398:
allocates which area should be given control over the motor system. Varying levels of dopamine are believed to influence the optimization of this filter system by providing expectations about the outcomes of an event. The ERN, then, serves as a beacon to highlight the violation of an expectation. Research on the occurrence of the feedback ERN shows evidence that this potential has larger amplitudes when violations of expectancy are large. In other words, if an event is not likely to happen, the feedback ERN will be larger if no error is detected. Other studies have examined whether the ERN is elicited by varying the cost of an error and the evaluation of a response.
732:
772:
760:
193:
468:
participants reported being frustrated when making mistakes. Because the ACC is intricately involved with error detection and affective responses, it may very well be that this area forms the basis of self-confidence. Taken together, these findings indicate that both the dorsal and rostral areas are involved in evaluating the extent of the error and optimizing subsequent responses. A study confirming this notion explored the functions of both the dorsal and rostral areas of the ACC involved using a saccade task.
744:
42:
704:. PTSD diagnosis and related symptoms such as skin conductance response (SCR) to "potentially startling sounds" were found to be correlated with reduced ACC volume. Further, childhood trauma and executive dysfunction seem to correlate with reduced ACC connectivity to surrounding neural regions. In a longitudinal study, this reduced connectivity was able to predict high-risk drinking (binge drinking at least once per week for the past 12 months) up to four years later.
54:
529:(verbal fluency), the attention-demanding tasks increased signal intensity in a region of the ACC anterior and/or superior to the pain-related activation region. The ACC is the cortical area that has been most frequently linked to the experience of pain. It appears to be involved in the emotional reaction to pain rather than to the perception of pain itself.
368:. However, ACC is also active during correct response, and this has been shown using a letter task, whereby participants had to respond to the letter X after an A was presented and ignore all other letter combinations with some letters more competitive than others. They found that for more competitive stimuli ACC activation was greater.
533:
which the ball was never thrown to the participant, the ACC showed activation. Further, this activation was correlated with a self-reported measure of social distress, indicating that the ACC may be involved in the detection and monitoring of social situations which may cause social/emotional pain, rather than just physical pain.
460:
learning. The rostral part of the ACC, on the other hand, is believed to be involved more with affective responses to errors. In an interesting expansion of the previously described experiment, the effects of rewards and costs on ACC's activation during error commission was examined. Participants performed a version of the
638:, along with the amygdala part of the brain, but this research is still in its early stages. A more recent study, by the Wake Forest Baptist Medical Centre, confirms the relationship between the ACC and anxiety regulation, by revealing mindfulness practice as a meditator for anxiety precisely through the ACC.
209:
582:
in the anterior cingulate cortex, compared to participants without OCD. They used magnetic resonance spectroscopy to assess the balance of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission by measuring glutamate and GABA levels in anterior cingulate cortex and supplementary motor area of healthy volunteers
467:
Targets were flanked by either a congruent or an incongruent set of letters. Using an image of a thumb (up, down, or neutral), participants received feedback on how much money they gained or lost. The researchers found greater rostral ACC activation when participants lost money during the trials. The
414:
Studies examining task performance related to error and conflict processes in patients with ACC damage cast doubt on the necessity of this region for these functions. The error detection and conflict monitoring theories cannot explain some evidence obtained by electrical studies that demonstrate the
397:
Reinforcement learning ERN theory poses that there is a mismatch between actual response execution and appropriate response execution, which results in an ERN discharge. Furthermore, this theory predicts that, when the ACC receives conflicting input from control areas in the brain, it determines and
658:
of the region could act to alleviate depressive symptoms. Although people with depression had smaller subgenual ACCs, their ACCs were more active when adjusted for size. This correlates well with increased subgenual ACC activity during sadness in healthy people, and normalization of activity after
471:
Participants were shown a cue that indicated whether they had to make either a pro-saccade or an anti-saccade. An anti-saccade requires suppression of a distracting cue because the target appears in the opposite location causing the conflict. Results showed differing activation for the rostral and
459:
Largest activation in the dACC was shown during loss trials. This stimulus did not elicit any errors, and, thus, error detection and monitoring theories cannot fully explain why this ACC activation would occur. The dorsal part of the ACC seems to play a key role in reward-based decision-making and
498:
One study found an ERN even when subjects were not aware of their error. Awareness may not be necessary to elicit an ERN, but it could influence the effect of the amplitude of the feedback ERN. Relating to the reward-based learning theory, awareness could modulate expectancy violations. Increased
532:
Evidence from social neuroscience studies have suggested that, in addition to its role in physical pain, the ACC may also be involved in monitoring painful social situations as well, such as exclusion or rejection. When participants felt socially excluded in an fMRI virtual ball throwing game in
528:
The ACC registers physical pain as shown in functional MRI studies that showed an increase in signal intensity, typically in the posterior part of area 24 of the ACC, that was correlated with pain intensity. When this pain-related activation was accompanied by attention-demanding cognitive tasks
401:
In these trials, feedback is given about whether the participant has gained or lost money after a response. Amplitudes of ERN responses with small gains and small losses were similar. No ERN was elicited for any losses as opposed to an ERN for no wins, even though both outcomes are the same. The
405:
The rostral ACC seems to be active after an error commission, indicating an error response function, whereas the dorsal ACC is active after both an error and feedback, suggesting a more evaluative function (for fMRI evidence, see also ). This evaluation is emotional in nature and highlights the
450:
A more comprehensive and recent theory describes the ACC as a more active component and poses that it detects and monitors errors, evaluates the degree of the error, and then suggests an appropriate form of action to be implemented by the motor system. Earlier evidence from electrical studies
487:
The ACC area in the brain is associated with many functions that are correlated with conscious experience. Greater ACC activation levels were present in more emotionally aware female participants when shown short 'emotional' video clips. Better emotional awareness is associated with improved
418:
It has been stated that "The cognitive consequences of anterior cingulate lesions remain rather equivocal, with a number of case reports of intact general neuropsychological and executive function in the presence of large anterior dorsal cingulate lesions. For an alternative view of anterior
406:
amount of distress associated with a certain error. Summarizing the evidence found by ERN studies, it appears to be the case that ACC receives information about a stimulus, selects an appropriate response, monitors the action, and adapts behavior if there is a violation of expectancy.
402:
finding in this paradigm suggests that monitoring for wins and losses is based on the relative expected gains and losses. If you get a different outcome than expected, the ERN will be larger than for expected outcomes. ERN studies have also localized specific functions of the ACC.
659:
successful treatment. Of note, the activity of the subgenual cingulate cortex correlates with individual differences in negative affect during the baseline resting state; in other words, the greater the subgenual activity, the greater the negative affectivity in temperament.
303:
and consists of an arrow pointing to the left or right, which is flanked by two distractor arrows creating either compatible (<<<<<) or incompatible (>><>>) trials. Another very common conflict-inducing stimulus that activates the ACC is the
427:
Activity in the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) has been implicated in processing both the detection and appraisal of social processes, including social exclusion. When exposed to repeated personal social evaluative tasks, non-depressed women showed reduced
541:
Studying the effects of damage to the ACC provides insights into the type of functions it serves in the intact brain. Behavior that is associated with lesions in the ACC includes: inability to detect errors, severe difficulty with resolving stimulus conflict in a
2254:
Biria, Marjan; Banca, Paula; Healy, Máiréad P.; Keser, Engin; Sawiak, Stephen J.; Rodgers, Christopher T.; Rua, Catarina; de Souza, Ana Maria Frota Lisbôa
Pereira; Marzuki, Aleya A.; Sule, Akeem; Ersche, Karen D.; Robbins, Trevor W. (27 June 2023).
455:
studies. The dorsal and rostral areas of the ACC both seem to be affected by rewards and losses associated with errors. During one study, participants received monetary rewards and losses for correct and incorrect responses, respectively.
2210:
Bush G, Frazier JA, Rauch SL, Seidman LJ, Whalen PJ, Jenike MA, Rosen BR, Biederman J (June 1999). "Anterior cingulate cortex dysfunction in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder revealed by fMRI and the
Counting Stroop".
1981:
Lane RD, Reiman EM, Axelrod B, Yun LS, Holmes A, Schwartz GE (July 1998). "Neural correlates of levels of emotional awareness. Evidence of an interaction between emotion and attention in the anterior cingulate cortex".
499:
awareness could result in decreased violations of expectancies and decreased awareness could achieve the opposite effect. Further research is needed to completely understand the effects of awareness on ACC activation.
375:, incompatible trials produce the most conflict and the most activation by the ACC. Upon detection of a conflict, the ACC then provides cues to other areas in the brain to cope with the conflicting control systems.
264:, and is involved in assessing the salience of emotion and motivational information. The ACC seems to be especially involved when effort is needed to carry out a task, such as in early learning and problem-solving.
675:
exposure as children had decreased brain size as adults. This effect was most pronounced in the ACC (Cecil et al., 2008) and is thought to relate to the cognitive and behavioral deficits of affected individuals.
