428:” or as only a phosphorus and energy source providing the survival of microorganisms under extreme conditions. These compounds are now known to also have regulatory roles, and to occur in representatives of all kingdoms of living organisms, participating in metabolic correction and control on both genetic and enzymatic levels. Polyphosphate is directly involved in the switching-over of the genetic program characteristic of the exponential growth stage of bacteria to the program of cell survival under stationary conditions, "a life in the slow lane". They participate in many regulatory mechanisms occurring in bacteria:
142:
98:
113:
127:
1000:
EFSA Panel on Food
Additives and Flavourings (FAF), Younes, M., Aquilina, G., Castle, L., Engel, K. H., Fowler, P., ... & Mennes, W. (2019). Re‐evaluation of phosphoric acid–phosphates–di‐, tri‐and polyphosphates (E 338–341, E 343, E 450–452) as food additives and the safety of proposed extension
487:
Sodium polyphosphate (E452(i)), potassium polyphosphate (E452(ii)), sodium calcium polyphosphate (E452(iii)) and calcium polyphosphate (E452(iv)) are used as food additives (emulsifiers, humectants, sequestrants, stabilisers, and thickeners). They are not known to pose any potential health risk other
478:
from the blood vessels and thrombosis. Bacterial-derived polyphosphates impair the host immune response during infection and targeting polyphosphates with recombinant exopolyphosphatase improves sepsis survival in mice. Inorganic polyphosphates play a crucial role in tolerance of yeast cells to
453:
An important function of polyphosphate in microorganisms—prokaryotes and the lower eukaryotes—is to handle changing environmental conditions by providing phosphate and energy reserves. Polyphosphates are present in animal cells, and there are many data on its participation in the
159:
units linked together by sharing oxygen centres. For the linear chains, the end phosphorus groups share one oxide and the others phosphorus centres share two oxide centres. The corresponding phosphates are related to the acids by loss of the
227:
can be seen as the end product of condensation reactions, where each tetrahedron shares three corners with the others. Conversely, a complex mix of polymers is produced when a small amount of water is added to phosphorus pentoxide.
373:
stands for inorganic phosphate, which is protonated at biological pH. However, it is not large by inorganic standards. The term "high energy" refers to the fact that it is high relative to the amount of energy released in the
449:
Polyphosphates participate in the formation of channels across the living cell membranes. The above channels formed by polyphosphate and poly-b-hydroxybutyrate with Ca are involved in the transport processes in a variety of
330:
is particularly large. The formation of the magnesium complex is a critical element in the process of ATP hydrolysis, as it weakens the link between the terminal phosphate group and the rest of the molecule.
496:, these seem to be relevant only for exaggerated consumption of phosphate sources. In all, reasonable consumption (up to 40 mg phosphate per kg of body weight per day) seem to pose no health risk.
413:
High-polymeric inorganic polyphosphates were found in living organisms by L. Liberman in 1890. These compounds are linear polymers containing a few to several hundred residues of
66:
are involved in energy storage. A variety of polyphosphates find application in mineral sequestration in municipal waters, generally being present at 1 to 5 ppm.
436:, an RNA-polymerase subunit which is responsible for the expression of a large group of genes involved in adjustments to the stationary growth phase and many stressful agents.
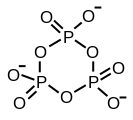
58:) structural units linked together by sharing oxygen atoms. Polyphosphates can adopt linear or a cyclic (also called, ring) structures. In biology, the polyphosphate esters
394:. Crystalline high molecular weight polyphosphates include Kurrol’s salt and Maddrell’s salt (white powder practically insoluble in water). These species have the formula
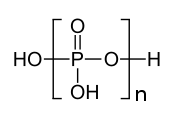
492:
sources (including those naturally occurring in food). While concerns have been raised regarding detrimental effects on the bones and cardiovascular diseases, as well as
367:
324:
280:
446:
participate in the regulation of the levels of the stringent response factor, guanosine 5'-diphosphate 3'-diphosphate (ppGpp), a second messenger in bacterial cells.
1011:
Ritz, E., Hahn, K., Ketteler, M., Kuhlmann, M. K., & Mann, J. (2012). Phosphate additives in food—a health risk. Deutsches Ärzteblatt
International, 109(4), 49.
