564:
nucleoside-diphosphate kinase, serine/threonine-specific protein kinase, geranyl and farnesyl pyrophosphate kinase, histidine protein kinase, and 3'-5' exonuclease activities. Its processes are involved with cell proliferation, differentiation and development, and gene expression in human cells. It is also part of the neural development process, which includes neural patterning and cell fate determination. Furthermore, NDPK is involved with the signal transduction processes and G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis as it transfers a phosphate group onto the G β-subunits and convert GDP to GTP. This increase in GTP concentration near G protein α-subunits causes activation of G protein α-subunits for G-protein signaling. In addition to signaling, NDPK is involved in controlling K+ channels, cell secretion, and cellular energy production.
507:((p)ppGpp) molecule. (p)ppGpp biosynthesis is a part of the purine metabolism pathway and coordinates a series of cellular activities in response to nutritional abundances. Synthesis of (p)ppGpp is triggered by carbon starvation, or the lack of carbon in the cell's environment, and causes the protein SpoT to activate. SpoT works in conjunction with NDPK and both serve as essential enzymes in the (p)ppGpp biosynthesis cycle. NDPK synthesizes the formation of GDP from GTP via dephosphorylation.
573:
responses in plants. Type II NDPK is concentrated in the chloroplast and it is believed to be involved in the photosynthesis process and the oxidative stress management, but its function is not yet known clearly. Type III NDPK targets both mitochondria and chloroplast, and it is mainly involved in energy metabolism. The localization and exact function of the type IV NDPK is not yet well known and needs further investigations. In addition, NDPK is associated with H
346:
3238:
629:. When Nme2 gene products were over-produced in gastric cancer cells, there was a decrease in proliferation, migration, and invasion of such cancer cells. The cell cultures revealed that Nme2 impacts gastric cancer cells, but the question still remains about what regulates Nme2 activities among various cancer types. Nme1 was found in great number in poorly metastatic sublines of
20:
594:
suppressor protein and its gene Nm23 was less activated in metastatic cells. In a different experiment, human Nm23 was cultured with cancer cells and showed inhibition of metastasis. The level of NM23 protein was inversely proportional to the metastatic potential for human solid tumors. However, other tumor types such as ovarian cancers,
253:. Many NDP serve as acceptor while NTP are donors of phosphate group. The general reaction via ping-pong mechanism is as follows: XDP + YTP ←→ XTP + YDP (X and Y each represent different nitrogenous base). NDPK activities maintain an equilibrium between the concentrations of different nucleoside triphosphates such as, for example, when
427:. To be more specific, NDPK supports the production of nucleotides in high-energy and low-stress cellular states. However, this can only happen when AMPK is inactivated because low-stress cellular states of ATP triggers the activation of AMPK, which eventually decreases NDPK activity by phosphorylating serine residues.
463:. Nucleoside diphosphate kinase activity involves the transfer of the γ-phosphate of nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) to nucleoside diphosphate (NDP), where N1 and N2 can be ribo- or deoxyribonucleosides. This is done via a high energy phosphohistidine intermediate. Besides involvement in the synthesis of
633:
cells. Also, the transfection of Nme1 into a highly metastatic melanoma line significantly reduced metastasis. This theory has been tested with mice as well; the Nme1-deficient mice formed greater lung metastases than wild type mice, showing that this gene has suppressing activity. Invasion of cancer
624:
There was a lot of debate on whether NM23 gene is responsible for suppressing or activating metastasis. The two contradicting sides on this subject remained ambiguous and undefined throughout the course of NDPK studies. However, recent experiments began to show evidence for NM23 being a suppressor of
593:
code for the proteins NDPKs, which are separated into two groups. The first group encodes proteins with NDPK functions. The other group genes code for other various proteins that display low or no NDPK activities. In the first group, one of the genes named NM23 was identified as the first metastasis
572:
The biochemical reactions catalyzed by NDP kinase in plants are analogous to activities described in humans as autophosphorylation activity takes place from ATP and GTP. In addition to this, plants have four types of NDPK isoforms. Cytosolic type I NDPK is involved in metabolism, growth, and stress
554:
There are at least four enzymatically active isoforms of NDPK in humans: NDPK-A, NDPK-B, NDPK-C and NDPK-D. All four isoforms have very similar structures and can combine in any form to become functional NDPK hexamers. NDPK is suggested to participate in transmembrane signaling in eukaryotic cells.
611:
functions. Nme2 gene is known to form a complex with the beta subunit of the heterotrimetric G protein in heart cells and regulates the contractility of heart. There are two functions of Nme2 that allow for such regulation; one is the histidine kinase activity, which is the phosphorylation of the
563:
In
Eukaryotic systems, the role of the NDK is to synthesize nucleoside triphosphates other than ATP. The ATP gamma phosphate is transferred to the NDP beta phosphate via a ping-pong mechanism, using a phosphorylated active-site intermediate, and synthesize products such as UTP. NDK possesses
404:
activated from receptor binding; once ATP donates a phosphate group via activity of NDPK, GTP is consecutively bound. Increased activity of membrane-associated NDPK yields cAMP synthesis. NDPK controls K+ channels, G proteins, cell secretion, cellular energy production, and UTP synthesis.
325:
residue by transferring terminal phosphate group (γ-phosphate) from ATP to NDP β-phosphate in order to produce a NTP, and NDPK catalyzes such reversible reactions. NTP phosphorylates a histidine, which in turn phosphorylates NDP. NDPK are involved in the synthesis of
515:
While the biomolecular mechanism by which the Nm23 gene works in cells is currently unknown, like in most prokaryotes, nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK) expression levels determine cell growth and differentiation. Normally, the Nm23 gene (NME) is involved in
483:
418:
NDPK usually consumes ATP, the most abundant cellular nucleotide, and stores the nucleotides. However, consumption of ATP would definitely influence the cellular energy balance, which brings upon the regulation of AMP-activated protein kinase
646:
events, EMT hallmarks, and other transcriptional programs that have been linked to the Nme1 proteins. These proteins go about interrupting metastasis by binding metastasis-promoting proteins. The Nme1 proteins bind to viral proteins,
616:. The depletion of Nme2/caveolin interaction exhibited a decreased rate of cardiac contractility. Furthermore, more studies with zebra fish revealed that the NDPK depletion has a detrimental effect on heart functioning.
2765:
598:
and hematological malignancies displayed upregulated NM23 levels in patient samples. Therefore, understanding the biological basis of the Nm23 gene family is necessary to have a firm knowledge of its diverse results.