472:
dorsal ACC areas. Early correct anti-saccade performance was associated with rostral activation. The dorsal area, on the other hand, was activated when errors were committed, but also for correct responses.
1396:
Nieuwenhuis S, Ridderinkhof KR, Blom J, Band GP, Kok A (September 2001). "Error-related brain potentials are differentially related to awareness of response errors: evidence from an antisaccade task".
491:
The idea of awareness being associated with the ACC is supported by some evidence, in that it seems to be the case that, when subjects' responses are not congruent with actual responses, a larger
684:
Impairments in the development of the anterior cingulate, together with impairments in the dorsal medial-frontal cortex, may constitute a neural substrate for socio-cognitive deficits in
2024:
Davis, Karen D., Stephen J. Taylor, Adrian P. Crawley, Michael L. Wood, and David J. Mikulis. "Functional MRI of pain- and attention-related activations in the human cingulate cortex",
439:
exhibited enhanced BOLD activation. This differential activity may reflect enhanced rumination about social evaluation or enhanced arousal associated with repeated social evaluation.
320:, during which people count either neutral stimuli ('dog' presented four times) or interfering stimuli ('three' presented four times) by pressing a button. Another version of the
583:
and participants with OCD. Participants with OCD had significantly higher levels of glutamate and lower levels of GABA in the ACC and a higher Glu:GABA ratio in that region.
332:
test, except that it also uses segmented or repeated emotional words such as "murder" during the interference part of the task. Thus, ACC affects decision making of a task.
299:
A typical task that activates the ACC involves eliciting some form of conflict within the participant that can potentially result in an error. One such task is called the
316:
written in blue). Conflict occurs because people's reading abilities interfere with their attempt to correctly name the word's ink color. A variation of this task is the
479:
performance. The second finding showed that, during error trials, the ACC activated later than for correct responses, clearly indicating a kind of evaluative function.
731:
554:, where studies have shown patients have difficulty in dealing with conflicting spatial locations in a Stroop-like task and having abnormal ERNs. Participants with
1439:
Carter CS, Braver TS, Barch DM, Botvinick MM, Noll D, Cohen JD (May 1998). "Anterior cingulate cortex, error detection, and the online monitoring of performance".
4235:
716:
demonstrated diminished volume of the dorsal part of the ACC in the former group, indicating relationship between cortical thickness of ACC and general risk of
1873:
Rushworth MF, Behrens TE, Rudebeck PH, Walton ME (April 2007). "Contrasting roles for cingulate and orbitofrontal cortex in decisions and social behaviour".
1188:
Allman JM, Hakeem A, Erwin JM, Nimchinsky E, Hof P (May 2001). "The anterior cingulate cortex. The evolution of an interface between emotion and cognition".
1122:
Allman JM, Hakeem A, Erwin JM, Nimchinsky E, Hof P (May 2001). "The anterior cingulate cortex. The evolution of an interface between emotion and cognition".
2589:
George MS, Ketter TA, Parekh PI, Horwitz B, Herscovitch P, Post RM (March 1995). "Brain activity during transient sadness and happiness in healthy women".
1239:
Botvinick M, Nystrom LE, Fissell K, Carter CS, Cohen JD (November 1999). "Conflict monitoring versus selection-for-action in anterior cingulate cortex".
743:
516:
in humans. Crick bases this suggestion on scans of patients with specific lesions that seem to interfere with their sense of independent will, such as
3117:
2989:
415:
effects of giving feedback after responses because the theory describes the ACC as strictly monitoring conflict, not as having evaluative properties.
3108:
771:
610:/anterior cingulate cortex. These findings contrast with those in people with other anxiety disorders, who evince decreased (rather than increased)
759:
3094:
958:
2049:
1918:"Dorsal Anterior Cingulate Cortex Responses to Repeated Social Evaluative Feedback in Young Women with and without a History of Depression"
432:
2870:"Impact of Childhood Trauma on Executive Function in Adolescence-Mediating Functional Brain Networks and Prediction of High-Risk Drinking"
2769:"Annotation: The neural basis of social impairments in autism: the role of the dorsal medial-frontal cortex and anterior cingulate system"
2768:
2716:
Cecil KM, Brubaker CJ, Adler CM, Dietrich KN, Altaye M, Egelhoff JC, Wessel S, Elangovan I, Hornung R, Jarvis K, Lanphear BP (May 2008).
562:. Together, these findings corroborate results from imaging and electrical studies about the variety of functions attributed to the ACC.
2257:"Cortical glutamate and GABA are related to compulsive behaviour in individuals with obsessive compulsive disorder and healthy controls"
244:
stimuli and assigning appropriate control to other areas in the brain. By contrast, the ventral part of the ACC is connected with the
571:
2641:
1593:
1551:
1106:
391:
following incorrect responses (response ERN) and a signal after subjects receive feedback after erroneous responses (feedback ERN).
1097:
Posner MI, DiGirolamo GJ (1998). "Executive attention: Conflict, target detection, and cognitive control". In
Parasuraman R (ed.).
111:
3993:
3581:
3273:
701:
2366:"Meta-analytical comparison of voxel-based morphometry studies in obsessive-compulsive disorder vs other anxiety disorders"
1490:
Gehring WJ, Goss B, Coles MG, Meyer DE, Donchin E (November 1993). "A neural system for error-detection and compensation".
4196:
2982:
2818:"Association among anterior cingulate cortex volume, psychophysiological response, and PTSD diagnosis in a Veteran sample"
1354:"Dorsal anterior cingulate cortex resolves conflict from distracting stimuli by boosting attention toward relevant events"
241:
237:
512:
identifies the anterior cingulate, to be specific the anterior cingulate sulcus, as a likely candidate for the center of
3569:
2546:
Ongür D, Ferry AT, Price JL (June 2003). "Architectonic subdivision of the human orbital and medial prefrontal cortex".
575:
475:
Whenever the dorsal area was active, fewer errors were committed providing more evidence that the ACC is involved with
3661:
2116:
Eisenberger NI, Lieberman MD, Williams KD (October 2003). "Does rejection hurt? An FMRI study of social exclusion".
4073:
3629:
803:
504:
3730:
3593:
3574:
1719:"Rostral and dorsal anterior cingulate cortex make dissociable contributions during antisaccade error commission"
685:
4230:
3904:
3851:
3772:
3739:
3639:
3455:
3438:
3378:
2975:
1580:
Luu P, Pederson SM (2004). "The anterior cingulate cortex: Regulating actions in context". In Posner MI (ed.).
492:
384:
3800:
3856:
3746:
3390:
3131:
3126:
2659:"Brain activity in ventromedial prefrontal cortex correlates with individual differences in negative affect"
591:
388:
668:
4117:
3183:
3081:
3035:
973:
959:"Empathy examined through the neural mechanisms involved in imagining how I feel versus how you feel pain"
655:
579:
171:
1779:
Taylor SF, Martis B, Fitzgerald KD, Welsh RC, Abelson JL, Liberzon I, Himle JA, Gehring WJ (April 2006).
1295:"The anterior cingulate cortex mediates processing selection in the Stroop attentional conflict paradigm"
1045:
Bush G, Luu P, Posner MI (June 2000). "Cognitive and emotional influences in anterior cingulate cortex".
834:"The anterior cingulate cortex mediates processing selection in the Stroop attentional conflict paradigm"
574:. A recent study from the University of Cambridge showed that participants with OCD had higher levels of
4104:
3963:
3877:
3777:
808:
713:
2167:
Janer KW, Pardo JV (1991). "Deficits in selective attention following bilateral anterior cingulotomy".
387:(ERN) uniquely generated within the ACC upon error occurrences. A distinction has been made between an
275:. These cells are a relatively recent occurrence in evolutionary terms (found only in humans and other
208:
1828:
Critchley HD (December 2005). "Neural mechanisms of autonomic, affective, and cognitive integration".
41:
4077:
3925:
3817:
3494:
3354:
3251:
3200:
3057:
2670:
2268:
2125:
2074:
1730:
1668:
1543:
1535:
1448:
1306:
1248:
1197:
1131:
845:
623:
607:
587:
461:
372:
300:
2967:
1007:
978:
91:
4054:
3464:
594:
studies comparing people with OCD and healthy controls has found people with OCD to have increased
517:
2405:
Lieberman MD, Eisenberger NI (February 2009). "Neuroscience. Pains and pleasures of social life".
287:) and contribute to this brain region's emphasis on addressing difficult problems, as well as the
4112:
3935:
3909:
3510:
3480:
3402:
3334:
3322:
3223:
3219:
2954:
2919:"Brain structural correlates of cognitive-attentional syndrome – a Voxel-Based Morphometry Study"
2571:
2528:
2430:
2236:
2192:
2149:
2098:
2007:
1898:
1853:
1634:
1507:
1472:
1421:
1272:
1221:
1155:
1070:
999:
939:
615:
599:
272:
233:
3760:
2065:
Price DD (June 2000). "Psychological and neural mechanisms of the affective dimension of pain".
