218:
261:
different symptoms, including severe symptoms such as cardiomyopathy and liver disease and mild symptoms such as episodic metabolic decomposition, muscle weakness and respiratory failure. MADD is a genetic disorder, caused by a mutation in the ETFA, ETFB, and ETFDH genes. MADD is known as an "autosomal recessive disorder" because for one to get this disorder, one must receive this recessive gene from both parents.
36:
70:
256:
Cellular acyl-CoA content correlates with insulin resistance, suggesting that it can mediate lipotoxicity in non-adipose tissues. Acyl-CoA: diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT) plays an important role in energy metabolism on account of key enzyme in triglyceride biosynthesis. The synthetic role of
260:
A rare disease called multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (MADD) is a fatty acid metabolism disorder. Acyl-CoA is important because this enzyme helps make Acyl-CoA from free fatty acids, and this activates the fatty acid to be metabolized. This compromised fatty acid oxidation leads to many
137:
Three types of acyl-CoA synthases are employed, depending on the chain length of the fatty acid. For example, the substrates for medium chain acyl-CoA synthase are 4-11 carbon fatty acids. The enzyme acyl-CoA thioesterase takes of the acyl-CoA to form a free fatty acid and coenzyme A.
257:
DGAT in adipose tissue such as the liver and the intestine, sites where endogenous levels of its activity and triglyceride synthesis are high and comparatively clear. Also, any changes in the activity levels might cause changes in systemic insulin sensitivity and energy homeostasis.
146:
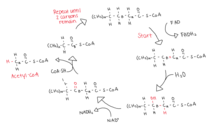
The second step of fatty acid degradation is beta oxidation. Beta oxidation occurs in mitochondria. After formation in the cytosol, acyl-CoA is transported into the mitochondria, the locus of beta oxidation. Transport of acyl-CoA into the mitochondria requires
151:(CPT1), which converts acyl-CoA into acylcarnitine, which gets transported into the mitochondrial matrix. Once in the matrix, acylcarnitine is converted back to acyl-CoA by CPT2. Beta oxidation may begin now that Acyl-CoA is in the mitochondria.
201:
This four step process repeats until acyl-CoA has removed all carbons from the chain, leaving only Acetyl-CoA. During one cycle of beta oxidation, Acyl-CoA creates one molecule of Acetyl-CoA, FADH2, and NADH. Acetyl-CoA is then used in the
516:
121:
Fats are broken down by conversion to acyl-CoA. This conversion is one response to high energy demands such as exercise. The oxidative degradation of fatty acids is a two-step process, catalyzed by
888:
881:
253:
Heart muscle primarily metabolizes fat for energy and Acyl-CoA metabolism has been identified as a critical molecule in early stage heart muscle pump failure.
874:
813:
646:
Goldenberg, Joseph R.; Carley, Andrew N.; Ji, Ruiping; Zhang, Xiaokan; Fasano, Matt; Schulze, P. Christian; Lewandowski, E. Douglas (26 March 2019).
462:
426:
245:
8 cycles will need to occur to completely break down Acyl-CoA. This will produce 9 Acetyl-CoA that have 2 carbons each, 8 FADH2, and 8 NADH.
122:
691:
230:
125:. Fatty acids are converted to their acyl phosphate, the precursor to acyl-CoA. The latter conversion is mediated by acyl-CoA synthase"
572:
229:. The peroxisome handles beta oxidation of fatty acids that have more than 20 carbons in their chain because the peroxisome contains
1033:
180:
148:
176:
648:"Preservation of Acyl-CoA Attenuates Pathological and Metabolic Cardiac Remodeling Through Selective Lipid Trafficking"
162:
233:. These enzymes are better equipped to oxidize Acyl-CoA with long chains that the mitochondria cannot handle.
1003:
54:
860:
207:
161:
catalyzes dehydrogenation of the acyl-CoA, creating a double bond between the alpha and beta carbons.
900:
285:
211:
158:
105:
601:"PEROXISOMAL β-OXIDATION AND PEROXISOME PROLIFERATOR–ACTIVATED RECEPTOR α: An Adaptive Metabolic System"
295:
290:
45:
169:
812:
Rashmi, S.; Gayathri, N.; Kumar, M. Veerendra; Sumanth, S.; Subasree, R.; Pooja, M. (1 January 2017).
