1960:
280:
864:. The neurotransmitter chemical then diffuses across to receptors located on the membrane of the target cell. The neurotransmitter binds to these receptors and activates them. Depending on the type of receptors that are activated, the effect on the target cell can be to excite the target cell, inhibit it, or alter its metabolism in some way. This entire sequence of events often takes place in less than a thousandth of a second. Afterward, inside the presynaptic terminal, a new set of vesicles is moved into position next to the membrane, ready to be released when the next action potential arrives. The action potential is the final electrical step in the integration of synaptic messages at the scale of the neuron.
192:. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites receive signals whereas axons transmit them). Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. In some species, axons can emanate from dendrites known as axon-carrying dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other.
839:
339:
939:
can potentially become the axon. This alteration of polarity only occurs when the axon is cut at least 10 μm shorter than the other neurites. After the incision is made, the longest neurite will become the future axon and all the other neurites, including the original axon, will turn into dendrites. Imposing an external force on a neurite, causing it to elongate, will make it become an axon. Nonetheless, axonal development is achieved through a complex interplay between extracellular signaling, intracellular signaling and
1948:
separated from the axon origin. In many species some of the neurons have axons that emanate from the dendrite and not from the cell body, and these are known as axon-carrying dendrites. In many cases, an axon originates at an axon hillock on the soma; such axons are said to have "somatic origin". Some axons with somatic origin have a "proximal" initial segment adjacent the axon hillock, while others have a "distal" initial segment, separated from the soma by an extended axon hillock.
829:
38:
656:
733:, electrical currents produced at each node of Ranvier are conducted with little attenuation to the next node in line, where they remain strong enough to generate another action potential. Thus in a myelinated axon, action potentials effectively "jump" from node to node, bypassing the myelinated stretches in between, resulting in a propagation speed much faster than even the fastest unmyelinated axon can sustain.
645:
512:
1054:
889:(~250μs). 2. The voltage change is triphasic. 3. Activity recorded on a tetrode is seen on only one of the four recording wires. In recordings from freely moving rats, axonal signals have been isolated in white matter tracts including the alveus and the corpus callosum as well hippocampal gray matter.
938:
that are equivalent, yet only one of these neurites is destined to become the axon. It is unclear whether axon specification precedes axon elongation or vice versa, although recent evidence points to the latter. If an axon that is not fully developed is cut, the polarity can change and other neurites
846:
Most axons carry signals in the form of action potentials, which are discrete electrochemical impulses that travel rapidly along an axon, starting at the cell body and terminating at points where the axon makes synaptic contact with target cells. The defining characteristic of an action potential is
554:
The axon initial segment is unmyelinated and contains a specialized complex of proteins. It is between approximately 20 and 60 μm in length and functions as the site of action potential initiation. Both the position on the axon and the length of the AIS can change showing a degree of plasticity
1184:
play an important role in regulating the length of axons. Based on this observation, researchers developed an explicit model for axonal growth describing how motor proteins could affect the axon length on the molecular level. These studies suggest that motor proteins carry signaling molecules from
1947:
In other cases as seen in rat studies an axon originates from a dendrite; such axons are said to have "dendritic origin". Some axons with dendritic origin similarly have a "proximal" initial segment that starts directly at the axon origin, while others have a "distal" initial segment, discernibly
1263:
Later findings by other researchers identified two groups of Aa fibers that were sensory fibers. These were then introduced into a system (Lloyd classification) that only included sensory fibers (though some of these were mixed nerves and were also motor fibers). This system refers to the sensory
1158:
is a type of neurite outgrowth inhibitory component that is present in the central nervous system myelin membranes (found in an axon). It has a crucial role in restricting axonal regeneration in adult mammalian central nervous system. In recent studies, if Nogo-A is blocked and neutralized, it is
600:
in the cell. Microtubules form in the axoplasm at the axon hillock. They are arranged along the length of the axon, in overlapping sections, and all point in the same direction – towards the axon terminals. This is noted by the positive endings of the microtubules. This overlapping
855:
When an action potential reaches a presynaptic terminal, it activates the synaptic transmission process. The first step is rapid opening of calcium ion channels in the membrane of the axon, allowing calcium ions to flow inward across the membrane. The resulting increase in intracellular calcium
1203:
can be classified based on their physical features and signal conduction properties. Axons were known to have different thicknesses (from 0.1 to 20 μm) and these differences were thought to relate to the speed at which an action potential could travel along the axon – its
1959:
1179:
Axons vary largely in length from a few micrometers up to meters in some animals. This emphasizes that there must be a cellular length regulation mechanism allowing the neurons both to sense the length of their axons and to control their growth accordingly. It was discovered that
1903:
for this work in 1963. The formulae detailing axonal conductance were extended to vertebrates in the
Frankenhaeuser–Huxley equations. The understanding of the biochemical basis for action potential propagation has advanced further, and includes many details about individual
543:(AIS) is a structurally and functionally separate microdomain of the axon. One function of the initial segment is to separate the main part of an axon from the rest of the neuron; another function is to help initiate action potentials. Both of these functions support neuron
377:, which is specialized to conduct signals very rapidly, is close to 1 millimeter in diameter, the size of a small pencil lead. The numbers of axonal telodendria (the branching structures at the end of the axon) can also differ from one nerve fiber to the next. Axons in the
227:
of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear along the length of an axon as it extends; these are called
851:
characteristic allows action potentials to be transmitted from one end of a long axon to the other without any reduction in size. There are, however, some types of neurons with short axons that carry graded electrochemical signals, of variable amplitude.
601:
arrangement provides the routes for the transport of different materials from the cell body. Studies on the axoplasm has shown the movement of numerous vesicles of all sizes to be seen along cytoskeletal filaments – the microtubules, and
900:
In addition to propagating action potentials to axonal terminals, the axon is able to amplify the action potentials, which makes sure a secure propagation of sequential action potentials toward the axonal terminal. In terms of molecular mechanisms,
1143:
It has also been discovered through research that if the axons of a neuron were damaged, as long as the soma (the cell body of a neuron) is not damaged, the axons would regenerate and remake the synaptic connections with neurons with the help of
1216:
proved this hypothesis, and identified several types of nerve fiber, establishing a relationship between the diameter of an axon and its nerve conduction velocity. They published their findings in 1941 giving the first classification of axons.
860:(tiny containers enclosed by a lipid membrane) filled with a neurotransmitter chemical to fuse with the axon's membrane and empty their contents into the extracellular space. The neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic nerve through
555:
that can fine-tune the neuronal output. A longer AIS is associated with a greater excitability. Plasticity is also seen in the ability of the AIS to change its distribution and to maintain the activity of neural circuitry at a constant level.
795:
that function in the release of neurotransmitters. However, axonal varicosities are also present in neurodegenerative diseases where they interfere with the conduction of an action potential. Axonal varicosities are also the hallmark of
867:
Extracellular recordings of action potential propagation in axons has been demonstrated in freely moving animals. While extracellular somatic action potentials have been used to study cellular activity in freely moving animals such as
1756:
takes place at the part of the axon furthest from the cell body. This degeneration takes place quickly following the injury, with the part of the axon being sealed off at the membranes and broken down by macrophages. This is known as
729:, which are found periodically interspersed between segments of the myelin sheath. Therefore, at the point of the node of Ranvier, the axon is reduced in diameter. These nodes are areas where action potentials can be generated. In
896:
in the neurons. Although previous studies indicate an axonal origin of a single spike evoked by short-term pulses, physiological signals in vivo trigger the initiation of sequential spikes at the cell bodies of the neurons.
1034:
content are inversely correlated; when PGMS becomes enriched at the tip of a neurite, its f-actin content is substantially decreased. In addition, exposure to actin-depolimerizing drugs and toxin B (which inactivates
1073:. The filopodia are the mechanism by which the entire process adheres to surfaces and explores the surrounding environment. Actin plays a major role in the mobility of this system. Environments with high levels of
880:
can also be recorded. Extracellular recordings of axon action potential propagation is distinct from somatic action potentials in three ways: 1. The signal has a shorter peak-trough duration (~150μs) than of
1136:, are typically other neurons that are sometimes immature. When the axon has completed its growth at its connection to the target, the diameter of the axon can increase by up to five times, depending on the
474:
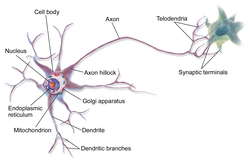
The structure of a neuron is seen to consist of two separate functional regions, or compartments – the cell body together with the dendrites as one region, and the axonal region as the other.
3181:
Fletcher TL, Banker GA (December 1989). "The establishment of polarity by hippocampal neurons: the relationship between the stage of a cell's development in situ and its subsequent development in culture".
636:. Dynein is minus-end directed. There are many forms of kinesin and dynein motor proteins, and each is thought to carry a different cargo. The studies on transport in the axon led to the naming of kinesin.
1159:
possible to induce long-distance axonal regeneration which leads to enhancement of functional recovery in rats and mouse spinal cord. This has yet to be done on humans. A recent study has also found that
3517:
Hedgecock EM, Culotti JG, Hall DH (January 1990). "The unc-5, unc-6, and unc-40 genes guide circumferential migrations of pioneer axons and mesodermal cells on the epidermis in C. elegans".
3425:
Serafini T, Kennedy TE, Galko MJ, Mirzayan C, Jessell TM, Tessier-Lavigne M (August 1994). "The netrins define a family of axon outgrowth-promoting proteins homologous to C. elegans UNC-6".
483:
The axonal region or compartment, includes the axon hillock, the initial segment, the rest of the axon, and the axon telodendria, and axon terminals. It also includes the myelin sheath. The
181:, and group C are unmyelinated. These groups include both sensory fibers and motor fibers. Another classification groups only the sensory fibers as Type I, Type II, Type III, and Type IV.
487:
that produce the neuronal proteins are absent in the axonal region. Proteins needed for the growth of the axon, and the removal of waste materials, need a framework for transport. This
1895:
also employed the squid giant axon (1939) and by 1952 they had obtained a full quantitative description of the ionic basis of the action potential, leading to the formulation of the
424:
Schwann cells form the myelin sheath of a myelinated axon. Oligodendrocytes form the insulating myelin in the CNS. Along myelinated nerve fibers, gaps in the myelin sheath known as
967:
netrin receptor is mutated, several neurites are irregularly projected out of neurons and finally a single axon is extended anteriorly. The neurotrophic factors –
1765:, particularly when axonal transport is impaired, this is known as Wallerian-like degeneration. Studies suggest that the degeneration happens as a result of the axonal protein
4336:
219:
but can also make contact with muscle or gland cells. In some circumstances, the axon of one neuron may form a synapse with the dendrites of the same neuron, resulting in an
1220:
Axons are classified in two systems. The first one introduced by
Erlanger and Gasser, grouped the fibers into three main groups using the letters A, B, and C. These groups,
771:. This makes multiple synaptic connections with other neurons possible. Sometimes the axon of a neuron may synapse onto dendrites of the same neuron, when it is known as an
1077:(CAMs) create an ideal environment for axonal growth. This seems to provide a "sticky" surface for axons to grow along. Examples of CAMs specific to neural systems include
114:
998:
at the tip of neutrites, is required for the elongation of axons. PMGS asymmetrically distributes to the tip of the neurite that is destined to become the future axon.
4458:"Perturbed interactions of mutant proteolipid protein/DM20 with cholesterol and lipid rafts in oligodendroglia: implications for dysmyelination in spastic paraplegia"
678:, or unmyelinated. This is the provision of an insulating layer, called a myelin sheath. The myelin membrane is unique in its relatively high lipid to protein ratio.
1121:. Some of these are surface bound to cells and thus act as short range attractants or repellents. Others are difusible ligands and thus can have long range effects.
235:
A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can target multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals. A bundle of axons make a
149:
to the cell body and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction can be the cause of many inherited and acquired
70:
4595:
1039:) causes the formation of multiple axons. Consequently, the interruption of the actin network in a growth cone will promote its neurite to become the axon.
232:("in passing boutons") and can be in the hundreds or even the thousands along one axon. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches.
1812:
that axonal damage from a single mild traumatic brain injury, can leave a susceptibility to further damage, after repeated mild traumatic brain injuries.
4890:
1011:
4904:
Hsu K, Terakawa S (July 1996). "Fenestration in the myelin sheath of nerve fibers of the shrimp: a novel node of excitation for saltatory conduction".
