:Stream bed
2156:Macrophyte
2109:Freshwater
1941:Food chain
1854:Water bird
842:2024-04-21
705:(9): 678.
588:References
543:, such as
517:monomictic
405:Lake Taihu
397:polymictic
389:meromictic
366:Definition
316:epilimnion
177:Lake types
136:Epilimnion
65:Lake zones
39:Epilimnion
2853:Limnology
2720:Tide pool
2625:Cold seep
2409:Upwelling
2173:Rheotaxis
2166:Fish pond
2141:Limnology
2066:Substrate
2051:Siltation
1921:Dead zone
1746:0002-8487
1707:0706-652X
1647:2041-1723
1604:0024-3590
1565:1757-7780
1526:128440164
1518:2169-8996
1337:134203871
1287:0924-7963
1248:233921281
1240:1944-8007
1192:233921281
1184:1944-8007
1118:2041-1723
1079:1861-9533
1032:1614-7499
993:233921281
985:0094-8276
721:2073-4441
487:fisheries
442:Lake Kivu
430:Lake Nyos
373:temperate
361:4°C mark.
50:III. The
2827:Category
2753:HERMIONE
2670:Mangrove
2480:Seagrass
2026:Pleuston
2021:Plankton
2001:Particle
1946:Food web
1665:33875656
1136:33727551
1040:29948715
551:See also
521:dimictic
483:plankton
438:Cameroon
256:See also
43:II. The
2680:Mudflat
2640:Estuary
2610:Bay mud
2588:Seabird
2344:f-ratio
2327:General
2208:Wetland
1996:Neuston
1961:Hypoxia
1906:Biomass
1896:Benthos
1812:General
1656:8055693
1496:Bibcode
1426:Bibcode
1388:Bibcode
1317:Bibcode
1220:Bibcode
1164:Bibcode
1127:7966760
965:Bibcode
869:Bibcode
567:Hypoxia
545:walleye
36:I. The
2665:Lagoon
1991:Nekton
1849:Mammal
1844:Insect
1744:
1705:
1663:
1653:
1645:
1602:
1590:(S1).
1563:
1524:
1516:
1358:
1335:
1285:
1246:
1238:
1190:
1182:
1134:
1124:
1116:
1077:
1038:
1030:
991:
983:
833:
719:
670:
467:oxygen
454:oxygen
446:Rwanda
426:Africa
345:, and
245:
243:
234:
232:
221:
219:
210:
208:
199:
197:
188:
186:
166:
164:
155:
153:
144:
142:
133:
131:
109:
107:
98:
96:
87:
85:
76:
74:
2848:Lakes
2056:Spawn
1522:S2CID
1333:S2CID
1305:(PDF)
1244:S2CID
1188:S2CID
989:S2CID
699:Water
660:(PDF)
312:lakes
2161:Pond
1742:ISSN
1703:ISSN
1661:PMID
1643:ISSN
1600:ISSN
1561:ISSN
1514:ISSN
1356:ISBN
1283:ISSN
1236:ISSN
1180:ISSN
1132:PMID
1114:ISSN
1075:ISSN
1036:PMID
1028:ISSN
981:ISSN
831:ISBN
717:ISSN
668:ISBN
440:and
432:and
2223:Fen
2213:Bog
1734:doi
1730:128
1695:doi
1651:PMC
1635:doi
1592:doi
1553:doi
1504:doi
1492:120
1464:doi
1434:doi
1396:doi
1325:doi
1275:doi
1228:doi
1172:doi
1122:PMC
1106:doi
1067:doi
1020:doi
973:doi
933:doi
906:doi
877:doi
865:161
823:doi
753:doi
749:138
707:doi
627:doi
519:to
444:in
436:in
2844::
1740:.
1728:.
1724:.
1701:.
1691:79
1689:.
1685:.
1673:^
1659:.
1649:.
1641:.
1631:12
1629:.
1625:.
1612:^
1598:.
1588:67
1586:.
1582:.
1559:.
1547:.
1543:.
1520:.
1512:.
1502:.
1490:.
1486:.
1460:34
1458:.
1446:^
1432:.
1420:.
1408:^
1394:.
1382:.
1370:^
1331:.
1323:.
1313:12
1311:.
1307:.
1281:.
1271:60
1269:.
1265:.
1242:.
1234:.
1226:.
1216:48
1214:.
1210:.
1186:.
1178:.
1170:.
1160:48
1158:.
1154:.
1130:.
1120:.
1112:.
1102:12
1100:.
1096:.
1073:.
1063:29
1061:.
1057:.
1034:.
1026:.
1016:25
1014:.
1010:.
987:.
979:.
971:.
961:48
959:.
955:.
929:53
927:.
902:40
900:.
875:.
863:.
859:.
829:,
817:,
805:^
795:.
782:^
765:^
747:.
729:^
715:.
701:.
697:.
681:^
662:,
641:^
623:42
621:.
617:.
596:^
469:.
391:.
337:,
1779:e
1772:t
1765:v
1748:.
1736::
1709:.
1697::
1667:.
1637::
1606:.
1594::
1567:.
1555::
1549:3
1528:.
1506::
1498::
1470:.
1466::
1440:.
1436::
1428::
1422:8
1402:.
1398::
1390::
1384:8
1364:.
1339:.
1327::
1319::
1289:.
1277::
1250:.
1230::
1222::
1194:.
1174::
1166::
1138:.
1108::
1081:.
1069::
1042:.
1022::
995:.
975::
967::
939:.
935::
912:.
908::
885:.
879::
871::
825::
799:.
759:.
755::
723:.
709::
703:9
635:.
629::
428:(
296:e
289:t
282:v
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.