50:
1028:
241:
Beta oxidation removes 2 carbons at a time, so in the oxidation of an 18 carbon fatty acid such as
210:. These intermediates all end up providing energy for the body as they are ultimately converted to
600:
791:
835:
783:
742:
677:
628:
620:
458:
422:
391:
373:
329:
203:
101:
825:
773:
732:
724:
667:
659:
612:
450:
414:
381:
365:
856:
85:
172:
catalyzes the addition of water across the newly formed double bond to make an alcohol.
998:
977:
737:
712:
672:
647:
454:
418:
386:
369:
353:
275:
217:
93:
89:
663:
485:
1022:
982:
972:
967:
866:
692:"Scientists find metabolic target to prevent, treat heart failure at earliest stage"
795:
242:
191:
616:
108:. In this way, fats are converted to ATP, the common biochemical energy carrier.
73:
General chemical structure of an acyl-CoA, where R is a carboxylic acid side chain
762:"The role of acyl-CoA:diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT) in energy metabolism"
728:
919:
544:
445:
Bhagavan, N.V.; Ha, Chung-Eun (2015). "Lipids I: Fatty Acids and
Eicosanoids".
321:
17:
950:
940:
914:
897:
778:
761:
280:
270:
226:
195:
97:
830:
814:"Multiple Acyl CoA dehydrogenase deficiency: Uncommon yet treatable disorder"
624:
377:
839:
787:
746:
681:
632:
395:
333:
717:
Biochimica et
Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids
352:
Grevengoed, Trisha J.; Klett, Eric L.; Coleman, Rosalind A. (2014-07-17).
81:
69:
959:
216:
187:
68:
573:"6.32 Fatty Acid Oxidation (Beta-oxidation) | Nutrition Flexbook"
870:
711:
Li, Lei O.; Klett, Eric L.; Coleman, Rosalind A. (March 2010).
225:
Beta oxidation, as well as alpha-oxidation, also occurs in the
179:
oxidizes the alcohol group to a ketone. NADH is produced from
29:
409:
Blanco, Antonio; Blanco, Gustavo (2017). "Lipid
Metabolism".
713:"Acyl-CoA synthesis, lipid metabolism and lipotoxicity"
440:
438:
807:
805:
599:
Reddy, Janardan K; Hashimoto, Takashi (2001-07-01).
991:
958:
949:
928:
907:
198:and the Acyl-CoA which is now 2 carbons shorter.
154:Beta oxidation of acyl-CoA occurs in four steps.
328:, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
320:Talley, Jacob T.; Mohiuddin, Shamim S. (2020),
27:Group of coenzymes that metabolize fatty acids
882:
8:
221:Example of Beta Oxidation using Stearic Acid
104:, eventually forming several equivalents of
760:Yu, Yi-Hao; Ginsberg, Henry (8 July 2009).
955:
889:
875:
867:
165:is the hydrogen acceptor, yielding FADH2.
859:at the U.S. National Library of Medicine
829:
777:
736:
671:
385:
307:
354:"Acyl-CoA Metabolism and Partitioning"
194:and ketone to release one molecule of
206:while FADH2 and NADH are sent to the
7:
594:
592:
567:
565:
539:
537:
511:
509:
507:
505:
480:
478:
476:
474:
322:"Biochemistry, Fatty Acid Oxidation"
315:
313:
311:
231:very-long-chain Acyl-CoA synthetases
486:"Fatty acid beta oxidation | Abcam"
455:10.1016/B978-0-12-416687-5.00016-6
447:Essentials of Medical Biochemistry
419:10.1016/B978-0-12-803550-4.00015-X
370:10.1146/annurev-nutr-071813-105541
25:
664:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.119.039610
129:acyl-P + HS-CoA → acyl-S-CoA + P
149:carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1
34:
690:Marti Leitch (March 26, 2019).
177:3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase
1:
617:10.1146/annurev.nutr.21.1.193
729:10.1016/j.bbalip.2009.09.024
517:"6.11: Fatty Acid Oxidation"
100:. The acetyl-CoA enters the
43:It has been suggested that
1050:
1004:Very long chain fatty acid
605:Annual Review of Nutrition
358:Annual Review of Nutrition
237:Example using stearic acid
142:Beta oxidation of acyl-CoA
779:10.1080/07853890410028429
577:courses.lumenlearning.com
1034:Thioesters of coenzyme A
861:Medical Subject Headings
831:10.4103/0028-3886.198186
208:electron transport chain
60:Proposed since May 2024.
