172:
glucose which they called diastase at the time. In 1880, H.T. Brown discovered mucosal maltase activity and differentiated it from diastase, now called amylase. In the 1960s advances in protein chemistry allowed Arne
Dahlqvist and Giorgio Semenza to fractionate and characterize small intestinal maltase activities. Both groups showed there were four major fractions of maltase activity that were intrinsic to two different peptide structures, sucrase-isomaltase and maltase-glucoamylase. Fifty years later entering the genomic age, cloning and sequencing of the mucosal starch hydrolase confirmed Dahlqvist and Semenza's findings.
37:
45:
27:
139:
1425:
183:(AMD) also known as Pompe disease was first described by Dutch pathologist JC Pompe in 1932. AMD is a non sex linked autosomal recessive condition in which excessive accumulation of glycogen build up within lysosome vacuoles in nearly all types of cells all over the body. It is one of the more serious glycogen storage diseases affecting muscle tissue.
171:
The history of maltase discovery began when
Napoleon Bonaparte declared a continental blockade in his “Berlin decree” in 1806. This initiated the search for alternative sources of sugar. In 1833 French chemists Anselm Payen and Jean-Francois Persoz discovered a malt extract that converted starch into
146:
The mechanism of all FamilyGH13 enzymes is to break a α-glucosidase linkage by hydrolyzing it. Maltase focuses on breaking apart maltose, a disaccharide that is a link between 2 units of glucose, at the α-(1->4) bond. The rate of hydrolysis is controlled by the size of the substrate (carbohydrate
186:
AMD is categorized into three separate types based on the age of onset of symptoms in the affected individual. Infantile (Type a), childhood (Type b), and adulthood (Type c). The type of AMD is determined by the type of gene mutation localized on 17q23. Mutation type will determine production level
66:
Digestion of starch requires six intestinal enzymes. Two of these enzymes are luminal endo-glucosidases named alpha-amylases. The other four enzymes have been identified as different maltases, exo-glucosidases bound to the luminal surface of enterocytes. Two of these maltase activities were
162:
Other than brewing, maltose glucoamylase has been studied by introducing specific inhibitors to stop the hydrolysis of the α-glucosidase linkages. By inhibiting the cleave of the linkages, scientists are hoping to devise a drug that is more efficient and less toxic to treating diabetes.
124:
which is coded on the AMY1A gene is responsible of cleaving α-glucosidase linkages in oligosaccharides and polysaccharides in order to produce starches and glycogen for the previous enzymes to catalyze. Higher quantities of this gene in the brain have been shown to lower the risk of
155:
Alpha-amylase has an important function in degradation of starches, so it is used frequently in the baking industry. It is mostly used a means of flavor enhancing to improve bread quality. Without alpha-amylase, yeast would not be able to ferment.
187:
of acid maltase. AMD is extremely fatal. Type a generally die of heart failure prior to age one. Type b die of respiratory failure between ages three to twenty-four. Type c die of respiratory failure 10–20 years of the onset of symptoms.
87:) that are responsible for breaking apart the α-glucosidase linkages of complex carbohydrates into simple to use glucose molecules. The glucose molecules would then be used as a sort of "food" for cells to produce energy (
642:
75:(maltases II and III). The activities of these four maltases are also described as alpha-glucosidase because they all digest linear starch oligosaccharides to glucose.
112:
which is coded on the MGAM gene plays a role in the digestion of starches. It is due to this enzyme in humans that starches of plant origin are able to digested.
762:
159:
Maltose-glucoamylase is commonly used as a fermentation source as it is able to cut starch into maltose, which is then used for brewing beers and sake.
663:
735:
1144:
1026:
755:
682:
1300:
1038:
84:
1415:
118:
which is coded on the SI gene is essential for the digestion of carbohydrates including starch, sucrose and isomaltose.
885:
350:"The maltase-glucoamylase gene: common ancestry to sucrase-isomaltase with complementary starch digestion activities"
643:"Lysosomal Acid Alpha-Glucosidase Deficiency (Pompe Disease, Glycogen Storage Disease II, Acid Maltase Deficiency)"
1285:
1401:
1388:
1375:
1362:
1349:
1336:
1323:
1096:
784:
748:
1295:
1249:
1192:
775:
729:
36:
20:
407:
Byman E, Nägga K, Gustavsson AM, Andersson-Assarsson J, Hansson O, Sonestedt E, Wennström M (November 2020).
