1081:(ZBR), where the number of sectors dividing each track varies with the location of groups of tracks on the surface of the platter. Tracks nearer to the edge of the platter contain more blocks of data than tracks close to the spindle, because there is more physical space within a given track near the edge of the platter. Thus, the CHS addressing scheme cannot correspond directly with the physical geometry of such drives, due to the varying number of sectors per track for different regions on a platter. Because of this, many drives still have a surplus of sectors (less than 1 cylinder in size) at the end of the drive, since the total number of sectors rarely, if ever, ends on a cylinder boundary.
124:
93:) and drive sizes grew over time, the CHS addressing method became restrictive. Since the late 1980s, hard drives began shipping with an embedded disk controller that had good knowledge of the physical geometry; they would however report a false geometry to the computer, e.g., a larger number of heads than actually present, to gain more addressable space. These logical CHS values would be translated by the controller, thus CHS addressing no longer corresponded to any physical attributes of the drive.
20:
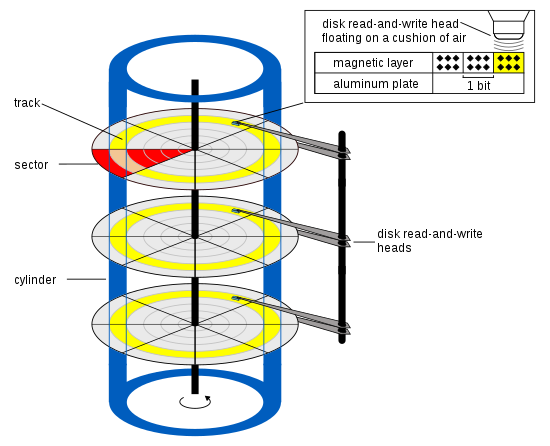
314:), collecting the respective circular tracks aligned through the stack of platters. The number of cylinders of a disk drive exactly equals the number of tracks on a single surface in the drive. It comprises the same track number on each platter, spanning all such tracks across each platter surface that is able to store data (without regard to whether or not the track is "bad"). Cylinders are vertically formed by
1043:
since at least the 1960s. This is largely comparable to the
Cylinder Head Sector format used by PCs, save that the sector size was not fixed but could vary from track to track based on the needs of each application. In contemporary use, the disk geometry presented to the mainframe is emulated by the
726:
and declared CHS addressing as obsolete, but still allowed to implement the ATA-5 translations. Unsurprisingly the CHS to LBA translation formula given below also matches the last ATA-5 CHS translation. In the ATA-5 specification CHS support was mandatory for up to 16 514 064 sectors and
1723:
While computers begin counting at 0, DOS would begin counting at 1. In order to do this, DOS would add a 1 to the head count before displaying it on the screen. However, instead of converting the 8-bit unsigned integer to a larger size (such as a 16-bit integer) first, DOS just added the 1. This
345:
reads and writes data in a hard drive by manipulating the magnetic medium that composes the surface of an associated disk platter. Naturally, a platter has 2 sides and thus 2 surfaces on which data can be manipulated; usually there are 2 heads per platter, one per side. (Sometimes the term
1088:
with any configuration of cylinders, heads and sectors that do not exceed the capacity of the drive (or the BIOS), since the drive will convert any given CHS value into an actual address for its specific hardware configuration. This however can cause compatibility problems.
945:(LSN) are synonyms. The formula does not use the number of cylinders, but requires the number of heads and the number of sectors per track in the disk geometry, because the same CHS tuple addresses different logical sector numbers depending on the geometry.
85:
drive attached to the controller, to correctly address data blocks. The traditional limits were 512 bytes/sector × 63 sectors/track × 255 heads (tracks/cylinder) × 1024 cylinders, resulting in a limit of 8032.5 MiB for the total capacity of a disk.
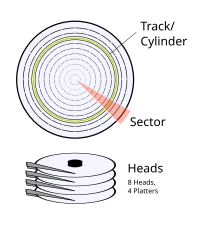
62:. Sector finally selects which data block in this track is to be addressed, as the track is subdivided into several equally-sized portions, each of which is an arc of (360/n) degrees, where n is the number of sectors in the track.
