217:
166:
333:
146:
100:
240:
61:. A shift indicates a severe imbalance of pressures inside the chest. Mediastinal shifts are generally caused by increased lung volume, decreased lung volume, or abnormalities in the pleural space. Additionally, masses inside the mediastinum or musculoskeletal abnormalities can also lead to abnormal mediastinal arrangement. Typically, these shifts are observed on x-ray but also on computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). On chest x-ray,
318:
this occurs asymmetrically, one lung can be larger than the other. A severe variant of this condition is called giant bullous emphysema. On chest x-ray, one lung will be significantly more inflated than the other, causing a mediastinal shift. Bullous emphysema's radiographic appearance on x-ray mimics a tension pneumothorax. This presents a medical challenge as these diseases are treated differently despite appearing similarly on x-ray.
293:
123:
310:
157:
CT imaging is necessary to evaluate the structure of the empyema and evaluate for loculation or separation of the pus into different compartments. Finally, ultrasound is becoming a more commonly used imaging technique to evaluate an empyema. Ultrasound is more readily available at the bedside, is better at detecting pleural effusion, and can be used to guide thoracentesis to remove the empyema.
265:
29:
248:
194:
156:
An empyema is a collection of pus inside the pleural cavity. It is a complication of pneumonia or thoracic injury or surgery and also requires urgent diagnosis and treatment. Radiographic appearance is similar to that of a pleural effusion with costophrenic angle blunting and white out of lung zones.
300:
Foreign body aspiration is a major cause of death in young children due to their underdeveloped swallowing coordination. Young children most commonly ingest toys, coins, or food. On chest x-ray, the most frequent sign is air trapping that can lead to a mediastinal shift. Atelectasis and pneumothorax
201:
Atelectasis is the partial collapse of a lung that is reversible. There are numerous etiologies, including post-operative atelectasis, surfactant deficiency, mucus plugging, and foreign body aspiration. Notably, post-operative atelectasis is thought to be caused by general anesthesia administration.
340:
Congenital pulmonary airway malformation (CPAM) is a rare disease in which the lung airways develop abnormally in the fetus. This leads to infants having pockets of air and cystic masses in their lungs. These can expand in size and cause a mediastinal shift, especially in the higher grades of CPAM.
173:
Masses such as tumors can also cause compression and displacement of mediastinal structures. There are various mediastinal tumors, and they are classified by their location in the chest. Notable examples include germ cell tumors and lymphomas. Teratomas are a class of germ cell tumors that arise in
107:
A pleural effusion is an accumulation of fluid inside the pleural space. If this collection of fluid gets large enough, it can also push structures in the chest away from it and cause a mediastinal shift. However, a pleural effusion can also pull the mediastinal structure towards itself. If this is
130:
Hemothorax, or accumulation of blood in the pleural space, can result from trauma or surgical procedures in the chest. This accumulation of blood can grow large enough to compress the lung and push away other structures in the chest, thus causing a mediastinal shift. On a chest x-ray, a hemothorax
317:
Bullous emphysema is a condition seen in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The units making up the substructure of the lung (alveoli) become permanently enlarged due to the destruction of their walls. This leads to hyperinflation of the alveoli and, thus, the lungs. When
84:
Tension pneumothorax is an emergent condition in which air gets trapped in the space between the chest wall and the lung. This space is referred to as the pleural space. Because air can't escape from this space, the air pocket grows larger and larger, resulting in the lung collapse closest to the
272:
A pneumonectomy is a surgical procedure in which an entire lung is removed. A common reason for performing this procedure is for lung cancer originating in the lung itself. This leads to a mediastinal shift towards the empty side of the thorax. Notably, patients can experience post pneumonectomy
224:
Fetal conditions can also cause a mediastinal shift during development. For example, pulmonary hypoplasia is the underdevelopment of a lung due to various etiologies. These include agenesis due to gene mutation, fetal hydrothorax, and congenital diaphragmatic hernia. These conditions lead to
255:
This condition is often called "funnel chest" and is observed as depression of the anterior chest at the xiphisternum. Pectus excavatum is commonly unilateral and, therefore, can lead to asymmetric distribution of thoracic organs. Therefore, a mediastinal shift can be seen in severe cases.
