196:, which could imply raised intracranial pressure or tumors. True papilledema may present with exudates or cotton-wool spots, unlike ODD. The optic disc margins are characteristically irregular in ODD but not blurred as there is no swelling of the retinal nerve fibers. Spontaneous venous pulsations are present in about 80 percent of patients with ODD, but absent in cases of true disc edema. Other causes of disc elevation clinicians must exclude may be: hyaloid traction, epipapillary glial tissue, myelinated nerve fibres, scleral infiltration, vitreopapillary traction and high
39:
63:
256:
should be screened for. Both the severity of optic disc drusen and the degree of intraocular pressure elevation have been associated with visual field loss. There is no widely accepted treatment for ODD, although some clinicians will prescribe eye drops designed to decrease the intra-ocular pressure
265:
Optic nerve damage is progressive and insidious. Some of patients will develop some peripheral field defects. These can include nasal step defects, enlarged blind spots, arcuate scotomas, sectoral field loss and altitudinal defects. Clinical symptoms correlate to visibility of the drusen. Central
282:
Optic disc drusen are found clinically in about 1% of the population but this increases to 3.4% in individuals with a family history of ODD. About two thirds to three quarters of clinical cases are bilateral. A necropsy study of 737 cases showed a 2.4% incidence with 2 out of 15 (13%) bilateral,
257:
and theoretically relieve mechanical stress on fibers of the optic disc. Rarely choroidal neovascular membranes may develop adjacent to the optic disc threatening bleeding and retinal scarring. Laser treatment or photodynamic therapy or other evolving therapies may prevent this complication.
166:
In children, optic disc drusen are usually buried and undetectable by fundoscopy except for a mild or moderate elevation of the optic disc. With age, the overlying axons become atrophied and the drusen become exposed and more visible. They may become apparent with an
283:
perhaps indicating the insidious nature of many cases. An autosomal dominant inheritance pattern with incomplete penetrance and associated inherited dysplasia of the optic disc and its blood supply is suspected. Males and females are affected at equal rates.
1231:
1216:
1323:
192:
In most patients, optic disc drusen are an incidental finding. It is important to differentiate them from other conditions that present with optic disc elevation, especially
784:
Delyfer MN, Rougier MB, Fourmaux E, Cousin P, Korobelnik JF (April 2004). "Laser photocoagulation for choroidal neovascular membrane associated with optic disc drusen".
175:
neovascularization may develop as the juxtapapillary nerve fibers are disrupted, with subsequent subretinal hemorrhage and retinal scarring. Even more rarely,
453:
Kapur R, Pulido JS, Abraham JL, Sharma M, Buerk B, Edward DP (January 2008). "Histologic findings after surgical excision of optic nerve head drusen".
741:
Grippo TM, Shihadeh WA, Schargus M, et al. (March 2008). "Optic nerve head drusen and visual field loss in normotensive and hypertensive eyes".
171:
and some visual field loss at the end of adolescence. ODD can compress and eventually compromise the vasculature and retinal nerve fibers. Rarely,
868:
Chaudhry NA, Lavaque AJ, Shah A, Liggett PE (2005). "Photodynamic therapy for choroidal neovascular membrane secondary to optic nerve drusen".
99:. ODD have also been referred to as congenitally elevated or anomalous discs, pseudopapilledema, pseudoneuritis, buried disc drusen, and disc
1080:
612:
583:
1250:
1149:
1095:
642:
627:
1071:
Riordan-Eva P, Hoyt WF (2004). "Neuro-ophthalmology". In John P. Whitcher, Riordan-Eva, Paul, Vaughan, Daniel, Asbury, Taylor (eds.).
271:
351:
Golnik, K. (2006). Congenital anomalies and acquired abnormalities of the optic nerve, (Version 14.3). UptoDate (On-Line Serial)
507:
267:
245:
1111:
Nischal KK, Hingorani M, Bentley CR, et al. (January 1997). "Ocular ultrasound in
Alagille syndrome: a new sign".
154:
beneath it to detect light. The central retinal artery and vein can be seen in the middle of the disc as it exits the
989:"Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy secondary to optic nerve head drusen - A case report and review of literature"
158:
with the optic nerve to supply the retina. The vessels send branches out in all directions to supply the retina.
