169:. Private housing developments were to become common at this time, and were to profoundly change the pattern of Australian residential development. The Waller estate is said to represent the first and most intact example of housing development built by a private consortium in Ballarat. John Muir and the practice of Muir and Shepherd are attributed to the design of the majority of the houses built by the Waller syndicate within this estate. To create architectural diversity throughout the development Muir was commissioned to design a variety of domestic types. It has been noted that in a number of the firms designs that although the front elevations were similar, the plans differed. Described as post-war suburban, most of these houses were brick veneer in construction with terracotta roof tiles with small front porches and windows that wrap around corners. This estate was developed by the Waller consortium until 1961.
154:
287:
190:
182:
267:
229:
219:
136:
creating the 'foundations for
Australian functionalist modernism'. While with the practice Muir was to work on health buildings such as the 'perfectly styled', Maternal and Infant Welfare Pathological Block (1939) at The Royal Women's hospital and the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute Building (1939) at the Royal Melbourne Hospital. Both Muir and Shepherd were to work for this firm. During World War II Arthur Shepherd enlisted with the Australian Army (
277:
198:
for winter solar access. The front façade contains a window that wraps around the corner, and the slight angle of the plan begins to reveal the main entrance through the terrace. The gallery/sun-room that faces the terrace forms the hub of the house. The interior colours are stated to be soft pastels, however the journal speaks of the owners’ desire to experiment with bolder colours.
140:) in May 1943 and was discharged in May 1946. In 1945, Muir began preliminary work on a major Ballarat housing development: the Waller Estate. The practice of Muir and Shepherd was subsequently established in 1947. The practice was to remain small. Early employees included Ted Gillies, Richard Allen and James Earle. The firm ceased in 1980.
197:
This
Ballarat residence is described as, ‘contemporary in feeling without any particularly bold features... well adapted for modern living’. The Henderson’s appear to have valued the role of an architect in the design of their house. This single storey brick residence was orientated on a narrow block
172:
Throughout the 1950s both professional and popular journals promoted breaking from traditional housing designs and interior schemes and moving toward a modern style. A few of Muir and
Shepherd's residential works featured in popular Australian housing journals of the 1950s as follows. Trends observed
249:
residence was described as a ‘modified contemporary home... which combines the good ideas in modern architecture with the softer finish of the traditional’. The overall form reflects the past colonial
Australian homestead with gabled roof and long, broad and low verandas. This dwelling also presents
210:
residence has a very similar plan to the earlier
Henderson residence with a central terrace, entrance and sunroom. Designed for an average-sized allotment this house was described as possessing a ‘remarkable degree of comfort, spaciousness and beauty’ with garden spaces for outdoor living. In this
135:
John Muir began practising architecture in his hometown of
Ballarat in 1933. Following this he moved to Melbourne and joined the practice of Stephenson & Turner, where he was to become a senior draftsman by the 1940s. Stephenson & Turner's health buildings of the 1930s have been noted as
211:
residence Muir and
Shepherd used a change in level to differentiate between lounge and dining spaces. The transition between outside and inside was also more expressed. This design included considerably more built-in furniture and fittings than the previous residence.
254:
that faces the street is completely glazed with floor to ceiling sliding glass panels that overlook the stone terrace from the living room. The plan is modern in form with living spaces moving toward an open plan style, and more built in furniture.
127:. Their projects were predominantly residential buildings. Non-residential work included churches, a funeral parlour and commercial tenancy fitouts. Muir and Shepherd are one of the lesser-known post-war modern Victorian architectural firms.
307:, now demolished, was the first purpose built post-war funeral building in Victoria. The building, designed in 1953, was minimalist in form made from cream brick with simple white
496:
501:
173:
through these journals include: the progression of the firm’s designs towards a more modern style, more open-plan designs, more in-built furniture and fittings.
161:
John Muir was to bring this important project to the newly formed practice. Work on the Waller estate was to last for over a decade, with their
491:
137:
165:
office servicing the development of this ongoing project. Australia experienced severe housing shortages after
246:
112:
153:
124:
71:
304:
207:
189:
181:
266:
228:
218:
286:
411:
485:
166:
276:
354:
466:
Somers, Alma (1957). "There's a "Homestead" look about this
Melbourne modern".
385:
Richardson, Elizabeth (2018). "Methodist Church, Katamatite, Victoria (1961)".
120:
67:
251:
115:
established in 1947 by John Muir and Arthur
Shepherd with offices in both
162:
116:
308:
250:
a central entry into the key living spaces and a sunroom. The north
285:
275:
265:
227:
217:
188:
180:
152:
408:
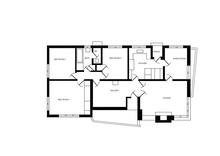
City of
Ballarat Heritage Study (Stage 2): Heritage Precincts
447:
Somers, Alma (1953). "The Small House that has Everything".