225:
incomplete development of lung tissue or hypoplasia. This can be unilateral or bilateral and is seen on x-ray as a mediastinal shift towards the side of the underdeveloped lung. Additionally, mediastinal shifts can also be detected using antenatal ultrasonography.
174:
the chest due to failure of germ cell migration during development. They can expand to large sizes and cause hemoptysis and pleural effusion. Radiographic features of teratomas typically include fluid and fat but also muscle, teeth, and bones inside the mass.
65:, or movement of the trachea away from its midline position can be used as a sign of a shift. Other structures, like the heart, can also be used as reference points. Below are examples of pathologies that can cause a mediastinal shift and their appearance.
273:
syndrome due to a severe mediastinal shift. This presents as difficulty breathing due to a shift of airways and rotation of the heart and great vessels. On x-ray, white out of the operated side and hyperinflation of the remaining lung is often observed.
202:
Collapse of the affected lung shifts mediastinal structure towards the same side and can be observed on chest x-ray or CT. Radiographic features include increased opacification of collapsed lung and/or tracheal shift.
341:
Diagnosis is usually made on ultrasound and supplemented with x-ray, CT, or MRI to further define the malformation. On chest x-ray, CPAM has varying appearances but may look like "bubbles" within the lung fields.
131:
can appear similarly to a pleural effusion with blunting of the pleural recess and white out of normal lung zones. In the setting of traumatic chest injury, rib fractures are also commonly observed on x-ray.
108:
the case, then there is an underlying condition causing the collapse of the lung on that side. An example is a tumor obstructing a bronchus and causing lung collapse and pleural effusion.
256:
Radiographic features include a leftward deviation of the heart and deformed third to seventh ribs. Patients often present with exercise tolerance, cardiac arrythmias, and heart murmur.
216:
563:
Salim, Shihas; Ganeshram, Prasanthi; Patel, Amish Dilip; Kumar, Anita A.; Vemuri, Divya; Jeyachandran, Vijay; Rajamanickam, Deepan; Shantha, Ghanshyam
Palamaner Subash (2008-10-07).
301:
may also occur in the setting of foreign body aspiration. The diagnosis is made in conjunction with clinical symptoms and confirmed and treated with bronchoscopy.
1455:
327:
336:
Chest x-ray of infant showing CPAM in the left lung causing a mediastinal shift towards the right. The cysts appear as bubbles in the left lung.
420:"Respiratory Clinics: MEDIASTINAL SHIFT: A SIGN OF SIGNIFICANT CLINICAL AND RADIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE IN DIAGNOSIS OF MALIGNANT PLEURAL EFFUSION"
85:
pneumothorax. Forces are transmitted to the mediastinum and effectively "push" the mediastinal structures to the opposite side of the chest.
367:
165:
332:
1448:
1346:
Samanta, Rudra P.; Agarwal, Srikant; Sengupta, Susmita; Samanta, Rudra P.; Agarwal, Srikant; Sengupta, Susmita (2022-11-07).
565:"Unilateral hemothorax in a 46 year old South Indian male due to a giant arteriovenous hemodialysis fistula: a case report"
220:
Chest x-ray demonstrating pulmonary agenesis. There is a mediastinal toward the left and hyperinflation of the right lung.
145:
1287:
Ascano, Maria
Patricia; Kramer, Nicholas; Le, Khoa; Ascano, Maria Patricia; Kramer, Nicholas; Le, Khoa (2024-03-11).
239:
197:
Chest x-ray demonstrating severe atelectasis or collapse of the right lung and mediastinal shift towards the right.
1025:
Colombani, M.; Rubesova, E.; Potier, A.; Quarello, E.; Barth, R. A.; Devred, P.; Petit, P.; Gorincour, G. (2011).
1728:
1642:
1441:
268:
Chest x-ray showing an individual who had their right lung removed with fluid accumulating in the operated side.
99:
1677:
313:
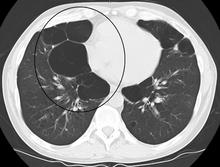
An axial CT image showing bullous emphysema of the lungs. There are larger air pockets on the right than left.
1586:
1558:
817:"Mediastinal tumours and pseudo-tumours: a comprehensive review with emphasis on multidisciplinary approach"
287:
391:
1629:
1538:
1533:
211:
1619:
296:
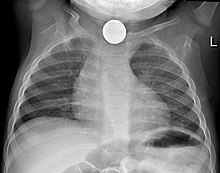
Chest x-ray in an infant showing aspiration of a metallic coin without signs of mediastinal shift.