470:
which is essential for blood clot formation. Factor XII, also called
Hageman factor, initiates fibrin formation and the generation of a proinflammatory mediator,
183:
Polyphosphates arise by polymerization of phosphoric acid derivatives. The process begins with two phosphate units coming together in a condensation reaction.
252:
interaction. This has profound significance in biology. For instance, adenosine triphosphate is about 25% protonated in aqueous solution at pH 7.
876:
Roewe J, Stavrides G, Strueve M, Sharma A, Marini F, Mann A, Smith SA, Kaya Z, Strobl B, Mueller M, Reinhardt C, Morrissey JH, Bosmann M (August 2020).
155:
The structure of tripolyphosphoric acid illustrates the principles which define the structures of polyphosphates. It consists of three tetrahedral PO
78:
are also nucleotides important in the protein synthesis, lipid synthesis, and carbohydrate metabolism, respectively. Polyphosphates are also used as
591:"Concentration of MgATP2- and other ions in solution. Calculation of the true concentrations of species present in mixtures of associating ions"
724:
739:
Klaus Schrödter, Gerhard
Bettermann, Thomas Staffel, Friedrich Wahl, Thomas Klein, Thomas Hofmann "Phosphoric Acid and Phosphates" in
141:
1027:"A high-conductance mode of a poly-3-hydroxybutyrate/calcium/polyphosphate channel isolated from competent Escherichia coli cells"
454:
regulatory processes during development and cellular proliferation and differentiation—especially in bone tissues and brain.
299:
762:"Human platelet dense granules contain polyphosphate and are similar to acidocalcisomes of bacteria and unicellular eukaryotes"
414:
97:
1163:
801:
Müller F, Mutch NJ, Schenk WA, Smith SA, Esterl L, Spronk HM, Schmidbauer S, Gahl WA, Morrissey JH, Renné T (Dec 2009).
1158:
937:"Adaptation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to toxic manganese concentration triggers changes in inorganic polyphosphates"
1153:
219:) unit is added to the chain, as indicated by the part in brackets in the illustration of polyphosphoric acid. P
515:
112:
1076:
Kulaev I, Vagabov V, Kulakovskaya T (1999). "New aspects of inorganic polyphosphate metabolism and function".
126:
510:
67:
63:
535:
Jessen, Henning J.; Dürr-Mayer, Tobias; Haa, Thomas M.; Ripp, Alexander; Cummins, Christopher C. (2021).
164:
protons. In the case of the cyclic trimer each tetrahedron shares two vertices with adjacent tetrahedra.
716:
147:
71:
59:
1038:
889:
586:
208:
75:
999:
1143:
638:
Wilson J, Chin A (1991). "Chelation of divalent cations by ATP, studied by titration calorimetry".
118:
1064:
564:
443:
104:
976:
1148:
1122:
1093:
1056:
958:
917:
832:
783:
720:
690:
655:
620:
556:
493:
375:
352:
309:
265:
172:
1114:
1085:
1046:
948:
907:
897:
822:
814:
773:
744:
708:
682:
647:
610:
602:
548:
505:
425:
418:
401:
where n can be as great as 2000. In terms of their structures, these polymers consist of PO
391:
237:
35:
1042:
893:
673:
Garfinkel L, Altschuld R, Garfinkel D (1986). "Magnesium in cardiac energy metabolism".
536:
912:
877:
827:
802:
615:
590:
79:
1089:
686:
1137:
651:
568:
133:
1068:
1118:
475:
241:
1051:
1026:
748:
552:
803:"Platelet polyphosphates are proinflammatory and procoagulant mediators in vivo"
459:
47:
902:
818:
215:, is also possible. The process may continue in steps; at each step another (PO
878:"Bacterial polyphosphates interfere with the innate host defense to infection"
471:
467:
249:
245:
212:
168:
17:
953:
936:
850:
489:
295:
171:
of the linear polymer. Crosslinked polyphosphates adopt the sheet-structure
55:
1126:
1097:
1060:
962:
921:
836:
787:
778:
761:
560:
386:
High molecular weight polyphosphates are well known. One derivative is the
935:
Andreeva N, Ryazanova L, Dmitriev V, Kulakovskaya T, Kulaev I (Aug 2013).