1010:
is increased at the tip of destined axon. Disrupting the activity of PI3K inhibits axonal development. Activation of PI3K results in the production of
3606:
Da Silva JS, Hasegawa T, Miyagi T, Dotti CG, Abad-Rodriguez J (May 2005). "Asymmetric membrane ganglioside sialidase activity specifies axonal fate".
361:. Some axons can extend up to one meter or more while others extend as little as one millimeter. The longest axons in the human body are those of the
3470:"A ligand-gated association between cytoplasmic domains of UNC5 and DCC family receptors converts netrin-induced growth cone attraction to repulsion"
5077:
4344:
2981:"CLARITY reveals a more protracted temporal course of axon swelling and disconnection than previously described following traumatic brain injury"
2140:
1867:
was the first to describe the gaps or nodes found on axons and for this contribution these axonal features are now commonly referred to as the
4830:
Grant G (December 2006). "The 1932 and 1944 Nobel Prizes in physiology or medicine: rewards for ground-breaking studies in neurophysiology".
4522:
4287:
3165:
2820:
2738:
2710:
1900:
369:
to the big toe of each foot. The diameter of axons is also variable. Most individual axons are microscopic in diameter (typically about one
4631:"Repeated mild traumatic brain injuries induce persistent changes in plasma protein and magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers in the rat"
847:
that it is "all-or-nothing" – every action potential that an axon generates has essentially the same size and shape. This
4917:
4773:
4884:
4803:
4333:
4312:
3750:
972:
927:
523:
is the area formed from the cell body of the neuron as it extends to become the axon. It precedes the initial segment. The received
842:
Neurotransmitter released from presynaptic axon terminal, and transported across synaptic cleft to receptors on postsynaptic neuron
5701:
5631:
648:
5696:
5626:
5241:
4738:
338:
1090:
910:
801:
551:) of a neuron receive input signals at the basal region, and at the apical region the neuron's axon provides output signals.
1932:
has the largest axon known. Its size ranges from 0.5 (typically) to 1 mm in diameter and is used in the control of its
428:
occur at evenly spaced intervals. The myelination enables an especially rapid mode of electrical impulse propagation called
5316:
4743:
1078:
800:. Axonal damage is usually to the axon cytoskeleton disrupting transport. As a consequence protein accumulations such as
65:
4607:
1014:(PtdIns) which can cause significant elongation of a neurite, converting it into an axon. As such, the overexpression of
892:
In fact, the generation of action potentials in vivo is sequential in nature, and these sequential spikes constitute the
5311:
5299:
5070:
1608:
1240:). The first group A, was subdivided into alpha, beta, gamma, and delta fibers – Aα, Aβ, Aγ, and Aδ. The
902:
624:
carries cell waste materials from the axon terminal to the cell body. Outgoing and ingoing tracks use different sets of
563:
5351:
5289:
2220:
1852:
1805:
1570:
531:
in the neuron are transmitted to the axon hillock for the generation of an action potential from the initial segment.
528:
1185:
the soma to the growth cone and vice versa whose concentration oscillates in time with a length-dependent frequency.
566:
in the initial segment where the action potential is initiated. The ion channels are accompanied by a high number of
5346:
1875:, a Spanish anatomist, proposed that axons were the output components of neurons, describing their functionality.
5856:
5706:
5641:
5269:
4716:
3694:"The axonal glycoprotein TAG-1 is an immunoglobulin superfamily member with neurite outgrowth-promoting activity"
3361:
Arimura N, Kaibuchi K (March 2007). "Neuronal polarity: from extracellular signals to intracellular mechanisms".
3030:"Short duration waveforms recorded extracellularly from freely moving rats are representative of axonal activity"
1872:
1762:
1534:
1200:
1194:
1137:
421:
248:
154:
146:
2077:"Receptive fields, geometry and conduction block of sensory neurones in the central nervous system of the leech"
1936:
system. The fastest recorded conduction speed of 210 m/s, is found in the ensheathed axons of some pelagic
1896:
5636:
5362:
4505:
Matalon R, Michals-Matalon K, Surendran S, Tyring SK (2006). "Canavan
Disease: Studies on the Knockout Mouse".
4231:"Axonal conduction velocity changes following muscle tenotomy or deafferentation during development in the rat"
1628:
1369:
1327:
797:
53:
1883:
earlier developed the classification system for peripheral nerve fibers, based on axonal conduction velocity,
787:
In the normally developed brain, along the shaft of some axons are located pre-synaptic boutons also known as
955:
surrounding neurons play a prominent role in axonal development. These signaling molecules include proteins,
389:
extend. Elaborate branching allows for the simultaneous transmission of messages to a large number of target
5896:
5335:
5063:
1986:
382:
133:. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands. In certain
2271:"Axonal Membranes and Their Domains: Assembly and Function of the Axon Initial Segment and Node of Ranvier"
1745:. The dysfunction of axons in the nervous system is one of the major causes of many inherited and acquired
5803:
5330:
5094:
3411:
1856:
1816:
1797:
1758:
1753:
1213:
1102:
1074:
567:
459:
in the CNS. Where these tracts cross the midline of the brain to connect opposite regions they are called
378:
240:
158:
77:
5661:
5651:
5586:
2001:
1921:
1864:
1801:
1772:
1746:
1742:
1738:
1716:
1712:
1682:
1510:
1455:
1036:
496:
150:
138:
20:
4993:"Heterogeneity of the Axon Initial Segment in Interneurons and Pyramidal Cells of Rodent Visual Cortex"
1863:
were the first to identify and characterize the axon initial segment. Kölliker named the axon in 1896.
1721:
In order of degree of severity, injury to a nerve in the peripheral nervous system can be described as
747:
An axon can divide into many branches called telodendria (Greek for 'end of tree'). At the end of each
5786:
5683:
5613:
5439:
5294:
4952:
4642:
4146:
4028:
3779:
3658:
3110:
3099:"Axons amplify somatic incomplete spikes into uniform amplitudes in mouse cortical pyramidal neurons"
2845:
1663:
1237:
1233:
1225:
1098:
956:
952:
730:
701:
451:
of the cerebral cortex which contains the neuronal cell bodies. A similar arrangement is seen in the
429:
142:
1855:
is generally credited with the discovery of the axon by distinguishing it from the dendrites. Swiss
5826:
5671:
5666:
5201:
5134:
2812:
1981:
1590:
1229:
1221:
968:
906:
828:
697:
468:
174:
170:
166:
4509:. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Vol. 576. pp. 77–93, discussion 361–3.
5861:
5831:
5762:
5731:
5721:
5716:
5711:
5656:
5432:
5342:
5196:
4855:
4556:"Further evidence for altered myelin biosynthesis and glutamatergic dysfunction in schizophrenia"
4536:
4170:
4136:
3850:
3723:
3631:
3585:
3542:
3499:
3450:
3386:
3242:
2877:
2861:
2668:
2445:
2322:"Ankyrin G Membrane Partners Drive the Establishment and Maintenance of the Axon Initial Segment"
2251:
1776:
1503:
1352:
1310:
1257:
1249:
1245:
689:. In the central nervous system the myelin sheath is provided by another type of glial cell, the
696:
The composition of myelin is different in the two types. In the CNS the major myelin protein is
37:
2420:
Rasband MN (August 2010). "The axon initial segment and the maintenance of neuronal polarity".
5846:
5836:
5821:
5726:
5591:
5372:
5324:
5129:
5124:
5024:
4970:
4921:
4880:
4847:
4809:
4799:
4668:
4577:
4528:
4518:
4487:
4438:
4387:
4283:
4260:
4211:
4162:
4105:
4054:
3997:
3948:
3899:
3842:
3807:
3746:
3715:
3674:
3623:
3577:
3534:
3491:
3442:
3378:
3340:
3291:
3234:
3199:
3161:
3138:
3061:
3010:
2958:
2869:
2816:
2785:
2734:
2706:
2702:
2696:
2660:
2606:
2552:
2503:
2437:
2402:
2353:
2302:
2243:
2192:
2136:
2106:
2057:
1976:
1820:
1561:
1387:
1334:
1253:
1149:
425:
3573:
1105:
also provide a sticky substrate for axons to grow along. Examples of these molecules include
1065:, which is at the tip of the axon. The growth cone has a broad sheet-like extension called a
775:. Some synaptic junctions appear along the length of an axon as it extends; these are called
381:(CNS) typically show multiple telodendria, with many synaptic end points. In comparison, the
5813:
5776:
5771:
5119:
5014:
5004:
4960:
4913:
4874:
4839:
4658:
4650:
4629:
Wright DK, Brady RD, Kamnaksh A, Trezise J, Sun M, McDonald SJ, et al. (October 2019).
4603:
4567:
4510:
4477:
4469:
4428:
4418:
4377:
4369:
4250:
4242:
4201:
4154:
4095:
4085:
4044:
4036:
3987:
3979:
3938:
3930:
3889:
3881:
3834:
3797:
3787:
3705:
3666:
3615:
3569:
3526:
3481:
3434:
3370:
3330:
3322:
3281:
3273:
3262:"Experimental observations on the development of polarity by hippocampal neurons in culture"
3226:
3191:
3128:
3118:
3051:
3041:
3000:
2992:
2948:
2938:
2853:
2804:
2775:
2767:
2650:
2640:
2596:
2586:
2542:
2534:
2493:
2483:
2429:
2392:
2384:
2343:
2333:
2292:
2282:
2235:
2182:
2174:
2096:
2088:
2047:
2037:
1991:
1800:
can result in widespread lesions to nerve tracts damaging the axons in a condition known as
1612:
1437:
857:
813:
768:
764:
760:
621:
617:
609:
587:
571:
559:
524:
488:
436:
374:
126:
3768:"Laser-based single-axon transection for high-content axon injury and regeneration studies"
2472:"Axon Initial Segment Cytoskeleton: Architecture, Development, and Role in Neuron Polarity"
1264:
groups as Types and uses Roman numerals: Type Ia, Type Ib, Type II, Type III, and Type IV.
5581:
5550:
5545:
5427:
5422:
5246:
4340:
4124:
3919:"Kinesin-5 regulates the growth of the axon by acting as a brake on its microtubule array"
3649:
Bradke F, Dotti CG (March 1999). "The role of local actin instability in axon formation".
2927:"Rapid and Reversible Development of Axonal Varicosities: A New Form of Neural Plasticity"
1876:
1868:
1575:
1403:
1395:
1209:
1145:
1125:
848:
718:
713:
693:. Schwann cells myelinate a single axon. An oligodendrocyte can myelinate up to 50 axons.
690:
464:
417:
309:
260:
203:. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely. The end branches of an axon are called
5045:
4686:
4304:
2805:
926:
The development of the axon to its target, is one of the six major stages in the overall
4956:
4646:
4373:
4150:
4032:
3783:
3662:
3114:
2849:
2655:
2628:
779:("in passing boutons") and can be in the hundreds or even the thousands along one axon.
373:(μm) across). The largest mammalian axons can reach a diameter of up to 20 μm. The
5871:
5841:
5798:
5618:
5576:
5554:
5474:
5357:
5181:
5086:
5019:
4992:
4663:
4630:
4482:
4457:
4433:
4406:
4382:
4357:
4255:
4230:
4100:
4073:
4049:
4016:
3992:
3967:
3943:
3918:
3894:
3869:
3802:
3767:
3560:
Huang EJ, Reichardt LF (2003). "Trk receptors: roles in neuronal signal transduction".
3407:
3335:
3310:
3286:
3261:
3133:
3098:
3056:
3029:
3005:
2980:
2953:
2926:
2780:
2755:
2601:
2574:
2547:
2522:
2498:
2471:
2397:
2372:
2348:
2321:
2297:
2270:
2187:
2162:
2101:
2076:
2052:
2025:
1933:
1925:
1880:
1786:
1528:
1473:
1181:
1094:
976:
882:
548:
386:
354:
244:
134:
130:
3966:
Rishal I, Kam N, Perry RB, Shinder V, Fisher EM, Schiavo G, Fainzilber M (June 2012).
3486:
3469:
5890:
5520:
5505:
5186:
4206:
4189:
4174:
3710:
3693:
3530:
3438:
3195:
1892:
1790:
1547:
1391:
1168:
1133:
1129:
1066:
1048:
893:
819:
752:
742:
664:
625:
602:
544:
500:
444:
362:
316:
224:
208:
4991:
Höfflin F, Jack A, Riedel C, Mack-Bucher J, Roos J, Corcelli C, et al. (2017).