872:
57:
intersection through the stack of platters in a disk, centered around the disk's spindle. Combined, cylinder and head intersect to a circular line, or more precisely: a circular strip of physical data blocks called
1405:
218:
of IBM-PC compatible machines, the sector number was encoded in six bits, resulting in a maximal number of 111111 (63) sectors per track. This maximum is still in use for virtual CHS geometries.
397:
up to and including 7.10 will cause these operating systems to crash on boot when encountering volumes with 256 heads. Therefore, all compatible BIOSes will use mappings with up to 255 heads (
545:
for 24 bits with (256 or) 255 heads. In CHS tuples specifying a geometry S actually means sectors per track, and where the (virtual) geometry still matches the capacity the disk contains
1306:
163:
Floppy disks and controllers had used physical sector sizes of 128, 256, 512 and 1024 bytes (e.g., PC/AX), but formats with 512 bytes per physical sector became dominant in the 1980s.
166:
The most common physical sector size for hard disks today is 512 bytes, but there have been hard disks with 520 bytes per sector as well for non-IBM compatible machines. In 2005 some
560:) permits eight bits for sectors still starting at 1, i.e., sectors 1...255, four bits for heads 0...15, and sixteen bits for cylinders 0...65535. This results in a roughly
758:
104:(MBR) partition table still aligned partitions to cylinder boundaries; thus, artifacts of CHS addressing were still seen in partitioning software by the late 2000s.
1652:
1619:
926:
1773:
1596:
If the device's capacity is greater than or equal to one sector and less than or equal to 16,514,064 sectors, then the device shall support CHS translation.
1711:
This rule is true at least for all formats where the physical sectors are named 1 upwards. However, there are a few odd floppy formats (e.g., the 640
1055:
drives, divided each cylinder into an equal number of sectors, so the CHS values matched the physical properties of the drive. A drive with a CHS tuple of
333:, might give blocks addresses that include a cylinder address, although the cylinder address doesn't select a (geometric) cylindrical slice of the device.
1416:
1465:
1433:
930:
155:
stores fewer sectors in shorter (inner) tracks, physical disk formats are not necessarily cylindrical, and sector numbers in a track can be skewed.
1553:
In standards ATA/ATAPI-5 and earlier, a CHS translation was defined. This translation is obsolete but may be implemented as defined in ATA/ATAPI-5.
1107:(Windows XP included) may disregard this rule, but doing so can still cause some compatibility issues, especially if the user wants to perform
1317:
621:
mitigated this limitation by using 128 or 240 instead of 16 heads, simultaneously reducing the numbers of cylinders and sectors to fit into
549:
sectors. As larger hard disks have come into use, a cylinder has become also a logical disk structure, standardised at 16 065 sectors (
683:
are not directly affected by the physical or virtual geometry of the disk, i.e., a cluster can begin at a sector near the end of a given
1768:
1059:
would have 500 tracks per side on each platter, two platters (4 heads), and 32 sectors per track, with a total of 32 768 000
1522:
1778:
1565:
1763:
1644:
1070:
1164:
584:
234:
circular strips of sectors. At least one head is required to read a single track. With respect to disk geometries the terms
1048:
1783:
1611:
322:
151:
is the smallest unit. Disk controllers can introduce address translations to map logical to physical positions, e.g.,
1216:
1246:
123:
537:. CHS values used to specify the geometry of a disk have to count cylinder 0 and head 0 resulting in a maximum (
1682:
1254:
1111:
on the same drive. Microsoft does not follow this rule with internal disk partition tools since
Windows Vista.
723:
713:
342:
296:
204:
97:
1645:"Information processing -- Volume and file structure of flexible disk cartridges for information interchange"
1497:
203:, which can lead to confusion since logical sector addressing schemes typically start counting with 0, e.g.,
1480:
1448:
1753:
1715:
format used by BBC Master 512 with DOS Plus 2.1), where the first sector in a track is named "0" not "1".
1140:
934:
668:
185:
81:
controller card was used, so that the operating system had to know the exact physical "geometry" of the
188:
use sector sizes of 512 and 1024 bytes on 5.25-inch drives and 512 and 2048 bytes on 3.5-inch drives.