1173:
62:
122:
1707:
1662:
1657:
1508:
1485:
1414:
1387:
1369:
1328:
1310:
1264:
1232:
1200:
1165:
1157:
1113:
1081:
1054:
1046:
1002:
975:
957:
913:
881:
854:
836:
797:
779:
735:
708:
700:
661:
643:
604:
586:
540:
508:
476:
449:
431:
373:
363:
1682:
1667:
1563:
1513:
1480:
1377:
1359:
1318:
1300:
1149:
1038:
965:
949:
844:
828:
787:
771:
692:
651:
635:
594:
576:
439:
234:
94:
624:"Chest Trauma: Current Recommendations for Rib Fractures, Pneumothorax, and Other Injuries"
1596:
1568:
1553:
1543:
1464:
149:
58:
1323:
1288:
292:
1647:
1472:
1382:
1347:
970:
937:
849:
792:
759:
656:
623:
599:
564:
444:
419:
1722:
1687:
1652:
1604:
1518:
1177:
816:
1672:
1614:
1609:
1548:
1528:
1523:
169:
Axial CT image showing a large left sided mass that appears attached to the pleura.
79:
1289:"Differentiating Giant Bullous Emphysema From Tension Pneumothorax: A Case Report"
309:
1042:
1637:
1500:
264:
188:
54:
1406:
1256:
1224:
1192:
1153:
1105:
1073:
994:
905:
873:
832:
727:
639:
532:
500:
468:
28:
1578:
775:
377:
247:
117:
1373:
1314:
1161:
1050:
961:
840:
783:
704:
647:
590:
435:
103:
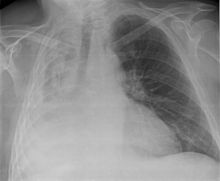
A massive left pleural effusion displacing the heart and trachea to the right
1697:
1490:
1223:
Cramer, Natan; Jabbour, Noel; Tavarez, Melissa M.; Taylor, Roger S. (2024),
953:
680:
581:
1418:
1391:
1332:
1268:
1236:
1204:
1169:
1137:
1117:
1085:
1058:
1026:
1006:
979:
917:
885:
858:
801:
739:
712:
665:
608:
544:
512:
480:
453:
696:
193:
152:
progression seen on the left side of the chest over the course of 2 weeks.
1364:
1305:
243:
Chest x-ray showing pectus excavatum with leftward shift of heart shadow.
1027:"[Management of fetal mediastinal shift: a practical approach]"
140:
126:
Massive right sided pleural effusion later confirmed to be a hemothorax
36:
Left tension pneumothorax with a large, well-demarcated area devoid of
760:"VATS and Intrapleural Fibrinolytic Therapy for Parapneumonic Empyema"
1138:"Postoperative Imaging and Complications in Resection of Lung Cancer"
1136:
de Groot, Patricia M.; Truong, Mylene T.; Godoy, Myrna C. B. (2018).
1433:
815:
Ghigna, Maria-Rosa; Montpreville, Vincent Thomas de (2021-12-31).
331:
308:
291:
263:
246:
238:
215:
192:
164:
144:
121:
98:
41:
872:
Jilani, Talha N.; Killeen, Robert B.; Siddiqui, Abdul H. (2024),
1255:
Siddiqui, Najam A.; Mansour, Mohamed K.; Nookala, Vinod (2024),
37:
1437:
1348:"Giant Bullous Emphysema Mimicking Spontaneous Pneumothorax"
467:
Stoddard, Nathan; Heil, Jenna R.; Lowery, David R. (2024),
904:
Grott, Kelly; Chauhan, Shaylika; Dunlap, Julie D. (2024),
758:
Ohara, Gen; Iguchi, Kesato; Satoh, Hiroaki (2018-10-19).
251:
CT axial view showing pectus excavatum of the chest.
40:
markings with tracheal deviation and movement of the
360:
Chest radiology: patterns and differential diagnoses
1696:
1628:
1595:
1577:
1499:
1471:
679:Feller-Kopman, David; Light, Richard (2018-02-22).
21:
362:(Seventh ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier.
