313:(<= 50 years) with an almost two-fold difference between men and women. The patterns in the number of micronuclei after 70 years of age is controversial. Some studies have shown that in individuals over 70 years of age, micronucleus frequency increases in both sexes. On the other hand, other studies have found that in the oldest age groups, micronuclei frequencies level off. The deficiency of micronuclei in some of the oldest age groups may be explained by the fact that micro nucleated cells are preferentially eliminated by apoptosis. However, higher micronuclei frequency corresponds to a decreased efficiency of DNA repair and increased genomic instability, which are typical in older subjects. Age-related increases in micronuclei frequency also correspond well with age-related increases in the hypoploidy and the age-related increase in sex chromosome loss. Alternatively, the leveling off of frequency of micronuclei in older subjects would suggest a threshold of genomic instability that cannot be crossed if the person is to survive. If this were the case, women appear to reach this threshold faster than men.
164:
unrepaired double-stranded DNA breaks may also result in acentric chromosome fragments. Another way eccentric chromosome fragments may arise is when defects in genes related to homologous recombinational repair (ex: ATM, BRCA1, BRCA2, and RAD51) result in a dysfunctional error-free homologous recombinational DNA repair pathway and causes the cell to resort to the error-prone non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) repair pathway, increasing the likelihood of incorrect repair of DNA breaks, formation of dicentric chromosomes, and acentric chromosome fragments. If enzymes in the NHEJ repair pathway are defective as well, DNA breaks may not be repaired at all. Additionally, simultaneous excision repair of damaged or inappropriate bases incorporated in DNA that are in proximity and on opposite complementary DNA strands may lead to DNA double-stranded breaks and micronucleus formation, especially if the gap-filling step of the repair pathway is not completed.
297:
288:
chromosomal damage. In particular, the CBMNcyt (cytokinesis-block micronucleus cytome) assay is extremely versatile and is one of the preferred methods to measure the level of chromosomal damage and chromosomal instability in cells. The cytokinesis-block micronucleus (CBMN) assay was first developed to score micronuclei in cells that completed nuclear division by blocking them at the binucleate stage before cytokinesis. It later evolved into the CBMN 'cytome' assay to further explore cell death, cytostasis, and biomarkers of DNA damage. The major drawback of using micronucleus tests is that they cannot determine different types of chromosomal aberrations and can be influenced by the mitotic rate and proportion of cell death, skewing the results.
284:
frequency of micronucleated cells is measured. If there is a marked increase in the number of cells with micronuclei, it can be concluded that the chemical induces structural and/or numerical chromosomal damage. Since micronucleus tests must be performed on actively dividing cells, bone marrow stem cells and the erythrocytes they produce through cell divisions are ideal candidates. These cells experience constant, rapid turnover and the lack of a true nucleus in erythrocytes makes micronuclei easily visible under a microscope.
180:
Other possible causes of chromosome loss that could lead to micronuclei formation are defects in kinetochore and microtubule interactions, defects in mitotic spindle assembly, mitosis check point defects, abnormal centrosome amplification, and telomeric end fusions that result in dicentric chromosomes that detach from the spindle during anaphase. Micronuclei originating from chromosome loss events and acentric chromosome fragments can be distinguished using pancentromeric DNA probes.
2154:
317:
have shown that the frequencies of autosome-positive micronuclei in both genders and of sex chromosome-positive MN in men were similar and remained unchanged in older groups while the frequency of X-positive MN in women was higher than the average frequency of autosome-positive MN and continued to increase until the oldest age.
152:
fragments are eventually enclosed by a nuclear membranes and are structurally similar to conventional nuclei, albeit smaller in size. This small nucleus is referred to as a micronucleus. The formation of micronuclei can only be observed in cells undergoing nuclear division and can be clearly seen using
316:
Sex chromosomes contribute to the majority of chromosome loss events with increasing age. In females, the X chromosome can account for up to 72% of the observed micronuclei of which 37% appear to be lacking a functional kinetochore assembly possibly due to X chromosome inactivation. Multiple studies
312:
Multiple studies have found that micronuclei frequency in women is higher than in men and that the number of micronuclei increase until around 70 years of age. Micronuclei levels ranged from 0.5 to 1.4% in men to 0.9 to 1.8% in women. Gender-related differences were mainly seen in younger age groups
287:
Micronucleus assay systems are very economical, require much less skill in scoring that conventional metaphase tests, and are much faster than these conventional tests. Since micronucleus assays reflect chromosomal aberrations reliably and rapidly, they are extremely useful for a quick assessment of
179:
proteins at centromeres is affected by the methylation of cytosine and histone proteins, a reduction in heterochromatin integrity as a result of hypomethylation can interfere with microtubule attachment to chromosomes and with the sensing of tension from correct microtubule-kinetochore connections.
