995:
a central metabolic intermediate that is also the acetyl donor in histone acetylation. Glucose is converted to acetyl-CoA by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC), which produces acetyl-CoA from glucose-derived pyruvate; and by adenosine triphosphate-citrate lyase (ACLY), which generates acetyl-CoA from glucose-derived citrate. PDC and ACLY activity depend on glucose availability, which thereby influences histone acetylation and consequently modulates gene expression and cell cycle progression. Dysregulation of ACLY and PDC contributes to metabolic reprogramming and promotes the development of multiple cancers. At the same time, glucose metabolism maintains the NAD+/NADH ratio, and NAD+ participates in SIRT-mediated histone deacetylation. SIRT enzyme activity is altered in various malignancies, and inhibiting SIRT6, a histone deacetylase that acts on acetylated H3K9 and H3K56, promotes tumorigenesis. SIRT7, which deacetylates H3K18 and thereby represses transcription of target genes, is activated in cancer to stabilize cells in the transformed state. Nutrients appear to modulate SIRT activity. For example, long-chain fatty acids activate the deacetylase function of SIRT6, and this may affect histone acetylation.
227:
structural changes at their specific points, but can cause many structural changes in distant locations which inevitably affects function. As the chromosome is replicated, the modifications that exist on the parental chromosomes are handed down to daughter chromosomes. The modifications, as part of their function, can recruit enzymes for their particular function and can contribute to the continuation of modifications and their effects after replication has taken place. It has been shown that, even past one replication, expression of genes may still be affected many cell generations later. A study showed that, upon inhibition of HDAC enzymes by
Trichostatin A, genes inserted next to centric heterochromatin showed increased expression. Many cell generations later, in the absence of the inhibitor, the increased gene expression was still expressed, showing modifications can be carried through many replication processes such as mitosis and meiosis.
274:. Major features of the GNAT family include HAT domains approximately 160 residues in length and a conserved bromodomain that has been found to be an acetyl-lysine targeting motif. Gcn5 has been shown to acetylate substrates when it is part of a complex. Recombinant Gcn5 has been found to be involved in the acetylation of the H3 histones of the nucleosome. To a lesser extent, it has been found to also acetylate H2B and H4 histones when involved with other complexes. PCAF has the ability to act as a HAT protein and acetylate histones, it can acetylate non-histone proteins related to transcription, as well as act as a coactivator in many processes including
156:
223:
association, leading to weaker binding of the nucleosomal components. By doing this, the DNA is more accessible and leads to more transcription factors being able to reach the DNA. Thus, acetylation of histones is known to increase the expression of genes through transcription activation. Deacetylation performed by HDAC molecules has the opposite effect. By deacetylating the histone tails, the DNA becomes more tightly wrapped around the histone cores, making it harder for transcription factors to bind to the DNA. This leads to decreased levels of gene expression and is known as gene silencing.
815:, the acetylation of histones can attract proteins to elongated chromatin that has been marked by acetyl groups. It has been hypothesized that the histone tails offer recognition sites that attract proteins responsible for transcriptional activation. Unlike histone core proteins, histone tails are not part of the nucleosome core and are exposed to protein interaction. A model proposed that the acetylation of H3 histones activates gene transcription by attracting other transcription related complexes. Therefore, the acetyl mark provides a site for protein recognition where
836:
cores can be interpreted by transcription factors and complexes which leads to functional implications. This process is facilitated by enzymes such as HATs and HDACs that add or remove modifications on histones, and transcription factors that process and "read" the modification codes. The outcome can be activation of transcription or repression of a gene. For example, the combination of acetylation and phosphorylation have synergistic effects on the chromosomes overall structural condensation level and, hence, induces transcription activation of
652:. HDACs 4 and 5 have been found to most closely resemble each other while HDAC7 maintains a resemblance to both of them. There have been three discovered variants of HDAC9 including HDAC9a, HDAC9b and HDAC9c/HDRP, while more have been suspected. The variants of HDAC9 have been found to have similarities to the rest of the Class IIA HDACs. For HDAC9, the splicing variants can be seen as a way of creating a "fine-tuned mechanism" for differentiation expression levels in the cell. Different cell types may take advantage and utilize different
326:. HAT domains for this family are approximately 250 residues which include cysteine-rich, zinc binding domains as well as N-terminal chromodomains. The MYST proteins Esa1, Sas2 and Sas3 are found in yeast, MOF is found in Drosophila and mice while Tip60, MOZ, MORF, and HBO1 are found in humans. Tip60 has roles in the regulation of gene transcription, HBO has been found to impact the DNA replication process, MORF is able to acetylate free histones (especially H3 and H4) as well as nucleosomal histones.
734:, meaning this HDAC is prone to degradation. HDAC10 has two catalytic domains as well. One active domain is located in the N-terminus and a putative catalytic domain is located in the C-terminus along with an NES domain. Two putative Rb-binding domains have also been found on HDAC10 which shows it may have roles in the regulation of the cell cycle. Two variants of HDAC10 have been found, both having slight differences in length. HDAC6 is the only HDAC to be shown to act on
742:. It is mostly found in the cytoplasm but has been known to be found in the nucleus, complexed together with HDAC11. HDAC10 has been seen to act on HDACs 1, 2, 3 (or SMRT), 4, 5 and 7. Some evidence has been shown that it may have small interactions with HDAC6 as well. This leads researchers to believe that HDAC10 may function more as a recruiter rather than a factor for deacetylation. However, experiments conducted with HDAC10 did indeed show deacetylation activity.
31:
788:. Histone modification is now considered a major regulatory mechanism that is involved in many different stages of genetic functions. Our current understanding is that acetylated lysine residues on histone tails is associated with transcriptional activation. In turn, deacetylated histones are associated with transcriptional repression. In addition, negative correlations have been found between several histone acetylation marks.
522:) leads to increased deacetylase activity, but degrades complex formation between HDACs 1 and 2 and between HDAC1 and mSin3A/YY1. A lower than normal amount of phosphorylation (hypophosphorylation) leads to a decrease in the amount of deacetylase activity, but increases the amount of complex formation. Mutation studies found that major phosphorylation happens at residues
804:. Repression of gene transcription is achieved by the reverse of this mechanism. The acetyl group is removed by one of the HDAC enzymes during deacetylation, allowing histones to interact with DNA more tightly to form compacted nucleosome assembly. This increase in the rigid structure prevents the incorporation of transcriptional machinery, effectively
1174:. Current studies indicate that inhibitors of the HDAC family have therapeutic benefits in a wide range of neurological and psychiatric disorders. Many neurological disorders only affect specific brain regions; therefore, understanding of the specificity of HDACs is still required for further investigations for improved treatments.
236:
526:
and Ser. Indeed, when these residues were mutated, a drastic reduction was seen in the amount of deacetylation activity. This difference in the state of phosphorylation is a way of keeping an optimal level of phosphorylation to ensure there is no over or under expression of deacetylation. HDACs 1 and
994:
Carbon source availability is reflected in histone acetylation in cancer. Glucose and glutamine are the major carbon sources of most mammalian cells, and glucose metabolism is closely related to histone acetylation and deacetylation. Glucose availability affects the intracellular pool of acetyl-CoA,
851:
in order to modify long-term gene expression. The acetylation pattern is regulated by HAT and HADC enzymes and, in turn, sets the local chromatin structure. In this way, acetylation patterns are transmitted and interconnected with protein binding ability and functions in subsequent cell generation.
758:
has been shown to be related to HDACs 3 and 8, but its overall sequence is quite different from the other HDACs, leading it to be in its own category. HDAC11 has a catalytic domain located in its N-terminus. It has not been found incorporated in any HDAC complexes such as Nurd or SMRT which means it
598:
factors must be utilized by HDAC3 in order to activate it. Upon doing so, it gains the ability to co-precipitate with HDACs 4, 5, and 7. HDAC3 can also be found complexed together with HDAC-related protein (HDRP). HDACs 1 and 3 have been found to mediate Rb-RbAp48 interactions which suggests that it
252:
Histone
Acetyltransferases, also known as HATs, are a family of enzymes that acetylate the histone tails of the nucleosome. This, and other modifications, are expressed based on the varying states of the cellular environment. Many proteins with acetylating abilities have been documented and, after a
191:
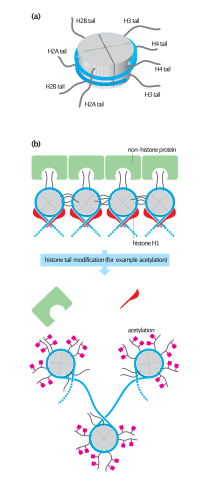
of the DNA and extend through the double helix, which leaves them open for modifications involved in transcriptional activation. Acetylation has been closely associated with increases in transcriptional activation while deacetylation has been linked with transcriptional deactivation. These reactions
888:
and have a significance in regulating gene expression. Structural analysis of transcription factors has shown that highly conserved bromodomains are essential for protein to bind to acetylated lysine. This suggests that specific histone site acetylation has a regulatory role in gene transcriptional
680:
in muscle control differentiation as well as cellular hypertrophy in muscle and cartilage tissues. HDACs 5 and 7 have been shown to work in opposition to HDAC4 during muscle differentiation regulation so as to keep a proper level of expression. There has been evidence that these HDACs also interact
618:
has been found to be most similar to HDAC3. Its major feature is its catalytic domain which contains an NLS region in the center. Two transcripts of this HDAC have been found which include a 2.0kb transcript and a 2.4kb transcript. Unlike the other HDAC molecules, when purified, this HDAC showed to
298:
MOZ (Monocytic
Leukemia Zinc Finger Protein), Ybf2/Sas3, Sas2 and Tip60 (Tat Interacting Protein) all make up MYST, another well known family that exhibits acetylating capabilities. This family includes Sas3, essential SAS-related acetyltransferase (Esa1), Sas2, Tip60, MOF, MOZ, MORF, and HBO1. The
186:
histones. This protein complex forms a cylindrical shape that dsDNA wraps around with approximately 147 base pairs. Nucleosomes are formed as a beginning step for DNA compaction that also contributes to structural support as well as serves functional roles. These functional roles are contributed by
1103:
In rodent models, many agents causing addiction, including tobacco smoke products, alcohol, cocaine, heroin and methamphetamine, cause DNA damage in the brain. During repair of DNA damages some individual repair events may alter the acetylations of histones at the sites of damage, or cause other
685:
factors in the nucleus. Absence of the HDAC3 enzyme has shown to lead to inactivity which makes researchers believe that HDACs 4, 5 and 7 help the incorporation of DNA-binding recruiters for the HDAC3-containing HDAC complexes located in the nucleus. When HDAC4 is knocked out in mice, they suffer
656:
of the HDAC9 enzyme allowing for different forms of regulation. HDACs 4, 5 and 7 have their catalytic domains located in the C-terminus along with an NLS region while HDAC9 has its catalytic domain located in the N-terminus. However, the HDAC9 variant HDAC9c/HDRP lacks a catalytic domain but has a
835:
hypothesis suggests the idea that patterns of post-translational modifications on histones, collectively, can direct specific cellular functions. Chemical modifications of histone proteins often occur on particular amino acids. This specific addition of single or multiple modifications on histone
222:
Acetylation has the effect of changing the overall charge of the histone tail from positive to neutral. Nucleosome formation is dependent on the positive charges of the H4 histones and the negative charge on the surface of H2A histone fold domains. Acetylation of the histone tails disrupts this
347:
make up the next family of HATs. This family of HATs contain HAT domains that are approximately 500 residues long and contain bromodomains as well as three cysteine-histidine rich domains that help with protein interactions. These HATs are known to acetylate all of the histone subunits in the
242:
Shown in this illustration, the dynamic state of histone acetylation/deacetylation regulated by HAT and HDAC enzymes. Acetylation of histones alters accessibility of chromatin and allows DNA binding proteins to interact with exposed sites to activate gene transcription and downstream cellular
226:
Acetylated histones, the octomeric protein cores of nucleosomes, represent a type of epigenetic marker within chromatin. Studies have shown that one modification has the tendency to influence whether another modification will take place. Modifications of histones can not only cause secondary
472:
are in the first class of HDACs are most closely related to one another. By analyzing the overall sequences of both HDACs, their similarity was found to be approximately 82% homologous. These enzymes have been found to be inactive when isolated which led to the conclusion that they must be
3058:
Substance Abuse and Mental Health
Services Administration, Results from the 2013 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: Summary of National Findings, NSDUH Series H-48, HHS Publication No. (SMA) 14-4863. Rockville, MD: Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration,
722:. These two HDACs are most closely related to each other in overall sequence. However, HDAC6's catalytic domain is most similar to HDAC9. A unique feature of HDAC6 is that it contains two catalytic domains in tandem of one another. Another unique feature of HDAC6 is the HDAC6-,
261:
General
Control Non-Derepressible 5 (Gcn5) –related N-Acetyltransferases (GNATs) is one of the many studied families with acetylation abilities. This superfamily includes the factors Gcn5 which is included in the SAGA, SLIK, STAGA, ADA, and A2 complexes, Gcn5L,
930:
showed there is an overall decrease in HDAC activity with unchanged levels of HAT activity. Results have shown that there is an important role for HAT/HDAC activity balance in inflammatory lung diseases and provided insights on possible therapeutic targets.