1405:"Nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDPK, NM23, AWD): recent regulatory advances in endocytosis, metastasis, psoriasis, insulin release, fetal erythroid lineage and heart failure; translational medicine exemplified"
2775:
1354:"Progress on Nme (NDP kinase/Nm23/Awd) gene family-related functions derived from animal model systems: studies on development, cardiovascular disease, and cancer metastasis exemplified"
2770:
1647:
1556:
2890:
2868:
423:). AMPK acts as the energy sensor and regulates ATP pathways by turning the generating pathways or not. Because of such activity, AMPK could directly inhibit NDPK through
1113:
de la Rosa A, Williams RL, Steeg PS (January 1995). "Nm23/nucleoside diphosphate kinase: toward a structural and biochemical understanding of its biological functions".
313:
as substrates or donors. Therefore, NDPK is the source of RNA and DNA precursors, except ATP. NDPK utilize specific enzyme kinetics for multi-substrate reaction, namely
2686:
174:
1756:
193:
1292:"NDP kinase 2 interacts with two oxidative stress-activated MAPKs to regulate cellular redox state and enhances multiple stress tolerance in transgenic plants"
2796:
1632:
1549:
2691:
289:
NDPK are homohexameric proteins made up of monomers approximately 152 amino acids long with a theoretical weight of 17.17KDa. The complex is found in
1722:
2858:
1642:
1865:
1542:
690:
635:
2497:
731:
1290:
Moon H, Lee B, Choi G, Shin D, Prasad DT, Lee O, Kwak SS, Kim DH, Nam J, Bahk J, Hong JC, Lee SY, Cho MJ, Lim CO, Yun DJ (January 2003).
2631:
903:"Increased activity of membrane-associated nucleoside diphosphate kinase and inhibition of cAMP synthesis in failing human myocardium"
2957:
2201:
1995:
1761:
1097:
1002:
885:
520:
suppression in humans. In prokaryotes, the Nm23 gene is involved in normal cell development and differentiation. Highly conserved
2342:
1869:
1622:
186:
1902:
1835:
1782:
270:
1840:
1652:
1627:
397:
129:
3113:
153:
2915:
2910:
2470:
1637:
3228:
2780:
2668:
2636:
2621:
1860:
420:
353:
Behind this apparently simple reaction is a multistep mechanism. The key steps of transphosphorylation are as follows:
467:
nucleotides, prokaryotic NDPK is also involved in several metabolism cycles. NDPK has also been discovered to act as a
2303:
475:, NDPK expression levels are involved in the cell growth, development and differentiation of the organism, especially
384:
NDPK's roles in these NTPs differ; generally, kinases bring in NTPs for nucleic acid synthesis. CTP is provided for
3098:
3214:
3201:
3188:
3175:
3162:
3149:
3136:
2901:
2879:
2854:
2829:
2749:
2357:
2317:
2262:
2239:
2211:
2179:
2045:
1676:
3108:
2132:
1062:"spoT - Bifunctional (p)ppGpp synthase/hydrolase SpoT - Escherichia coli (strain K12) - spoT gene & protein"
3062:
3005:
2366:
2347:
2278:
2012:
1942:
1526:
1520:
670:
538:
have been closed and characterized as a nucleoside diphosphate kinase (ndk gene) and seems to be essential for
504:
147:
40:
3010:
2224:
1962:
1706:
1665:
675:
471:, which involves a reversible histidine phosphorylation as a well-known regulatory signal. However, in most
327:
250:
246:
134:
1534:
2678:
2451:
2361:
1681:
451:
331:
262:
254:
1516:
802:
Dumas C, Lascu I, Moréra S, Glaser P, Fourme R, Wallet V, Lacombe ML, Véron M, Janin J (September 1992).
495:
In the (p)ppGpp biosynthesis cycle, NDPK serves an important role. When there is an absence of a charged
376:
Each step is part of a reversible process, such that the multistep equilibrium is of the following form.
3031:
2950:
2532:
2487:
2189:
2174:
2110:
2090:
1988:
1916:
1811:
335:
198:
3103:
122:
1973:
651:, and other metastasis-promoting factors. The binding may be indirect by using the signaling complex.
23:
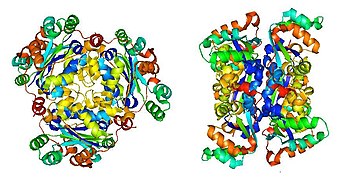
Crystal structure of NDPK in human, viewed from front and side, respectively: X-ray diffraction, 2.2 Å
2446:
2441:
2321:
2184:
2164:
2073:
1957:
1468:
1306:
695:
626:
339:
57:
1018:
Attwood PV, Wieland T (February 2015). "Nucleoside diphosphate kinase as protein histidine kinase".
3067:
2709:
2701:
2482:
2149:
2085:
2049:
1934:
1907:
1777:
393:
314:
310:
266:
52:
150:
3000:
2572:
2510:
2461:
2196:
2023:
1748:
1607:
1571:
1272:
1181:
1138:
1043:
685:
546:
development, nucleoside diphosphate kinase activity has also been shown to drastically decrease.
526:
521:
455:
74:
1457:"NME2 reduces proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells to limit metastasis"
612:
channels to regulate what goes through and the other is a scaffold function of the formation of
3263:
2587:
2577:
2567:
2492:
2476:
2435:
2421:
2416:
2154:
2117:
1787:
1717:
1589:
1496:
1434:
1385:
1334:
1264:
1222:
1173:
1130:
1093:
1035:
998:
973:
924:
881:
833:
727:
723:
447:
258:
141:
944:"AMPK directly inhibits NDPK through a phosphoserine switch to maintain cellular homeostasis"
625:
metastasis. Nme2 was tagged as an anti-metastasis gene, using the tissue chip technology and
3258:
3046:
3041:
3015:
2943:
2920:
2582:
2562:
2504:
2400:
2298:
2283:
2229:
2127:
2122:
1981:
1792:
1486:
1476:
1424:
1416:
1375:
1365:
1324:
1314:
1256:
1212:
1165:
1122:
1027:
963:
955:
914:
823:
815:
680:
590:
468:
441:
3093:
3077:
2990:
2843:
2833:
2655:
2626:
2252:
2159:
2144:
634:
occurs due to changes in cell adhesion and it is caused by gene expression changes in the
424:
385:
318:
278:
110:
852:"NME1 - Nucleoside diphosphate kinase A - Homo sapiens (Human) - NME1 gene & protein"
400:-mediated signal transduction, NDPK is responsible for phosphorylating GDP released from
1472:
1380:
1353:
1310:
86:
3242:
3131:
3072:
2811:
2650:
2557:
2549:
2426:
2389:
1952:
1882:
1845:
1491:
1456:
1429:
1404:
1217:
1200:
968:
943:
819:
608:
389:
169:
45:
1329:
919:
902:
828:
803:
748:"PDB 1jxv structure summary ‹ Protein Data Bank in Europe (PDBe) ‹ EMBL-EBI"
486:
NDPK is the enzyme triggering the dephosphorylation of GTP to GDP in the ppGpp cycle.
