871:. The BCPNN approach uses biologically plausible learning and structural plasticity for unsupervised generation of a sparse hidden representation, followed by a one-layer classifier that associates this representation to the output layer. It achieves a classification performance on the full MNIST test set around 98%, comparable to other methods based on unsupervised representation learning. The performance is notably slightly lower than that of the best methods that employ end-to-end error back-propagation. However, the extreme performance comes with a cost of lower biological plausibility and higher complexity of the learning machinery. The BCPNN method is also quite well suited for semi-supervised learning.
347:
38:, which regards neural computation and processing as probabilistic inference. Neural unit activations represent probability ("confidence") in the presence of input features or categories, synaptic weights are based on estimated correlations and the spread of activation corresponds to calculating posterior probabilities. It was originally proposed by Anders Lansner and Örjan Ekeberg at
883:-like modular architecture and massively parallel correlation based Hebbian learning makes it quite hardware friendly. Implementation with reduced number of bits in synaptic state variables have been shown to be feasible. BCPNN has further been the target for parallel simulators on cluster computers and GPU:s. It was recently implemented on the
161:
as in naïve Bayes formalism. BCPNN represents a straight-forward way of deriving a neural network from Bayes rule. In order to allow the use the standard equation for propagating activity between neurons, transformation to log space was necessary. The basic equations for postsynaptic unit intrinsic excitability
160:
The BCPNN learning rule was derived from Bayes rule and is
Hebbian such that neural units with activity correlated over time get excitatory connections between them whereas anti-correlation generates inhibition and lack of correlation gives zero connections. The independence assumptions are the same
844:
model and simulated with abstract non-spiking as well as spiking neural units. This made it possible to demonstrate online learning of temporal sequences as well as one-shot encoding and immediate recall in human word list learning. These findings further lead to the proposal and investigation of a
832:
These cortical models have mainly been used to provide a better understanding of the mechanisms underlying cortical dynamics and oscillatory structure associated with different activity states. Cortical oscillations in the range from theta, over alpha and beta to gamma are generated by this model.
760:
necessary to allow delayed reward to affect synaptic parameters. E traces are subsequently filtered into the P traces that finally determine the values of bias and weight values. This summarizes many complex protein and non-protein dependent synaptic processes behind
765:, exhibiting highly variable timescales, from several seconds up to potentially days or months. The parameter κ ∈ regulates the degree of plasticity or learning rate and is supposed to represent the release and action of some endogenous neuromodulator, e.g.,
833:
The embedded memories can be recalled from partial input and when activated they show signs of fixpoint attractor dynamics, though neural adaptation and synaptic depression terminates activity within some hundred milliseconds. Notably, a few cycles of
76:, for example for discovery of adverse drug reactions. The BCPNN learning rule has also been used to model biological synaptic plasticity and intrinsic excitability in large-scale spiking neural network (
828:
representing earlier encoded memories. Neuron and synapse properties have been tuned to represent their real counterparts in terms of e.g. spike frequency adaptation and fast non-Hebbian synaptic plasticity.
112:
is typically represented by some 30 pyramidal cells and one double bouquet cell. The latter turns the negative BCPNN-weights formed between neurons with anti-correlated activity into di-synaptic inhibition.
342:
1976:
Farahini N, Hemani A, Lansner A, Clermidy F, Svensson C (January 2014). "A scalable custom simulation machine for the
Bayesian Confidence Propagation Neural Network model of the brain".
50:
264:
837:
are generated during such a brief memory recall. Cognitive phenomena like attentional blink and its modulation by benzodiazepine has also been replicated in this model.
186:
699:
570:
216:
42:
Royal
Institute of Technology. This probabilistic neural network model can also be run in generative mode to produce spontaneous activations and temporal sequences.
662:
631:
601:
413:
378:
1178:
Lundqvist M, Herman P, Lansner A (October 2011). "Theta and gamma power increases and alpha/beta power decreases with memory load in an attractor network model".
750:
730:
550:
529:
496:
474:
449:
2017:
Lansner A, Hemani A, Farahini N (January 2014). "Spiking brain models: Computation, memory and communication constraints for custom hardware implementation".
148:, partitioned into some hundred areas. In addition to sparse activity, a large-scale BCPNN would also have very sparse connectivity, given that the real
427:
corresponds to a single stage in the exponentially weighted moving average (EWMA) estimate of the terms used in the incremental
Bayesian weight update.
1853:
Ravichandran NB, Lansner A, Herman P (May 2020). "Brain-like approaches to unsupervised learning of hidden representations--a comparative study".