280:"Contribution of mucosal maltase-glucoamylase activities to mouse small intestinal starch alpha-glucogenesis"
1197:
948:
409:"Alpha-amylase 1A copy number variants and the association with memory performance and Alzheimer's dementia"
180:
1111:
856:
126:
99:
88:
1218:
1137:
1290:
1070:
1021:
510:
361:
207:
109:
92:
72:
319:
1254:
965:
953:
788:
278:
Quezada-Calvillo R, Robayo-Torres CC, Opekun AR, Sen P, Ao Z, Hamaker BR, et al. (July 2007).
234:
Nichols BL, Baker SS, Quezada-Calvillo R (June 2018). "Metabolic
Impacts of Maltase Deficiencies".
71:(maltase Ib, maltase Ia). The other two maltases with no distinguishing characteristics were named
1187:
1009:
1004:
982:
970:
809:
255:
212:
115:
68:
44:
1445:
977:
851:
705:
580:
538:
440:
389:
301:
247:
601:
1233:
1228:
1202:
1130:
987:
873:
697:
570:
528:
518:
430:
420:
379:
369:
291:
239:
1280:
1264:
1177:
1107:
623:
55:
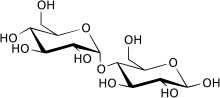
is an informal name for a family of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of disaccharide
514:
365:
1429:
1318:
1259:
1048:
960:
797:
740:
533:
498:
435:
408:
384:
349:
1439:
1223:
1182:
994:
923:
906:
736:
Structure and evolution of the mammalian maltase-glucoamylase and sucrase-isomaltase
725:
259:
1172:
838:
461:
195:
575:
562:
523:
243:
142:
Hydrolysis reaction of
Maltose being broken at the 1-4 alpha-glucosidase linkage.
1396:
1331:
1167:
1065:
1031:
999:
63:. Maltases are found in plants, bacteria, yeast, humans, and other vertebrates.
26:
1424:
425:
354:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
138:
102:
which is coded on the GAA gene is essential to breakdown complex sugars called
1075:
1043:
479:
683:"Diet and the evolution of digestion and renal function in phyllostomid bats"
1370:
1344:
913:
846:
823:
813:
771:
701:
374:
296:
279:
709:
584:
542:
444:
393:
348:
Nichols BL, Avery S, Sen P, Swallow DM, Hahn D, Sterchi E (February 2003).
305:
251:
198:
are the only vertebrates known to not exhibit intestinal maltase activity.
918:
103:
83:
Maltases are members of a group of intestinal enzymes called FamilyGH13 (
901:
828:
805:
60:
56:
30:
1383:
1153:
1357:
1080:
861:
499:"The effect of polyhydroxylated alkaloids on maltase-glucoamylase"
137:
121:
43:
35:
25:
1058:
1053:
1014:
943:
938:
933:
928:
878:
866:
1126:
744:
1122:
681:
Schondube JE, Herrera-M LG, Martínez del Rio C (2001).
273:
271:
269:
1413:
95:. The following are genes that can code for maltase:
1309:
1273:
1242:
1211:
1160:
1095:
894:
837:
796:
783:
567:
Journal of
Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition
236:
Journal of
Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition
628:Practice Essentials, Pathophysiology, Epidemiology
48:Interactions of oligosaccharides in Alpha-amylase
40:Ligand (NAG) interactions in Maltase-Glucoamylase
497:Shang Q, Xiang J, Zhang H, Li Q, Tang Y (2013).
563:"The History of Maltose-active Disaccharidases"
229:
227:
1138:
756:
556:
554:
552:
8:
320:"Glycoside Hydrolase Family 13 - CAZypedia"
1145:
1131:
1123:
793:
763:
749:
741:
728:at the U.S. National Library of Medicine
574:
532:
522:
434:
424:
383:
373:
295:
622:Kishner S, Sterne FE (5 December 2020).
1420:
223:
668:Gale Encyclopedia of Genetic Disorders
468:. Worthington Biochemical Corporation.
658:
656:
617:
615:
596:
594:
7:
456:
454:
343:
341:
339:
641:Merritt II LJ (20 December 2020).
624:"Acid Maltase Deficiency Myopathy"
413:Alzheimer's Research & Therapy
14:
670:. Encyclopedia.com. 5 March 2021.
