106:, and collections of these cells can be considered to be mental maps. Individual place cells do not only respond to one unique area only however, the patterns of activation of these cells overlap to form layered mental maps within the hippocampus. A good analogy is the example of the same television or computer screen pixels being used to light up any trillions of possible combinations to produce images, just as the place cells can be used in any multiple possible combinations to represent mental maps. The hippocampus' right side is more oriented towards responding to spatial aspects, whereas the left side is associated with other context information. Also, there is evidence that experience in building extensive mental maps, such as driving a city taxi for a long time (since this requires considerable memorization of routes), can increase the volume of one's hippocampus.
248:, which is the process of transferring information that is currently in working memory into ones long-term memory. This process is also known as memory modulation. The amygdala works to encode recent emotional information into memory. Memory research has shown that the greater ones emotional arousal level at the time of the event, the greater the chance that the event will be remembered. This may be due to the amygdala enhancing the emotional aspect of the information during encoding, causing the memory to be processed at a deeper level and therefore, more likely to withstand forgetting.
257:
475:
and provides spatial awareness and navigational skills. Also, it integrates all of our sensory information (touch, sight, pain etc.) to form a single perception. Parietal lobe gives the ability to focus our attention on different stimuli at the same time, PET scans show high activity in the parietal lobe when participates being studied were asked to focus their attention at two separate areas of attention. Parietal lobe also assists with verbal short term memory and damage to the supramarginal gyrus cause short term memory loss.
402:. For example, when you are thinking about how to get to a mall you have never been to before, you combine various bits of knowledge you already have: the layout of the city the mall is in, information from a map, knowledge of traffic patterns in that area and conversations with your friends about the location of the mall. By actively using all of this information, you can determine the best route for you to take. This action involves the controlled use of information in working memory, coordinated by the frontal lobes.
567:
left side of the brain can lead to language discrepancies, i.e. difficulty in properly identifying letters, numbers and words, inability to incorporate visual stimuli to comprehend multiple ways an object can be found. Right side damage causes non-verbal problems, i.e. identifying geometric shapes, perception of figures and faces. In almost all regions of the brain left side damage leads to general language problems whereas right side damage leads to general perception and problem solving skills.
355:
546:. The ventral stream is responsible for object representation and recognition and is also commonly known as the "what" stream. The dorsal stream is responsible for guiding our actions and recognizing where objects are in space, commonly known as the "where" or "how" stream. Once in the information is organized and sent through the pathways it continues to the other areas of the brain responsible for visual processing.
157:
52:
409:. For example, the knowledge of the information itself, as well as knowing where information came from must be put together into a single memory representation; this is called source monitoring. Sometimes we experience situations where information becomes separated, such as when we recall something, but cannot remember where we remember it from; this is referred to as a
2457:
208:
2445:
595:
is largely affected by this disease. In one study, FTLD patients were interviewed and asked to describe a significant event from five different periods of their lives. Using the interview and different methods of imaging, the experimenters hoped to find links between patterns of brain volume loss and
198:
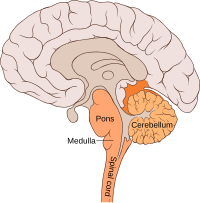
This separation makes sense if the cerebellum, which is far removed from the hippocampus, is responsible for procedural learning. The cerebellum is more generally involved in motor learning, and damage to it can result in problems with movement, specifically it is considered to co-ordinate timing and
603:
volumes that encompass the frontal and temporal lobes were found. Through comparison to a control group of patients it was found that parenchymal volumes increased during episodic recall, and decreased during semantic recall. The experimenters discussed that lifespan autobiographical episodic recall
566:
damage to the visual field. When damage occurs in the occipital lobe it is most common to see the effects on the opposite side of the brain. Since the brain regions are so specialized in their functioning, damages done to specific areas of the brain can cause specific type of damage. Damage to the
549:
The most important function of the
Occipital lobe is vision. Due to the positioning of this lobe at the back of the head it is not susceptible to much injury but any significant damage to the brain can cause a variety of damage to our visual perception system. Common problems in the occipital lobe
474:
The parietal lobe has many functions and duties in the brain and its main functioning can be divided down into two main areas: (1) sensation and perception (2) constructing a spatial coordinate system to represent the world around us. The parietal lobe helps us to mediate attention when necessary
219:
Located above the hippocampus in the medial temporal lobes are two amygdalae (singular "amygdala"). The amygdalae are associated with both emotional learning and memory, as it responds strongly to emotional stimuli, especially fear. These neurons assist in encoding emotional memories and enhancing
495:) and the inability to perceive objects. Damage to the right parietal lobe can result in neglecting part of the body or space (contralateral neglect), which can impair many self-care skills such as dressing and washing. Right side damage can also cause difficulty in making things (constructional
619:
Most people can instantly and easily use visual-spatial memory to remember locations and pictures, but a person with
Parkinson's disease would find this difficult. He or she would also have trouble encoding this visual and spatial information into long-term memory. This suggests that the basal
451:
Damage to the temporal lobe can affect an individual in a litany of ways ranging from: disturbance of auditory sensation and perception, disturbance of selective attention of auditory and visual input, disorders of visual perception, impaired organization and categorization of verbal material,
231:
tests have shown the active role of the amygdala in fear conditioning in rats. Research involving lesions to the basolateral nucleus have shown a strong association with memories involving fear. The central nucleus is linked with the behavioral responses that are dependent on the basolateral's
503:) and drawing ability. Neglect syndrome tends to be more prevalent on the right side of the parietal lobe, because the right mediates attention to both the left and right fields. Damage in the somatic sensory cortex results in loss of perception of bodily sensations, namely sense of touch.