1736:) instead of the 256 that would be expected. This was fixed with DOS 8, but by then, it had become a
1125:
108:
1612:"Information technology -- Volume and file structure of disk cartridges for information interchange"
307:
53:. Head selects a circular surface: a platter in the disk (and one of its two sides). Cylinder is a
1224:
1078:
1052:
922:
330:
315:
227:
167:
152:
101:
90:
1103:, each partition must start and end at a cylinder boundary. Only some of the relatively modern
1023:
All the heads/tracks of the same cylinder get counted before incrementing to the next cylinder.
634:
354:
since platters might be separated from their head assemblies, as with the removable media of a
1145:
1100:
311:
1017:
The first LBA sector is sector # zero, the same sector in a CHS model is called sector # one.
1725:
1104:
420:(512 bytes/sector)×(63 sectors/track)×(255 heads (tracks/cylinder))×(1024 cylinders)=8032.5
1537:
1350:
1135:
1020:
All the sectors of each head/track get counted before incrementing to the next head/track.
171:
74:
35:
1580:
318:. In other words, track 12 on platter 0 plus track 12 on platter 1 etc. is cylinder 12.
107:
In the early 2010s, the disk size limitations imposed by MBR became problematic and the
1040:
1036:
1190:
867:{\displaystyle A=(c\times N_{\mathrm {heads} }+h)\times N_{\mathrm {sectors} }+(s-1),}
1758:
1747:
19:
1130:
719:
595:
580:
557:
292:
16:
Historical method for giving addresses to physical data blocks on hard disk drives
1172:
1013:
To help visualize the sequencing of sectors into a linear LBA model, note that:
1379:
1354:
464:
326:
243:
1674:
1579:
Technical
Committee T13 ATA Storage Interface. 2000. p. 19. Archived from
1536:
Technical
Committee T13 ATA Storage Interface. 2002. p. 22. Archived from
89:
As the geometry became more complicated (for example, with the introduction of
394:
231:
34:) is an early method for giving addresses to each physical block of data on a
1383:
1284:
1108:
1093:
1044:
storage firmware, and no longer has any relation to physical disk geometry.
1026:
The outside half of a whole hard drive would be the first half of the drive.
210:
For physical disk geometries the maximal sector number is determined by the
115:
firmware without MBR support no longer use any notions from CHS addressing.
65:
CHS addresses were exposed, instead of simple linear addresses (going from
1217:"Volume and File Structure of Disk Cartridges for Information Interchange"
1073:
drives were much more efficient at storing data and have replaced the now
1737:
1712:
1064:
626:
605:
572:
563:
510:
498:
492:
446:
442:
437:
431:
423:
300:
54:
1258:
657:
utility, before version 2.25, displayed partition sizes using 1024-byte
1412:
1313:
587:, and an old working draft of this now expired standard was published.
484:
409:
1576:
1533:
1479:
Technical
Committee T10 SCSI Storage Interfaces. 1994. Archived from
1476:
1444:
1280:
1120:
471:
code supported ten bits in CHS addressing with up to 1024 cylinders (
463:
are counted from 0, i.e., track 0 is the first (outer-most) track on
413:
390:
96:
By the mid 1990s, hard drive interfaces replaced the CHS scheme with
1447:
Technical
Committee T13 AT Attachment. 18 March 1996. Archived from
1281:"Western Digital's Advanced Format: The 4K Sector Transition Begins"
408:
This historical oddity can affect the maximum disk size in old BIOS
147:
numbers. The terms are explained bottom up, for disk addressing the
1060:
750:
654:
122:
18:
653:
to refer to a sector or group of sectors. For example, the Linux
178:) since 2010, but will also be able to emulate 512 byte sectors (
1085:
672:
646:
610:
591:
468:
377:
code used eight bits for a maximum of 256 heads counted as head
374:
215:
179:
112:
933: 9293:1994 (superseding ISO 9293:1987) standards for
692:
track, and end in a sector on the physically or logically next
135:(aka. physical block of data) on a disk by their position in a
41:
It is a 3D-coordinate system made out of a vertical coordinate
1096:
753:
can be mapped onto LBA addresses using the following formula:
727:
optional for larger disks. The ATA-5 limit corresponds to CHS
299:
disk or the cylinder–head–record (CCHHR) addressing mode of a
175:
170:
custom hard disks used sector sizes of 1024 bytes per sector.