2633:
1968:"When Can We Be Bothered to Help Others? Brain Region Responsible for This Behavior Discovered"
4191:
4020:
3986:
3981:
3976:
3565:
3175:
3154:
3027:
2946:
2938:
2899:
2847:
2791:
2749:
2698:
2637:
2606:
2563:
2520:
2479:
2422:
2387:
2343:
2302:
2284:
2228:
2184:
2141:
2090:
2045:
1999:
1949:
1890:
1845:
1810:
1758:
1696:
1626:
1589:
1547:
1464:
1413:
1375:
1334:
1264:
1213:
1147:
1102:
1062:
991:
931:
873:
436:
249:
225:
2799:
4143:
4092:
4087:
4082:
4064:
4059:
4047:
4042:
4037:
4025:
4008:
3998:
3930:
3861:
3842:
3837:
3832:
3827:
3822:
3810:
3782:
3764:
3756:
3751:
3701:
3682:
3649:
3644:
3485:
3469:
3460:
3314:
3299:
3290:
3285:
3278:
3266:
3261:
3256:
3240:
3228:
3149:
3141:
3113:
3104:
3090:
3085:
3072:
3067:
2930:
2889:
2881:
2837:
2829:
2783:
2739:
2729:
2688:
2678:
2625:
2598:
2555:
2510:
2469:
2461:
2414:
2377:
2333:
2292:
2276:
2220:
2176:
2133:
2082:
1991:
1939:
1929:
1882:
1837:
1800:
1792:
1748:
1738:
1686:
1676:
1618:
1609:
Gehring WJ, Knight RT (May 2000). "Prefrontal-cingulate interactions in action monitoring".
1582:
1499:
1456:
1405:
1365:
1324:
1314:
1256:
1205:
1139:
1054:
983:
923:
863:
853:
798:
788:
651:
217:
160:
156:
152:
141:
987:
4012:
3940:
3734:
3598:
3586:
3549:
3542:
3530:
3525:
3520:
3515:
3448:
3443:
3407:
3395:
3383:
3371:
3366:
3359:
3327:
3210:
3205:
3193:
3188:
3062:
3050:
3045:
3040:
2999:
793:
717:
689:
619:
603:
547:
361:
341:
229:
175:
145:
3099:
892:
371:
A similar theory poses that the ACC's primary function is the monitoring of conflict. In
2917:
Kowalski, Joachim; Wypych, Marek; Marchewka, Artur; Dragan, Małgorzata (10 March 2022).
2674:
2297:
2272:
2256:
2129:
2078:
1967:
1734:
1672:
1452:
1310:
1252:
1201:
1135:
849:
558:
were found to have reduced activation in the dorsal area of the ACC when performing the
17:
4175:
4167:
3899:
3894:
3805:
3634:
3614:
3304:
3235:
2894:
2869:
2868:
Silveira S, Shah R, Nooner KB, Nagel BJ, Tapert SF, de Bellis MD, Mishra J (May 2020).
2842:
2817:
2744:
2717:
2474:
2449:
1944:
1917:
1805:
1780:
1753:
1718:
1503:
1209:
1143:
750:
647:
635:
288:
261:
192:
2693:
2658:
2382:
2365:
2224:
1691:
1656:
1058:
267:
On a cellular level, the ACC is unique in its abundance of specialized neurons called
4224:
4209:
4127:
4122:
3715:
3694:
3677:
3656:
3473:
3423:
2958:
2626:
2434:
2240:
1476:
1329:
1294:
943:
868:
833:
813:
551:
509:
476:
268:
149:
2532:
2196:
2153:
2102:
2011:
1857:
1638:
1511:
1225:
1159:
1074:
3247:
3011:
2816:
Young DA, Chao L, Neylan TC, O'Donovan A, Metzler TJ, Inslicht SS (November 2018).
2575:
2515:
2498:
2029:
1902:
1796:
1425:
1276:
1003:
253:
2322:"Voxel-wise meta-analysis of grey matter changes in obsessive-compulsive disorder"
2086:
914:
Decety J, Jackson PL (June 2004). "The functional architecture of human empathy".
383:
Evidence for ACC as having an error detection function comes from observations of
2734:
1655:
Bush G, Vogt BA, Holmes J, Dale AM, Greve D, Jenike MA, Rosen BR (January 2002).
1460:
3954:
3003:
712:
A study on differences in brain structure of adults with high and low levels of
611:
595:
559:
543:
488:
recognition of emotional cues or targets, which is reflected by ACC activation.
365:
305:
257:
199:
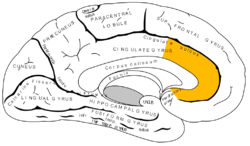
MRI slice with highlighting indicating location of the anterior cingulate cortex
129:
104:
2934:
2885:
2663:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
2280:
1886:
1723:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
1717:
Polli FE, Barton JJ, Cain MS, Thakkar KN, Rauch SL, Manoach DS (October 2005).
1661:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
1299:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
838:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
46:
Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere, with anterior cingulate highlighted
2833:
2338:
2321:
2180:
1409:
667:
A study of brain MRIs taken on adults that had previously participated in the
349:
216:
The anterior cingulate cortex can be divided anatomically based on cognitive (
86:
53:
2942:
2918:
2288:
1934:
927:
435:
activation in the dACC on the second exposure, while women with a history of
3537:
2787:
2497:
Hamani C, Mayberg H, Stone S, Laxton A, Haber S, Lozano AM (February 2011).
2418:
2137:
1995:
1743:
1370:
1353:
513:
345:
284:
280:
167:
2950:
2903:
2851:
2795:
2753:
2702:
2683:
2567:
2524:
2483:
2426:
2391:
2347:
2306:
2232:
2188:
2145:
2094:
1953:
1894:
1849:
1814:
1762:
1700:
1681:
1630:
1417:
1379:
1268:
1217:
1151:
1066:
995:
935:
464:
using a set of letters assigned to each response button instead of arrows.
451:
indicate the ACC has an evaluative component, which is indeed confirmed by
394:
Patients with lateral prefrontal cingulate (PFC) damage show reduced ERNs.
2610:
2602:
2465:
2003:
1657:"Dorsal anterior cingulate cortex: a role in reward-based decision making"
1468:
1338:
1319:
877:
858:
442:
The anterior cingulate cortex gyrus is involved in effort to help others.
308:, which involves naming the color ink of words that are either congruent (
4153:
700:
An increasing number of studies are investigating the role of the ACC in
276:
245:
196:
178:, impulse control (e.g. performance monitoring and error detection), and
98:
1352:
Weissman DH, Gopalakrishnan A, Hazlett CJ, Woldorff MG (February 2005).
117:
1536:"Anterior cingulate cortex, selection for action, and error processing"
360:
The most basic form of ACC theory states that the ACC is involved with
221:
179:
2559:
2448:
Zeidan F, Martucci KT, Kraft RA, McHaffie JG, Coghill RC (June 2014).
1916:
Dedovic K, Slavich GM, Muscatell KA, Irwin MR, Eisenberger NI (2016).
1841:
3689:
2364:
Radua J, van den Heuvel OA, Surguladze S, Mataix-Cols D (July 2010).
1781:"Medial frontal cortex activity and loss-related responses to errors"
2628:
Biology of
Depression: From Novel Insights to Therapeutic Strategies
2499:"The subcallosal cingulate gyrus in the context of major depression"
2450:"Neural correlates of mindfulness meditation-related anxiety relief"
550:. There is evidence that damage to ACC is present in patients with
4148:
1622:
1260:
212:
Anterior cingulate gyrus of left cerebral hemisphere, shown in red
207:
191:
74:
58:
Medial surface of right hemisphere, with
Brodmann's areas numbered
893:"Predicting repeat offenders with brain scans: You be the judge"
672:
555:
452:
429:
2971:
2718:"Decreased brain volume in adults with childhood lead exposure"
622:, while also decreased grey matter volumes in bilateral dorsal
410:
Evidence against error detection and conflict monitoring theory
224:) components. The dorsal part of the ACC is connected with the
2874:
Biological Psychiatry. Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging
144:
that resembles a "collar" surrounding the frontal part of the
570:
There is strong evidence that this area may have a role in
606:, while decreased grey matter volumes in bilateral dorsal
166:
It is involved in certain higher-level functions, such as
1293:
Pardo JV, Pardo PJ, Janer KW, Raichle ME (January 1990).
832:
Pardo JV, Pardo PJ, Janer KW, Raichle ME (January 1990).
2044:(8th ed.). Boston: Allyn & Bacon. p. 181.
634:
The ACC has been suggested to have possible links with
1534:
Holroyd CB, Nieuwenhuis S, Mars RB, Coles MG (2004).
