149:
481:) as new wizir. Safdar Jung, supported by Balram Jat and Surajmal Jat, revolted against the Mughal king. Murtija Khan's son Aqaibet Mahmud Khan was the chief diwan of Gaziuddin Khan, he and Balram agreed to meet to negotiate the terms of truce. Balram arrived with his son, diwan and 250 men, angry words flew, Balram put his hand on his sword, Aquibat's guard suddenly fell upon Balram and killed him, his son, diwan and 9 other escorts. Maharaja
36:
513:
In 1793, Ajit Singh was killed by his brother Zalim Singh, and Ajit's son
Bahadur Singh became the king. Till 1803 Ballabhgarh rulers remained under Marathas .In 1785 mahadji capture deeg but not capture bharatpur after 1787 to keep peace with Jats gave 11 paragana to ranjit singh and make friendly relation with bharatpur to make peace ref agra province.
364:
545:. Bahadur Singh killed in 1806. His son Narain Singh became king but he too was killed in 1806. Narain's son Anirudh Singh became king and ruled till he was killed in 1819. His infant son Sahib Singh ruled till 1825 when he died childless. Sahib's paternal uncle and Narain Singh's brother Ram Singh ruled till 1829 till his death.
148:
512:
On 20 April 1774, Ajit Singh with title of "Raja" and Hira Singh with titles of "Raja" and "Salar Jang" were restored to
Ballabhgarh as descendant of Balram by Mughal king after they were removed by Bharatpur king. In 1775, Ajit Singh was formally appointed Raja of Ballabhgarh under Mughal authority.
493:
there and slayed the qanungo
Santokh Rai for scheming Balram's murder. In November 1755, Jats under Suraj Mal also recaptured Ballabgarh and Ghasira from Mughals. Suraj Mal appointed sons of Balram, Bishan Singh as Nazim and Kishan Singh as kiledar, who stayed in these roles till 1774 under Suraj
576:(1842–1844), whom he had met as a young man, seeking his protection. According to a 2011 auction catalogue, "it seems was written as a ruse to deceive the British in the event of his capture... as he was fully committed to the cause of Indian Independence".
476:
On 30 June 1750, Safdar Jung, marched against Balram but Balram managed to evade him using stratagem with the help of
Marathas. Mughal king Ahmad Shah Bahadur replaced Safdar Jung with Gaziuddin Khan ("Intizam-Ud-Daullahas" or "lmad-ul-Mulk", the imperial
862:
867:
552:
ascended the throne in 1829 after his father Ram Singh's death and proved to be a just ruler. Nahar Singh was ruler of 101 villages of
Ballabhgarh. He, Nawab Ahmed Ali Khan of
509:
on 12 June 1761, Suraj Mal recaptured
Ballabhgarh from Abdali's forced in 1762 and reinstated Balram's sons Kishan Singh and Bishan Singh in their roles under Bharatpur State.
445:
of that area with the help of local Jat villagers. He became more powerful and richer and started looting the mughal travelers on Delhi–Agra royal route during the reign of
699:
But the
Bulandshahr joint-magistrate, as observed, now had cavalry at his disposal, which was of great help on that part of the Ballabgarh estate which was level ground.
857:
812:
468:(r. 1713–1719). His son Balram Singh freed him by pretending to pay the ransom. Charan Das's son, Balram Singh, later rose to be a powerful king.
782:
460:
Gopal's successor was his son Charan Das
Tewatia, who was also ambitious. When Charan Das saw weakening of the Mughal rule, he stopped paying
852:
692:
662:
464:(octroi) to Mughals. As a result, Mughals arrested and imprisoned Charan Das at Faridabad fort for a short time in 1714 during the reign of
573:
53:
842:
119:
100:
328:
303:
72:
57:
425:
Jat, the founder of the princely state of
Ballabgarh, migrated from Alwalpur village in 1705, and established himself at
79:
820:
86:
754:
569:
522:
847:
631:
565:
542:
68:
568:. On 10 September 1857, just four days before the British Army stormed Delhi, Nahar Singh wrote a letter to
506:
46:
790:
153:
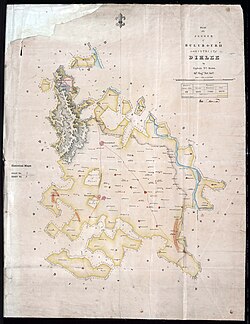
Map of the plan of the Jagir (estate) of
Ballabhgarh in Delhi District, surveyed by W. Brown, 1840
498:
688:
658:
591:
184:
93:
725:
549:
684:
Grass in their Mouths: The Upper Doab of India under the Company's Magna Charta, 1793-1830
654:
Grass in their Mouths: The Upper Doab of India under the Company's Magna Charta, 1793-1830
538:
529:. British confirmed Ajit Singh's son Bahadur Singh as independent ruler of Ballabhgarh
526:
502:
450:
266:
243:
190:
836:
454:
308:
553:
465:
433:
rulers there. Gopal Singh Tewatia of Sihi started establishing his power in Delhi,
741:
711:
682:
652:
17:
618:
368:
321:
229:
162:
35:
363:
429:(5 kilometres (3.1 mi) from Ballabhgarh) after attacking the local Tyagi
786:
482:
446:
816:
561:
438:
430:
389:
355:
669:
the jagir of the Ballabgarh raja, a Jat of the Tevatiya got, or clan.