3252:
3036:
2995:
2080:
1797:
1732:
1691:
1611:
1247:
Dorion S, Rivoal J (February 2015). "Clues to the functions of plant NDPK isoforms".
716:
639:
595:
531:
369:
Phosphoryl group is transferred from NDPK-His to NDP2 or dNDP2, creating a bound NTP2
265:(ATP). Other activities include cell proliferation, differentiation and development,
1455:
Liu YF, Yang A, Liu W, Wang C, Wang M, Zhang L, Wang D, Dong JF, Li M (2015-01-01).
1185:
1156:
Otero AS (June 2000). "NM23/nucleoside diphosphate kinase and signal transduction".
1142:
1047:
2985:
2169:
2139:
2068:
1276:
994:
From
Metabolite, to Metabolism, to Metabolon: Current Topics in Cellular Regulation
942:
Onyenwoke RU, Forsberg LJ, Liu L, Williams T, Alzate O, Brenman JE (January 2012).
496:
460:
439:. It has been reported in a number of pathogens. NDPK function has been studied in
345:
290:
301:
NDPK are found in all cells, displaying not much specificity towards the types of
1481:
1291:
1087:
992:
3209:
3144:
2980:
2735:
2725:
2326:
2063:
2004:
777:
643:
472:
306:
274:
3237:
1299:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
482:
2537:
2380:
2293:
2058:
2008:
1830:
1576:
1567:
1420:
1370:
1260:
1169:
1031:
665:
660:
517:
464:
302:
242:
19:
901:
Lutz S, Mura R, Baltus D, Movsesian M, Kübler W, Niroomand F (January 2001).
3183:
3157:
2816:
2729:
2266:
2032:
959:
747:
401:
322:
1500:
1438:
1389:
1338:
1319:
1268:
1226:
1177:
1126:
1039:
977:
928:
1134:
837:
2663:
2243:
1061:
851:
648:
630:
500:
476:
436:
360:
A phosphoryl group from NTP1 is transferred to His in active site of NDPK
238:
2614:
2599:
2215:
1529:
613:
117:
98:
3196:
2966:
2592:
2027:
1579:
234:
181:
93:
81:
69:
524:
of the Nm23 gene have been found in prokaryotes, more specifically,
3170:
2609:
2604:
2456:
1201:"G proteins: more than transducers of receptor-generated signals?"
2766:
CDP-diacylglycerol—glycerol-3-phosphate 3-phosphatidyltransferase
2520:
2515:
2411:
2406:
2105:
2100:
2095:
1920:
1911:
581:-mediated mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in plants.
105:
2939:
1977:
1538:
366:
Initially bound NDP1 is released from NDPK bringing in new NDP2
503:, the ribosome will stall and trigger the synthesis of the
2935:
638:(EMT). Surprisingly, there are many adhesion molecules,
1648:
Phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide synthase
392:
synthesis while GTP is used for protein elongation and
607:
Nme2, one of the NDPK genes, has been associated with
3226:
2776:
CDP-diacylglycerol—inositol 3-phosphatidyltransferase
1352:
Hsu T, Steeg PS, Zollo M, Wieland T (February 2015).
241:
the exchange of terminal phosphate between different
2781:
CDP-diacylglycerol—choline O-phosphatidyltransferase
3122:
3086:
3055:
3024:
2973:
2900:
2878:
2853:
2828:
2809:
2789:
2771:
CDP-diacylglycerol—serine O-phosphatidyltransferase
2758:
2748:
2718:
2700:
2677:
2649:
2548:
2388:
2379:
2356:
2316:
2261:
2238:
2210:
2044:
2020:
1933:
1895:
1819:
1810:
1770:
1747:
1702:
1661:
1604:
1597:
1588:
192:
180:
168:
163:
140:
128:
116:
104:
92:
80:
68:
63:
51:
39:
34:
29:
804:"X-ray structure of nucleoside diphosphate kinase"
715:
380:NDPK + NTP ↔ NDPK~NTP ↔ NDPK-P~NDP ↔ NDPK-P + NDP
1086:Lengeler J, Drews G, Schlegel H (10 July 2009).
1757:Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase
1358:Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology
1249:Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology
1020:Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology
2951:
1989:
1550:
8:
2797:N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate transferase
2687:UTP—glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase
1633:Phosphoribosylglycinamide formyltransferase
778:"Nucleoside diphosphate kinase (IPR001564)"
620:Nme1 and Nme2 as a suppressor of metastasis
2958:
2944:
2936:
2825:
2755:
2385:
2376:
2041:
1996:
1982:
1974:
1823:
1816:
1601:
1594:
1557:
1543:
1535:
160:
2891:serine/threonine-specific protein kinases
2869:serine/threonine-specific protein kinases
2692:Galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase
1519:at the U.S. National Library of Medicine
1490:
1480:
1428:
1379:
1369:
1328:
1318:
1216:
1158:Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes
967:
918:
827:
1643:Phosphoribosylaminoimidazole carboxylase
481:
435:In most prokaryotes, the NDPK enzyme is
344:
249:(NTP) in a reversible manner to produce
18:
3233:
714:Berg JM, Tymoczko JL, Stryer L (2002).
706:
293:and in the soluble cytoplasm of cells.
1199:Engelhardt S, Rochais F (April 2007).
691:Thymidine kinase in clinical chemistry
459:. Prokaryotic NDPK forms a functional
26:
1450:
1448:
1403:Mehta A, Orchard S (September 2009).
1242:
1240:
1238:
1236:
534:soil bacteria. Homologues of Nm23 in
342:(UTP), thymidine triphosphate (TTP).
7:
1866:Orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase
991:Stadtman ER, Chock PB (2014-06-28).
880:. UK: Wiley Blackwell. p. 110.