321:
Damage to the basal ganglia has been linked to dysfunctional learning of motor and perceptual-motor skills. Most disorders that are associated with damage to these areas of the brain involve some type of motor dysfunction, as well as trouble with mental switching between tasks in
623:
People with
Parkinson's disease display working memory impairment during sequence tasks and tasks involving events in time. They also have difficulty in knowing how to use their memory, such as when to change strategies or maintain a train of thought.
471:, superior to the occipital lobe and posterior to the frontal lobe, visually at the top of the back of the head. The make up of the parietal lobe is defined by four anatomical boundaries in the brain, providing a division of all the four lobes.
478:
Damage to the parietal lobe results in the syndrome ‘neglect' which is when patients treat part of their body or objects in their visual field as though it never existed. Damage to the left side of the parietal lobe can result in what is called
615:
involves both damage to the basal ganglia and certain memory dysfunctions, suggesting that the basal ganglia are involved in specific types of memory. Those who have this disease have problems with both their working memory and spatial memory.
190:
that have difficulty forming new memories and/or remembering old events may sometimes retain the ability to perform complex musical pieces, suggesting that procedural memory is completely dissociated from conscious memory, also known as
186:, and motor learning, such as skills requiring co-ordination and fine motor control. An example of a skill requiring procedural memory would be playing a musical instrument, or driving a car or riding a bike. Individuals with
307:. The basic functions of these nuclei deal with cognition, learning, and motor control and activities. The basal ganglia are also associated with learning, memory, and unconscious memory processes, such as motor skills and
443:
The temporal lobes are also concerned with recognition memory. This is the capacity to identify an item as one that was recently encountered. Recognition memory is widely viewed as consisting of two components, a
387:. The cortex here serves our ability to plan the day, organize work, type a letter, pay attention to details and control the movements of your arms and legs. It also contributed to your personality and behaviour.
220:
them. This process results in emotional events being more deeply and accurately encoded into memory. Lesions to the amygdalae in monkeys have been shown to impair motivation, as well as the processing of emotions.
240:
Emotional experiences and events are somewhat fragile and take a while to be completely set into memory. This slow process, referred to as consolidation, allows emotions to influence the way the memory is stored.
562:, inability to recognize words and inability to recognize movement. A study was done in which patients suffered from a tumour on the occipital lobe and the results shows that the most frequent consequence was
1119:
Winograd, E. (1988). Some observations on prospective remembering. In M. M. Gruneberg, P. E. Morris & R. N. Sykes (Eds.), Practical
Aspects of Memory: Current Research and Issues. Vol. 2, pp. 348-353.
575:
Many studies of different disease and disorders that have symptoms of memory loss have provided reinforcing evidence to the study of the anatomy of the brain and which parts are more utilized in memory.
1337:
Warrington, E., & Weiskrantz, L. (1973). An analysis of short-term and long-term memory defects in man. In J.A. Deutsch, ed. The
Physiological Basis of Memory. New York: Academic Press.
137:. This is supported by studies in which lesions are applied to rat hippocampi at different times after learning. The process of consolidation may take up to a couple years.
1349:
Westmoreland, B. et al. (1994). Medical
Neurosciences: An Approach to Anatomy, Pathology, and Physiology by Systems and Levels. New York: NY. Little, Brown and Company.
591:
due to the degeneration of the frontal and temporal lobes. Studies have found significant decreases in the essential needs for proper functioning in these lobes. The
311:. Particularly, one division within the ventral striatum, the nucleus accumbens core, is involved in the consolidation, retrieval and reconsolidation of drug memory.
511:
The occipital lobe is the smallest of all four lobes in the human cerebral cortex and located in the rearmost part of the skull and considered to be part of the
318:. Specifically, research has shown that this part of the basal ganglia plays a role in acquiring stimulus-response habits, as well as in solving sequence tasks.
405:
The frontal lobes help a person select out memories that are most relevant on a given occasion. It can coordinate various types of information into a coherent
148:, which means that explicit descriptions of actual events (episodic) cannot be learned, but some meaning and knowledge is gained from experiences (semantic).
2045:
1628:
1059:
Kuypers, H. (1981). Anatomy of the descending pathways. V. Brooks, ed. The
Nervous System, Handbook of Physiology, vol. 2. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins.
1909:
1003:"Activation of PKCzeta and PKMzeta in the nucleus accumbens core is necessary for the retrieval, consolidation and reconsolidation of the drug memory"
448:
component (i.e. Do I know this person waving at me?) and a recollective component (i.e. That is my friend Julia, from evolutionary psychology class).
1479:
Robbins, TW; Kadhim, Z; Ersche KD; Everitt BJ (2008). "Drug
Addiction and the memory systems of the brain". New York Academy of Sciences 1141
683:
653:
98:
in humans. In one study, single-cell recordings were taken from electrodes implanted in a rat's hippocampus, and it was found that certain
2119:
436:
on both the left and right hemispheres of the brain. Lobes in this cortex are more closely associated with memory and in particular
584:
1418:
McKinnon, M.C.; Nica, E.I.; Sengdy, P.; Kovacevic, N.; Moscovitch, M.; Freedman, M.; Miller, B.L.; Black, S.E.; Levine, B. (2008).