1261:
38:
571:
96:
287:
are the most susceptible ethnic group. Certain conditions have been associated with disc drusen such as
124:
364:
Friedman AH, Henkind P, Gartner S (April 1975). "Drusen of the optic disc. A histopathological study".
315:
288:
253:
237:
229:
62:
1235:
601:"Ch 3: Congenital anomalies of the optic disc: Pseudopapilledema associated with optic disc drusen"
143:
1018:
928:
766:
723:
478:
84:
821:"Laser treatment of drusen to prevent progression to advanced age-related macular degeneration"
1272:
1182:
1128:
1076:
1053:
1010:
969:
920:
885:
850:
801:
758:
715:
671:
608:
600:
579:
552:
470:
435:
400:
373:
304:
249:
201:
51:
1172:
1120:
1045:
1000:
959:
912:
877:
840:
832:
793:
750:
705:
574:. In Jameson JN, Kasper DL, Harrison TR, Braunwald E, Fauci AS, Hauser SL, Longo DL (eds.).
542:
462:
427:
92:
300:
292:
176:
46:
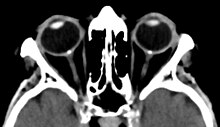
Bilateral optic disc drusen in computed tomography seen as dense spots at the optical disc
988:
1244:
1240:
1177:
1160:
845:
820:
308:
296:
284:
221:
168:
135:
1124:
1049:
431:
418:
Tso MO (October 1981). "Pathology and pathogenesis of drusen of the optic nervehead".
1317:
1022:
797:
710:
693:
547:
530:
225:
205:
727:
607:(6th ed.). Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 178–87.
482:
932:
836:
233:
1301:
770:
659:
1266:
903:
Sivaprasad S, Moore AT (April 2008). "Choroidal neovascularisation in children".
881:
754:
466:
134:
is the anterior end of the nerve that is in the eye and hence is visible with an
1161:"Optic nerve axons and acquired alterations in the appearance of the optic disc"
193:
112:
80:
1277:
515:
1225:
1075:(16th ed.). New York: Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill. pp. 261–306.
964:
947:
131:
88:
1014:
1296:
1005:
916:
241:
197:
151:
56:
1057:
973:
924:
889:
854:
805:
762:
719:
675:
556:
474:
404:
1186:
1132:
439:
377:
1036:
Antcliff RJ, Spalton DJ (July 1999). "Are optic disc drusen inherited?".
987:
Gupta, Divya; Chaubey, Anupriya; Singh, Ritu; Gupta, SanjivKumar (2021).
147:
1208:
658:
Calvo-González C, Santos-Bueso E, Díaz-Valle D, et al. (May 2006).
172:
100:
1220:
531:"Progression from anomalous optic discs to visible optic disc drusen"
327:
311:
220:
Patients with optic disc drusen should be monitored periodically via
155:
139:
116:
578:(16th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical Publishing Division.
948:"Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy in eyes with optic disc drusen"
819:
Virgili G, Michelessi M, Parodi MB, Bacherini D, Evans JR (2015).
266:
vision loss is a rare complication of bleeding from peripapillar
120:
1255:
1153:
1099:
646:
631:
209:
127:
694:"Visual manifestations of visible and buried optic disc drusen"
603:. In Hoyt, William Graves; Miller, Neil; Walsh, Frank (eds.).
660:"[Optic nerve drusen and deep visual fields defects]"
252:
thickness. Associated conditions such as angioid streaks and
529:
Spencer TS, Katz BJ, Weber SW, Digre KB (December 2004).
200:. Disorders associated with disc elevation include:
138:. It is located nasally and slightly inferior to the
115:
is a cable connection that transmits images from the
1198:
946:
Purvin V, King R, Kawasaki A, Yee R (January 2004).
1287:
1202:
50:
26:
21:
647:Schimmelpenning-Feuerstein-MIMS Syndrome - 163200
514:. Jobson Publishing L.L.C. 2001. Archived from
391:Rosen E, Almog Y, Assia E (November 2005). "".
