132:
60:
199:
135:
Change with ionizing density. This figure illustrates the trend in the relative radiosensitivity or OER with oxygen tension for radiations of different ionizing density or linear energy transfer (LET, keV/μm). The inhibition of clone-formation by cultured human cells was measured after exposure to
63:
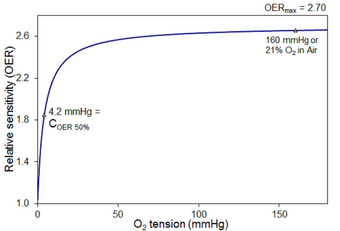
Relative sensitivity. This figure illustrates the typical change in the relative radiosensitivity for a biological effect such as cell death when exposed to radiations of low ionizing density (e.g. x-rays). The hyperbolic relationship shown has a maximum OER of 2.70 for 100% oxygen (at 760 mmHg),
136:
alpha-particles, deuterons and 250 kVp x-rays by
Barendsen et al. (1966). The range of the maximum OER for 100% oxygen (at 760 mmHg) was 2.7 for 250 kVp x-rays dropping to 1.0 for 2.5 MeV alpha-particles. In each case the OER curves shown assume a half-range OER value of 4.2 mmHg or 0.55% oxygen.
202:
Cell survival. This figure is illustrative of the reduction in the OER from aerobic to anoxic conditions for lower compared to higher doses, which has a bearing on the choice of dose fractionation exposures for radiotherapy of
565:
Howard-Flanders, P, Moore, D (1958). "The time interval after pulsed irradiation within which injury to bacteria can be modified by dissolved oxygen. I. A search for an effect of oxygen 0.02 second after pulsed irradiation".
224:), which is the ratio of doses under pure oxygen and anoxic conditions. Consequently, OER varies from unity in anoxia to a maximum value for 100% oxygen of typically up to three for low ionizing-density-radiation (
918:
Barendsen GW, Koot CJ, Van Kersen GR, Bewley DK, Field SB, Parnell CJ (1966). "The effect of oxygen on impairment of the proliferative capacity of human cells in culture by ionizing radiations of different LET".
175:
with similar effects to oxygen observed in tumour cells. Another important observation is that oxygen must be present at irradiation or within milliseconds afterward for the oxygen effect to take place.
390:
Richardson, RB (2008). "Age-dependent changes in oxygen tension, radiation dose and sensitivity within normal and diseased coronary arteries-Part B: modeling oxygen diffusion into vessel walls".
179:
The best known explanation of the oxygen effect is the oxygen fixation hypothesis developed by
Alexander in 1962, which posited that radiation-induced non-restorable or "fixed" nuclear
243:
Radiosensitivity varies most rapidly for oxygen partial pressures below ~1% atmospheric (Fig. 1). Howard-Flanders and Alper (1957) developed a formula for the
253:
identified additional characteristics of the oxygen effect that influence radiotherapy practices. They found that the maximum OER value diminishes as the
187:. Recent hypotheses include one based on oxygen-enhanced damage from first principles. Another hypothesis posits that ionizing radiation provokes
696:
261:
for alpha-particles of high-LET around 200 keV/μm. The OER is reduced for low doses as evaluated for cultured mammalian cells exposed to
221:
343:"Physiologic hypoxia and oxygen homeostasis in the healthy intestine. A review in the theme: Cellular responses to hypoxia"
257:-density of the radiation increases (Fig. 2), from low-LET to high-LET radiations. The OER is unity irrespective of the
867:
Howard-Flanders P, Alper T (1957). "The sensitivity of microorganisms to irradiation under controlled gas conditions".
1014:
89:
beams in well oxygenated regions can be up to three times greater than in a poorly vasculated portion of the tumour.
1029:
617:
Alexander P (1962). "On the mode of action of some treatments that influence the radiation sensitivity of cells".
192:
167:
A key observation limiting hypotheses to explain the biological mechanisms of the oxygen effect is that the gas
120:. In addition, there are non-malignant diseases where oxygenated tissues can become hypoxic such as in stenosed
1019:
213:
195:
that varies with a hyperbolic saturation relationship observed with both the oxygen and nitric oxide effects.
40:
237:
125:
117:
269:
treatments are daily 2 Gy exposures, as below this dose the so-called 'shoulder' or repair region of the
1034:
1009:
763:"Mitochondrial stress controls the radiosensitivity of the oxygen effect: Implications for radiotherapy"
514:
Gray LH, Green FO, Hawes CA (1958). "Effect of nitric oxide on the radiosensitivity of tumour cells".
