193:
42:
160:
167:
The identification of a suitable base is often an important step when optimizing a Wittig reaction. Because phosphonium ylides are seldom isolated, the byproduct(s) generated upon deprotonation essentially plays the role of an additive in a Wittig reaction. As a result, the choice of base has a
156:), or sodium hydride (NaH) are also commonly used. For stabilized Wittig reagents bearing conjugated electron-withdrawing groups, even relatively weak bases like aqueous sodium hydroxide or potassium carbonate can be employed.
176:
Electron-withdrawing groups (EWGs) enhance the ease of deprotonation of phosphonium salts. This behavior is illustrated by the finding that deprotonation of triphenylcarbethoxymethylphosphonium requires only
226:
Wittig reagents are prepared by deprotonation of alkyl phosphonium salts, and this reaction can be reversed. The methodology can be useful in the preparation of unusual Wittig reagents.
85:. Quaternization of triphenylphosphine with secondary halides is typically inefficient. For this reason, Wittig reagents are rarely used to prepare tetrasubstituted alkenes.
185:
is somewhat air-stable. It is however less reactive than ylides lacking EWGs. For example they usually fail to react with ketones, necessitating the use of the
521:; Basil, J. D. (1982). "Oxidative Addition of Methyl Iodide to a Dinuclear gold(I) Complex. The X-Ray Crystal Structure of Bis-iodomethyldigold(II)(Au-Au), Au
186:
362:
182:
347:
352:
189:
as an alternative. Such stabilized ylides usually give rise to an E-alkene product when they react, rather than the more usual Z-alkene.
614:
57:. They are typically generated and used in situ. THF is a typical solvent. Some are sufficiently stable to be sold commercially.
357:
416:
Crystallographic characterization of methylenetriphenylphosphorane shows that the phosphorus atom is tetrahedral. The PCH
367:
298:
Although ylides are "electron-rich", they are susceptible to deprotonation of alkyl substituents. Treatment of Me
25:
168:
strong influence on the efficiency and, when applicable, the stereochemical outcome of the Wittig reaction.
555:
Schmidbaur, H. (1983). "Phosphorus Ylides in the
Coordination Sphere of Transition Metals: An Inventory".
211:
582:
Bart, J. C. J. (1969). "Structure of the Non-Stabilized
Phosphonium Ylid Methylenetriphenylphosphorane".
41:
469:
448:
Wittig reaction in
Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 5, p. 361 (1973); Vol. 45, p. 33 (1965). (
145:
518:
379:
74:
54:
438:
17:
591:
564:
537:
500:
335:
178:
66:
215:
53:
Because they typically hydrolyze and oxidize readily, Wittig reagents are prepared using
449:
442:
192:
94:
70:
608:
279:
428:
distance is 1.661 Å, which is much shorter than the other P-C distances (1.823 Å).
82:
78:
491:
Appel, Rolf; Morbach, Wolfgang (1977). "(Chloromethylene)triphenylphosphorane".
568:
504:
159:
595:
541:
319:
93:
The alkylphosphonium salt is deprotonated with a strong base such as
33:
441:, Coll. Vol. 10, p. 703 (2004); Vol. 75, p. 153 (1998). (
318:
Li. Having carbanion-like properties, lithiated ylides function as
191:
378:
Wittig reagents are usually described as a combination of two
36:. They are used to convert ketones and aldehydes to alkenes:
81:. Wittig reagents are usually derived from a primary
134:
BuLi), other strong bases like sodium and potassium
557:Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English
493:Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English
413:form, which is the more familiar representation.
8:
246:−X, produces substituted phosphonium salts:
89:Bases for deprotonation of phosphonium salts
65:Wittig reagents are usually prepared from a
470:"(Carbethoxymethylene)triphenylphosphorane"
148:(LiHMDS, NaHMDS, KHDMS, where HDMS = N(SiMe
158:
461:
363:Triphenylcarbethoxymethylenephosphorane
183:triphenylcarbethoxymethylenephosphorane
348:(Chloromethylene)triphenylphosphorane
144:BuOK), lithium, sodium and potassium
7:
353:Methoxymethylenetriphenylphosphorane
69:, which is in turn prepared by the
409:form and the latter is called the
14:
584:Journal of the Chemical Society B
242:with a primary alkyl halide R−CH
187:Horner–Wadsworth–Emmons reaction
40:
196:A "stabilized" Wittig reagent.
1:
358:Methylenetriphenylphosphorane
306:with butyl lithium affords Me
210:Wittig reagents are used for
163:Br, typical phosphonium salt.