65:(losing the strict interpretation of their activations as probabilities) but becoming a possible abstract model of biological neural networks and
2034:
1993:
1251:
49:
comprising neural units with continuous activation, having a bias representing prior, and being connected by
Bayesian weights in the form of
2182:
867:
BCPNN has recently been successfully applied to
Machine Learning classification benchmarks, most notably the hand written digits of the
864:
The point-wise mutual information weights of BCPNN is since long one of the standard methods for detection of drug adverse reactions.
39:
2060:"eBrainII: a 3 kW Realtime Custom 3D DRAM Integrated ASIC Implementation of a Biologically Plausible Model of a Human Scale Cortex"
1051:
Fransén E, Lansner A (January 1998). "A model of cortical associative memory based on a horizontal network of connected columns".
804:
and a population of basket cells that mediate local feedback inhibition. A modelled network is composed of about ten or more such
66:
1298:
Orre R, Lansner A, Bate A, Lindquist M (2000). "Bayesian neural networks with confidence estimations applied to data mining".
887:
compute platform as well as in a series of dedicated neuromorphic VLSI designs. From these it has been estimated that a human
1224:
Ravichandran NB, Lansner A, Herman P (2020). "Learning representations in
Bayesian Confidence Propagation neural networks".
1804:"Functional Relevance of Different Basal Ganglia Pathways Investigated in a Spiking Model with Reward Dependent Plasticity"
1434:"Action selection performance of a reconfigurable basal ganglia inspired model with Hebbian-Bayesian Go-NoGo connectivity"
773:
853:
1019:
Lansner A (June 1991). "A recurrent bayesian ANN capable of extracting prototypes from unlabeled and noisy examples.".
121:
1021:
Artificial Neural
Networks. Proceedings of the 1991 International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks (ICANN-91)
976:
Sandberg A, Lansner A, Petersson KM, Ekeberg O (May 2002). "A Bayesian attractor network with incremental learning".
891:
sized BCPNN with continuous learning could be executed in real time with a power dissipation on the order of few kW.
104:
serve as the smallest units and they typically feature a membrane time constant and adaptation. In spiking models of
603:
are estimated from the training set, which can be done e.g. by exponentially weighted moving averages (see Figure).
270:
46:
62:
31:
908:
Lansner A, Ekeberg Ö (1989). "A one-layer feedback artificial neural network with a
Bayesian learning rule".
769:
activating D1R-like receptors, triggered by some unexpected emotionally salient situation, and resulting in
17:
223:
753:
665:
77:
1094:
Lansner A, Fransen E (January 1992). "Modelling
Hebbian cell assemblies comprised of cortical neurons".
1131:"Associative memory models: from the cell-assembly theory to biophysically detailed cortex simulations"
788:
inspired modular architecture of BCPNN has been the basis for several spiking neural network models of
136:
is on the order of a hundred, which makes the activity sparse, at the level of 1% or less, given that
2081:
1756:
1646:
96:. This modular structure is inspired by and generalized from the modular structure of the mammalian
813:
809:
801:
793:
129:
109:
101:
93:
54:
2107:
2071:
2040:
1999:
1854:
1561:
1269:
1257:
1229:
1203:
1160:
1001:
164:
2158:
2099:
2030:
1989:
1958:
1907:
1835:
1784:
1725:
1674:
1635:"Bistable, irregular firing and population oscillations in a modular attractor memory network"
1615:
1553:
1514:
1465:
1411:
1359:
1247:
1195:
1152:
1111:
1076:
1068:
993:
955:
346:
35:
2058:
Stathis D, Sudarshan C, Yang Y, Jung M, Weis C, Hemani A, Lansner A, Wehn N (November 2020).
671:
555:
2148:
2138:
2089:
2022:
1981:
1948:
1938:
1897:
1887:
1825:
1815:
1774:
1764:
1715:
1705:
1664:
1654:
1605:
1595:
1545:
1504:
1496:
1455:
1445:
1401:
1393:
1349:
1341:
1307:
1239:
1187:
1142:
1103:
1060:
985:
947:
938:
Lansner A, Holst A (May 1996). "A higher order Bayesian neural network with spiking units".
917:
757:
191:
856:
in a Go-NoGo connected non-spiking and spiking neural network models of the Basal ganglia.
640:
609:
606:
There has been proposals for a biological interpretation of the BCPNN learning rule.