557:
486:
442:
422:
401:
530:
478:
434:
393:
384:
346:
172:
534:
490:
426:
397:
200:
405:
29:
730:. Concept Publishing Company. p. 10. GGKEY:KQWQCNNELB2.
501:
waged war against Jats and Marathas. After the defeat of
449:(d. 1707). In 1710, during the reign of Aurangzeb's son
863:
States and territories established in the 17th century
489:
from Mughals on 27 September 1754. He also caught the
727:
The Province of Agra: Its History and Administration
556:, and rulers of neighbouring principalities such as
342:
263:
253:
239:
223:
213:
199:
178:
168:
158:
134:
60:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
533:, as a buffer state between British border and
868:States and territories disestablished in 1858
8:
147:
131:
457:officer Murtaza Khan killed him in 1711.
120:Learn how and when to remove this message
712:Sir Syed Ahmed Khan: A Centenary Tribute
362:
858:1858 disestablishments in British India
755:"REVOLT OF 1857 AND MUSLIMS IN HARYANA"
742:Haryana: Studies in History and Culture
643:
525:Haryana was transferred to British by
262:
252:
248:
222:
212:
208:
198:
7:
58:adding citations to reliable sources
819:. 14 September 2011. Archived from
783:"Photos of Mysore may get £200,000"
472:Expansion: Balram Singh (Ballu Jat)
382:was originally a state and later a
789:. 24 September 201. Archived from
585:Ch Gopal singh Tewatia (1705–1711)
25:
609:Anirudh singh Tewatia (1806–1819)
603:Bahadur singh Tewatia (1793–1806)
537:, and it remained an independent
408:king Raja Gopal Tewatia on 1705.
681:Kolff, Dirk H. A. (2010-08-13).
651:Kolff, Dirk H. A. (2010-08-13).
606:Narain singh Tewatia (1806-1806)
326:
301:
34:
612:Sahib singh Tewatia (1819–1825)
597:Bisan singh Tewatia (1753–1774)
45:needs additional citations for
600:Ajit singh Tewatia (1774–1793)
588:Ch CharanDas singh (1711–1714)
1:
813:"Princely letter up for sale"
615:Ram singh Tewatia (1825–1829)
853:1705 establishments in India
485:Jat retaliated by capturing
27:Hindu Jat Kingdom in Haryana
517:Jat rule during British era
884:
762:shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in
570:Governor General of India
523:Treaty of Surji-Anjangaon
371:last ruler of Ballabhgarh
280:
276:
249:
235:
215:• 1705–1711 (first)
209:
146:
141:
843:Princely states of India
632:Indian Rebellion of 1857
566:Indian Rebellion of 1857
543:Indian Rebellion of 1857
417:The founder: Gopal Singh
404:clan. It was founded by
378:, historically known as
265:• State annexed by
225:• 1829–1858 (last)
507:Third Battle of Panipat
69:"Ballabgarh" jagir
687:. BRILL. p. 162.
657:. BRILL. p. 162.
372:
724:Dharma Bhanu (1979).
366:
169:Common languages
793:on 30 September 2011
710:Asloub Ansari, 2001,
54:improve this article
823:on 17 October 2012.
