46:
599:
31:
38:
200:
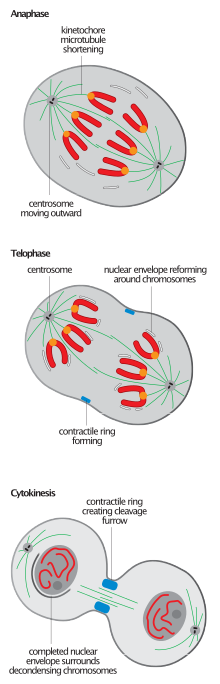
The second part of anaphase is driven by its own distinct mechanisms. Force is generated by several actions. Interpolar microtubules begin at each centrosome and join at the equator of the dividing cell. They push against one another, causing each centrosome to move further apart. Meanwhile, astral
201:
microtubules begin at each centrosome and join with the cell membrane. This allows them to pull each centrosome closer to the cell membrane. Movement created by these microtubules is generated by a combination of microtubule growth or shrinking, and by motor proteins such as
173:, from which mitotic microtubules are generated and organised). The movement for this is primarily generated by the action of kinetochores, and a subclass of microtubule called kinetochore microtubules.
176:
The second motion, anaphase B, involves the separation of these poles from each other. The movement for this is primarily generated by the action of interpolar microtubules and astral microtubules.
184:
A combination of different forces have been observed acting on chromatids in anaphase A, but the primary force is exerted centrally. Microtubules attach to the midpoint of chromosomes (the
192:). The attached microtubules depolymerise and shorten, which together with motor proteins creates movement that pulls chromosomes towards centrosomes located at each pole of the cell.
151:
The centromeres are split, and the sister chromatids are pulled toward the poles by kinetochore microtubules. They take on a V-shape or Y-shape as they are pulled to either pole.
631:
154:
While the chromosomes are drawn to each side of the cell, interpolar microtubules and astral microtubules generate forces that stretch the cell into an oval.
923:
817:
347:
567:
Heath IB, Rethoret K (June 1980). "Temporal analysis of the nuclear cycle by serial section electron microscopy of the fungus, Saprolegnia ferax".
144:
unique to mitosis are involved in creating the forces necessary to separate the chromatids: kinetochore microtubules, interpolar microtubules, and
169:
Anaphase is characterized by two distinct motions. The first of these, anaphase A, moves chromosomes to either pole of a dividing cell (marked by
863:
624:
617:
933:
1074:
777:
238:
237:, which is required for the function of metaphase cyclin-dependent kinases (M-Cdks). In essence, Activation of the
110:
45:
772:
767:
762:
757:
752:
747:
742:
737:
732:
724:
351:
57:
1056:
807:
603:
145:
114:
1069:
874:
447:
322:
76:
1064:
576:
549:
498:
439:
404:
221:'s duration. It begins with the regulated triggering of the metaphase-to-anaphase transition.
1129:
539:
529:
488:
478:
431:
394:
386:
544:
517:
493:
466:
399:
374:
63:
1123:
1003:
451:
1025:
287:
272:
1046:
1015:
234:
189:
141:
24:
435:
967:
851:
640:
467:"Anaphase A: Disassembling Microtubules Move Chromosomes toward Spindle Poles"
390:
262:
250:
218:
185:
170:
103:
99:
91:
20:
241:(APC) causes the APC to cleave the M-phase cyclin and the inhibitory protein
1090:
1040:
1030:
713:
709:
699:
695:
691:
681:
677:
667:
663:
282:
277:
230:
222:
158:
122:
95:
87:
553:
534:
502:
483:
408:
598:
580:
443:
1095:
1020:
989:
975:
705:
687:
673:
659:
267:
130:
126:
102:
also reach their overall maximum condensation in late anaphase, to help
37:
1104:
1011:
984:
643:
297:
292:
246:
242:
206:
134:
133:. The destruction of securin unleashes separase which then breaks down
118:
83:
609:
943:
859:
845:
841:
837:
829:
787:
782:
651:
226:
202:
516:
Scholey JM, Civelekoglu-Scholey G, Brust-Mascher I (December 2016).
68:
30:
918:
913:
802:
797:
792:
302:
44:
36:
947:
938:
908:
887:
825:
137:, a protein responsible for holding sister chromatids together.
613:
928:
892:
882:
855:
833:
375:"Rho-kinase controls cell shape changes during cytokinesis"
41:
A cell during anaphase. Microtubules are visible in green.
422:
Schafer KA (November 1998). "The cell cycle: a review".
94:
are split and the newly-copied chromosomes (daughter
373:
Hickson GR, Echard A, O'Farrell PH (February 2006).
245:
which activates the separase protease to cleave the
1083:
1055:
1002:
966:
957:
901:
873:
816:
723:
650:
106:segregation and the re-formation of the nucleus.
157:Once anaphase is complete, the cell moves into
217:Anaphase accounts for approximately 1% of the
625:
8:
98:) are moved to opposite poles of the cell.