579:
423:
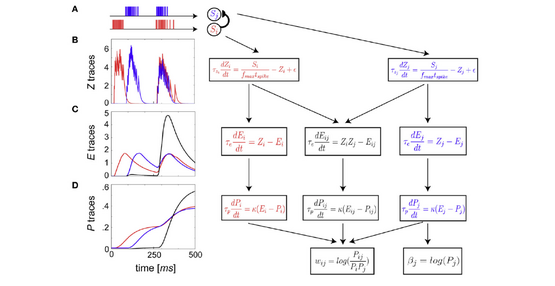
neuron spike trains are presented as arbitrary example input patterns. Each subsequent row
391:
356:
61:, representing discrete coded features or attributes. The units can also be connected as a
1533:
1281:
1035:
888:
880:
841:
821:
817:
805:
797:
789:
785:
770:
149:
145:
137:
133:
125:
117:
105:
97:
58:
2085:
1874:
Vogginger B, Schüffny R, Lansner A, Cederström L, Partzsch J, Höppner S (January 2015).
1760:
1650:
2153:
2126:
1953:
1926:
1902:
1875:
1830:
1803:
1779:
1744:
1720:
1693:
1669:
1634:
1610:
1583:
1509:
1484:
1460:
1433:
1406:
1381:
1354:
1329:
868:
846:
825:
735:
715:
535:
514:
481:
459:
434:
1311:
2176:
2111:
1261:
1005:
762:
706:
634:
2044:
2003:
1565:
1534:"A modular attractor associative memory with patchy connectivity and weight pruning"
1243:
1164:
351:
Schematic flow of BCPNN update equations reformulated as spike-based plasticity. (A)
1485:"Introducing double bouquet cells into a modular cortical associative memory model"
1345:
1207:
89:
1769:
1659:
1549:
2026:
1985:
1397:
73:
2094:
2059:
1500:
1147:
1130:
824:
is sparse and excitatory and is typically set up to form number of distributed
1107:
1064:
951:
921:
834:
80:) models of cortical associative memory and reward learning in Basal ganglia.
2143:
2103:
1943:
1927:"Large-Scale Simulations of Plastic Neural Networks on Neuromorphic Hardware"
1892:
1820:
1802:
Berthet P, Lindahl M, Tully PJ, Hellgren-Kotaleski J, Lansner A (July 2016).
1710:
1600:
1450:
1115:
1072:
989:
884:
141:
2162:
1962:
1911:
1839:
1788:
1729:
1678:
1619:
1584:"Synaptic and nonsynaptic plasticity approximating probabilistic inference"
1557:
1518:
1469:
1415:
1363:
1199:
1156:
1037:
INVESTIGATIONS INTO THE PATIERN PROCESSING CAPABILITIES OF ASSOCIATIVE NETS
997:
1080:
959:
1330:"A Spiking Working Memory Model Based on Hebbian Short-Term Potentiation"
1191:
766:
1382:"An Indexing Theory for Working Memory Based on Fast Hebbian Plasticity"
2019:
2014 19th Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASP-DAC)
1978:
2014 19th Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASP-DAC)
1743:
Tully PJ, Lindén H, Hennig MH, Lansner A (May 2016). Morrison A (ed.).
709:
channel phosphorylation, and eventually enhanced synaptic conductance.
499:
traces at slower time scale. Co-activity now enters in a mutual trace
792:
aimed at studying its associative memory functions. In these models,
702:
840:
In recent years, Hebbian plasticity has been incorporated into this
2076:
1925:
Knight JC, Tully PJ, Kaplan BA, Lansner A, Furber SB (April 2016).
1876:"Reducing the computational footprint for real-time BCPNN learning"
1859:
1234:
53:. The original network has been extended to a modular structure of
2125:
Yang Y, Stathis D, Jordão R, Hemani A, Lansner A (August 2020).
1633:
Lundqvist M, Compte A, Lansner A (June 2010). Morrison A (ed.).
152:
is sparsely connected at the level of 0.01 - 0.001% on average.
1226:
2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN)
668:
reaching the synapse. The conjunction of these events lead to
1745:"Spike-Based Bayesian-Hebbian Learning of Temporal Sequences"
1694:"Is attentional blink a byproduct of neocortical attractors?"
140:
can also be silent. A BCPNN network with a size of the human
852:
A similar approach was applied to model reward learning and
572:
represent a "print-now" signal that modulates learning rate.
552:
traces that have the slowest plasticity and longest memory.
72:
BCPNN has been used for machine learning classification and
477:
traces compute a low pass filtered representation of the
188:
and synaptic weight between pre- and postsynaptic units,
820:
via model basket cells. Long-range connectivity between
1483:
Chrysanthidis N, Fiebig F, Lansner A (December 2019).