1413:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
1263:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
1231:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
1199:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
1112:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
1080:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
1001:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
912:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
880:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
734:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
539:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
507:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
475:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
413:
411:
1449:
764:Annals of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery
499:Jalota Sahota, Ruchi; Sayad, Edouard (2024),
8:
993:Tisekar, Owais R.; Ak, Ajith Kumar (2024),
1456:
1442:
1434:
1407:"Congenital Pulmonary Airway Malformation"
1072:Sharma, Girish; Carter, Yvonne M. (2024),
938:"Fetal pleural effusion and Down syndrome"
27:
18:
1381:
1363:
1322:
1304:
969:
848:
791:
655:
598:
580:
443:
1405:Mehta, Pooja A.; Sharma, Girish (2024),
1191:Rose, David; Dubensky, Laurence (2024),
1104:Beshara, Michael; Bora, Vaibhav (2024),
942:Intractable & Rare Diseases Research
328:Congenital pulmonary airway malformation
322:Congenital pulmonary airway malformation
80:Pneumothorax § Tension_pneumothorax
622:Kim, Michelle; Moore, James E. (2020).
531:Taghavi, Sharven; Askari, Reza (2024),
350:
726:Garvia, Veronica; Paul, Manju (2024),
936:Cao, Li; Du, Yan; Wang, Ling (2017).
7:
1615:Fat pad sign/Sail sign of the elbow
685:The New England Journal of Medicine
1142:Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MR
14:
1708:Hyperdense middle cerebral artery
53:is an abnormal movement of the
628:Current Anesthesiology Reports
469:"Anatomy, Thorax, Mediastinum"
1:
1043:10.1016/j.jradio.2010.12.002
305:Asymmetric bullous emphysema
44:away from the affected side.
821:European Respiratory Review
69:Pleural space abnormalities
1745:
1154:10.1053/j.sult.2018.02.008
995:"Hypoplastic Lung Disease"
833:10.1183/16000617.0309-2020
640:10.1007/s40140-020-00374-w
424:Malaysian Family Physician
325:
285:
232:
209:
186:
138:
115:
92:
77:
1225:"Foreign Body Aspiration"
776:10.5761/atcs.lte.18-00092
35:
26:
1678:Pneumatosis intestinalis
1559:Traction bronchiectasis
1193:"Airway Foreign Bodies"
954:10.5582/irdr.2017.01028
582:10.1186/1757-1626-1-225
358:Reed, James C. (2018).
288:Foreign body aspiration
282:Foreign body aspiration
57:toward one side of the
1539:Sail sign of the chest
501:"Tension Pneumothorax"
392:"Mediastinal Position"
337:
314:
297:
269:
260:Post-operative changes
252:
244:
221:
198:
170:
153:
127:
104:
55:mediastinal structures
1534:Peribronchial cuffing
1031:Journal de Radiologie
697:10.1056/NEJMra1403503
418:Khajotia, R. (2012).
335:
312:
295:
277:Increased lung volume
267:
250:
242:
219:
196:
178:Decreased lung volume
168:
148:
125:
102:
1587:Canga's bead symptom
1365:10.7759/cureus.31182