687:
685:
993:Indian Journal of Ophthalmology: Case Reports
605:Walsh and Hoyt's clinical neuro-ophthalmology
91:. They are thought to be the remnants of the
8:
1324:Disorders of optic nerve and visual pathways
1073:Vaughan & Asbury's general ophthalmology
314:which have been associated with age-related
1199:
576:Harrison's principles of internal medicine
502:
500:
498:
496:
494:
492:
359:
357:
61:
37:
18:
1176:
1004:
963:
844:
709:
546:
347:
345:
343:
339:
307:. Optic disc drusen are not related to
244:. For those with visual field defects
146:at the optic disc because there are no
248:has been recommended for follow-up of
692:Wilkins JM, Pomeranz HD (June 2004).
632:Kenny-Caffey Syndrome type 2 - 127000
512:Handbook of Ocular Disease Management
212:and linear nevus sebaceous syndrome.
7:
274:(AION) is a potential complication.
1150:Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man
1096:Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man
643:Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man
628:Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man
272:Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy
123:. It consists of over one million
87:that progressively calcify in the
14:
210:Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy
798:10.1111/j.1600-0420.2004.00231.x
711:10.1097/00041327-200406000-00006
548:10.1097/00041327-200412000-00006
268:choroidal neovascular membranes
132:optic nerve head, or optic disc
870:Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging
837:10.1002/14651858.CD006537.pub3
1:
1125:10.1016/s0161-6420(97)30358-3
1050:10.1016/S0161-6420(99)00708-3
432:10.1016/s0161-6420(81)80038-3
882:10.3928/15428877-20050101-09
755:10.1097/IJG.0b013e31814b995a
467:10.1097/IAE.0b013e31815e98d8
246:optical coherence tomography
1340:
1154:Pseudopapilledema - 177800
825:Cochrane Database Syst Rev
965:10.1001/archopht.122.1.48
508:"Optic Nerve Head Drusen"
208:, Kenny-Caffey syndrome,
45:
36:
1159:Wirtschafter JD (1983).
1100:Noonan syndrome - 163950
366:Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K
179:hemorrhage may develop.
1165:Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc
1006:10.4103/ijo.IJO_3795_20
917:10.1136/bjo.2007.124586
242:threshold visual fields
142:of the eye. There is a
31:Optic nerve head drusen
572:"Disorders of the Eye"
188:Differential diagnosis
97:retinal ganglion cells
95:system of degenerated
786:Acta Ophthalmol Scand
664:Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol
125:retinal ganglion cell
599:Brodsky, MC (2005).
316:macular degeneration
312:drusen of the retina
289:retinitis pigmentosa
254:retinitis pigmentosa
238:intraocular pressure
230:contrast sensitivity
570:Horton, J. (2005).
399:(11): 785–89, 822.
85:mucopolysaccharides
79:) are globules of
1288:External resources
1311:
1310:
1082:978-0-07-137831-4
698:J Neuroophthalmol
614:978-0-7817-4811-7
585:978-0-07-140235-4
535:J Neuroophthalmol
305:Alagille syndrome
250:nerve fiber layer
202:Alagille syndrome
73:Optic disc drusen
70:
69:
22:Optic disc drusen
16:Medical condition
1331:
1200:
1190:
1180:
1144:Further reading
1137:
1136:
1108:
1102:
1093:
1087:
1086:
1068:
1062:
1061:
1033:
1027:
1026:
1008:
984:
978:
977:
967:
952:Arch. Ophthalmol
943:
937:
936:
900:
894:
893:
865:
859:
858:
848:
831:(10): CD006537.
816:
810:
809:
781:
775:
774:
738:
732:
731:
713:
689:
680:
679:
655:
649:
640:
634:
625:
619:
618:
596:
590:
589:
567:
561:
560:
550:
526:
520:
519:
504:
487:
486:
450:
444:
443:
415:
409:
408:
388:
382:
381:
361:
352:
349:
93:axonal transport
66:
65:
41:
19:
1339:
1338:
1334:
1333:
1332:
1330:
1329:
1328:
1314:
1313:
1312:
1307:
1306:
1283:
1282:
1211:
1197:
1158:
1146:
1141:
1140:
1110:
1109:
1105:
1094:
1090:
1083:
1070:
1069:
1065:
1035:
1034:
1030:
986:
985:
981:
945:
944:
940:
905:Br J Ophthalmol
902:
901:
897:
867:
866:
862:
818:
817:
813:
783:
782:
778:
740:
739:
735:
691:
690:
683:
657:
656:
652:
641:
637:
626:
622:
615:
598:
597:
593:
586:
569:
568:
564:
528:
527:
523:
506:
505:
490:
452:
451:
447:
426:(10): 1066–80.