145:
Holthusen (1921) first quantified the oxygen effect finding 2.5 to 3.0-fold less hatching eggs of the
876:
823:
575:
523:
244:
48:
270:
892:
849:
591:
547:
454:
415:
157:
131:
985:
936:
900:
841:
792:
743:
692:
669:
634:
599:
539:
407:
372:
323:
161:
121:
97:
74:
44:
975:
967:
928:
884:
831:
782:
774:
733:
725:
714:"A mechanistic investigation of the oxygen fixation hypothesis and oxygen enhancement ratio"
661:
626:
583:
531:
496:
446:
399:
362:
354:
313:
303:
28:
472:
Petry EJ (1923). "Kenntnis der
Bedingungen der biologischen Wir kung der Rontgenstrahlen".
1024:
184:
172:
152:
in oxygenated compared to anoxic conditions, which was incorrectly assigned to changes in
880:
827:
579:
527:
247:
function of OER and its variation with oxygen concentration, or oxygen pressure in air.
980:
955:
787:
762:
738:
729:
713:
630:
367:
342:
318:
291:
258:
225:
93:
156:. However, two years later, Petry (1923) first attributed oxygen tension as affecting
1003:
665:
266:
188:
153:
551:
458:
419:
59:
853:
250:
168:
78:
32:
20:
812:"Effect of oxygen on the frequency of chromosome aberrations produced by X-rays"
500:
180:
160:
effects on vegetable seeds. Later, the implications of the effects of oxygen on
109:
358:
932:
403:
217:
113:
778:
308:
229:
191:
to produce reactive oxygen (and nitrogen species), which are leakage during
105:
101:
904:
845:
796:
747:
638:
603:
543:
411:
376:
327:
265:
under aerobic (21% O2, 159 mmHg) and anoxic (nitrogen) conditions. Typical
198:
989:
940:
673:
212:
The oxygen effect is quantified by measuring the radiation sensitivity or
971:
487:
Mottram JC (1936). "Factor of importance in radiosensitiity of tumours".
254:
146:
86:
896:
595:
450:
149:
836:
811:
535:
82:
36:
888:
587:
434:
652:
Ewing D (1998). "The oxygen fixation hypothesis: a reevaluation".
262:
233:
197:
130:
58:
69:
Explanation of the oxygen effect and relevance to hypoxic tissues
956:"Survival measurements at low doses: oxygen enhancement ratio"
290:
Parmar K, Mauch P, Vergilio JA, Sackstein R, Down JD (2007).
73:
The oxygen effect has particular importance in external beam
64:
with a half-range OER value at 4.2 mmHg or 0.55% of oxygen.
208:
Oxygen
Enhancement Ratio and the effect of radiation LET
51:(i.e., <1% of 101.3 kPa, 760 mmHg or 760 torr).
691:. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer. p. 597.
292:"The oxygen fixation hypothesis: a reevaluation"
296:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
216:(OER) of a particular biological effect (e.g.,
100:conditions present in the normal physiology of
273:is encroached upon reducing the OER (Fig. 3).
8:
718:Biomedical Physics & Engineering Express
954:Palcic B, Brosing JW, Skarsgard LD (1982).
435:"Beitrage zur Biologie der Strahlenwirkung"
921:Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med
979:
835:
786:
737:
366:
317:
307:
141:Historical research on the oxygen effect
96:, the oxygen effect is also relevant to
282:
183:are lethal to cells in the presence of
341:Zheng L, Kelly CJ, Colgan SP (2015).
7:
27:refers to a tendency for increased
631:10.1111/j.2164-0947.1962.tb01456.x
164:were discussed by Mottram (1936).
14:
761:Richardson RB, Harper ME (2016).
35:and organisms in the presence of
689:Radiobiology for the Radiologist
666:10.1097/00000421-199808000-00008
712:Grimes DR, Partridge M (2015).
687:Hall, EJ; Giaccia, AJ (2019).
1:
730:10.1088/2057-1976/1/4/045209
501:10.1259/0007-1285-9-105-606
1051:
810:Thoday JM, Read J (1947).