364:. Evidence has been derived from studies involving a
957:
Jackson PL, Brunet E, Meltzoff AN, Decety J (2006).
352:, and modulation of emotional responses to the ACC.
4184:
4166:
4136:
4103:
4007:
3962:
3953:
3918:
3887:
3876:
3793:
3723:
3714:
3670:
3622:
3613:
3558:
3503:
3431:
3422:
3347:
3313:
3174:
3167:
3140:
3026:
3019:
3010:
2863:
2861:
97:
85:
73:
68:
63:
34:
4208:Some categorizations are approximations, and some
1581:
340:Many studies attribute specific functions such as
2632:. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. pp.
2657:Zald DH, Mattson DL, Pardo JV (February 2002).
737:Medial surface of human cerebral cortex - gyri
2983:
916:Behavioral and Cognitive Neuroscience Reviews
236:, making it a central station for processing
8:
2359:
2357:
1529:
1527:
1525:
1523:
1521:
671:found that people that had higher levels of
2454:Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience
1774:
1772:
3959:
3884:
3720:
3619:
3428:
3171:
3023:
3016:
2990:
2976:
2968:
2776:Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry
1391:
1389:
1288:
1286:
1190:Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences
1124:Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences
1092:
1090:
1088:
1086:
1084:
546:, emotional instability, inattention, and
419:cingulate, see Rushworth's review (2007).
52:
40:
2893:
2841:
2743:
2733:
2692:
2682:
2514:
2473:
2381:
2337:
2296:
1943:
1933:
1804:
1752:
1742:
1690:
1680:
1650:
1648:
1369:
1328:
1318:
977:
867:
857:
2320:Radua J, Mataix-Cols D (November 2009).
1712:
1710:
1575:
1573:
1571:
1569:
1567:
1565:
1563:
1040:
1038:
1036:
1034:
1032:
1030:
1028:
1863:See Review by Critchely related to this
824:
727:
356:Error detection and conflict monitoring
2624:Licinio J, Wong ML (29 January 2008).
988:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2005.07.015
232:, as well as the motor system and the
115:
31:
4236:Medial surface of cerebral hemisphere
1542:. New York: Guilford Press. pp.
749:Anterior Cingulate Cortex of monkey (
7:
2548:The Journal of Comparative Neurology
1922:Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience
1830:The Journal of Comparative Neurology
3900:Lateral (frontal+parietal+temporal)
2822:Neurobiology of Learning and Memory
1584:Cognitive neuroscience of attention
1540:Cognitive neuroscience of attention
2591:The American Journal of Psychiatry
1504:10.1111/j.1467-9280.1993.tb00586.x
1210:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03476.x
1144:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03476.x
25:
2383:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.70
2326:The British Journal of Psychiatry
2169:Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience
2028:volume 77: pages 3370–3380, 1997
1984:Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience
777:Rostral Anterior Cingulate gyrus
770:
758:
742:
730:
379:Evidence from electrical studies
312:written in red) or incongruent (
112:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
3994:Posterior parahippocampal gyrus
3936:Collateral (temporal+occipital)
765:Caudal Anterior Cingulate gyrus
708:General risk of psychopathology
688:, such as social orienting and
3582:Secondary somatosensory cortex
3274:Ventromedial prefrontal cortex
2516:10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.09.034
2370:Archives of General Psychiatry
1797:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4709-05.2006
1101:. Cambridge, Mass: MIT Press.
714:cognitive-attentional syndrome
702:post-traumatic stress disorder
1:
4197:Poles of cerebral hemispheres
3931:Cingulate (frontal+cingulate)
2225:10.1016/S0006-3223(99)00083-9
2087:10.1126/science.288.5472.1769
1059:10.1016/S1364-6613(00)01483-2
572:obsessive–compulsive disorder
140:) is the frontal part of the
3570:Primary somatosensory cortex
2735:10.1371/journal.pmed.0050112
1875:Trends in Cognitive Sciences
1588:. New York: Guilford Press.
1461:10.1126/science.280.5364.747
1047:Trends in Cognitive Sciences
654:and research indicates that
446:Reward-based learning theory
187:anterior midcingulate cortex
3662:Transverse occipital sulcus
1785:The Journal of Neuroscience
648:subcallosal cingulate gyrus
626:/ anterior cingulate gyri.
185:Some research calls it the
4252:
4074:Isthmus of cingulate gyrus
3895:Central (frontal+parietal)
3630:Occipital pole of cerebrum
2935:10.1007/s11682-022-00649-2
2923:Brain Imaging and Behavior
2886:10.1016/j.bpsc.2020.01.011
2281:10.1038/s41467-023-38695-z
1887:10.1016/j.tics.2007.01.004
891:Hewitt J (26 March 2013).
804:subgenual cingulate cortex
505:The Astonishing Hypothesis
80:cortex cingularis anterior
4205:
3731:Transverse temporal gyrus
3594:Posterior parietal cortex
2834:10.1016/j.nlm.2018.08.006
2339:10.1192/bjp.bp.108.055046
2181:10.1162/jocn.1991.3.3.231
1410:10.1111/1469-8986.3850752
344:, anticipation of tasks,
326:Emotional Counting Stroop
134:anterior cingulate cortex
110:
51:
39:
35:Anterior cingulate cortex
3852:Inferior temporal sulcus
3773:Superior temporal sulcus
3456:Inferior parietal lobule
3439:Superior parietal lobule
3379:Supplementary motor area
1935:10.3389/fnbeh.2016.00064
928:10.1177/1534582304267187
524:Role in registering pain
493:error-related negativity
385:error-related negativity
18:Anterior cingulate gyrus
3857:Inferior temporal gyrus
3801:Occipitotemporal sulcus
3747:Superior temporal gyrus
3640:Lateral occipital gyrus
3391:Supplementary eye field
3132:Inferior frontal sulcus
3127:Superior frontal sulcus
2788:10.1111/1469-7610.00165
2419:10.1126/science.1170008
2138:10.1126/science.1089134
1996:10.1162/089892998562924
1744:10.1073/pnas.0503657102
650:has been implicated in
592:voxel-based morphometry
4118:Fimbria of hippocampus
3184:Superior frontal gyrus
3082:Inferior frontal gyrus
3036:Superior frontal gyrus
2684:10.1073/pnas.042457199
1682:10.1073/pnas.012470999
1538:. In Posner MI (ed.).
656:deep-brain stimulation
213:
200:
4105:Hippocampal formation
3964:Parahippocampal gyrus
3778:Middle temporal gyrus
2603:10.1176/ajp.152.3.341
2503:Biological Psychiatry
2261:Nature Communications
2213:Biological Psychiatry
1492:Psychological Science
1371:10.1093/cercor/bhh125
1320:10.1073/pnas.87.1.256
859:10.1073/pnas.87.1.256
669:Cincinnati Lead Study
614:volumes in bilateral
598:volumes in bilateral
483:Role in consciousness
211:
195:
4078:Retrosplenial cortex
3926:Longitudinal fissure
3818:Medial temporal lobe
3495:Intraparietal sulcus
3355:Primary motor cortex
3252:Orbitofrontal cortex
3201:Medial frontal gyrus
3058:Middle frontal gyrus
2767:Peter Mundy (2003).
1175:The Human Brain Book
578:and lower levels of
462:Eriksen flanker task
373:Eriksen flanker task
328:is identical to the
301:Eriksen flanker task
291:related to the ACC.
4055:Posterior cingulate
3465:Supramarginal gyrus
2675:2002PNAS...99.2450Z
2466:10.1093/scan/nst041
2273:2023NatCo..14.3324B
2130:2003Sci...302..290E
2079:2000Sci...288.1769P
1735:2005PNAS..10215700P
1673:2002PNAS...99..523B
1611:Nature Neuroscience
1453:1998Sci...280..747C
1311:1990PNAS...87..256P
1253:1999Natur.402..179B
1202:2001NYASA.935..107A
1136:2001NYASA.935..107A
1099:The attentive brain
1013:on 24 February 2021
895:. medicalxpress.com
850:1990PNAS...87..256P
602:, extending to the
518:alien hand syndrome
273:von Economo neurons
172:reward anticipation
4113:Hippocampal sulcus
4033:Anterior cingulate
3910:Preoccipital notch
3511:Paracentral lobule
3481:Parietal operculum
3403:Frontal eye fields
3335:Paracentral sulcus
3323:Paracentral lobule
3224:Paraolfactory area
3220:Paraterminal gyrus
809:subcallosal cortex
234:frontal eye fields
220:), and emotional (
214:
201:
4218:
4217:
4162:
4161:
3987:Postrhinal cortex
3982:Perirhinal cortex
3977:Entorhinal cortex
3949:
3948:
3905:Parieto-occipital
3872:
3871:
3710:
3709:
3609:
3608:
3566:Postcentral gyrus
3418:
3417:
3343:
3342:
3163:
3162:
3155:Precentral sulcus
3118:Pars triangularis
2560:10.1002/cne.10609
2073:(5472): 1769–72.