772:
770:
768:
363:Phosphoenzyme intermediate is formed
349:Ping-pong mechanism utilized by NDPK
1409:Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry
878:Metabolism at a Glance, 4th edition
722:. WH Freeman and Company. pp.
317:. A ping-pong mechanism integrates
305:bases and are capable of accepting
1218:10.1161/01.RES.0000266971.15127.e8
820:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05397.x
14:
2202:Glucose-1,6-bisphosphate synthase
1762:Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase
636:epithelial-mesenchymal transition
3236:
2343:Ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase
1870:Uridine monophosphate synthetase
1623:Ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase
1903:Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase
1836:Carbamoyl phosphate synthase II
1783:Purine nucleoside phosphorylase
1841:Aspartate carbamoyltransferase
1628:Amidophosphoribosyltransferase
211:Nucleoside-diphosphate kinases
1:
2916:Protein-histidine tele-kinase
2911:Protein-histidine pros-kinase
2790:Glycosyl-1-phosphotransferase
1948:Nucleoside-diphosphate kinase
1638:AIR synthetase (FGAM cyclase)
1517:Nucleoside-Diphosphate+Kinase
948:Molecular Biology of the Cell
920:10.1016/S0008-6363(00)00222-4
30:Nucleoside-diphosphate kinase
2622:RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
1861:Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
1482:10.1371/journal.pone.0115968
2529:RNA-directed DNA polymerase
2397:DNA-directed DNA polymerase
3280:
2882:: protein-dual-specificity
1089:Biology of the Prokaryotes
454:, Microccocus luteus, and
372:NDPK releases the new NTP2
271:G protein-coupled receptor
231:nucleoside diphosphokinase
3114:Michaelis–Menten kinetics
1878:
1856:
1826:
1677:Adenylosuccinate synthase
1421:10.1007/s11010-009-0114-5
1371:10.1007/s00210-014-1079-9
1261:10.1007/s00210-014-1009-x
1092:. John Wiley & Sons.
1032:10.1007/s00210-014-1003-3
259:citric acid (Krebs) cycle
159:
3006:Diffusion-limited enzyme
2859:protein-serine/threonine
2759:Phosphatidyltransferases
2348:Thiamine diphosphokinase
1943:Ribonucleotide reductase
1521:Medical Subject Headings
671:Nucleoside monophosphate
585:Diseases related to NDPK
505:guanosine pentaphosphate
469:protein histidine kinase
328:nucleoside triphosphates
251:nucleotide triphosphates
1963:Dihydrofolate reductase
1170:10.1023/A:1005589029959
960:10.1091/mbc.E11-08-0699
907:Cardiovascular Research
676:Nucleoside triphosphate
243:nucleoside diphosphates
2679:Nucleotidyltransferase
2362:nucleotidyltransferase
2289:Nucleoside-diphosphate
1682:Adenylosuccinate lyase
1320:10.1073/pnas.252641899
1127:10.1002/bies.950170111
642:, signaling pathways,
603:Cardiovascular disease
487:
452:Salmonella typhimurium
350:
332:guanosine triphosphate
263:adenosine triphosphate
257:(GTP) produced in the
255:guanosine triphosphate
24:
3099:Eadie–Hofstee diagram
3032:Allosteric regulation
2533:Reverse transcriptase
1917:Beta-ureidopropionase
1812:Pyrimidine metabolism
1572:amino acid metabolism
485:
348:
336:cytidine triphosphate
22:
3109:Lineweaver–Burk plot
2322:diphosphotransferase
2304:Thiamine-diphosphate
2011:-containing groups (
1958:Thymidylate synthase
1935:Deoxyribonucleotides
1205:Circulation Research
876:Salway, J.G (2017).
696:Thymidylate synthase
627:immunohistochemistry
357:NDPK binds to a NTP1
340:uridine triphosphate
311:deoxyribonucleotides
2904:: protein-histidine
2822:; protein acceptor)
2710:mRNA capping enzyme
2702:Guanylyltransferase
1908:Dihydropyrimidinase
1778:Adenosine deaminase
1473:2015PLoSO..1015968L
1311:2003PNAS..100..358M
499:in the A site of a
491:(p)ppGpp metabolism
431:Prokaryotic systems
394:signal transduction
315:ping-pong mechanism
267:signal transduction
3068:Enzyme superfamily
3001:Enzyme promiscuity
2180:Phosphoinositide 3
2024:phosphotransferase
1749:Nucleotide salvage
718:Biochemistry - 5th
686:Thymidylate kinase
550:Eukaryotic systems
527:Myxococcus xanthus
511:Nm23 gene function
488:
456:Myxococcus xanthus
414:Inhibition by AMPK
351:
227:nucleotide kinases
25:
3224:
3223:
2933:
2932:
2929:
2928:
2805:
2804:
2744:
2743:
2645:
2644:
2558:Template-directed
2312:
2311:
2279:Phosphomevalonate
1971:
1970:
1929:
1928:
1891:
1890:
1806:
1805:
1788:Guanine deaminase
1743:
1742:
1718:IMP dehydrogenase
1590:Purine metabolism
733:978-0-7167-4684-3
448:Bacillus subtilis
208:
207:
204:
203:
123:metabolic pathway
3271:
3241:
3240:
3232:
3104:Hanes–Woolf plot
3047:Enzyme activator
3042:Enzyme inhibitor
3016:Enzyme catalysis
2960:
2953:
2946:
2937:
2921:Histidine kinase
2844:tyrosine kinases
2834:protein-tyrosine
2826:
2756:
2563:RNA polymerase I
2386:
2377:
2230:Aspartate kinase
2225:Phosphoglycerate
2042:
1998:
1991:
1984:
1975:
1824:
1817:
1793:Xanthine oxidase
1711:
1670:
1616:
1602:
1595:
1559:
1552:
1545:
1536:
1505:
1504:
1494:
1484:
1452:
1443:
1442:
1432:
1400:
1394:
1393:
1383:
1373:
1349:
1343:
1342:
1332:
1322:
1296:
1287:
1281:
1280:
1244:
1231:
1230:
1220:
1196:
1190:
1189:
1153:
1147:
1146:
1110:
1104:
1103:
1083:
1077:
1076:
1074:
1072:
1058:
1052:
1051:
1015:
1009:
1008:
988:
982:
981:
971:
939:
933:
932:
922:
898:
892:
891:
873:
867:
866:
864:
862:
848:
842:
841:
831:
808:The EMBO Journal
799:
793:
792:
790:
788:
774:
763:
762:
760:
758:
744:
738:
737:
721:
711:
681:Thymidine kinase
640:motility factors
591:paralogous genes
542:growth. During
442:Escherichia coli
261:is converted to
161:
27:
16:Class of enzymes
3279:
3278:
3274:
3273:
3272:
3270:
3269:
3268:
3249:
3248:
3247:
3235:
3227:
3225:
3220:
3132:Oxidoreductases
3118:
3094:Enzyme kinetics
3082:
3078:List of enzymes
3051:
3020:
2991:Catalytic triad
2969:
2964:
2934:
2925:
2896:
2874:
2849:
2820:
2814:
2810:2.7.10-2.7.13:
2801:
2785:
2752:: miscellaneous
2740:
2714:
2696:
2673:
2656:exoribonuclease
2653:
2641:
2627:Polyadenylation
2544:
2370:
2364:
2352:
2334:
2330:
2324:
2308:
2270:
2257:
2234:
2206:
2036:
2030:
2022:
2016:
2002:
1972:
1967:
1925:
1887:
1874:
1852:
1802:
1766:
1739:
1703:
1698:
1662:
1657:
1605:
1584:
1563:
1513:
1508:
1467:(2): e0115968.
