37:
216:
IPS/UPS is synchronously interconnected with the Baltic countries, but on 16 July 2024, the three Baltic states formally notified Russia and
Belarus of their decision to withdraw from the BRELL agreement. In addition, it has an interlink to the
253:
157:
UPS of Russia came into existence as a result of
Russian Federation Decision #526 dated 11 July 2001 "On the Restructuring of the Russian Federation United Energy System". Up until 1 July 2008
563:
568:
573:
473:
72:
The unified power system was started in 1956 by interconnecting the power systems of Center and Middle Volga. By 1978, the unified power system included all of the
394:. TEN-E Conference: Developing a Secure and Sustainable Trans European Energy Network. Union for the Co-ordination of Transmission of Electricity. Archived from
500:
337:
386:
304:
367:
278:
240:
spanning 13 time zones. There was also a proposal to interconnect the
Russian grid to China and other Asian systems with HVDC links as part of an
578:
201:
108:
558:
154:: ECO Center, ECO South, ECO North-West, ECO Middle Volga, ECO Urals and ECO Siberia. ECO East operates in isolation from UPS of Russia.
53:
420:
205:
449:"ENTSO-E agrees to start trial synchronization of continental European power grids with those of Ukraine, Moldova from March 16"
200:
In early 2021 Ukraine announced that it would be disconnecting from Russia and
Belarus by the end of 2023 and integrating into
36:
208:, also disconnecting Moldova. In early March 2022, Ukraine completed an emergency synchronization with the European grid.
341:
151:
56:, with a common mode of operation and centralized supervisory control. It has an installed generation capacity of 300
524:
507:
388:
Reliable electricity system and requested extensions towards CIS and Baltic countries, North Africa and Middle East
88:
49:
395:
236:
In 2005, Russia and the EU considered unifying the IPS/UPS network with the ENTSO-E to form a single synchronous
311:
520:
273:
226:
190:
64:-hours (TWh) per year for its 280 million customers. The system spans eight time zones.
241:
143:
142:
The
Russian portion of the interconnection is known as Unified Power System of Russia (UPS;
173:
The
Integrated Power System (IPS) portion of the network includes the national networks of
259:
448:
92:
17:
552:
115:
77:
73:
263:
267:
237:
186:
178:
174:
123:
119:
541:(See "Operation of Power Systems" link for title page and table of contents.)
435:"Ukraine to disconnect from Russia and Belarus' power systems by end of 2023"
111:(ENTSO-E), operated synchronously with the Unified Power System of the USSR.
230:
57:
421:"Kyiv: Ukraine will cut itself off from power grids of Russia and Belarus"
194:
104:
61:
182:
162:
158:
131:
127:
100:
96:
28:
474:"Baltic states give Russia notice of electricity grid switch-off date"
516:
338:"Energy blockade reportedly costs Sangtudinskaya GES-1 at US$ 20 mln"
310:. Brussels: UCTE-IPSUPS Study presentation. p. 5. Archived from
218:
84:
122:
disconnected from the system resulting also in the disconnection of
35:
434:
254:
European
Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity
519:: Institute for Electrical Equipment and Power Plants (IAEW) at
222:
27:"Unified Energy System" redirects here. For other uses, see
499:
Haubrich, Hans-Jürgen; Dieter Denzel (30 October 2008).
118:) were added to the integrated system in 2001. In 2009,
40:
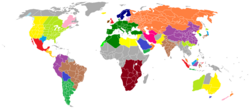
Worldwide synchronous grids. IPS/UPS is shown in orange.
368:"EU to urgently link electricity grid with Ukraine's"
161:
operated UPS. It is currently being operated by the
204:. In February 2022, Ukraine disconnected due to the
262:- proposal for combining ENTSO-E, IPS/UPS and some
130:disconnected, resulting in the disconnection of
564:Electric power transmission systems in Europe
8:
569:Electric power transmission systems in Asia
361:
359:
298:
296:
294:
509:Operation of Interconnected Power Systems
223:back-to-back high-voltage direct current
574:Electric power infrastructure in Russia
290:
279:Baltic states synchronization with UCTE
50:wide area synchronous transmission grid
336:Chorshanbiyev, Payrav (30 July 2010).
109:synchronous grid of Continental Europe
7:
148:Единая энергетическая система России
229:to Finland with a capacity of 1420
212:Interconnections with other systems
114:Central Asian countries (excluding
501:"Interconnected systems in Europe"
83:In 1979–1993 the power systems of
25:
366:Abnett, Kate (28 February 2022).
206:2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
152:regional transmission operators
303:Sergei Lebed (20 April 2005).
1:
579:Eurasian economic integration
202:the continental European grid
523:. p. 16. Archived from
559:Wide area synchronous grids
340:. ASIA-Plus. Archived from
595:
423:. UAWire. 25 January 2021.
