119:
205:, can be mobile and participate in the regulation of gene expression in the nucleoplasm. The nuclear pore is where molecules travel from inside the nucleoplasm to the cytoplasm and vice versa. The nucleoplasm is also a route for many molecules to travel through. Smaller molecules are able to pass freely through the nuclear pore to get into and out of the nucleoplasm, while larger proteins need the help of receptors on the surface of the nuclear envelope. The nuclear matrix is also believed to be contained in the nucleoplasm where it functions to maintain the size and shape of the nucleus, in a role similar to that of the cytoskeleton found in the cytoplasm. However, the existence and the exact function of the nuclear matrix remain unclear and heavily debated.
20:
314:
413:. These proteins also differ in function, as proteins that localize to the nucleoplasm are largely involved in DNA-dependent processes including cell division and gene regulation, while cytosolic proteins are mainly involved in protein modification, mRNA degradation, metabolic processes, signal transduction, and cell death.
67:
of a eukaryotic cell in that it is a gel-like substance found within a membrane, although the nucleoplasm only fills out the space in the nucleus and has its own unique functions. The nucleoplasm suspends structures within the nucleus that are not membrane-bound and is responsible for maintaining the
387:
protein, its presence has been recorded in the nuclear envelope, controlling the ionic gradient between the cytoplasm and nucleoplasm of the cell and contributing to the homeostasis of calcium within the cell. These ions also determine the concentration gradient that exists between the cytoplasm and
184:
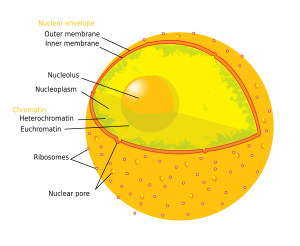
Many important cell functions take place in the nucleus, more specifically in the nucleoplasm. The main function of the nucleoplasm is to provide the proper environment for essential processes that take place in the nucleus, serving as the suspension substance for all organelles inside the nucleus,
441:
within their respective compartments. The cytoplasm contains the cytoskeleton, a network of protein filaments found in all cells, while the nucleoplasm is believed to contain the nuclear matrix, a hypothetically analogous network of filaments that organizes the organelles and genetic information
396:
Nucleoplasm is quite similar to the cytoplasm, with the main difference being that nucleoplasm is found inside the nucleus while the cytoplasm is located inside the cell, outside of the nucleus. Their ionic compositions are nearly identical due to the ion pumps and permeability of the nuclear
388:
nucleoplasm, serving to control the flow of ions across the nuclear envelope. They are important in maintaining the osmolarity of the nucleoplasm which in turn provides structural integrity to the nuclear envelope as well as the organelles suspended in the dense nucleoplasm.
230:, act as receptors for the NLS, escorting the protein to a nuclear pore complex to be transported into the nucleoplasm. Proteins in the nucleoplasm are mainly tasked with participating in and regulating cellular functions that are DNA-dependent, including transcription,
442:
within the nucleus. While the structure and function of the cytoskeleton have been well documented, the exact function, and even the presence, of the nuclear matrix is disputed. While the exact composition of the nuclear matrix has not been confirmed, type V
421:
membrane, the nuclear envelope that compartmentalizes the nucleoplasm consists of two separate lipid bilayers- an outer membrane and an inner membrane. The cytoplasm is also found in all known cells while nucleoplasm is only found in eukaryotic cells, as
416:
The cytoplasm and the nucleoplasm are both highly gelatinous structures enclosed by membranous structures- the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope, respectively. However, while the cytoplasm is contained by a single
242:, and a variety of metabolic processes. These proteins are divided into histone proteins, a class of proteins that bind to DNA and give chromosomes their shape and regulate gene activity, and non-histone proteins.
213:
The nucleoplasm is a highly viscous liquid that is enveloped by the nuclear membrane and consists mainly of water, proteins, dissolved ions, and a variety of other substances including nucleic acids and minerals.
446:, known as nuclear lamins, have been documented in the nucleoplasm, functioning in the structural support of the nucleus as well as the regulation of DNA replication, transcription, and chromatin organization.
450:, the circular flow of cytoplasm driven by the cytoskeleton, has been well documented in the cytoplasm, aiding in intracellular transport, but this process has not been documented in the nucleoplasm.