901:metabolic intermediates
186:4.
175:3.
168:2.
157:1.
96:, forming, ultimately,
286:Acyl CoA dehydrogenase
222:
159:Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase
92:'s are susceptible to
74:
296:Fatty acyl-CoA esters
291:Fatty acid metabolism
249:Clinical significance
220:
117:Fatty acid activation
72:
46:Fatty acyl-CoA esters
449:. pp. 269–297.
413:. pp. 325–365.
411:Medical Biochemistry
190:cleaves between the
53:into this article. (
123:acyl-CoA synthetase
766:Annals of Medicine
549:Biology Dictionary
521:Biology LibreTexts
223:
75:
1016:
1015:
1012:
1011:
658:(24): 2765–2777.
464:978-0-12-416687-5
428:978-0-12-803550-4
204:citric acid cycle
170:Enoyl-CoA hydrase
102:citric acid cycle
67:
66:
62:
16:(Redirected from
1041:
956:
891:
884:
877:
868:
844:
843:
833:
809:
800:
799:
781:
757:
751:
750:
740:
708:
702:
699:
688:Lay summary in:
685:
675:
643:
637:
636:
596:
587:
586:
584:
583:
569:
560:
559:
557:
556:
545:"Beta Oxidation"
541:
532:
531:
529:
528:
513:
500:
499:
497:
496:
482:
469:
468:
442:
433:
432:
406:
400:
399:
389:
349:
343:
342:
341:
340:
317:
86:carboxylic acids
84:that metabolize
58:
38:
37:
30:
21:
1049:
1048:
1044:
1043:
1042:
1040:
1039:
1038:
1019:
1018:
1017:
1008:
987:
945:
924:
903:
895:
857:Acyl+Coenzyme+A
853:
848:
847:
818:Neurology India
811:
810:
803:
759:
758:
754:
710:
709:
705:
696:Ohio State News
689:
645:
644:
640:
598:
597:
590:
581:
579:
571:
570:
563:
554:
552:
543:
542:
535:
526:
524:
515:
514:
503:
494:
492:
484:
483:
472:
465:
444:
443:
436:
429:
408:
407:
403:
351:
350:
346:
338:
336:
319:
318:
309:
304:
267:
251:
239:
144:
132:
119:
114:
63:
39:
35:
28:
23:
22:
18:Acyl-coenzyme A
15:
12:
11:
5:
1047:
1045:
1037:
1036:
1031:
1021:
1020:
1014:
1013:
1010:
1009:
1007:
1006:
1001:
999:Mevalonic acid
995:
993:
989:
988:
986:
985:
980:
978:Pristanic acid
975:
970:
964:
962:
953:
947:
946:
944:
943:
938:
932:
930:
926:
925:
923:
922:
917:
911:
909:
905:
904:
896:
894:
893:
886:
879:
871:
865:
864:
852:
851:External links
849:
846:
845:
801:
772:(4): 252–261.
752:
723:(3): 246–251.
703:
701:
700:
638:
611:(1): 193–230.