359:10.1152/ajpcell.00191.2015
16:Phenomenon in biochemistry
933:10.1080/09553006614550421
404:10.1080/09553000802389645
347:Am J Physiol Cell Physiol
193:oxidative phosphorylation
779:10.18632/oncotarget.7412
474:Biochemische Zeitschrift
214:Oxygen Enhancement Ratio
309:10.1073/pnas.0701152104
238:linear energy transfer
204:
137:
126:cardiovascular disease
65:
43:conditions, where the
201:
134:
77:where the killing of
62:
55:Physiology and causes
972:10.1038/bjc.1982.312
433:Holthusen H (1921).
236:), or so-called low
108:adjacent to bone in
49:atmospheric pressure
881:1957RadR....7..518H
828:1947Natur.160..608T
773:(16): 21469–21483.
580:1958RadR....9..422H
528:1958Natur.182..952G
271:cell survival curve
104:niches such as the
47:is less than 1% of
1015:Ionizing radiation
619:Trans N Y Acad Sci
451:10.1007/BF01722061
240:(LET) radiations.
205:
158:ionizing radiation
138:
66:
1030:Radiation therapy
698:978-1-49-633541-8
522:(4640): 952–953.
392:Int J Radiat Biol
302:(13): 5431–5436.
122:coronary arteries
75:radiation therapy
41:anoxic or hypoxic
1042:
994:
993:
983:
951:
945:
944:
915:
909:
908:
864:
858:
857:
839:
837:10.1038/160608a0
807:
801:
800:
790:
758:
752:
751:
741:
709:
703:
702:
684:
678:
677:
649:
643:
642:
614:
608:
607:
562:
556:
555:
536:10.1038/182952a0
511:
505:
504:
484:
478:
477:
469:
463:
462:
430:
424:
423:
387:
381:
380:
370:
353:(6): C350–C360.
338:
332:
331:
321:
311:
287:
124:associated with
114:epithelium layer
29:radiosensitivity
1050:
1049:
1045:
1044:
1043:
1041:
1040:
1039:
1020:Medical physics
1000:
999:
998:
997:
953:
952:
948:
917:
916:
912:
889:10.2307/3570400
866:
865:
861:
809:
808:
804:
760:
759:
755:
711:
710:
706:
699:
686:
685:
681:
654:Am J Clin Oncol
651:
650:
646:
616:
615:
611:
588:10.2307/3570768
564:
563:
559:
513:
512:
508:
486:
485:
481:
471:
470:
466:
439:Pflügers Archiv
432:
431:
427:
398:(10): 849–857.
389:
388:
384:
340:
339:
335:
289:
288:
284:
279:
251:Radiobiologists
210:
185:diatomic oxygen
173:radiosensitizer
143:
71:
57:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1048:
1046:
1038:
1037:
1032:
1027:
1022:
1017:
1012:
1002:
1001:
996:
995:
966:(6): 980–984.
946:
927:(4): 317–327.
910:
875:(5): 518–540.
859:
802:
753:
704:
697:
679:
660:(4): 355–361.
644:
609:
574:(4): 422–437.
557:
506:
479:
464:
425:
382:
333:
281:
280:
278:
275:
259:oxygen tension
209:
206:
142:
139:
94:tumour hypoxia
70:
67:
56:
53:
45:oxygen tension
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1047:
1036:
1033:
1031:
1028:
1026:
1023:
1021:
1018:
1016:
1013:
1011:
1008:
1007:
1005:
991:
987:
982:
977:
973:
969:
965:
961:
957:
950:
947:
942:
938:
934:
930:
926:
922:
914:
911:
906:
902:
898:
894:
890:
886:
882:
878:
874:
870:
863:
860:
855:
851:
847:
843:
838:
833:
829:
825:
822:(4070): 608.
821:
817:
813:
806:
803:
798:
794:
789:
784:
780:
776:
772:
768:
764:
757:
754:
749:
745:
740:
735:
731:
727:
724:(4): 045209.