118:, the inability to form new memories. This implies that the hippocampus is important not only for storing cognitive maps, but for
1504:
2482:
1069:
1992:
182:
Unlike the hippocampus which is involved in the encoding of complex memories, the cerebellum plays a role in the learning of
232:
reaction to fear. The central nucleus of the amygdala is also linked to emotions and behaviors motivated by food and sex.
1190:
Conway, M. A.; Pleydell Pearce, C. W. (2000). "The construction of autobiographical memories in the self memory system".
2040:
1941:
1828:
1471:
Montomery, P. Siverstein, P., et al. (1993). Spatial updating in
Parkinson's disease, Brain and Cognition, 23, 113-126.
1312:
Kandel, E., Schwartz, J., & Jessell, T. (1991). Principles of Neural
Science. 3rd edition. New York: NY. Elsevier.
2166:
2091:
1924:
531:
910:
McGaugh, JL (2004). "The Amygdala modulates the consolidation of memories of emotionally arousing experiences".
416:
The frontal lobes are also involved in the ability to remember what we need to do in the future; this is called
2204:
2149:
2124:
1954:
1931:
1881:
1786:
520:
256:
187:
1891:
1657:
592:
459:. Thus, general semantic knowledge or more personal episodic memories of one's childhood could be affected.
437:
410:
339:
2298:
2258:
2159:
2128:
1766:
1371:
1280:
Kolb, B., & Whishaw, I. (1990). Fundamentals of Human Neuropsychology. W.H. Freeman and Co., New York.
1199:
1146:
612:
343:
272:
228:
2313:
2028:
1914:
1886:
1871:
1866:
1704:
535:
2197:
2181:
2060:
1818:
1771:
1761:
1549:
1497:
1138:
1014:
810:
763:
380:
331:
315:
245:
126:
1376:
1235:
Rugg, M.; Yonelinas, A.P. (2003). "Human recognition memory: a cognitive neuroscience perspective".
1204:
1151:
2328:
2228:
1919:
1803:
1751:
1719:
1699:
516:
368:
280:
115:
2425:
2248:
2193:
2186:
2154:
2055:
2050:
2002:
1980:
1949:
1776:
1397:
1260:
1172:
983:
935:
836:
480:
417:
2410:
335:
604:
was largely damaged in FTLD patients and semantic autobiographical memory seemed to be spared.
2461:
2449:
2420:
2268:
2139:
2114:
2070:
1997:
1975:
1876:
1813:
1781:
1756:
1724:
1709:
1619:
1589:
1527:
1449:
1389:
1252:
1217:
1164:
1102:
1042:
975:
927:
885:
828:
779:
733:
679:
649:
524:
314:
The caudate nucleus is thought to assist in learning and memory of associations taught during
183:
145:
141:
130:
119:
346:. Huntington's and Parkinson's disease involve both motor deficits and cognitive impairment.
2400:
2353:
2323:
2278:
2134:
2065:
2018:
1823:
1798:
1684:
1644:
1532:
1439:
1431:
1420:"Autobiographical memory and patterns of brain atrophy in frontotemporal lobar degeneration"
1381:
1244:
1209:
1156:
1094:
1032:
1022:
967:
919:
875:
867:
818:
771:
723:
715:
539:
456:
384:
292:
284:
134:
971:
923:
2338:
2318:
2293:
2283:
2238:
2233:
1987:
1959:
1694:
1677:
1672:
1667:
1662:
1537:
1490:
958:
Packard, M.G.; Knowlton, B. (2002). "Learning and Memory Functions of the Basal Ganglia".
433:
429:
308:
304:
296:
288:
192:
176:
704:"Hippocampal resections impair associative learning and recognition memory in the monkey"
199:
accuracy of movements, and to make long-term changes (learning) to improve these skills.
1142:
1018:
814:
767:
51:
2405:
2369:
2263:
1861:
1808:
1634:
1604:
1584:
1571:
1444:
1419:
1037:
1002:
880:
855:
728:
719:
703:
555:
543:
468:
399:
376:
323:
83:
1362:
Goodale, MA; Milner, AD (1992). "Separate visual pathways for perception and action".
1248:
775:
354:
102:
responded strongly only when the rat was in certain locations. These cells are called
2476:
2384:
2374:
2348:
2343:
2303:
2288:
2253:
2176:
2023:
1851:
1714:
1689:
1652:
1609:
1599:
1594:
1579:
1385:
563:
268:
260:
95:
79:
71:
1264:
939:
395:
2415:
2379:
2333:
2243:
2086:
1901:
1856:
1843:
1833:
1793:
1513:
1176:
987:
840:
534:. Once the Lateral Geniculate Nucleus receives the information it is sent down the
406:
279:
and connected to the cerebral cortex. Specifically, the basal ganglia includes the
156:
1401:
74:, and lies next to the medial temporal lobe. It is made up of two structures, the
17:
1027:
856:"Associative Structure of Fear Memory After Basolateral Amygdala Lesions in Rats"
2273:
2144:
2098:
1213:
1129:
Squire, L.R.; Zola-Morgan, S. (1991). "The medial temporal lobe memory system".
1001:
Crespo, JA.; Stöckl P; Ueberall F; Marcel J; Saria A; Zernig G (February 2012).
600:
500:
383:, which controls voluntary movements of specific body parts associated with the
172:
103:
63:
56:
2308:
2171:
1738:
1098:
168:
161:
1544:
1435:
1160:
823:
798:
512:
488:
445:
1453:
1321:
Cowan, Nelson. (2005). Working Memory Capacity. Psychology Press. New York.