1380:"Windows NT 4.0 supports maximum of 7.8-GB system partition"
111:(GPT) was designed as a replacement; modern computers using
937:
file systems matches exactly the LBA formula given above:
73:), because early hard drives didn't come with an embedded
449:
is another incorrect limit, because it would require CHS
131:
CHS addressing is the process of identifying individual
667:
are allocation units for data on various file systems (
761:
441:
limit. In this context relevant definition of 8
207:(LBA), or "relative sector addressing" used in DOS.
1333:
512 byte emulation is sometimes referred to as 512e
637:) for the given total number of sectors on a disk.
1247:"Standard Floppy Disk Formats Supported by MS-DOS"
866:
242:are closely related. For a single or double sided
77:, that would hide the physical layout. A separate
1639:
1637:
1606:
1604:
898:is the maximum number of sectors per track, and
487:. Subtracting the disallowed sector number 0 in
249:is the common term; and for more than two heads
1165:"Overview and History of the IDE/ATA Interface"
214:of the disk. However, for disk access with the
174:hard disks use 4096 bytes per physical sector (
714:Logical Block Addressing § CHS conversion
1406:"5K500.B SATA OEM Specification Revision 1.2"
1035:Cylinder Head Record format has been used by
722:specification introduced an optional 48 bits
8:
1047:Earlier hard drives used in the PC, such as
1415:. 17 March 2009. p. 51. Archived from
100:(LBA), but many tools for manipulating the
23:Cylinder, head, and sector of a hard drive.
1211:
1209:
1207:
1084:An ATA/IDE drive can be set in the system
598:limit of 16 heads the combined effect was
373:addressing supported in IBM-PC compatible
295:, as used in the CHS addressing mode of a
818:
817:
782:
781:
760:
268:
253:is the common term. Strictly speaking a
1740:standard to not use a head value of 255.
1156:
139:, where the track is determined by the
1345:
1343:
1341:
1221:Standard ECMA-107 (2nd ed., June 1995)
291:A cylinder is a division of data in a
45:, a horizontal (or radial) coordinate
1191:"The gen on disc partition alignment"
571:sectors corresponding to 130560
389:). However, a bug in all versions of
7:
1774:Rotating disc computer storage media
1184:
1182:
1008:1504 = ((3 × 15) + 2) × 32 + (1 – 1)
1002:of a disk with 1028160 sectors, CHS
994:48321=((3 × 255) + 2) × 63 + (1 – 1)
988:of a disk with 1028160 sectors, CHS
980:3570 = ((3 × 4) + 2) × 255 + (1 – 1)
974:of a disk with 1028160 sectors, CHS
965:3150 = ((3 × 16) + 2) × 63 + (1 – 1)
959:of a disk with 1028160 sectors, CHS
889:is the number of heads on the disk,
614:
575:for a sector size of 512 bytes. The
483:results in the 24 bits supported by
127:schematic of the hard drive geometry
310:slices through the physical disks (
306:The concept is concentric, hollow,
1307:"Advanced Format Technology Brief"
1189:Jonathan de Boyne Pollard (2011).
837:
834:
831:
828:
825:
822:
819:
795:
792:
789:
786:
783:
583:specification are also covered by
14:
1316:. 2010. p. 1. Archived from
1355:"History of BIOS and IDE limits"
694:
685:
594:limit of 1024 cylinders and the
495:for a sector size of 512 bytes (
467:or other cylindrical disks. Old
363:
259:
1498:"Util-linux 2.25 Release Notes"
1171:. 17 April 2001. Archived from
633:(revised ECHS limit: 7560
491:tracks corresponds to 128
1092:For operating systems such as
858:
846:
807:
768:
731:or equivalent disk capacities
416:or similar operating systems:
369:
144:
1:
1257:. 12 May 2003. Archived from
1077:MFM and RLL drives. They use
613:translation schemes known as
556:CHS addressing with 28 bits (
401:) only, including in virtual
279:
182:) for a transitional period.
71:total block count on disk - 1
1679:Microsoft Windows XP Support
697:
688:
649:communities employ the term
476:
366:
323:Direct Access Storage Device
262:
132:
49:, and an angular coordinate
733:(16514064 = 16383 × 16 × 63
701:
609:limit for sector size 512.
585:Ralf Brown's Interrupt List
533:for 24 bits limited to 255
501:=1024×256×(512 byte/sector)
453:with 64 sectors per track.