88:
The BCPNN network architecture is modular in terms of
28:
Bayesian Confidence Propagation Neural Network (BCPNN)
738:
718:
674:
643:
612:
582:
576:
where the activation and co-activation probabilities
558:
538:
517:
484:
462:
437:
394:
359:
273:
226:
194:
167:
1219:
1217:
1432:Berthet P, Hellgren-Kotaleski J, Lansner A (2012).
2127:"Optimizing BCPNN Learning Rule for Memory Access"
744:
724:
693:
656:
625:
595:
564:
544:
523:
490:
468:
443:
407:
372:
336:
258:
210:
180:
1427:
1425:
971:
969:
1375:
1373:
1323:
1321:
933:
931:
796:comprise about 30 model pyramidal cells and a
1582:Tully PJ, Hennig MH, Lansner A (April 2014).
1577:
1575:
337:{\displaystyle w_{ij}=\log P_{ij}/P_{i}P_{j}}
8:
1380:Fiebig F, Herman P, Lansner A (March 2020).
1300:Computational Statistics & Data Analysis
1293:
1291:
849:based on fast Hebbian synaptic plasticity.
732:traces are further filtered into the
452:traces low pass filter input spike trains.
1023:. Vol. 1–2. Espoo, Finland: Elsevier.
2152:
2142:
2093:
2075:
1952:
1942:
1901:
1891:
1858:
1829:
1819:
1778:
1768:
1719:
1709:
1668:
1658:
1609:
1599:
1508:
1459:
1449:
1405:
1353:
1233:
1146:
752:traces, which serve as temporal buffers,
737:
717:
682:
673:
648:
642:
617:
611:
587:
581:
557:
537:
516:
483:
461:
436:
399:
393:
364:
358:
328:
318:
309:
300:
278:
272:
250:
231:
225:
199:
193:
172:
166:
812:and support feedback inhibition between
345:
1698:Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience
940:International Journal of Neural Systems
910:International Journal of Neural Systems
900:
1538:Network: Computation in Neural Systems
1277:
1267:
1096:Network: Computation in Neural Systems
1053:Network: Computation in Neural Systems
633:may represent binding of glutamate to
2021:. Singapore: IEEE. pp. 556–562.
1980:. Singapore: IEEE. pp. 578–585.
1489:Journal of Computational Neuroscience
780:Models of brain systems and functions
259:{\displaystyle \beta _{j}=\log P_{j}}
7:
2064:Journal of Signal Processing Systems
1438:Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience
1328:Fiebig F, Lansner A (January 2017).
1040:. KTH Royal Institute of Technology.
808:. Connectivity is excitatory within
1532:Meli C, Lansner A (December 2013).
1692:Silverstein DN, Lansner A (2011).
1588:Frontiers in Synaptic Neuroscience
14:
1180:Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience
666:back-propagating action potential
879:The structure of BCPNN with its
1244:10.1109/IJCNN48605.2020.9207061
144:would have a couple of million
1346:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1989-16.2016
156:Bayesian-Hebbian learning rule
116:Lateral inhibition within the
1:
1312:10.1016/S0167-9473(99)00114-0
860:Machine learning applications
774:activity dependent plasticity
51:point-wise mutual information
18:Bayesian Neural Network (BNN)
1808:Frontiers in Neural Circuits
1770:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004954
1660:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000803
1550:10.3109/0954898X.2013.859323
2027:10.1109/ASPDAC.2014.6742950
1986:10.1109/ASPDAC.2014.6742953
1398:10.1523/ENEURO.0374-19.2020
1334:The Journal of Neuroscience
800:comprises ten or more such
2199:
2183:Artificial neural networks
2095:10.1007/s11265-020-01562-x
1749:PLOS Computational Biology
1639:PLOS Computational Biology
1501:10.1007/s10827-019-00729-1
1392:(2): ENEURO.0374–19.2020.
1148:10.1016/j.tins.2008.12.002
875:Hardware designs for BCPNN
701:influx via NMDA channels,
181:{\displaystyle \beta _{j}}
100:. In abstract models, the
47:feedforward neural network
15:
2131:Frontiers in Neuroscience
1931:Frontiers in Neuroanatomy
1880:Frontiers in Neuroscience
1108:10.1088/0954-898x_3_2_002
1065:10.1088/0954-898x_9_2_006
952:10.1142/S0129065796000816
922:10.1142/S0129065789000499
32:artificial neural network
23:Artificial neural network
2144:10.3389/fnins.2020.00878
1944:10.3389/fnana.2016.00037
1893:10.3389/fnins.2015.00002
1821:10.3389/fncir.2016.00053
1711:10.3389/fncom.2011.00013
1601:10.3389/fnsyn.2014.00008
1451:10.3389/fnbeh.2012.00065
1129:Lansner A (March 2009).