1256:
1221:
1046:
979:
931:
889:
832:
171:("little brain") is a structure located at the rear of the brain, near the
1393:
1168:
1106:
783:
737:
2033:
588:
559:
515:. The occipital lobe sits directly above the cerebellum and is situated
484:
372:
327:
276:
212:
1085:
Johnson, M.K.; Hashtroudi, S.; Lindsay, S. (1993). "Source Monitoring".
1746:
1292:
Blakemore & Frith (2005). The Learning Brain. Blackwell Publishing.
551:
523:, or parieto-occipital sulcus. This lobe is known as the centre of the
496:
492:
300:
99:
871:
391:
67:
207:
538:
where it is organized and sent down one of two possible path ways;
527:
system, the main function of the occipital lobe is that of vision.
353:
255:
206:
155:
66:
is a structure in the brain that has been associated with various
50:
35:
620:
ganglia work in both encoding and recalling spatial information.
452:
disturbance of language comprehension, and altered personality.
1486:
1482:
754:
Mishkin, M.; Appenzeller, T. (1987). "The anatomy of memory".
398:
of information. Therefore, the frontal lobes are important in
483:. It includes right-left confusion, difficulty with writing (
530:
Retinal sensors send signals through the optic tract to the
326:. Such symptoms are often present in those who suffer from
34:
encompasses a wide variety of anatomical structures in the
599:
Through image processing, patterns of significant reduced
275:
which are located in the medial temporal lobe, above the
114:
Damage to the hippocampus and surrounding area can cause
129:, the slow process by which memories are converted from
140:
It has also been found that it is possible to form new
455:
In regard to memory, temporal lobe damage can impair
799:"Drug Addiction and the memory systems of the brain"
27:
Variety of structures in the brain related to memory
2393:
2362:
2221:
2214:
2107:
2079:
2011:
1968:
1940:
1900:
1842:
1737:
1643:
1618:
1570:
1563:
1520:
367:The frontal lobes are located at the front of each
467:The parietal lobe is located directly behind the
390:When considering the frontal lobes in regards to
379:. It is separated from the parietal lobe by the
179:, in that it has a wavy, or convoluted surface.
94:There is evidence that the hippocampus contains
1345:
1343:
1070:The organization of recent and remote memories
491:). It can also produce disorders of language (
1498:
1333:
1331:
1329:
1327:
676:The Student's Guide to Cognitive Neuroscience
646:Fundamentals of Human Neuropsychology, 6th ed
8:
1467:
1465:
1463:
1288:
1286:
1276:
1274:
580:Frontotemporal lobar degeneration and memory
1629:The Magical Number Seven, Plus or Minus Two
1413:
1411:
797:Robbins, TW; Ersche KD; Everitt BJ (2008).
175:. It looks like a miniature version of the
2218:
1567:
1505:
1491:
1483:
1357:
1355:
1080:
1078:
803:Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences
394:, we see that it is very important in the
1443:
1375:
1308:
1306:
1304:
1302:
1300:
1298:
1203:
1150:
1036:
1026:
953:
951:
949:
905:
903:
901:
899:
879:
822:
749:
747:
727:
702:Mahut, H; Zola-Morgan S; Moss M (1982).
697:
695:
633:
428:The temporal lobes are a region of the
972:10.1146/annurev.neuro.25.112701.142937
924:10.1146/annurev.neuro.27.070203.144157
669:
667:
665:
639:
637:
554:, movement and colour discrimination,
82:, each containing different types of
7:
1068:Frankland P.W., Bontempi B. (2005).
125:The hippocampus is also involved in
487:) and difficulty with mathematics (
263:(red) and related structures (blue)
720:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-09-01214.1982
607:
25:
1910:Deese–Roediger–McDermott paradigm
1424:Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience
776:10.1038/scientificamerican0687-80
593:autobiographical domain in memory
585:Frontotemporal lobar degeneration
144:without the hippocampus, but not
2455:
2443:
2120:Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model
1993:Memory and social interactions
1072:. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 119–130.
648:. New York: Worth Publishers.
608:Parkinson's disease and memory
596:performance in the interview.
252:Basal ganglia and motor memory
1:
1249:10.1016/s1364-6613(03)00131-1
960:Annual Review of Neuroscience
912:Annual Review of Neuroscience
854:Rabinak, CA; Maren S (2008).
70:functions. It is part of the
1829:Retrieval-induced forgetting
1386:10.1016/0166-2236(92)90344-8
1028:10.1371/journal.pone.0030502
432:that is located beneath the
244:The amygdala is involved in
1214:10.1037/0033-295x.107.2.261
708:The Journal of Neuroscience
644:Kolb, B; Whishaw I (2008).
587:(FTLD) is a common form of
224:Memory of fear conditioning
2499:
2167:Levels of Processing model
2092:World Memory Championships
1925:Lost in the mall technique
1772:dissociative (psychogenic)
532:Lateral geniculate nucleus
2438:
1099:10.1037/0033-2909.114.1.3
2205:The Seven Sins of Memory
2150:Intermediate-term memory
1955:Indirect tests of memory
1932:Recovered-memory therapy
1882:Misattribution of memory
521:Parieto-occipital sulcus
299:, which consists of the
188:transient global amnesia
1892:Source-monitoring error
1436:10.1162/jocn.2008.20126
1161:10.1126/science.1896849
860:Behavioral Neuroscience
824:10.1196/annals.1441.020
499:), denial of deficits (
438:autobiographical memory
411:source monitoring error
358:The cortical structures
2483:Neuroscience of memory
2299:George Armitage Miller
2259:Patricia Goldman-Rakic
1087:Psychological Bulletin
550:are field defects and
359:
264:
229:Pavlovian conditioning
216:
164:
59:
42:Subcortical structures
32:neuroanatomy of memory
2462:Philosophy portal
2450:Psychology portal
2314:Henry L. Roediger III
1915:False memory syndrome
1887:Misinformation effect
1867:Imagination inflation
536:primary visual cortex
357:
259:
210:
159:
54:
1819:Motivated forgetting
1192:Psychological Review
678:. Psychology Press.