89:German Democratic Republic
60:, and produces 1,200
26:
437:. TASS. 23 February 2021.
385:Luther, Matthias (2004).
147:
521:RWTH Aachen University
41:
18:Unified Energy Systems
165:(FGC UES) of Russia.
39:
163:Federal Grid Company
274:European super grid
150:) and includes six
305:"IPS/UPS Overview"
107:, now part of the
42:
16:(Redirected from
586:
543:
539:
537:
535:
529:
514:
505:
496:
490:
489:
487:
485:
470:
464:
463:
461:
459:
453:Interfax-Ukraine
445:
439:
438:
431:
425:
424:
417:
411:
410:
408:
406:
400:
393:
382:
376:
375:
363:
354:
353:
351:
349:
344:on 18 April 2013
333:
327:
326:
324:
322:
316:
309:
300:
242:Asian Super Grid
149:
21:
594:
593:
589:
588:
587:
585:
584:
583:
549:
548:
547:
546:
533:
531:
530:on 19 July 2011
527:
512:
503:
498:
497:
493:
483:
481:
472:
471:
467:
457:
455:
447:
446:
442:
433:
432:
428:
419:
418:
414:
404:
402:
401:on 28 July 2011
398:
391:
384:
383:
379:
365:
364:
357:
347:
345:
335:
334:
330:
320:
318:
317:on 28 July 2011
314:
307:
302:
301:
292:
287:
260:SuperSmart Grid
250:
214:
171:
140:
70:
32:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
592:
590:
582:
581:
576:
571:
566:
561:
551:
550:
545:
544:
491:
480:. 16 July 2024
465:
440:
426:
412:
377:
355:
328:
289:
288:
286:
283:
282:
281:
276:
271:
266:networks with
257:
249:
246:
213:
210:
170:
167:
139:
136:
93:Czechoslovakia
69:
66:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
591:
580:
577:
575:
572:
570:
567:
565:
562:
560:
557:
556:
554:
542:
526:
522:
518:
511:
510:
502:
495:
492:
479:
475:
469:
466:
454:
450:
444:
441:
436:
430:
427:
422:
416:
413:
397:
390:
389:
381:
378:
373:
369:
362:
360:
356:
343:
339:
332:
329:
313:
306:
299:
297:
295:
291:
284:
280:
277:
275:
272:
269:
265:
261:
258:
255:
252:
251:
247:
245:
243:
239:
234:
232:
228:
224:
221:system via a
220:
211:
209:
207:
203:
198:
196:
192:
188:
184:
180:
176:
168:
166:
164:
160:
155:
153:
145:
137:
135:
133:
129:
125:
121:
117:
112:
110:
106:
102:
98:
94:
90:
86:
81:
79:
75:
67:
65:
63:
59:
55:
54:CIS countries
51:
47:
38:
34:
30:
19:
540:
532:. Retrieved
525:the original
508:
494:
482:. Retrieved
477:
468:
456:. Retrieved
452:
443:
429:
415:
403:. Retrieved
396:the original
387:
380:
371:
346:. Retrieved
342:the original
331:
319:. Retrieved
312:the original
270:capabilities
235:
215:
199:
172:
156:
141:
116:Turkmenistan
113:
82:
78:Central Asia
74:Soviet Union
71:
45:
43:
33:
405:12 December
348:13 November
264:Middle East
126:. In 2022,
553:Categories
534:6 December
321:7 December
285:References
268:smart grid
238:super grid
227:connection
187:Azerbaijan
179:Kyrgyzstan
175:Kazakhstan
124:Tajikistan
120:Uzbekistan
256:(ENTSO-E)
231:megawatts
58:gigawatts
458:16 March
248:See also
195:Mongolia
105:Bulgaria
62:terawatt
52:of some
484:16 July
372:Reuters
225:(HVDC)
191:Georgia
183:Belarus
159:RAO UES
144:Russian
132:Moldova
128:Ukraine
101:Romania
97:Hungary
76:except
68:History
46:IPS/UPS
29:RAO UES
517:Aachen
219:Nordic
193:, and
87:, the
85:Poland
528:(PDF)
513:(PDF)
504:(PDF)
399:(PDF)
392:(PDF)
315:(PDF)
308:(PDF)
48:is a
536:2008
486:2024
460:2022
407:2008
350:2010
323:2008
103:and
44:The
478:LSM
169:IPS
138:UPS
555::
515:.
506:.
476:.
451:.
370:.
358:^
293:^
244:.
233:.
197:.
189:,
185:,
181:,
177:,
146::
134:.
99:,
95:,
91:,
80:.
538:.
488:.
462:.
409:.
374:.
352:.
325:.
31:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.