564:, took part in the
521:In 1803, after the
497:From 1757 to 1760,
441:areas. He attacked
255:• Established
376:Ballabhgarh estate
373:
694:978-90-04-18802-0
664:978-90-04-18802-0
592:Raja Balram Singh
574:Lord Ellenborough
499:Ahmad Shah Abdali
380:Ballabgarh estate
361:
360:
338:
337:
334:
333:
314:
313:
185:Absolute monarchy
136:Ballabhgarh State
130:
129:
122:
104:
18:Ballabhgarh State
16:(Redirected from
875:
825:
824:
809:
803:
802:
800:
798:
779:
773:
772:
770:
768:
759:
751:
745:
738:
732:
731:
721:
715:
708:
702:
701:
678:
672:
671:
648:
550:Raja Nahar Singh
330:
329:
318:
317:
305:
304:
298:
297:
282:
281:
151:
132:
125:
118:
114:
111:
105:
103:
62:
38:
30:
21:
883:
882:
878:
877:
876:
874:
873:
872:
848:Hindu dynasties
833:
832:
829:
828:
811:
810:
806:
796:
794:
781:
780:
776:
766:
764:
757:
753:
752:
748:
739:
735:
723:
722:
718:
709:
705:
695:
680:
679:
675:
665:
650:
649:
645:
640:
628:
582:
519:
474:
421:Gopal Singh, a
419:
414:
349:
327:
302:
269:
256:
226:
216:
154:
137:
126:
115:
109:
106:
63:
61:
51:
39:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
881:
879:
871:
870:
865:
860:
855:
850:
845:
835:
834:
827:
826:
804:
774:
746:
733:
716:
703:
693:
673:
663:
642:
641:
639:
636:
635:
634:
627:
624:
623:
622:
616:
613:
610:
607:
604:
601:
598:
595:
589:
586:
581:
578:
539:princely state
527:Maratha Empire
518:
515:
503:Maratha Empire
473:
470:
451:Bahadur Shah I
418:
415:
413:
410:
359:
358:
344:
340:
339:
336:
335:
332:
331:
324:
315:
312:
311:
306:
294:
293:
288:
278:
277:
274:
273:
270:
267:British Empire
264:
261:
260:
257:
254:
251:
250:
247:
246:
244:Medieval India
241:
240:Historical era
237:
236:
233:
232:
227:
224:
221:
220:
217:
214:
211:
210:
207:
206:
203:
197:
196:
195:
194:
191:Princely state
188:
180:
176:
175:
170:
166:
165:
160:
156:
155:
152:
144:
143:
139:
138:
135:
128:
127:
42:
40:
33:
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
880:
869:
866:
864:
861:
859:
856:
854:
851:
849:
846:
844:
841:
840:
838:
831:
822:
818:
814:
808:
805:
792:
788:
784:
778:
775:
763:
756:
750:
747:
743:
737:
734:
729:
728:
720:
717:
713:
707:
704:
700:
696:
690:
686:
685:
677:
674:
670:
666:
660:
656:
655:
647:
644:
637:
633:
630:
629:
625:
620:
617:
614:
611:
608:
605:
602:
599:
596:
593:
590:
587:
584:
583:
579:
577:
575:
571:
567:
563:
559:
555:
551:
546:
544:
540:
536:
532:
528:
524:
516:
514:
510:
508:
504:
500:
495:
492:
488:
484:
480:
471:
469:
467:
463:
458:
456:
452:
448:
444:
440:
436:
432:
428:
424:
416:
411:
409:
407:
403:
399:
395:
391:
387:
386:
381:
377:
370:
365:
357:
353:
348:
345:
343:Today part of
341:
325:
323:
320:
319:
316:
310:
309:Mughal Empire
307:
300:
299:
296:
295:
292:
289:
287:
284:
283:
279:
275:
271:
268:
258:
245:
242:
238:
234:
231:
228:
219:Gopal Tewatia
218:
204:
202:
192:
189:
186:
183:
182:
181:
177:
174:
171:
167:
164:
161:
157:
150:
145:
140:
133:
124:
121:
113:
102:
99:
95:
92:
88:
85:
81:
78:
74:
71: –
70:
66:
65:Find sources:
59:
55:
49:
48:
43:This article
41:
37:
32:
31:
19:
830:
821:the original
807:
797:24 September
795:. Retrieved
791:the original
777:
765:. Retrieved
761:
749:
736:
726:
719:
706:
698:
683:
676:
668:
653:
646:
554:Farrukhnagar
547:
535:Sikhs rulers
520:
511:
496:
475:
466:Farrukhsiyar
461:
459:
420:
396:, ruled by
388:(estate) in
383:
379:
375:
374:
351:
291:Succeeded by
290:
285:
116:
107:
97:
90:
83:
76:
64:
52:Please help
47:verification
44:
767:20 November
714:, Page 166.
621:(1829–1858)
619:Nahar Singh
594:(1714–1753)
479:Mir Bakhshi
369:Nahar Singh
322:British Raj
286:Preceded by
230:Nahar Singh
193:(1803–1858)
187:(1705–1803)
163:Ballabhgarh
837:Categories
744:, Page 74.
638:References
541:until the
179:Government
110:April 2022
80:newspapers
787:Asian Age
483:Suraj Mal
462:malgujari
447:Aurangzeb
142:1705–1858
817:IBN Live
626:See also
562:Jhajjar
505:in the
443:Rajputs
439:Mathura
431:Brahman
423:Tewatia
412:History
402:Tewatia
390:Haryana
356:Haryana
159:Capital
94:scholar
740:1968,
691:
661:
580:Rulers
558:Rewari
487:Palwal
455:Mughal
453:, the
354:
352:·
350:
205:
96:
89:
82:
75:
67:
758:(PDF)
531:jagir
494:Mal.
435:Khair
394:India
385:jagir
367:Raja
347:India
173:Hindi
101:JSTOR
87:books
799:2011
769:2019
689:ISBN
659:ISBN
560:and
491:qazi
437:and
427:Sihi
398:Jats
272:1858
259:1705
201:Raja
73:news
548:In
406:Jat
400:of
56:by
839::
815:.
785:.
760:.
697:.
667:.
572:,
392:,
801:.
771:.
123:)
117:(
112:)
108:(
98:·
91:·
84:·
77:·
50:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.