1034:Lansner, Anders (1986).
990:10.1080/net.13.2.179.194
124:module. Looking at real
63:recurrent neural network
16:Not to be confused with
1135:Trends in Neurosciences
694:{\displaystyle Ca^{2+}}
565:{\displaystyle \kappa }
1228:. IEEE. pp. 1–7.
746:
726:
695:
658:
627:
597:
573:
566:
546:
525:
492:
470:
445:
409:
374:
338:
260:
212:
211:{\displaystyle w_{ij}}
182:
747:
727:
696:
659:
657:{\displaystyle Z_{j}}
628:
626:{\displaystyle Z_{i}}
598:
596:{\displaystyle P_{*}}
567:
547:
526:
493:
471:
446:
410:
408:{\displaystyle S_{j}}
375:
373:{\displaystyle S_{i}}
349:
339:
261:
213:
183:
45:The basic model is a
1192:10.1162/jocn_a_00029
736:
716:
672:
641:
610:
580:
556:
536:
515:
482:
460:
435:
392:
357:
271:
224:
192:
165:
84:Network architecture
2086:2020JSPSy..92.1323S
1761:2016PLSCB..12E4954T
1651:2010PLSCB...6E0803L
854:behavior selection
835:gamma oscillations
754:eligibility traces
742:
722:
691:
664:could represent a
654:
623:
593:
574:
562:
542:
521:
488:
466:
441:
405:
370:
334:
256:
208:
178:
67:associative memory
2070:(11): 1323–1343.
2036:978-1-4799-2816-3
1995:978-1-4799-2816-3
1253:978-1-7281-6926-2
745:{\displaystyle E}
725:{\displaystyle Z}
545:{\displaystyle P}
532:traces feed into
524:{\displaystyle E}
491:{\displaystyle Z}
469:{\displaystyle E}
444:{\displaystyle Z}
2190:
2167:
2166:
2156:
2146:
2122:
2116:
2115:
2097:
2079:
2055:
2049:
2048:
2014:
2008:
2007:
1973:
1967:
1966:
1956:
1946:
1922:
1916:
1915:
1905:
1895:
1871:
1865:
1864:
1862:
1850:
1844:
1843:
1833:
1823:
1799:
1793:
1792:
1782:
1772:
1740:
1734:
1733:
1723:
1713:
1689:
1683:
1682:
1672:
1662:
1630:
1624:
1623:
1613:
1603:
1579:
1570:
1569:
1529:
1523:
1522:
1512:
1495:(2–3): 223–230.
1480:
1474:
1473:
1463:
1453:
1429:
1420:
1419:
1409:
1377:
1368:
1367:
1357:
1325:
1316:
1315:
1295:
1286:
1285:
1279:
1275:
1273:
1265:
1237:
1221:
1212:
1211:
1175:
1169:
1168:
1150:
1126:
1120:
1119:
1091:
1085:
1084:
1048:
1042:
1041:
1031:
1025:
1024:
1016:
1010:
1009:
973:
964:
963:
935:
926:
925:
905:
845:novel theory of
751:
749:
748:
743:
731:
729:
728:
723:
700:
698:
697:
692:
690:
689:
663:
661:
660:
655:
653:
652:
632:
630:
629:
624:
622:
621:
602:
600:
599:
594:
592:
591:
571:
569:
568:
563:
551:
549:
548:
543:
530:
528:
527:
522:
497:
495:
494:
489:
475:
473:
472:
467:
450:
448:
447:
442:
414:
412:
411:
406:
404:
403:
379:
377:
376:
371:
369:
368:
343:
341:
340:
335:
333:
332:
323:
322:
313:
308:
307:
286:
285:
265:
263:
262:
257:
255:
254:
236:
235:
217:
215:
214:
209:
207:
206:
187:
185:
184:
179:
177:
176:
128:, the number of
120:makes it a soft
2198:
2197:
2193:
2192:
2191:
2189:
2188:
2187:
2173:
2172:
2171:
2170:
2124:
2123:
2119:
2057:
2056:
2052:
2037:
2016:
2015:
2011:
1996:
1975:
1974:
1970:
1924:
1923:
1919:
1873:
1872:
1868:
1852:
1851:
1847:
1801:
1800:
1796:
1755:(5): e1004954.
1742:
1741:
1737:
1691:
1690:
1686:
1645:(6): e1000803.