2051:978-0-205-83256-9
2040:Pinel JP (2011).
1970:. 26 August 2022.
1842:10.1002/cne.20749
724:Additional images
600:lenticular nuclei
588:SDM meta-analyses
423:Social evaluation
250:nucleus accumbens
226:prefrontal cortex
148:. It consists of
126:
125:
121:
16:(Redirected from
4243:
4144:Indusium griseum
4009:Cingulate cortex
3999:Prepyriform area
3960:
3885:
3765:Planum temporale
3721:
3702:Calcarine sulcus
3620:
3429:
3300:Olfactory sulcus
3286:Subcallosal area
3172:
3150:Precentral gyrus
3109:Pars opercularis
3024:
3017:
2992:
2985:
2978:
2969:
2963:
2962:
2929:(4): 1914–1918.
2914:
2908:
2907:
2897:
2865:
2856:
2855:
2845:
2813:
2807:
2806:
2805:on 7 March 2012.
2804:
2798:. Archived from
2773:
2764:
2758:
2757:
2747:
2737:
2713:
2707:
2706:
2696:
2686:
2654:
2648:
2647:
2631:
2621:
2615:
2614:
2586:
2580:
2579:
2543:
2537:
2536:
2518:
2494:
2488:
2487:
2477:
2445:
2439:
2438:
2402:
2396:
2395:
2385:
2361:
2352:
2351:
2341:
2317:
2311:
2310:
2300:
2251:
2245:
2244:
2207:
2201:
2200:
2164:
2158:
2157:
2113:
2107:
2106:
2062:
2056:
2055:
2037:
2031:
2026:J. Neurophysiol.
2022:
2016:
2015:
1978:
1972:
1971:
1964:
1958:
1957:
1947:
1937:
1913:
1907:
1906:
1870:
1864:
1861:
1825:
1819:
1818:
1808:
1776:
1767:
1766:
1756:
1746:
1714:
1705:
1704:
1694:
1684:
1652:
1643:
1642:
1606:
1600:
1599:
1587:
1577:
1558:
1557:
1531:
1516:
1515:
1487:
1481:
1480:
1436:
1430:
1429:
1398:Psychophysiology
1393:
1384:
1383:
1373:
1349:
1343:
1342:
1332:
1322:
1290:
1281:
1280:
1247:(6758): 179–81.
1236:
1230:
1229:
1185:
1179:
1178:
1170:
1164:
1163:
1119:
1113:
1112:
1094:
1079:
1078:
1042:
1023:
1022:
1020:
1018:
1012:
1006:. Archived from
981:
966:Neuropsychologia
963:
954:
948:
947:
911:
905:
904:
902:
900:
888:
882:
881:
871:
861:
829:
799:Cingulate sulcus
789:Cingulate cortex
774:
762:
746:
734:
652:major depression
315:
311:
142:cingulate cortex
118:edit on Wikidata
56:
44:
32:
21:
4251:
4250:
4246:
4245:
4244:
4242:
4241:
4240:
4231:Cerebral cortex
4221:
4220:
4219:
4214:
4201:
4180:
4158:
4132:
4099:
4003:
3945:
3941:Callosal sulcus
3919:Medial/inferior
3914:
3879:
3868:
3794:Medial/inferior
3789:
3761:Wernicke's area
3735:Auditory cortex
3706:
3671:Medial/inferior
3666:
3605:
3554:
3550:Marginal sulcus
3504:Medial/inferior
3499:
3414:
3367:Premotor cortex
3339:
3309:
3168:Medial/inferior
3159:
3136:
3006:
3000:cerebral cortex
2998:Anatomy of the
2996:
2966:
2916:
2915:
2911:
2867:
2866:
2859:
2815:
2814:
2810:
2802:
2771:
2766:
2765:
2761:
2715:
2714:
2710:
2656:
2655:
2651:
2644:
2623:
2622:
2618:
2588:
2587:
2583:
2545:
2544:
2540:
2496:
2495:
2491:
2447:
2446:
2442:
2413:(5916): 890–1.
2404:
2403:
2399:
2363:
2362:
2355:
2319:
2318:
2314:
2253:
2252:
2248:
2219:(12): 1542–52.
2209:
2208:
2204:
2166:
2165:
2161:
2124:(5643): 290–2.
2115:
2114:
2110:
2064:
2063:
2059:
2052:
2039:
2038:
2034:
2023:
2019:
1980:
1979:
1975:
1966:
1965:
1961:
1915:
1914:
1910:
1872:
1871:
1867:
1862:
1827:
1826:
1822:
1791:(15): 4063–70.
1778:
1777:
1770:
1729:(43): 15700–5.
1716:
1715:
1708:
1654:
1653:
1646:
1608:
1607:
1603:
1596:
1579:
1578:
1561:
1554:
1533:
1532:
1519:
1489:
1488:
1484:
1447:(5364): 747–9.
1438:
1437:
1433:
1395:
1394:
1387:
1358:Cerebral Cortex
1351:
1350:
1346:
1292:
1291:
1284:
1238:
1237:
1233:
1187:
1186:
1182:
1172:
1171:
1167:
1121:
1120:
1116:
1109:
1096:
1095:
1082:
1044:
1043:
1026:
1016:
1014:
1010:
979:10.1.1.333.2783
961:
956:
955:
951:
913:
912:
908:
898:
896:
890:
889:
885:
831:
830:
826:
822:
794:Cingulate gyrus
785:
778:
775:
766:
763:
754:
747:
738:
735:
726:
718:psychopathology
710:
698:
690:joint attention
682:
665:
644:
632:
568:
548:akinetic mutism
539:
526:
485:
448:
425:
412:
381:
362:error detection
358:
342:error detection
338:
330:Counting Stroop
318:Counting-Stroop
313:
309:
297:
260:, and anterior
230:parietal cortex
206:
176:decision-making
146:corpus callosum
122:
59:
47:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
4249:
4247:
4239:
4238:
4233:
4223:
4222:
4216:
4215:
4210:Brodmann areas
4206:
4203:
4202:
4200:
4199:
4194:
4188:
4186:
4182:
4181:
4179:
4178:
4176:Insular cortex
4172:
4170:
4168:Insular cortex
4164:
4163:
4160:
4159:
4157:
4156:
4151:
4146:
4140:
4138:
4134:
4133:
4131:
4130:
4125:
4120:
4115:
4109:
4107:
4101:
4100:
4098:
4097:
4096:
4095:
4090:
4085:
4070:
4069:
4068:
4067:
4062:
4052:
4051:
4050:
4045:
4040:
4030:
4029:
4028:
4021:Subgenual area
4017:
4015:
4005:
4004:
4002:
4001:
3996:
3991:
3990:
3989:
3984:
3979:
3968:
3966:
3957:
3951:
3950:
3947:
3946:
3944:
3943:
3938:
3933:
3928:
3922:
3920:
3916:
3915:
3913:
3912:
3907:
3902:
3897:
3891:
3889:
3882:
3880:sulci/fissures
3874:
3873:
3870:
3869:
3867:
3866:
3865:
3864:
3854:
3848:
3847:
3846:
3845:
3840:
3835:
3830:
3825:
3815:
3814:
3813:
3806:Fusiform gyrus
3803:
3797:
3795:
3791:
3790:
3788:
3787:
3786:
3785:
3775:
3770:
3769:
3768:
3754:
3744:
3743:
3742:
3727:
3725:
3718:
3712:
3711:
3708:
3707:
3705:
3704:
3698:
3697:
3692:
3687:
3686:
3685:
3674:
3672:
3668:
3667:
3665:
3664:
3659:
3654:
3653:
3652:
3647:
3637:
3635:Occipital gyri
3632:
3626:
3624:
3617:
3615:Occipital lobe
3611:
3610:
3607:
3606:
3604:
3603:
3602:
3601:
3591:
3590:
3589:
3579:
3578:
3577:
3562:
3560:
3556:
3555:
3553:
3552:
3547:
3546:
3545:
3535:
3534:
3533:
3528:
3523:
3518:
3507:
3505:
3501:
3500:
3498:
3497:
3491:
3490:
3489:
3488:
3478:
3477:
3476:
3467:
3453:
3452:
3451:
3446:
3435:
3433:
3426:
3420:
3419:
3416:
3415:
3413:
3412:
3411:
3410:
3400:
3399:
3398:
3388:
3387:
3386:
3376:
3375:
3374:
3364:
3363:
3362:
3351:
3349:
3345:
3344:
3341:
3340:
3338:
3337:
3332:
3331:
3330:
3319:
3317:
3311:
3310:
3308:
3307:
3305:Orbital sulcus
3302:
3296:
3295:
3294:
3293:
3283:
3282:
3281:
3271:
3270:
3269:
3264:
3259:
3245:
3244:
3243:
3236:Straight gyrus
3233:
3232:
3231:
3216:
3215:
3214:
3213:
3208:
3198:
3197:
3196:
3191:
3180:
3178:
3169:
3165:
3164:
3161:
3160:
3158:
3157:
3152:
3146:
3144:
3138:
3137:
3135:
3134:
3129:
3123:
3122:
3121:
3120:
3111:
3097:
3095:Pars orbitalis
3088:
3078:
3077:
3076:
3075:
3070:
3065:
3055:
3054:
3053:
3048:
3043:
3032:
3030:
3021:
3014:
3008:
3007:
2997:
2995:
2994:
2987:
2980:
2972:
2965:
2964:
2909:
2880:(5): 499–509.