1756:
118:
201:
in the nucleoplasm. Proteins located in the nucleoplasm are involved in the activation of genes that are used in the cell cycle. Some nucleoporins which typically make up the
383:
that pumps three sodium ions out of the cell for every two potassium ions it pumps into the cell, creating an ionic gradient. While this pump is generally considered to be a
149:
253:
which function in DNA replication and RNA transcription, respectively. Additionally, the nucleoplasm is host to many of the enzymes that play essential roles in
397:
envelope, however, the proteins in these two fluids differ greatly. Proteins in the cytoplasm are termed cytosolic proteins which are produced by free
1189:
156:
in 1831. The nucleoplasm, while described by Bauer and Brown, was not specifically isolated as a separate entity until its naming in 1882 by
818:
616:
434:, while the nucleoplasm is released with the dissolution of the nuclear envelope, refilling only after the nuclear envelope reforms.
1320:
222:
Nearly a third of the human protein-coding genes (6784 genes) have been found to localize to the nucleoplasm via targeting by a
1799:
223:
140:
The existence of the nucleus, including the nucleoplasm, was first documented as early as 1682 by the Dutch microscopist
983:"Acetyl-coenzyme A synthetase 2 is a nuclear protein required for replicative longevity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae"
1690:
1774:
1528:
552:
Kühn, T; Ihalainen, TO; Hyväluoma, J; Dross, N; Willman, SF; Langowski, J; Vihinen-Ranta, M; Timonen, J (2011).
1511:
1506:
1501:
1496:
1491:
1486:
266:
372:. These ions are key players in a variety of biological functions. Sodium and potassium play key roles in the
294:
647:
270:
678:"Nucleoporins Directly Stimulate Expression of Developmental and Cell-Cycle Genes Inside the Nucleoplasm"
277:
is also found in the nucleoplasm in significant quantities; this enzyme is involved in the final step of
1794:
1313:
447:
443:
402:
373:
318:
290:
352:
within the cell and the organism as a whole. Ions that have been documented in the nucleoplasm include
245:
The nucleoplasm contains many enzymes that are instrumental in the synthesis of DNA and RNA, including
1253:
Dechat, Thomas; Adam, Stephen A.; Taimen, Pekka; Shimi, Takeshi; Goldman, Robert D. (November 2010).
1298:
1169:
512:
282:
254:
836:"Evidence for the presence of nonhistone chromosomal proteins in the nucleoplasm of HeLa S3 cells"
527:
467:
1451:
1164:
865:
707:
165:
133:
1115:"The correlation between cell and nucleus size is explained by an eukaryotic cell growth model"
1284:
1235:
1146:
1095:
1012:
963:
914:
857:
814:
765:
699:
612:
585:
507:
410:
302:
194:
1342:
1306:
1274:
1266:
1225:
1217:
1184:
1136:
1126:
1085:
1077:
1039:
1002:
994:
953:
945:
904:
896:
847:
755:
745:
689:
575:
565:
438:
423:
330:
60:
19:
1545:
1334:
437:
The organelles and other structures within the cytoplasm and nucleoplasm are organized by
406:
384:
274:
239:
198:
153:
93:
56:
885:"The Secret Life of NAD+: An Old Metabolite Controlling New Metabolic Signaling Pathways"
258:
1721:
1391:
1347:
1279:
1254:
1141:
1114:
1090:
1065:
1007:
982:
958:
933:
909:
884:
760:
733:
580:
553:
262:
250:
246:
77:
1788:
1230:
1205:
852:
835:
632:
Brown R (1866). "On the Organs and Mode of
Fecundation of Orchidex and Asclepiadea".
427:
418:
377:
326:
322:
1113:
Wu, Yufei; Pegoraro, Adrian; Weitz, David; Janmey, Paul; Sun, Sean (February 2022).
869:
784:
711:
676:
Kalverda, Bernike; Pickersgill, Helen; Shloma, Victor V.; Fornerod, Maarten (2010).