1632:
1631:
1627:
1581:
1580:
1573:
1531:
1530:
1526:
1482:
1481:
1477:
1431:
1430:
1423:
1379:
1378:
1371:
1327:
1326:
1319:
1297:
1296:
1289:
1276:
1266:
1254:
1223:
1222:
1215:
1186:(10): 3008–20.
1177:
1176:
1172:
1128:
1127:
1123:
1093:
1092:
1088:
1050:
1049:
1045:
1033:
1032:
1028:
1018:
1017:
1013:
975:
974:
967:
937:
936:
929:
907:
906:
902:
897:
877:
862:
826:cell assemblies
782:
734:
733:
714:
713:
678:
670:
669:
644:
639:
638:
613:
608:
607:
583:
578:
577:
554:
553:
534:
533:
513:
512:
480:
479:
458:
457:
433:
432:
395:
390:
389:
360:
355:
354:
324:
314:
296:
274:
269:
268:
246:
227:
222:
221:
195:
190:
189:
168:
163:
162:
158:
122:winner-take-all
86:
24:
21:
12:
11:
5:
2196:
2194:
2186:
2185:
2175:
2174:
2169:
2168:
2117:
2050:
2035:
2009:
1994:
1968:
1917:
1866:
1845:
1794:
1735:
1684:
1625:
1571:
1524:
1475:
1421:
1369:
1317:
1306:(4): 473–493.
1287:
1278:|journal=
1252:
1213:
1170:
1121:
1102:(2): 105–119.
1086:
1059:(2): 235–264.
1043:
1026:
1011:
965:
927:
899:
898:
896:
893:
876:
873:
869:MNIST database
861:
858:
847:working memory
781:
778:
776:and learning.
771:neuromodulated
741:
721:
688:
685:
681:
677:
651:
647:
635:NMDA receptors
620:
616:
590:
586:
561:
541:
520:
487:
465:
440:
402:
398:
367:
363:
331:
327:
321:
317:
312:
306:
303:
299:
295:
292:
289:
284:
281:
277:
253:
249:
245:
242:
239:
234:
230:
205:
202:
198:
175:
171:
157:
154:
108:, a layer 2/3
85:
82:
36:Bayes' theorem
22:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2195:
2184:
2181:
2180:
2178:
2164:
2160:
2155:
2150:
2145:
2140:
2136:
2132:
2128:
2121:
2118:
2113:
2109:
2105:
2101:
2096:
2091:
2087:
2083:
2078:
2073:
2069:
2065:
2061:
2054:
2051:
2046:
2042:
2038:
2032:
2028:
2024:
2020:
2013:
2010:
2005:
2001:
1997:
1991:
1987:
1983:
1979:
1972:
1969:
1964:
1960:
1955:
1950:
1945:
1940:
1936:
1932:
1928:
1921:
1918:
1913:
1909:
1904:
1899:
1894:
1889:
1885:
1881:
1877:
1870:
1867:
1861:
1856:
1849:
1846:
1841:
1837:
1832:
1827:
1822:
1817:
1813:
1809:
1805:
1798:
1795:
1790:
1786:
1781:
1776:
1771:
1766:
1762:
1758:
1754:
1750:
1746:
1739:
1736:
1731:
1727:
1722:
1717:
1712:
1707:
1703:
1699:
1695:
1688:
1685:
1680:
1676:
1671:
1666:
1661:
1656:
1652:
1648:
1644:
1640:
1636:
1629:
1626:
1621:
1617:
1612:
1607:
1602:
1597:
1593:
1589:
1585:
1578:
1576:
1572:
1567:
1563:
1559:
1555:
1551:
1547:
1544:(4): 129–50.
1543:
1539:
1535:
1528:
1525:
1520:
1516:
1511:
1506:
1502:
1498:
1494:
1490:
1486:
1479:
1476:
1471:
1467:
1462:
1457:
1452:
1447:
1443:
1439:
1435:
1428:
1426:
1422:
1417:
1413:
1408:
1403:
1399:
1395:
1391:
1387:
1383:
1376:
1374:
1370:
1365:
1361:
1356:
1351:
1347:
1343:
1339:
1335:
1331:
1324:
1322:
1318:
1313:
1309:
1305:
1301:
1294:
1292:
1288:
1283:
1271:
1263:
1259:
1255:
1249:
1245:
1241:
1236:
1231:
1227:
1220:
1218:
1214:
1209:
1205:
1201:
1197:
1193:
1189:
1185:
1181:
1174:
1171:
1166:
1162:
1158:
1154:
1149:
1144:
1141:(3): 178–86.