694:
659:
463:
43:
624:
439:
They are important for cell motility, biofilms formation and virulence.
606:
1105:
Kulaev I, Kulakovskaya T (2000). "Polyphosphate and phosphate pump".
405:"monomers", with the chains are terminated by protonated phosphates.
161:
387:
39:
240:. A lone pair of electrons on an oxygen atom can be donated to a
433:
458:
In humans polyphosphates are shown to play a key role in blood
167:
Sharing of three corners is possible. This motif represents
175:, but such structures occur only under extreme conditions.
1025:
Pavlov E, Grimbly C, Diao CT, French RJ (September 2005).
537:"Lost in Condensation: Poly-, Cyclo-, and Ultraphosphates"
851:"Newly discovered mechanism by which blood clots form"
355:
312:
268:
286:
Further protonation occurs at lower pH values.
760:Ruiz FA, Lea CR, Oldfield E, Docampo R (Oct 2004).
361:
318:
274:
369:-36.8 kJ mol is large by biological standards. P
27:Compounds formed from phosphate monomeric units
741:Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry
8:
378:reactions that can occur in living systems.
1050:
952:
911:
901:
826:
777:
614:
488:than those generally attributed to other
424:Previously, it was considered either as “
354:
311:
267:
580:
578:
527:
382:High-polymeric inorganic polyphosphates
334:The energy released in ATP hydrolysis,
93:
432:They participate in the induction of
244:(proton) or a metal ion in a typical
232:Acid-base and complexation properties
7:
1001:of use. EFSA Journal, 17(6), e05674.
25:
466:they activate blood coagulation
290:The "high energy" phosphate bond
207:The condensation is shown as an
140:
125:
111:
96:
298:complexes with metal ions. The
1119:10.1146/annurev.micro.54.1.709
211:because the reverse reaction,
1:
1090:10.1016/S1389-1723(99)80189-3
1052:10.1016/j.febslet.2005.08.032
749:10.1002/14356007.a19_465.pub3
687:10.1016/S0022-2828(86)80289-9
541:Accounts of Chemical Research
306:ATP + Mg ⇌ MgATP, log β
652:10.1016/0003-2697(91)90036-S
553:10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00370
743:2008, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.
479:toxic heavy metal cations.
462:. Produced and released by
1180:
903:10.1038/s41467-020-17639-x
819:10.1016/j.cell.2009.11.001
713:Chemistry of the Elements
711:; Earnshaw, Alan (1997).
516:Sodium hexametaphosphate
362:{\displaystyle \approx }
319:{\displaystyle \approx }
275:{\displaystyle \approx }
954:10.1111/1567-1364.12049
511:Sodium trimetaphosphate
179:Formation and synthesis
779:10.1074/jbc.M406261200
474:, that contributes to
417:linked by energy-rich
363:
320:
276:
977:"E452 Polyphosphates"
882:Nature Communications
717:Butterworth-Heinemann
709:Greenwood, Norman N.
483:Use as food additives
364:
321:
277:
148:Adenosine diphosphate
1107:Annu. Rev. Microbiol
353:
310:
302:for the equilibrium
266:
1164:Concrete admixtures
1043:2005FEBSL.579.5187P
894:2020NatCo..11.4035R
857:. December 10, 2009
444:exopolyphosphatases
442:Polyphosphates and
236:Polyphosphates are
119:Polyphosphoric acid
1159:E-number additives
675:J Mol Cell Cardiol
390:(i.e., amorphous)
359:
316:
300:stability constant
272:
105:triphosphoric acid
1078:J. Biosci. Bioeng
981:openfoodfacts.org
726:978-0-08-037941-8
607:10.1042/bj1590001
547:(21): 4036–4050.
494:hyperphosphatemia
342:O → ADP + P
256:ATP + H ⇌ ATPH, p
16:(Redirected from
1171:
1154:Food stabilizers
1130:
1101:
1072:
1054:
1012:
1009:
1003:
997:
991:
990:
988:
987:
973:
967:
966:
956:
932:
926:
925:
915:
905:
873:
867:
866:
864:
862:
847:
841:
840:
830:
798:
792:
791:
781:
757:
751:
737:
731:
730:
715:(2nd ed.).