61:Formation of phosphonium salt
368:Hexaphenylcarbodiphosphorane
282:in the usual way to give Ph
32:P=CHR', where R is usually
631:
615:Organophosphorus compounds
26:organophosphorus compounds
420:centre is planar and the
405:The former is called the
569:10.1002/anie.198309071
505:10.1002/anie.197701801
197:
164:
212:olefination reactions
195:
162:
596:10.1039/J29690000350
380:resonance structures
146:hexamethyldisilazide
542:10.1021/om00066a021
437:Wittig reaction in
278:These salts can be
172:Substituent effects
55:air-free techniques
334:Li is a potential
198:
165:
75:triphenylphosphine
439:Organic Syntheses
18:organic chemistry
622:
600:
599:
579:
573:
572:
552:
546:
545:
515:
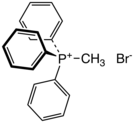
509:
508:
488:
482:
481:
479:
477:
466:
336:bidentate ligand
234:Alkylation of Ph
181:. The resulting
179:sodium hydroxide
67:phosphonium salt
44:
28:of the formula R
630:
629:
625:
624:
623:
621:
620:
619:
605:
604:
603:
581:
580:
576:
563:(12): 907–927.
554:
553:
549:
530:Organometallics
527:
524:
517:
516:
512:
490:
489:
485:
475:
473:
472:. Sigma-Aldrich
468:
467:
463:
459:
434:
427:
419:
401:
397:
393:
389:
376:
344:
333:
329:
325:
317:
313:
309:
305:
301:
296:
289:
285:
273:
269:
265:
261:
257:
253:
245:
241:
237:
232:
224:
216:Wittig reaction
208:
203:
174:
155:
151:
131:-butyllithium (
123:
119:
116:P=CHR + LiX + C
115:
111:
107:
91:
63:
51:
31:
22:Wittig reagents
12:
11:
5:
628:
626:
618:
617:
607:
606:
602:
601:
574:
547:
536:(6): 871–873.
525:
522:
519:Fackler, J. P.
510:
499:(3): 180–181.
483:
460:
458:
455:
454:
453:
446:
433:
432:External links
430:
425:
417:
403:
402:
399:
395:
391:
387:
375:
372:
371:
370:
365:
360:
355:
350:
343:
340:
331:
327:
323:
315:
311:
307:
303:
299:
295:
292:
287:
283:
276:
275:
271:
267:
263:
259:
255:
251:
243:
239:
235:
231:
228:
223:
220:
207:
204:
202:
199:
173:
170:
153:
149:
125:
124:
121:
117:
113:
109:
105:
90:
87:
71:quaternization
62:
59:
50:
47:
46:
45:
29:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
627:
616:
613:
612:
610:
597:
593:
589:
585:
578:
575:
570:
566:
562:
558:
551:
548:
543:
539:
535:
531:
520:
514:
511:
506:
502:
498:
494:
487:
484:
471:
465:
462:
456:
451:
447:
444:
440:
436:
435:
431:
429:
423:
414:
412:
408:
385:
384:
383:
381:
373:
369:
366:
364:
361:
359:
356:
354:
351:
349:
346:
345:
341:
339:
337:
321:
294:Deprotonation
293:
291:
281:
249:
248:
247:
229:
227:
221:
219:
217:
213:
205:
200:
194:
190:
188:
184:
180:
171:
169:
161:
157:
147:
143:
140:
137:
133:
130:
103:
102:
101:
99:
98:-butyllithium
97:
88:
86:
84:
80:
76:
72:
68:
60:
58:
56:
48:
43:
39:
38:
37:
35:
27:
23:
19:
587:
583:
577:
560:
556:
550:
533:
529:
513:
496:
492:
486:
474:. Retrieved
464:
421:
415:
410:
406:
404:
377:
297:
280:deprotonated
277:
233:
225:
209:
175:
166:
142:
139:
135:
132:
128:
126:
95:
92:
83:alkyl halide
79:alkyl halide
64:
52:
21:
15:
590:: 350–365.
411:phosphorane
222:Protonation
214:, i.e. the
206:Olefination
138:-butoxide (
49:Preparation
457:References
230:Alkylation
528:(CH3)I".
374:Structure
322:. Thus Me
201:Reactions
609:Category
342:Examples
127:Besides
77:with an
476:27 June
450:Article
443:Article
320:ligands
286:P=CH−CH
141:BuONa,
112:Li → Ph
262:X → Ph
34:phenyl
407:ylide
258:+ RCH
104:X + C
588:1969
478:2019
398:P=CR
394:↔ Ph
326:P(CH
310:P(CH
290:R.
254:P=CH
238:P=CH
24:are
592:doi
565:doi
538:doi
501:doi
422:P=C
390:PCR
302:PCH
274:R X
266:PCH
73:of
16:In
611::
586:.
561:22
559:.
532:.
497:16
495:.
386:Ph
382::
338:.
270:CH
250:Ph
218:.
122:10
100::
20:,
598:.
594::
571:.
567::
544:.
540::
534:1
526:2
523:2
507:.
503::
480:.
452:)
445:)
426:2
424:H
418:2
400:2
396:3
392:2
388:3
332:2
330:)
328:2
324:2
316:2
314:)
312:2
308:2
304:2
300:3
288:2
284:3
272:2
268:2
264:3
260:2
256:2
252:3
244:2
240:2
236:3
154:2
152:)
150:3
136:t
129:n
120:H
118:4
114:3
110:9
108:H
106:4
96:n
30:3
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.