1140:
1136:
1132:
1125:
1122:
1117:
1113:
1109:
1105:
1101:
1097:
1090:
1087:
1082:
1078:
1074:
1070:
1066:
1062:
1058:
1054:
1047:
1044:
1039:
1038:
1030:
1027:
1022:
1015:
1012:
1007:
1003:
999:
995:
991:
987:
984:(2): 179–94.
983:
979:
972:
970:
966:
961:
957:
953:
949:
946:(2): 115–28.
945:
941:
934:
932:
928:
923:
919:
915:
911:
904:
901:
894:
892:
890:
886:
882:
874:
872:
870:
865:
859:
857:
855:
850:
848:
843:
838:
836:
830:
827:
823:
819:
815:
811:
807:
803:
799:
795:
791:
787:
779:
777:
775:
772:
768:
764:
759:
758:synaptic tags
755:
739:
719:
710:
708:
704:
686:
683:
679:
675:
667:
649:
645:
636:
618:
614:
604:
588:
584:
559:
539:
531:
518:
510:
506:
502:
498:
485:
476:
463:
455:
451:
438:
430:
426:
422:
418:
415:postsynaptic
400:
396:
387:
383:
365:
361:
352:
348:
344:
329:
325:
319:
315:
310:
304:
301:
297:
293:
290:
287:
282:
279:
275:
266:
251:
247:
243:
240:
237:
232:
228:
219:
203:
200:
196:
173:
169:
155:
153:
151:
147:
143:
139:
135:
131:
127:
123:
119:
114:
111:
107:
103:
99:
95:
91:
83:
81:
79:
75:
70:
68:
64:
60:
56:
52:
48:
43:
41:
37:
33:
29:
19:
2134:
2130:
2120:
2067:
2063:
2053:
2018:
2012:
1977:
1971:
1934:
1930:
1920:
1883:
1879:
1869:
1848:
1811:
1807:
1797:
1752:
1748:
1738:
1701:
1697:
1687:
1642:
1638:
1628:
1591:
1587:
1541:
1537:
1527:
1492:
1488:
1478:
1441:
1437:
1389:
1385:
1340:(1): 83–96.
1337:
1333:
1303:
1299:
1225:
1183:
1179:
1173:
1138:
1134:
1124:
1099:
1095:
1089:
1056:
1052:
1046:
1036:
1029:
1020:
1014:
981:
977:
943:
939:
916:(1): 77–87.
913:
909:
903:
878:
866:
863:
851:
839:
831:
822:hypercolumns
816:in the same
806:hypercolumns
783:
711:
705:activation,
605:
575:
511:
508:
504:
500:
478:
456:
453:
431:
428:
424:
420:
416:
385:
381:
350:
267:
220:
159:
146:hypercolumns
138:hypercolumns
115:
90:hypercolumns
87:
71:
59:hypercolumns
44:
34:inspired by
27:
25:
818:hypercolumn
814:minicolumns
810:minicolumns
802:minicolumns
798:hypercolumn
794:minicolumns
134:hypercolumn
130:minicolumns
118:hypercolumn
102:minicolumns
94:minicolumns
74:data mining
55:minicolumns
2077:1911.00889
1860:2005.03476
1235:2003.12415
895:References
637:, whereas
110:minicolumn
2112:207870792
2104:1939-8018
1280:ignored (
1270:cite book
1262:214692985
1116:0954-898X
1073:0954-898X
1006:218898276
885:SpiNNaker
589:∗
560:κ
294:
244:
229:β
170:β
142:neocortex
132:within a
2177:Category
2163:32982673
2045:18476370
2004:15069505
1963:27092061
1912:25657618
1840:27493625
1789:27213810
1730:21625630
1679:20532199
1620:24782758
1566:14848878
1558:24251411
1519:31502234
1470:23060764
1416:32127347
1364:28053032
1200:21452933
1165:11912288
1157:19187979
998:12061419
767:dopamine
2154:7487417
2137:: 878.
2082:Bibcode
1954:4823276
1903:4302947
1831:4954853
1780:4877102
1757:Bibcode
1721:3096845
1670:2880555
1647:Bibcode
1611:3986567
1510:6879442
1461:3462417
1407:7189483
1355:5214637
1208:2044858
1081:9861988
978:Network
960:8823623
503:, black
218:, are:
2161:
2151:
2110:
2102:
2043:
2033:
2002:
1992:
1961:
1951:
1937:: 37.
1910:
1900:
1838:
1828:
1814:: 53.
1787:
1777:
1728:
1718:
1704:: 13.
1677:
1667:
1618:
1608:
1564:
1556:
1517:
1507:
1468:
1458:
1444:: 65.