1575:
1355:
1330:
1043:
231:
202:
190:
48:
605:
1131:
949:
570:
1590:
1580:
1463:
1361:
1270:
431:
426:
lack a well-defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Additionally, during
349:
333:
as well as the ionic makeup of the nucleoplasm through the selective pumping of
145:
141:
89:
85:
694:
677:
401:
while proteins that localize to the nucleoplasm must undergo processing in the
1668:
1481:
1066:"Nuclear Na+/K+-ATPase plays an active role in nucleoplasmic Ca2+ homeostasis"
998:
365:
298:
278:
235:
69:
44:
24:
750:
1621:
1570:
1473:
369:
357:
338:
81:
64:
52:
28:
1288:
1239:
1150:
1099:
1016:
967:
918:
769:
703:
589:
861:
68:
shape of the nucleus. The structures suspended in the nucleoplasm include
1550:
1221:
900:
732:
Khan, Asmat Ullah; Qu, Rongmei; Ouyang, Jun; Dai, Jingxing (2020-04-03).
398:
286:
227:
169:
129:
148:. However, the cell nucleus was not named and described in detail until
1599:
1081:
361:
193:
are ones that localize to the nucleoplasm. These proteins take part in
186:
173:
161:
126:
73:
734:"Role of Nucleoporins and Transport Receptors in Cell Differentiation"
313:
1651:
1641:
1631:
1626:
1538:
1521:
1456:
1446:
1441:
1436:
1431:
1426:
1421:
1416:
380:
353:
334:
261:
is stored in the nucleoplasm and functions in electron transport and
157:
122:
185:
and storing the structures that are used in these processes. 34% of
63:, also known as the nuclear membrane. The nucleoplasm resembles the
1031:
348:
The ionic composition of the nucleoplasm is crucial in maintaining
1741:
1646:
1636:
1609:
1604:
1533:
1516:
1411:
1406:
1401:
1396:
1386:
1381:
1376:
1371:
1366:
312:
117:
1706:
1701:
1678:
1673:
1661:
1656:
1614:
1302:
1064:
Galva, Charitha; Artigas, Pablo; Gatto, Craig (December 2012).
341:
305:, and ATP, which is involved in energy storage and transfer.
99:
The soluble, liquid portion of the nucleoplasm is called the
934:"Pyruvate kinase: Function, regulation and role in cancer"
883:
Houtkooper; Cantó, C.; Wanders, R.J.; Auwerx, J. (2010).
409:
before being delivered to the nucleoplasm as part of the
172:
of the 19th century, and the first person to discover
293:(ADP) to ATP. Importantly, the nucleoplasm contains
1689:
1589:
1559:
1472:
1341:
604:
1757:transcription factors and intracellular receptors
981:Falcón; Chen, S.; Wood, M.S.; Aris, J.P. (2010).
554:"Protein diffusion in mammalian cell cytoplasm"
325:, which controls the ionic gradient across the
1032:"Molecule of the Month: Sodium-Potassium Pump"
1314:
8:
938:Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology
1563:
1321:
1307:
1299:
1259:Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology
16:Protoplasm that permeates a cell's nucleus
1278:
1229:
1140:
1130:
1089:
1006:
957:
908:
851:
759:
749:
693:
579:
569:
1206:"Half a Century of "The Nuclear Matrix""
1190:National Human Genome Research Institute
18:
932:Israelsen; Vander Heiden, M.G. (2015).
459:
27:material of the nucleus including the
144:and was later described and drawn by
7:
727:
725:
723:
721:
671:
669:
611:. New Haven: Yale University Press.
502:
500:
498:
496:
494:
492:
490:
488:
226:(NLS). Cytosolic proteins, known as
987:Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry
301:, which plays a vital role in the
289:along with the phosphorylation of
14:
1030:Goodsell, David (October 2009).
634:Miscellaneous Botanical Works I
508:"The human cell in nucleoplasm"
430:, the cytoplasm divides during
281:, catalyzing the conversion of
1204:Pederson, Thoru (March 2000).
783:Hed, Greer (October 6, 2022).
1:
1210:Molecular Biology of the Cell
1165:"The human cell in cytoplasm"
813:. Elsevier. pp. 73–103.
224:nuclear localization sequence
1132:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009400
1044:10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2009_10
950:10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.08.004
853:10.1016/0014-5793(73)80732-X
834:Stein; Thrall, C.L. (1973).