4859:
4711:
4540:
4407:"Endogenous Nmnat2 is an essential survival factor for maintenance of healthy axons"
3727:
3635:
3589:
3546:
3503:
3454:
3390:
3246:
2881:
2672:
2449:
2255:
5766:
5688:
5601:
5482:
5412:
5191:
5114:
4473:
4246:
3885:
3868:
Gensel JC, Nakamura S, Guan Z, van
Rooijen N, Ankeny DP, Popovich PG (March 2009).
3854:
2388:
2178:
2092:
1996:
1917:
1888:
1860:
1824:
1708:
1303:
1241:
1086:
980:
940:
873:
838:
686:
660:
613:
520:
484:
440:
413:
401:
347:
321:
304:
299:
256:
4190:"Properties of fast and slow motor units in hind limb and tail muscles of the rat"
3670:
3087:
Rongjing Ge, Hao Qian, Na Chen and Jin-Hui Wang* (2014) Molecular Brain 7(26):1-16
1843:. However, medical sources generally use "nerve fiber" to refer to the axon only.
279:
4456:
Krämer-Albers EM, Gehrig-Burger K, Thiele C, Trotter J, Nave KA (November 2006).
4423:
3983:
3792:
3123:
2895:
2320:
Leterrier C, Clerc N, Rueda-Boroni F, Montersino A, Dargent B, Castets F (2017).
804:
can build up in a swelling resulting in a number of varicosities along the axon.
58:
5781:
5596:
5500:
5458:
5390:
5385:
5206:
5144:
5139:
5109:
5049:
3410:
express UNC-6 to provide global and local netrin cues for guiding migrations in
1929:
1905:
1730:
1726:
1722:
1155:
1110:
1082:
1062:
1015:
987:
963:(also known as UNC-6) a secreted protein, functions in axon formation. When the
931:
886:
877:
869:
823:
792:
655:
644:
492:
456:
448:
366:
343:
264:
252:
236:
204:
5048:
at the
University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center – "Slide 3
4654:
4158:
3838:
3692:
Furley AJ, Morton SB, Manalo D, Karagogeos D, Dodd J, Jessell TM (April 1990).
2239:
2026:"Axons emanating from dendrites: phylogenetic repercussions with Cajalian hues"
511:
215:
connection. Axons usually make contact with other neurons at junctions called
5851:
5540:
5417:
5380:
4965:
4940:
4843:
4572:
4555:
4040:
3468:
Hong K, Hinck L, Nishiyama M, Poo MM, Tessier-Lavigne M, Stein E (June 1999).
2943:
2771:
2645:
1785:
is the abnormal formation of the myelin sheath. This is implicated in several
1734:
1604:
1566:
1399:
1160:
1053:
861:
668:
452:
370:
289:
211:
or end-foot which joins the dendrite or cell body of another neuron forming a
122:
5009:
4090:
3046:
2591:
2538:
2338:
2287:
2042:
5866:
5251:
5224:
4813:
4514:
3403:
2698:
Essential cell biology: an introduction to the molecular biology of the cell
1937:
1070:
991:
756:
682:
597:
575:
409:
408:
is a layer of a fatty insulating substance, which is formed by two types of
185:
5028:
4974:
4851:
4672:
4581:
4532:
4491:
4442:
4391:
4166:
4109:
4058:
4001:
3952:
3903:
3846:
3811:
3678:
3627:
3581:
3495:
3382:
3344:
3277:
3238:
3142:
3065:
3014:
2962:
2873:
2857:
2789:
2664:
2610:
2556:
2507:
2488:
2441:
2406:
2357:
2306:
2247:
2196:
2061:
605:, in both directions between the axon and its terminals and the cell body.
4925:
4305:"Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) - Definition, Epidemiology, Pathophysiology"
4264:
4215:
3934:
3719:
3538:
3446:
3326:
3295:
3203:
3078:
Rongjing Ge, Hao Qian and Jin-Hui Wang* (2011) Molecular Brain 4(19), 1~11
2110:
5530:
5515:
5510:
5234:
5229:
5156:
5151:
4194:
Quarterly
Journal of Experimental Physiology and Cognate Medical Sciences
2838:
Proceedings of the Royal
Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences
2811:(11th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott William & Wilkins. p.
1840:
1118:
1114:
593:
284:
200:
196:
189:
4918:
10.1002/(SICI)1097-4695(199607)30:3<397::AID-NEU8>3.0.CO;2-#
5793:
5754:
3230:
1836:
1106:
935:
832:
772:
629:
220:
216:
212:
4796:
Origins of neuroscience: a history of explorations into brain function
2996:
2219:
Debanne D, Campanac E, Bialowas A, Carlier E, Alcaraz G (April 2011).
1167:
receptor are capable of promoting axon recovery, also however causing
385:
axon is characterized by a single T-shaped branch node from which two
83:
5453:
5408:
5173:
4876:
The Brain, the
Nervous System, and Their Diseases [3 volumes]
4282:(2nd ed.). New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 187–189.
3870:"Macrophages promote axon regeneration with concurrent neurotoxicity"
2865:
2756:"Oligodendroglial membrane dynamics in relation to myelin biogenesis"
1884:
1782:
1766:
1164:
960:
726:
675:
633:
405:
397:
390:
326:
178:
118:
4074:"A frequency-dependent decoding mechanism for axonal length sensing"
3374:
2433:
2135:(4th ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier/Academic Press. pp. 61–65.
1018:
that dephosphorylate PtdIns leads into the failure of polarization.
4141:
3619:
3311:"Mechanical tension can specify axonal fate in hippocampal neurons"
3028:
Robbins AA, Fox SE, Holmes GL, Scott RC, Barry JM (November 2013).
2163:"The development of the corpus callosum in the healthy human brain"
1775:
causes the multitude of neurological symptoms found in the disease
1163:
activated through a specific inflammatory pathway activated by the
4554:
Tkachev D, Mimmack ML, Huffaker SJ, Ryan M, Bahn S (August 2007).
2575:"Structural and Functional Plasticity at the Axon Initial Segment"
1052:
1031:
1027:
964:
827:
654:
643:
510:
358:
337:
16:
Long projection on a neuron that conducts signals to other neurons
5055:
3309:
Lamoureux P, Ruthel G, Buxbaum RE, Heidemann SR (November 2002).
3217:
Jiang H, Rao Y (May 2005). "Axon formation: fate versus growth".
1965:
Recordings in the hippocampus from different cell types and axons
5400:
5216:
1823:, and is one of the many treatments used for different kinds of
1007:
995:
515:
Detail showing microtubules at axon hillock and initial segment.
188:
protrusions from the cell body of a neuron; the other type is a
5059:
4765:
1944:
100–120 m/s for the fastest myelinated vertebrate axon.)
1941:
1809:
1030:
filament content will become the axon. PGMS concentration and
2979:
Weber MT, Arena JD, Xiao R, Wolf JA, Johnson VE (May 2019).
2754:
Ozgen, H; Baron, W; Hoekstra, D; Kahya, N (September 2016).
141:), such as those for touch and warmth, the axons are called
3160:(5th ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 520–524.
2629:"Activity-dependent regulation of excitable axonal domains"
443:
in the brain. The myelin gives the white appearance to the
2836:
Hess A, Young JZ (November 1952). "The nodes of
Ranvier".
3825:
Schwab ME (February 2004). "Nogo and axon regeneration".
3766:
Kunik D, Dion C, Ozaki T, Levin LA, Costantino S (2011).
1940:
and the usual range is between 90 and 200 meters/s (
979:(NTF3) are also involved in axon development and bind to
681:
In the peripheral nervous system axons are myelinated by
558:
The AIS is highly specialized for the fast conduction of
1819:
is an artificial means of guiding axon growth to enable
934:
neurons suggest that neurons initially produce multiple
574:
that anchor them to the cytoskeleton. Interactions with
145:
and the electrical impulse travels along these from the
578:
are important as it is the major organizer in the AIS.
125:, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as
1835:
Some general dictionaries define "nerve fiber" as any
1260:
having the Aα, Aβ, and Aγ nerve fibers, respectively.
755:(also called a terminal bouton or synaptic bouton, or
2733:(4th ed.). New York: Garland. pp. 979–981.
1394:
are innervated by type Ia, Ib and II sensory fibers,
1061:
Growing axons move through their environment via the
951:
The extracellular signals that propagate through the
4560:
1761:. Dying back of an axon can also take place in many
396:
There are two types of axons in the nervous system:
117:) is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or
5812:
5753:
5746:
5682:
5612:
5569:
5529:
5491:
5473:
5466:
5452:
5399:
5371:
5277:
5268:
5215:
5172:
5165:
5102:
5093:
4127:, Kruse K (May 2019). "Sound of an axon's growth".
1057:
Axon of nine-day-old mouse with growth cone visible
959:, and extracellular matrix and adhesion molecules.
659:Cross section of an axon: (1) Axon (2) Nucleus (3)
491:is provided for in the axoplasm by arrangements of
207:. The swollen end of a telodendron is known as the
64:
52:
47:
30:
3968:"A motor-driven mechanism for cell-length sensing"
4017:"Delayed feedback model of axonal length sensing"
3097:Chen N, Yu J, Qian H, Ge R, Wang JH (July 2010).
2523:"Electrogenic tuning of the axon initial segment"
1769:, being prevented from reaching all of the axon.
1749:that affect both peripheral and central neurons.
4818:Kölliker would give the "axon" its name in 1896.
2373:"The Axon Initial Segment: An Updated Viewpoint"
620:needed for growth to the axon terminal. Ingoing
353:Axons are the primary transmission lines of the
3601:
3599:
3356:
3354:
2521:Clark BD, Goldberg EM, Rudy B (December 2009).
1132:of neuronal axon growth. These cells that help
994:(PMGS), which is involved in the activation of
990:-converting enzyme plasma membrane ganglioside
2161:Luders E, Thompson PM, Toga AW (August 2010).
1899:. Hodgkin and Huxley were awarded jointly the
1752:When an axon is crushed, an active process of
562:. This is achieved by a high concentration of
5071:
1272:Lower motor neurons have two kind of fibers:
1097:superfamily. Another set of molecules called
547:, in which dendrites (and, in some cases the
8:
2701:(2nd ed.). New York: Garland. pp.
2690:
2688:
2686:
2684:
2682:
791:and these have been found in regions of the
632:, and ingoing return traffic is provided by
195:Axons are covered by a membrane known as an
4832:Journal of the History of the Neurosciences
4358:"Wallerian degeneration, wld(s), and nmnat"
4278:Pocock G, Richards CD, et al. (2004).
1390:innervate different types of nerve fibers.
1006:During axonal development, the activity of
612:from the cell body along the axon, carries
5750:
5470:
5463:
5274:
5169:
5099:
5078:
5064:
5056:
2019:
2017:
1012:phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate
455:. Bundles of myelinated axons make up the
439:form the bulk of the neural tissue called
263:, formed of some 200 million axons in the
36:
5018:
5008:
4964:
4873:Hellier, Jennifer L. (16 December 2014).
4662:
4571:
4481:
4432:
4422:
4381:
4254:
4205:
4140:
4099:
4089:
4048:
3991:
3942:
3893:
3801:
3791:
3709:
3485:
3334:
3285:
3132:
3122:
3055:
3045:
3004:
2952:
2942:
2779:
2654:
2644:
2622:
2620:
2600:
2590:
2568:
2566:
2546:
2497:
2487:
2396:
2347:
2337:
2296:
2286:
2214:
2212:
2210:
2208:
2206:
2186:
2100:
2051:
2041:
3574:10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161629
2974:
2972:
2465:
2463:
2461:
2459:
2156:
2154:
2152:
1633:
1581:
1538:
1478:
1408:
1274:
1244:of the different motor fibers, were the
837:
471:, and this has around 20 million axons.
4798:. Oxford University Press. p. 47.
4345:University of California, San Francisco
4015:Karamched BR, Bressloff PC (May 2015).
2013:
1955:
725:) are short unmyelinated segments of a
4356:Coleman MP, Freeman MR (1 June 2010).
2724:
2722:
1808:. It has been shown in studies on the
1398:by type II and III sensory fibers and
651:of a myelinated axon in cross-section.