1423:
1027:Alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminidase
606:World of Enzymes and Probiotics
1:
1039:Alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase
480:"Maltase: Baking Ingredients"
85:Glycoside hydrolase family 13
576:10.1097/MPG.0000000000001960
524:10.1371/journal.pone.0070841
244:10.1097/MPG.0000000000001955
238:. 66 Suppl 3 (3): S24–S29.
1462:
426:10.1186/s13195-020-00726-y
59:into two simple sugars of
18:
1301:Michaelis–Menten kinetics
664:"Acid maltase deficiency"
569:. 66 Suppl 3 (3): S4–S6.
466:Worthington Enzyme Manual
1193:Diffusion-limited enzyme
730:Medical Subject Headings
284:The Journal of Nutrition
19:Not to be confused with
949:Bacterial neuraminidase
702:10.1078/0944-2006-00007
561:Lentze MJ (June 2018).
375:10.1073/pnas.0237170100
181:Acid maltase deficiency
151:Industrial applications
1112:Oxoguanine glycosylase
191:Comparative physiology
143:
100:Acid alpha-glucosidase
89:Adenosine triphosphate
49:
41:
33:
1286:Eadie–Hofstee diagram
1219:Allosteric regulation
297:10.1093/jn/137.7.1725
141:
47:
39:
29:
1296:Lineweaver–Burk plot
1101:N-Glycosyl compounds
1071:Maltase-glucoamylase
1022:Galactosylceramidase
789:Glycoside hydrolases
774:: sugar hydrolases (
208:Maltase-glucoamylase
110:Maltase-glucoamylase
93:Cellular respiration
73:maltase-glucoamylase
954:Viral neuraminidase
515:2013PLoSO...870841S
366:2003PNAS..100.1432N
127:Alzheimer's disease
1255:Enzyme superfamily
1188:Enzyme promiscuity
1005:Glucosylceramidase
886:Debranching enzyme
810:Sucrase-isomaltase
486:. 14 January 2021.
213:Sucrase-isomaltase
176:Maltase deficiency
144:
116:Sucrase-isomaltase
69:sucrase-isomaltase
50:
42:
34:
1411:
1410:
1120:
1119:
1091:
1090:
978:alpha-Mannosidase
852:Alpha-glucosidase
324:www.cazypedia.org
1453:
1428:
1427:
1419:
1291:Hanes–Woolf plot
1234:Enzyme activator
1229:Enzyme inhibitor
1203:Enzyme catalysis
1147:
1140:
1133:
1124:
1108:DNA glycosylases
874:Beta-glucosidase
794:
765:
758:
751:
742:
714:
713:
687:
678:
672:
671:
660:
651:
650:
638:
632:
631:
619:
610:
609:
598:
589:
588:
578:
558:
547:
546:
536:
526:
494:
488:
487:
476:
470:
469:
458:
449:
448:
438:
428:
404:
398:
397:
387:
377:
345:
334:
333:
331:
330:
316:
310:
309:
299:
275:
264:
263:
231:
67:associated with
1461:
1460:
1456:
1455:
1454:
1452:
1451:
1450:
1436:
1435:
1434:
1422:
1414:
1412:
1407:
1319:Oxidoreductases
1305:
1281:Enzyme kinetics
1269:
1265:List of enzymes
1238:
1207:
1178:Catalytic triad
1156:
1151:
1121:
1116:
1100:
1087:
890:
833:
779:
769:
722:
717:
685:
680:
679:
675:
662:
661:
654:
640:
639:
635:
621:
620:
613:
600:
599:
592:
560:
559:
550:
496:
495:
491:
478:
477:
473:
460:
459:
452:
406:
405:
401:
347:
346:
337:
328:
326:
318:
317:
313:
277:
276:
267:
233:
232:
225:
221:
204:
193:
178:
169:
153:
136:
122:Alpha-amylase 1
81:
24:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1459:
1457:
1449:
1448:
1438:
1437:
1433:
1432:
1409:
1408:
1406:
1405:
1392:
1379:
1366:
1353:
1340:
1327:
1313:
1311:
1307:
1306:
1304:
1303:
1298:
1293:
1288:
1283:
1277:
1275:
1271:
1270:
1268:
1267:
1262:
1257:
1252:
1246:
1244:
1243:Classification
1240:
1239:
1237:
1236:
1231:
1226:
1221:
1215:
1213:
1209:
1208:
1206:
1205:
1200:
1195:
1190:
1185:
1180:
1175:
1170:
1164:
1162:
1158:
1157:
1152:
1150:
1149:
1142:
1135:
1127:
1118:
1117:
1115:
1114:
1104:
1102:
1093:
1092:
1089:
1088:
1086:
1085:
1084:
1083:
1073:
1068:
1063:
1062:
1061:
1056:
1049:Hexosaminidase
1046:
1041:
1036:
1035:
1034:
1024:
1019:
1018:
1017:
1012:
1002:
997:
992:
991:
990:
980:
975:
974:
973:
968:
961:Galactosidases
958:
957:
956:
951:
946:
941:
936:
931:
921:
916:
911:
910:
909:
898:
896:
892:
891:
889:
888:
883:
882:
881:
871:
870:
869:
864:
859:
849:
843:
841:
835:
834:
832:
831:
826:
821:
816:
802:
800:
798:Disaccharidase
791:
781:
780:
770:
768:
767:
760:
753:
745:
739:
738:
733:
721:
720:External links
718:
716:
715:
673:
652:
633:
611:
590:
548:
489:
471:
450:
399:
335:
311:
290:(7): 1725–33.