1306:10.7759/cureus.55988
874:"Mediastinal Cancer"
533:"Mediastinal Trauma"
212:Pulmonary hypoplasia
206:Pulmonary hypoplasia
74:Tension pneumothorax
1620:Osteopathia striata
1257:"Bullous Emphysema"
396:www.meddean.luc.edu
1074:"Pectus Excavatum"
338:
315:
298:
270:
253:
245:
222:
199:
171:
154:
128:
105:
63:tracheal deviation
1716:
1715:
1663:Hot quadrate sign
1509:Air crescent sign
1486:Dense artery sign
681:"Pleural Disease"
51:Mediastinal shift
48:
47:
22:Mediastinal shift
16:Medical condition
1736:
1729:Radiologic signs
1630:Gastrointestinal
1564:Tree-in-bud sign
1514:Deep sulcus sign
1481:Aortic unfolding
1465:Radiologic signs
1458:
1451:
1444:
1435:
1428:
1427:
1426:
1425:
1402:
1396:
1395:
1385:
1367:
1343:
1337:
1336:
1326:
1308:
1284:
1278:
1277:
1276:
1275:
1252:
1246:
1245:
1244:
1243:
1220:
1214:
1213:
1212:
1211:
1188:
1182:
1181:
1133:
1127:
1126:
1125:
1124:
1101:
1095:
1094:
1093:
1092:
1069:
1063:
1062:
1022:
1016:
1015:
1014:
1013:
990:
984:
983:
973:
933:
927:
926:
925:
924:
901:
895:
894:
893:
892:
869:
863:
862:
852:
812:
806:
805:
795:
755:
749:
748:
747:
746:
723:
717:
716:
676:
670:
669:
659:
619:
613:
612:
602:
584:
560:
554:
553:
552:
551:
528:
522:
521:
520:
519:
496:
490:
489:
488:
487:
464:
458:
457:
447:
415:
406:
405:
403:
402:
388:
382:
381:
355:
235:Pectus excavatum
229:Pectus excavatum
95:Pleural effusion
89:Pleural effusion
31:
19:
1744:
1743:
1739:
1738:
1737:
1735:
1734:
1733:
1719:
1718:
1717:
1712:
1692:
1624:
1597:Musculoskeletal
1591:
1573:
1569:Westermark sign
1554:Thumbprint sign
1544:Silhouette sign
1495:
1467:
1462:
1432:
1431:
1423:
1421:
1404:
1403:
1399:
1345:
1344:
1340:
1286:
1285:
1281:
1273:
1271:
1254:
1253:
1249:
1241:
1239:
1222:
1221:
1217:
1209:
1207:
1190:
1189:
1185:
1135:
1134:
1130:
1122:
1120:
1106:"Pneumonectomy"
1103:
1102:
1098:
1090:
1088:
1071:
1070:
1066:
1024:
1023:
1019:
1011:
1009:
992:
991:
987:
935:
934:
930:
922:
920:
903:
902:
898:
890:
888:
871:
870:
866:
814:
813:
809:
757:
756:
752:
744:
742:
725:
724:
720:
678:
677:
673:
621:
620:
616:
562:
561:
557:
549:
547:
530:
529:
525:
517:
515:
498:
497:
493:
485:
483:
466:
465:
461:
417:
416:
409:
400:
398:
390:
389:
385:
370:
357:
356:
352:
347:
330:
324:
307:
290:
284:
279:
262:
237:
231:
214:
208:
191:
185:
180:
163:
143:
137:
120:
114:
97:
91:
82:
76:
71:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1742:
1740:
1732:
1731:
1721:
1720:
1714:
1713:
1711:
1710:
1705:
1702:
1700:
1694:
1693:
1691:
1690:
1685:
1680:
1675:
1670:
1665:
1660:
1658:Hampton's line
1655:
1650:
1648:Endoexoenteric
1645:
1640:
1634:
1632:
1626:
1625:
1623:
1622:
1617:
1612:
1607:
1601:
1599:
1593:
1592:
1590:
1589:
1583:
1581:
1575:
1574:
1572:
1571:
1566:
1561:
1556:
1551:
1546:
1541:
1536:
1531:
1526:
1521:
1516:
1511:
1505:
1503:
1497:
1496:
1494:
1493:
1488:
1483:
1477:
1475:
1473:Cardiovascular
1469:
1468:
1463:
1461:
1460:
1453:
1446:
1438:
1430:
1429:
1397:
1358:(11): e31182.
1338:
1279:
1247:
1215:
1183:
1148:(3): 289–296.
1128:
1096:
1064:
1037:(2): 118–124.
1017:
985:
948:(3): 158–162.
928:
896:
864:
807:
770:(5): 263–264.
750:
718:
691:(8): 740–751.