81:
27:
4986:
4984:
4405:Gilley J, Coleman MP (January 2010).
2920:
2918:
2916:
2633:The Journal of Physiological Sciences
393:within a single region of the brain.
199:; the cytoplasm of an axon is called
7:
3917:Myers KA, Baas PW (September 2007).
2760:Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences
2126:
2124:
2122:
2120:
1631:has two kinds of peripheral fibers:
674:In the nervous system, axons may be
628:. Outgoing transport is provided by
4893:from the original on 14 March 2018.
4374:10.1146/annurev-neuro-060909-153248
4072:Bressloff PC, Karamched BR (2015).
1920:have been extensively studied. The
1406:by type III and IV sensory fibers.
162:
4997:Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience
4939:Salzer JL, Zalc B (October 2016).
4774:American Psychological Association
4078:Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience
2579:Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience
2326:Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience
2275:Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience
1199:The axons of neurons in the human
913:in response to short-term pulses.
165:into three types –
14:
4334:Trauma and Wallerian Degeneration
4315:from the original on 12 June 2018
4188:Andrew BL, Part NJ (April 1972).
3260:Goslin K, Banker G (April 1989).
1232:include both the sensory fibers (
1069:which contain protrusions called
973:brain-derived neurotrophic factor
928:development of the nervous system
833:Synaptic connections from an axon
365:, which run from the base of the
342:A dissected human brain, showing
4207:10.1113/expphysiol.1972.sp002151
1958:
1928:has the longest known axon. The
278:
5242:Oligodendrocyte progenitor cell
3827:Current Opinion in Neurobiology
3745:(Sixth ed.). p. 947.
2627:Susuki K, Kuba H (March 2016).
1741:. Axonal injury can also cause
1093:, all of which are part of the
184:An axon is one of two types of
4474:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3581-06.2006
4247:10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013085
3886:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3992-08.2009
2896:"Medical Definition of bouton"
2470:Jones SL, Svitkina TM (2016).
2389:10.1523/jneurosci.1922-17.2018
2269:Nelson AD, Jenkins PM (2017).
2179:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5122-09.2010
2093:10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011643
1148:. This is also referred to as
802:amyloid-beta precursor protein
463:. The largest of these is the
435:The myelinated axons from the
42:An axon of a multipolar neuron
1:
4362:Annual Review of Neuroscience
3743:Molecular biology of the cell
3671:10.1126/science.283.5409.1931
3562:Annual Review of Biochemistry
3487:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80804-1
2731:Molecular biology of the cell
2371:Leterrier C (February 2018).
1737:is considered a mild form of
903:voltage-gated sodium channels
564:voltage-gated sodium channels
333:Structure of a typical neuron
4770:APA Dictionary of Psychology
4424:10.1371/journal.pbio.1000300
4303:Dawodu ST (16 August 2017).
3984:10.1016/j.celrep.2012.05.013
3793:10.1371/journal.pone.0026832
3711:10.1016/0092-8674(90)90223-2
3531:10.1016/0896-6273(90)90444-K
3439:10.1016/0092-8674(94)90420-0
3363:Nature Reviews. Neuroscience
3196:10.1016/0012-1606(89)90269-8
3124:10.1371/journal.pone.0011868
3034:Frontiers in Neural Circuits
2807:Langman's medical embryology
2422:Nature Reviews. Neuroscience
1609:anterior spinothalamic tract
1085: – an axonal
1026:The neurite with the lowest
5352:Postganglionic nerve fibers
4462:The Journal of Neuroscience
4229:Russell NJ (January 1980).
3923:The Journal of Cell Biology
3874:The Journal of Neuroscience
3315:The Journal of Cell Biology
3266:The Journal of Cell Biology
2377:The Journal of Neuroscience
2167:The Journal of Neuroscience
1853:Otto Friedrich Karl Deiters
1839:, including both axons and
1806:persistent vegetative state
1571:lateral spinothalamic tract
930:. Studies done on cultured
905:in the axons possess lower
357:, and as bundles they form
5913:
5646:
5347:Preganglionic nerve fibers
4744:Taber's Medical Dictionary
4655:10.1038/s41598-019-51267-w
4159:10.1103/PhysRevE.99.050401
3839:10.1016/j.conb.2004.01.004
2240:10.1152/physrev.00048.2009
1857:Rüdolf Albert von Kölliker
1763:neurodegenerative diseases
1706:
1535:cutaneous mechanoreceptors
1192:
1046:
872:, axonal activity in both
817:
811:
759:). Axon terminals contain
740:
711:
585:
259:tract in the brain is the
18:
5857:Olfactory receptor neuron
5521:Neurofibril/neurofilament
4966:10.1016/j.cub.2016.07.074
4844:10.1080/09647040600638981
4717:Oxford English Dictionary
4596:"Brain Injury, Traumatic"
4573:10.1017/S1461145706007334
4235:The Journal of Physiology
4041:10.1016/j.bpj.2015.03.055
3158:Principles of development
2944:10.3389/fnmol.2021.610857
2772:10.1007/s00018-016-2228-8
2646:10.1007/s12576-015-0413-4
2573:Yamada R, Kuba H (2016).
2081:The Journal of Physiology
2030:Frontiers in Neuroanatomy
1579:
1483:
1481:
1201:peripheral nervous system
1195:Nerve conduction velocity
422:peripheral nervous system
249:peripheral nervous system
76:
35:
5010:10.3389/fncel.2017.00332
4091:10.3389/fncel.2015.00281
3047:10.3389/fncir.2013.00181
2592:10.3389/fncel.2016.00250
2539:10.1177/1073858409341973
2339:10.3389/fncel.2017.00006
2288:10.3389/fncel.2017.00136
2133:Fundamental neuroscience
2075:Yau KW (December 1976).
2043:10.3389/fnana.2014.00133
1629:autonomic nervous system
1370:Intrafusal muscle fibers
1328:Extrafusal muscle fibers
1236:) and the motor fibers (
798:traumatic brain injuries
4906:Journal of Neurobiology
4515:10.1007/0-387-30172-0_6
3741:Alberts, Bruce (2015).
3156:Wolpert, Lewis (2015).
2900:www.merriam-webster.com
1987:Giant axonal neuropathy
1527:Secondary receptors of
1075:cell adhesion molecules
1002:Intracellular signaling
947:Extracellular signaling
700:, and in the PNS it is
568:cell adhesion molecules
383:cerebellar granule cell
5804:Neuromuscular junction
5667:III or Aδ or fast pain
3278:10.1083/jcb.108.4.1507
2858:10.1098/rspb.1952.0063
2131:Squire, Larry (2013).
1873:Santiago Ramón y Cajal
1817:nerve guidance conduit
1798:traumatic brain injury
1773:Demyelination of axons
1759:Wallerian degeneration
1747:neurological disorders
1531:(flower-spray ending).
1353:Gamma (γ) motor neuron
1311:Alpha (α) motor neuron
1089: – and
1058:
917:Development and growth
843:
835:
671:
652:
541:axonal initial segment
535:Axonal initial segment
516:
497:intermediate filaments
467:that connects the two
379:central nervous system
350:
241:central nervous system
151:neurological disorders
139:pseudounipolar neurons
78:Anatomical terminology
5046:Histology image: 3_09
3935:10.1083/jcb.200702074
3327:10.1083/jcb.200207174
3184:Developmental Biology
2228:Physiological Reviews
2002:Single-unit recording
1922:longfin inshore squid
1865:Louis-Antoine Ranvier
1804:. This can lead to a
1802:diffuse axonal injury
1743:central chromatolysis
1739:diffuse axonal injury
1717:Demyelinating disease
1713:Peripheral neuropathy
1703:Clinical significance
1683:postganglionic fibers
1564:of touch and pressure
1476:(annulospiral ending)
1472:Primary receptors of
1335:Beta (β) motor neuron
1193:Further information:
1056:
1022:Cytoskeletal dynamics
856:concentration causes
841:
831:
818:Further information:
658:
647:
610:anterograde transport
596:is the equivalent of
514:
341:
177:. Groups A and B are
153:that affect both the
143:afferent nerve fibers
21:Axon (disambiguation)
5822:Meissner's corpuscle
5787:Postsynaptic density
5684:Efferent nerve fiber
5672:IV or C or slow pain
5614:Afferent nerve fiber
5440:Satellite glial cell
4123:Folz F, Wettmann L,
2489:10.1155/2016/6808293
2024:Triarhou LC (2014).
1897:Hodgkin–Huxley model
1664:preganglionic fibers
1410:Sensory fiber types
1206:conductance velocity
1099:extracellular matrix
957:neurotrophic factors
953:extracellular matrix
731:saltatory conduction
702:myelin basic protein
622:retrograde transport
469:cerebral hemispheres
430:saltatory conduction
223:. At a synapse, the
175:group C nerve fibers
171:group B nerve fibers
167:group A nerve fibers
115:spelling differences
19:For other uses, see
5827:Merkel nerve ending
4957:2016CBio...26.R971S
4647:2019NatSR...914626W
4151:2019PhRvE..99e0401F
4033:2015BpJ...108.2408K
4021:Biophysical Journal
3784:2011PLoSO...626832K
3663:1999Sci...283.1931B
3608:Nature Neuroscience
3219:Nature Neuroscience
3115:2010PLoSO...511868C
2850:1952RSPSB.140..301H
2803:Sadler, T. (2010).
1982:Ganglionic eminence
1754:axonal degeneration
1636:
1411:
1297:Conduction velocity
1277:
1246:lower motor neurons
1138:speed of conduction
969:nerve growth factor
789:axonal varicosities
783:Axonal varicosities
767:for release at the
698:proteolipid protein
447:in contrast to the
161:. Nerve fibers are
5862:Photoreceptor cell
5832:Pacinian corpuscle
5763:Electrical synapse
5717:Lower motor neuron
5712:Upper motor neuron
5433:Internodal segment
5373:Connective tissues
5343:Autonomic ganglion
4635:Scientific Reports
4339:2 May 2006 at the
3231:10.1038/nn0505-544
2931:Front Mol Neurosci
2729:Alberts B (2002).
2695:Alberts B (2004).
2527:The Neuroscientist
2142:978-0-12-385-870-2
1924:, often used as a
1887:, fiber size etc.
1777:multiple sclerosis
1634:
1562:Free nerve endings
1504:Golgi tendon organ
1409:
1276:Motor fiber types
1275:
1258:gamma motor neuron
1250:alpha motor neuron
1248: –
1103:adhesion molecules
1059:
844:
836:
777:en passant boutons
723:myelin sheath gaps
672:
653:
517:
351:
230:en passant boutons
5884:
5883:
5880:
5879:
5847:Free nerve ending
5814:Sensory receptors
5742:
5741:
5657:Ib or Golgi or Aα
5565:
5564:
5448:
5447:
5325:Ramus communicans
5264:
5263:
5260:
5259:
5130:Commissural fiber
5125:Association fiber
5120:Projection fibers
4951:(20): R971–R975.
4794:Finger S (1994).
4524:978-0-387-30171-6
4507:N-Acetylaspartate
4289:978-0-19-858527-5
4129:Physical Review E
3167:978-0-19-967814-3
2997:10.1111/bpa.12677
2822:978-0-7817-9069-7
2740:978-0-8153-4072-0
2712:978-0-8153-3481-1
2476:Neural Plasticity
2221:"Axon physiology"
1977:Electrophysiology
1952:Additional images
1851:German anatomist
1821:neuroregeneration
1700:
1699:
1620:
1619:
1438:sensory receptors
1388:sensory receptors
1375:
1374:
1254:beta motor neuron
1175:Length regulation
1150:neuroregeneration
911:refractory period
858:synaptic vesicles
808:Action potentials
761:synaptic vesicles
618:membrane proteins
572:scaffold proteins
525:action potentials
253:placental mammals
127:action potentials
98:(from Greek ἄξων
92:
91:
87:
5904:
5777:Synaptic vesicle
5772:Chemical synapse
5751:
5471:
5464:
5275:
5170:
5100:
5080:
5073:
5066:
5057:
5033:
5032:
5022:
5012:
4988:
4979:
4978:
4968:
4936:
4930:
4929:
4901:
4895:
4894:
4870:
4864:
4863:
4827:
4821:
4820:
4791:
4785:
4784:
4782:
4780:
4762:
4756:
4755:
4753:
4751:
4735:
4729:
4728:
4726:
4724:
4708:
4702:
4701:
4699:
4697:
4683:
4677:
4676:
4666:
4626:
4620:
4619:
4617:
4615:
4606:. Archived from
4592:
4586:
4585:
4575:
4551:
4545:
4544:
4502:
4496:
4495:
4485:
4468:(45): 11743–52.