811:Case Studies in Cell Biology
571:10.1371/journal.pone.0022962
1271:10.1101/cshperspect.a000547
648:"Strasburger, Eduard Adolf"
1816:
1691:Transition nuclear protein
1119:PLOS Computational Biology
809:Casem, Merri Lynn (2016).
695:10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.011
532:Collins English Dictionary
472:Collins English Dictionary
297:and co-enzymes, including
132:and namer of nucleoplasm,
1770:
1750:
1737:
1717:
1566:
1529:Perinucleolar compartment
999:10.1007/s11010-009-0209-z
168:, one of the most famous
751:10.3389/fphys.2020.00239
267:electron transport chain
59:. It is enclosed by the
31:labelled as nucleoplasm.
1070:Journal of Cell Science
738:Frontiers in Physiology
392:Similarity to cytoplasm
785:"What is Nucleoplasm?"
444:intermediate filaments
345:
271:adenosine triphosphate
137:
32:
1800:Nuclear substructures
607:The Birth of the Cell
448:Cytoplasmic streaming
403:endoplasmic reticulum
374:sodium-potassium pump
319:sodium-potassium pump
316:
291:adenosine diphosphate
121:
51:, the most prominent
22:
1222:10.1091/mbc.11.3.799
901:10.1210/er.2009-0026
152:presentation to the
1482:Cajal (coiled) body
1343:Envelope (membrane)
1170:Human Protein Atlas
513:Human Protein Atlas
283:phosphoenolpyruvate
255:cellular metabolism
1329:Structures of the
1185:"Nuclear Membrane"
1082:10.1242/jcs.114959
346:
317:An example of the
265:involved with the
166:Eduard Strasburger
138:
134:Eduard Strasburger
108:nuclear hyaloplasm
47:that makes up the
33:
1782:
1781:
1766:
1765:
1076:(24): 6137–6147.
889:Endocrine Reviews
820:978-0-12-801394-6
618:978-0-300-07384-3
603:Harris H (1999).
439:protein filaments
424:prokaryotic cells
411:secretory pathway
303:citric acid cycle
269:and synthesis of
195:RNA transcription
43:, is the type of
1807:
1775:nucleus diseases
1724:(Nucleoskeleton)
1564:
1323:
1316:
1309:
1300:
1293:
1292:
1282:
1255:"Nuclear Lamins"
1250:
1244:
1243:
1233:
1201:
1195:
1194:
1181:
1175:
1174:
1161:
1155:
1154:
1144:
1134:
1110:
1104:
1103:
1093:
1061:
1055:
1054:
1052:
1050:
1027:
1021:
1020:
1010:
978:
972:
971:
961:
929:
923:
922:
912:
880:
874:
873:
855:
831:
825:
824:
806:
800:
799:
797:
795:
780:
774:
773:
763:
753:
729:
716:
715:
697:
673:
664:
663:
661:
659:
644:
638:
637:
629:
623:
622:
610:
600:
594:
593:
583:
573:
549:
543:
542:
540:
538:
524:
518:
517:
504:
483:
482:
480:
478:
464:
331:nuclear envelope
94:nuclear speckles
61:nuclear envelope
39:, also known as
1815:
1814:
1810:
1809:
1808:
1806:
1805:
1804:
1785:
1784:
1783:
1778:
1762:
1746:
1733:
1713:
1685:
1585:
1555:
1468:
1346:
1337:
1335:nuclear protein
1327:
1297:
1296:
1265:(11): a000547.
1252:
1251:
1247:
1203:
1202:
1198:
1183:
1182:
1178:
1163:
1162:
1158:
1125:(2): e1009400.
1112:
1111:
1107:
1063:
1062:
1058:
1048:
1046:
1029:
1028:
1024:
993:(1–2): 99–108.