672:. All three HDACs work to repress the myogenic transcription factor MEF2 which an essential role in muscle differentiation as a DNA binding transcription factor. Binding of HDACs to MEF2 inhibits muscle differentiation, which can be reversed by action of
253:
time, were categorized based on sequence similarities between them. These similarities are high among members of a family, but members from different families show very little resemblance. Some of the major families identified so far are as follows.
795:
tails of histones have a tendency to weaken the chromatin's overall structure. Addition of an acetyl group, which carries a negative charge, effectively removes the positive charge and hence, reduces the interaction between the histone tail and the
1165:
Epigenetic modifications also play a role in neurological disorders. Deregulation of histones modification are found to be responsible for deregulated gene expression and hence associated with neurological and psychological disorders, such as
959:, suggesting an important regulatory role of histone deacetylation on the expression of tumor suppressor genes. One of the examples is the regulation role of histone acetylation/deacetylation in P300 and CBP, both of which contribute to
974:
represents a new category for anticancer drugs that are in development. Vorinostat targets histone acetylation mechanisms and can effectively inhibit abnormal chromatin remodeling in cancerous cells. Targets of
Vorinostat includes
902:
Gene expression is regulated by histone acetylation and deacetylation, and this regulation is also applicable to inflammatory genes. Inflammatory lung diseases are characterized by expression of specific inflammatory genes such as
452:. Classes of HDAC proteins are divided and grouped together based on the comparison to the sequence homologies of Rpd3, Hos1 and Hos2 for Class I HDACs, HDA1 and Hos3 for the Class II HDACs and the sirtuins for Class III HDACs.
3234:
D'Addario C, Caputi FF, Ekström TJ, Di
Benedetto M, Maccarrone M, Romualdi P, Candeletti S (February 2013). "Ethanol induces epigenetic modulation of prodynorphin and pronociceptin gene expression in the rat amygdala complex".
299:
members of this family have multiple functions, not only with activating and silencing genes, but also affect development and have implications in human diseases. Sas2 and Sas3 are involved in transcription silencing, MOZ and
1130:
models, it has been demonstrated that cardiac stress can result in gene expression changes and alter cardiac function. These changes are mediated through HATs/HDACs posttranslational modification signaling. HDAC inhibitor
1014:, and much of the work on addiction has focused on histone acetylation. Once particular epigenetic alterations occur, they appear to be long lasting "molecular scars" that may account for the persistence of addictions.
498:
which make up the core of each complex. Other complexes may be needed though in order to initiate the maximum amount of available activity possible. HDACs 1 and 2 can also bind directly to DNA binding proteins such as
1099:
of mice after chronic cocaine exposure, were found to be associated with hyperacetylation of H3 or H4. Many of these individual genes are directly related to aspects of addiction associated with cocaine exposure.
554:
of the other Class I HDACs could compensate for the loss of HDAC1. This inability to recover from HDAC1 KO leads researchers to believe that there are both functional uniqueness to each HDAC as well as regulatory
582:. The NLS functions as a signal for nuclear action while an NES functions with HDACs that perform work outside of the nucleus. A presence of both signals for HDAC3 suggests it travels between the nucleus and the
477:
in order to activate their deacetylase abilities. There are three major protein complexes that HDAC 1 & 2 may incorporate themselves into. These complexes include Sin3 (named after its characteristic protein
1123:, regulatory functions of histone acetylation and deacetylation can have implications with genes that cause other diseases. Studies on histone modifications may reveal many novel therapeutic targets.
3494:
de Souza MF, Gonçales TA, Steinmetz A, Moura DJ, Saffi J, Gomez R, Barros HM (April 2014). "Cocaine induces DNA damage in distinct brain areas of female rats under different hormonal conditions".
3352:
Renthal W, Kumar A, Xiao G, Wilkinson M, Covington HE, Maze I, Sikder D, Robison AJ, LaPlant Q, Dietz DM, Russo SJ, Vialou V, Chakravarty S, Kodadek TJ, Stack A, Kabbaj M, Nestler EJ (May 2009).
199:
groups of lysine amino acid residues. These residues are located on the tails of histones that make up the nucleosome of packaged dsDNA. The process is aided by factors known as
1568:
Gallinari P, Di Marco S, Jones P, Pallaoro M, Steinkühler C (March 2007). "HDACs, histone deacetylation and gene transcription: from molecular biology to cancer therapeutics".
131:. Acetylation removes the positive charge on the histones, thereby decreasing the interaction of the N termini of histones with the negatively charged phosphate groups of
623:
have revealed that different tissue types show varying degrees of HDAC8 expression but has been observed in smooth muscles and is thought to contribute to contractility.
3414:"Biomarkers of disease can be detected in mice as early as 4 weeks after initiation of exposure to third-hand smoke levels equivalent to those found in homes of smokers"
2533:
Mroz RM, Noparlik J, Chyczewska E, Braszko JJ, Holownia A (November 2007). "Molecular basis of chronic inflammation in lung diseases: new therapeutic approach".
3537:
Qiusheng Z, Yuntao Z, Rongliang Z, Dean G, Changling L (July 2005). "Effects of verbascoside and luteolin on oxidative damage in brain of heroin treated mice".
4106:
4060:
Grayson DR, Kundakovic M, Sharma RP (February 2010). "Is there a future for histone deacetylase inhibitors in the pharmacotherapy of psychiatric disorders?".
872:
of N- and C-terminal histone tails attracts various transcription initiation factors that contain bromodomains, including human transcriptional coactivator
673:
4132:
1111:
In 2013, 22.7 million persons aged 12 or older needed treatment for an illicit drug or alcohol use problem (8.6 percent of persons aged 12 or older).
540:
4972:
574:
region that was found to be required for transcriptional repression as well as its deacetylase activity. It also contains two regions, one called a
1061:. In rats exposed to alcohol for up to 5 days, there was an increase in histone 3 lysine 9 acetylation in the pronociceptin promoter in the brain
4519:
3564:
Johnson Z, Venters J, Guarraci FA, Zewail-Foote M (June 2015). "Methamphetamine induces DNA damage in specific regions of the female rat brain".
2124:
Spange S, Wagner T, Heinzel T, Krämer OH (January 2009). "Acetylation of non-histone proteins modulates cellular signalling at multiple levels".
800:. This opens up the usually tightly packed nucleosome and allows transcription machinery to come into contact with the DNA template, leading to
619:
be enzymatically active. At this point, due to its recent discovery, it is not yet known if it is regulated by co-repressor protein complexes.
1245:
927:
348:
nucleosome. They also have the ability to acetylate and mediate non-histone proteins involved in transcription and are also involved in the
776:
activity can be traced back to the work of Vicent
Allfrey and colleagues in 1964. The group hypothesized that histone proteins modified by
368:
There are other proteins that have acetylating abilities but differ in structure to the previously mentioned families. One HAT is called
843:
Experiments investigating acetylation patterns of H4 histones suggested that these modification patterns are collectively maintained in
135:. As a consequence, the condensed chromatin is transformed into a more relaxed structure that is associated with greater levels of gene
139:. This relaxation can be reversed by deacetylation catalyzed by HDAC activity. Relaxed, transcriptionally active DNA is referred to as
4184:
4164:
1339:
4272:
3295:
2901:
1818:
676:
which works to dissociate the HDAC/MEF2 complex by phosphorylating the HDAC portion. They have been seen to be involved in cellular
1842:
Jiang H, Gao Q, Zheng W, Yin S, Wang L, Zhong L, Ali A, Khan T, Hao Q, Fang H, Sun X, Xu P, Pandita TK, Jiang X, Shi Q (May 2018).
155:
791:
The regulatory mechanism is thought to be twofold. Lysine is an amino acid with a positive charge when unmodified. Lysines on the
922:
Specifically, gene expression data demonstrated increased activity of HAT and decreased level of HDAC activity in patients with
706:. HDAC9 KO mice are shown to suffer from cardiac hypertrophy which is exacerbated in mice that are double KO for HDACs 9 and 5.
4869:
4426:
4370:
682:
595:
591:
551:
3455:"Alcohol induces DNA damage and the Fanconi anemia D2 protein implicating FANCD2 in the DNA damage response pathways in brain"
4365:
2689:
Duvic M, Talpur R, Ni X, Zhang C, Hazarika P, Kelly C, Chiao JH, Reilly JF, Ricker JL, Richon VM, Frankel SR (January 2007).
869:
812:
369:
300:
1797:
Torok MS, Grant PA (2004). "Histone acetyltransferase proteins contribute to transcriptional processes at multiple levels".
1670:
170:
that are wrapped around protein complexes called histone cores. These histone cores are composed of 8 subunits, two each of
939:
Due to the regulatory role during transcription of epigenetic modifications in genes, it is not surprising that changes in
4453:
4384:
4125:
3069:
2691:"Phase 2 trial of oral vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, SAHA) for refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL)"
1092:
575:
85:
4189:
967:
4512:
3083:
Levine A, Huang Y, Drisaldi B, Griffin EA, Pollak DD, Xu S, Yin D, Schaffran C, Kandel DB, Kandel ER (November 2011).
335:
303:
are involved with the formation of leukemic transclocation products while MOF is involved in dosage compensation in
4962:
4545:
4404:
3913:
Shikama N, Lutz W, Kretzschmar R, Sauter N, Roth JF, Marino S, Wittwer J, Scheidweiler A, Eckner R (October 2003).