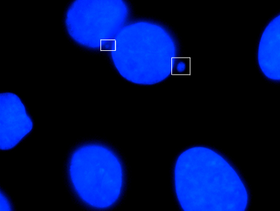
151:
Micronuclei primarily result from acentric chromosome fragments or lagging whole chromosomes that are not included in the daughter nuclei produced by mitosis because they fail to correctly attach to the spindle during the segregation of chromosomes in anaphase. These full chromosomes or chromatid
142:
because these structures were first identified and described in erythrocytes by hematologists
William Howell and Justin Jolly. These structures were later found to be associated with deficiencies in vitamins such as folate and B12. The relationship between formation of micronuclei and exposure to
170:
Micronuclei formation may also result from chromosome malsegregation during anaphase. Hypomethylation of cytosine in centromeric and pericentromeric areas and higher-order repeats of satellite DNA in centromeric DNA can result in such chromosomal loss events. Classical satellite DNA is normally
283:
The micronucleus tests provide important information about a chemical's ability to interfere with chromosome structure and function. For instance, many known human carcinogens test positive in mammalian micronucleus tests. In these tests, organisms are treated with a chemical and the resulting
20:
163:
Acentric chromosome fragments may arise in a variety of ways. One way is that disrepair of DNA double-strand breaks can lead to symmetrical or asymmetrical chromatid and chromosome exchanges as well as chromatid and chromosome fragments. If DNA damage exceeds the repair capacity of the cell,
172:
2092:
Umbreit, Neil T.; Zhang, Cheng-Zhong; Lynch, Luke D.; Blaine, Logan J.; Cheng, Anna M.; Tourdot, Richard; Sun, Lili; Almubarak, Hannah F.; Judge, Kim; Mitchell, Thomas J.; Spektor, Alexander (2020-04-17).
143:
environmental factors was first reported in root tip cells exposed to ionizing radiation. Micronucleus induction by a chemical was first reported in
Ehrlich ascites tumor cells treated with colchicine.
82:. Many micronucleus assays have been developed to test for the presence of these structures and determine their frequency in cells exposed to certain chemicals or subjected to stressful conditions.
296:
262:
AF is the number of acentric fragments and F = 0.5 - 0.5P, where P equals the probability of fragments being included in the traditional nucleus and not forming a micronucleus.
259:
2308:
Bandana
Ganguly, Bani (1993-08-01). "Cell division, chromosomal damage and micronucleus formation in peripheral lymphocytes of healthy donors: related to donor's age".
327:. Hence high frequencies of micronuclei in human peripheral blood indicate a ruptured or absent spleen. In mice, these are not removed, which is the basis for the
380:
51:. Micronuclei are commonly seen in cancerous cells and may indicate genomic damage events that can increase the risk of developmental or degenerative diseases.
66:
of chromosomes. This improper segregation of chromosomes may result from hypomethylation of repeat sequences present in pericentromeric DNA, irregularities in
809:
2224:
Countryman, Paul I.; Heddle, John A. (1976-12-01). "The production of micronuclei from chromosome aberrations in irradiated cultures of human lymphocytes".
2174:
175:(Immunodeficiency, centromere instability, and facial anomalies syndrome) or after treatment by DNA methyl transferase inhibitors. Since assembly of
2043:
Fenech, M.; Kirsch-Volders, M.; Natarajan, A. T.; Surralles, J.; Crott, J. W.; Parry, J.; Norppa, H.; Eastmond, D. A.; Tucker, J. D. (2011-01-01).
1999:
2169:
275:
5) no more than two associated with one primary nucleus (3 or more micronuclei are likely polymorphs or prorubicytes with nuclear fragments).
167:
Micronuclei can also form from fragmented chromosomes when nucleoplasmic bridges (NPB) are formed, stretched, and broken during telophase.
323:
In normal people and many other mammals, which do not have nuclei in their red blood cells, the micronuclei are removed rapidly by the
373:
802:
320:
The frequencies of chromosomal aberrations, damaged cells, and micronuclei are significantly higher in smokers than non-smokers.
2189:
Savage, John R. K. (1988-01-01). "A comment on the quantitative relationship between micronuclei and chromosomal aberrations".