980:
979:
975:
931:
930:
926:
882:
881:
877:
833:
832:
828:
821:
808:
807:
803:
793:
791:
782:
781:
777:
731:
730:
719:
675:
674:
667:
657:
655:
646:
645:
641:
631:
630:
626:
619:
602:
601:
597:
551:
550:
546:
536:
534:
526:
525:
521:
506:
505:
486:
476:
474:
466:
465:
461:
456:
407:golgi apparatus
394:
385:plasma membrane
311:
275:Pyruvate kinase
263:redox reactions
240:DNA replication
220:
211:
199:gene regulation
189:encoded in the
182:
154:Linnean Society
116:
57:eukaryotic cell
17:
12:
11:
5:
1813:
1811:
1803:
1802:
1797:
1787:
1786:
1780:
1779:
1771:
1768:
1767:
1764:
1763:
1761:
1760:
1751:
1748:
1747:
1745:
1744:
1738:
1735:
1734:
1732:
1731:
1725:
1722:Nuclear matrix
1718:
1715:
1714:
1712:
1711:
1710:
1709:
1704:
1696:
1694:
1687:
1686:
1684:
1683:
1682:
1681:
1676:
1666:
1665:
1664:
1659:
1654:
1649:
1644:
1639:
1634:
1629:
1619:
1618:
1617:
1612:
1607:
1596:
1594:
1587:
1586:
1584:
1583:
1578:
1576:Dot (PML body)
1573:
1567:
1561:
1557:
1556:
1554:
1553:
1548:
1543:
1542:
1541:
1536:
1526:
1525:
1524:
1519:
1514:
1509:
1504:
1499:
1494:
1489:
1478:
1476:
1470:
1469:
1467:
1466:
1461:
1460:
1459:
1454:
1449:
1444:
1439:
1434:
1429:
1424:
1419:
1414:
1409:
1404:
1399:
1394:
1389:
1384:
1379:
1374:
1369:
1359:
1352:
1350:
1348:nuclear lamina
1339:
1338:
1328:
1326:
1325:
1318:
1311:
1303:
1295:
1294:
1245:
1216:(3): 799–805.
1196:
1176:
1156:
1105:
1056:
1022:
973:
924:
895:(2): 194–223.
875:
826:
819:
801:
775:
717:
688:(3): 306–383.
665:
639:
624:
617:
595:
544:
519:
484:
458:
457:
455:
452:
393:
390:
310:
307:
251:RNA polymerase
247:DNA polymerase
219:
216:
210:
207:
181:
178:
150:Robert Brown's
115:
112:
78:nuclear bodies
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1812:
1801:
1798:
1796:
1793:
1792:
1790:
1777:
1776:
1769:
1759:
1758:
1753:
1752:
1749:
1743:
1740:
1739:
1736:
1729:
1726:
1723:
1720:
1719:
1716:
1708:
1705:
1703:
1700:
1699:
1698:
1697:
1695:
1692:
1688:
1680:
1677:
1675:
1672:
1671:
1670:
1667:
1663:
1660:
1658:
1655:
1653:
1650:
1648:
1645:
1643:
1640:
1638:
1635:
1633:
1630:
1628:
1625:
1624:
1623:
1620:
1616:
1613:
1611:
1608:
1606:
1603:
1602:
1601:
1598:
1597:
1595:
1592:
1588:
1582:
1579:
1577:
1574:
1572:
1569:
1568:
1565:
1562:
1558:
1552:
1549:
1547:
1544:
1540:
1537:
1535:
1532:
1531:
1530:
1527:
1523:
1520:
1518:
1515:
1513:
1510:
1508:
1505:
1503:
1500:
1498:
1495:
1493:
1490:
1488:
1485:
1484:
1483:
1480:
1479:
1477:
1475:
1471:
1465:
1462:
1458:
1455:
1453:
1450:
1448:
1445:
1443:
1440:
1438:
1435:
1433:
1430:
1428:
1425:
1423:
1420:
1418:
1415:
1413:
1410:
1408:
1405:
1403:
1400:
1398:
1395:
1393:
1390:
1388:
1385:
1383:
1380:
1378:
1375:
1373:
1370:
1368:
1365:
1364:
1363:
1360:
1357:
1354:
1353:
1351:
1349:
1344:
1340:
1336:
1332:
1324:
1319:
1317:
1312:
1310:
1305:
1304:
1301:
1290:
1286:
1281:
1276:
1272:
1268:
1264:
1260:
1256:
1249:
1246:
1241:
1237:
1232:
1227:
1223:
1219:
1215:
1211:
1207:
1200:
1197:
1192:
1191:
1186:
1180:
1177:
1172:
1171:
1166:
1160:
1157:
1152:
1148:
1143:
1138:
1133:
1128:
1124:
1120:
1116:
1109:
1106:
1101:
1097:
1092:
1087:
1083:
1079:
1075:
1071:
1067:
1060:
1057:
1045:
1041:
1037:
1033:
1026:
1023:
1018:
1014:
1009:
1004:
1000:
996:
992:
988:
984:
977:
974:
969:
965:
960:
955:
951:
947:
943:
939:
935:
928:
925:
920:
916:
911:
906:
902:
898:
894:
890:
886:
879:
876:
871:
867:
863:
859:
854:
849:
845:
841:
837:
830:
827:
822:
816:
812:
805:
802:
790:
786:
779:
776:
771:
767:
762:
757:
752:
747:
743:
739:
735:
728:
726:
724:
722:
718:
713:
709:
705:
701:
696:
691:
687:
683:
679:
672:
670:
666:
653:
649:
643:
640:
635:
628:
625:
620:
614:
609:
608:
599:
596:
591:
587:
582:
577:
572:
567:
564:(8): e22962.