3085:"Molecular mechanism for a gateway drug: epigenetic changes initiated by nicotine prime gene expression by cocaine"
1024:. After 7 days of nicotine treatment of mice, acetylation of both histone H3 and histone H4 was increased at the
4742:
4678:
4648:
4626:
1183:
908:
377:
200:
188:
93:
1370:
4922:
4897:
4864:
4536:
4528:
4448:
4236:
4149:
4118:
1120:
773:
723:
504:
353:
286:-signaled activation. Elp3 has the ability to acetylate all histone subunits and also shows involvement in the
136:
3705:
Cao DJ, Wang ZV, Battiprolu PK, Jiang N, Morales CR, Kong Y, Rothermel BA, Gillette TG, Hill JA (March 2011).
2302:"Mitogen-stimulated phosphorylation of histone H3 is targeted to a small hyperacetylation-sensitive fraction"
112:) to another. Deacetylation is simply the reverse reaction where an acetyl group is removed from a molecule.
4917:
4885:
4859:
4843:
4532:
4409:
4226:
4211:
474:
304:
2400:
Filippakopoulos P, Knapp S (May 2014). "Targeting bromodomains: epigenetic readers of lysine acetylation".
1326:
Kuo MH, Allis CD (August 1998). "Roles of histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases in gene regulation".
759:
may have a special function unique to itself. It has been found that HDAC11 remains mainly in the nucleus.
235:
123:, the basic structural unit of the chromosomes and ultimately higher order structures, represent a type of
4752:
4505:
4414:
4339:
4231:
695:
373:
4936:
4931:
4799:
4701:
4329:
4314:
4194:
1741:"HATs and HDACs: from structure, function and regulation to novel strategies for therapy and prevention"
1155:
816:
579:
469:
1893:
Marmorstein R, Roth SY (April 2001). "Histone acetyltransferases: function, structure, and catalysis".
404:
There are a total of four classes that categorize
Histone Deacetylases (HDACs). Class I includes HDACs
4833:
4747:
4713:
4607:
4436:
4334:
4252:
3718:
3661:
3188:
2313:
1941:
1385:
1108:. Such epigenetic scars likely contribute to the persistent epigenetic changes found in addictions.
1036:
943:
markers, such as acetylation, can contribute to cancer development. HDACs expression and activity in
881:
837:
519:
344:
3964:"Disease- and age-related changes in histone acetylation at gene promoters in psychiatric disorders"
3915:"Essential function of p300 acetyltransferase activity in heart, lung and small intestine formation"
1930:"Acetylation and Methylation of Histones and Their Possible Role in the Regulation of RNA Synthesis"
4816:
4784:
4670:
4644:
4262:
2030:
Zentner GE, Henikoff S (March 2013). "Regulation of nucleosome dynamics by histone modifications".
1193:
1188:
1143:
1136:
1127:
1035:
of the brain, causing 61% increase in FosB expression. This would also increase expression of the
1028:
885:
556:
212:
97:
1050:
functions as a "sustained molecular switch" and "master control protein" in the development of an
4585:
4397:
4280:
4085:
3589:
3519:
3323:
3260:
3157:
3132:
Ruffle JK (November 2014). "Molecular neurobiology of addiction: what's all the (Δ)FosB about?".
2929:
2763:
2622:
2425:
2233:
2190:
2055:
1770:
1593:
1409:
1351:
1171:
1119:
Suggested by the idea that the structure of chromatin can be modified to allow or deny access of
1072:
801:
780:
groups added negative charges to the positive lysines, and thus, reduced the interaction between
570:
has been found to be most closely related to HDAC8. HDAC3 contains a non-conserved region in the
919:
for inflammatory lung diseases interfere with HAT/HDAC activity to turn off inflammatory genes.
1065:
complex. This acetylation is an activating mark for pronociceptin. The nociceptin/nociceptin
30:
4967:
4904:
4481:
4077:
4042:
3993:
3944:
3895:
3844:
3795:
3746:
3707:"Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors attenuate cardiac hypertrophy by suppressing autophagy"
3687:
3630:
3581:
3546:
3511:
3476:
3435:
3383:
3311:
3291:
3252:
3216:
3149:
3114:
3038:
2986:
2917:
2897:
2866:
2814:
2755:
2720:
2671:
2614:
2579:
2538:
2515:
2466:
2417:
2382:
2341:
2282:
2225:
2182:
2141:
2106:
2047:
1969:
1910:
1875:
1824:
1814:
1762:
1716:
1674:
1634:
1585:
1509:
1401:
1343:
1301:
1241:
1096:
1043:
1032:
811:
Another implication of histone acetylation is to provide a platform for protein binding. As a
507:. HDACs 1 and 2 have been found to express regulatory roles in key cell cycle genes including
483:
287:
204:
109:
2075:"Uncovering correlated variability in epigenomic datasets using the Karhunen-Loeve transform"
4826:
4809:
4069:
4032:
4024:
3983:
3975:
3934:
3926:
3885:
3875:
3834:
3826:
3785:
3777:
3736:
3726:
3677:
3669:
3620:
3573:
3503:
3466:
3425:
3373:
3365:
3301:
3283:
3244:
3206:
3196:
3141:
3104:
3096:
3028:
3020:
2976:
2968:
2907:
2889:
2856:
2848:
2804:
2794:
2747:
2710:
2702:
2661:
2653:
2606:
2569:
2505:
2497:
2456:
2409:
2372:
2331:
2321:
2272:
2264:
2253:"Covalent histone modifications--miswritten, misinterpreted and mis-erased in human cancers"
2217:
2172:
2133:
2096:
2086:
2039:
2010:
2000:
1959:
1949:
1902:
1865:
1855:
1806:
1752:
1708:
1666:
1624:
1577:
1499:
1491:
1393:
1335:
1291:
1091:
region and deacetylation at 206 genes. At least 45 genes, shown in previous studies to be
420:. Class II is divided into two subgroups, Class IIA and Class IIB. Class IIA includes HDACs
279:
1146:
with cellular HAT activity suggesting an essential role of histone acetylation status with
4690:
4458:
4295:
4141:
3766:"Class II histone deacetylases act as signal-responsive repressors of cardiac hypertrophy"
3400:
3335:
2941:
2888:. Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science. Vol. 128. pp. 51–87.
1203:
1066:
912:
653:
515:
315:
308:
147:. Condensation can be brought about by processes including deacetylation and methylation.
144:
78:
3864:"Dysregulation of histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases in cardiovascular diseases"
738:, acting as a tubulin deacetylase which helps in the regulation of microtubule-dependent
4497:
3722:
3665:
3192:
2317:
1945:
1389:
4900:
4888:
4838:
4285:
4257:
4037:
4012:
3988:
3963:
3890:
3863:
3839:
3814:
3790:
3765:
3741:
3706:
3682:
3649:
3378:
3353:
3306:
3287:
3109:
3084:
3033:
3008:
2981:
2956:
2912:
2893:
2861:
2836:
2809:
2782:
2715:
2690:
2666:
2641:
2510:
2485:
2377:
2360:
2277:
2252:
2101:
2074:
2015:
1988:
1870:
1843:
1504:
1479:
1132:
960:
952:
948:
805:
792:
739:
669:
532:
17:
3939:
3914:
3781:
2177:
2160:
1964:
1929:
1906:
1844:"MOF influences meiotic expansion of H2AX phosphorylation and spermatogenesis in mice"
1810:
4956:
4602:
4486:
4173:
3471:
3454:
3354:"Genome-wide analysis of chromatin regulation by cocaine reveals a role for sirtuins"
3211:
3176:
2767:
2336:
2301:
1167:
1088:
620:
587:
536:
283:
3593:
3523:
3264:
3161:
2429:
2237:
2194:
2059:
1774:
1597:
1355:
203:(HATs). HAT molecules facilitate the transfer of an acetyl group from a molecule of
4360:
4290:
4159:
4089:
2626:
2208:
Winston F, Allis CD (July 1999). "The bromodomain: a chromatin-targeting module?".
1413:
916:
832:
691:
660:
For HDACs 4, 5 and 7, conserved binding domains have been discovered that bind for
528:
372:, which has a HAT domain located at the C-terminus end of the protein along with a
2501:
3369:
3145:
3100:
3024:
2706:
2574:
2558:"Histone acetylation and deacetylation: importance in inflammatory lung diseases"
2557:
2461:
2445:"Histone acetylation and deacetylation: importance in inflammatory lung diseases"
2444:
2137:
1860:
4789:
4757:
4660:
4463:
4392:
3609:"The peroxidative DNA damage and apoptosis in methamphetamine-treated rat brain"
1478:
de
Ruijter AJ, van Gennip AH, Caron HN, Kemp S, van Kuilenburg AB (March 2003).
1198:
1147:
1003:
861:
820:
727:
687:
677:
393:
385:
175:
171:
140:
101:
3711:
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
3181:
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
2306:
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
1934:
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
50:
core histones, and DNA. The view is from the top through the superhelical axis.
4941:
4635:
4590:
4580:
4575:
4570:
4565:
4421:
4028:
3830:
3673:
3248:
2972:
2799:
2091:
1208:
1084:
1080:
1058:
971:
956:
940:
797:
571:
381:
349:
275:
187:
the tails of the histone subunits. The histone tails insert themselves in the
183:
179:
163:
124:
120:
70:
62:
2884:
Hitchcock LN, Lattal KM (2014). "Histone-mediated epigenetics in addiction".
2657:
1480:"Histone deacetylases (HDACs): characterization of the classical HDAC family"
539:
and showed a drastic reduction in the production but increased expression of
4597:
3731:
3577:
3507:
2361:"The role of human bromodomains in chromatin biology and gene transcription"
2326:
2005:
1139:
1105:
1051:
1017:
1011:
731:
699:
600:
583:
357:
319:
128:
74:
4081:
4073:
4046:
3997:
3948:
3930:
3899:
3848:
3799:
3764:
Zhang CL, McKinsey TA, Chang S, Antos CL, Hill JA, Olson EN (August 2002).
3750:
3691:
3634:
3585:
3550:
3515:
3480:
3439:
3387:
3315:
3256:
3220:
3201:
3153:
3118:
3042:
2990:
2921:
2870:
2818:
2759:
2724:
2675:
2618:
2610:
2583:
2542:
2519:
2470:
2421:
2386:
2286:
2229:
2186:
2145:
2110:
2051:
1973:
1914:
1879:
1828:
1766:
1757:
1740:
1720:
1712:
1678:
1589:
1513:
1305:
3880:
2345:
1954:
1657:
Turner BM (September 2000). "Histone acetylation and an epigenetic code".
1638:
1581:
1405:
1347:
1296:
1279:
1069:
system is involved in the reinforcing or conditioning effects of alcohol.
4804:
4794:
4441:
4431:
4355:
1629:
1612:
1340:
10.1002/(sici)1521-1878(199808)20:8<615::aid-bies4>3.0.co;2-h
1062:
1021:
904:
785:
1699:
Marmorstein R (August 2001). "Structure of histone acetyltransferases".
490:. The Sin3 complex and the NuRD complex both contain HDACs 1 and 2, the
4764:
4631:
4177:
3979:
3625:
3608:
3430:
3413:
1495:
1076:
1007:
951:
and increased activity of HDACs has been shown to be characteristic of
848:
844:
735:
604:
445:
323:
211:
group on lysine. When a lysine is to be deacetylated, factors known as
116:
66:
2043:
396:
located at the C-terminus region and a HAT domain located in-between.
4560:
3607:
Tokunaga I, Ishigami A, Kubo S, Gotohda T, Kitamura O (August 2008).