265:
222:
220:
217:
216:
215:
210:
203:
200:
192:
189:
177:
174:
168:
165:
152:
149:
135:
132:
131:
130:
119:
113:
107:
80:
77:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1458:
1447:
1444:
1443:
1441:
1431:
1426:
1421:
1417:
1403:
1399:
1398:
1393:
1390:
1386:
1385:
1380:
1377:
1373:
1372:
1367:
1364:
1360:
1359:
1354:
1351:
1347:
1346:
1341:
1338:
1334:
1333:
1328:
1325:
1321:
1320:
1315:
1314:
1312:
1308:
1302:
1299:
1297:
1294:
1292:
1289:
1287:
1284:
1282:
1279:
1278:
1276:
1272:
1266:
1263:
1261:
1260:Enzyme family
1258:
1256:
1253:
1251:
1248:
1247:
1245:
1241:
1235:
1232:
1230:
1227:
1225:
1224:Cooperativity
1222:
1220:
1217:
1216:
1214:
1210:
1204:
1201:
1199:
1196:
1194:
1191:
1189:
1186:
1184:
1183:Oxyanion hole
1181:
1179:
1176:
1174:
1171:
1169:
1166:
1165:
1163:
1159:
1155:
1148:
1143:
1141:
1136:
1134:
1129:
1128:
1125:
1113:
1109:
1106:
1105:
1103:
1099:: Hydrolysing
1098:
1094:
1082:
1079:
1078:
1077:
1074:
1072:
1069:
1067:
1064:
1060:
1057:
1055:
1052:
1051:
1050:
1047:
1045:
1042:
1040:
1037:
1033:
1030:
1029:
1028:
1025:
1023:
1020:
1016:
1015:non-lysosomal
1013:
1011:
1008:
1007:
1006:
1003:
1001:
998:
996:
995:Hyaluronidase
993:
989:
986:
985:
984:
983:Glucuronidase
981:
979:
976:
972:
969:
967:
964:
963:
962:
959:
955:
952:
950:
947:
945:
942:
940:
937:
935:
932:
930:
927:
926:
925:
924:Neuraminidase
922:
920:
917:
915:
912:
908:
907:Alpha-amylase
905:
904:
903:
900:
899:
897:
893:
887:
884:
880:
877:
876:
875:
872:
868:
865:
863:
860:
858:
855:
854:
853:
850:
848:
845:
844:
842:
840:
836:
830:
827:
825:
822:
820:
817:
815:
811:
807:
804:
803:
801:
799:
795:
792:
790:
786:
782:
777:
773:
766:
761:
759:
754:
752:
747:
746:
743:
737:
734:
731:
727:
724:
723:
719:
711:
707:
703:
699:
695:
691:
684:
677:
674:
669:
665:
659:
657:
653:
648:
644:
637:
634:
629:
625:
618:
616:
612:
607:
603:
597:
595:
591:
586:
582:
577:
572:
568:
564:
557:
555:
553:
549:
544:
540:
535:
530:
525:
520:
516:
512:
509:(8): e70841.
508:
504:
500:
493:
490:
485:
481:
475:
472:
467:
463:
457:
455:
451:
446:
442:
437:
432:
427:
422:
418:
414:
410:
403:
400:
395:
391:
386:
381:
376:
371:
367:
363:
360:(3): 1432–7.