563:
559:
555:
548:
545:
533:
529:
523:
520:
515:
514:
509:
503:
501:
499:
497:
495:
493:
491:
489:
485:
473:
469:
463:
460:
453:
451:
449:
445:
440:
435:
433:
429:
428:cell division
425:
420:
419:lipid bilayer
414:
412:
408:
404:
400:
391:
389:
386:
382:
379:
378:transmembrane
375:
371:
367:
363:
359:
355:
351:
343:
340:
336:
332:
328:
327:cell membrane
324:
323:P-type ATPase
320:
315:
308:
306:
304:
300:
296:
292:
288:
284:
280:
276:
272:
268:
264:
260:
259:NAD+ synthase
256:
252:
248:
243:
241:
237:
233:
229:
225:
217:
215:
208:
206:
204:
200:
196:
192:
188:
179:
177:
175:
171:
167:
163:
159:
155:
151:
147:
143:
135:
131:
128:
124:
120:
113:
111:
109:
105:
102:
97:
95:
91:
87:
83:
79:
75:
71:
66:
62:
58:
54:
50:
46:
42:
38:
30:
26:
21:
1795:Cell anatomy
1772:
1754:
1727:
1356:Pore complex
1331:cell nucleus
1262:
1258:
1248:
1213:
1209:
1199:
1188:
1179:
1168:
1159:
1122:
1118:
1108:
1073:
1069:
1059:
1047:. Retrieved
1035:
1025:
990:
986:
976:
941:
937:
927:
892:
888:
878:
846:(1): 41–45.
843:
840:FEBS Letters
839:
829:
810:
804:
792:. Retrieved
788:
778:
741:
737:
685:
681:
656:. Retrieved
652:Universalium
651:
642:
633:
627:
606:
598:
561:
557:
547:
535:. Retrieved
531:
528:"karyolymph"
522:
511:
475:. Retrieved
471:
468:"karyoplasm"
462:
436:
415:
395:
347:
244:
232:RNA splicing
221:
212:
203:nuclear pore
191:human genome
183:
139:
107:
103:
100:
98:
86:nucleoporins
49:cell nucleus
40:
36:
34:
25:protoplasmic
1730:(Nucleosol)
1728:Nucleoplasm
1591:SMC protein
1581:Paraspeckle
1362:Nucleoporin
1049:October 30,
794:October 28,
658:October 31,
432:cytokinesis
350:homeostasis
209:Composition
176:in plants.
146:Franz Bauer
142:Leeuwenhoek
90:nucleotides
70:chromosomes
37:nucleoplasm
1789:Categories
1669:DNA repair
636:: 511–514.
537:2 December
477:2 December
454:References
366:phosphorus
299:acetyl-CoA
295:co-factors
279:glycolysis
236:DNA repair
164:scientist
101:karyolymph
72:, various
45:protoplasm
41:karyoplasm
1773:see also
1755:see also
1622:Condensin
1571:Chromatin
1474:Nucleolus
944:: 43–51.