4453:
4447:
4446:
4436:
4426:
4402:
4396:
4395:
4385:
4353:
4347:
4331:
4325:
4324:
4322:
4320:
4300:
4294:
4293:
4280:Human Physiology
4275:
4269:
4268:
4258:
4226:
4220:
4219:
4209:
4185:
4179:
4178:
4144:
4120:
4114:
4113:
4103:
4093:
4069:
4063:
4062:
4052:
4012:
4006:
4005:
3995:
3963:
3957:
3956:
3946:
3914:
3908:
3907:
3897:
3865:
3859:
3858:
3822:
3816:
3815:
3805:
3795:
3763:
3757:
3756:
3738:
3732:
3731:
3713:
3689:
3683:
3682:
3657:(5409): 1931–4.
3646:
3640:
3639:
3603:
3594:
3593:
3557:
3551:
3550:
3514:
3508:
3507:
3489:
3465:
3459:
3458:
3422:
3416:
3401:
3395:
3394:
3358:
3349:
3348:
3338:
3306:
3300:
3299:
3289:
3257:
3251:
3250:
3214:
3208:
3207:
3178:
3172:
3171:
3153:
3147:
3146:
3136:
3126:
3094:
3088:
3085:
3079:
3076:
3070:
3069:
3059:
3049:
3025:
3019:
3018:
3008:
2976:
2967:
2966:
2956:
2946:
2922:
2911:
2910:
2908:
2906:
2892:
2886:
2885:
2833:
2827:
2826:
2810:
2800:
2794:
2793:
2783:
2766:(17): 3291–310.
2751:
2745:
2744:
2726:
2717:
2716:
2692:
2677:
2676:
2658:
2648:
2624:
2615:
2614:
2604:
2594:
2570:
2561:
2560:
2550:
2518:
2512:
2511:
2501:
2491:
2467:
2454:
2453:
2417:
2411:
2410:
2400:
2383:(9): 2135–2145.
2368:
2362:
2361:
2351:
2341:
2317:
2311:
2310:
2300:
2290:
2266:
2260:
2259:
2225:
2216:
2201:
2200:
2190:
2173:(33): 10985–90.
2158:
2147:
2146:
2128:
2115:
2114:
2104:
2072:
2066:
2065:
2055:
2045:
2021:
1992:Neuronal tracing
1962:
1869:nodes of Ranvier
1837:neuronal process
1787:leukodystrophies
1637:
1613:Warmth receptors
1450:thermoreceptors
1412:
1396:mechanoreceptors
1382:
1381:
1278:
814:Action potential
765:neurotransmitter
719:Nodes of Ranvier
708:Nodes of Ranvier
588:Axonal transport
582:Axonal transport
489:axonal transport
437:cortical neurons
426:nodes of Ranvier
418:oligodendrocytes
375:squid giant axon
282:
84:edit on Wikidata
40:
28:
5912:
5911:
5907:
5906:
5905:
5903:
5902:
5901:
5887:
5886:
5885:
5876:
5808:
5738:
5687:
5678:
5662:II or Aβ and Aγ
5617:
5608:
5561:
5551:Apical dendrite
5546:Dendritic spine
5525:
5487:
5457:
5444:
5428:Node of Ranvier
5423:Myelin incisure
5395:
5367:
5256:
5247:Oligodendrocyte
5230:Ependymal cells
5211:
5161:
5089:
5084:
5042:
5037:
5036:
4990:
4989:
4982:
4945:Current Biology
4938:
4937:
4933:
4903:
4902:
4898:
4887:
4872:
4871:
4867:
4829:
4828:
4824:
4806:
4793:
4792:
4788:
4778:
4776:
4764:
4763:
4759:
4749:
4747:
4737:
4736:
4732:
4722:
4720:
4710:
4709:
4705:
4695:
4693:
4691:Merriam-Webster
4685:
4684:
4680:
4628:
4627:
4623:
4613:
4611:
4594:
4593:
4589:
4553:
4552:
4548:
4525:
4504:
4503:
4499:
4455:
4454:
4450:
4417:(1): e1000300.
4404:
4403:
4399:
4355:
4354:
4350:
4341:Wayback Machine
4332:
4328:
4318:
4316:
4302:
4301:
4297:
4290:
4277:
4276:
4272:
4228:
4227:
4223:
4187:
4186:
4182:
4135:(5–1): 050401.
4122:
4121:
4117:
4071:
4070:
4066:
4014:
4013:
4009:
3965:
3964:
3960:
3916:
3915:
3911:
3880:(12): 3956–68.
3867:
3866:
3862:
3824:
3823:
3819:
3765:
3764:
3760:
3753:
3740:
3739:
3735:
3691:
3690:
3686:
3648:
3647:
3643:
3605:
3604:
3597:
3559:
3558:
3554:
3516:
3515:
3511:
3467:
3466:
3462:
3424:
3423:
3419:
3408:pioneer neurons
3402:
3398:
3375:10.1038/nrn2056
3360:
3359:
3352:
3308:
3307:
3303:
3259:
3258:
3254:
3216:
3215:
3211:
3180:
3179:
3175:
3168:
3155:
3154:
3150:
3096:
3095:
3091:
3086:
3082:
3077:
3073:
3027:
3026:
3022:
2978:
2977:
2970:
2924:
2923:
2914:
2904:
2902:
2894:
2893:
2889:
2844:(900): 301–20.
2835:
2834:
2830:
2823:
2802:
2801:
2797:
2753:
2752:
2748:
2741:
2728:
2727:
2720:
2713:
2694:
2693:
2680:
2626:
2625:
2618:
2572:
2571:
2564:
2520:
2519:
2515:
2469:
2468:
2457:
2434:10.1038/nrn2852
2419:
2418:
2414:
2370:
2369:
2365:
2319:
2318:
2314:
2268:
2267:
2263:
2223:
2218:
2217:
2204:
2160:
2159:
2150:
2143:
2130:
2129:
2118:
2074:
2073:
2069:
2023:
2022:
2015:
2010:
1973:
1966:
1963:
1954:
1938:Penaeid shrimps
1914:
1877:Joseph Erlanger
1849:
1833:
1719:
1707:Main articles:
1705:
1658:velocity (m/s)
1657:
1649:
1644:
1643:Erlanger-Gasser
1625:
1611:
1576:thermoreceptors
1573:
1565:
1532:
1449:
1448:Nociceptors and
1432:
1424:
1419:
1418:Erlanger-Gasser
1404:thermoreceptors
1384:
1379:
1378:
1299:(meters/second)
1298:
1290:
1285:
1284:Erlanger-Gasser
1270:
1197:
1191:
1177:
1171:in the neuron.
1146:guidepost cells
1126:guidepost cells
1051:
1045:
1024:
1004:
949:
924:
919:
883:pyramidal cells
826:
816:
810:
785:
763:that store the
745:
739:
727:myelinated axon
721:(also known as
716:
714:Node of Ranvier
710:
691:oligodendrocyte
642:
590:
584:
537:
509:
481:
465:corpus callosum
387:parallel fibers
336:
335:
334:
331:
330:
329:
324:
319:
314:
311:
307:
302:
297:
292:
287:
273:
261:corpus callosum
159:central neurons
135:sensory neurons
131:nerve cell body
88:
43:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
5910:
5908:
5900:
5899:
5897:Neurohistology
5889:
5888:
5882:
5881:
5878:
5877:
5875:
5874:
5872:Taste receptor
5869:
5864:
5859:
5854:
5849:
5844:
5842:Muscle spindle
5839:
5837:Ruffini ending
5834:
5829:
5824:
5818:
5816:
5810:
5809:
5807:
5806:
5801:
5799:Ribbon synapse
5796:
5791:
5790:
5789:
5784:
5779:
5769:
5759:
5757:
5748:
5744:
5743:
5740:
5739:
5737:
5736:
5735:
5734:
5729:
5724:
5714:
5709:
5704:
5699:
5693:
5691:
5680:
5679:
5677:
5676:
5675:
5674:
5669:
5664:
5659:
5654:
5644:
5639:
5634:
5629:
5623:
5621:
5619:Sensory neuron
5610:
5609:
5607:
5606:
5605:
5604:
5594:
5589:
5587:Pseudounipolar
5584:
5579:
5573:
5571:
5567:
5566:
5563:
5562:
5560:
5559:
5558:
5557:
5555:Basal dendrite
5548:
5543:
5535:
5533:
5527:
5526:
5524:
5523:
5518:
5513:
5508:
5506:Axon terminals
5503:
5497:
5495:
5489:
5488:
5486:
5485:
5479:
5477:
5468:
5461:
5450:
5449:
5446:
5445:
5443:
5442:
5437:
5436:
5435:
5430:
5425:
5420:
5405:
5403:
5397:
5396:
5394:
5393:
5388:
5383:
5377:
5375:
5369:
5368:
5366:
5365:
5360:
5358:Nerve fascicle
5355:
5349:
5340:
5339:
5338:
5333:
5321:
5320:
5319:
5314:
5304:
5303:
5302:
5297:
5292:
5281:
5279:
5272:
5266:
5265:
5262:
5261:
5258:
5257:
5255:
5254:
5249:
5244:
5239:
5238:
5237:
5227:
5221:
5219:
5213:
5212:
5210:
5209:
5204:
5199:
5194:
5189:
5184:
5178:
5176:
5167:
5163:
5162:
5160:
5159:
5154:
5149:
5148:
5147:
5142:
5137:
5132:
5127:
5122:
5112:
5106:
5104:
5097:
5091:
5090:
5087:Nervous tissue
5085:
5083:
5082:
5075:
5068:
5060:
5054:
5053:
5041:
5040:External links
5038:
5035:
5034:
4980:
4931:
4912:(3): 397–409.
4896:
4885:
4865:
4822:
4804:
4786:
4757:
4730:
4703:
4678:
4621:
4610:on 26 May 2011
4600:Medcyclopaedia
4587:
4546:
4523:
4497:
4448:
4397:
4348:
4326:
4295:
4288:
4270:
4221:
4180:
4115:
4064:
4027:(9): 2408–19.
4007:
3958:
3929:(6): 1081–91.
3909:
3860:
3817:
3778:(11): e26832.
3758:
3751:
3733:
3684:
3641:
3620:10.1038/nn1442
3595:
3552:
3509:
3460:
3417:
3396:
3369:(3): 194–205.
3350:
3321:(3): 499–508.
3301:
3272:(4): 1507–16.
3252:
3209:
3173:
3166:
3148:
3089:
3080:
3071:
3020:
2991:(3): 437–450.
2968:
2912:
2887:
2828:
2821:
2795:
2746:
2739:
2718:
2711:
2678:
2616:
2562:
2513:
2455:
2412:
2363:
2312:
2261:
2234:(2): 555–602.