588:
561:
533:
501:
470:
463:
434:
427:
401:
344:
306:
305:
303:
300:
299:
298:
293:
288:
283:
278:
276:Beta oxidation
273:
266:
263:
250:
247:
238:
235:
143:
140:
135:
134:
130:
118:
115:
113:
110:
94:beta oxidation
90:Fatty acyl-CoA
80:is a group of
65:
64:
42:
40:
33:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1046:
1035:
1032:
1030:
1027:
1026:
1024:
1005:
1002:
1000:
997:
996:
994:
990:
984:
983:Propionyl-CoA
981:
979:
976:
974:
973:Phytanoyl-CoA
971:
969:
968:Phytanic acid
966:
965:
963:
961:
957:
954:
952:
948:
942:
939:
937:
934:
933:
931:
927:
921:
918:
916:
913:
912:
910:
906:
902:
899:
892:
887:
885:
880:
878:
873:
872:
869:
862:
858:
855:
854:
850:
841:
837:
832:
827:
823:
819:
815:
808:
806:
802:
797:
793:
789:
785:
780:
775:
771:
767:
763:
756:
753:
748:
744:
739:
734:
730:
726:
722:
718:
714:
707:
704:
697:
693:
687:
686:
683:
679:
674:
669:
665:
661:
657:
653:
649:
642:
639:
634:
630:
626:
622:
618:
614:
610:
606:
602:
595:
593:
589:
578:
574:
568:
566:
562:
550:
546:
540:
538:
534:
522:
518:
512:
510:
508:
506:
502:
491:
490:www.abcam.com
487:
481:
479:
477:
475:
471:
466:
460:
456:
452:
448:
441:
439:
435:
430:
424:
420:
416:
412:
405:
402:
397:
393:
388:
383:
379:
375:
371:
367:
363:
359:
355:
348:
345:
335:
331:
327:
323:
316:
314:
312:
308:
301:
297:
294:
292:
289:
287:
284:
282:
279:
277:
274:
272:
269:
268:
264:
262:
258:
254:
248:
246:
244:
236:
234:
232:
228:
219:
215:
213:
209:
205:
199:
197:
193:
189:
184:
182:
178:
173:
171:
166:
164:
160:
155:
152:
150:
141:
139:
128:
127:
126:
124:
116:
111:
109:
107:
103:
99:
95:
91:
87:
83:
79:
71:
61:
56:
52:
48:
47:
41:
32:
31:
19:
935:
824:(1): 177–8.
821:
817:
769:
765:
755:
720:
716:
706:
695:
655:
651:
641:
608:
604:
580:. Retrieved
576:
553:. Retrieved
551:. 2017-06-03
548:
525:. Retrieved
523:. 2016-02-26
520:
493:. Retrieved
489:
446:
410:
404:
361:
357:
347:
337:, retrieved
325:
259:
255:
252:
243:Stearic Acid
240:
224:
200:
192:alpha carbon
185:
174:
167:
156:
153:
145:
136:
120:
77:
76:
59:
44:
951:Peroxisomal
929:Degradation
920:Malonyl-CoA
652:Circulation
364:(1): 1–30.
1029:Metabolism
1023:Categories
941:Acetyl-CoA
915:Acetyl-CoA
898:Fatty acid
582:2021-02-23
555:2021-02-23
527:2021-02-23
495:2021-02-23
339:2021-02-23
326:StatPearls
302:References
281:Coenzyme A
271:Acetyl-CoA
227:peroxisome
196:Acetyl-CoA
98:acetyl-CoA
908:Synthesis
625:0199-9885
378:0199-9885
112:Functions
82:coenzymes
936:Acyl-CoA
840:28084266
788:15224651
747:19818872
682:30909726
633:11375435
396:24819326
334:32310462
265:See also
188:Thiolase
78:Acyl-CoA
796:9174481
738:2824076
673:6557671
387:5881898
55:Discuss
960:Phytol
863:(MeSH)
838:
794:
786:
745:
735:
680:
670:
631:
623:
461:
425:
394:
384:
376:
332:
51:merged
992:Other
792:S2CID
836:PMID
784:PMID
743:PMID
721:1801
678:PMID
629:PMID
621:ISSN
459:ISBN
423:ISBN
392:PMID
374:ISSN
330:PMID
181:NAD+
133:+ H
826:doi
774:doi
733:PMC
725:doi
668:PMC
660:doi
656:139
613:doi
451:doi
415:doi
382:PMC
366:doi
212:ATP
163:FAD
106:ATP
49:be
1025::
834:.
822:65
820:.
816:.
804:^
790:.
782:.
770:36
768:.
764:.
741:.
731:.
719:.
715:.
694:.
676:.
666:.
654:.
650:.
627:.
619:.
609:21
607:.
603:.
591:^
575:.
564:^
547:.
536:^
519:.
504:^
488:.
473:^
457:.
437:^
421:.
390:.
380:.
372:.
362:34
360:.
356:.
324:,
310:^
214:.
183:.
88:.
890:e
883:t
876:v
842:.
828::
798:.
776::
749:.
727::
698:.
684:.
662::
635:.
615::
585:.
558:.
530:.
498:.
467:.
453::
431:.
417::
398:.
368::
131:i
57:)
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.