923:
865:
777:
755:
730:(HUB) domain in the C-terminus which shows some functions related to
719:
703:
599:
functions in cell cycle progression. HDAC3 also shows involvement in
547:
523:
449:
441:
215:(HDACs) catalyze the removal of the acetyl group with a molecule of H
195:
The mechanism for acetylation and deacetylation takes place on the NH
105:
89:
58:
4013:"Epigenetic mechanisms of neurodegeneration in Huntington's disease"
2852:
2751:
2597:
Glozak MA, Seto E (August 2007). "Histone deacetylases and cancer".
2484:
Kuo CH, Hsieh CC, Lee MS, Chang KT, Kuo HF, Hung CH (January 2014).
2413:
2268:
1010:
tails in specific regions of the brain are of central importance in
34:
The crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle consisting of
3650:"Epigenetic abnormalities in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure"
3453:
Rulten SL, Hodder E, Ripley TL, Stephens DN, Mayne LV (July 2008).
3282:. Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Vol. 148. pp. 747–765.
1671:
10.1002/1521-1878(200009)22:9<836::AID-BIES9>3.0.CO;2-X
4821:
4673:
4199:
4110:
2221:
1397:
1151:
988:
984:
980:
976:
944:
715:
661:
649:
645:
641:
637:
615:
567:
495:
491:
487:
479:
465:
437:
433:
429:
425:
421:
417:
413:
409:
405:
340:
312:
234:
154:
29:
1020:
smokers (about 21% of the US population) are usually addicted to
108:
functional group is transferred from one molecule (in this case,
4892:
4722:
4653:
3278:
Walker DM, Nestler EJ (2018). "Neuroepigenetics and addiction".
2486:"Epigenetic regulation in allergic diseases and related studies"
1159:
1047:
1039:
1025:
877:
873:
665:
389:
271:
267:
263:
4501:
4114:
2738:
Grant S, Easley C, Kirkpatrick P (January 2007). "Vorinostat".
1613:"Histone acetylation and transcriptional regulatory mechanisms"
1278:
Verdone L, Agricola E, Caserta M, Di Mauro E (September 2006).
1231:
1229:
1227:
1225:
1223:
592:
Silencing Mediator for Retinoic Acid and Thyroid Hormone (SMRT)
4169:
1371:"Histone acetylation in chromatin structure and transcription"
781:
543:
508:
500:
167:
132:
1104:
epigenetic alterations, and thus leave an epigenetic scar on
84:
Histone acetylation and deacetylation are essential parts of
2126:
The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology
868:
recognition on histones by nucleosome remodelling proteins.
4011:
Lee J, Hwang YJ, Kim KY, Kowall NW, Ryu H (October 2013).
2640:
Cohen I, Poręba E, Kamieniarz K, Schneider R (June 2011).
2300:
Barratt MJ, Hazzalin CA, Cano E, Mahadevan LC (May 1994).
702:. This interaction leads to a role in clonal expansion of
4105:
Animation of histone tail acetylation and deacetylation:
3862:
Wang Y, Miao X, Liu Y, Li F, Liu Q, Sun J, Cai L (2014).
2837:"Transcriptional and epigenetic mechanisms of addiction"
772:
The discovery of histone acetylation causing changes in
392:
which has a Kinase domain at the N-terminus region, two
143:. More condensed (tightly packed) DNA is referred to as
3813:
Lehmann LH, Worst BC, Stanmore DA, Backs J (May 2014).
3566:
Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology & Physiology
3496:
Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology & Physiology
3401:
https://www.drugsandalcohol.ie/12728/1/NIDA_Cocaine.pdf
3177:"DeltaFosB: a sustained molecular switch for addiction"
1236:
Watson JD, Baker TA, Gann A, Levine M, Losik R (2014).
484:
Nucleosome Remodelling and Deacetylating complex (NuRD)
159:
Histone tails and their function in chromatin formation
2161:"Signaling to chromatin through histone modifications"
1075:
occurs in about 0.5% of the US population. Repeated
819:
interact with the acetylated histone tails via their
2159:
Cheung P, Allis CD, Sassone-Corsi P (October 2000).
4913:
4878:
4852:
4777:
4735:
4712:
4689:
4625:
4618:
4553:
4544:
4474:
4383:
4348:
4322:
4313:
4271:
4245:
4219:
4210:
4148:
3815:"Histone deacetylase signaling in cardioprotection"
2886:
Epigenetics and Neuroplasticity—Evidence and Debate
2365:
Current Opinion in Drug Discovery & Development
1079:administration in mice induces hyperacetylation of
657:50% similarity to the N-terminus of HDACs 4 and 5.
3412:Adhami N, Chen Y, Martins-Green M (October 2017).
2957:"Epigenetic regulation in substance use disorders"
1142:. Studies on p300 and CREB-binding protein linked
681:with HDAC3 as a co-recruitment factor to the SMRT/
341:Adenoviral E1A-associated protein of 300kDa (p300)
264:p300/CREB-binding protein associated factor (PCAF)
119:, octameric proteins that organize chromatin into
3009:"Epigenome Maintenance in Response to DNA Damage"
2830:
2828:
1284:Briefings in Functional Genomics & Proteomics
586:. HDAC3 has even been found to interact with the
380:in the middle. Another is ATF-2 which contains a
3175:Nestler EJ, Barrot M, Self DW (September 2001).
2642:"Histone modifiers in cancer: friends or foes?"
1989:"Vincent Allfrey's Work on Histone Acetylation"
1240:(Seventh ed.). Boston: Pearson/CSH Press.
947:cells is very different from normal cells. The
240:Histone acetylation alters chromatin structure.
3459:Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research
3134:The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse
1928:Allfrey VG, Faulkner R, Mirsky AE (May 1964).
864:is a motif that is responsible for acetylated
311:in mice as it is involved in the expansion of
4513:
4126:
2783:"Metabolic recoding of epigenetics in cancer"
1895:Current Opinion in Genetics & Development
1694:
1692:
1690:
1688:
1057:About 7% of the US population is addicted to
88:. These reactions are typically catalysed by
8:
3654:Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine
1563:
1561:
1559:
1557:
1555:
1553:
1551:
1549:
1547:
1545:
1543:
1473:
1471:
1469:
1467:
1465:
1463:
1461:
1459:
1457:
1455:
1453:
1451:
1449:
1447:
1445:
1443:
27:Biological processes used in gene regulation
3962:Tang B, Dean B, Thomas EA (December 2011).
1541:
1539:
1537:
1535:
1533:
1531:
1529:
1527:
1525:
1523:
1441:
1439:
1437:
1435:
1433:
1431:
1429:
1427:
1425:
1423:
514:Activity of these HDACs can be affected by
192:occur post-translation and are reversible.
4622:
4550:
4520:
4506:
4498:
4319:
4281:Precursor mRNA (pre-mRNA / hnRNA)
4216:
4133:
4119:
4111:
3347:
3345:
2556:Barnes PJ, Adcock IM, Ito K (March 2005).
2443:Barnes PJ, Adcock IM, Ito K (March 2005).
541:Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitors (CDKIs)
527:2 have been found only exclusively in the
518:. An increased amount of phosphorylation (
388:with a HAT domain in-between. The last is
4036:
3987:
3938:
3889:
3879:
3868:Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
3838:
3789:
3740:
3730:
3681:
3624:
3470:
3429:
3377:
3305:
3210:
3200:
3108:
3032:
3007:Dabin J, Fortuny A, Polo SE (June 2016).
2980:
2911:
2860:
2808:
2798:
2714:
2665:
2573:
2509:
2460:
2376:
2335:
2325:
2276:
2176:
2100:
2090:
2032:Nature Structural & Molecular Biology
2014:
2004:
1963:
1953:
1869:
1859:
1756:
1628:
1503:
1295:
1273:
1271:
1269:
1267:
1265:
1263:
1261:
1259:
1257:
231:Histone acetylation/deacetylation enzymes
3054:
3052:
3002:
3000:
1792:
1790:
1788:
1786:
1784:
1652:
1650:
1648:
1280:"Histone acetylation in gene regulation"
603:and a transcription independent role in
2835:Robison AJ, Nestler EJ (October 2011).
1734:
1732:
1730:
1219:
382:transcriptional activation (ACT) domain
3331:
3321:
2937:
2927:
2535:Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology
2251:Chi P, Allis CD, Wang GG (July 2010).
1135:was reported to reduce stress induced
386:basic zipper DNA-binding (bZip) domain
4666:Histone acetylation and deacetylation
4301:Histone acetylation and deacetylation
2359:Sanchez R, Zhou MM (September 2009).
2073:Madrigal P, Krajewski P (July 2015).
1321:
1319:
1317:
1315:
928:chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
674:Ca/calmodulin-dependent kinase (CaMK)
596:Nuclear Receptor Co-Repressor (N-CoR)
370:steroid receptor coactivator 1 (SRC1)
55:Histone acetylation and deacetylation
7:
4366:Ribosome-nascent chain complex (RNC)
3819:Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences
3613:The Journal of Medical Investigation
694:. HDAC7 has been shown to suppress
690:hypertrophy and die due to extreme
376:and PAS A and PAS B domains with a
3288:10.1016/B978-0-444-64076-5.00048-X
2955:McQuown SC, Wood MA (April 2010).
2894:10.1016/B978-0-12-800977-2.00003-6
25:
3237:Journal of Molecular Neuroscience
662:C-terminal binding protein (CtBP)
576:Nuclear Localization Signal (NLS)
492:Rb-associated protein 48 (RbAp48)
3472:10.1111/j.1530-0277.2008.00673.x
2562:The European Respiratory Journal
2449:The European Respiratory Journal
666:myocyte enhancer factor 2 (MEF2)
535:, mice were found to die during
378:LXXLL receptor interacting motif
248:Histone acetyltransferase (HATs)
4973:Post-translational modification
4870:Archaeal transcription factor B
4371:Post-translational modification
1993:Journal of Biological Chemistry
1739:Yang XJ, Seto E (August 2007).
870:Posttranslational modifications
436:while Class IIB includes HDACs
57:are the processes by which the
3089:Science Translational Medicine
2740:Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery
2402:Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery
1369:Grunstein M (September 1997).
813:posttranslational modification
1:
3782:10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00861-9
2537:. 58 Suppl 5 (Pt 2): 453–60.
2502:10.5415/apallergy.2014.4.1.14
2178:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00118-5
1907:10.1016/S0959-437X(00)00173-8
1811:10.1016/S0065-3233(04)67007-0
1799:Advances in Protein Chemistry
1238:Molecular biology of the gene
966:Approved in 2006 by the U.S.
636:The Class IIA HDACs includes
3370:10.1016/j.neuron.2009.03.026
3146:10.3109/00952990.2014.933840
3101:10.1126/scitranslmed.3003062
3025:10.1016/j.molcel.2016.04.006
2841:Nature Reviews. Neuroscience
2781:Wang YP, Lei QY (May 2018).