671:
614:
555:
523:
491:
459:
407:
383:
368:
349:
348:
346:
343:
326:Main article:
323:
320:
306:
303:
286:Main article:
283:
280:
278:
275:
261:
258:
233:Main article:
230:
227:
210:Main article:
207:
204:
187:Main article:
184:
181:
179:
176:
162:
159:
139:Main article:
136:
133:
116:Main article:
113:
110:
93:Main article:
90:
87:
78:Main article:
75:
72:
70:
67:
46:
45:
33:
32:
24:
23:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1741:
1730:
1727:
1726:
1724:
1709:
1706:
1704:
1703:
1701:
1699:
1695:
1689:
1688:Sentinel loop
1686:
1684:
1683:Rigler's sign
1681:
1679:
1676:
1674:
1671:
1669:
1668:Mumoli's sign
1666:
1664:
1661:
1659:
1656:
1654:
1653:Football sign
1651:
1649:
1646:
1644:
1643:Double bubble
1641:
1639:
1636:
1635:
1633:
1631:
1627:
1621:
1618:
1616:
1613:
1611:
1608:
1606:
1605:Crescent sign
1603:
1602:
1600:
1598:
1594:
1588:
1585:
1584:
1582:
1580:
1576:
1570:
1567:
1565:
1562:
1560:
1557:
1555:
1552:
1550:
1547:
1545:
1542:
1540:
1537:
1535:
1532:
1530:
1527:
1525:
1522:
1520:
1519:Golden S sign
1517:
1515:
1512:
1510:
1507:
1506:
1504:
1502:
1498:
1492:
1489:
1487:
1484:
1482:
1479:
1478:
1476:
1474:
1470:
1466:
1459:
1454:
1452:
1447:
1445:
1440:
1439:
1436:
1420:
1416:
1412:
1408:
1401:
1398:
1393:
1389:
1384:
1379:
1375:
1371:
1366:
1361:
1357:
1353:
1349:
1342:
1339:
1334:
1330:
1325:
1320:
1316:
1312:
1307:
1302:
1299:(3): e55988.
1298:
1294:
1290:
1283:
1280:
1270:
1266:
1262:
1258:
1251:
1248:
1238:
1234:
1230:
1226:
1219:
1216:
1206:
1202:
1198:
1194:
1187:
1184:
1179:
1175:
1171:
1167:
1163:
1159:
1155:
1151:
1147:
1143:
1139:
1132:
1129:
1119:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1100:
1097:
1087:
1083:
1079:
1075:
1068:
1065:
1060:
1056:
1052:
1048:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1032:
1028:
1021:
1018:
1008:
1004:
1000:
996:
989:
986:
981:
977:
972:
967:
963:
959:
955:
951:
947:
943:
939:
932:
929:
919:
915:
911:
907:
906:"Atelectasis"
900:
897:
887:
883:
879:
875:
868:
865:
860:
856:
851:
846:
842:
838:
834:
830:
826:
822:
818:
811:
808:
803:
799:
794:
789:
785:
781:
777:
773:
769:
765:
761:
754:
751:
741:
737:
733:
729:
722:
719:
714:
710:
706:
702:
698:
694:
690:
686:
682:
675:
672:
667:
663:
658:
653:
649:
645:
641:
637:
633:
629:
625:
618:
615:
610:
606:
601:
596:
592:
588:
583:
578:
574:
570:
569:Cases Journal
566:
559:
556:
546:
542:
538:
534:
527:
524:
514:
510:
506:
502:
495:
492:
482:
478:
474:
470:
463:
460:
455:
451:
446:
441:
437:
433:
429:
425:
421:
414:
412:
408:
397:
393:
387:
384:
379:
375:
371:
369:9780323510219
365:
361:
354:
351:
344:
342:
334:
329:
321:
319:
311:
304:
302:
294:
289:
281:
276:
274:
266:
259:
257:
249:
241:
236:
228:
226:
218:
213:
205:
203:
195:
190:
182:
177:
175:
167:
160:
158:
151:
147:
142:
134:
132:
124:
119:
111:
109:
101:
96:
88:
86:
81:
73:
68:
66:
64:
60:
56:
52:
43:
39:
34:
30:
25:
20:
1698:Neurological
1673:Omental cake
1610:Fabella sign
1549:Steeple sign
1529:Kerley lines
1524:Hampton hump
1422:, retrieved
1410:
1400:
1355:
1351:
1341:
1296:
1292:
1282:
1272:, retrieved
1260:
1250:
1240:, retrieved
1228:
1218:
1208:, retrieved
1196:
1186:
1145:
1141:
1131:
1121:, retrieved
1109:
1099:
1089:, retrieved
1077:
1067:
1034:
1030:
1020:
1010:, retrieved
998:
988:
945:
941:
931:
921:, retrieved
909:
899:
889:, retrieved
877:
867:
824:
820:
810:
767:
763:
753:
743:, retrieved
731:
721:
688:
684:
674:
634:(1): 61–68.
631:
627:
617:
572:
568:
558:
548:, retrieved
536:
526:
516:, retrieved
504:
494:
484:, retrieved
472:
462:
430:(1): 34–36.