571:Damage to the cortex
381:primary motor cortex
340:Huntington's disease
332:athymhormic syndrome
316:operant conditioning
246:memory consolidation
236:Memory consolidation
127:memory consolidation
2329:Arthur P. Shimamura
2229:Richard C. Atkinson
2046:Effects of exercise
1920:Memory implantation
1804:Interference theory
1720:Selective retention
1700:Meaningful learning
1143:1991Sci...253.1380S
1137:(5026): 1380–1386.
1019:2012PLoSO...730502C
815:2008NYASA1141....1R
768:1987SciAm.256f..80M
756:Scientific American
613:Parkinson's disease
369:cerebral hemisphere
350:Cortical structures
344:Parkinson's disease
281:subthalamic nucleus
116:anterograde amnesia
2426:Andriy Slyusarchuk
2249:Hermann Ebbinghaus
2155:Involuntary memory
2056:Memory improvement
2041:Effects of alcohol
2003:Transactive memory
1981:Politics of memory
1950:Exceptional memory
481:Gerstmann syndrome
418:prospective memory
360:
265:
217:
165:
60:
18:Memory pathologies
2470:
2469:
2434:
2433:
2421:Cosmos Rossellius
2269:Marcia K. Johnson
2140:Exosomatic memory
2125:Context-dependent
2115:Absent-mindedness
1998:Memory conformity
1976:Collective memory
1877:Memory conformity
1814:Memory inhibition
1733:
1732:
1725:Tip of the tongue
1430:(10): 1839–1853.
685:978-1-84872-003-9
655:978-0-7167-9586-5
525:visual perception
184:procedural memory
146:episodic memories
142:semantic memories
120:encoding memories
16:(Redirected from
2490:
2460:
2459:
2458:
2448:
2447:
2446:
2401:Jonathan Hancock
2354:Robert Stickgold
2324:Richard Shiffrin
2279:Elizabeth Loftus
2219:
2135:Childhood memory
1942:Research methods
1824:Repressed memory
1799:Forgetting curve
1787:transient global
1658:Autobiographical
1568:
1507:
1500:
1493:
1484:
1472:
1469:
1458:
1457:
1447:
1415:
1406:
1405:
1379:
1359:
1350:
1347:
1338:
1335:
1322:
1319:
1313:
1310:
1293:
1290:
1281:
1278:
1269:
1268:
1237:Trends Cogn. Sci
1232:
1226:
1225:
1207:
1187:
1181:
1180:
1154:
1126:
1120:
1117:
1111:
1110:
1082:
1073:
1066:
1060:
1057:
1051:
1050:
1040:
1030:
998:
992:
991:
955:
944:
943:
907:
894:
893:
883:
872:10.1037/a0012903
866:(6): 1284–1294.
851:
845:
844:
826:
794:
788:
787:
751:
742:
741:
731:
714:(9): 1214–1229.
699:
690:
689:
674:Ward, J (2009).
671:
660:
659:
641:
457:long-term memory
385:precentral gyrus
293:ventral striatum
285:substantia nigra
135:long term memory
21:
2498:
2497:
2493:
2492:
2491:
2489:
2488:
2487:
2473:
2472:
2471:
2466:
2456:
2454:
2444:
2442:
2430:
2411:Dominic O'Brien
2389:
2358:
2339:Susumu Tonegawa
2319:Daniel Schacter
2294:Eleanor Maguire
2284:Geoffrey Loftus
2239:Stephen J. Ceci
2234:Robert A. Bjork
2210:
2129:state-dependent
2103:
2075:
2007:
1988:Cultural memory
1964:
1960:Memory disorder
1936:
1896:
1838:
1729:
1639:
1614:
1559:
1516:
1511:
1476:
1475:
1470:
1461:
1417:
1416:
1409:
1377:10.1.1.207.6873
1364:Trends Neurosci
1361:
1360:
1353:
1348:
1341:
1336:
1325:
1320:
1316:
1311:
1296:
1291:
1284:
1279:
1272:
1234:
1233:
1229:
1205:10.1.1.621.9717
1189:
1188:
1184:
1152:10.1.1.421.7385
1128:
1127:
1123:
1118:
1114:
1084:
1083:
1076:
1067:
1063:
1058:
1054:
1000:
999:
995:
957:
956:
947:
909:
908:
897:
853:
852:
848:
796:
795:
791:
753:
752:
745:
701:
700:
693:
686:
673:
672:
663:
656:
643:
642:
635:
630:
610:
582:
573:
509:
465:
434:Sylvian fissure
430:cerebral cortex
426:
371:and positioned
365:
352:
336:Fahr's syndrome
309:implicit memory
305:caudate nucleus
297:dorsal striatum
289:globus pallidus
271:are a group of
254:
238:
226:
205:
193:explicit memory
177:cerebral cortex
154:
112:
92:
49:
44:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2496:
2494:
2486:
2485:
2475:
2474:
2468:
2467:
2465:
2464:
2452:
2439:
2436:
2435:
2432:
2431:
2429:
2428:
2423:
2418:
2413:
2408:
2406:Paul R. McHugh
2403:
2397:
2395:
2391:
2390:
2388:
2387:
2382:
2377:
2372:
2366:
2364:
2360:
2359:
2357:
2356:
2351:
2346:
2341:
2336:
2331:
2326:
2321:
2316:
2311:
2306:
2301:
2296:
2291:
2286:
2281:
2276:
2271:
2266:
2264:Ivan Izquierdo
2261:
2256:
2251:
2246:
2241:
2236:
2231:
2225:
2223:
2216:
2212:
2211:
2209:
2208:
2201:
2191:
2190:
2189:
2179:
2174:
2169:
2164:
2163:
2162:
2152:
2147:
2142:
2137:
2132:
2122:
2117:
2111:
2109:
2105:
2104:
2102:
2101:
2096:
2095:
2094:
2083:
2081:
2077:
2076:
2074:
2073:
2068:
2063:
2058:
2053:
2048:
2043:
2038:
2037:
2036:
2031:
2021:
2015:
2013:
2009:
2008:
2006:
2005:
2000:
1995:
1990:
1985:
1984:
1983:
1972:
1970:
1966:
1965:
1963:
1962:
1957:
1952:
1946:
1944:
1938:
1937:
1935:
1934:
1929:
1928:
1927:
1917:
1912:
1906:
1904:
1898:
1897:
1895:
1894:
1889:
1884:
1879:
1874:
1869:
1864:
1862:Hindsight bias
1859:
1854:
1848:
1846:
1840:
1839:
1837:
1836:
1831:
1826:
1821:
1816:
1811:
1809:Memory erasure
1806:
1801:
1796:
1791:
1790:
1789:
1784:
1779:
1774:
1769:
1767:post-traumatic
1764:
1759:
1754:
1743:
1741:
1735:
1734:
1731:
1730:
1728:
1727:
1722:
1717:
1712:
1707:
1705:Personal-event
1702:
1697:
1692:
1687:
1682:
1681:
1680:
1675:
1670:
1660:
1655:
1649:
1647:
1641:
1640:
1638:
1637:
1635:Working memory
1632:
1624:
1622:
1616:
1615:
1613:
1612:
1607:
1605:Motor learning
1602:
1597:
1592:
1587:
1582:
1576:
1574:
1565:
1561:
1560:
1558:
1557:
1552:
1547:
1541:
1540:
1535:
1530:
1524:
1522:
1521:Basic concepts
1518:
1517:
1512:
1510:
1509:
1502:
1495:
1487:
1481:
1480:
1474:
1473:
1459:
1407:
1351:
1339:
1323:
1314:
1294:
1282:
1270:
1227:
1198:(2): 261–288.
1182:
1121:
1112:
1074:
1061:
1052:
993:
945:
895:
846:
789:
743:
691:
684:
661:
654:
632:
631:
629:
626:
609:
606:
581:
578:
572:
569:
556:hallucinations
544:ventral stream
508:
507:Occipital lobe
505:
469:central sulcus
464:
461:
425:
422:
400:working memory
377:parietal lobes
364:
361:
351:
348:
324:working memory
253:
250:
237:
234:
225:
222:
204:
201:
153:
150:
111:
108:
96:cognitive maps
91:
90:Cognitive maps
88:
48:
45:
43:
40:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2495:
2484:
2481:
2480:
2478:
2463:
2453:
2451:
2441:
2440:
2437:
2427:
2424:
2422:
2419:
2417:
2414:
2412:
2409:
2407:
2404:
2402:
2399:
2398:
2396:
2392:
2386:
2385:Clive Wearing
2383:
2381:
2378:
2376:
2373:
2371:
2368:
2367:
2365:
2361:
2355:
2352:
2350:
2349:Endel Tulving
2347:
2345:
2344:Anne Treisman
2342:
2340:
2337:
2335:
2332:
2330:
2327:
2325:
2322:
2320:
2317:
2315:
2312:
2310:
2307:
2305:
2304:Brenda Milner
2302:
2300:
2297:
2295:
2292:
2290:
2289:James McGaugh
2287:
2285:
2282:
2280:
2277:
2275:
2272:
2270:
2267:
2265:
2262:
2260:
2257:
2255:
2254:Sigmund Freud
2252:
2250:
2247:
2245:
2242:
2240:
2237:
2235:
2232:
2230:
2227:
2226:
2224:
2220:
2217:
2213:
2207:
2206:
2202:
2199:
2198:retrospective
2195:
2192:
2188:
2185:
2184:
2183:
2180:
2178:
2177:Muscle memory
2175:
2173:
2170:
2168:
2165:
2161:
2158:
2157:
2156:
2153:
2151:
2148:
2146:
2143:
2141:
2138:
2136:
2133:
2130:
2126:
2123:
2121:
2118:
2116:
2113:
2112:
2110:
2106:
2100:
2097:
2093:
2090:
2089:
2088:
2085:
2084:
2082:
2078:
2072:
2069:
2067:
2064:
2062:
2059:
2057:
2054:
2052:
2049:
2047:
2044:
2042:
2039:
2035:
2032:
2030:
2027:
2026:
2025:
2024:Art of memory
2022:
2020:
2017:
2016:
2014:
2010:
2004:
2001:
1999:
1996:
1994:
1991:
1989:
1986:
1982:
1979:
1978:
1977:
1974:
1973:
1971:
1967:
1961:
1958:
1956:
1953:
1951:
1948:
1947:
1945:
1943:
1939:
1933:
1930:
1926:
1923:
1922:
1921:
1918:
1916:
1913:
1911:
1908:
1907:
1905:
1903:
1899:
1893:
1890:
1888:
1885:
1883:
1880:
1878:
1875:
1873:
1872:Memory biases
1870:
1868:
1865:
1863:
1860:
1858:
1855:
1853:
1852:Confabulation
1850:
1849:
1847:
1845:
1844:Memory errors
1841:
1835:
1832:
1830:
1827:
1825:
1822:
1820:
1817:
1815:
1812:
1810:
1807:
1805:
1802:
1800:
1797:
1795:
1792:
1788:
1785:
1783:
1780:
1778:
1775:
1773:
1770:
1768:
1765:
1763:
1762:post-hypnotic
1760:
1758:
1755:
1753:
1750:
1749:
1748:
1745:
1744:
1742:
1740:
1736:
1726:
1723:
1721:
1718:
1716:
1715:Rote learning
1713:
1711:
1708:
1706:
1703:
1701:
1698:
1696:
1693:
1691:
1690:Hyperthymesia
1688:
1686:
1683:
1679:
1676:
1674:
1671:
1669:
1666:
1665:
1664:
1661:
1659:
1656:
1654:
1653:Active recall
1651:
1650:
1648:
1646:
1642:
1636:
1633:
1630:
1626:
1625:
1623:
1621:
1617:
1611:
1608:
1606:
1603:
1601:
1598:
1596:
1593:
1591:
1588:
1586:
1583:
1581:
1578:
1577:
1575:
1573:
1569:
1566:
1562:
1556:
1553:
1551:
1550:Consolidation
1548:
1546:
1543:
1542:
1539:
1536:
1534:
1531:
1529:
1526:
1525:
1523:
1519:
1515:
1508:
1503:
1501:
1496:
1494:
1489:
1488:
1485:
1478:
1477:
1468:
1466:
1464:
1460:
1455:
1451:
1446:
1441:
1437:
1433:
1429:
1425:
1421:
1414:
1412:
1408:
1403:
1399:
1395:
1391:
1387:
1383:
1378:
1373:
1369:
1365:
1358:
1356:
1352:
1346:
1344:
1340:
1334:
1332:
1330:
1328:
1324:
1318:
1315:
1309:
1307:
1305:
1303:
1301:
1299:
1295:
1289:
1287:
1283:
1277:
1275:
1271:
1266:
1262:
1258:
1254:
1250:
1246:
1243:(7): 313–19.
1242:
1238:
1231:
1228:
1223:
1219:
1215:
1211:
1206:
1201:
1197:
1193:
1186:
1183:
1178:
1174:
1170:
1166:
1162:
1158:
1153:
1148:
1144:
1140:
1136:
1132:
1125:
1122:
1116:
1113:
1108:
1104:
1100:
1096:
1092:
1088:
1081:
1079:
1075:
1071:
1065:
1062:
1056:
1053:
1048:
1044:
1039:
1034:
1029:
1024:
1020:
1016:
1013:(2): e30502.
1012:
1008:
1004:
997:
994:
989:
985:
981:
977:
973:
969:
965:
961:
954:
952:
950:
946:
941:
937:
933:
929:
925:
921:
917:
913:
906:
904:
902:
900:
896:
891:
887:
882:
877:
873:
869:
865:
861:
857:
850:
847:
842:
838:
834:
830:
825:
820:
816:
812:
808:
804:
800:
793:
790:
785:
781:
777:
773:
769:
765:
761:
757:
750:
748:
744:
739:
735:
730:
725:
721:
717:
713:
709:
705:
698:
696:
692:
687:
681:
677:
670:
668:
666:
662:
657:
651:
647:
640:
638:
634:
627:
625:
621:
617:
614:
605:
602:
597:
594:
590:
586:
579:
577:
570:
568:
565:
564:contralateral
561:
557:
553:
547:
545:
541:
537:
533:
528:
526:
522:
518:
514:
506:
504:
502:
498:
494:
490:
486:
482:
476:
472:
470:
463:Parietal lobe
462:
460:
458:
453:
449:
447:
441:
439:
435:
431:
424:Temporal lobe
423:
421:
419:
414:
412:
408:
403:
401:
397:
393:
388:
386:
382:
378:
374:
370:
362:
356:
349:
347:
345:
341:
337:
333:
329:
325:
319:
317:
312:
310:
306:
302:
298:
294:
290:
286:
282:
278:
274:
270:
269:basal ganglia
262:
261:Basal ganglia
258:
251:
249:
247:
242:
235:
233:
230:
223:
221:
214:
209:
202:
200:
196:
194:
189:
185:
180:
178:
174:
170:
163:
158:
151:
149:
147:
143:
138:
136:
132:
128:
123:
121:
117:
109:
107:
105:
101:
97:
89:
87:
85:
81:
80:Dentate gyrus
77:
73:
72:limbic system
69:
65:
58:
53:
46:
41:
39:
37:
33:
19:
2416:Ben Pridmore
2334:Larry Squire
2244:Susan Clancy
2203:
2087:Memory sport
2012:Other topics
1902:False memory
1857:Cryptomnesia
1834:Weapon focus
1794:Decay theory
1555:Neuroanatomy
1554:
1514:Human memory
1427:
1423:
1367:
1363:
1317:
1240:
1236:
1230:
1195:
1191:
1185:
1134:
1130:
1124:
1115:
1090:
1086:
1064:
1055:
1010:
1006:
996:
963:
959:
915:
911:
863:
859:
849:
806:
802:
792:
762:(6): 80–89.