2707:10.1182/blood-2006-06-025999
2575:10.1183/09031936.05.00117504
2462:10.1183/09031936.05.00117504
2138:10.1016/j.biocel.2008.08.027
1861:10.1371/journal.pgen.1007300
1701:Journal of Molecular Biology
1087:at 1,696 genes in one brain
968:Food and Drug Administration
714:The Class IIB HDACs include
77:and deacetylated as part of
580:Nuclear Export Signal (NES)
503:, Rb binding protein 1 and
448:and Class IV contains only
400:Histone deacetylase (HDACs)
336:p300-CBP coactivator family
168:double-stranded DNA (dsDNA)
4989:
4546:Transcriptional regulation
2961:Current Psychiatry Reports
345:CREB-binding protein (CBP)
333:
201:histone acetyltransferases
4743:Transcription coregulator
4679:Histone acetyltransferase
4649:Histone methyltransferase
4627:Histone-modifying enzymes
4029:10.1007/s13311-013-0206-5
3831:10.1007/s00018-013-1516-9
3674:10.1007/s12199-007-0007-8
3249:10.1007/s12031-012-9829-y
2973:10.1007/s11920-010-0099-5
2800:10.1186/s40880-018-0302-3
2210:Nature Structural Biology
2092:10.1186/s13040-015-0051-7
1184:Histone acetyltransferase
1150:responsive genes such as
909:AP-1 transcription factor
444:. Class III contains the
282:-mediated activation and
94:histone acetyltransferase
65:tail protruding from the
4432:sequestration (P-bodies)
3968:Translational Psychiatry
3070:"Is nicotine addictive?"
2658:10.1177/1947601911417176
1121:transcription activators
768:Transcription regulation
104:is the process where an
4844:Internal control region
4410:Gene regulatory network
3732:10.1073/pnas.1015081108
3648:Mano H (January 2008).
3578:10.1111/1440-1681.12404
3508:10.1111/1440-1681.12218
2327:10.1073/pnas.91.11.4781
2006:10.1074/jbc.O112.000248
1987:Mukhopadhyay R (2012).
1617:Genes & Development
1611:Struhl K (March 1998).
1484:The Biochemical Journal
827:Histone code hypothesis
322:to pachytene stages of
307:. MOF also influences
18:Acetylation of histones
4415:cis-regulatory element
4074:10.1124/mol.109.061333
4062:Molecular Pharmacology
3280:Neurogenetics, Part II
3202:10.1073/pnas.191352698
2611:10.1038/sj.onc.1210610
2257:Nature Reviews. Cancer
1758:10.1038/sj.onc.1210599
1713:10.1006/jmbi.2001.4859
601:stem cell self-renewal
374:basic helix-loop-helix
244:
207:(Acetyl-CoA) to the NH
160:
51:
4937:Intrinsic termination
4702:DNA methyltransferase
2787:Cancer Communications
1955:10.1073/pnas.51.5.786
1582:10.1038/sj.cr.7310149
898:Inflammatory diseases
817:transcription factors
238:
158:
33:
4714:Chromatin remodeling
4437:alternative splicing
4427:Post-transcriptional
4253:Transcription factor
3931:10.1093/emboj/cdg502
2490:Asia Pacific Allergy
1630:10.1101/gad.12.5.599
882:CREB-binding protein
838:immediate early gene
808:gene transcription.
763:Biological functions
726:, and Brap2-related
520:hyperphosphorylation
501:Yin and Yang 1 (YY1)
213:histone deacetylases
61:residues within the
4671:Histone deacetylase
4661:Histone demethylase
4645:Histone methylation
4361:Transfer RNA (tRNA)
3881:10.1155/2014/641979
3723:2011PNAS..108.4123C
3666:2008EHPM...13...25M
3193:2001PNAS...9811042N
2318:1994PNAS...91.4781B
1946:1964PNAS...51..786A
1390:1997Natur.389..349G
1297:10.1093/bfgp/ell028
1194:Histone methylation
1189:Histone deacetylase
1144:cardiac hypertrophy
1128:cardiac hypertrophy
1126:Based on different
151:Mechanism of action
100:" (HDAC) activity.
98:histone deacetylase
4475:Influential people
4454:Post-translational
4273:Post-transcription
3980:10.1038/tp.2011.61
3626:10.2152/jmi.55.241
3431:10.1042/CS20171053
2646:Genes & Cancer
1496:10.1042/BJ20021321
1172:Huntington disease
911:. Treatments with
802:gene transcription
686:from a pronounced
533:knockout (KO) mice
473:incorporated with
245:
161:
52:
4963:Organic reactions
4950:
4949:
4905:RNA polymerase II
4773:
4772:
4731:
4730:
4495:
4494:
4379:
4378:
4309:
4308:
4185:Special transfers
4017:Neurotherapeutics
3424:(19): 2409–2426.
3095:(107): 107ra109.
2044:10.1038/nsmb.2470
1247:978-0-321-76243-6
1073:Cocaine addiction
1044:nucleus accumbens
1033:nucleus accumbens
1006:modifications of
926:. Patients with
728:zinc finger motif
559:between factors.
461:HDAC1 & HDAC2
288:RNA polymerase II
205:acetyl-coenzyme A
110:acetyl coenzyme A
16:(Redirected from
4980:
4827:Response element
4810:Response element
4623:
4551:
4522:
4515:
4508:
4499:
4320:
4217:
4135:
4128:
4121:
4112:
4094:
4093:
4057:
4051:
4050:
4040:
4008:
4002:
4001:
3991:
3959:
3953:
3952:
3942:
3919:The EMBO Journal
3910:
3904:
3903:
3893:
3883:
3859:
3853:
3852:
3842:
3810:
3804:
3803:
3793:
3761:
3755:
3754:
3744:
3734:
3702:
3696:
3695:
3685:
3645:
3639:
3638:
3628:
3604:
3598:
3597:
3561:
3555:
3554:
3534:
3528:
3527:
3491:
3485:
3484:
3474:
3450:
3444:
3443:
3433:
3418:Clinical Science
3409:
3403:
3398:
3392:
3391:
3381:
3349:
3340:
3339:
3333:
3329:
3327:
3319:
3309:
3275:
3269:
3268:
3231:
3225:
3224:
3214:
3204:
3172:
3166:
3165:
3129:
3123:
3122:
3112:
3080:
3074:
3073:
3066:
3060:
3056:
3047:
3046:
3036:
3004:
2995:
2994:
2984:
2952:
2946:
2945:
2939:
2935:
2933:
2925:
2915:
2881:
2875:
2874:
2864:
2832:
2823:
2822:
2812:
2802:
2778:
2772:
2771:
2735:
2729:
2728:
2718:
2686:
2680:
2679:
2669:
2637:
2631:
2630:
2594:
2588:
2587:
2577:
2553:
2547:
2546:
2530:
2524:
2523:
2513:
2481:
2475:
2474:
2464:
2440:
2434:
2433:
2397:
2391:
2390:
2380:
2356:
2350:
2349:
2339:
2329:
2297:
2291:
2290:
2280:
2248:
2242:
2241:
2205:
2199:
2198:
2180:
2156:
2150:
2149:
2121:
2115:
2114:
2104:
2094:
2070:
2064:
2063:
2027:
2021:
2020:
2018:
2008:
1999:(3): 2270–2271.
1984:
1978:
1977:
1967:
1957:
1925:
1919:
1918:
1890:
1884:
1883:
1873:
1863:
1839:
1833:
1832:
1794:
1779:
1778:
1760:
1736:
1725:
1724:
1696:
1683:
1682:
1654:
1643:
1642:
1632:
1608:
1602:
1601:
1565:
1518:
1517:
1507:
1490:(Pt 3): 737–49.
1475:
1418:
1417:
1384:(6649): 349–52.
1375:
1366:
1360:
1359:
1323:
1310:
1309:
1299:
1275:
1252:
1251:
1233:
280:nuclear-receptor
166:are portions of
49:
45:
41:
37:
21:
4988:
4987:
4983:
4982:
4981:
4979:
4978:
4977:
4953:
4952:
4951:
4946:
4921:
4915:
4909:
4874:
4848:
4769:
4727:
4708:
4691:DNA methylation
4685:
4629:
4614:
4540:
4526:
4496:
4491:
4470:
4405:Transcriptional
4375:
4344:
4305:
4296:Polyadenylation
4267:
4241:
4206:
4200:Protein→Protein
4151:
4144:
4142:Gene expression
4139:
4102:
4097:
4059:
4058:
4054:
4010:
4009:
4005:
3961:
3960:
3956:
3925:(19): 5175–85.
3912:
3911:
3907:
3861:
3860:
3856:
3812:
3811:
3807:
3763:
3762:
3758:
3704:
3703:
3699:
3647:
3646:
3642:
3606:
3605:
3601:
3563:
3562:
3558:
3536:
3535:
3531:
3493:
3492:
3488:
3452:
3451:
3447:
3411:
3410:
3406:
3399:
3395:
3351:
3350:
3343:
3330:
3320:
3298:
3277:
3276:
3272:
3233:
3232:
3228:
3187:(20): 11042–6.
3174:
3173:
3169:
3131:
3130:
3126:
3082:
3081:
3077:
3068:
3067:
3063:
3057:
3050:
3006:
3005:
2998:
2954:
2953:
2949:
2936:
2926:
2904:
2883:
2882:
2878:
2853:10.1038/nrn3111
2834:
2833:
2826:
2780:
2779:
2775:
2752:10.1038/nrd2227
2737:
2736:
2732:
2688:
2687:
2683:
2639:
2638:
2634:
2605:(37): 5420–32.
2596:
2595:
2591:
2555:
2554:
2550:
2532:
2531:
2527:
2483:
2482:
2478:
2442:
2441:
2437:
2414:10.1038/nrd4286
2399:
2398:
2394:
2358:
2357:
2353:
2299:
2298:
2294:
2269:10.1038/nrc2876
2250:
2249:
2245:
2207:
2206:
2202:
2158:
2157:
2153:
2123:
2122:
2118:
2072:
2071:
2067:
2029:
2028:
2024:
1986:
1985:
1981:
1927:
1926:
1922:
1892:
1891:
1887:
1854:(5): e1007300.
1841:
1840:
1836:
1821:
1796:
1795:
1782:
1738:
1737:
1728:
1698:
1697:
1686:
1656:
1655:
1646:
1610:
1609:
1605:
1567:
1566:
1521:
1477:
1476:
1421:
1373:
1368:
1367:
1363:
1325:
1324:
1313:
1277:
1276:
1255:
1248:
1235:
1234:
1221:
1217:
1204:Phosphorylation
1180:
1117:
1115:Other disorders
1067:opioid receptor
1001:
937:
913:corticosteroids
900:
895:
858:
829:
770:
765:
753:
748:
712:
634:
629:
613:
588:plasma membrane
565:
516:phosphorylation
463:
458:
402:
366:
354:differentiation
338:
332:
330:p300/CBP family
316:phosphorylation
309:spermatogenesis
296:
259:
250:
233:
218:
210:
198:
153:
145:heterochromatin
86:gene regulation
79:gene regulation
47:
43:
39:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
4986:
4984:
4976:
4975:
4970:
4965:
4955:
4954:
4948:
4947:
4945:
4944:
4939:
4934:
4928:
4926:
4911:
4910:
4908:
4907:
4901:RNA polymerase
4895:
4889:RNA polymerase
4882:
4880:
4876:
4875:
4873:
4872:
4867:
4862:
4856:
4854:
4850:
4849:
4847:
4846:
4841:
4836:
4831:
4830:
4829:
4824:
4814:
4813:
4812:
4807:
4802:
4797:
4792:
4781:
4779:
4775:
4774:
4771:
4770:
4768:
4767:
4762:
4761:
4760:
4755:
4750:
4739:
4737:
4733:
4732:
4729:
4728:
4726:
4725:
4719:
4717:
4710:
4709:
4707:
4706:
4705:
4704:
4696:
4694:
4687:
4686:
4684:
4683:
4682:
4681:
4676:
4663:
4658:
4657:
4656:
4641:
4639:
4620:
4616:
4615:
4613:
4612:
4611:
4610:
4605:
4595:
4594:
4593:
4588:
4583:
4578:
4573:
4568:
4557:
4555:
4548:
4542:
4541:
4527:
4525:
4524:
4517:
4510:
4502:
4493:
4492:
4490:
4489:
4484:
4482:François Jacob
4478:
4476:
4472:
4471:
4469:
4468:
4467:
4466:
4461:
4451:
4446:
4445:
4444:
4439:
4434:
4424:
4419:
4418:
4417:
4412:
4402:
4401:
4400:
4389:
4387:
4381:
4380:
4377:
4376:
4374:
4373:
4368:
4363:
4358:
4352:
4350:
4346:
4345:
4343:
4342:
4337:
4332:
4326:
4324:
4317:
4311:
4310:
4307:
4306:
4304:
4303:
4298:
4293:
4288:
4283:
4277:
4275:
4269:
4268:
4266:
4265:
4260:
4258:RNA polymerase
4255:
4249:
4247:
4243:
4242:
4240:
4239:
4234:
4229:
4223:
4221:
4214:
4208:
4207:
4205:
4204:
4203:
4202:
4197:
4192:
4182:
4181:
4180:
4162:
4156:
4154:
4146:
4145:
4140:
4138:
4137:
4130:
4123:
4115:
4109:
4108:
4101:
4100:External links
4098:
4096:
4095:
4052:
4003:
3954:
3905:
3854:
3825:(9): 1673–90.