428:
Blanks, Harvey (1954). "They Wanted "Something Different"".
83:
78:
63:
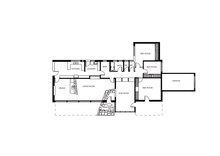
55:
47:
30:
25:
20:
349:
347:
345:
343:
341:
339:
303:The Funeral Parlour for WG Apps & Sons in
8:
497:Australian companies disestablished in 1980
402:
400:
17:
502:Australian companies established in 1947
423:
421:
320:
7:
380:
378:
376:
14:
359:Dictionary of Unsung Architects
332:. 4 September 1947. p. 16.
241:Fraser residence, Balwyn North
99:Fraser residence, Balwyn North
1:
430:The Australian Home Beautiful
361:. Built Heritage Pty Ltd. n.d
177:Henderson residence, Ballarat
93:Henderson residence, Ballarat
202:Jacobson residence, Brighton
193:Henderson residence interior
185:Henderson residence exterior
96:Jacobson residence, Brighton
79:Significant works and honors
492:Victoria (state) architects
468:Australian House and Garden
449:Australian House and Garden
518:
328:"New architectural firm".
138:Royal Australian Engineers
157:Waller estate floor plan
299:Non-residential designs
149:Waller estate, Ballarat
90:Waller estate, Ballarat
387:Architecture Australia
291:
281:
271:
233:
223:
194:
186:
158:
113:architectural practice
289:
279:
269:
231:
221:
192:
184:
156:
26:Practice information
455:(6): 20–21, 72, 74.
355:"Muir and Shepherd"
144:Residential designs
292:
282:
272:
234:
224:
195:
187:
159:
111:was an Australian
296:
295:
238:
237:
109:Muir and Shepherd
106:
105:
21:Muir and Shepherd
509:
476:
475:
463:
457:
456:
444:
438:
437:
425:
416:
415:
412:City of Ballarat
404:
395:
394:
382:
371:
370:
368:
366:
351:
334:
333:
325:
258:
257:
214:
213:
18:
517:
516:
512:
511:
510:
508:
507:
506:
482:
481:
480:
479:
465:
464:
460:
446:
445:
441:
427:
426:
419:
406:
405:
398:
384:
383:
374:
364:
362:
353:
352:
337:
327:
326:
322:
317:
301:
243:
204:
179:
151:
146:
133:
102:
43:
40:Arthur Shepherd
12:
11:
5:
515:
513:
505:
504:
499:
494:
484:
483:
478:
477:
458:
439:
417:
396:
372:
335:
319:
318:
316:
313:
300:
297:
294:
293:
283:
280:Exterior, 2014
273:
270:Exterior, 2014
263:
261:
242:
239:
236:
235:
232:Interior, 1953
225:
222:Exterior, 1953
203:
200:
178:
175:
150:
147:
145:
142:
132:
129:
104:
103:
101:
100:
97:
94:
91:
87:
85:
81:
80:
76:
75:
65:
61:
60:
57:
53:
52:
49:
45:
44:
42:
41:
38:
34:
32:
28:
27:
23:
22:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
514:
503:
500:
498:
495:
493:
490:
489:
487:
473:
469:
462:
459:
454:
450:
443:
440:
435:
431:
424:
422:
418:
413:
409:
403:
401:
397:
392:
388:
381:
379:
377:
373:
360:
356:
350:
348:
346:
344:
342:
340:
336:
331:
324:
321:
314:
312:
310:
306:
298:
288:
284:
278:
274:
268:
264:
262:
260:
259:
256:
253:
248:
240:
230:
226:
220:
216:
215:
212:
209:
201:
199:
191:
183:
176:
174:
170:
168:
164:
155:
148:
143:
141:
139:
130:
128:
126:
122:
118:
114:
110:
98:
95:
92:
89:
88:
86:
82:
77:
73:
69:
66:
62:
58:
54:
50:
46:
39:
36:
35:
33:
29:
24:
19:
16:
474:(3): 25, 86.
471:
467:
461:
452:
448:
442:
433:
429:
407:
390:
386:
363:. Retrieved
358:
329:
323:
302:
247:Balwyn North
244:
205:
196:
171:
167:World War II
160:
134:
108:
107:
15:
436:(3): 24–25.
393:(3): 76–77.
74:, Australia
486:Categories
315:References
290:Floor plan
330:The Argus
121:Melbourne
84:Buildings
68:Melbourne
56:Dissolved
37:John Muir
305:St Kilda
208:Brighton
163:Ballarat
131:Practice
125:Victoria
117:Ballarat
72:Victoria
64:Location
31:Partners
414:. 2003.
309:pilotis
48:Founded
365:6 July
252:façade
245:This
206:This
367:2014
119:and
59:1980
51:1947
391:108
488::
472:17
470:.
451:.
434:33
432:.
420:^
410:.
399:^
389:.
375:^
357:.
338:^
311:.
123:,
70:,
453:9
369:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.