417:
416:
412:
390:
389:
385:
363:
362:
355:
350:
341:
336:
324:
301:Noonan syndrome
293:angioid streaks
280:
263:
218:
190:
185:
164:
162:Pathophysiology
109:
60:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1337:
1335:
1327:
1326:
1316:
1315:
1309:
1308:
1305:
1304:
1292:
1291:
1289:
1285:
1284:
1281:
1280:
1269:
1258:
1247:
1228:
1212:
1207:
1206:
1204:
1203:Classification
1196:
1195:External links
1193:
1192:
1191:
1156:
1145:
1142:
1139:
1138:
1103:
1088:
1081:
1063:
1044:(7): 1278–81.
1028:
979:
938:
895:
860:
811:
776:
733:
681:
666:(in Spanish).
650:
635:
620:
613:
591:
584:
562:
521:
518:on 2004-12-09.
488:
445:
410:
383:
353:
338:
337:
335:
332:
331:
330:
323:
320:
309:Bruch membrane
297:Usher syndrome
279:
276:
262:
259:
226:Snellen acuity
222:ophthalmoscopy
217:
214:
189:
186:
184:
181:
169:ophthalmoscope
163:
160:
136:ophthalmoscope
108:
105:
68:
67:
54:
48:
47:
43:
42:
34:
33:
28:
24:
23:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1336:
1325:
1322:
1321:
1319:
1303:
1299:
1298:
1294:
1293:
1290:
1286:
1279:
1275:
1274:
1270:
1268:
1264:
1263:
1259:
1257:
1253:
1252:
1248:
1246:
1242:
1238:
1237:
1233:
1229:
1227:
1223:
1222:
1218:
1214:
1213:
1210:
1205:
1201:
1194:
1188:
1184:
1179:
1174:
1170:
1166:
1162:
1157:
1155:
1151:
1148:
1147:
1143:
1134:
1130:
1126:
1122:
1118:
1114:
1113:Ophthalmology
1107:
1104:
1101:
1097:
1092:
1089:
1084:
1078:
1074:
1067:
1064:
1059:
1055:
1051:
1047:
1043:
1039:
1038:Ophthalmology
1032:
1029:
1024:
1020:
1016:
1012:
1007:
1002:
998:
994:
990:
983:
980:
975:
971:
966:
961:
957:
953:
949:
942:
939:
934:
930:
926:
922:
918:
914:
911:(4): 451–54.
910:
906:
899:
896:
891:
887:
883:
879:
875:
871:
864:
861:
856:
852:
847:
842:
838:
834:
830:
826:
822:
815:
812:
807:
803:
799:
795:
792:(2): 236–38.
791:
787:
780:
777:
772:
768:
764:
760:
756:
752:
749:(2): 100–04.
748:
744:
737:
734:
729:
725:
721:
717:
712:
707:
704:(2): 125–29.
703:
699:
695:
688:
686:
682:
677:
673:
670:(5): 269–73.
669:
665:
661:
654:
651:
648:
644:
639:
636:
633:
629:
624:
621:
616:
610:
606:
602:
595:
592:
587:
581:
577:
573:
566:
563:
558:
554:
549:
544:
541:(4): 297–98.
540:
536:
532:
525:
522:
517:
513:
509:
503:
501:
499:
497:
495:
493:
489:
484:
480:
476:
472:
468:
464:
461:(1): 143–46.
460:
456:
449:
446:
441:
437:
433:
429:
425:
421:
420:Ophthalmology
414:
411:
406:
402:
398:
395:(in Hebrew).
394:
387:
384:
379:
375:
371:
367:
360:
358:
354:
348:
346:
344:
340:
333:
329:
326:
325:
321:
319:
317:
313:
310:
306:
302:
298:
294:
290:
286:
277:
275:
273:
269:
260:
258:
255:
251:
247:
243:
239:
235:
231:
227:
223:
215:
213:
211:
207:
206:Down syndrome
203:
199:
195:
187:
182:
180:
178:
174:
170:
161:
159:
157:
156:scleral canal
153:
149:
145:
141:
137:
133:
129:
126:
122:
118:
114:
106:
104:
102:
98:
94:
90:
86:
82:
78:
74:
64:
58:
55:
53:
49:
44:
40:
35:
32:
29:
25:
20:
1295:
1271:
1260:
1249:
1230:
1215:
1168:
1164:
1119:(1): 79–85.