442:
265:
One study, which used Giemsa stain to stain nuclear material, established the following criteria for identifying micronuclei:
2261:"Effects of age and gender on micronucleus and chromosome nondisjunction frequencies in centenarians and younger subjects"
544:
366:
795:
2045:"Molecular mechanisms of micronucleus, nucleoplasmic bridge and nuclear bud formation in mammalian and human cells"
2354:
1504:
539:
1744:
48:
504:
1941:
1880:
1819:
1533:
479:
1901:
1892:
743:
529:
422:
345:
192:
1885:
776:
2349:
1829:
402:
139:
59:
910:
115:
75:
2325:
2290:
2282:
2241:
2206:
2134:
2116:
2074:
2066:
1875:
1834:
726:
564:
447:
157:
71:
1478:
2317:
2272:
2233:
2198:
2159:
One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the
2124:
2106:
2056:
1849:
1693:
1640:
1592:
1551:
1516:
1509:
1446:
1323:
1249:
1625:
857:
427:
350:
273:
4) location within 3 or 4 nuclear diameters of the main nucleus without touching it, and
39:
or a fragment of a chromosome is not incorporated into one of the daughter nuclei during
271:
3) color the same as or lighter than the main nucleus (excludes large stain particles),
171:
heavily methylated at cytosine residues but may become almost fully unmethylated due to
2129:
2094:
1809:
1650:
1560:
1546:
1347:
1203:
1151:
1008:
927:
787:
390:
305:
153:
111:
79:
63:
358:
2343:
2321:
2237:
2202:
2165:
2160:
1906:
1739:
1711:
1615:
1588:
1585:
1519:
1013:
987:
937:
673:
633:
608:
524:
437:
412:
62:
or chromatid fragments caused by incorrectly repaired or unrepaired DNA breaks or by
40:
1926:
1896:
1756:
1407:
1254:
1156:
1092:
956:
822:
818:
653:
625:
603:
596:
576:
516:
432:
417:
340:
90:
32:
2095:"Mechanisms generating cancer genome complexity from a single cell division error"
188:
The number of micronuclei per cell can be predicted using the following formula:
1956:
1931:
1919:
1734:
1688:
1489:
1456:
1436:
1357:
1270:
1141:
1109:
1047:
1037:
972:
947:
895:
878:
755:
721:
648:
643:
534:
176:
127:
67:
1970:
1965:
1946:
1936:
1914:
1570:
1494:
1314:
1285:
1213:
1192:
1078:
1063:
951:
905:
847:
750:
690:
683:
668:
663:
658:
613:
559:
549:
499:
494:
484:
102:
36:
2286:
2120:
2070:
2277:
2260:
2111:
2061:
2044:
1951:
1824:
1814:
1678:
1660:
1635:
1604:
1565:
1417:
1397:
1383:
1362:
1290:
1187:
1170:
1073:
1052:
998:
961:
890:
869:
771:
733:
706:
678:
586:
571:
554:
489:
462:
394:
97:
44:
2294:
2138:
2078:
2329:
2210:
2245:
1844:
1839:
1751:
1716:
1645:
1630:
1620:
1499:
1422:
1373:
1337:
1304:
1218:
1130:
1027:
982:
862:
842:
716:
472:
457:
452:
55:
2178:. Vol. 18 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 391.
1780:
1761:
1280:
1234:
873:
826:
738:
638:
591:
467:
107:
94:
2226:
Mutation
Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis
1683:
1541:
1244:
1120:
900:
852:
581:
324:
123:
119:
74:, or flawed anaphase checkpoint genes. Micronuclei can contribute to
138:
Micronuclei in newly formed red blood cells in humans are known as
19:
2007:
1655:
1223:
885:
130:
and micronuclei of the individuals of the next cycle of fission.
791:
362:
711:
2259:
Wojda, Alina; Ziętkiewicz, Ewa; Witt, Michał (2007-05-01).