136:
1800:
1769:Hard disk computer storage
711:
679:mainly consists of files.
534:
480:
140:
1502:The Linux Kernel Archives
517:CHS addressing starts at
266:combination consisting of
1779:Computer storage devices
1683:Microsoft Knowledge Base
1255:Microsoft Knowledge Base
724:Logical Block Addressing
434:yields what is known as
297:Fixed Block Architecture
205:logical block addressing
195:numbers always start at
98:logical block addressing
1734:0x100 & 0xFF = 0x00
625:(ECHS limit: 4032
507:confirms the (roughly)
475:). Adding six bits for
868:
569:65536×16×255=267386880
191:In CHS addressing the
186:Magneto-optical drives
128:
24:
1764:Computer file systems
1728:a head count of 255 (
1422:on 27 September 2011.
1359:Large Disk HOWTO v2.5
1141:File Allocation Table
943:Logical Sector Number
939:Logical Block Address
919:Logical Sector Number
869:
521:with a maximal value
126:
22:
1323:on 27 September 2011
1126:Block (data storage)
1099:or older version of
1039:(CKD) hard disks on
914:is the CHS address.
880:is the LBA address,
759:
740:24 = 14 + 4 + 6 bits
428:512×63×256×1024=8064
412:code as well as old
109:GUID Partition Table
28:Cylinder-head-sector
1784:IBM storage devices
1353:(1 November 2004).
1175:on 4 February 2019.
641:Blocks and clusters
479:and eight bits for
350:is substituted for
1386:. 23 February 2007
1287:. 18 December 2009
1261:on 31 January 2009
1079:zone bit recording
864:
736:= 1032 × 254 × 63)
708:CHS to LBA mapping
600:1024×16×63=1032192
485:BIOS interrupt 13h
341:A device called a
331:IBM 2321 Data Cell
153:zone bit recording
129:
102:master boot record
91:zone bit recording
25:
1616:ISO/IEC 9293:1994
1486:on 21 March 2012.
1146:Disk partitioning
1105:operating systems
602:sectors, i.e., a
272:sectors, while a
1791:
1735:
1731:
1722:
1710:
1695:
1694:
1692:
1690:
1671:
1665:
1664:
1662:
1660:
1641:
1632:
1631:
1629:
1627:
1608:
1599:
1598:
1593:
1591:
1585:
1570:
1562:
1556:
1555:
1550:
1548:
1542:
1527:
1519:
1513:
1512:
1510:
1508:
1494:
1488:
1487:
1485:
1470:
1462:
1456:
1455:
1454:on 28 July 2011.
1453:
1438:
1430:
1424:
1423:
1421:
1410:
1402:
1396:
1395:
1393:
1391:
1376:
1370:
1369:
1367:
1365:
1347:
1336:
1335:
1330:
1328:
1322:
1311:
1303:
1297:
1296:
1294:
1292:
1277:
1271:
1270:
1268:
1266:
1243:
1237:
1236:
1234:
1232:
1213:
1202:
1201:
1199:
1197:
1186:
1177:
1176:
1161:
1058:
1009:
1005:
1001:
995:
991:
987:
981:
977:
973:
966:
962:
958:
913:
897:
888:
879:
873:
871:
870:
865:
842:
841:
840:
800:
799:
798:
745:
741:
737:
734:
730:
700:
699:
696:
691:
690:
687:
632:
624:
616:
601:
578:
570:
567:limit; actually
552:
548:
544:
540:
532:
528:
524:
520:
506:
502:
490:
474:
452:
429:
421:
404:
400:
388:
372:
371:
368:
365:
325:(DASD), such as
282:
281:
271:
270:
265:
264:
261:
212:low level format
1799:
1798:
1794:
1793:
1792:
1790:
1789:
1788:
1744:
1743:
1733:
1729:
1719:
1707:
1703:
1698:
1688:
1686:
1673:
1672:
1668:
1658:
1656:
1655:catalogue. 1987
1643:
1642:
1635:
1625:
1623:
1622:catalogue. 1994
1610:
1609:
1602:
1589:
1587:
1586:on 28 July 2011
1583:
1568:
1564:
1563:
1559:
1546:
1544:
1543:on 28 July 2011
1540:
1525:
1521:
1520:
1516:
1506:
1504:
1496:
1495:
1491:
1483:
1468:
1464:
1463:
1459:
1451:
1436:
1432:
1431:
1427:
1419:
1408:
1404:
1403:
1399:
1389:
1387:
1378:
1377:
1373:
1363:
1361:
1351:Andries Brouwer
1349:
1348:
1339:
1326:
1324:
1320:
1309:
1305:
1304:
1300:
1290:
1288:
1279:
1278:
1274:
1264:
1262:
1245:
1244:
1240:
1230:
1228:
1215:
1214:
1205:
1195:
1193:
1188:
1187:
1180:
1163:
1162:
1158:
1154:
1136:Disk formatting
1117:
1056:
1033:
1007:
1003:
999:
993:
989:
986: 64 255 63
985:
979:
975:
971:
964:
960:
956:
921:formula in the
899:
896:
890:
887:
881:
877:
813:
777:
757:
756:
743:
739:
738:, and requires
735:
732:
728:
716:
710:
693:
684:
675:, etc.), where
643:
630:
622:
599:
576:
568:
550:
546:
542:
538:
530:
526:
522:
518:
504:
496:
488:
472:
450:
427:
426:, but actually
419:
402:
398:
386:
362:
339:
329:devices or the
321:Other forms of
289:
277:
267:
258:
224:
172:Advanced Format
161:
121:
75:disk controller
36:hard disk drive
17:
12:
11:
5:
1797:
1795:
1787:
1786:
1781:
1776:
1771:
1766:
1761:
1756:
1746:
1745:
1742:
1741:
1716:
1702:
1699:
1697:
1696:
1685:. 23 July 2009
1666:
1633:
1600:
1557:
1514:
1489:
1457:
1425:
1397:
1371:
1337:
1298:
1272:
1238:
1203:
1178:
1155:
1153:
1150:
1149:
1148:
1143:
1138:
1133:
1128:
1123:
1116:
1113:
1041:IBM mainframes
1037:Count Key Data
1032:
1029:
1028:
1027:
1024:
1021:
1018:
1011:
1010:
996:
982:
968:
894:
885:
863:
860:
857:
854:
851:
848:
845:
839:
836:
833:
830:
827:
824:
821:
816:
812:
809:
806:
803:
797:
794:
791:
788:
785:
780:
776:
773:
770:
767:
764:
712:Main article:
709:
706:
642:
639:
558:EIDE and ATA-2
338:
335:
288:
285:
223:
220:
199:, there is no
160:
157:
120:
117:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1796:
1785:
1782:
1780:
1777:
1775:
1772:
1770:
1767:
1765:
1762:
1760:
1757:
1755:
1754:AT Attachment
1752:
1751:
1749:
1739:
1727:
1721:
1717:
1714:
1709:
1705:
1704:
1700:
1684:
1680:
1676:
1670:
1667:
1654:
1650:
1649:ISO 9293:1987
1646:
1640:
1638:
1634:
1621:
1617:
1613:
1607:
1605:
1601:
1597:
1582:
1578:
1574:
1567:
1561:
1558:
1554:
1539:
1535:
1531:
1524:
1518:
1515:
1503:
1499:
1493:
1490:
1482:
1478:
1474:
1467:
1461:
1458:
1450:
1446:
1442:
1435:
1429:
1426:
1418:
1414:
1407:
1401:
1398:
1385:
1381:
1375:
1372:
1360:
1356:
1352:
1346:
1344:
1342:
1338:
1334:
1319:
1315:
1308:
1302:
1299:
1286:
1282:
1276:
1273:
1260:
1256:
1252:
1248:
1242:
1239:
1226:
1222:
1218:
1212:
1210:
1208:
1204:
1192:
1185:
1183:
1179:
1174:
1170:
1166:
1160:
1157:
1151:
1147:
1144:
1142:
1139:
1137:
1134:
1132:
1129:
1127:
1124:
1122:
1121:CD-ROM format
1119:
1118:
1114:
1112:
1110:
1106:
1102:
1098:
1095:
1090:
1087:
1082:
1080:
1076:
1072:
1068:
1066:
1062:
1054:
1050:
1045:
1042:
1038:
1030:
1025:
1022:
1019:
1016:
1015:
1014:
998:For geometry
997:
984:For geometry
983:
970:For geometry
969:
955:For geometry
954:
953:
952:
950:
946:
944:
940:
936:
932:
928:
924:
920:
915:
911:
907:
903:
893:
884:
874:
861:
855:
852:
849:
843:
814:
810:
804:
801:
778:
774:
771:
765:
762:
754:
752:
747:
744:16383 + 1 = 2
725:
721:
715:
707:
705:
703:
682:
678:
674:
670:
666:
662:
660:
656:
652:
648:
640:
638:
636:
628:
620:
612:
608:
607:
597:
593:
588:
586:
582:
574:
566:
565:
559:
554:
536:
515:
513:
512:
505:8192-128=8064
500:
494:
486:
482:
478:
470:
466:
462:
458:
454:
448:
444:
440:
439:
433:
425:
417:
415:
411:
406:
396:
392:
391:Microsoft DOS
384:
380:
376:
359:
357:
353:
349:
344:
336:
334:
332:
328:
324:
319:
317:
313:
309:
304:
302:
298:
294:
286:
284:
275:
256:
252:
248:
245:
241:
237:
233:
230:are the thin
229:
221:
219:
217:
213:
208:
206:
202:
198:
194:
189:
187:
183:
181:
177:
173:
169:
164:
158:
156:
154:
150:
146:
142:
138:
134:
125:
118:
116:
114:
110:
105:
103:
99:
94:
92:
87:
84:
80:
76:
72:
68:
63:
61:
56:
52:
48:
44:
39:
37:
33:
29:
21:
1720:
1708:
1687:. Retrieved
1678:
1669:
1657:. Retrieved
1648:
1624:. Retrieved
1615:
1595:
1588:. Retrieved
1581:the original
1572:
1560:
1552:
1545:. Retrieved
1538:the original
1529:
1517:
1505:. Retrieved
1501:
1492:
1481:the original
1472:
1460:
1449:the original
1440:
1428:
1417:the original
1400:
1388:. Retrieved
1374:
1362:. Retrieved
1358:
1332:
1325:. Retrieved
1318:the original
1301:
1289:. Retrieved
1275:
1263:. Retrieved
1259:the original
1250:
1241:
1229:. Retrieved
1220:
1194:. Retrieved
1173:the original
1169:The PC Guide
1168:
1159:
1131:Disk storage
1109:dual booting
1091:
1083:
1074:
1069:
1063:(31.25
1046:
1034:
1012:
948:
947:
942:
938:
918:
916:
909:
905:
901:
891:
882:
875:
755:
748:
718:In 2002 the
717:
680:
676:
664:
663:
658:
650:
644:
619:revised ECHS
618:
603:
590:With an old
589:
579:bits in the
561:
555:
551:16065=255×63
516:
508:
460:
456:
455:
445:= 8192
435:
418:
407:
405:geometries.
382:
378:
360:
355:
351:
347:
340:
320:
305:
290:
273:
254:
250:
246:
239:
235:
225:
211:
209:
200:
196:
192:
190:
184:
165:
162:
148:
130:
106:
95:
88:
82:
78:
70:
66:
64:
59:
50:
46:
42:
40:
31:
27:
26:
1441:X3T10/0948D
1196:21 November
729:16383 16 63
631:1024/240/63
623:1024/128/63
543:1024/255/63
539:1024/256/63
531:1023/254/63
523:1023/255/63
327:drum memory
308:cylindrical
276:consists of
257:is a given
244:floppy disk
119:Definitions
55:cylindrical
1748:Categories
1732:) into 0 (
1675:"KB931760"
1473:X3T10/791D
1152:References
1000:2142 15 32
972:1008 4 255
957:1020 16 63
451:512×64×256
395:IBM PC DOS
293:disk drive
232:concentric
1659:6 January
1626:6 January
1573:T13/1321D
1530:T13/1410D
1384:Microsoft
1285:AnandTech
1094:Microsoft
925:-107 and
853:−
811:×
775:×
604:504
577:28=16+4+8
562:128
529:bits, or
527:24=10+8+6
497:128
461:cylinders
287:Cylinders
283:sectors.