399:ribosomes
370:magnesium
358:potassium
339:potassium
285:(PEP) to
228:importins
170:botanists
104:nucleosol
82:nucleolus
65:cytoplasm
53:organelle
29:nucleolus
1289:20826548
1240:10712500
1151:35180215
1100:23077175
1017:19618123
968:26277545
919:20007326
870:20285491
789:wisegeek
770:32308628
712:17260209
704:20144760
590:21886771
558:PLOS ONE
329:and the
287:pyruvate
218:Proteins
187:proteins
130:botanist
74:proteins
1600:Cohesin
1280:2964183
1142:8893647
1091:3585523
1036:PDB-101
1008:3618671
959:4662905
910:2852209
862:4715686
761:7145948
744:: 239.
581:3158749
362:calcium
273:(ATP).
174:mitosis
114:History
55:of the
1652:NCAPH2
1642:NCAPG2
1632:NCAPD3
1627:NCAPD2
1539:CUGBP1
1512:GEMIN7
1507:GEMIN6
1502:GEMIN5
1497:GEMIN4
1492:GEMIN2
1457:NUP214
1452:NUP210
1447:NUP205
1442:NUP188
1437:NUP160
1432:NUP155
1427:NUP153
1422:NUP133
1417:NUP107
1287:
1277:
1238:
1228:
1149:
1139:
1098:
1088:
1015:
1005:
966:
956:
917:
907:
868:
860:
817:
768:
758:
710:
702:
654:. 2010
615:
588:
578:
381:ATPase
368:, and
354:sodium
335:sodium
162:German
158:Polish
127:German
123:Polish
92:, and
80:, the
1742:LITAF
1647:NCAPH
1637:NCAPG
1610:SMC1B
1605:SMC1A
1560:Other
1551:ATXN7
1534:PTBP1
1517:DDX20
1412:NUP98
1407:NUP93
1402:NUP88
1397:NUP85
1392:NUP62
1387:NUP54
1382:NUP50
1377:NUP43
1372:NUP37
1367:NUP35
1231:14811
866:S2CID
708:S2CID
106:, or
1707:TNP2
1702:TNP1
1679:SMC6
1674:SMC5
1662:SMC4
1657:SMC2
1615:SMC3
1546:TCOF
1522:COIL
1464:AAAS
1285:PMID
1236:PMID
1147:PMID
1096:PMID
1051:2022
1013:PMID
964:PMID
915:PMID
858:PMID
815:ISBN
796:2022
766:PMID
700:PMID
682:Cell
660:2022
613:ISBN
586:PMID
539:2022
479:2022
405:and
376:, a
342:ions
337:and
321:, a
309:Ions
249:and
197:and
180:Role
35:The
23:The
1487:SMN
1275:PMC
1267:doi
1226:PMC
1218:doi
1137:PMC
1127:doi
1086:PMC
1078:doi
1074:125
1040:doi
1003:PMC
995:doi
991:333
954:PMC
946:doi
905:PMC
897:doi
848:doi
756:PMC
746:doi
690:doi
686:140
576:PMC
566:doi
1791::
1333:/
1283:.
1273:.
1261:.
1257:.
1234:.
1224:.
1214:11
1212:.
1208:.
1187:.
1167:.
1145:.
1135:.
1123:18
1121:.
1117:.
1094:.
1084:.
1072:.
1068:.
1038:.
1034:.
1011:.
1001:.
989:.
985:.
962:.
952:.
942:43
940:.
936:.
913:.
903:.
893:31
891:.
887:.
864:.
856:.
844:32
842:.
838:.
787:.
764:.
754:.
742:11
740:.
736:.
720:^
706:.
698:.
684:.
680:.
668:^
650:.
584:.
574:.
560:.
556:.
530:.
510:.
487:^
470:.
364:,
360:,
356:,
257:.
238:,
234:,
110:.
96:.
88:,
84:,
76:,
1693::
1593::
1358::
1345:/
1322:e
1315:t
1308:v
1291:.
1269::
1263:2
1242:.
1220::
1193:.
1173:.
1153:.
1129::
1102:.
1080::
1053:.
1042::
1019:.
997::
970:.
948::
921:.
899::
872:.
850::
823:.
798:.
772:.
748::
714:.
692::
662:.
621:.
592:.
568::
562:6
541:.
516:.
481:.
344:.
160:-
136:.
125:-
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.