1454:
1453:
1446:
1402:
1401:
1397:
1351:
1350:
1346:
1294:
1289:
1288:
1284:
1246:
1245:
1234:
1198:
1197:
1193:
1155:
1154:
1150:
1112:
1111:
1107:
1100:
1085:
1084:
1080:
1070:
1068:
1066:www.uniprot.org
1060:
1059:
1055:
1017:
1016:
1012:
1005:
990:
989:
985:
941:
940:
936:
900:
899:
895:
888:
875:
874:
870:
860:
858:
856:www.uniprot.org
850:
849:
845:
801:
800:
796:
786:
784:
776:
775:
766:
756:
754:
746:
745:
741:
734:
713:
712:
708:
704:
657:
622:
605:
587:
580:
576:
570:
561:
552:
513:
493:
433:
425:phosphorylation
416:
411:
386:lipid synthesis
330:(NTP), such as
319:phosphorylation
299:
287:
279:gene expression
17:
12:
11:
5:
3277:
3275:
3267:
3266:
3261:
3251:
3250:
3246:
3245:
3222:
3221:
3219:
3218:
3205:
3192:
3179:
3166:
3153:
3140:
3126:
3124:
3120:
3119:
3117:
3116:
3111:
3106:
3101:
3096:
3090:
3088:
3084:
3083:
3081:
3080:
3075:
3070:
3065:
3059:
3057:
3056:Classification
3053:
3052:
3050:
3049:
3044:
3039:
3034:
3028:
3026:
3022:
3021:
3019:
3018:
3013:
3008:
3003:
2998:
2993:
2988:
2983:
2977:
2975:
2971:
2970:
2965:
2963:
2962:
2955:
2948:
2940:
2931:
2930:
2927:
2926:
2924:
2923:
2918:
2913:
2907:
2905:
2898:
2897:
2895:
2894:
2885:
2883:
2876:
2875:
2873:
2872:
2863:
2861:
2851:
2850:
2848:
2847:
2838:
2836:
2823:
2818:
2812:protein kinase
2807:
2806:
2803:
2802:
2800:
2799:
2793:
2791:
2787:
2786:
2784:
2783:
2778:
2773:
2768:
2762:
2760:
2753:
2746:
2745:
2742:
2741:
2739:
2738:
2733:
2722:
2720:
2716:
2715:
2713:
2712:
2706:
2704:
2698:
2697:
2695:
2694:
2689:
2683:
2681:
2675:
2674:
2672:
2671:
2666:
2660:
2658:
2651:Phosphorolytic
2647:
2646:
2643:
2642:
2640:
2639:
2634:
2629:
2624:
2619:
2618:
2617:
2612:
2607:
2597:
2596:
2595:
2585:
2580:
2575:
2570:
2565:
2560:
2554:
2552:
2550:RNA polymerase
2546:
2545:
2543:
2542:
2541:
2540:
2530:
2526:
2525:
2524:
2523:
2518:
2513:
2502:
2501:
2500:
2495:
2490:
2485:
2474:
2468:
2467:
2466:
2459:
2454:
2449:
2444:
2433:
2432:
2431:
2424:
2419:
2414:
2409:
2398:
2394:
2392:
2390:DNA polymerase
2383:
2374:
2368:
2354:
2353:
2351:
2350:
2345:
2339:
2337:
2332:
2328:
2314:
2313:
2310:
2309:
2307:
2306:
2301:
2296:
2291:
2286:
2281:
2275:
2273:
2268:
2259:
2258:
2256:
2255:
2249:
2247:
2236:
2235:
2233:
2232:
2227:
2221:
2219:
2208:
2207:
2205:
2204:
2199:
2194:
2193:
2192:
2187:
2177:
2175:Diacylglycerol
2172:
2167:
2162:
2157:
2152:
2147:
2142:
2137:
2136:
2135:
2125:
2120:
2115:
2114:
2113:
2108:
2103:
2098:
2093:
2086:Phosphofructo-
2083:
2078:
2077:
2076:
2066:
2061:
2055:
2053:
2039:
2034:
2018:
2017:
2003:
2001:
2000:
1993:
1986:
1978:
1969:
1968:
1966:
1965:
1960:
1955:
1953:DCMP deaminase
1950:
1945:
1939:
1937:
1931:
1930:
1927:
1926:
1924:
1923:
1914:
1905:
1899:
1897:
1893:
1892:
1889:
1888:
1886:
1885:
1883:CTP synthetase
1879:
1876:
1875:
1873:
1872:
1863:
1857:
1854:
1853:
1851:
1850:
1849:
1848:
1846:Dihydroorotase
1843:
1838:
1827:
1821:
1814:
1808:
1807:
1804:
1803:
1801:
1800:
1795:
1790:
1785:
1780:
1774:
1772:
1768:
1767:
1765:
1764:
1759:
1753:
1751:
1745:
1744:
1741:
1740:
1738:
1737:
1736:
1735:
1725:
1720:
1714:
1712:
1700:
1699:
1697:
1696:
1695:
1694:
1684:
1679:
1673:
1671:
1659:
1658:
1656:
1655:
1650:
1645:
1640:
1635:
1630:
1625:
1619:
1617:
1599:
1592:
1586:
1585:
1583:
1582:
1574:
1564:
1562:
1561:
1554:
1547:
1539:
1533:
1532:
1524:
1512:
1511:External links
1509:
1507:
1506:
1444:
1395:
1344:
1282:
1232:
1211:(8): 1109–11.