1116:
1112:
1106:
1091:
1072:
1066:
1041:
1037:
1031:
996:
992:
982:
958:(1): 48–53.
955:
951:
941:
908:
904:
898:
876:(1): 70–72.
873:
869:
863:
828:
824:
814:
789:
785:
779:
746:
742:
736:
701:
697:
667:
663:
653:
638:
623:
604:
594:
575:
565:
538:
534:
524:
516:the original
511:
458:
454:
448:
423:
419:
413:
396:
392:
386:
369:
365:
281:
278:Epidemiology
264:
234:color vision
219:
191:
165:
110:
81:mucoproteins
76:
72:
71:
30:
1171:: 1034–91.
743:J. Glaucoma
194:papilledema
113:optic nerve
27:Other names
1273:DiseasesDB
999:(4): 771.
372:(1): 4–9.
334:References
285:Caucasians
216:Management
144:blind spot
89:optic disc
1297:eMedicine
1023:239031007
1015:2772-3070
261:Prognosis
198:hyperopia
183:Diagnosis
173:choroidal
57:Neurology
52:Specialty
1318:Category
1152:(OMIM):
1098:(OMIM):
1058:10406605
974:14718294
925:18369058
890:15688974
855:26493180
806:15043550
763:18344754
728:23851816
720:15179065
676:16752318
645:(OMIM):
630:(OMIM):
557:15662245
483:21285492
475:18185151
405:16358654
393:Harefuah
322:See also
177:vitreous
103:bodies.
1302:oph/615
1267:D015594
1187:6203209
1178:1312472
1133:9022108
933:9963072
846:4733883
440:7335311
378:1064209
119:to the
107:Anatomy
101:hyaline
1256:177800
1245:377.24
1241:377.21
1185:
1175:
1131:
1079:
1056:
1021:
1013:
972:
931:
923:
888:
853:
843:
804:
771:801305
769:
761:
726:
718:
674:
611:
582:
555:
481:
473:
455:Retina
438:
403:
376:
328:Drusen
240:and
140:macula
130:. The
117:retina
59:
1278:31338
1226:H47.3
1019:S2CID
929:S2CID
767:S2CID
724:S2CID
479:S2CID
152:cones
128:axons
121:brain
1262:MeSH
1251:OMIM
1236:9-CM
1183:PMID
1129:PMID
1077:ISBN
1054:PMID
1011:ISSN
970:PMID
921:PMID
886:PMID
851:PMID
829:2015
802:PMID
759:PMID
716:PMID
672:PMID
609:ISBN
580:ISBN
553:PMID
471:PMID
436:PMID
401:PMID
374:PMID
303:and
148:rods
111:The
83:and
1232:ICD
1217:ICD
1173:PMC
1121:doi
1117:104
1046:doi
1042:106
1001:doi
960:doi
956:122
913:doi
878:doi
841:PMC
833:doi
794:doi
751:doi
706:doi
543:doi
463:doi
428:doi
397:144
150:or
77:ODD
1320::
1300::
1276::
1265::
1254::
1243:,
1239::
1224::
1221:10
1181:.
1169:81
1167:.
1163:.
1127:.
1115:.
1052:.
1040:.
1017:.
1009:.
995:.
991:.
968:.
954:.
950:.
927:.
919:.
909:92
907:.
884:.
874:36
872:.
849:.
839:.
827:.
823:.
800:.
790:82
788:.
765:.
757:.
747:17
745:.
722:.
714:.
702:24
700:.
696:.
684:^
668:81
662:.
551:.
539:24
537:.
533:.
510:.
491:^
477:.
469:.
459:28
457:.
434:.
424:88
422:.
370:95
368:.
356:^
342:^
318:.
299:,
295:,
291:,
270:.
236:,
232:,
228:,
224:,
204:,
1234:-
1219:-
1209:D
1189:.
1135:.
1123::
1085:.
1060:.
1048::
1025:.
1003::
997:1
976:.
962::
935:.
915::
892:.
880::
857:.
835::
808:.
796::
773:.
753::
730:.
708::
678:.
617:.
588:.
559:.
545::
485:.
465::
442:.
430::
407:.
380:.
75:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.