2857:
2808:
2782:(6): 793–809.
2759:
2708:
2649:
2642:
2616:
2581:
2538:
2489:
2440:
2397:
2353:
2332:(5): 393–402.
2312:
2246:
2202:
2159:
2108:
2057:
2050:
2032:
2017:
1973:
1959:
1908:
1865:
1820:
1768:
1706:
1644:
1601:
1594:
1559:
1552:
1517:
1482:
1431:
1385:
1344:
1282:
1231:
1180:
1177:. p. 124.
1165:
1114:
1107:
1080:
1053:(6): 215–222.
1024:
949:
906:
883:
823:
821:
818:
817:
816:
811:
806:
801:
796:
791:
784:
781:
780:
779:
776:
769:
767:
764:
757:
755:
751:Macaca mulatta
748:
741:
739:
736:
729:
725:
722:
709:
706:
697:
694:
681:
678:
664:
661:
643:
640:
636:social anxiety
631:
628:
624:medial frontal
620:caudate nuclei
608:medial frontal
604:caudate nuclei
567:
564:
538:
535:
525:
522:
484:
481:
447:
444:
424:
421:
411:
408:
380:
377:
357:
354:
337:
334:
296:
293:
205:
202:
150:Brodmann areas
124:
123:
114:
108:
107:
102:
95:
94:
89:
83:
82:
77:
71:
70:
66:
65:
61:
60:
57:
49:
48:
45:
37:
36:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4248:
4237:
4234:
4232:
4229:
4228:
4226:
4213:
4211:
4204:
4198:
4195:
4193:
4190:
4189:
4187:
4183:
4177:
4174:
4173:
4171:
4169:
4165:
4155:
4152:
4150:
4147:
4145:
4142:
4141:
4139:
4135:
4129:
4128:Rhinal sulcus
4126:
4124:
4123:Dentate gyrus
4121:
4119:
4116:
4114:
4111:
4110:
4108:
4106:
4102:
4094:
4091:
4089:
4086:
4084:
4081:
4080:
4079:
4075:
4072:
4071:
4066:
4063:
4061:
4058:
4057:
4056:
4053:
4049:
4046:
4044:
4041:
4039:
4036:
4035:
4034:
4031:
4027:
4024:
4023:
4022:
4019:
4018:
4016:
4014:
4010:
4006:
4000:
3997:
3995:
3992:
3988:
3985:
3983:
3980:
3978:
3975:
3974:
3973:
3970:
3969:
3967:
3965:
3961:
3958:
3956:
3952:
3942:
3939:
3937:
3934:
3932:
3929:
3927:
3924:
3923:
3921:
3917:
3911:
3908:
3906:
3903:
3901:
3898:
3896:
3893:
3892:
3890:
3888:Superolateral
3886:
3883:
3881:
3875:
3863:
3860:
3859:
3858:
3855:
3853:
3850:
3849:
3844:
3841:
3839:
3836:
3834:
3831:
3829:
3826:
3824:
3821:
3820:
3819:
3816:
3812:
3809:
3808:
3807:
3804:
3802:
3799:
3798:
3796:
3792:
3784:
3781:
3780:
3779:
3776:
3774:
3771:
3766:
3762:
3758:
3755:
3753:
3750:
3749:
3748:
3745:
3741:
3738:
3737:
3736:
3732:
3729:
3728:
3726:
3724:Superolateral
3722:
3719:
3717:
3716:Temporal lobe
3713:
3703:
3700:
3699:
3696:
3695:Lingual gyrus
3693:
3691:
3688:
3684:
3681:
3680:
3679:
3678:Visual cortex
3676:
3675:
3673:
3669:
3663:
3660:
3658:
3657:Lunate sulcus
3655:
3651:
3648:
3646:
3643:
3642:
3641:
3638:
3636:
3633:
3631:
3628:
3627:
3625:
3623:Superolateral
3621:
3618:
3616:
3612:
3600:
3597:
3596:
3595:
3592:
3588:
3585:
3584:
3583:
3580:
3576:
3573:
3572:
3571:
3567:
3564:
3563:
3561:
3557:
3551:
3548:
3544:
3541:
3540:
3539:
3536:
3532:
3529:
3527:
3524:
3522:
3519:
3517:
3514:
3513:
3512:
3509:
3508:
3506:
3502:
3496:
3493:
3492:
3487:
3484:
3483:
3482:
3479:
3475:
3474:Angular gyrus
3471:
3468:
3466:
3462:
3459:
3458:
3457:
3454:
3450:
3447:
3445:
3442:
3441:
3440:
3437:
3436:
3434:
3432:Superolateral
3430:
3427:
3425:
3424:Parietal lobe
3421:
3409:
3406:
3405:
3404:
3401:
3397:
3394:
3393:
3392:
3389:
3385:
3382:
3381:
3380:
3377:
3373:
3370:
3369:
3368:
3365:
3361:
3358:
3357:
3356:
3353:
3352:
3350:
3346:
3336:
3333:
3329:
3326:
3325:
3324:
3321:
3320:
3318:
3316:
3312:
3306:
3303:
3301:
3298:
3297:
3292:
3289:
3288:
3287:
3284:
3280:
3277:
3276:
3275:
3272:
3268:
3265:
3263:
3260:
3258:
3255:
3254:
3253:
3249:
3246:
3242:
3239:
3238:
3237:
3234:
3230:
3227:
3226:
3225:
3221:
3218:
3217:
3212:
3209:
3207:
3204:
3203:
3202:
3199:
3195:
3192:
3190:
3187:
3186:
3185:
3182:
3181:
3179:
3177:
3173:
3170:
3166:
3156:
3153:
3151:
3148:
3147:
3145:
3143:
3139:
3133:
3130:
3128:
3125:
3124:
3119:
3115:
3112:
3110:
3106:
3103:
3102:
3101:
3098:
3096:
3092:
3089:
3087:
3083:
3080:
3079:
3074:
3071:
3069:
3066:
3064:
3061:
3060:
3059:
3056:
3052:
3049:
3047:
3044:
3042:
3039:
3038:
3037:
3034:
3033:
3031:
3029:
3025:
3022:
3020:Superolateral
3018:
3015:
3013:
3009:
3005:
3001:
2993:
2988:
2986:
2981:
2979:
2974:
2973:
2970:
2960:
2956:
2952:
2948:
2944:
2940:
2936:
2932:
2928:
2924:
2920:
2913:
2910:
2905:
2901:
2896:
2891:
2887:
2883:
2879:
2875:
2871:
2864:
2862:
2858:
2853:
2849:
2844:
2839:
2835:
2831:
2827:
2823:
2819:
2812:
2809:
2801:
2797:
2793:
2789:
2785:
2781:
2777:
2770:
2763:
2760:
2755:
2751:
2746:
2741:
2736:
2731:
2727:
2723:
2722:PLOS Medicine
2719:
2712:
2709:
2704:
2700:
2695:
2690:
2685:
2680:
2676:
2672:
2669:(4): 2450–4.
2668:
2664:
2660:
2653:
2650:
2645:
2643:9783527307852
2639:
2635:
2630:
2629:
2620:
2617:
2612:
2608:
2604:
2600:
2597:(3): 341–51.
2596:
2592:
2585:
2582:
2577:
2573:
2569:
2565:
2561:
2557:
2554:(3): 425–49.
2553:
2549:
2542:
2539:
2534:
2530:
2526:
2522:
2517:
2512:
2508:
2504:
2500:
2493:
2490:
2485:
2481:
2476:
2471:
2467:
2463:
2459:
2455:
2451:
2444:
2441:
2436:
2432:
2428:
2424:
2420:
2416:
2412:
2408:
2401:
2398:
2393:
2389:
2384:
2379:
2376:(7): 701–11.
2375:
2371:
2367:
2360:
2358:
2354:
2349:
2345:
2340:
2335:
2331:
2327:
2323:
2316:
2313:
2308:
2304:
2299:
2294:
2290:
2286:
2282:
2278:
2274:
2270:
2266:
2262:
2258:
2250:
2247:
2242:
2238:
2234:
2230:
2226:
2222:
2218:
2214:
2206:
2203:
2198:
2194:
2190:
2186:
2182:
2178:
2175:(3): 231–41.