1191:
1148:
1105:
1098:
1078:
1053:
1010:
1003:
983:
934:
893:
886:
868:
843:
794:
764:
739:
732:
705:
703:
700:
699:
698:
693:
688:
683:
678:
673:
668:
663:
656:
653:
621:
618:
609:cardiovascular
604:
601:
586:
583:
578:
574:
569:
566:
560:
557:
551:
548:
512:
509:
492:
489:
432:
429:
415:
412:
410:
407:
390:polysaccharide
382:
381:
374:
373:
370:
367:
364:
361:
358:
298:
295:
286:
283:
206:
205:
202:
201:
196:
190:
189:
184:
178:
177:
172:
166:
165:
157:
156:
145:
138:
137:
132:
126:
125:
120:
114:
113:
108:
102:
101:
96:
90:
89:
84:
78:
77:
72:
66:
65:
61:
60:
55:
49:
48:
43:
37:
36:
32:
31:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3276:
3265:
3262:
3260:
3257:
3256:
3254:
3244:
3239:
3234:
3230:
3216:
3212:
3211:
3206:
3203:
3199:
3198:
3193:
3190:
3186:
3185:
3180:
3177:
3173:
3172:
3167:
3164:
3160:
3159:
3154:
3151:
3147:
3146:
3141:
3138:
3134:
3133:
3128:
3127:
3125:
3121:
3115:
3112:
3110:
3107:
3105:
3102:
3100:
3097:
3095:
3092:
3091:
3089:
3085:
3079:
3076:
3074:
3073:Enzyme family
3071:
3069:
3066:
3064:
3061:
3060:
3058:
3054:
3048:
3045:
3043:
3040:
3038:
3037:Cooperativity
3035:
3033:
3030:
3029:
3027:
3023:
3017:
3014:
3012:
3009:
3007:
3004:
3002:
2999:
2997:
2996:Oxyanion hole
2994:
2992:
2989:
2987:
2984:
2982:
2979:
2978:
2976:
2972:
2968:
2961:
2956:
2954:
2949:
2947:
2942:
2941:
2938:
2922:
2919:
2917:
2914:
2912:
2909:
2908:
2906:
2903:
2899:
2893:
2892:
2887:
2886:
2884:
2881:
2877:
2871:
2870:
2865:
2864:
2862:
2860:
2856:
2852:
2846:
2845:
2840:
2839:
2837:
2835:
2831:
2827:
2824:
2821:
2813:
2808:
2798:
2795:
2794:
2792:
2788:
2782:
2779:
2777:
2774:
2772:
2769:
2767:
2764:
2763:
2761:
2757:
2754:
2751:
2747:
2737:
2734:
2731:
2727:
2724:
2723:
2721:
2717:
2711:
2708:
2707:
2705:
2703:
2699:
2693:
2690:
2688:
2685:
2684:
2682:
2680:
2676:
2670:
2667:
2665:
2662:
2661:
2659:
2657:
2652:
2648:
2638:
2635:
2633:
2630:
2628:
2625:
2623:
2620:
2616:
2613:
2611:
2608:
2606:
2603:
2602:
2601:
2598:
2594:
2591:
2590:
2589:
2586:
2584:
2581:
2579:
2576:
2574:
2571:
2569:
2566:
2564:
2561:
2559:
2556:
2555:
2553:
2551:
2547:
2539:
2536:
2535:
2534:
2531:
2528:
2527:
2522:
2519:
2517:
2514:
2512:
2509:
2508:
2506:
2503:
2499:
2496:
2494:
2491:
2489:
2486:
2484:
2481:
2480:
2478:
2475:
2472:
2469:
2465:
2464:
2460:
2458:
2455:
2453:
2450:
2448:
2445:
2443:
2440:
2439:
2437:
2434:
2430:
2429:
2425:
2423:
2420:
2418:
2415:
2413:
2410:
2408:
2405:
2404:
2402:
2399:
2396:
2395:
2393:
2391:
2387:
2384:
2382:
2378:
2375:
2372:
2363:
2359:
2355:
2349:
2346:
2344:
2341:
2340:
2338:
2335:
2323:
2319:
2315:
2305:
2302:
2300:
2297:
2295:
2292:
2290:
2287:
2285:
2282:
2280:
2277:
2276:
2274:
2271:
2264:
2260:
2254:
2251:
2250:
2248:
2245:
2241:
2237:
2231:
2228:
2226:
2223:
2222:
2220:
2217:
2213:
2209:
2203:
2200:
2198:
2195:
2191:
2190:Class II PI 3
2188:
2186:
2183:
2182:
2181:
2178:
2176:
2173:
2171:
2168:
2166:
2165:Deoxycytidine
2163:
2161:
2158:
2156:
2153:
2151:
2148:
2146:
2143:
2141:
2138:
2134:
2133:ADP-thymidine
2131:
2130:
2129:
2126:
2124:
2121:
2119:
2116:
2112:
2109:
2107:
2104:
2102:
2099:
2097:
2094:
2092:
2089:
2088:
2087:
2084:
2082:
2079:
2075:
2072:
2071:
2070:
2067:
2065:
2062:
2060:
2057:
2056:
2054:
2051:
2047:
2043:
2040:
2037:
2029:
2025:
2019:
2014:
2010:
2006:
1999:
1994:
1992:
1987:
1985:
1980:
1979:
1976:
1964:
1961:
1959:
1956:
1954:
1951:
1949:
1946:
1944:
1941:
1940:
1938:
1936:
1932:
1922:
1918:
1915:
1913:
1909:
1906:
1904:
1901:
1900:
1898:
1894:
1884:
1881:
1880:
1877:
1871:
1867:
1864:
1862:
1859:
1858:
1855:
1847:
1844:
1842:
1839:
1837:
1834:
1833:
1832:
1829:
1828:
1825:
1822:
1818:
1815:
1813:
1809:
1799:
1798:Urate oxidase
1796:
1794:
1791:
1789:
1786:
1784:
1781:
1779:
1776:
1775:
1773:
1769:
1763:
1760:
1758:
1755:
1754:
1752:
1750:
1746:
1734:
1733:GMP reductase
1731:
1730:
1729:
1726:
1724:
1721:
1719:
1716:
1715:
1713:
1710:
1708:
1701:
1693:
1692:AMP deaminase
1690:
1689:
1688:
1685:
1683:
1680:
1678:
1675:
1674:
1672:
1669:
1667:
1660:
1654:
1651:
1649:
1646:
1644:
1641:
1639:
1636:
1634:
1631:
1629:
1626:
1624:
1621:
1620:
1618:
1615:
1613:
1609:
1603:
1600:
1596:
1593:
1591:
1587:
1581:
1578:
1575:
1573:
1569:
1566:
1565:
1560:
1555:
1553:
1548:
1546:
1541:
1540:
1537:
1531:
1528:
1525:
1522:
1518:
1515:
1514:
1510:
1502:
1498:
1493:
1488:
1483:
1478:
1474:
1470:
1466:
1462:
1458:
1451:
1449:
1445:
1440:
1436:
1431:
1426:
1422:
1418:
1415:(1–2): 3–15.