2202:
2148:
2141:
2116:
2067:
2012:
2011:
2009:
2006:
2005:
2004:
1999:
1994:
1989:
1984:
1979:
1972:
1969:
1968:
1967:
1964:
1957:
1953:
1950:
1934:jet propulsion
1926:model organism
1913:
1910:
1881:Herbert Gasser
1848:
1845:
1832:
1829:
1789:, and also in
1783:Dysmyelination
1704:
1701:
1698:
1697:
1694:
1691:
1688:
1685:
1679:
1678:
1675:
1672:
1669:
1666:
1660:
1659:
1654:
1651:
1646:
1645:Classification
1641:
1624:
1621:
1618:
1617:
1615:
1602:
1599:
1596:
1593:
1588:
1584:
1583:
1580:
1578:
1559:
1556:
1553:
1550:
1545:
1541:
1540:
1537:
1529:muscle spindle
1525:
1522:
1519:
1516:
1513:
1507:
1506:
1501:
1498:
1495:
1492:
1489:
1485:
1484:
1482:
1480:
1477:
1474:muscle spindle
1470:
1467:
1464:
1461:
1458:
1452:
1451:
1446:
1445:Mechanoceptors
1443:
1442:Proprioceptors
1440:
1434:
1433:velocity (m/s)
1429:
1426:
1421:
1420:Classification
1416:
1392:Proprioceptors
1383:
1376:
1373:
1372:
1367:
1364:
1361:
1358:
1355:
1349:
1348:
1346:
1344:
1342:
1340:
1337:
1331:
1330:
1325:
1322:
1319:
1316:
1313:
1307:
1306:
1300:
1295:
1292:
1287:
1286:Classification
1282:
1269:
1266:
1190:
1189:Classification
1187:
1182:motor proteins
1176:
1173:
1128:assist in the
1095:immunoglobulin
1047:Main article:
1044:
1041:
1023:
1020:
1003:
1000:
977:neurotrophin-3
948:
945:
923:
920:
918:
915:
849:all-or-nothing
812:Main article:
809:
806:
784:
781:
741:Main article:
738:
737:Axon terminals
735:
712:Main article:
709:
706:
641:
638:
626:motor proteins
603:neurofilaments
586:Main article:
583:
580:
560:nerve impulses
536:
533:
508:
505:
501:neurofilaments
480:
477:
355:nervous system
332:
325:
320:
315:
308:
303:
298:
293:
288:
283:
277:
276:
275:
274:
272:
269:
129:away from the
90:
89:
80:
74:
73:
68:
62:
61:
56:
50:
49:
45:
44:
41:
33:
32:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
5909:
5898:
5895:
5894:
5892:
5873:
5870:
5868:
5865:
5863:
5860:
5858:
5855:
5853:
5850:
5848:
5845:
5843:
5840:
5838:
5835:
5833:
5830:
5828:
5825:
5823:
5820:
5819:
5817:
5815:
5811:
5805:
5802:
5800:
5797:
5795:
5792:
5788:
5785:
5783:
5780:
5778:
5775:
5774:
5773:
5770:
5768:
5764:
5761:
5760:
5758:
5756:
5752:
5749:
5745:
5733:
5732:γ motorneuron
5730:
5728:
5727:β motorneuron
5725:
5723:
5722:α motorneuron
5720:
5719:
5718:
5715:
5713:
5710:
5708:
5705:
5703:
5700:
5698:
5695:
5694:
5692:
5690:
5685:
5681:
5673:
5670:
5668:
5665:
5663:
5660:
5658:
5655:
5653:
5650:
5649:
5648:
5645:
5643:
5640:
5638:
5635:
5633:
5630:
5628:
5625:
5624:
5622:
5620:
5615:
5611:
5603:
5600:
5599:
5598:
5595:
5593:
5590:
5588:
5585:
5583:
5580:
5578:
5575:
5574:
5572:
5568:
5556:
5552:
5549:
5547:
5544:
5542:
5539:
5538:
5537:
5536:
5534:
5532:
5528:
5522:
5519:
5517:
5514:
5512:
5509:
5507:
5504:
5502:
5499:
5498:
5496:
5494:
5490:
5484:
5481:
5480:
5478:
5476:
5472:
5469:
5465:
5462:
5460:
5455:
5451:
5441:
5438:
5434:
5431:
5429:
5426:
5424:
5421:
5419:
5416:
5415:
5414:
5410:
5407:
5406:
5404:
5402:
5398:
5392:
5389:
5387:
5384:
5382:
5379:
5378:
5376:
5374:
5370:
5364:
5361:
5359:
5356:
5353:
5350:
5348:
5344:
5341:
5337:
5334:
5332:
5329:
5328:
5327:
5326:
5322:
5318:
5315:
5313:
5310:
5309:
5308:
5305:
5301:
5298:
5296:
5293:
5291:
5288:
5287:
5286:
5283:
5282:
5280:
5276:
5273:
5271:
5267:
5253:
5250:
5248:
5245:
5243:
5240:
5236:
5233:
5232:
5231:
5228:
5226:
5223:
5222:
5220:
5218:
5214:
5208:
5205:
5203:
5200:
5198:
5195:
5193:
5190:
5188:
5185:
5183:
5180:
5179:
5177:
5175:
5171:
5168:
5164:
5158:
5155:
5153:
5150:
5146:
5143:
5141:
5138:
5136:
5133:
5131:
5128:
5126:
5123:
5121:
5118:
5117:
5116:
5113:
5111:
5108:
5107:
5105:
5101:
5098:
5096:
5092:
5088:
5081:
5076:
5074:
5069:
5067:
5062:
5061:
5058:
5051:
5047:
5044:
5043:
5039:
5030:
5026:
5021:
5016:
5011:
5006:
5002:
4998:
4994:
4987:
4985:
4981:
4976:
4972:
4967:
4962:
4958:
4954:
4950:
4946:
4942:
4941:"Myelination"
4935:
4932:
4927:
4923:
4919:
4915:
4911:
4907:
4900:
4897:
4892:
4888:
4886:9781610693387
4882:
4878:
4877:
4869:
4866:
4861:
4857:
4853:
4849:
4845:
4841:
4838:(4): 341–57.
4837:
4833:
4826:
4823:
4819:
4815:
4811:
4807:
4805:9780195146943
4801:
4797:
4790:
4787:
4775:
4771:
4767:
4766:"nerve fiber"
4761:
4758:
4746:
4745:
4740:
4739:"nerve fiber"
4734:
4731:
4719:
4718:
4713:
4712:"nerve fibre"
4707:
4704:
4692:
4688:
4687:"nerve fiber"
4682:
4679:
4674:
4670:
4665:
4660:
4656:
4652:
4648:
4644:
4640:
4636:
4632:
4625:
4622:
4609:
4605:
4601:
4597:
4591:
4588:
4583:
4579:
4574:
4569:
4566:(4): 557–63.
4565:
4561:
4557:
4550:
4547:
4542:
4538:
4534:
4530:
4526:
4520:
4516:
4512:
4508:
4501:
4498:
4493:
4489:
4484:
4479:
4475:
4471:
4467:
4463:
4459:
4452:
4449:
4444:
4440:
4435:
4430:
4425:
4420:
4416:
4412:
4408:
4401:
4398:
4393:
4389:
4384:
4379:
4375:
4371:
4368:(1): 245–67.
4367:
4363:
4359:
4352:
4349:
4346:
4342:
4338:
4335:
4330:
4327:
4314:
4310:
4306:
4299:
4296:
4291:
4285:
4281:
4274:
4271:
4266:
4262:
4257:
4252:
4248:
4244:
4240:
4236:
4232:
4225:
4222:
4217:
4213:
4208:
4203:
4200:(2): 213–25.
4199:
4195:
4191:
4184:
4181:
4176:
4172:
4168:
4164:
4160:
4156:
4152:
4148:
4143:
4138:
4134:
4130:
4126:
4119:
4116:
4111:
4107:
4102:
4097:
4092:
4087:
4083:
4079:
4075:
4068:
4065:
4060:
4056:
4051:
4046:
4042:
4038:
4034:
4030:
4026:
4022:
4018:
4011:
4008:
4003:
3999:
3994:
3989:
3985:
3981:
3978:(6): 608–16.
3977:
3973:
3969:
3962:
3959:
3954:
3950:
3945:
3940:
3936:
3932:
3928:
3924:
3920:
3913:
3910:
3905:
3901:
3896:
3891:
3887:
3883:
3879:
3875:
3871:
3864:
3861:
3856:
3852:
3848:
3844:
3840:
3836:
3833:(1): 118–24.
3832:
3828:
3821:
3818:
3813:
3809:
3804:
3799:
3794:
3789:
3785:
3781:
3777:
3773:
3769:
3762:
3759:
3754:
3752:9780815344643
3748:
3744:
3737:
3734:
3729:
3725:
3721:
3717:
3712:
3707:
3704:(1): 157–70.
3703:
3699:
3695:
3688:
3685:
3680:
3676:
3672:
3668:
3664:
3660:
3656:
3652:
3645:
3642:
3637:
3633:
3629:
3625:
3621:
3617:
3614:(5): 606–15.
3613:
3609:
3602:
3600:
3596:
3591:
3587:
3583:
3579:
3575:
3571:
3567:
3563:
3556:
3553:
3548:
3544:
3540:
3536:
3532:
3528:
3524:
3520:
3513:
3510:
3505:
3501:
3497:
3493:
3488:
3483:
3480:(7): 927–41.
3479:
3475:
3471:
3464:
3461:
3456:
3452:
3448:
3444:
3440:
3436:
3433:(3): 409–24.
3432:
3428:
3421:
3418:
3415:
3414:
3409:
3405:
3400:
3397:
3392:
3388:
3384:
3380:
3376:
3372:
3368:
3364:
3357:
3355:
3351:
3346:
3342:
3337:
3332:
3328:
3324:
3320:
3316:
3312:
3305:
3302:
3297:
3293:
3288:
3283:
3279:
3275:
3271:
3267:
3263:
3256:
3253:
3248:
3244:
3240:
3236:
3232:
3228:
3224:
3220:
3213:
3210:
3205:
3201:
3197:
3193:
3190:(2): 446–54.
3189:
3185:
3177:
3174:
3169:
3163:
3159:
3152:
3149:
3144:
3140:
3135:
3130:
3125:
3120:
3116:
3112:
3109:(7): e11868.
3108:
3104:
3100:
3093:
3090:
3084:
3081:
3075:
3072:
3067:
3063:
3058:
3053:
3048:
3043:
3039:
3035:
3031:
3024:
3021:
3016:
3012:
3007:
3002:
2998:
2994:
2990:
2986:
2982:
2975:
2973:
2969:
2964:
2960:
2955:
2950:
2945:
2940:
2936:
2932:
2928:
2925:Gu C (2021).
2921:
2919:
2917:
2913:
2901:
2897:
2891:
2888:
2883:
2879:
2875:
2871:
2867:
2863:
2859:
2855:
2851:
2847:
2843:
2839:
2832:
2829:
2824:
2818:
2814:
2809:
2808:
2799:
2796:
2791:
2787:
2782:
2777:
2773:
2769:
2765:
2761:
2757:
2750:
2747:
2742:
2736:
2732:
2725:
2723:
2719:
2714:
2708:
2704:
2700:
2699:
2691:
2689:
2687:
2685:
2683:
2679:
2674:
2670:
2666:
2662:
2657:
2652:
2647:
2642:
2639:(2): 99–104.
2638:
2634:
2630:
2623:
2621:
2617:
2612:
2608:
2603:
2598:
2593:
2588:
2584:
2580:
2576:
2569:
2567:
2563:
2558:
2554:
2549:
2544:
2540:
2536:
2533:(6): 651–68.
2532:
2528:
2524:
2517:
2514:
2509:
2505:
2500:
2495:
2490:
2485:
2481:
2477:
2473:
2466:
2464:
2462:
2460:
2456:
2451:
2447:
2443:
2439:
2435:
2431:
2428:(8): 552–62.
2427:
2423:
2416:
2413:
2408:
2404:
2399:
2394:
2390:
2386:
2382:
2378:
2374:
2367:
2364:
2359:
2355:
2350:
2345:
2340:
2335:
2331:
2327:
2323:
2316:
2313:
2308:
2304:
2299:
2294:
2289:
2284:
2280:
2276:
2272:
2265:
2262:
2257:
2253:
2249:
2245:
2241:
2237:
2233:
2229:
2222:
2215:
2213:
2211:
2209:
2207:
2203:
2198:
2194:
2189:
2184:
2180:
2176:
2172:
2168:
2164:
2157:
2155:
2153:
2149:
2144:
2138:
2134:
2127:
2125:
2123:
2121:
2117:
2112:
2108:
2103:
2098:
2094:
2090:
2087:(3): 513–38.