723:
719:
715:
708:
705:
700:
694:
690:
683:
680:
675:
671:
667:
663:
659:
655:
648:
645:
640:
636:
632:
628:
624:
620:
613:
610:
605:
601:
597:
593:
589:
585:
581:
577:
573:
569:
561:
558:
553:
549:
545:
541:
537:
533:
529:
525:
521:
517:
510:
507:
502:
498:
494:
490:
483:
480:
475:
468:
465:
460:
456:
452:
448:
444:
440:
436:
429:
426:
421:
417:
413:
409:
405:
401:
397:
393:
386:
383:
378:
374:
369:
364:
360:
356:
352:
348:
344:
337:
334:
329:
325:
320:
315:
310:
305:
301:
297:
293:
286:
283:
276:
274:
272:
268:
267:fractionation
264:
260:
256:
252:
248:
246:
241:
239:
235:
231:
227:
223:
219:
215:
207:
200:
196:
194:
190:
186:
182:
177:
174:
170:
165:
163:
159:
155:
154:cell division
151:
148:
140:
133:
129:
127:
123:
119:
115:
111:
107:
103:
99:
95:
90:
88:
84:
80:
76:
68:
61:
54:
52:
50:
46:
42:
38:
34:
30:
26:
25:oxygen effect
22:
1035:Radiobiology
1010:Biochemistry
963:
959:
949:
924:
920:
913:
872:
868:
862:
819:
815:
805:
770:
766:
756:
721:
717:
707:
688:
682:
657:
653:
647:
622:
618:
612:
571:
567:
560:
519:
515:
509:
492:
488:
482:
473:
467:
442:
438:
428:
395:
391:
385:
350:
346:
336:
299:
295:
285:
249:
242:
211:
189:mitochondria
178:
169:nitric oxide
166:
162:radiotherapy
144:
91:
79:tumour cells
72:
33:living cells
24:
21:biochemistry
18:
960:Br J Cancer
625:: 966–978.
495:: 606–614.
489:Br J Radiol
181:DNA lesions
110:bone marrow
1004:Categories
869:Radiat Res
767:Oncotarget
568:Radiat Res
476:: 135–353.
277:References
245:hyperbolic
222:DNA damage
218:cell death
118:intestine
106:endosteum
102:stem cell
905:13485393
846:20271559
797:26894978
748:26925254
639:14011969
604:13591515
552:27573591
544:13590191
459:26030155
445:: 1–24.
420:24585967
412:18979320
377:26179603
328:17374716
255:ionizing
203:tumours.
147:nematode
112:and the
92:Besides
87:electron
39:than in
31:of free
990:7150493
981:2011221
941:5297012
897:3570400
877:Bibcode
854:4068339
824:Bibcode
788:5008299
739:4765087
674:9708633
596:3570768
576:Bibcode
524:Bibcode
368:4572369
319:1838452
150:Ascaris
116:of the
98:hypoxia
1025:Oxygen
988:
978:
939:
903:
895:
852:
844:
816:Nature
795:
785:
746:
736:
695:
672:
637:
602:
594:
550:
542:
516:Nature
457:
418:
410:
375:
365:
326:
316:
263:x-rays
234:x-rays
232:-, or
83:photon
37:oxygen
23:, the
893:JSTOR
850:S2CID
592:JSTOR
548:S2CID
455:S2CID
416:S2CID
230:gamma
171:is a
81:with
986:PMID
937:PMID
901:PMID
842:PMID
793:PMID
744:PMID
693:ISBN
670:PMID
635:PMID
600:PMID
540:PMID
408:PMID
373:PMID
324:PMID
226:beta
85:and
976:PMC
968:doi
929:doi
885:doi
832:doi
820:160
783:PMC
775:doi
734:PMC
726:doi
662:doi
627:doi
584:doi
532:doi
520:182
497:doi
447:doi
443:187
400:doi
363:PMC
355:doi
351:309
314:PMC
304:doi
300:104
228:-,
220:or
19:In
1006::
984:.
974:.
964:46
962:.
958:.
935:.
925:10
923:.
899:.
891:.
883:.
871:.
848:.
840:.
830:.
818:.
814:.
791:.
781:.
769:.
765:.
742:.
732:.
720:.
716:.
668:.
658:21
656:.
633:.
623:24
621:.
598:.
590:.
582:.
570:.
546:.
538:.
530:.
518:.
491:.
453:.
441:.
437:.
414:.
406:.
396:84
394:.
371:.
361:.
349:.
345:.
322:.
312:.
298:.
294:.
128:.
992:.
970::
943:.
931::
907:.
887::
879::
873:7
856:.
834::
826::
799:.
777::
771:7
750:.
728::
722:1
701:.
676:.
664::
641:.
629::
606:.
586::
578::
572:9
554:.
534::
526::
503:.
499::
493:9
461:.
449::
422:.
402::
379:.
357::
330:.
306::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.