705:
699:
698:
670:
664:
663:
635:
629:
628:
618:
587:Cornish-Bowden A
582:
573:
572:
532:
506:Phosphoric acids
426:molecular fossil
419:phosphoanhydride
376:organic chemical
368:
366:
365:
360:
325:
323:
322:
317:
281:
279:
278:
273:
144:
129:
115:
100:
21:
1179:
1178:
1174:
1173:
1172:
1170:
1169:
1168:
1134:
1133:
1104:
1075:
1037:(23): 5187–92.
1024:
1021:
1016:
1015:
1010:
1006:
998:
994:
985:
983:
975:
974:
970:
934:
933:
929:
875:
874:
870:
860:
858:
849:
848:
844:
800:
799:
795:
772:(43): 44250–7.
759:
758:
754:
738:
734:
727:
707:
706:
702:
681:(10): 1003–13.
672:
671:
667:
637:
636:
632:
584:
583:
576:
534:
533:
529:
524:
502:
485:
411:
404:
400:
397:
384:
372:
351:
350:
345:
341:
308:
307:
292:
264:
263:
262:
234:
226:
222:
218:
202:
198:
194:
190:
181:
173:Phyllosilicates
158:
151:
145:
136:
130:
121:
116:
107:
101:
92:
53:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1177:
1175:
1167:
1166:
1161:
1156:
1151:
1146:
1136:
1135:
1132:
1131:
1102:
1073:
1020:
1019:External links
1017:
1014:
1013:
1004:
992:
968:
947:(5): 463–470.
941:FEMS Yeast Res
927:
868:
842:
813:(6): 1143–56.
793:
752:
732:
725:
700:
665:
630:
574:
526:
525:
523:
520:
519:
518:
513:
508:
501:
498:
484:
481:
456:
455:
451:
447:
440:
437:
415:orthophosphate
410:
407:
402:
398:
395:
383:
380:
370:
358:
347:
346:
343:
339:
328:
327:
315:
291:
288:
284:
283:
271:
260:
233:
230:
224:
220:
216:
205:
204:
200:
196:
192:
188:
180:
177:
156:
153:
152:
146:
139:
137:
131:
124:
122:
117:
110:
108:
102:
95:
91:
88:
80:food additives
51:
26:
24:
18:Polyphosphates
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1176:
1165:
1162:
1160:
1157:
1155:
1152:
1150:
1147:
1145:
1142:
1141:
1139:
1128:
1124:
1120:
1116:
1112:
1108:
1103:
1099:
1095:
1091:
1087:
1084:(2): 111–29.
1083:
1079:
1074:
1070:
1066:
1062:
1058:
1053:
1048:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1032:
1028:
1023:
1022:
1018:
1008:
1005:
1002:
996:
993:
982:
978:
972:
969:
964:
960:
955:
950:
946:
942:
938:
931:
928:
923:
919:
914:
909:
904:
899:
895:
891:
887:
883:
879:
872:
869:
856:
852:
846:
843:
838:
834:
829:
824:
820:
816:
812:
808:
804:
797:
794:
789:
785:
780:
775:
771:
767:
763:
756:
753:
750:
746:
742:
736:
733:
728:
722:
718:
714:
710:
704:
701:
696:
692:
688:
684:
680:
676:
669:
666:
661:
657:
653:
649:
645:
641:
634:
631:
626:
622:
617:
612:
608:
604:
600:
596:
592:
588:
581:
579:
575:
570:
566:
562:
558:
554:
550:
546:
542:
538:
531:
528:
521:
517:
514:
512:
509:
507:
504:
503:
499:
497:
495:
491:
482:
480:
477:
473:
469:
465:
461:
452:
448:
445:
441:
438:
435:
431:
430:
429:
427:
422:
420:
416:
408:
406:
393:
392:Graham's salt
389:
381:
379:
377:
356:
337:
336:
335:
332:
313:
305:
304:
303:
301:
297:
289:
287:
269:
259:
255:
254:
253:
251:
247:
243:
239:
231:
229:
214:
210:
186:
185:
184:
178:
176:
174:
170:
165:
163:
149:
143:
138:
135:
134:metaphosphate
128:
123:
120:
114:
109:
106:
103:Structure of
99:
94:
89:
87:
85:
81:
77:
73:
69:
65:
61:
57:
49:
45:
42:of polymeric
41:
37:
33:
32:polyphosphate
19:
1110:
1106:
1081:
1077:
1034:
1030:
1007:
995:
984:. Retrieved
980:
971:
944:
940:
930:
885:
881:
871:
859:. Retrieved
854:
845:
810:
806:
796:
769:
765:
755:
740:
735:
712:
703:
678:
674:
668:
643:
640:Anal Biochem
639:
633:
598:
594:
544:
540:
530:
486:
457:
423:
412:
385:
348:
333:
329:
293:
285:
257:
242:hydrogen ion
235:
206:
182:
169:crosslinking
166:
154:
83:
46:formed from
31:
29:
888:(1): 4035.
