229:
29:
41:
206:
198:. The intermediate lobe lies between the anterior and posterior lobes over the maxilla. The intermediate lobe seems to lose a significant amount of volume between childhood and adulthood. The posterior lobe of the buccal fat pad runs from the infraorbital fissure and temporal muscle to the upper rim of the mandible and back to the
178:
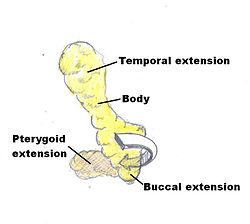
The buccal fat pad is composed of several parts, although exactly how many parts seems to be a point of disagreement and no single consistent nomenclature of these parts has been observed. It was described as being divided into three lobes, the anterior, intermediate, and posterior, “according to the
218:
Some people describe the buccal fat pad’s primary function in relation to chewing and suckling, especially in infants. This theory derives some support from the loss of volume to the intermediate lobe, which would be most directly involved in chewing and sucking, from infancy to adulthood.
183:, and the source of the nutritional vessels”. Also, there are four extensions from the body of the buccal fat pad: the sublevator, the melolabial, the buccal, and the pterygoid. The nomenclature of these extensions derives from their location and proximal muscles.
247:
Buccal flaps (not always including the buccal fat pad) are used in reconstruction of the periorbital area after injury. They are also used to repair congenital defects of the oral cavity or for repair of congenital
166:. It should not be confused with the malar fat pad, which is directly below the skin of the cheek. It should also not be confused with jowl fat pads. It is implicated in the formation of hollow cheeks and the
258:
is also sometimes used to reduce cheek prominence, although this procedure may carry with it a significant risk of damage to the buccal branch of the facial nerve and the parotid ducts.
573:
Holton Lh; Rodriguez, ED; Silverman, RP; Singh, N; Tufaro, AP; Grant, MP (2004). "The buccal fat pad flap for periorbital reconstruction: a cadaver dissection and report of two cases".
643:
Landes; Seitz, O; Ballon, A; Stübinger, S; Robert, S; Kovács, AF (2009). "Six years clinical experience with the dorsally pedicled buccal musculomucosal flap".
102:
191:
530:
Tapia; Ruiz-De-Erenchun, R; Rengifo, M (2006). "Combined approach for facial contour restoration: treatment of malar and cheek areas during rhytidectomy".
240:
The buccal fat pad is commonly used in facial recontouring. Several authors discuss the importance of the buccal fat pad in attaining good results from a
452:
Rohrich; Ghavami, A; Lemmon, JA; Brown, SA (2009). "The individualized component face lift: developing a systematic approach to facial rejuvenation".
365:
Reece; Pessa, JE; Rohrich, RJ (2008). "The mandibular septum: anatomical observations of the jowls in aging-implications for facial rejuvenation".
790:
495:
Lambros; Stuzin, JM (2008). "The cross-cheek depression: surgical cause and effect in the development of the "joker line" and its treatment".
78:
225:
The buccal fat pad may also function as a cushion to protect sensitive facial muscles from injury due to muscle action or exterior force.
729:
Hwang; Cho, HJ; Battuvshin, D; Chung, IH; Hwang, SH (2005). "Interrelated buccal fat pad with facial buccal branches and parotid duct".
190:, which conveys saliva from the parotid gland to the mouth. It is a triangular mass with one vertex at the buccinators, one at the
1146:
284:
Zhang; Yan, YP; Qi, KM; Wang, JQ; Liu, ZF (2002). "Anatomical structure of the buccal fat pad and its clinical adaptations".
97:
1192:
322:
Rohrich; Pessa, JE (2007). "The fat compartments of the face: anatomy and clinical implications for cosmetic surgery".
783:
831:
686:
Levi; Kasten, SJ; Buchman, SR (2009). "Utilization of the buccal fat pad flap for congenital cleft palate repair".
1103:
209:
The buccal fat pads are clearly visible on the cheeks of children of different age, complexion and constitution.
1197:
159:
155:
608:
Egyedi (1977). "Utilization of the buccal fat pad for closure of oro-antral and/or oro-nasal communications".
1026:
195:
1113:
1046:
776:
109:
85:
73:
1161:
1141:
1019:
945:
935:
930:
826:
255:
199:
222:
Another proposed function is as gliding pads that facilitate the action of the muscles of mastication.