759:
755:
711:
707:
675:
645:
622:
618:
611:
598:
583:
574:
548:
529:
510:
477:
473:
466:
454:
450:
442:
427:
415:
407:memory trace
404:
396:coordination
389:
366:
363:Frontal lobe
320:
313:
266:
243:
239:
227:
218:
197:
181:
166:
139:
124:
113:
93:
76:Ammon's Horn
75:
61:
31:
29:
2274:Eric Kandel
2222:Researchers
2194:Prospective
2145:Free recall
2099:Shas Pollak
1752:anterograde
1668:Declarative
1370:(1): 20–5.
1093:(1): 3–28.
918:(1): 1–28.
809:(1): 1–21.
601:parenchymal
501:anosognosia
446:familiarity
173:spinal cord
104:place cells
64:hippocampus
57:hippocampus
47:Hippocampus
2309:Lynn Nadel
2187:intertrial
2172:Metamemory
2160:flashbacks
2080:In society
1777:retrograde
1739:Forgetting
1710:Procedural
1620:Short-term
1590:Eyewitness
966:: 563–93.
628:References
169:cerebellum
162:cerebellum
152:Cerebellum
78:, and the
2061:Nutrition
1969:In groups
1782:selective
1757:childhood
1685:Flashbulb
1645:Long-term
1545:Attention
1372:CiteSeerX
1200:CiteSeerX
1147:CiteSeerX
560:illusions
517:posterior
513:forebrain
489:acalculia
2477:Category
2363:Patients
2034:mnemonic
2029:chunking
1695:Implicit
1678:Semantic
1673:Episodic
1663:Explicit
1528:Encoding
1454:18370601
1265:16522300
1257:12860190
1222:10789197
1047:22348011
1007:PLOS ONE
980:12052921
940:17502659
932:15217324
890:19045948
833:18991949
589:dementia
552:scotomas
485:agraphia
373:anterior
328:dystonia
303:and the
295:and the
277:thalamus
213:amygdala
203:Amygdala
110:Encoding
2182:Priming
2108:Related
2051:Emotion
1747:Amnesia
1585:Eidetic
1572:Sensory
1533:Storage
1445:6553881
1394:1374953
1177:5449289
1169:1896849
1139:Bibcode
1131:Science
1107:8346328
1038:3277594
1015:Bibcode
988:1536485
881:2593860
841:6694636
811:Bibcode
784:3589645
764:Bibcode
738:7119874
729:6564312
519:to the
497:apraxia
493:aphasia
375:to the
301:putamen
100:neurons
2215:People
2200:memory
2131:memory
2071:Trauma
1610:Visual
1600:Iconic
1595:Haptic
1580:Echoic
1538:Recall
1452:
1442:
1402:793980
1400:
1392:
1374:
1263:
1255:
1220:
1202:
1175:
1167:
1149:
1105:
1045:
1035:
986:
978:
938:
930:
888:
878:
839:
831:
782:
736:
726:
682:
652:
540:dorsal
392:memory
291:, the
287:, the
273:nuclei
68:memory
2394:Other
2066:Sleep
2019:Aging
1564:Types
1398:S2CID
1261:S2CID
1173:S2CID
984:S2CID
936:S2CID
837:S2CID
131:short
84:cells
36:brain
2196:and
2127:and
1450:PMID
1390:PMID
1253:PMID
1218:PMID
1165:PMID
1103:PMID
1043:PMID
976:PMID
928:PMID
886:PMID
829:PMID
807:1141
780:PMID
734:PMID
680:ISBN
650:ISBN
267:The
211:The
167:The
160:The
62:The
55:The
30:The
1440:PMC
1432:doi
1382:doi
1245:doi
1210:doi
1196:107
1157:doi
1135:253
1095:doi
1091:114
1033:PMC
1023:doi
968:doi
920:doi
876:PMC
868:doi
864:122
819:doi
772:doi
760:256
724:PMC
716:doi
542:or
342:or
133:to
122:.
2479::
2380:NA
2375:KC
2370:HM
1462:^
1448:.
1438:.
1428:20
1426:.
1422:.
1410:^
1396:.
1388:.
1380:.
1368:15
1366:.
1354:^
1342:^
1326:^
1297:^
1285:^
1273:^
1259:.
1251:.
1239:.
1216:.
1208:.
1194:.
1171:.
1163:.
1155:.
1145:.
1133:.
1101:.
1089:.
1077:^
1041:.
1031:.
1021:.
1009:.
1005:.
982:.
974:.
964:25
962:.
948:^
934:.
926:.
916:27
914:.
898:^
884:.
874:.
862:.
858:.
835:.
827:.
817:.
805:.
801:.
778:.
770:.
758:.
746:^
732:.
722:.
710:.
706:.
694:^
664:^
636:^
558:,
440:.
420:.
413:.
338:,
334:,
330:,
283:,
195:.
86:.
38:.
1631:"
1627:"
1506:e
1499:t
1492:v
1456:.
1434::
1404:.
1384::
1267:.
1247::
1241:7
1224:.
1212::
1179:.
1159::
1141::
1109:.
1097::
1049:.
1025::
1017::
1011:7
990:.
970::
942:.
922::
892:.
870::
843:.
821::
813::
786:.
774::
766::
740:.
718::
712:2
688:.
658:.
215:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.