1414:
1410:
1406:
1399:
1396:
1391:
1387:
1382:
1377:
1372:
1367:
1364:(2): 109–17.
1363:
1359:
1355:
1348:
1345:
1340:
1336:
1331:
1326:
1321:
1316:
1312:
1308:
1305:(1): 358–63.
1304:
1300:
1293:
1286:
1283:
1278:
1274:
1270:
1266:
1262:
1258:
1255:(2): 119–32.
1254:
1250:
1243:
1241:
1239:
1237:
1233:
1228:
1224:
1219:
1214:
1210:
1206:
1202:
1195:
1192:
1187:
1183:
1179:
1175:
1171:
1167:
1164:(3): 269–75.
1163:
1159:
1152:
1149:
1144:
1140:
1136:
1132:
1128:
1124:
1120:
1116:
1109:
1106:
1101:
1099:9781444313307
1095:
1091:
1090:
1082:
1079:
1067:
1063:
1057:
1054:
1049:
1045:
1041:
1037:
1033:
1029:
1026:(2): 153–60.
1025:
1021:
1014:
1011:
1006:
1004:9781483217321
1000:
996:
995:
987:
984:
979:
975:
970:
965:
961:
957:
953:
949:
945:
938:
935:
930:
926:
921:
916:
912:
908:
904:
897:
894:
889:
887:9781119277781
883:
879:
872:
869:
857:
853:
847:
844:
839:
835:
830:
825:
821:
817:
814:(9): 3203–8.
813:
809:
805:
798:
795:
783:
779:
773:
771:
769:
765:
753:
752:www.ebi.ac.uk
749:
743:
740:
735:
729:
725:
720:
719:
710:
707:
701:
697:
694:
692:
689:
687:
684:
682:
679:
677:
674:
672:
669:
667:
664:
662:
659:
658:
654:
652:
650:
645:
641:
637:
632:
628:
619:
617:
615:
610:
602:
600:
597:
596:neuroblastoma
592:
584:
582:
567:
565:
558:
556:
549:
547:
545:
541:
537:
533:
532:gram negative
529:
528:
523:
519:
510:
508:
506:
502:
498:
490:
484:
480:
478:
474:
470:
466:
462:
458:
457:
453:
449:
444:
443:
438:
430:
428:
426:
422:
413:
408:
406:
403:
399:
395:
391:
387:
379:
378:
377:
371:
368:
365:
362:
359:
356:
355:
354:
347:
343:
341:
337:
333:
329:
324:
320:
316:
312:
308:
304:
296:
294:
292:
284:
282:
280:
276:
272:
268:
264:
260:
256:
252:
248:
247:triphosphates
244:
240:
236:
232:
228:
224:
220:
216:
212:
200:
197:
195:
191:
188:
185:
183:
179:
176:
173:
171:
167:
162:
158:
155:
152:
149:
146:
143:
139:
136:
133:
131:
127:
124:
121:
119:
115:
112:
109:
107:
103:
100:
99:NiceZyme view
97:
95:
91:
88:
85:
83:
79:
76:
73:
71:
67:
62:
59:
56:
54:
50:
47:
44:
42:
38:
33:
28:
21:
3210:Translocases
3207:
3194:
3181:
3168:
3155:
3145:Transferases
3142:
3129:
2986:Binding site
2888:
2866:
2841:
2462:
2427:
2288:
2185:Class I PI 3
2150:Pantothenate
2021:2.7.1-2.7.4:
2005:Transferases
1947:
1727:
1723:GMP synthase
1704:
1686:
1663:
1653:IMP synthase
1606:
1464:
1460:
1412:
1408:
1398:
1361:
1357:
1347:
1302:
1298:
1285:
1252:
1248:
1208:
1204:
1194:
1161:
1157:
1151:
1121:(1): 53–62.
1118:
1114:
1108:
1088:
1081:
1069:. Retrieved
1065:
1056:
1023:
1019:
1013:
997:. Elsevier.
993:
986:
954:(2): 381–9.
951:
947:
937:
913:(1): 48–55.
910:
906:
896:
877:
871:
859:. Retrieved
855:
846:
811:
807:
797:
785:. Retrieved
781:
755:. Retrieved
751:
742:
717:
709:
623:
606:
588:
571:
562:
553:
543:
539:
535:
525:
514:
494:
461:homotetramer
446:
440:
434:
417:
383:
375:
352:
300:
291:mitochondria
288:
230:
226:
222:
218:
214:
210:
209:
87:BRENDA entry
2981:Active site
2736:Transposase
2726:Recombinase
2371:-nucleoside
2197:Sphingosine
1071:17 November
861:17 November
644:proteolytic
473:prokaryotes
307:nucleotides
275:endocytosis
75:IntEnz view
35:Identifiers
3253:Categories
3184:Isomerases
3158:Hydrolases
3025:Regulation
2538:Telomerase
2381:Polymerase
2155:Mevalonate
2118:Riboflavin
2009:phosphorus
1896:Catabolism
1771:Catabolism
1577:nucleotide
1568:Metabolism
787:15 October
757:2 November
702:References
666:Nucleotide
661:Nucleoside
544:M. xanthus
540:M. xanthus
536:M. xanthus
522:homologues
518:metastasis
465:pyrimidine
437:tetrameric
409:Regulation
402:G proteins
388:, UTP for
338:(CTP) and
303:nucleoside
245:(NDP) and
219:NDP kinase
144:structures
111:KEGG entry
58:9026-51-1
3063:EC number
2730:Integrase
2654:3' to 5'
2299:Guanylate
2294:Uridylate
2284:Adenylate
2128:Thymidine
2123:Shikimate
1820:Anabolism
1598:Anabolism
1115:BioEssays
649:oncogenes
568:In plants
559:In humans
396:. During
323:histidine
285:Structure
64:Databases
3264:EC 2.7.4
3087:Kinetics
3011:Cofactor
2974:Activity
2664:RNase PH
2272:acceptor
2253:Creatine
2246:acceptor
2218:acceptor
2160:Pyruvate
2145:Glycerol
2106:Platelet
2081:Galacto-
2052:acceptor
1501:25700270
1461:PLOS ONE
1439:19415463
1390:25585611
1381:10153104
1339:12506203
1269:24964975
1227:17463326
1186:24708684
1178:11768310
1143:29304629
1048:18115068
1040:24961462
978:22114351
929:11121795
782:InterPro
655:See also
631:melanoma
614:caveolae
501:ribosome
477:bacteria
297:Function
239:catalyze
199:proteins
187:articles
175:articles
148:RCSB PDB
3259:Enzymes
3243:Biology
3197:Ligases
2967:Enzymes
2615:PrimPol
2600:Primase
2074:Hepatic
2069:Fructo-
1728:reverse
1687:reverse
1580:enzymes
1530:2.7.4.6
1492:4336288
1469:Bibcode
1430:2721137
1307:Bibcode
1277:1227825
1135:7702594
969:3258181
838:1324167
334:(GTP),
235:enzymes
233:s) are
217:, also
135:profile
118:MetaCyc
53:CAS no.