2174:
2170:
2163:
2160:
2155:
2151:
2147:
2143:
2139:
2135:
2131:
2127:
2123:
2119:
2112:
2109:
2104:
2100:
2096:
2092:
2088:
2084:
2080:
2076:
2072:
2068:
2061:
2058:
2053:
2047:
2043:
2042:Biopsychology
2036:
2033:
2030:
2027:
2021:
2018:
2013:
2009:
2005:
2001:
1997:
1993:
1990:(4): 525–35.
1989:
1985:
1977:
1974:
1969:
1963:
1960:
1955:
1951:
1946:
1941:
1936:
1931:
1927:
1923:
1919:
1912:
1909:
1904:
1900:
1896:
1892:
1888:
1884:
1881:(4): 168–76.
1880:
1876:
1869:
1866:
1859:
1855:
1851:
1847:
1843:
1839:
1836:(1): 154–66.
1835:
1831:
1824:
1821:
1816:
1812:
1807:
1802:
1798:
1794:
1790:
1786:
1782:
1775:
1773:
1769:
1764:
1760:
1755:
1750:
1745:
1740:
1736:
1732:
1728:
1724:
1720:
1713:
1711:
1707:
1702:
1698:
1693:
1688:
1683:
1678:
1674:
1670:
1666:
1662:
1658:
1651:
1649:
1645:
1640:
1636:
1632:
1628:
1624:
1623:10.1038/74899
1620:
1617:(5): 516–20.
1616:
1612:
1605:
1602:
1597:
1595:1-59385-048-4
1591:
1586:
1585:
1576:
1574:
1572:
1570:
1568:
1566:
1564:
1560:
1555:
1553:1-59385-048-4
1549:
1545:
1541:
1537:
1530:
1528:
1526:
1524:
1522:
1518:
1513:
1509:
1505:
1501:
1498:(6): 385–90.
1497:
1493:
1486:
1483:
1478:
1474:
1470:
1466:
1462:
1458:
1454:
1450:
1446:
1442:
1435:
1432:
1427:
1423:
1419:
1415:
1411:
1407:
1404:(5): 752–60.
1403:
1399:
1392:
1390:
1386:
1381:
1377:
1372:
1367:
1364:(2): 229–37.
1363:
1359:
1355:
1348:
1345:
1340:
1336:
1331:
1326:
1321:
1316:
1312:
1308:
1304:
1300:
1296:
1289:
1287:
1283:
1278:
1274:
1270:
1266:
1262:
1261:10.1038/46035
1258:
1254:
1250:
1246:
1242:
1235:
1232:
1227:
1223:
1219:
1215:
1211:
1207:
1203:
1199:
1196:(1): 107–17.
1195:
1191:
1184:
1181:
1176:
1169:
1166:
1161:
1157:
1153:
1149:
1145:
1141:
1137:
1133:
1130:(1): 107–17.
1129:
1125:
1118:
1115:
1110:
1108:0-262-16172-9
1104:
1100:
1093:
1091:
1089:
1087:
1085:
1081:
1076:
1072:
1068:
1064:
1060:
1056:
1052:
1048:
1041:
1039:
1037:
1035:
1033:
1031:
1029:
1025:
1009:
1005:
1001:
997:
993:
989:
985:
980:
975:
972:(5): 752–61.
971:
967:
960:
953:
950:
945:
941:
937:
933:
929:
925:
922:(2): 71–100.
921:
917:
910:
907:
894:
887:
884:
879:
875:
870:
865:
860:
855:
851:
847:
843:
839:
835:
828:
825:
819:
815:
814:Reward system
812:
810:
807:
805:
802:
800:
797:
795:
792:
790:
787:
786:
782:
773:
768:
761:
756:
752:
745:
740:
733:
728:
723:
721:
719:
715:
707:
705:
703:
695:
693:
691:
687:
679:
677:
674:
670:
663:Lead exposure
662:
660:
657:
653:
649:
646:The adjacent
641:
639:
637:
629:
627:
625:
621:
617:
613:
609:
605:
601:
597:
593:
589:
584:
581:
577:
573:
565:
563:
561:
557:
553:
552:schizophrenia
549:
545:
536:
534:
530:
523:
521:
519:
515:
511:
510:Francis Crick
507:
506:
500:
496:
495:is produced.
494:
489:
482:
480:
478:
473:
469:
465:
463:
457:
454:
445:
443:
440:
438:
434:
431:
422:
420:
416:
409:
407:
403:
399:
395:
392:
390:
386:
378:
376:
374:
369:
367:
363:
355:
353:
351:
347:
343:
335:
333:
331:
327:
323:
319:
307:
302:
294:
292:
290:
286:
282:
278:
274:
270:
269:spindle cells
265:
263:
259:
255:
251:
247:
243:
239:
235:
231:
227:
223:
219:
210:
203:
198:
194:
190:
188:
183:
181:
177:
173:
169:
164:
162:
158:
154:
151:
147:
143:
139:
135:
131:
119:
113:
109:
106:
103:
100:
96:
93:
90:
88:
84:
81:
78:
76:
72:
67:
62:
55:
50:
43:
38:
33:
30:
19:
4207:
4032:
3971:
3248:Orbital gyri
3100:Broca's area
3012:Frontal lobe
2926:
2922:
2912:
2877:
2873:
2825:
2821:
2811:
2800:the original
2779:
2775:
2762:
2725:
2721:
2711:
2666:
2662:
2652:
2627:
2619:
2594:
2590:
2584:
2551:
2547:
2541:
2509:(4): 301–8.
2506:
2502:
2492:
2460:(6): 751–9.
2457:
2453:
2443:
2410:
2406:
2400:
2373:
2369:
2329:
2325:
2315:
2264:
2260:
2249:
2216:
2212:
2205:
2172:
2168:
2162:
2121:
2117:
2111:
2070:
2066:
2060:
2041:
2035:
2025:
2020:
1987:
1983:
1976:
1962:
1925:
1921:
1911:
1878:
1874:
1868:
1833:
1829:
1823:
1788:
1784:
1726:
1722:
1667:(1): 523–8.
1664:
1660:
1614:
1610:
1604:
1583:
1539:
1495:
1491:
1485:
1444:
1440:
1434:
1401:
1397:
1361:
1357:
1347:
1305:(1): 256–9.
1302:
1298:
1244:
1240:
1234:
1193:
1189:
1183:
1174:
1168:
1127:
1123:
1117:
1098:
1050:
1046:
1017:12 September
1015:. Retrieved
1008:the original
969:
965:
952:
919:
915:
909:
897:. Retrieved
886:
844:(1): 256–9.
841:
837:
827:
711:
699:
683:
666:
645:
633:
585:
569:
540:
531:
527:
503:
501:
497:
490:
486:
474:
470:
466:
458:
449:
441:
426:
417:
413:
404:
400:
396:
393:
382:
370:
359:
339:
329:
325:
321:
317:
298:
266:
254:hypothalamus
215:
186:
184:
170:allocation,
165:
137:
133:
127:
79:
29:
27:Brain region
3955:Limbic lobe
3004:human brain
2828:: 189–196.
2728:(5): e112.
2267:(1): 3324.
612:grey matter
596:grey matter
560:Stroop task
544:Stroop task
366:Stroop task
322:Stroop task
306:Stroop task
289:pathologies
258:hippocampus
130:human brain
105:birnlex_936
69:Identifiers
4225:Categories
4212:span gyri.
3878:Interlobar
3575:3, 1 and 2
3315:Precentral
3176:Prefrontal
3142:Precentral
3028:Prefrontal
1173:Carter R.
820:References
642:Depression
616:lenticular
437:depression
350:motivation
324:named the
87:NeuroNames
4192:Operculum
3740:41 and 42
3538:Precuneus
2959:247360689
2943:1931-7565
2435:206518219
2289:2041-1723
2241:205870638
1477:264267292
974:CiteSeerX
944:145310279
576:glutamate
537:Pathology
514:free will
477:effortful
346:attention
336:Functions
285:elephants
281:cetaceans
242:bottom-up
189:(aMCC).