3805:
3756:
3717:(10): 4123–8.
3697:
3640:
3619:(3–4): 241–5.
3599:
3556:
3529:
3486:
3465:(7): 1186–96.
3445:
3404:
3393:
3341:
3332:|journal=
3296:
3270:
3226:
3167:
3124:
3075:
3061:
3048:
3013:Molecular Cell
2996:
2947:
2938:|journal=
2902:
2876:
2847:(11): 623–37.
2824:
2773:
2730:
2681:
2632:
2589:
2548:
2525:
2476:
2435:
2392:
2351:
2312:(11): 4781–5.
2292:
2243:
2200:
2151:
2116:
2079:BioData Mining
2065:
2022:
1979:
1920:
1885:
1834:
1819:
1780:
1751:(37): 5310–8.
1726:
1684:
1644:
1623:(5): 599–606.
1603:
1576:(3): 195–211.
1519:
1419:
1361:
1311:
1253:
1246:
1218:
1216:
1213:
1212:
1211:
1206:
1201:
1196:
1191:
1186:
1179:
1176:
1133:trichostatin A
1116:
1113:
1085:histone 4 (H4)
1081:histone 3 (H3)
1046:of the brain,
1037:splice variant
1000:
997:
949:overexpression
936:
933:
899:
896:
894:
893:Human diseases
891:
884:(CBP), to the
857:
854:
828:
825:
793:amino terminal
769:
766:
764:
761:
752:
749:
747:
746:Class IV HDACs
744:
732:ubiquitination
711:
708:
633:
630:
628:
627:Class II HDACs
625:
621:Northern blots
612:
609:
594:receptors and
564:
561:
462:
459:
457:
454:
401:
398:
365:
362:
334:Main article:
331:
328:
295:
292:
258:
255:
249:
246:
232:
229:
216:
208:
196:
152:
149:
127:marker within
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4985:
4974:
4971:
4969:
4966:
4964:
4961:
4960:
4958:
4943:
4940:
4938:
4935:
4933:
4930:
4929:
4927:
4924:
4919:
4912:
4906:
4902:
4899:
4896:
4894:
4890:
4887:
4884:
4883:
4881:
4877:
4871:
4868:
4866:
4863:
4861:
4858:
4857:
4855:
4851:
4845:
4842:
4840:
4837:
4835:
4832:
4828:
4825:
4823:
4820:
4819:
4818:
4815:
4811:
4808:
4806:
4803:
4801:
4798:
4796:
4793:
4791:
4788:
4787:
4786:
4783:
4782:
4780:
4776:
4766:
4763:
4759:
4756:
4754:
4751:
4749:
4746:
4745:
4744:
4741:
4740:
4738:
4734:
4724:
4721:
4720:
4718:
4715:
4711:
4703:
4700:
4699:
4698:
4697:
4695:
4692:
4688:
4680:
4677:
4675:
4672:
4669:
4668:
4667:
4664:
4662:
4659:
4655:
4652:
4651:
4650:
4646:
4643:
4642:
4640:
4637:
4633:
4628:
4624:
4621:
4617:
4609:
4608:trp repressor
4606:
4604:
4603:lac repressor
4601:
4600:
4599:
4596:
4592:
4589:
4587:
4584:
4582:
4579:
4577:
4574:
4572:
4569:
4567:
4564:
4563:
4562:
4559:
4558:
4556:
4552:
4549:
4547:
4543:
4538:
4534:
4530:
4529:Transcription
4523:
4518:
4516:
4511:
4509:
4504:
4503:
4500:
4488:
4487:Jacques Monod
4485:
4483:
4480:
4479:
4477:
4473:
4465:
4462:
4460:
4457:
4456:
4455:
4452:
4450:
4449:Translational
4447:
4443:
4440:
4438:
4435:
4433:
4430:
4429:
4428:
4425:
4423:
4420:
4416:
4413:
4411:
4408:
4407:
4406:
4403:
4399:
4396:
4395:
4394:
4391:
4390:
4388:
4386:
4382:
4372:
4369:
4367:
4364:
4362:
4359:
4357:
4354:
4353:
4351:
4347:
4341:
4338:
4336:
4333:
4331:
4328:
4327:
4325:
4321:
4318:
4316:
4312:
4302:
4299:
4297:
4294:
4292:
4289:
4287:
4284:
4282:
4279:
4278:
4276:
4274:
4270:
4264:
4261:
4259:
4256:
4254:
4251:
4250:
4248:
4244:
4238:
4235:
4233:
4230:
4228:
4225:
4224:
4222:
4218:
4215:
4213:
4212:Transcription
4209:
4201:
4198:
4196:
4193:
4191:
4188:
4187:
4186:
4183:
4179:
4175:
4171:
4168:
4167:
4166:
4165:Central dogma
4163:
4161:
4158:
4157:
4155:
4153:
4147:
4143:
4136:
4131:
4129:
4124:
4122:
4117:
4116:
4113:
4107:
4104:
4103:
4099:
4091:
4087:
4083:
4079:
4075:
4071:
4068:(2): 126–35.
4067:
4063:
4056:
4053:
4048:
4044:
4039:
4034:
4030:
4026:
4023:(4): 664–76.
4022:
4018:
4014:
4007:
4004:
3999:
3995:
3990:
3985:
3981:
3977:
3973:
3969:
3965:
3958:
3955:
3950:
3946:
3941:
3936:
3932:
3928:
3924:
3920:
3916:
3909:
3906:
3901:
3897:
3892:
3887:
3882:
3877:
3873:
3869:
3865:
3858:
3855:
3850:
3846:
3841:
3836:
3832:
3828:
3824:
3820:
3816:
3809:
3806:
3801:
3797:
3792:
3787:
3783:
3779:
3776:(4): 479–88.
3775:
3771:
3767:
3760:
3757:
3752:
3748:
3743:
3738:
3733:
3728:
3724:
3720:
3716:
3712:
3708:
3701:
3698:
3693:
3689:
3684:
3679:
3675:
3671:
3667:
3663:
3659:
3655:
3651:
3644:
3641:
3636:
3632:
3627:
3622:
3618:
3614:
3610:
3603:
3600:
3595:
3591:
3587:
3583:
3579:
3575:
3571:
3567:
3560:
3557:
3552:
3548:
3545:(7): 539–43.
3544:
3540:
3539:Die Pharmazie
3533:
3530:
3525:
3521:
3517:
3513:
3509:
3505:
3501:
3497:
3490:
3487:
3482:
3478:
3473:
3468:
3464:
3460:
3456:
3449:
3446:
3441:
3437:
3432:
3427:
3423:
3419:
3415:
3408:
3405:
3402:
3397:
3394:
3389:
3385:
3380:
3375:
3371:
3367:
3364:(3): 335–48.
3363:
3359:
3355:
3348:
3346:
3342:
3337:
3325:
3317:
3313:
3308:
3303:
3299:
3297:9780444640765
3293:
3289:
3285:
3281:
3274:
3271:
3266:
3262:
3258:
3254:
3250:
3246:
3242:
3238:
3230:
3227:
3222:
3218:
3213:
3208:
3203:
3198:
3194:
3190:
3186:
3182:
3178:
3171:
3168:
3163:
3159:
3155:
3151:
3147:
3143:
3140:(6): 428–37.
3139:
3135:
3128:
3125:
3120:
3116:
3111:
3106:
3102:
3098:
3094:
3090:
3086:
3079:
3076:
3071:
3065:
3062:
3055:
3053:
3049:
3044:
3040:
3035:
3030:
3026:
3022:
3019:(5): 712–27.
3018:
3014:
3010:
3003:
3001:
2997:
2992:
2988:
2983:
2978:
2974:
2970:
2967:(2): 145–53.
2966:
2962:
2958:
2951:
2948:
2943:
2931:
2923:
2919:
2914:
2909:
2905:
2903:9780128009772
2899:
2895:
2891:
2887:
2880:
2877:
2872:
2868:
2863:
2858:
2854:
2850:
2846:
2842:
2838:
2831:
2829:
2825:
2820:
2816:
2811:
2806:
2801:
2796:
2792:
2788:
2784:
2777:
2774:
2769:
2765:
2761:
2757:
2753:
2749:
2745:
2741:
2734:
2731:
2726:
2722:
2717:
2712:
2708:
2704:
2700:
2696:
2692:
2685:
2682:
2677:
2673:
2668:
2663:
2659:
2655:
2652:(6): 631–47.
2651:
2647:
2643:
2636:
2633:
2628:
2624:
2620:
2616:
2612:
2608:
2604:
2600:
2593:
2590:
2585:
2581:
2576:
2571:
2568:(3): 552–63.
2567:
2563:
2559:
2552:
2549:
2544:
2540:
2536:
2529:
2526:
2521:
2517:
2512:
2507:
2503:
2499:
2495:
2491:
2487:
2480:
2477:
2472:
2468:
2463:
2458:
2455:(3): 552–63.
2454:
2450:
2446:
2439:
2436:
2431:
2427:
2423:
2419:
2415:
2411:
2408:(5): 337–56.
2407:
2403:
2396:
2393:
2388:
2384:
2379:
2374:
2371:(5): 659–65.
2370:
2366:
2362:
2355:
2352:
2347:
2343:
2338:
2333:
2328:
2323:
2319:
2315:
2311:
2307:
2303:
2296:
2293:
2288:
2284:
2279:
2274:
2270:
2266:
2263:(7): 457–69.
2262:
2258:
2254:
2247:
2244:
2239:
2235:
2231:
2227:
2223:
2222:10.1038/10640
2219:
2215:
2211:
2204:
2201:
2196:
2192:
2188:
2184:
2179:
2174:
2171:(2): 263–71.
2170:
2166:
2162:
2155:
2152:
2147:
2143:
2139:
2135:
2132:(1): 185–98.
2131:
2127:
2120:
2117:
2112:
2108:
2103:
2098:
2093:
2088:
2084:
2080:
2076:
2069:
2066:
2061:
2057:
2053:
2049:
2045:
2041:
2038:(3): 259–66.
2037:
2033:
2026:
2023:
2017:
2012:
2007:
2002:
1998:
1994:
1990:
1983:
1980:
1975:
1971:
1966:
1961:
1956:
1951:
1947:
1943:
1940:(5): 786–94.