46:2.7.4.6
3229:Portal
3171:Lyases
2902:2.7.13
2880:2.7.12
2855:2.7.11
2830:2.7.10
2669:PNPase
2637:PNPase
2593:POLRMT
2588:ssRNAP
2101:Muscle
2064:Gluco-
2028:kinase
1523:(MeSH)
1499:
1489:
1437:
1427:
1388:
1378:
1337:
1330:140977
1327:
1275:
1267:
1225:
1184:
1176:
1141:
1133:
1096:
1046:
1038:
1001:
976:
966:
927:
884:
836:
829:556853
826:
730:
277:, and
182:PubMed
164:Search
154:PDBsum
94:ExPASy
82:BRENDA
70:IntEnz
41:EC no.
3123:Types
2750:2.7.8
2719:Other
2358:2.7.7
2318:2.7.6
2263:2.7.4
2240:2.7.3
2212:2.7.2
2096:Liver
2059:Hexo-
2046:2.7.1
1295:(PDF)
1273:S2CID
1182:S2CID
1139:S2CID
1044:S2CID
321:of a
237:that
215:NDPKs
130:PRIAM
3215:list
3208:EC7
3202:list
3195:EC6
3189:list
3182:EC5
3176:list
3169:EC4
3163:list
3156:EC3
3150:list
3143:EC2
3137:list
3130:EC1
2889:see
2867:see
2842:see
2216:COOH
2015:2.7)
1921:UPB1
1912:DPYS
1705:IMP→
1664:IMP→
1497:PMID
1435:PMID
1386:PMID
1335:PMID
1265:PMID
1223:PMID
1174:PMID
1131:PMID
1094:ISBN
1073:2015
1036:PMID
999:ISBN
974:PMID
925:PMID
882:ISBN
863:2015
834:PMID
789:2015
759:2015
728:ISBN
589:Ten
530:, a
497:tRNA
421:AMPK
398:cAMP
309:and
229:and
223:poly
194:NCBI
151:PDBe
106:KEGG
2632:PAP
2573:III
2507:/Y
2498:TDT
2479:/X
2471:III
2463:Pfu
2438:/B
2428:Taq
2403:/A
2170:PFP
2140:NAD
1831:CAD
1707:GMP
1666:AMP
1612:IMP
1608:R5P
1487:PMC
1477:doi
1425:PMC
1417:doi
1413:329
1376:PMC
1366:doi
1362:388
1325:PMC
1315:doi
1303:100
1257:doi
1253:388
1213:doi
1209:100
1166:doi
1123:doi
1028:doi
1024:388
964:PMC
956:doi
915:doi
824:PMC
816:doi
724:476
221:, (
170:PMC
142:PDB
3255::
2857::
2832::
2817:PO
2578:IV
2568:II
2477:IV
2473:/C
2436:II
2422:T7
2367:PO
2360::
2320::
2267:PO
2265::
2242::
2214::
2050:OH
2048::
2033:PO
2013:EC
2007::
1570::
1527:EC
1495:.
1485:.
1475:.
1465:10
1463:.
1459:.
1447:^
1433:.
1423:.
1411:.
1407:.
1384:.
1374:.
1360:.
1356:.
1333:.
1323:.
1313:.
1301:.
1297:.
1271:.
1263:.
1251:.
1235:^
1221:.
1207:.
1203:.
1180:.
1172:.
1162:32
1160:.
1137:.
1129:.
1119:17
1117:.
1064:.
1042:.
1034:.
1022:.
972:.
962:.
952:23
950:.
946:.
923:.
911:49
909:.
905:.
854:.
832:.
822:.
812:11
810:.
806:.
780:.
767:^
750:.
726:.
479:.
450:,
445:,
281:.
273:,
269:,
3231::
3217:)
3213:(
3204:)
3200:(
3191:)
3187:(
3178:)
3174:(
3165:)
3161:(
3152:)
3148:(
3139:)
3135:(
2959:e
2952:t
2945:v
2819:4
2815:(
2732:)
2728:(
2610:2
2605:1
2583:V
2521:κ
2516:ι
2511:η
2505:V
2493:μ
2488:λ
2483:β
2457:ζ
2452:ε
2447:δ
2442:α
2417:ν
2412:θ
2407:γ
2401:I
2373:)
2369:4
2365:(
2336:)
2333:7
2331:O
2329:2
2327:P
2325:(
2269:4
2244:N
2111:2
2091:1
2038:)
2035:4
2031:(
2026:/
1997:e
1990:t
1983:v
1919:/
1910:/
1868:/
1709::
1668::
1614::
1610:→
1558:e
1551:t
1544:v
1503:.
1479::
1471::
1441:.
1419::
1392:.
1368::
1341:.
1317::
1309::
1279:.
1259::
1229:.
1215::
1188:.
1168::
1145:.
1125::
1102:.
1075:.
1050:.
1030::
1007:.
980:.
958::
931:.
917::
890:.
865:.
840:.
818::
791:.
761:.
736:.
579:2
577:O
575:2
419:(
225:)
213:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.