249:
1108:
1002:
940:
910:
1156:
1098:
1007:
754:
711:
668:
555:
477:
390:
347:
970:
746:
703:
660:
625:
590:
547:
512:
469:
434:
382:
339:
301:
147:
1014:
892:
816:
738:
695:
652:
617:
582:
539:
504:
461:
424:
374:
331:
293:
228:
1171:
1166:
1088:
925:
920:
915:
167:
151:
146:
masses in the cheek. It is a deep fat pad located on either side of the face between the
1118:
982:
887:
821:
742:
586:
543:
378:
335:
621:
1186:
990:
297:
135:
758:
715:
672:
559:
394:
351:
28:
995:
950:
481:
241:
187:
163:
40:
699:
656:
508:
465:
1036:
882:
877:
800:
429:
412:
1136:
841:
90:
1068:
413:"Surgical anatomy of the face: implications for modern face-lift techniques"
205:
750:
707:
664:
594:
551:
516:
473:
438:
411:
Gassner; Rafii, A; Young, A; Murakami, C; Moe, KS; Larrabee Jr, WF (2008).
386:
343:
305:
960:
955:
836:
629:
180:
115:
965:
768:
143:
162:). The inferior portion of the buccal fat pad is contained within the
1083:
1078:
1073:
1057:
869:
1151:
851:
204:
61:
902:
772:
808:
227:
150:
and several more superficial muscles (including the
1129:
1056:
1035:
981:
901:
868:
850:
807:
179:structure of the lobar envelopes, the formation of
96:
84:
72:
60:
55:
50:
21:
186:The anterior lobe of the buccal fat surrounds the
784:
8:
791:
777:
769:
39:
27:
428:
406:
404:
317:
315:
279:
277:
275:
273:
271:
267:
113:
18:
192:levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
170:, but not in the formation of jowls.
7:
731:The Journal of Craniofacial Surgery
743:10.1097/01.SCS.0000157019.35407.55
688:Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
587:10.1097/01.prs.0000138257.44949.bb
575:Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
544:10.1097/01.prs.0000235265.26138.66
532:Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
497:Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
454:Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
417:Archives of Facial Plastic Surgery
379:10.1097/01.prs.0000302462.61624.26
367:Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
336:10.1097/01.prs.0000265403.66886.54
330:(7): 2219–27, discussion 2228–31.
324:Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
292:(7): 2509–18, discussion 2519–20.
286:Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
14:
142:) is one of several encapsulated
610:Journal of Maxillofacial Surgery
538:(2): 491–7, discussion 498–501.
298:10.1097/00006534-200206000-00052
1147:Plica semilunaris of the fauces
1:
622:10.1016/S0301-0503(77)80117-3
256:Removal of the buccal fat pad
700:10.1097/PRS.0b013e318199f80f
657:10.1097/SAP.0b013e318180cd3e
509:10.1097/PRS.0b013e31818894d3
466:10.1097/PRS.0b013e31819c91b0
1214:
832:Labial commissure of mouth
430:10.1001/archfacial.2007.16
174:Nomenclature and structure
645:Annals of Plastic Surgery
108:
38:
26:
1027:Tubarial salivary gland
1114:Glossoepiglottic folds
232:
210:
110:Anatomical terminology
67:corpus adiposum buccae
45:Buccal fat pad diagram
1162:Palatopharyngeal arch
936:Mucogingival junction
931:Junctional epithelium
827:Frenulum of lower lip
231:
208:
971:Periodontal ligament
33:Extracted buccal fat
1193:Human head and neck
1109:Sublingual caruncle
1003:Submandibular gland
941:Sulcular epithelium
911:Interdental papilla
1157:Palatoglossal arch
233:
211:
1180:
1179:
194:, and one at the
160:zygomaticus minor
156:zygomaticus major
148:buccinator muscle
140:buccal pad of fat
124:
123:
119:
16:Organ of the face
1205:
1015:Sublingual gland
893:Incisive papilla
817:Vermilion border
793:
786:
779:
770:
763:
762:
726:
720:
719:
683:
677:
676:
640:
634:
633:
605:
599:
598:
570:
564:
563:
527:
521:
520:
492:
486:
485:
449:
443:
442:
432:
408:
399:
398:
362:
356:
355:
319:
310:
309:
281:
200:mandibular ramus
196:orbicularis oris
132:Bichat’s fat pad
116:edit on Wikidata
43:
31:
19:
1213:
1212:
1208:
1207:
1206:
1204:
1203:
1202:
1198:Facial features
1183:
1182:
1181:
1176:
1172:Palatine tonsil
1167:Tonsillar fossa
1125:
1104:Fimbriated fold
1089:Lingual tonsils
1079:Terminal sulcus
1052:
1031:
977:
926:Gingival fibers
921:Gingival margin
916:Gingival sulcus
897:
864:
846:
803:
799:Anatomy of the
797:
767:
766:
728:
727:
723:
685:
684:
680:
642:
641:
637:
607:
606:
602:
572:
571:
567:
529:
528:
524:
494:
493:
489:
451:
450:
446:
410:
409:
402:
364:
363:
359:
321:
320:
313:
283:
282:
269:
264:
238:
216:
176:
168:nasolabial fold
120:
46:
34:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1211:
1209:
1201:
1200:
1195:
1185:
1184:
1178:
1177:
1175:
1174:
1169:
1164:
1159:
1154:
1149:
1144:
1139:
1133:
1131:
1127:
1126:
1124:
1123:
1122:
1121:
1119:Lingual septum
1116:
1111:
1106:
1101:
1093:
1092:
1091:
1086:
1081:
1076:
1071:
1062:
1060:
1054:
1053:
1051:
1050:
1041:
1039:
1033:
1032:
1030:
1029:
1024:
1023:
1022:
1012:
1011:
1010:
1000:
999:
998:
987:
985:
979:
978:
976:
975:
974:
973:
968:
963:
958:
948:
943:
938:
933:
928:
923:
918:
913:
907:
905:
899:
898:
896:
895:
890:
888:Palatine raphe
885:
880:
874:
872:
866:
865:
863:
862:
860:Buccal fat pad
856:
854:
848:
847:
845:
844:
839:
834:
829:
824:
819:
813:
811:
805:
804:
798:
796:
795:
788:
781:
773:
765:
764:
721:
694:(3): 1018–21.
678:
635:
600:
581:(6): 1529–33.
565:
522:
503:(5): 1543–52.
487:
460:(3): 1050–63.
444:
400:
373:(4): 1414–20.
357:
311:
266:
265:
263:
260:
237:
234:
215:
212:
175:
172:
128:buccal fat pad
122:
121:
112:
106:
105:
100:
94:
93:
88:
82:
81:
76:
70:
69:
64:
58:
57:
53:
52:
48:
47:
44:
36:
35:
32:
24:
23:
22:Buccal fat pad
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1210:
1199:
1196:
1194:
1191:
1190:
1188:
1173:
1170:
1168:
1165:
1163:
1160:
1158:
1155:
1153:
1150:
1148:
1145:
1143:
1140:
1138:
1135:
1134:
1132:
1130:Back of mouth
1128:
1120:
1117:
1115:
1112:
1110:
1107:
1105:
1102:
1100:
1097:
1096:
1094:
1090:
1087:
1085:
1084:Foramen cecum
1082:
1080:
1077:
1075:
1074:Median sulcus
1072:
1070:
1067:
1066:
1064:
1063:
1061:
1059:
1055:
1049:
1048:
1047:tooth anatomy
1043:
1042:
1040:
1038:
1034:
1028:
1025:
1021:
1018:
1017:
1016:
1013:
1009:
1006:
1005:
1004:
1001:
997:
994:
993:
992:
991:Parotid gland
989:
988:
986:
984:
980:
972:
969:
967:
964:
962:
959:
957:
954:
953:
952:
949:
947:
944:
942:
939:
937:
934:
932:
929:
927:
924:
922:
919:
917:
914:
912:
909:
908:
906:
904:
900:
894:
891:
889:
886:
884:
881:
879:
876:
875:
873:
871:
867:
861:
858:
857:
855:
853:
849:
843:
840:
838:
835:
833:
830:
828:
825:
823:
820:
818:
815:
814:
812:
810:
806:
802:
794:
789:
787:
782:
780:
775:
774:
771:
760:
756:
752:
748:
744:
740:
737:(4): 658–60.