1939:
1935:
1931:
1924:
1921:
1916:
1912:
1908:
1904:
1901:(2): 155–61.
1900:
1896:
1889:
1886:
1881:
1877:
1872:
1867:
1862:
1857:
1853:
1849:
1848:PLOS Genetics
1845:
1838:
1835:
1830:
1826:
1822:
1820:9780120342679
1816:
1812:
1808:
1804:
1800:
1793:
1791:
1789:
1787:
1785:
1781:
1776:
1772:
1768:
1764:
1759:
1754:
1750:
1746:
1742:
1735:
1733:
1731:
1727:
1722:
1718:
1714:
1710:
1707:(3): 433–44.
1706:
1702:
1695:
1693:
1691:
1689:
1685:
1680:
1676:
1672:
1668:
1665:(9): 836–45.
1664:
1660:
1653:
1651:
1649:
1645:
1640:
1636:
1631:
1626:
1622:
1618:
1614:
1607:
1604:
1599:
1595:
1591:
1587:
1583:
1579:
1575:
1571:
1570:Cell Research
1564:
1562:
1560:
1558:
1556:
1554:
1552:
1550:
1548:
1546:
1544:
1542:
1540:
1538:
1536:
1534:
1532:
1530:
1528:
1526:
1524:
1520:
1515:
1511:
1506:
1501:
1497:
1493:
1489:
1485:
1481:
1474:
1472:
1470:
1468:
1466:
1464:
1462:
1460:
1458:
1456:
1454:
1452:
1450:
1448:
1446:
1444:
1442:
1440:
1438:
1436:
1434:
1432:
1430:
1428:
1426:
1424:
1420:
1415:
1411:
1407:
1403:
1399:
1398:10.1038/38664
1395:
1391:
1387:
1383:
1379:
1372:
1365:
1362:
1357:
1353:
1349:
1345:
1341:
1337:
1334:(8): 615–26.
1333:
1329:
1322:
1320:
1318:
1316:
1312:
1307:
1303:
1298:
1293:
1290:(3): 209–21.
1289:
1285:
1281:
1274:
1272:
1270:
1268:
1266:
1264:
1262:
1260:
1258:
1254:
1249:
1243:
1239:
1232:
1230:
1228:
1226:
1224:
1220:
1214:
1210:
1207:
1205:
1202:
1200:
1197:
1195:
1192:
1190:
1187:
1185:
1182:
1181:
1177:
1175:
1173:
1169:
1168:Schizophrenia
1163:
1161:
1157:
1153:
1149:
1145:
1141:
1138:
1137:cardiomyocyte
1134:
1129:
1124:
1122:
1114:
1112:
1109:
1107:
1101:
1098:
1094:
1090:
1086:
1082:
1078:
1074:
1070:
1068:
1064:
1060:
1055:
1053:
1049:
1045:
1041:
1038:
1034:
1030:
1027:
1023:
1019:
1015:
1013:
1009:
1005:
998:
996:
992:
990:
986:
982:
978:
973:
969:
964:
962:
958:
954:
953:tumorigenesis
950:
946:
942:
934:
932:
929:
925:
920:
918:
914:
910:
906:
897:
892:
890:
887:
883:
879:
875:
871:
867:
863:
855:
853:
850:
846:
841:
839:
834:
826:
824:
822:
818:
814:
809:
807:
803:
799:
794:
789:
787:
783:
779:
775:
774:transcription
767:
762:
760:
757:
750:
745:
743:
741:
740:cell motility
737:
733:
729:
725:
721:
717:
709:
707:
705:
701:
697:
693:
689:
684:
679:
675:
671:
667:
663:
658:
655:
651:
647:
643:
639:
631:
626:
624:
622:
617:
610:
608:
606:
602:
597:
593:
589:
585:
581:
578:as well as a
577:
573:
569:
562:
560:
558:
553:
549:
545:
542:
538:
537:embryogenesis
534:
530:
525:
521:
517:
512:
510:
506:
502:
497:
493:
489:
485:
481:
476:
471:
467:
460:
456:Class I HDACs
455:
453:
451:
447:
443:
439:
435:
431:
427:
423:
419:
415:
411:
407:
399:
397:
395:
391:
387:
383:
379:
375:
371:
363:
361:
359:
355:
351:
346:
342:
337:
329:
327:
325:
321:
317:
314:
310:
306:
302:
293:
291:
289:
285:
284:growth-factor
281:
277:
273:
269:
265:
256:
254:
247:
241:
237:
230:
228:
224:
220:
214:
206:
202:
193:
190:
189:minor grooves
185:
181:
177:
173:
169:
165:
157:
150:
148:
146:
142:
138:
137:transcription
134:
130:
126:
122:
118:
113:
111:
107:
103:
99:
95:
91:
87:
82:
80:
76:
72:
68:
64:
60:
56:
32:
19:
4665:
4464:irreversible
4349:Key elements
4300:
4246:Key elements
4160:Genetic code
4150:Introduction
4065:
4061:
4055:
4020:
4016:
4006:
3971:
3967:
3957:
3922:
3918:
3908:
3871:
3867:
3857:
3822:
3818:
3808:
3773:
3769:
3759:
3714:
3710:
3700:
3657:
3653:
3643:
3616:
3612:
3602:
3572:(6): 570–5.
3569:
3565:
3559:
3542:
3538:
3532:
3502:(4): 265–9.
3499:
3495:
3489:
3462:
3458:
3448:
3421:
3417:
3407:
3396:
3361:
3357:
3279:
3273:
3243:(2): 312–9.
3240:
3236:
3229:
3184:
3180:
3170:
3137:
3133:
3127:
3092:
3088:
3078:
3064:
3016:
3012:
2964:
2960:
2950:
2885:
2879:
2844:
2840:
2790:
2786:
2776:
2743:
2739:
2733:
2698:
2694:
2684:
2649:
2645:
2635:
2602:
2598:
2592:
2565:
2561:
2551:
2534:
2528:
2493:
2489:
2479:
2452:
2448:
2438:
2405:
2401:
2395:
2368:
2364:
2354:
2309:
2305:
2295:
2260:
2256:
2246:
2216:(7): 601–4.
2213:
2209:
2203:
2168:
2164:
2154:
2129:
2125:
2119:
2082:
2078:
2068:
2035:
2031:
2025:
1996:
1992:
1982:
1937:
1933:
1923:
1898:
1894:
1888:
1851:
1847:
1837:
1802:
1798:
1748:
1744:
1704:
1700:
1662:
1658:
1620:
1616:
1606:
1573:
1569:
1487:
1483:
1381:
1377:
1364:
1331:
1327:
1287:
1283:
1237:
1164:
1125:
1118:
1110:
1102:
1071:
1056:
1016:
1002:
993:
965:
938:
921:
917:theophylline
901:
889:activation.
859:
842:
833:Histone code
830:
810:
790:
771:
754:
713:
692:ossification
659:
635:
614:
566:
552:upregulation
513:
464:
403:
394:bromodomains
367:
339:
297:
290:holoenzyme.
260:
251:
239:
225:
221:
194:
162:
114:
96:" (HAT) or "
83:
69:core of the
54:
53:
4914:Termination
4790:Pribnow box
4758:Corepressor
4753:Coactivator
4554:prokaryotic
4315:Translation
4152:to genetics
3974:(12): e64.
3660:(1): 25–9.
2746:(1): 21–2.
2701:(1): 31–9.
2496:(1): 14–8.
1199:Acetylation
1148:hypertrophy
1093:upregulated
961:oncogenesis
880:, GCN5 and
862:bromodomain
856:Bromodomain
821:bromodomain
698:-dependent
688:chondrocyte
678:hypertrophy
550:. Not even
531:. In HDAC1
318:during the
294:MYST family
270:, HPA2 and
257:GNAT family
164:Nucleosomes
141:euchromatin
121:nucleosomes
115:Acetylated
102:Acetylation
4957:Categories
4942:Rho factor
4932:Terminator
4923:eukaryotic
4898:eukaryotic
4879:Elongation
4865:Eukaryotic
4853:Initiation
4636:nucleosome
4619:eukaryotic
4591:gal operon
4586:ara operon
4581:Gua Operon
4576:gab operon
4571:trp operon
4566:lac operon
4537:Eukaryotic
4459:reversible
4422:lac operon
4398:imprinting
4393:Epigenetic
4385:Regulation
4340:Eukaryotic
4286:5' capping
4237:Eukaryotic
3874:: 641979.
1805:: 181–99.
1215:References
1209:Nucleosome
1048:Delta FosB
1042:. In the
1040:Delta FosB
1012:addictions
1004:Epigenetic
972:Vorinostat
957:metastasis
941:epigenetic
798:nucleosome
572:C-terminal
557:cross-talk
364:Other HATs
350:cell-cycle
305:Drosophila
276:myogenesis
243:functions.
125:epigenetic
75:acetylated
71:nucleosome
63:N-terminal
4918:bacterial
4886:bacterial
4860:Bacterial
4834:Insulator
4778:Promotion
4748:Activator
4598:Repressor
4533:Bacterial
4330:Bacterial
4227:Bacterial
3334:ignored (
3324:cite book
2940:ignored (
2930:cite book
2793:(1): 25.
2768:262487540
1659:BioEssays
1328:BioEssays
1140:autophagy
1106:chromatin
1052:addiction
1018:Cigarette
999:Addiction
806:silencing
710:Class IIB
700:apoptosis
632:Class IIA
584:cytoplasm
475:cofactors
358:apoptosis
320:leptotene
129:chromatin
4968:Proteins
4839:Silencer
4817:Enhancer
4805:CAAT box
4795:TATA box
4785:Promoter
4442:microRNA
4356:Ribosome
4335:Archaeal
4291:Splicing
4263:Promoter
4232:Archaeal
4176: →
4172: →
4082:19917878
4047:24006238
3998:22832356
3949:14517255
3900:24693336
3849:24310814
3800:12202037
3751:21367693
3692:19568876
3635:18797138
3594:24182756
3586:25867833
3551:16076083
3524:20849951
3516:24552452
3481:18482162
3440:28912356
3388:19447090
3316:29478612
3265:14013417
3257:22684622
3221:11572966
3162:19157711
3154:25083822
3119:22049069
3043:27259203
2991:20425300
2922:25410541
2871:21989194
2819:29784032
2760:17269160
2725:16960145
2676:21941619
2619:17694083
2599:Oncogene
2584:15738302
2543:18204158
2520:24527405
2471:15738302
2430:12172346
2422:24751816
2387:19736624
2287:20574448
2238:22196542
2230:10404206
2195:16237908
2187:11057899
2146:18804549
2111:26140054
2060:23873925
2052:23463310
1974:14172992
1915:11250138
1880:29795555
1829:14969728
1775:10662910
1767:17694074
1745:Oncogene
1721:11492997
1679:10944586
1598:30268983
1590:17325692
1514:12429021
1356:35433573
1306:16877467
1178:See also
1089:"reward"
1063:amygdala
1029:promoter
1022:nicotine
886:promoter
786:histones
654:isoforms
446:Sirtuins
390:TAFII250
343:and the
117:histones
4765:Inducer
4632:histone
4195:RNA→DNA
4190:RNA→RNA
4178:Protein
4090:3112549
4038:3805871
3989:3305989
3891:3945289
3840:3983897
3791:4459650
3742:3053983
3719:Bibcode
3683:2698246
3662:Bibcode
3379:2779727
3307:5868351
3189:Bibcode
3110:4042673
3034:5476208
2982:2847696
2913:5914502
2862:3272277
2810:5993135
2716:1785068
2667:3174261
2627:2976852
2511:3921865
2378:2921942
2346:8197135
2314:Bibcode
2278:3262678
2102:4488123
2016:3265906
1942:Bibcode
1871:6019819
1639:9499396
1505:1223209
1414:4419816
1406:9311776
1386:Bibcode
1348:9780836
1095:in the
1077:cocaine
1059:alcohol
1031:in the
1008:histone
970:(FDA),
849:meiosis
845:mitosis
736:tubulin
704:T cells
605:mitosis
529:nucleus
488:Co-REST
324:meiosis
90:enzymes
67:histone
4561:Operon
4088:
4080:
4045:
4035:
3996:
3986:
3947:
3940:204485
3937:
3898:
3888:
3847:
3837:
3798:
3788:
3749:
3739:
3690:
3680:
3633:
3592:
3584:
3549:
3522:
3514:
3479:
3438:
3386:
3376:
3358:Neuron
3314:
3304:
3294:
3263:
3255:
3219:
3209:
3160:
3152:
3117:
3107:
3041:
3031:
2989:
2979:
2920:
2910:
2900:
2869:
2859:
2817:
2807:
2766:
2758:
2723:
2713:
2674:
2664:
2625:
2617:
2582:
2541:
2518:
2508:
2469:
2428:
2420:
2385:
2375:
2344:
2334:
2285:
2275:
2236:
2228:
2193:
2185:
2144:
2109:
2099:
2085:: 20.