427:
423:
399:. Retrieved
395:
386:
359:
353:
339:
316:
299:
271:
254:
223:
200:
172:
155:
129:
106:
83:
59:chest cavity
50:
49:
1638:Cupola sign
1501:Respiratory
189:Atelectasis
183:Atelectasis
1579:Urogenital
1424:2024-03-20
1411:StatPearls
1274:2024-03-20
1261:StatPearls
1242:2024-03-20
1229:StatPearls
1210:2024-03-20
1197:StatPearls
1123:2024-03-10
1110:StatPearls
1091:2024-03-07
1078:StatPearls
1012:2024-03-07
999:StatPearls
923:2024-03-07
910:StatPearls
891:2024-03-06
878:StatPearls
745:2024-03-06
732:StatPearls
575:(1): 225.
550:2024-03-06
537:StatPearls
518:2024-02-21
505:StatPearls
486:2024-02-21
473:StatPearls
401:2024-02-21
378:1012134513
345:References
118:Hemothorax
112:Hemothorax
1491:Halo sign
1374:2168-8184
1315:2168-8184
1162:1558-5034
1051:1773-0384
962:2186-3644
841:0905-9180
784:2186-1005
728:"Empyema"
705:1533-4406
648:1523-3855
591:1757-1626
436:1985-207X
1723:Category
1419:31869128
1392:36505170
1333:38606232
1324:11007189
1269:30725928
1237:30285375
1205:30969578
1178:44142767
1170:29807639
1118:32310429
1086:28613668
1059:21352743
1007:32965810
980:28944136
918:31424900
886:30020603
859:34615701
802:29962389
740:29083780
713:29466146
666:32435162
609:18840271
545:30252287
513:32644516
481:30969641
454:25606244
1383:9727579
971:5608924
850:9488622
827:(162).
793:6198002
657:7223697
600:2567296
445:4170449
150:Empyema
141:Empyema
135:Empyema
1417:
1390:
1380:
1372:
1352:Cureus
1331:
1321:
1313:
1293:Cureus
1267:
1235:
1203:
1176:
1168:
1160:
1116:
1084:
1057:
1049:
1005:
978:
968:
960:
916:
884:
857:
847:
839:
800:
790:
782:
738:
711:
703:
664:
654:
646:
607:
597:
589:
543:
511:
479:
452:
442:
434:
376:
366:
161:Masses
1174:S2CID
42:heart
1415:PMID
1388:PMID
1370:ISSN
1329:PMID
1311:ISSN
1265:PMID
1233:PMID
1201:PMID
1166:PMID
1158:ISSN
1114:PMID
1082:PMID
1055:PMID
1047:ISSN
1003:PMID
976:PMID
958:ISSN
914:PMID
882:PMID
855:PMID
837:ISSN
798:PMID
780:ISSN
736:PMID
709:PMID
701:ISSN
662:PMID
644:ISSN
605:PMID
587:ISSN
541:PMID
509:PMID
477:PMID
450:PMID
432:ISSN
374:OCLC
364:ISBN
38:lung
1378:PMC
1360:doi
1319:PMC
1301:doi
1150:doi
1039:doi
966:PMC
950:doi
845:PMC
829:doi
788:PMC
772:doi
693:doi
689:378
652:PMC
636:doi
595:PMC
577:doi
440:PMC
1725::
1409:,
1386:.
1376:.
1368:.
1356:14
1354:.
1350:.
1327:.
1317:.
1309:.
1297:16
1295:.
1291:.
1259:,
1227:,
1195:,
1172:.
1164:.
1156:.
1146:39
1144:.
1140:.
1108:,
1076:,
1053:.
1045:.
1035:92
1033:.
1029:.
997:,
974:.
964:.
956:.
944:.
940:.
908:,
876:,
853:.
843:.
835:.
825:30
823:.
819:.
796:.
786:.
778:.
768:24
766:.
762:.
730:,
707:.
699:.
687:.
683:.
660:.
650:.
642:.
632:10
630:.
626:.
603:.
593:.
585:.
571:.
567:.
535:,
503:,
471:,
448:.
438:.
426:.
422:.
410:^
394:.
372:.
1457:e
1450:t
1443:v
1394:.
1362::
1335:.
1303::
1180:.
1152::
1061:.
1041::
982:.
952::
946:6
861:.
831::
804:.
774::
715:.
695::
668:.
638::
611:.
579::
573:1
456:.
428:7
404:.
380:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.