736:
732:
725:
722:
717:
713:
709:
705:
701:
697:
693:
689:
682:
679:
674:
670:
666:
662:
658:
654:
651:(6): 645–52.
650:
646:
639:
636:
631:
627:
623:
619:
615:
611:
604:
601:
596:
592:
588:
584:
580:
576:
569:
566:
561:
557:
553:
549:
545:
541:
537:
533:
526:
523:
518:
514:
510:
506:
502:
498:
491:
488:
483:
479:
475:
471:
467:
463:
459:
455:
448:
445:
440:
436:
431:
426:
422:
418:
414:
407:
405:
401:
396:
392:
388:
384:
380:
376:
372:
368:
361:
358:
353:
349:
345:
341:
337:
333:
329:
325:
318:
316:
312:
307:
303:
299:
295:
291:
287:
280:
278:
276:
274:
272:
268:
261:
259:
257:
253:
251:
245:
243:
236:Clinical uses
235:
230:
226:
223:
220:
213:
207:
203:
201:
197:
193:
189:
184:
182:
173:
171:
169:
165:
161:
157:
153:
149:
145:
141:
137:
136:Xavier Bichat
133:
130:(also called
129:
117:
111:
107:
104:
101:
99:
95:
92:
89:
87:
83:
80:
77:
75:
71:
68:
65:
63:
59:
54:
49:
42:
37:
30:
25:
20:
1044:
951:Periodontium
859:
734:
730:
724:
691:
687:
681:
648:
644:
638:
616:(4): 241–4.
613:
609:
603:
578:
574:
568:
535:
531:
525:
500:
496:
490:
457:
453:
447:
420:
416:
370:
366:
360:
327:
323:
289:
285:
254:
250:cleft palate
246:
239:
224:
221:
217:
188:parotid duct
185:
177:
164:buccal space
139:
131:
127:
125:
79:A05.1.01.015
66:
883:Soft palate
878:Hard palate
822:Cupid's bow
423:(1): 9–19.
56:Identifiers
1187:Categories
1137:Oropharynx
1095:Underside
842:White roll
262:References
158:, and the
138:, and the
1069:Taste bud
946:Stippling
181:ligaments
1099:Frenulum
961:Philtrum
956:Cementum
837:Philtrum
759:23030715
751:16077311
716:46125308
708:19319069
673:19589645
665:19461278
595:15509944
560:34619538
552:16874222
517:18971739
474:19319074
439:18209117
395:30007446
387:18349664
352:11443581
344:17519724
306:12045584
242:facelift
214:Function
152:masseter
134:, after
966:Gingiva
482:7960691
51:Details
1142:fauces
1058:Tongue
983:Glands
870:Palate
757:
749:
714:
706:
671:
663:
630:338848
628:
593:
558:
550:
515:
480:
472:
437:
393:
385:
350:
342:
304:
154:, the
1152:Uvula
1037:Teeth
852:Cheek
801:mouth
755:S2CID
712:S2CID
669:S2CID
556:S2CID
478:S2CID
391:S2CID
348:S2CID
114:[
103:59799
62:Latin
1065:Top
1045:see
1020:duct
1008:duct
996:duct
903:Gums
747:PMID
704:PMID
661:PMID
626:PMID
591:PMID
548:PMID
513:PMID
470:PMID
435:PMID
383:PMID
340:PMID
302:PMID
126:The
91:2141
74:TA98
809:Lip
739:doi
696:doi
692:123
653:doi
618:doi
583:doi
579:114
540:doi
536:118
505:doi
501:122
462:doi
458:123
425:doi
375:doi
371:121
332:doi
328:119
294:doi
290:109
144:fat
98:FMA
86:TA2
1189::
753:.
745:.
735:16
733:.
710:.
702:.
690:.
667:.
659:.
649:62
647:.
624:.
612:.
589:.
577:.
554:.
546:.
534:.
511:.
499:.
476:.
468:.
456:.
433:.
421:10
419:.
415:.
403:^
389:.
381:.
369:.
346:.
338:.
326:.
314:^
300:.
288:.
270:^
252:.
244:.
202:.
792:e
785:t
778:v
761:.
741::
718:.
698::
675:.
655::
632:.
620::
614:5
597:.
585::
562:.
542::
519:.
507::
484:.
464::
441:.
427::
397:.
377::
354:.
334::
308:.
296::
118:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.