359:
355:
351:
344:
342:
340:
336:
325:
321:
315:
312:
307:
303:
298:
293:
289:
285:
281:
274:
272:
270:
266:
261:
257:
253:
249:
245:
241:
237:
230:
228:
224:
218:
214:
211:
209:
206:
205:
201:
199:
197:
190:
188:
184:
182:
175:
173:
166:
164:
160:
157:
150:
148:
140:
133:
128:
123:
120:
117:
114:
111:
108:
106:into glucose.
105:
101:
98:
97:
96:
94:
90:
86:
78:
76:
74:
70:
64:
62:
58:
54:
46:
38:
32:
28:
22:
1397:Translocases
1394:
1381:
1368:
1355:
1342:
1332:Transferases
1329:
1316:
1173:Binding site
839:Glucosidases
818:
696:(1): 59–73.
693:
689:
676:
667:
646:
636:
627:
605:
566:
506:
502:
492:
483:
474:
465:
416:
412:
402:
357:
353:
327:. Retrieved
323:
314:
287:
283:
235:
196:Vampire bats
194:
185:
179:
170:
161:
158:
154:
145:
82:
65:
52:
51:
1168:Active site
1066:Iduronidase
1000:Pullulanase
630:. Medscape.
1371:Isomerases
1345:Hydrolases
1212:Regulation
1076:Heparanase
1044:Fucosidase
862:Neutral AB
484:BAKERpedia
419:(1): 158.
329:2021-03-06
219:References
1250:EC number
1010:lysosomal
914:Chitinase
879:cytosolic
867:Neutral C
847:Cellulase
824:Trehalase
814:Invertase
772:Hydrolase
602:"Maltase"
462:"Maltase"
134:Mechanism
91:) during
79:Structure
1446:EC 3.2.1
1440:Category
1274:Kinetics
1198:Cofactor
1161:Activity
919:Lysozyme
726:Maltases
710:16351819
647:UpToDate
585:29762367
543:23967118
503:PLOS ONE
445:33220711
394:12547908
306:17585022
260:46891498
252:29762372
202:See also
104:Glycogen
1430:Biology
1384:Ligases
1154:Enzymes
902:Amylase
829:Lactase
819:Maltase
806:Sucrase
690:Zoology
608:. 2012.
534:3742645
511:Bibcode
436:7680592
362:Bibcode
167:History
147:size).
61:glucose
57:maltose
53:Maltase
31:Maltose
21:Maltese
1416:Portal
1358:Lyases
988:Klotho
732:(MeSH)
708:
583:
541:
531:
443:
433:
392:
385:298790
382:
304:
258:
250:
16:Enzyme
1310:Types
1097:3.2.2
1081:HPSE2
966:Alpha
895:Other
785:3.2.1
686:(PDF)
256:S2CID
1402:list
1395:EC7
1389:list
1382:EC6
1376:list
1369:EC5
1363:list
1356:EC4
1350:list
1343:EC3
1337:list
1330:EC2
1324:list
1317:EC1
1059:HEXB
1054:HEXA
1032:NAGA
971:Beta
944:NEU4
939:NEU3
934:NEU2
929:NEU1
857:Acid
778:3.2)
706:PMID
581:PMID
539:PMID
441:PMID
390:PMID
302:PMID
248:PMID
698:doi
694:104
571:doi
529:PMC
519:doi
431:PMC
421:doi
380:PMC
370:doi
358:100
292:doi
288:137
240:doi
1442::
1110::
787::
776:EC
704:.
692:.
688:.
666:.
655:^
645:.
626:.
614:^
604:.
593:^
579:.
565:.
551:^
537:.
527:.
517:.
505:.
501:.
482:.
464:.
453:^
439:.
429:.
417:12
415:.
411:.
388:.
378:.
368:.
356:.
352:.
338:^
322:.
300:.
286:.
282:.
268:^
254:.
246:.
226:^
1418::
1404:)
1400:(
1391:)
1387:(
1378:)
1374:(
1365:)
1361:(
1352:)
1348:(
1339:)
1335:(
1326:)
1322:(
1146:e
1139:t
1132:v
812:/
808:/
764:e
757:t
750:v
712:.
700::
649:.
587:.
573::
545:.
521::
513::
507:8
447:.
423::
396:.
372::
364::
332:.
308:.
294::
262:.
242::
129:.
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.