2058:
2050:
2013:
1972:
1965:300163
1962:
1913:
1878:
1868:
1827:
1817:
1773:
1765:
1719:
1677:
1637:
1596:
1588:
1512:
1502:
1412:
1404:
1378:Nature
1354:
1346:
1304:
1244:
1158:, and
935:Cancer
924:Asthma
866:lysine
778:acetyl
756:HDAC11
751:HDAC11
720:HDAC10
670:14-3-3
496:RbAp46
486:, and
480:mSin3A
468:&
450:HDAC11
432:, and
416:, and
384:and a
106:acetyl
92:with "
59:lysine
4822:E-box
4674:HDAC1
4323:Types
4220:Types
4086:S2CID
3590:S2CID
3520:S2CID
3261:S2CID
3212:58680
3158:S2CID
2764:S2CID
2695:Blood
2623:S2CID
2426:S2CID
2337:43872
2234:S2CID
2191:S2CID
2056:S2CID
1771:S2CID
1594:S2CID
1410:S2CID
1374:(PDF)
1352:S2CID
1152:GATA4
989:HDAC6
985:HDAC3
981:HDAC2
977:HDAC1
945:tumor
905:NF-κB
716:HDAC6
696:Nur77
683:N-CoR
650:HDAC9
646:HDAC7
642:HDAC5
638:HDAC4
616:HDAC8
611:HDAC8
568:HDAC3
563:HDAC3
470:HDAC2
466:HDAC1
4893:rpoB
4736:both
4723:CHD7
4654:EZH2
4078:PMID
4043:PMID
3994:PMID
3945:PMID
3896:PMID
3872:2014
3845:PMID
3796:PMID
3770:Cell
3747:PMID
3688:PMID
3631:PMID
3582:PMID
3547:PMID
3512:PMID
3477:PMID
3436:PMID
3384:PMID
3336:help
3312:PMID
3292:ISBN
3253:PMID
3217:PMID
3150:PMID
3115:PMID
3059:2014
3039:PMID
2987:PMID
2942:help
2918:PMID
2898:ISBN
2867:PMID
2815:PMID
2756:PMID
2721:PMID
2672:PMID
2615:PMID
2580:PMID
2539:PMID
2516:PMID
2467:PMID
2418:PMID
2383:PMID
2342:PMID
2283:PMID
2226:PMID
2183:PMID
2165:Cell
2142:PMID
2107:PMID
2048:PMID
1970:PMID
1911:PMID
1876:PMID
1825:PMID
1815:ISBN
1763:PMID
1717:PMID
1675:PMID
1635:PMID
1586:PMID
1510:PMID
1402:PMID
1344:PMID
1302:PMID
1242:ISBN
1170:and
1160:MEF2
1026:FosB
987:and
955:and
915:and
907:and
878:TAF1
874:PCAF
860:The
847:and
831:The
784:and
718:and
668:and
648:and
546:and
494:and
440:and
356:and
313:H2AX
301:TIF2
272:HAT1
268:Elp3
182:and
73:are
46:and
40:H2B
36:H2A
4800:BRE
4174:RNA
4170:DNA
4070:doi
4033:PMC
4025:doi
3984:PMC
3976:doi
3935:PMC
3927:doi
3886:PMC
3876:doi
3835:PMC
3827:doi
3786:PMC
3778:doi
3774:110
3737:PMC
3727:doi
3715:108
3678:PMC
3670:doi
3621:doi
3574:doi
3504:doi
3467:doi
3426:doi
3422:131
3374:PMC
3366:doi
3302:PMC
3284:doi
3245:doi
3207:PMC
3197:doi
3142:doi
3105:PMC
3097:doi
3029:PMC
3021:doi
2977:PMC
2969:doi
2908:PMC
2890:doi
2857:PMC
2849:doi
2805:PMC
2795:doi
2748:doi
2711:PMC
2703:doi
2699:109
2662:PMC
2654:doi
2607:doi
2570:doi
2506:PMC
2498:doi
2457:doi
2410:doi
2373:PMC
2332:PMC
2322:doi
2273:PMC
2265:doi
2218:doi
2173:doi
2169:103
2134:doi
2097:PMC
2087:doi
2040:doi
2011:PMC
2001:doi
1997:287
1960:PMC
1950:doi
1903:doi
1866:PMC
1856:doi
1807:doi
1753:doi
1709:doi
1705:311
1667:doi
1625:doi
1578:doi
1500:PMC
1492:doi
1488:370
1394:doi
1382:389
1336:doi
1292:doi
1156:SRF
1097:NAc
1083:or
782:DNA
724:SP3
548:p27
544:p21
524:Ser
509:p21
505:Sp1
482:),
219:O.
176:H2B
172:H2A
133:DNA
81:.
48:H4
44:H3
4959::
4903::
4891::
4638:):
4535:,
4084:.
4076:.
4066:77
4064:.
4041:.
4031:.
4021:10
4019:.
4015:.
3992:.
3982:.
3970:.
3966:.
3943:.
3933:.
3923:22
3921:.
3917:.
3894:.
3884:.
3870:.
3866:.
3843:.
3833:.
3823:71
3821:.
3817:.
3794:.
3784:.
3772:.
3768:.
3745:.
3735:.
3725:.
3713:.
3709:.
3686:.
3676:.
3668:.
3658:13
3656:.
3652:.
3629:.
3617:55
3615:.
3611:.
3588:.
3580:.
3570:42
3568:.
3543:60
3541:.
3518:.
3510:.
3500:41
3498:.
3475:.
3463:32
3461:.
3457:.
3434:.
3420:.
3416:.
3382:.
3372:.
3362:62
3360:.
3356:.
3344:^
3328::
3326:}}
3322:{{
3310:.
3300:.
3290:.
3259:.
3251:.
3241:49
3239:.
3215:.
3205:.
3195:.
3185:98
3183:.
3179:.
3156:.
3148:.
3138:40
3136:.
3113:.
3103:.
3091:.
3087:.
3051:^
3037:.
3027:.
3017:62
3015:.
3011:.
2999:^
2985:.
2975:.
2965:12
2963:.
2959:.
2934::
2932:}}
2928:{{
2916:.
2906:.
2896:.
2865:.
2855:.
2845:12
2843:.
2839:.
2827:^
2813:.
2803:.
2791:38
2789:.
2785:.
2762:.
2754:.
2742:.
2719:.
2709:.
2697:.
2693:.
2670:.
2660:.
2648:.
2644:.
2621:.
2613:.
2603:26
2601:.
2578:.
2566:25
2564:.
2560:.
2514:.
2504:.
2492:.
2488:.
2465:.
2453:25
2451:.
2447:.
2424:.
2416:.
2406:13
2404:.
2381:.
2369:12
2367:.
2363:.
2340:.
2330:.
2320:.
2310:91
2308:.
2304:.
2281:.
2271:.
2261:10
2259:.
2255:.
2232:.
2224:.
2212:.
2189:.
2181:.
2167:.
2163:.
2140:.
2130:41
2128:.
2105:.
2095:.
2081:.
2077:.
2054:.
2046:.
2036:20
2034:.
2009:.
1995:.
1991:.
1968:.
1958:.
1948:.
1938:51
1936:.
1932:.
1909:.
1899:11
1897:.
1874:.
1864:.
1852:14
1850:.
1846:.
1823:.
1813:.
1803:67
1801:.
1783:^
1769:.
1761:.
1749:26
1747:.
1743:.
1729:^
1715:.
1703:.
1687:^
1673:.
1663:22
1661:.
1647:^
1633:.
1621:12
1619:.
1615:.
1592:.
1584:.
1574:17
1572:.
1522:^
1508:.
1498:.
1486:.
1482:.
1422:^
1408:.
1400:.
1392:.
1380:.
1376:.
1350:.
1342:.
1332:20
1330:.
1314:^
1300:.
1286:.
1282:.
1256:^
1222:^
1162:.
1154:,
1054:.
991:.
983:,
979:,
963:.
876:,
840:.
823:.
664:,
644:,
640:,
607:.
590:.
511:.
442:10
428:,
424:,
412:,
408:,
360:.
352:,
278:,
266:,
184:H4
180:H3
178:,
174:,
42:,
38:,
4925:)
4920:,
4916:(
4716::
4693::
4647:/
4634:/
4630:(
4539:)
4531:(
4521:e
4514:t
4507:v
4134:e
4127:t
4120:v
4092:.
4072::
4049:.
4027::
4000:.
3978::
3972:1
3951:.
3929::
3902:.
3878::
3851:.
3829::
3802:.
3780::
3753:.
3729::
3721::
3694:.
3672::
3664::
3637:.
3623::
3596:.
3576::
3553:.
3526:.
3506::
3483:.
3469::
3442:.
3428::
3390:.
3368::
3338:)
3318:.
3286::
3267:.
3247::
3223:.
3199::
3191::
3164:.
3144::
3121:.
3099::
3093:3
3072:.
3045:.
3023::
2993:.
2971::
2944:)
2924:.
2892::
2873:.
2851::
2821:.
2797::
2770:.
2750::
2744:6
2727:.
2705::
2678:.
2656::
2650:2
2629:.
2609::
2586:.
2572::
2545:.
2522:.
2500::
2494:4
2473:.
2459::
2432:.
2412::
2389:.
2348:.
2324::
2316::
2289:.
2267::
2240:.
2220::
2214:6
2197:.
2175::
2148:.
2136::
2113:.
2089::
2083:8
2062:.
2042::
2019:.
2003::
1976:.
1952::
1944::
1917:.
1905::
1882:.
1858::
1831:.
1809::
1777:.
1755::
1723:.
1711::
1681:.
1669::
1641:.
1627::
1600:.
1580::
1516:.
1494::
1416:.
1396::
1388::
1358:.
1338::
1308:.
1294::
1288:5
1250:.
438:6
434:9
430:7
426:5
422:4
418:8
414:3
410:2
406:1
217:2
209:3
197:3
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.