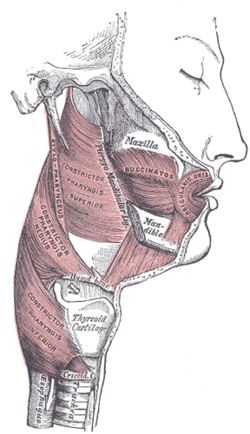
283:, although other sources report it is the submandibular space. Infections originating in either maxillary or mandibular teeth can spread into the buccal space, usually maxillary molars (most commonly) and premolars or mandibular premolars. Odontogenic infections which erode through the buccal cortical plate of the mandible or maxilla will either spread into the buccal vestibule (sulcus) and drain intra-orally, or into the buccal space, depending upon the level of the perforation in relation to the attachment of buccinator to the maxilla above and the mandible below (see diagrams). Frequently infection spreads in both directions as the buccinator is only a partial barrier. Infections associated with mandibular teeth with apices at a level inferior to the attachment, and maxillary teeth with apices at a level superior to the attachment are more likely to drain into the buccal space.
272:
219:
203:
238:
surgery. Buccal space abscesses typically cause a facial swelling over the cheek that may extend from the zygomatic arch above to the inferior border of the mandible below, and from the anterior border the masseter muscle posteriorly to the angle of the mouth anteriorly. Unless another space is also
26:
247:
to avoid damage to the duct, and forceps are used to divide buccinator and insert a surgical drain into the buccal space. The drain is kept in place for a variable period of time following the procedure.
275:
An abscess originating from a tooth which has spread to involve the buccal space. Above, deformation of the cheek on the second day. Below, deformation on the third day.
255:
at the inferior of the space, near the inferior border of the mandible and the angle of the mouth. An untreated cutaneous sinus can cause disfiguring soft tissue
849:
432:
62:
371:
343:
252:
788:
399:
206:
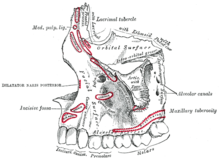
Diagram showing the origin of the upper part of the buccinator muscle to the maxilla (the middle part originates from the
844:
834:
116:
425:
211:
473:
745:
148:
243:, and the incision is located inside the mouth to avoid a scar on the face. The incision are placed below the
668:
222:
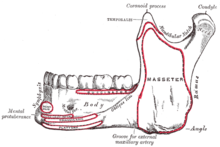
Diagram showing the origin of the lower part of the buccinator muscle on the lateral surface of the mandible
207:
136:
755:
688:
418:
36:
803:
783:
661:
587:
577:
572:
468:
240:
750:
644:
582:
552:
144:
140:
86:
798:
740:
649:
335:
612:
395:
367:
339:
78:
656:
534:
458:
327:
125:
the platysma muscle, subcutaneous tissue and skin laterally (the space is deep to platysma).
813:
808:
730:
567:
562:
557:
244:
82:
70:
279:
Sometimes the buccal space is reported to be the most commonly involved fascial space by
239:
involved, the tissues around the eye are not swollen. It is usually treated by surgical
839:
760:
624:
529:
501:
463:
280:
177:
828:
632:
328:
637:
592:
235:
184:
155:
122:
the buccinator muscle medially (the buccal space is superficial to the buccinator),
678:
524:
519:
442:
778:
483:
260:
231:
710:
271:
112:
the zygomatic process of the maxilla and the zygomaticus muscles superiorly,
602:
597:
478:
256:
227:
42:
607:
410:
725:
720:
715:
699:
511:
77:, and is paired on each side. The buccal space is superficial to the
66:
218:
202:
25:
793:
493:
270:
217:
201:
74:
251:
Long standing buccal abscesses tend to spontaneously drain via a
119:
and the attachment of the deep fascia to the mandible inferiorly,
544:
414:
450:
30:
The buccal space is located superficial to buccinator muscle.
334:(5th ed.). St. Louis, Mo.: Mosby Elsevier. pp.
394:. Edinburgh : Churchill Livingstone. pp. 263–267.
366:. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 374–375.
771:
698:
677:
623:
543:
510:
492:
449:
18:
357:
355:
85:and the skin. The buccal space is part of the
426:
390:Wray D, Stenhouse D, Lee D, Clark AJ (2003).
89:space, which is continuous from head to toe.
8:
321:
319:
317:
315:
385:
383:
330:Contemporary oral and maxillofacial surgery
313:
311:
309:
307:
305:
303:
301:
299:
297:
295:
433:
419:
411:
24:
230:may create the buccal space, e.g. due to
102:The boundaries of each buccal space are:
69:tissue spaces or tissue spaces). It is a
291:
193:the transverse facial artery and vein.
40:
15:
7:
392:Textbook of general and oral surgery
326:Hupp JR, Ellis E, Tucker MR (2008).
190:the anterior facial artery and vein,
106:the angle of the mouth anteriorly,
63:fascial space of the head and neck
14:
109:the masseter muscle posteriorly,
789:Plica semilunaris of the fauces
362:Kerawala C, Newlands C (2010).
172:In health, the space contains:
850:Oral and maxillofacial surgery
364:Oral and maxillofacial surgery
1:
210:, where buccinator joins the
117:depressor anguli oris muscle
259:, and the tract can become
212:superior constrictor muscle
156:infraorbital (canine) space
866:
474:Labial commissure of mouth
35:
23:
149:lateral pharyngeal space
669:Tubarial salivary gland
208:pterygomandibular raphe
137:pterygomandibular space
65:(sometimes also termed
756:Glossoepiglottic folds
276:
267:Odontogenic infections
223:
215:
37:Anatomical terminology
804:Palatopharyngeal arch
578:Mucogingival junction
573:Junctional epithelium
469:Frenulum of lower lip
274:
241:incision and drainage
221:
205:
198:Clinical significance
613:Periodontal ligament
845:Otorhinolaryngology
835:Human head and neck
751:Sublingual caruncle
645:Submandibular gland
583:Sulcular epithelium
553:Interdental papilla
145:submasseteric space
141:infratemporal space
799:Palatoglossal arch
277:
224:
216:
183:the parotid duct (
822:
821:
79:buccinator muscle
57:(also termed the
51:
50:
46:
857:
657:Sublingual gland
535:Incisive papilla
459:Vermilion border
435:
428:
421:
412:
406:
405:
387:
378:
377:
359:
350:
349:
333:
323:
281:dental abscesses
81:and deep to the
59:buccinator space
43:edit on Wikidata
28:
16:
865:
864:
860:
859:
858:
856:
855:
854:
825:
824:
823:
818:
814:Palatine tonsil
809:Tonsillar fossa
767:
746:Fimbriated fold
731:Lingual tonsils
721:Terminal sulcus
694:
673:
619:
568:Gingival fibers
563:Gingival margin
558:Gingival sulcus
539:
506:
488:
445:
441:Anatomy of the
439:
409:
402:
389:
388:
381:
374:
361:
360:
353:
346:
325:
324:
293:
289:
269:
253:cutaneous sinus
245:parotid papilla
200:
170:
165:
147:or even to the
132:
100:
95:
83:platysma muscle
71:potential space
47:
31:
12:
11:
5:
863:
861:
853:
852:
847:
842:
837:
827:
826:
820:
819:
817:
816:
811:
806:
801:
796:
791:
786:
781:
775:
773:
769:
768:
766:
765:
764:
763:
761:Lingual septum
758:
753:
748:
743:
735:
734:
733:
728:
723:
718:
713:
704:
702:
696:
695:
693:
692:
683:
681:
675:
674:
672:
671:
666:
665:
664:
654:
653:
652:
642:
641:
640:
629:
627:
621:
620:
618:
617:
616:
615:
610:
605:
600:
590:
585:
580:
575:
570:
565:
560:
555:
549:
547:
541:
540:
538:
537:
532:
530:Palatine raphe
527:
522:
516:
514:
508:
507:
505:
504:
502:Buccal fat pad
498:
496:
490:
489:
487:
486:
481:
476:
471:
466:
461:
455:
453:
447:
446:
440:
438:
437:
430:
423:
415:
408:
407:
400:
379:
372:
351:
344:
290:
288:
285:
268:
265:
199:
196:
195:
194:
191:
188:
181:
178:buccal fat pad
169:
166:
164:
161:
160:
159:
152:
131:
130:Communications
128:
127:
126:
123:
120:
113:
110:
107:
99:
96:
94:
91:
49:
48:
39:
33:
32:
29:
21:
20:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
862:
851:
848:
846:
843:
841:
838:
836:
833:
832:
830:
815:
812:
810:
807:
805:
802:
800:
797:
795:
792:
790:
787:
785:
782:
780:
777:
776:
774:
772:Back of mouth
770:
762:
759:
757:
754:
752:
749:
747:
744:
742:
739:
738:
736:
732:
729:
727:
726:Foramen cecum
724:
722:
719:
717:
716:Median sulcus
714:
712:
709:
708:
706:
705:
703:
701:
697:
691:
690:
689:tooth anatomy
685:
684:
682:
680:
676:
670:
667:
663:
660:
659:
658:
655:
651:
648:
647:
646:
643:
639:
636:
635:
634:
633:Parotid gland
631:
630:
628:
626:
622:
614:
611:
609:
606:
604:
601:
599:
596:
595:
594:
591:
589:
586:
584:
581:
579:
576:
574:
571:
569:
566:
564:
561:
559:
556:
554:
551:
550:
548:
546:
542:
536:
533:
531:
528:
526:
523:
521:
518:
517:
515:
513:
509:
503:
500:
499:
497:
495:
491:
485:
482:
480:
477:
475:
472:
470:
467:
465:
462:
460:
457:
456:
454:
452:
448:
444:
436:
431:
429:
424:
422:
417:
416:
413:
403:
397:
393:
386:
384:
380:
375:
373:9780199204830
369:
365:
358:
356:
352:
347:
345:9780323049030
341:
337:
332:
331:
322:
320:
318:
316:
314:
312:
310:
308:
306:
304:
302:
300:
298:
296:
292:
286:
284:
282:
273:
266:
264:
262:
258:
254:
249:
246:
242:
237:
233:
229:
220:
213:
209:
204:
197:
192:
189:
186:
182:
179:
175:
174:
173:
167:
162:
157:
153:
150:
146:
142:
138:
134:
133:
129:
124:
121:
118:
114:
111:
108:
105:
104:
103:
97:
92:
90:
88:
84:
80:
76:
72:
68:
64:
60:
56:
44:
38:
34:
27:
22:
17:
686:
593:Periodontium
391:
363:
329:
278:
250:
236:wisdom teeth
225:
185:Stensen duct
171:
151:posteriorly,
101:
87:subcutaneous
58:
55:buccal space
54:
52:
19:Buccal space
525:Soft palate
520:Hard palate
464:Cupid's bow
158:superiorly.
829:Categories
779:Oropharynx
737:Underside
484:White roll
401:0443070830
287:References
261:epithelial
234:following
232:hemorrhage
98:Boundaries
711:Taste bud
588:Stippling
93:Structure
741:Frenulum
603:Philtrum
598:Cementum
479:Philtrum
257:fibrosis
228:hematoma
168:Contents
163:Function
608:Gingiva
263:lined.
154:to the
135:to the
73:in the
67:fascial
61:) is a
784:fauces
700:Tongue
625:Glands
512:Palate
398:
370:
342:
338:–333.
840:Mouth
794:Uvula
679:Teeth
494:Cheek
443:mouth
75:cheek
41:[
707:Top
687:see
662:duct
650:duct
638:duct
545:Gums
396:ISBN
368:ISBN
340:ISBN
176:the
115:the
53:The
451:Lip
336:317
143:,
831::
382:^
354:^
294:^
226:A
187:),
139:,
434:e
427:t
420:v
404:.
376:.
348:.
214:)
180:,
45:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.