49:Stages of late M phase in a vertebrate cell
963:
632:
618:
610:
125:it. Securin is a protein which inhibits a
924:Cellular apoptosis susceptibility protein
543:
533:
492:
482:
398:
350:. Kimball's Biology Pages. Archived from
323:"Chromosome condensation through mitosis"
29:
314:
7:
82: 'appearance') is the stage of
140:At this point, three subclasses of
73: 'back, backward' and
233:which flags it for destruction by
14:
597:
569:European Journal of Cell Biology
225:ends with the destruction of B
1:
934:Maturation promoting factor
465:Asbury CL (February 2017).
1146:
1075:Postreplication checkpoint
436:10.1177/030098589803500601
239:Anaphase-promoting complex
229:. B cyclin is marked with
213:Relation to the cell cycle
111:anaphase promoting complex
18:
391:10.1016/j.cub.2005.12.043
188:) via protein complexes (
109:Anaphase starts when the
19:Not to be confused with
16:Stage of a cell division
1057:Cell cycle checkpoints
535:10.3390/biology5040051
484:10.3390/biology6010015
50:
42:
34:
1084:Other cellular phases
808:CDK-activating kinase
249:subunits holding the
86:after the process of
48:
40:
33:
606:at Wikimedia Commons
424:Veterinary Pathology
115:inhibitory chaperone
121:for destruction by
1070:Spindle checkpoint
875:P53 p63 p73 family
90:, when replicated
51:
43:
35:
1117:
1116:
1113:
1112:
1065:Restriction point
602:Media related to
1137:
964:
634:
627:
620:
611:
601:
585:
584:
564:
558:
557:
547:
537:
513:
507:
506:
496:
486:
462:
456:
455:
419:
413:
412:
402:
370:
364:
363:
361:
359:
348:"The Cell Cycle"
344:
338:
337:
335:
333:
319:
1145:
1144:
1140:
1139:
1138:
1136:
1135:
1134:
1120:
1119:
1118:
1109:
1099:
1079:
1051:
998:
993:
979:
959:
953:
897:
869:
812:
719:
646:
638:
594:
589:
588:
566:
565:
561:
515:
514:
510:
464:
463:
459:
421:
420:
416:
379:Current Biology
372:
371:
367:
357:
355:
346:
345:
341:
331:
329:
321:
320:
316:
311:
259:
215:
198:
182:
167:
28:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1143:
1141:
1133:
1132:
1122:
1121:
1115:
1114:
1111:
1110:
1108:
1107:
1102:
1097:
1093:
1087:
1085:
1081:
1080:
1078:
1077:
1072:
1067:
1061:
1059:
1053:
1052:
1050:
1049:
1044:
1038:
1033:
1028:
1023:
1018:
1008:
1006:
1000:
999:
997:
996:
991:
987:
982:
977:
972:
970:
961:
955:
954:
952:
951:
941:
936:
931:
926:
921:
916:
911:
905:
903:
899:
898:
896:
895:
890:
885:
879:
877:
871:
870:
868:
867:
849:
822:
820:
814:
813:
811:
810:
805:
800:
795:
790:
785:
780:
775:
770:
765:
760:
755:
750:
745:
740:
735:
729:
727:
721:
720:
718:
717:
703:
685:
671:
656:
654:
648:
647:
639:
637:
636:
629:
622:
614:
608:
607:
593:
592:External links
590:
587:
586:
559:
508:
457:
414:
365:
339:
313:
312:
310:
307:
306:
305:
300:
295:
290:
285:
280:
275:
270:
265:
258:
255:
214:
211:
197:
194:
181:
178:
166:
163:
148:microtubules.
123:ubiquitylating
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1142:
1131:
1128:
1127:
1125:
1106:
1103:
1101:
1094:
1092:
1089:
1088:
1086:
1082:
1076:
1073:
1071:
1068:
1066:
1063:
1062:
1060:
1058:
1054:
1048:
1045:
1042:
1039:
1037:
1034:
1032:
1029:
1027:
1024:
1022:
1019:
1017:
1013:
1010:
1009:
1007:
1005:
1001:
995:
988:
986:
983:
981:
974:
973:
971:
969:
965:
962:
956:
949:
945:
942:
940:
937:
935:
932:
930:
927:
925:
922:
920:
917:
915:
912:
910:
907:
906:
904:
900:
894:
891:
889:
886:
884:
881:
880:
878:
876:
872:
865:
861:
857:
853:
850:
847:
843:
839:
835:
831:
827:
824:
823:
821:
819:
818:CDK inhibitor
815:
809:
806:
804:
801:
799:
796:
794:
791:
789:
786:
784:
781:
779:
776:
774:
771:
769:
766:
764:
761:
759:
756:
754:
751:
749:
746:
744:
741:
739:
736:
734:
731:
730:
728:
726:
722:
715:
711:
707:
704:
701:
697:
693:
689:
686:
683:
679:
675:
672:
669:
665:
661:
658:
657:
655:
653:
649:
645:
642:
635:
630:
628:
623:
621:
616:
615:
612:
605:
600:
596:
595:
591:
582:
578:
575:(2): 208–13.