861:13 December
855:physorg.com
766:J Biol Chem
646:(1): 16–9.
460:coagulation
209:equilibrium
48:tetrahedral
1144:Phosphates
1138:Categories
1113:: 709–34.
986:2022-03-18
601:(1): 1–5.
585:Storer A,
522:References
472:bradykinin
468:factor XII
450:organisms.
294:ATP forms
250:Lewis base
246:Lewis acid
238:weak bases
213:hydrolysis
191:) ⇌ (P
132:Cyclic tri
1031:FEBS Lett
595:Biochem J
569:238989161
490:phosphate
464:platelets
409:In nature
357:≈
314:≈
270:≈
90:Structure
82:, marked
56:phosphate
44:oxyanions
1149:Polymers
1127:11018142
1098:16232585
1069:35616647
1061:16150446
963:23663411
922:32788578
837:20005807
788:15308650
589:(1976).
561:34648267
500:See also
1039:Bibcode
913:7423913
890:Bibcode
828:2796262
695:3537318
660:1645933
616:1164030
476:leakage
421:bonds.
338:ATP + H
296:chelate
1125:
1096:
1067:
1059:
961:
920:
910:
835:
825:
786:
723:
693:
658:
623:
613:
567:
559:
388:glassy
349:at ΔG
187:2 H(PO
162:acidic
74:, and
1065:S2CID
625:11772
565:S2CID
199:) + H
150:(ADP)
40:ester
34:is a
1123:PMID
1094:PMID
1057:PMID
959:PMID
918:PMID
863:2009
833:PMID
807:Cell
784:PMID
721:ISBN
691:PMID
656:PMID
621:PMID
557:PMID
434:rpoS
84:E452
62:and
36:salt
1115:doi
1086:doi
1047:doi
1035:579
949:doi
908:PMC
898:doi
823:PMC
815:doi
811:139
774:doi
770:279
745:doi
683:doi
648:doi
644:193
611:PMC
603:doi
599:159
549:doi
282:6.6
76:UTP
72:CTP
68:GTP
64:ATP
60:ADP
38:or
1140::
1121:.
1111:54
1109:.
1092:.
1082:88
1080:.
1063:.
1055:.
1045:.
1033:.
1029:.
979:.
957:.
945:13
943:.
939:.
916:.
906:.
896:.
886:11
884:.
880:.
853:.
831:.
821:.
809:.
805:.
782:.
768:.
764:.
719:.
689:.
679:18
677:.
654:.
642:.
619:.
609:.
597:.
593:.
577:^
563:.
555:.
545:54
543:.
539:.
225:10
86:.
70:,
50:PO
30:A
1129:.
1117::
1100:.
1088::
1071:.
1049::
1041::
989:.
965:.
951::
924:.
900::
892::
865:.
839:.
817::
790:.
776::
747::
729:.
697:.
685::
662:.
650::
627:.
605::
571:.
551::
403:3
399:2
396:n
371:i
344:i
340:2
326:4
261:a
258:K
248:-
223:O
221:4
217:3
203:O
201:2
197:7
195:O
193:2
189:4
157:4
54:(
52:4
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.