303:. Micronuclei in peripheral blood erythrocytes of penguins
269:
2) non-retractility (excludes small stain particles),
195:
78:
by promoting a catastrophic mutational event called
1866:
1800:
1725:
1702:
1669:
1602:
1476:
1469:
1444:
1435:
1405:
1396:
1371:
1345:
1336:
1312:
1303:
1268:
1232:
1201:
1178:
1169:
1139:
1118:
1100:
1091:
1061:
1035:
1026:
996:
970:
935:
926:
919:
833:
764:
699:
624:
515:
401:
267:1) diameter less than 1/3 of the primary nucleus,
253:
122:micronuclei undergo reciprocal fusion to form a
803:
374:
8:
70:proteins or their assembly, a dysfunctional
16:Small nucleus in the cells of some organisms
1473:
1441:
1402:
1342:
1309:
1175:
1097:
1032:
932:
923:
810:
796:
788:
381:
367:
359:
2276:
2128:
2110:
2060:
228:
202:
194:
295:
18:
1988:
7:
2038:
2036:
2034:
2032:
2030:
2028:
2026:
2024:
1994:
1992:
156:to block cytokinesis to produce a
14:
254:{\displaystyle MN/cell=AF/cell*F}
126:nucleus, which gives rise to the
2152:
1557:Membranous/thalloid/foliaceous
89:may also refer to the smaller
1:
1527:Tetrasporal/capsal/palmelloid
545:Microtubule organizing center
2322:10.1016/0921-8734(93)90015-U
2238:10.1016/0027-5107(76)90105-6
2203:10.1016/0165-7992(88)90008-5
23:Micronuclei visible in boxes
2371:
43:. It usually is a sign of
2310:Mutation Research/DNAging
2191:Mutation Research Letters
848:Mastigophora/Flagellates
540:Prokaryotic cytoskeleton
54:Micronuclei form during
2175:Encyclopædia Britannica
2112:10.1126/science.aba0712
1886:Baas-Becking hypothesis
49:chromosomal instability
1881:Microbial biogeography
309:
255:
35:that forms whenever a
24:
2278:10.1093/mutage/gem002
2062:10.1093/mutage/geq052
901:Fungus-like organisms
530:Intermediate filament
423:Endoplasmic reticulum
346:Cancerous micronuclei
299:
292:Patterns in formation
256:
22:
1616:Simple cell membrane
1552:Pseudoparenchymatous
1540:Filamentous/trichal/
1524:Colonial flagellated
1457:Collar of microvilli
777:Extracellular matrix
193:
60:acentric chromosomes
1830:Contractile vacuole
1781:Meiosis in protists
1762:Mitosis in protists
1740:Multinucleate cells
962:Flagellar apparatus
911:Ambiregnal protists
853:Sarcodina/Amoeboids
480:Cytoplasmic granule
331:micronucleus test.
140:Howell-Jolly bodies
2105:(6488): eaba0712.
1661:Periplast/pellicle
1384:Periplast/pellicle
1324:Cruciform division
505:Weibel–Palade body
389:Structures of the
310:
251:
76:genome instability
25:
2004:ntp.niehs.nih.gov
1979:
1978:
1876:Microbial ecology
1862:
1861:
1858:
1857:
1835:Eyespot apparatus
1465:
1464:
1447:Choanoflagellates
1431:
1430:
1392:
1391:
1332:
1331:
1299:
1298:
1165:
1164:
1087:
1086:
1022:
1021:
785:
784:
565:Spindle pole body
306:Pygoscelis papua.
158:binucleated cells
72:spindle apparatus
2362:
2334:
2333:
2305:
2299:
2298:
2280:
2256:
2250:
2249:
2232:(2–3): 321–331.
2221:
2215:
2214:
2186:
2180:
2179:
2158:
2156:
2155:
2149:
2143:
2142:
2132:
2114:
2089:
2083:
2082:
2064:
2040:
2019:
2018:
2016:
2015:
2006:. Archived from
1996:
1850:Mastigont system
1803:
1728:
1705:
1694:Gliding motility
1672:
1609:
1554:/plektenchymatic
1510:Amoeboflagellate
1483:
1474:
1450:
1442:
1411:
1403:
1377:
1351:
1343:
1317:
1310:
1274:
1238:
1207:
1181:
1176:
1145:
1124:
1103:
1098:
1067:
1041:
1033:
1002:
976:
940:
933:
924:
812:
805:
798:
789:
383:
376:
369:
360:
260:
258:
257:
252:
232:
206:
2370:
2369:
2365:
2364:
2363:
2361:
2360:
2359:
2355:Ciliate biology
2340:
2339:
2338:
2337:
2307:
2306:
2302:
2258:
2257:
2253:
2223:
2222:
2218:
2188:
2187:
2183:
2168:, ed. (1911). "
2164:
2153:
2151:
2150:
2146:
2091:
2090:
2086:
2042:
2041:
2022:
2013:
2011:
1998:
1997:
1990:
1985:
1980:
1975:
1868:
1854:
1801:
1796:
1726:
1721:
1703:
1698:
1670:
1665:
1606:
1603:
1598:
1480:
1477:
1461:
1445:
1427:
1406:
1388:
1372:
1367:
1346:
1328:
1313:
1295:
1269:
1264:
1233:
1228:
1204:Dinoflagellates
1202:
1197:
1179:
1161:
1140:
1135:
1119:
1114:
1101:
1083:
1062:
1057:
1036:
1018:
997:
992:
971:
966:
936:
915:
836:classifications
835:
829:
816:
786:
781:
760:
695:
620:
511:
428:Golgi apparatus
404:
397:
387:
356:
351:Microchromosome
337:
294:
281:
274:
272:
270:
268:
266:
261:
191:
190:
189:
186:
149:
136:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2368:
2366:
2358:
2357:
2352:
2342:
2341:
2336:
2335:
2316:(3): 135–148.