2086:
2082:
2078:
2071:
2068:
2063:
2059:
2054:
2049:
2044:
2039:
2035:
2031:
2027:
2020:
2018:
2014:
2007:
2003:
2000:
1998:
1995:
1993:
1990:
1988:
1985:
1983:
1980:
1978:
1975:
1974:
1970:
1961:
1956:
1951:
1949:
1945:
1943:
1939:
1935:
1931:
1927:
1923:
1919:
1918:invertebrates
1916:The axons in
1912:Other animals
1911:
1909:
1907:
1902:
1898:
1894:
1893:Andrew Huxley
1890:
1886:
1882:
1878:
1874:
1870:
1866:
1862:
1858:
1854:
1846:
1844:
1842:
1838:
1830:
1828:
1826:
1822:
1818:
1813:
1811:
1807:
1803:
1799:
1794:
1792:
1791:schizophrenia
1788:
1784:
1780:
1778:
1774:
1770:
1768:
1764:
1760:
1755:
1750:
1748:
1744:
1740:
1736:
1732:
1728:
1724:
1718:
1714:
1710:
1702:
1695:
1692:
1689:
1686:
1684:
1681:
1680:
1676:
1673:
1670:
1667:
1665:
1662:
1661:
1655:
1652:
1647:
1642:
1639:
1638:
1632:
1630:
1622:
1616:
1614:
1610:
1606:
1603:
1600:
1597:
1594:
1592:
1589:
1586:
1585:
1577:
1572:
1568:
1563:
1560:
1557:
1554:
1551:
1549:
1546:
1543:
1542:
1536:
1530:
1526:
1523:
1520:
1517:
1514:
1512:
1509:
1508:
1505:
1502:
1499:
1496:
1493:
1490:
1487:
1486:
1475:
1471:
1468:
1465:
1462:
1459:
1457:
1454:
1453:
1447:
1444:
1441:
1439:
1435:
1430:
1427:
1422:
1417:
1414:
1413:
1407:
1405:
1401:
1397:
1393:
1389:
1377:
1371:
1368:
1365:
1362:
1359:
1356:
1354:
1351:
1350:
1347:
1345:
1343:
1341:
1338:
1336:
1333:
1332:
1329:
1326:
1323:
1320:
1317:
1314:
1312:
1309:
1308:
1305:
1304:muscle fibers
1301:
1296:
1293:
1288:
1283:
1280:
1279:
1273:
1267:
1265:
1261:
1259:
1255:
1251:
1247:
1243:
1242:motor neurons
1239:
1235:
1231:
1227:
1223:
1218:
1215:
1211:
1207:
1202:
1196:
1188:
1186:
1183:
1174:
1172:
1170:
1169:neurotoxicity
1166:
1162:
1157:
1153:
1151:
1147:
1141:
1139:
1135:
1134:axon guidance
1131:
1127:
1124:Cells called
1122:
1120:
1116:
1112:
1108:
1104:
1100:
1096:
1092:
1088:
1084:
1080:
1076:
1072:
1068:
1067:lamellipodium
1064:
1055:
1050:
1049:Axon guidance
1042:
1040:
1038:
1037:Rho-signaling
1033:
1029:
1021:
1019:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1001:
999:
997:
993:
989:
984:
982:
981:Trk receptors
978:
974:
970:
966:
962:
958:
954:
946:
944:
942:
937:
933:
929:
921:
916:
914:
912:
908:
904:
898:
895:
894:digital codes
890:
888:
884:
879:
875:
871:
865:
863:
859:
853:
850:
840:
834:
830:
825:
821:
820:Neural coding
815:
807:
805:
803:
799:
794:
790:
782:
780:
778:
774:
770:
766:
762:
758:
754:
753:axon terminal
750:
744:
743:Axon terminal
736:
734:
732:
728:
724:
720:
715:
707:
705:
703:
699:
694:
692:
688:
687:Schwann cells
684:
679:
677:
670:
666:
665:Myelin sheath
662:
657:
650:
646:
639:
637:
635:
631:
627:
623:
619:
615:
611:
606:
604:
599:
595:
589:
581:
579:
577:
573:
569:
565:
561:
556:
552:
550:
546:
545:cell polarity
542:
534:
532:
530:
526:
522:
513:
506:
504:
502:
498:
494:
490:
486:
479:Axonal region
478:
476:
472:
470:
466:
462:
458:
454:
450:
446:
442:
438:
433:
431:
427:
423:
419:
415:
414:Schwann cells
411:
407:
403:
399:
394:
392:
388:
384:
380:
376:
372:
368:
364:
363:sciatic nerve
360:
356:
349:
345:
340:
328:
327:Myelin sheath
323:
318:
317:Axon terminal
313:
306:
301:
296:
291:
286:
281:
270:
268:
266:
262:
258:
254:
250:
246:
242:
238:
233:
231:
226:
222:
218:
214:
210:
209:axon terminal
206:
202:
198:
193:
191:
187:
182:
180:
176:
172:
168:
164:
160:
156:
152:
148:
144:
140:
136:
132:
128:
124:
120:
116:
112:
109:
105:
101:
97:
85:
79:
75:
72:
69:
67:
63:
60:
57:
55:
51:
46:
39:
34:
29:
26:
22:
5767:Gap junction
5689:Motor neuron
5492:
5483:Axon hillock
5459:nerve fibers
5413:Schwann cell
5323:
5306:
5284:
5202:Medium spiny
5115:White matter
5103:Tissue Types
5000:
4996:
4948:
4944:
4934:
4909:
4905:
4899:
4879:. ABC-CLIO.
4875:
4868:
4835:
4831:
4825:
4817:
4795:
4789:
4777:. Retrieved
4769:
4760:
4748:. Retrieved
4742:
4733:
4721:. Retrieved
4715:
4706:
4694:. Retrieved
4690:
4681:
4641:(1): 14626.
4638:
4634:
4624:
4612:. Retrieved
4608:the original
4599:
4590:
4563:
4559:
4549:
4506:
4500:
4465:
4461:
4451:
4414:
4411:PLOS Biology
4410:
4400:
4365:
4361:
4351:
4329:
4317:. Retrieved
4308:
4298:
4279:
4273:
4238:
4234:
4224:
4197:
4193:
4183:
4132:
4128:
4118:
4081:
4077:
4067:
4024:
4020:
4010:
3975:
3972:Cell Reports
3971:
3961:
3926:
3922:
3912:
3877:
3873:
3863:
3830:
3826:
3820:
3775:
3771:
3761:
3742:
3736:
3701:
3697:
3687:
3654:
3650:
3644:
3611:
3607:
3565:
3561:
3555:
3525:(1): 61–85.
3522:
3518:
3512:
3477:
3473:
3463:
3430:
3426:
3420:
3412:
3399:
3366:
3362:
3318:
3314:
3304:
3269:
3265:
3255:
3225:(5): 544–6.
3222:
3218:
3212:
3187:
3183:
3176:
3157:
3151:
3106:
3102:
3092:
3083:
3074:
3040:(181): 181.
3037:
3033:
3023:
2988:
2985:Brain Pathol
2984:
2934:
2930:
2905:21 September
2903:. Retrieved
2899:
2890:
2841:
2840:. Series B.
2837:
2831:
2806:
2798:
2763:
2759:
2749:
2730:
2697:
2636:
2632:
2582:
2578:
2530:
2526:
2516:
2479:
2475:
2425:
2421:
2415:
2380:
2376:
2366:
2329:
2325:
2315:
2278:
2274:
2264:
2231:
2227:
2170:
2166:
2132:
2084:
2080:
2070:
2033:
2029:
1997:Pioneer axon
1946:
1915:
1906:ion channels
1889:Alan Hodgkin
1861:Robert Remak
1850:
1834:
1825:nerve injury
1814:
1795:
1781:
1771:
1751:
1720:
1709:Nerve injury
1635:Fiber types
1626:
1385:
1271:
1262:
1219:
1205:
1198:
1178:
1154:
1142:
1123:
1087:glycoprotein
1060:
1025:
1016:phosphatases
1005:
985:
950:
941:cytoskeletal
925:
909:and shorter
899:
891:
887:interneurons
885:(~500μs) or
866:
854:
845:
788:
786:
776:
748:
746:
722:
717:
695:
680:
673:
661:Schwann cell
614:mitochondria
607:
591:
557:
553:
540:
538:
521:axon hillock
518:
507:Axon hillock
493:microtubules
485:Nissl bodies
482:
473:
460:
457:nerve tracts
441:white matter
434:
402:unmyelinated
395:
352:
348:white matter
322:Schwann cell
300:Axon hillock
294:
257:white matter
255:the largest
234:
229:
194:
183:
110:
107:
103:
99:
95:
93:
25:
5782:Active zone
5747:Termination
5597:Interneuron
5501:Telodendron
5409:Myelination
5391:Endoneurium
5386:Perineurium
5207:Interneuron
5197:Von Economo
5145:Decussation
5140:Nerve tract
5110:Grey matter
5050:Spinal cord
2482:: 6808293.
1930:giant squid
1901:Nobel Prize
1885:myelination
1859:and German
1831:Terminology
1731:neurotmesis
1727:axonotmesis
1723:neurapraxia
1605:Nociceptors
1567:Nociceptors
1436:Associated
1400:nociceptors
1302:Associated
1161:macrophages
1111:fibronectin
1063:growth cone
988:ganglioside
975:(BDNF) and
932:hippocampal
922:Development
878:gray matter
870:place cells
824:Active zone
793:hippocampus
749:telodendron
683:glial cells
640:Myelination
461:commissures
449:grey matter
410:glial cells
367:spinal cord
344:grey matter
265:human brain
237:nerve tract
205:telodendria
186:cytoplasmic
123:vertebrates
104:nerve fiber
102:, axis) or
48:Identifiers
5852:Nociceptor
5592:Multipolar
5541:Nissl body
5418:Neurilemma
5381:Epineurium
5166:Cell Types
4241:: 347–60.
4142:1807.04799
3568:: 609–42.
3413:C. elegans
2937:: 610857.
2008:References
1735:Concussion
1656:Conduction
1431:Conduction
1386:Different
1140:required.
943:dynamics.
862:exocytosis
676:myelinated
669:Neurilemma
453:cerebellum
398:myelinated
371:micrometer
179:myelinated
155:peripheral
5867:Hair cell
5401:Neuroglia
5363:Funiculus
5252:Microglia
5225:Astrocyte
5182:Pyramidal
5135:Lemniscus
4175:118682719
3404:Neuroglia
1841:dendrites
1796:A severe
1623:Autonomic
1238:efferents
1234:afferents
1071:filopodia
992:sialidase
907:threshold
685:known as
608:Outgoing
598:cytoplasm
576:ankyrin-G
527:that are
499:known as
420:. In the
147:periphery
5891:Category
5652:Ia or Aα
5582:Unipolar
5531:Dendrite
5516:Axolemma
5511:Axoplasm
5295:Ganglion
5235:Tanycyte
5187:Purkinje
5174:Neuronal
5157:Meninges
5152:Neuropil
5029:29170630
4975:27780071
4891:Archived
4860:37676544
4852:16997762
4814:27151391
4779:21 April
4750:21 April
4723:21 April
4696:21 April
4673:31602002
4582:17291371
4541:44405442
4533:16802706
4492:17093095
4443:20126265
4392:20345246
4337:Archived
4313:Archived
4309:Medscape
4167:31212501
4125:Morigi G
4110:26257607
4059:25954897
4002:22773964
3953:17846176
3904:19321792
3847:15018947
3812:22073205
3772:PLOS ONE
3728:28813676
3679:10082468
3636:25227765
3628:15834419
3590:10217268
3582:12676795
3547:23974242
3504:18043414
3496:10399920
3455:22666205
3391:15556921
3383:17311006
3345:12417580
3247:27728967
3239:15856056
3143:20686619
3103:PLOS ONE
3066:24348338
3015:30444552
2963:33613192
2882:11963512
2874:13003931
2790:27141942
2673:18862030
2665:26464228
2656:10717305
2611:27826229
2557:20007821
2508:27493806
2450:23996233
2442:20631711
2407:29378864
2358:28184187
2307:28536506
2256:13916255
2248:21527732
2197:20720105
2062:25477788
1971:See also
1696:0.5–2.0
1648:Diameter
1423:Diameter
1289:Diameter
1210:Erlanger
1165:Dectin-1
1130:guidance
1119:perlecan
1115:tenascin
936:neurites
757:end-foot
594:axoplasm
285:Dendrite
245:fascicle
243:, and a
225:membrane
217:synapses
213:synaptic
201:axoplasm
197:axolemma
190:dendrite
5794:Autapse
5755:Synapse
5602:Renshaw
5577:Bipolar
5454:Neurons
5307:Ventral
5278:General
5192:Granule
5020:5684645
5003:: 332.
4953:Bibcode
4926:8807532
4664:6787341
4643:Bibcode
4614:20 June
4483:6674790
4434:2811159
4383:5223592
4319:14 July
4265:7359413
4256:1279120
4216:4482075
4147:Bibcode
4101:4508512
4084:: 281.