1738:de facto
1726:overflow
1507:24 March
1327:1 August
1115:See also
1057:500 4 32
949:Examples
681:Clusters
665:Clusters
489:1024×256
399:00h..FEh
358:drive.)
312:platters
301:CKD disk
274:cylinder
251:cylinder
240:cylinder
201:sector 0
145:cylinder
83:specific
47:cylinder
1689:30 July
1590:30 July
1566:"ATA-5"
1547:30 July
1523:"ATA-6"
1466:"ATA-1"
1434:"ATA-2"
1413:Hitachi
1390:30 July
1364:30 July
1314:Hitachi
1291:29 July
1251:KB75131
1231:30 July
1101:Windows
1075:archaic
1071:ATA/IDE
1031:History
1006:is LBA
992:is LBA
978:is LBA
963:is LBA
895:sectors
514:limit.
509:8
503:); and
477:sectors
436:8
410:INT 13h
168:Seagate
159:Sectors
133:sectors
79:generic
69:to the
1724:would
1577:INCITS
1534:INCITS
1477:INCITS
1445:INCITS
1265:4 June
1227:. 1995
876:where
751:tuples
659:blocks
473:1024=2
465:floppy
457:Tracks
430:
422:
414:PC DOS
403:255×63
381:up to
375:BIOSes
356:floppy
316:tracks
228:tracks
222:Tracks
193:sector
149:sector
51:sector
1701:Notes
1584:(PDF)
1569:(PDF)
1541:(PDF)
1526:(PDF)
1484:(PDF)
1469:(PDF)
1452:(PDF)
1437:(PDF)
1420:(PDF)
1409:(PDF)
1321:(PDF)
1310:(PDF)
1061:bytes
1004:3 2 1
990:3 2 1
976:3 2 1
961:3 2 1
886:heads
720:ATA-6
702:track
655:fdisk
651:block
629:) or
581:ATA-2
547:C×H×S
535:heads
519:0/0/1
481:heads
352:head,
337:Heads
255:track
247:track
236:track
137:track
60:track
1759:BIOS
1730:0xFF
1691:2011
1661:2012
1628:2012
1592:2011
1549:2011
1509:2016
1392:2011
1366:2011
1329:2011
1293:2011
1267:2023
1233:2011
1225:ECMA
1198:2022
1086:BIOS
1051:and
941:and
923:ECMA
749:CHS
677:data
673:NTFS
647:Unix
645:The
617:and
615:ECHS
611:BIOS
592:BIOS
541:or)
525:for
469:BIOS
459:and
361:The
348:side
343:head
278:SPT×
238:and
226:The
216:BIOS
180:512e
143:and
141:head
113:UEFI
43:head
1653:ISO
1620:ISO
1097:DOS
1067:).
1065:MiB
1053:RLL
1049:MFM
935:FAT
931:IEC
927:ISO
746:).
669:FAT
596:ATA
553:).
387:FFh
383:255
269:SPT
176:4Kn
32:CHS
1750::
1718:2.
1713:KB
1706:1.
1681:.
1677:.
1651:.
1647:.
1636:^
1618:.
1614:.
1603:^
1594:.
1575:.
1571:.
1551:.
1532:.
1528:.
1500:.
1475:.
1471:.
1443:.
1439:.
1411:.
1382:.
1357:.
1340:^
1331:.
1312:.
1283:.
1253:.
1249:.
1223:.
1219:.
1206:^
1181:^
1167:.
951::
917:A
908:,
904:,
704:.
671:,
661:.
635:MB
627:MB
606:MB
573:MB
564:GB
511:GB
499:MB
493:MB
447:MB
443:GB
438:GB
432:MB
424:MB
303:.
38:.
1693:.
1663:.
1630:.
1511:.
1394:.
1368:.
1295:.
1269:.
1235:.
1200:.
967:;
929:/
912:)
910:s
906:h
902:c
900:(
892:N
883:N
878:A
862:,
859:)
856:1
850:s
847:(
844:+
838:s
835:r
832:o
829:t
826:c
823:e
820:s
815:N
808:)
805:h
802:+
796:s
793:d
790:a
787:e
784:h
779:N
772:c
769:(
766:=
763:A
742:(
698:H
695:C
689:H
686:C
393:/
385:(
379:0
370:S
367:H
364:C
280:H
263:H
260:C
197:1
67:0
30:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.