2300:
2271:(3): 195–200.
2251:
2216:
2181:
2166:Chisholm, Hugh
2144:
2084:
2055:(1): 125–132.
2020:
2000:"Micronucleus"
1987:
1986:
1984:
1981:
1977:
1976:
1974:
1973:
1968:
1963:
1962:
1961:
1960:
1959:
1954:
1944:
1939:
1934:
1924:
1923:
1922:
1911:
1910:
1909:
1904:
1890:
1889:
1888:
1883:
1872:
1870:
1864:
1863:
1860:
1859:
1856:
1855:
1853:
1852:
1847:
1842:
1837:
1832:
1827:
1822:
1817:
1812:
1806:
1804:
1798:
1797:
1795:
1794:
1793:
1792:
1789:
1786:
1778:
1777:
1776:
1773:
1770:
1767:
1759:
1754:
1749:
1748:
1747:
1737:
1731:
1729:
1723:
1722:
1720:
1719:
1714:
1708:
1706:
1700:
1699:
1697:
1696:
1691:
1686:
1681:
1675:
1673:
1667:
1666:
1664:
1663:
1658:
1653:
1648:
1643:
1638:
1633:
1628:
1623:
1618:
1612:
1610:
1600:
1599:
1597:
1596:
1583:
1582:
1581:
1580:
1579:
1578:Siphonocladous
1576:
1568:
1561:Multinucleated
1558:
1555:
1549:
1547:Parenchymatous
1544:
1538:
1537:
1536:
1531:
1528:
1525:
1514:
1513:
1512:
1507:
1502:
1497:
1486:
1484:
1471:
1467:
1466:
1463:
1462:
1460:
1459:
1453:
1451:
1439:
1433:
1432:
1429:
1428:
1426:
1425:
1420:
1414:
1412:
1400:
1394:
1393:
1390:
1389:
1387:
1386:
1380:
1378:
1369:
1368:
1366:
1365:
1360:
1354:
1352:
1348:Kinetoplastids
1340:
1334:
1333:
1330:
1329:
1327:
1326:
1320:
1318:
1307:
1301:
1300:
1297:
1296:
1294:
1293:
1288:
1283:
1277:
1275:
1266:
1265:
1263:
1262:
1257:
1252:
1247:
1241:
1239:
1230:
1229:
1227:
1226:
1221:
1216:
1210:
1208:
1199:
1198:
1196:
1195:
1190:
1184:
1182:
1173:
1167:
1166:
1163:
1162:
1160:
1159:
1154:
1148:
1146:
1137:
1136:
1134:
1133:
1127:
1125:
1116:
1115:
1113:
1112:
1106:
1104:
1095:
1089:
1088:
1085:
1084:
1082:
1081:
1076:
1070:
1068:
1059:
1058:
1056:
1055:
1050:
1044:
1042:
1030:
1024:
1023:
1020:
1019:
1017:
1016:
1014:Phycobilisomes
1011:
1009:Pit connection
1005:
1003:
994:
993:
991:
990:
988:Phycobilisomes
985:
979:
977:
968:
967:
965:
964:
959:
954:
943:
941:
938:Chloroplastida
930:
928:Archaeplastida
921:
917:
916:
914:
913:
908:
903:
898:
893:
888:
883:
882:
881:
876:
867:
866:
865:
860:
850:
839:
837:
831:
830:
817:
815:
814:
807:
800:
792:
783:
782:
780:
779:
774:
768:
766:
762:
761:
759:
758:
753:
748:
747:
746:
741:
731:
730:
729:
724:
719:
709:
703:
701:
700:Other internal
697:
696:
694:
693:
688:
687:
686:
681:
676:
671:
666:
661:
656:
651:
646:
636:
630:
628:
622:
621:
619:
618:
617:
616:
611:
601:
600:
599:
594:
589:
584:
574:
569:
568:
567:
562:
557:
552:
542:
537:
532:
527:
521:
519:
513:
512:
510:
509:
508:
507:
502:
497:
492:
487:
477:
476:
475:
470:
465:
460:
455:
450:
440:
435:
430:
425:
420:
415:
409:
407:
399:
398:
388:
386:
385:
378:
371:
363:
354:
353:
348:
343:
336:
333:
293:
290:
280:
277:
250:
247:
244:
241:
238:
235:
231:
227:
224:
221:
218:
215:
212:
209:
205:
201:
198:
185:
184:Identification
182:
154:cytochalasin B
148:
145:
135:
132:
110:it divides by
100:, such as the
80:chromothripsis
64:nondisjunction
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2367:
2356:
2353:
2351:
2348:
2347:
2345:
2331:
2327:
2323:
2319:
2315:
2311:
2304:
2301:
2296:
2292:
2288:
2284:
2279:
2274:
2270:
2266:
2262:
2255:
2252:
2247:
2243:
2239:
2235:
2231:
2227:
2220:
2217:
2212:
2208:
2204:
2200:
2196:
2192:
2185:
2182:
2177:
2176:
2171:
2167:
2162:
2161:public domain
2148:
2145:
2140:
2136:
2131:
2126:
2122:
2118:
2113:
2108:
2104:
2100:
2096:
2088:
2085:
2080:
2076:
2072:
2068:
2063:
2058:
2054:
2050:
2046:
2039:
2037:
2035:
2033:
2031:
2029:
2027:
2025:
2021:
2010:on 2016-10-18
2009:
2005:
2001:
1995:
1993:
1989:
1982:
1972:
1969:
1967:
1964:
1958:
1955:
1953:
1950:
1949:
1948:
1945:
1943:
1940:
1938:
1935:
1933:
1930:
1929:
1928:
1925:
1921:
1918:
1917:
1916:
1912:
1908:
1907:Fertilization
1905:
1903:
1900:
1899:
1898:
1894:
1891:
1887:
1884:
1882:
1879:
1878:
1877:
1874:
1873:
1871:
1865:
1851:
1848:
1846:
1843:
1841:
1838:
1836:
1833:
1831:
1828:
1826:
1823:
1821:
1818:
1816:
1813:
1811:
1808:
1807:
1805:
1799:
1790:
1787:
1784:
1783:
1782:
1779:
1775:Pleuromitosis
1774:
1771:
1768:
1765:
1764:
1763:
1760:
1758:
1755:
1753:
1750:
1746:
1743:
1742:
1741:
1738:
1736:
1733:
1732:
1730:
1724:
1718:
1715:
1713:
1712:Hydrogenosome
1710:
1709:
1707:
1701:
1695:
1692:
1690:
1687:
1685:
1682:
1680:
1677:
1676:
1674:
1668:
1662:
1659:
1657:
1654:
1652:
1649:
1647:
1644:
1642:
1639:
1637:
1634:
1632:
1629:
1627:
1624:
1622:
1619:
1617:
1614:
1613:
1611:
1608:
1601:
1594:
1590:
1587:
1586:Multicellular
1584:
1577:
1574:
1573:
1572:
1569:
1567:
1564:
1563:
1562:
1559:
1556:
1553:
1550:
1548:
1545:
1543:
1539:
1535:
1532:
1529:
1526:
1523:
1522:
1521:
1518:
1515:
1511:
1508:
1506:
1503:
1501:
1498:
1496:
1493:
1492:
1491:
1488:
1487:
1485:
1482:
1475:
1472:
1468:
1458:
1455:
1454:
1452:
1448:
1443:
1440:
1438:
1434:
1424:
1421:
1419:
1416:
1415:
1413:
1409:
1408:Dictyostelids
1404:
1401:
1399:
1395:
1385:
1382:
1381:
1379:
1375:
1370:
1364:
1361:
1359:
1356:
1355:
1353:
1349:
1344:
1341:
1339:
1335:
1325:
1322:
1321:
1319:
1316:
1311:
1308:
1306:
1302:
1292:
1289:
1287:
1284:
1282:
1279:
1278:
1276:
1272:
1271:Apicomplexans
1267:
1261:
1258:
1256:
1253:
1251:
1248:
1246:
1243:
1242:
1240:
1236:
1231:
1225:
1222:
1220:
1217:
1215:
1212:
1211:
1209:
1205:
1200:
1194:
1191:
1189:
1186:
1185:
1183:
1177:
1174:
1172:
1168:
1158:
1155:
1153:
1150:
1149:
1147:
1143:
1138:
1132:
1129:
1128:
1126:
1122:
1117:
1111:
1108:
1107:
1105:
1099:
1096:
1094:
1093:Stramenopiles
1090:
1080:
1077:
1075:
1072:
1071:
1069:
1065:
1060:
1054:
1051:
1049:
1046:
1045:
1043:
1039:
1034:
1031:
1029:
1025:
1015:
1012:
1010:
1007:
1006:
1004:
1000:
995:
989:
986:
984:
981:
980:
978:
974:
969:
963:
960:
958:
955:
953:
949:
945:
944:
942:
939:
934:
931:
929:
925:
922:
918:
912:
909:
907:
904:
902:
899:
897:
894:
892:
889:
887:
884:
880:
877:
875:
871:
868:
864:
861:
859:
856:
855:
854:
851:
849:
846:
845:
844:
841:
840:
838:
832:
828:
824:
820:
813:
808:
806:
801:
799:
794:
793:
790:
778:
775:
773:
770:
769:
767:
763:
757:
754:
752:
749:
745:
742:
740:
737:
736:
735:
732:
728:
725:
723:
720:
718:
715:
714:
713:
710:
708:
705:
704:
702:
698:
692:
689:
685:
682:
680:
677:
675:
674:Proteinoplast
672:
670:
667:
665:
662:
660:
657:
655:
652:
650:
647:
645:
642:
641:
640:
637:
635:
634:Mitochondrion
632:
631:
629:
627:
626:Endosymbionts
623:
615:
612:
610:
609:Lamellipodium
607:
606:
605:
602:
598:
595:
593:
590:
588:
585:
583:
580:
579:
578:
575:
573:
570:
566:
563:
561:
558:
556:
553:
551:
548:
547:
546:
543:
541:
538:
536:
533:
531:
528:
526:
525:Microfilament
523:
522:
520:
518:
514:
506:
503:
501:
498:
496:
493:
491:
488:
486:
483:
482:
481:
478:
474:
471:
469:
466:
464:
461:
459:
456:
454:
451:
449:
446:
445:
444:
441:
439:
438:Autophagosome
436:
434:
431:
429:
426:
424:
421:
419:
416:
414:
413:Cell membrane
411:
410:
408:
406:
403:Endomembrane
400:
396:
392:
384:
379:
377:
372:
370:
365:
364:
361:
357:
352:
349:
347:
344:
342:
339:
338:
334:
332:
330:
326:
321:
318:
314:
308:
307:
302:
298:
291:
289:
285:
278:
276:
263:
248:
245:
242:
239:
236:
233:
229:
225:
222:
219:
216:
213:
210:
207:
203:
199:
196:
183:
181:
178:
174:
168:
165:
161:
159:
155:
146:
144:
141:
133:
131:
129:
125:
121:
117:
113:
109:
105:
104:
99:
96:
92:
88:
83:
81:
77:
73:
69:
65:
61:
58:from lagging
57:
52:
50:
46:
42:
41:cell division
38:
34:
30:
21:
2313:
2309:
2303:
2268:
2264:
2254:
2229:
2225:
2219:
2197:(1): 33–36.
2194:
2190:
2184:
2173:
2170:Micronucleus
2147:
2102:
2098:
2087:
2052:
2048:
2012:. Retrieved
2008:the original
2003:
1927:Heterotrophy
1897:Reproduction
1772:Orthomitosis
1757:Heterokaryon
1704:Mitochondria
1605:Cell surface
1481:organization
1437:Opisthokonta
1260:Micronucleus
1259:
1255:Macronucleus
1157:Pneumatocyst
973:Glaucophytes
957:Phragmoplast
896:Thallophytes
823:Protistology
819:Microbiology
654:Gerontoplast
604:Pseudopodium
597:Radial spoke
577:Undulipodium
517:Cytoskeleton
433:Parenthesome
355:
341:Macronucleus
328:
322:
319:
315:
311:
304:
300:
286:
282:
264:
187:
173:ICF syndrome
169:
166:
162:
150:
137:
101:
87:micronucleus
86:
84:
53:
29:micronucleus
28:
26:
2265:Mutagenesis
2049:Mutagenesis
1957:Necrotrophy
1942:Saprotrophy
1932:Phagotrophy
1920:Phototrophy
1913:Nutrition:
1902:Life cycles
1893:Development
1867:Ecology and
1735:Nucleomorph
1689:Pseudopodia
1490:Unicellular
1374:Euglenoidea
1358:Kinetoplast
1142:Brown algae
1110:Mastigoneme
1048:Mastigoneme
1038:Cryptophyta
948:green algae
906:Slime molds
756:Magnetosome
722:Spliceosome
649:Chromoplast
644:Chloroplast
535:Microtubule
177:kinetochore
128:macronuclei
116:conjugation
68:kinetochore
47:events and
31:is a small
2350:Organelles
2344:Categories
2014:2016-10-14
1983:References
1971:Auxotrophy
1966:Mixotrophy
1947:Parasitism
1937:Osmotrophy
1915:Autotrophy
1869:physiology
1745:Plasmodium
1671:Locomotion
1607:structures
1571:Coenocytic
1315:Phytomyxea
1286:Apicoplast
1214:Dinokaryon
1193:Trichocyst