4050:4423051
4029:Bibcode
3993:3389498
3944:2064629
3895:2693768
3855:9672315
3803:3206876
3780:Bibcode
3720:2317872
3659:Bibcode
3651:Science
3539:2310575
3447:8062384
3336:2173080
3296:2925793
3287:2115496
3204:2583372
3134:2912328
3111:Bibcode
3057:3831546
3006:6482960
2954:7886671
2846:Bibcode
2781:4967101
2703:584–587
2602:5078684
2585:: 250.
2548:2951114
2499:4967436
2398:6596274
2349:5266712
2298:5422562
2281:: 136.
2188:3197828
2111:1018277
2102:1307715
2053:4235383
2036:: 133.
1847:History
1690:0.2–1.5
1601:0.5–2.0
1595:0.2–1.5
1380:Sensory
1230:group C
1226:group B
1222:group A
1107:laminin
1032:f-actin
971:(NGF),
773:autapse
769:synapse
630:kinesin
404:axons.
391:neurons
312:Ranvier
310:Node of
305:Nucleus
271:Anatomy
247:in the
239:in the
221:autapse
163:classed
59:D001369
5647:fibers
5285:Dorsal
5027:
5017:
4973:
4924:
4883:
4858:
4850:
4812:
4802:
4671:
4661:
4580:
4539:
4531:
4521:
4490:
4480:
4441:
4431:
4390:
4380:
4286:
4263:
4253:
4214:
4173:
4165:
4108:
4098:
4057:
4047:
4000:
3990:
3951:
3941:
3902:
3892:
3853:
3845:
3810:
3800:
3749:
3726:
3718:
3677:
3634:
3626:
3588:
3580:
3545:
3537:
3519:Neuron
3502:
3494:
3453:
3445:
3389:
3381:
3343:
3333:
3294:
3284:
3245:
3237:
3202:
3164:
3141:
3131:
3064:
3054:
3013:
3003:
2961:
2951:
2880:
2872:
2864:
2819:
2788:
2778:
2737:
2709:
2671:
2663:
2653:
2609:
2599:
2555:
2545:
2506:
2496:
2448:
2440:
2405:
2395:
2356:
2346:
2305:
2295:
2254:
2246:
2195:
2185:
2139:
2109:
2099:
2060:
2050:
1767:NMNAT2
1715:, and
1653:Myelin
1500:80–120
1469:80–120
1428:Myelin
1324:80–120
1294:Myelin
1256:, and
1228:, and
1214:Gasser
1156:Nogo-A
1117:, and
1043:Growth
961:Netrin
751:is an
634:dynein
529:summed
445:tissue
406:Myelin
359:nerves
173:, and
119:neuron
113:: see
5570:Types
5467:Parts
5336:White
5317:Ramus
5300:Ramus
5217:Glial
4856:S2CID
4537:S2CID
4171:S2CID
4137:arXiv
3851:S2CID
3724:S2CID
3632:S2CID
3586:S2CID
3543:S2CID
3500:S2CID
3451:S2CID
3387:S2CID
3243:S2CID
2878:S2CID
2866:82721
2862:JSTOR
2669:S2CID
2446:S2CID
2332:: 6.
2252:S2CID
2224:(PDF)
1729:, or
1677:3–15
1574:Cold
1524:33–75
1494:13–20
1463:13–20
1318:13–20
1268:Motor
1083:TAG-1
1079:N-CAM
1028:actin
965:UNC-5
874:white
251:. In
121:, in
111:fibre
108:nerve
82:[
71:67308
5493:Axon
5475:Soma
5331:Gray
5312:Root
5290:Root
5025:PMID
4971:PMID
4922:PMID
4881:ISBN
4848:PMID
4810:OCLC
4800:ISBN
4781:2023
4752:2023
4725:2023
4698:2023
4669:PMID
4616:2018
4578:PMID
4529:PMID
4519:ISBN
4488:PMID
4439:PMID
4388:PMID
4321:2018
4284:ISBN
4261:PMID
4212:PMID
4163:PMID
4106:PMID
4055:PMID
3998:PMID
3949:PMID
3900:PMID
3843:PMID
3808:PMID
3747:ISBN
3716:PMID
3698:Cell
3675:PMID
3624:PMID
3578:PMID
3535:PMID
3492:PMID
3474:Cell
3443:PMID
3427:Cell
3406:and
3379:PMID
3341:PMID
3292:PMID
3235:PMID
3200:PMID
3162:ISBN
3139:PMID
3062:PMID
3011:PMID
2959:PMID
2907:2024
2870:PMID
2817:ISBN
2786:PMID
2735:ISBN
2707:ISBN
2661:PMID
2607:PMID
2553:PMID
2504:PMID
2480:2016
2438:PMID
2403:PMID
2354:PMID
2303:PMID
2244:PMID
2193:PMID
2137:ISBN
2107:PMID
2058:PMID
1891:and
1879:and
1650:(μm)
1640:Type
1627:The
1558:3–30
1555:Thin
1544:III
1533:All
1518:6–12
1425:(μm)
1415:Type
1402:and
1366:4–24
1291:(μm)
1281:Type
1212:and
1008:PI3K
996:TrkA
986:The
876:and
822:and
667:(5)
663:(4)
616:and
592:The
570:and
549:soma
539:The
519:The
495:and
416:and
400:and
346:and
295:Axon
290:Soma
157:and
106:(or
100:áxōn
96:axon
54:MeSH
31:Axon
5707:SVE
5702:GVE
5697:GSE
5642:SVA
5637:SSA
5632:GVA
5627:GSA
5270:PNS
5095:CNS
5015:PMC
5005:doi
4961:doi
4914:doi
4840:doi
4659:PMC
4651:doi
4568:doi
4511:doi
4478:PMC
4470:doi
4429:PMC
4419:doi
4378:PMC
4370:doi
4251:PMC
4243:doi
4239:298
4202:doi
4155:doi
4096:PMC
4086:doi
4045:PMC
4037:doi
4025:108
3988:PMC
3980:doi
3939:PMC
3931:doi
3927:178
3890:PMC
3882:doi
3835:doi
3798:PMC
3788:doi
3706:doi
3667:doi
3655:283
3616:doi
3570:doi
3527:doi
3482:doi
3435:doi
3371:doi
3331:PMC
3323:doi
3319:159
3282:PMC
3274:doi
3270:108
3227:doi
3192:doi
3188:136
3129:PMC
3119:doi
3052:PMC
3042:doi
3001:PMC
2993:doi
2949:PMC
2939:doi
2854:doi
2842:140
2813:300
2776:PMC
2768:doi
2651:PMC
2641:doi
2597:PMC
2587:doi
2543:PMC
2535:doi
2494:PMC
2484:doi
2430:doi
2393:PMC
2385:doi
2344:PMC
2334:doi
2293:PMC
2283:doi
2236:doi
2183:PMC
2175:doi
2097:PMC
2089:doi
2085:263
2048:PMC
2038:doi
1810:rat
1674:Yes
1671:1–5
1607:of
1587:IV
1569:of
1552:1–5
1521:Yes
1497:Yes
1488:Ib
1466:Yes
1363:Yes
1360:5-8
1321:Yes
1091:MAG
649:TEM
94:An
66:FMA
5893::
5411::
5023:.
5013:.
5001:11
4999:.
4995:.
4983:^
4969:.
4959:.
4949:26
4947:.
4943:.
4920:.
4910:30
4908:.
4889:.
4854:.
4846:.
4836:15
4834:.
4816:.
4808:.
4772:.
4768:.
4741:.
4714:.
4689:.
4667:.
4657:.
4649:.
4637:.
4633:.
4604:GE
4602:.
4598:.
4576:.
4564:10
4562:.
4558:.
4535:.
4527:.
4517:.
4486:.
4476:.
4466:26
4464:.
4460:.
4437:.
4427:.
4413:.
4409:.
4386:.
4376:.
4366:33
4364:.
4360:.
4343:,
4311:.
4307:.
4259:.
4249:.
4237:.
4233:.
4210:.
4198:57
4196:.
4192:.
4169:.
4161:.
4153:.
4145:.
4133:99
4131:.
4104:.
4094:.
4080:.
4076:.
4053:.
4043:.
4035:.
4023:.
4019:.
3996:.
3986:.
3974:.
3970:.
3947:.
3937:.
3925:.
3921:.
3898:.
3888:.
3878:29
3876:.
3872:.
3849:.
3841:.
3831:14
3829:.
3806:.
3796:.
3786:.
3774:.
3770:.
3722:.
3714:.
3702:61
3700:.
3696:.
3673:.
3665:.
3653:.
3630:.
3622:.
3610:.
3598:^
3584:.
3576:.
3566:72
3564:.
3541:.
3533:.
3521:.
3498:.
3490:.
3478:97
3476:.
3472:.
3449:.
3441:.
3431:78
3429:.
3385:.
3377:.
3365:.
3353:^
3339:.
3329:.
3317:.
3313:.
3290:.
3280:.
3268:.
3264:.
3241:.
3233:.
3221:.
3198:.
3186:.
3137:.
3127:.
3117:.
3105:.
3101:.
3060:.
3050:.
3036:.
3032:.
3009:.
2999:.
2989:29
2987:.
2983:.
2971:^
2957:.
2947:.
2935:14
2933:.
2929:.
2915:^
2898:.
2876:.
2868:.
2860:.
2852:.
2815:.
2784:.
2774:.
2764:73
2762:.
2758:.
2721:^
2705:.
2681:^
2667:.
2659:.
2649:.
2637:66
2635:.
2631:.
2619:^
2605:.
2595:.
2583:10
2581:.
2577:.
2565:^
2551:.
2541:.
2531:15
2529:.
2525:.
2502:.
2492:.
2478:.
2474:.
2458:^
2444:.
2436:.
2426:11
2424:.
2401:.
2391:.
2381:38
2379:.
2375:.
2352:.
2342:.
2330:11
2328:.
2324:.
2301:.
2291:.
2279:11
2277:.
2273:.
2250:.
2242:.
2232:91
2230:.
2226:.
2205:^
2191:.
2181:.
2171:30
2169:.
2165:.
2151:^
2119:^
2105:.
2095:.
2083:.
2079:.
2056:.
2046:.
2032:.
2028:.
2016:^
1942:cf
1908:.
1871:.
1827:.
1815:A
1793:.
1779:.
1733:.
1725:,
1711:,
1693:No
1598:No
1582:✔
1548:Aδ
1539:✔
1515:Aβ
1511:II
1491:Aα
1460:Aα
1456:Ia
1357:Aγ
1339:Aβ
1315:Aα
1252:,
1224:,
1208:.
1152:.
1113:,
1109:,
1081:,
983:.
704:.
503:.
432:.
412::
267:.
169:,
5765:/
5686:/
5616:/
5553:/
5456:/
5354:)
5345:(
5079:e
5072:t
5065:v
5052:"
5031:.
5007::
4977:.
4963::
4955::
4928:.
4916::
4862:.
4842::
4783:.
4754:.
4727:.
4700:.
4675:.
4653::
4645::
4639:9
4618:.
4584:.
4570::
4543:.
4513::
4494:.
4472::
4445:.
4421::
4415:8
4394:.
4372::
4323:.
4292:.
4267:.
4245::
4218:.
4204::
4177:.
4157::
4149::
4139::
4112:.
4088::
4082:9
4061:.
4039::
4031::
4004:.
3982::
3976:1
3955:.
3933::
3906:.
3884::
3857:.
3837::
3814:.
3790::
3782::
3776:6
3755:.
3730:.
3708::
3681:.
3669::
3661::
3638:.
3618::
3612:8
3592:.
3572::
3549:.
3529::
3523:4
3506:.
3484::
3457:.
3437::
3393:.
3373::
3367:8
3347:.
3325::
3298:.
3276::
3249:.
3229::
3223:8
3206:.
3194::
3170:.
3145:.
3121::
3113::
3107:5
3068:.
3044::
3038:7
3017:.
2995::
2965:.
2941::
2909:.
2884:.
2856::
2848::
2825:.
2792:.
2770::
2743:.
2715:.
2675:.
2643::
2613:.
2589::
2559:.
2537::
2510:.
2486::
2452:.
2432::
2409:.
2387::
2360:.
2336::
2309:.
2285::
2258:.
2238::
2199:.
2177::
2145:.
2113:.
2091::
2064:.
2040::
2034:8
1687:C
1668:B
1591:C
1479:✔
1101:-
137:(
86:]
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.