574:
570:
563:
560:
555:
551:
546:
541:
536:
531:
527:
523:
519:
512:
509:
504:
500:
495:
490:
485:
480:
476:
472:
468:
461:
458:
453:
449:
445:
441:
437:
433:
430:(6): 461–78.
429:
425:
418:
415:
410:
406:
401:
396:
392:
388:
385:(4): 359–70.
384:
380:
376:
369:
366:
354:on 2012-11-19
353:
349:
343:
340:
328:
327:Science Daily
324:
318:
315:
308:
304:
301:
299:
296:
294:
291:
289:
286:
284:
281:
279:
276:
274:
271:
269:
266:
264:
261:
260:
256:
254:
252:
248:
244:
240:
236:
232:
228:
224:
220:
212:
210:
208:
204:
195:
193:
191:
187:
179:
177:
174:
172:
164:
162:
160:
155:
152:
149:
147:
143:
138:
136:
132:
128:
124:
120:
116:
112:
107:
105:
101:
97:
93:
89:
85:
81:
78:
75:
72:
70:
65:
62:
59:
58:Ancient Greek
55:
47:
39:
32:
26:
22:
1035:
1026:Prometaphase
572:
568:
562:
525:
521:
518:"Anaphase B"
511:
474:
470:
460:
427:
423:
417:
382:
378:
368:
356:. Retrieved
352:the original
342:
330:. Retrieved
326:
317:
288:Cytoskeleton
273:Prometaphase
216:
199:
190:kinetochores
183:
175:
168:
156:
153:
150:
139:
108:
79:
74:
66:
61:
53:
52:
1047:Cytokinesis
1016:Preprophase
960:checkpoints
298:Anaphase II
235:proteasomes
171:centrosomes
142:microtubule
100:Chromosomes
92:chromosomes
25:Anaphase II
968:Interphase
958:Phases and
641:Cell cycle
358:9 December
309:References
293:Anaphase I
263:Interphase
253:together.
251:chromatids
219:cell cycle
196:Anaphase B
186:centromere
180:Anaphase A
104:chromosome
96:chromatids
56:(from
21:Anaphase I
1091:Apoptosis
1041:Telophase
1031:Metaphase
826:INK4a/ARF
528:(4): 51.
477:(1): 15.
283:Telophase
278:Metaphase
231:ubiquitin
223:Metaphase
159:telophase
129:known as
113:marks an
88:metaphase
1124:Category
1036:Anaphase
1021:Prophase
644:proteins
604:Anaphase
554:27941648
503:28218660
452:43902779
409:16488869
268:Prophase
257:See also
207:kinesins
131:separase
127:protease
80:(phásis)
54:Anaphase
1130:Mitosis
1105:Meiosis
1012:Mitosis
1004:M phase
985:S phase
852:cip/kip
581:7398661
545:5192431
522:Biology
494:5372008
471:Biology
444:9823588
400:1525334
332:12 June
247:cohesin
243:securin
203:dyneins
135:cohesin
119:securin
117:called
84:mitosis
944:Cullin
830:p14arf
652:Cyclin
579:
552:
542:
501:
491:
450:
442:
407:
397:
227:cyclin
165:Phases
146:astral
1100:phase
994:phase
980:phase
919:Cdc42
914:Cdc25
902:Other
684:, B3)
448:S2CID
303:Cdc20
77:φάσις
60:
948:CUL7
909:Cdc2
577:PMID
550:PMID
499:PMID
440:PMID
405:PMID
360:2012
334:2007
69:ana-
64:ἀνα-
939:Wee
929:E2F
893:p73
888:p63
883:p53
864:p57
860:p27
856:p21
846:p19
842:p18
838:p15
834:p16
788:11B
783:11A
725:CDK
540:PMC
530:doi
489:PMC
479:doi
432:doi
395:PMC
387:doi
205:or
23:or
1126::
862:,
858:,
844:,
840:,
836:,
803:14
798:13
793:12
778:10
714:E2
712:,
710:E1
700:D3
698:,
696:D2
694:,
692:D1
682:B2
680:,
678:B1
668:A2
666:,
664:A1
573:21
571:.
548:.
538:.
524:.
520:.
497:.
487:.
473:.
469:.
446:.
438:.
428:35
426:.
403:.
393:.
383:16
381:.
377:.
325:.
209:.
161:.
1098:0
1096:G
1043:)
1014:(
992:2
990:G
978:1
976:G
950:)
946:(
866:)
854:(
848:)
832:/
828:(
773:9
768:8
763:7
758:6
753:5
748:4
743:3
738:2
733:1
716:)
708:(
706:E
702:)
690:(
688:D
676:(
674:B
670:)
662:(
660:A
633:e
626:t
619:v
583:.
556:.
532::
526:5
505:.
481::
475:6
454:.
434::
411:.
389::
362:.
336:.
71:)
67:(
27:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.