1064:Haptophyte
952:Phycoplast
920:Morphology
891:Cryptogams
751:Proteasome
744:Inclusions
691:Nitroplast
684:Apicoplast
669:Elaioplast
664:Amyloplast
659:Leucoplast
614:Filopodium
560:Basal body
550:Centrosome
500:Peroxisome
495:Glyoxysome
485:Melanosome
395:organelles
118:a pair of
103:Paramecium
98:protozoans
37:chromosome
2287:0267-8357
2121:0036-8075
2071:0267-8357
1952:Biotrophy
1825:Extrusome
1815:Cytostome
1679:Flagellum
1636:Cell wall
1595:/histonal
1575:Siphonous
1566:Syncytial
1534:Coenobial
1530:Sarcinoid
1479:Levels of
1418:Macrocyst
1398:Amoebozoa
1363:Glycosome
1291:Microneme
1171:Alveolata
1079:Haptonema
1074:Coccolith
1053:Periplast
999:Red algae
983:Cyanelles
870:Infusoria
772:Cell wall
734:Cytoplasm
707:Nucleolus
679:Tannosome
587:Flagellum
572:Myofibril
555:Centriole
490:Microbody
463:Phagosome
246:∗
147:Formation
134:Discovery
114:, and in
85:The term
45:genotoxic
2295:17284771
2139:32299917
2079:21164193
1845:Axostyle
1840:Pyrenoid
1820:Fimbriae
1752:Dikaryon
1717:Mitosome
1646:Skeleton
1631:Frustule
1621:Mucilage
1593:tissular
1517:Colonial
1500:Amoeboid
1495:Monadoid
1423:Sorocarp
1338:Excavate
1305:Rhizaria
1235:Ciliates
1219:Dinocyst
1180:General:
1131:Frustule
1102:General:
1028:Hacrobia
879:Sporozoa
874:Ciliates
863:Heliozoa
843:Protozoa
827:Protists
765:External
717:Ribosome
473:Acrosome
458:Endosome
453:Lysosome
335:See also
56:anaphase
2330:7689700
2211:3336377
2163::
2130:7347108
2099:Science
1788:Zygotic
1785:Gametic
1727:Nucleus
1505:Coccoid
1470:General
1281:Rhoptry
1188:Alveoli
1121:Diatoms
858:Testate
739:Cytosol
639:Plastid
592:Axoneme
468:Vacuole
448:Exosome
443:Vesicle
418:Nucleus
329:in vivo
112:fission
108:mitosis
95:ciliate
91:nucleus
33:nucleus
2328:
2293:
2285:
2246:796719
2244:
2209:
2157:
2137:
2127:
2119:
2077:
2069:
1791:Sporic
1769:Closed
1684:Cilium
1641:Lorica
1542:hyphal
1250:Cirrus
1245:Cilium
1152:Lamina
834:Former
582:Cilium
405:system
325:spleen
279:Assays
124:zygote
120:gamete
1802:Other
1656:Theca
1626:Scale
1224:Theca
886:Algae
727:Vault
106:. In
2326:PMID
2291:PMID
2283:ISSN
2242:PMID
2207:PMID
2135:PMID
2117:ISSN
2075:PMID
2067:ISSN
1810:Cyst
1766:Open
1651:Test
1589:s.s.
1520:s.s.
391:cell
301:B, C
2318:doi
2314:295
2273:doi
2234:doi
2199:doi
2195:207
2172:".
2125:PMC
2107:doi
2103:368
2057:doi
950:":
712:RNA
93:in
2346::
2324:.
2312:.
2289:.
2281:.
2269:22
2267:.
2263:.
2240:.
2230:41
2228:.
2205:.
2193:.
2133:.
2123:.
2115:.
2101:.
2097:.
2073:.
2065:.
2053:26
2051:.
2047:.
2023:^
2002:.
1991:^
825::
821::
393:/
160:.
27:A
2332:.
2320::
2297:.
2275::
2248:.
2236::
2213:.
2201::
2141:.
2109::
2081:.
2059::
2017:.
1895:/
1591:/
1449::
1410::
1376::
1350::
1273::
1237::
1206::
1144::
1123::
1066::
1040::
1001::
975::
946:"
872:/
811:e
804:t
797:v
382:e
375:t
368:v
249:F
243:l
240:l
237:e
234:c
230:/
226:F
223:A
220:=
217:l
214:l
211:e
208:c
204:/
200:N
197:M
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.