1414:
1404:
1386:eNeuro
1362:
1352:
1260:
1250:
1206:
1198:
1163:
1155:
1114:
1079:
1071:
1004:
996:
958:
889:cortex
881:cortex
842:cortex
790:cortex
786:cortex
703:CaMKII
419:, blue
150:cortex
126:cortex
106:cortex
98:cortex
30:is an
2108:S2CID
2072:arXiv
2041:S2CID
2000:S2CID
1886:: 2.
1855:arXiv
1594:: 8.
1562:S2CID
1258:S2CID
1230:arXiv
1204:S2CID
1161:S2CID
1002:S2CID
425:(B–D)
384:, red
380:pre-
2159:PMID
2100:ISSN
2031:ISBN
1990:ISBN
1959:PMID
1908:PMID
1836:PMID
1785:PMID
1726:PMID
1675:PMID
1616:PMID
1554:PMID
1515:PMID
1466:PMID
1412:PMID
1360:PMID
1282:help
1248:ISBN
1196:PMID
1153:PMID
1112:ISSN
1077:PMID
1069:ISSN
994:PMID
956:PMID
784:The
712:The
707:AMPA
501:(C,D
417:(A–D
388:and
382:(A–D
353:The
92:and
57:and
2149:PMC
2139:doi
2090:doi
2023:doi
1982:doi
1949:PMC
1939:doi
1898:PMC
1888:doi
1826:PMC
1816:doi
1775:PMC
1765:doi
1716:PMC
1706:doi
1665:PMC
1655:doi
1606:PMC
1596:doi
1546:doi
1505:PMC
1497:doi
1456:PMC
1446:doi
1402:PMC
1394:doi
1350:PMC
1342:doi
1308:doi
1240:doi
1188:doi
1143:doi
1104:doi
1061:doi
986:doi
948:doi
918:doi
763:LTP
756:or
509:(D)
454:(C)
429:(B)
291:log
241:log
78:SNN
40:KTH
2179::
2157:.
2147:.
2135:14
2133:.
2129:.
2106:.
2098:.
2088:.
2080:.
2068:92
2066:.
2062:.
2039:.
2029:.
1998:.
1988:.
1957:.
1947:.
1935:10
1933:.
1929:.
1906:.
1896:.
1882:.
1878:.
1834:.
1824:.
1812:10
1810:.
1806:.
1783:.
1773:.
1763:.
1753:12
1751:.
1747:.
1724:.
1714:.
1700:.
1696:.
1673:.
1663:.
1653:.
1641:.
1637:.
1614:.
1604:.
1590:.
1586:.
1574:^
1560:.
1552:.
1542:24
1540:.
1536:.
1513:.
1503:.
1493:47
1491:.
1487:.
1464:.
1454:.
1440:.
1436:.
1424:^
1410:.
1400:.
1388:.
1384:.
1372:^
1358:.
1348:.
1338:37
1336:.
1332:.
1320:^
1304:34
1302:.
1290:^
1274::
1272:}}
1268:{{
1256:.
1246:.
1238:.
1216:^
1202:.
1194:.
1184:23
1182:.
1159:.
1151:.
1139:32
1137:.
1133:.
1110:.
1098:.
1075:.
1067:.
1055:.
1000:.
992:.
982:13
980:.
968:^
954:.
942:.
930:^
912:.
507:.
69:.
26:A
2165:.
2141::
2114:.
2092::
2084::
2074::
2047:.
2025::
2006:.
1984::
1965:.
1941::
1914:.
1890::
1884:9
1863:.
1857::
1842:.
1818::
1791:.
1767::
1759::
1732:.
1708::
1702:5
1681:.
1657::
1649::
1643:6
1622:.
1598::
1592:6
1568:.
1548::
1521:.
1499::
1472:.
1448::
1442:6
1418:.
1396::
1390:7
1366:.
1344::
1314:.
1310::
1284:)
1264:.
1242::
1232::
1210:.
1190::
1167:.
1145::
1118:.
1106::
1100:3
1083:.
1063::
1057:9
1008:.
988::
962:.
950::
944:7
924:.
920::
914:1
740:E
720:Z
687:+
684:2
680:a
676:C
650:j
646:Z
619:i
615:Z
585:P
540:P
519:E
505:)
486:Z
464:E
439:Z
421:)
401:j
397:S
386:)
366:i
362:S
330:j
326:P
320:i
316:P
311:/
305:j
302:i
298:P
288:=
283:j
280:i
276:w
252:j
248:P
238:=
233:j
204:j
201:i
197:w
174:j
20:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.