168:attention
4154:Amygdala
3972:anterior
2951:35266100
2904:32299789
2852:30086395
2796:12959489
2754:18507499
2703:11842195
2568:12692859
2533:35458273
2525:21145043
2484:23615765
2427:19213907
2392:20603451
2348:19880927
2307:37369695
2298:10300066
2233:10376114
2197:39599951
2189:23964838
2154:21253445
2146:14551436
2103:15250446
2095:10846154
2012:27743177
1954:27065828
1895:17337237
1858:32616395
1850:16254997
1815:16611823
1763:16227444
1701:11756669
1639:11136447
1631:10769394
1512:17422146
1418:11577898
1380:15238434
1269:10647008
1226:10507342
1218:11411161
1160:10507342
1152:11411161
1075:16451230
1067:10827444
996:16140345
936:15537986
899:26 March
783:See also
277:primates
246:amygdala
238:top-down
197:Sagittal
99:NeuroLex
4185:General
3002:of the
2895:8366521
2843:6361720
2745:2689675
2671:Bibcode
2611:7864258
2576:9798173
2475:4040088
2407:Science
2269:Bibcode
2126:Bibcode
2118:Science
2075:Bibcode
2067:Science
2004:9712681
1945:4815251
1903:6755137
1806:6673891
1754:1255733
1731:Bibcode
1669:Bibcode
1469:9563953
1449:Bibcode
1441:Science
1426:7566915
1339:2296583
1307:Bibcode
1277:4425726
1249:Bibcode
1198:Bibcode
1132:Bibcode
1004:6848345
878:2296583
846:Bibcode
630:Anxiety
586:Recent
222:ventral
204:Anatomy
180:emotion
128:In the
64:Details
3690:Cuneus
2957:
2949:
2941:
2902:
2892:
2850:
2840:
2794:
2752:
2742:
2701:
2694:122385
2691:
2640:
2636:–466.
2609:
2574:
2566:
2531:
2523:
2482:
2472:
2433:
2425:
2390:
2346:
2305:
2295:
2287:
2239:
2231:
2195:
2187:
2152:
2144:
2101:
2093:
2048:
2010:
2002:
1952:
1942:
1928:: 64.
1901:
1893:
1856:
1848:
1813:
1803:
1761:
1751:
1699:
1692:117593
1689:
1637:
1629:
1592:
1550:
1544:219–31
1510:
1475:
1467:
1424:
1416:
1378:
1337:
1327:
1275:
1267:
1241:Nature
1224:
1216:
1158:
1150:
1105:
1073:
1065:
1002:
994:
976:
942:
934:
876:
866:
686:autism
680:Autism
283:, and
262:insula
218:dorsal
159:, and
132:, the
4149:Uncus
4137:Other
4013:gyrus
2955:S2CID
2803:(PDF)
2772:(PDF)
2572:S2CID
2529:S2CID
2431:S2CID
2237:S2CID
2193:S2CID
2150:S2CID
2099:S2CID
2008:S2CID
1899:S2CID
1854:S2CID
1635:S2CID
1508:S2CID
1473:S2CID
1422:S2CID
1330:53241
1273:S2CID
1222:S2CID
1156:S2CID
1071:S2CID
1011:(PDF)
1000:S2CID
962:(PDF)
940:S2CID
869:53241
295:Tasks
271:, or
116:[
75:Latin
3559:Both
3348:Both
2947:PMID
2939:ISSN
2900:PMID
2848:PMID
2792:PMID
2750:PMID
2699:PMID
2638:ISBN
2607:PMID
2564:PMID
2521:PMID
2480:PMID
2423:PMID
2388:PMID
2344:PMID
2303:PMID
2285:ISSN
2229:PMID
2185:PMID
2142:PMID
2091:PMID
2046:ISBN
2000:PMID
1950:PMID
1891:PMID
1846:PMID
1811:PMID
1759:PMID
1697:PMID
1627:PMID
1590:ISBN
1548:ISBN
1465:PMID
1414:PMID
1376:PMID
1335:PMID
1265:PMID
1214:PMID
1148:PMID
1103:ISBN
1063:PMID
1019:2019
992:PMID
932:PMID
901:2013
874:PMID
696:PTSD
673:lead
580:GABA
556:ADHD
453:fMRI
433:BOLD
430:fMRI
240:and
228:and
2931:doi
2890:PMC
2882:doi
2838:PMC
2830:doi
2826:155
2784:doi
2740:PMC
2730:doi
2689:PMC
2679:doi
2634:425
2599:doi
2595:152
2556:doi
2552:460
2511:doi
2470:PMC
2462:doi
2415:doi
2411:323
2378:doi
2334:doi
2330:195
2293:PMC
2277:doi
2221:doi
2177:doi
2134:doi
2122:302
2083:doi
2071:288
1992:doi
1940:PMC
1930:doi
1883:doi
1838:doi
1834:493
1801:PMC
1793:doi
1749:PMC
1739:doi
1727:102
1687:PMC
1677:doi
1619:doi
1500:doi
1457:doi
1445:280
1406:doi
1366:doi
1325:PMC
1315:doi
1257:doi
1245:402
1206:doi
1194:935
1140:doi
1128:935
1055:doi
984:doi
924:doi
864:PMC
854:doi
590:of
566:OCD
502:In
389:ERP
314:RED
310:RED
138:ACC
92:161
4227::
4093:30
4088:29
4083:26
4076::
4065:31
4060:23
4048:33
4043:32
4038:24
4026:25
3862:20
3843:36
3838:35
3833:34
3828:28
3823:27
3811:37
3783:21
3757:22
3752:38
3683:17
3650:19
3645:18
3486:43
3470:39
3461:40
3291:25
3279:10
3267:12
3262:11
3257:10
3241:11
3229:12
3114:45
3105:44
3091:47
3086:11
3084::
3073:46
3068:10
2953:.
2945:.
2937:.
2927:16
2925:.
2921:.
2898:.
2888:.
2876:.
2872:.
2860:^
2846:.
2836:.
2824:.
2820:.
2790:.
2780:44
2778:.
2774:.
2748:.
2738:.
2724:.
2720:.
2697:.
2687:.
2677:.
2667:99
2665:.
2661:.
2605:.
2593:.
2570:.
2562:.
2550:.
2527:.
2519:.
2507:69
2505:.
2501:.
2478:.
2468:.
2456:.
2452:.
2429:.
2421:.
2409:.
2386:.
2374:67
2372:.
2368:.
2356:^
2342:.
2328:.
2324:.
2301:.
2291:.
2283:.
2275:.
2265:14
2263:.
2259:.
2235:.
2227:.
2217:45
2215:.
2191:.
2183:.
2171:.
2148:.
2140:.
2132:.
2120:.
2097:.
2089:.
2081:.
2069:.
2006:.
1998:.
1988:10
1986:.
1948:.
1938:.
1926:10
1924:.
1920:.
1897:.
1889:.
1879:11
1877:.
1852:.
1844:.
1832:.
1809:.
1799:.
1789:26
1787:.
1783:.
1771:^
1757:.
1747:.
1737:.
1725:.
1721:.
1709:^
1695:.
1685:.
1675:.
1665:99
1663:.
1659:.
1647:^
1633:.
1625:.
1613:.
1562:^
1546:.
1520:^
1506:.
1494:.
1471:.
1463:.
1455:.
1443:.
1420:.
1412:.
1402:38
1400:.
1388:^
1374:.
1362:15
1360:.
1356:.
1333:.
1323:.
1313:.
1303:87
1301:.
1297:.
1285:^
1271:.
1263:.
1255:.
1243:.
1220:.
1212:.
1204:.
1192:.
1154:.
1146:.
1138:.
1126:.
1083:^
1069:.
1061:.
1049:.
1027:^
998:.
990:.
982:.
970:44
968:.
964:.
938:.
930:.
918:.
872:.
862:.
852:.
842:87
840:.
836:.
753:).
720:.
692:.
618:/
520:.
508:,
348:,
279:,
256:,
252:,
248:,
182:.
174:,
163:.
161:33
157:32
155:,
153:24
101:ID
4011:/
3767:)
3763:(
3759:/
3733:/
3599:7
3587:5
3568:/
3543:7
3531:5
3526:3
3521:2
3516:1
3472:-
3463:-
3449:7
3444:5
3408:8
3396:6
3384:6
3372:6
3360:4
3328:4
3250:/
3222:/
3211:9
3206:8
3194:6
3189:4
3116:-
3107:-
3093:-
3063:9
3051:8
3046:6
3041:4
2991:e
2984:t
2977:v
2961:.
2933::
2906:.
2884::
2878:5
2854:.
2832::
2786::
2756:.
2732::
2726:5
2705:.
2681::
2673::
2646:.
2613:.
2601::
2578:.
2558::
2535:.
2513::
2486:.
2464::
2458:9
2437:.
2417::
2394:.
2380::
2350:.
2336::
2309:.
2279::
2271::
2243:.
2223::
2199:.
2179::
2173:3
2156:.
2136::
2128::
2105:.
2085::
2077::
2054:.
2014:.
1994::
1956:.
1932::
1905:.
1885::
1860:.
1840::
1817:.
1795::
1765:.
1741::
1733::
1703:.
1679::
1671::
1641:.
1621::
1615:3
1598:.
1556:.
1514:.
1502::
1496:4
1479:.
1459::
1451::
1428:.
1408::
1382:.
1368::
1341:.
1317::
1309::
1279:.
1259::
1251::
1228:.
1208::
1200::
1162:.
1142::
1134::
1111:.
1077:.
1057::
1051:4
1021:.
986::
946:.
926::
920:3
903:.
880:.
856::
848::
136:(
120:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.