222:
372:
41:
29:
333:, affecting approximately 7% of all births. It is characterized by a failure of the cytotrophoblast to invade the uterus and its vasculature, specifically the spiral arteries that the endovascular cytotrophoblast should invade. The result of this is decreased blood flow to the fetus which may cause
316:
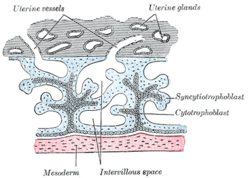
Proper cytotrophoblast function is essential in the implantation of a blastocyst. After hatching, the embryonic pole of the blastocyst faces the uterine endometrium. Once they make contact the trophoblast begins to rapidly proliferate. The cytotrophoblast secretes proteolytic enzymes to break down
317:
the extracellular matrix between the endometrial cells to allow finger-like projections of trophoblast to penetrate through. Projections of cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast pull the embryo into the endometrium until it is fully covered by endometrial epithelium, save for the
241:. An undifferentiated cytotrophoblastic stem cell will differentiate into an extravillous cytotrophoblast intermediate and then into an interstitial cytotrophoblast. An interstitial cytotrophoblast may then further differentiate into an endovascular cytotrophoblast or form a
280:. Although these invasive interstitial cytotrophoblasts can no longer divide, they retain their ability to form syncytia. Multinucleated giant cells (small syncytia) are found in the placental bed and myometrium as a result of the fusion of interstitial cytotrophoblasts.
184:
is from the fusion of two or more cytotrophoblasts via this fusion pathway. This pathway is important because the syncytiotrophoblast plays an important role in fetal-maternal gas exchange, nutrient exchange, and immunological and metabolic functions.
160:
because the layer surrounding the blastocyst remains while daughter cells differentiate and proliferate to function in multiple roles. There are two lineages that cytotrophoblastic cells may differentiate through: fusion and
497:
Cronier, L., Alsat, E., Hervé, J. C., Delèze, J., & Malassiné, A. (1998). "Dexamethasone stimulates gap junctional communication, peptide hormone production and differentiation of human term trophoblast."
587:
192:, and will eventually coalesce into villous syncytiotrophoblast. The formation of syncytiotrophoblast from cytotrophoblast is a terminal differentiation step of trophoblastic cells.
302:. This changes the phenotype of these cells from epithelial to endothelial. Endovascular cytotrophoblasts, like their interstitial predecessor, are non-proliferating and invasive.
484:
Dakour, J., Li, H., Chen, H., & Morrish, D. W. (1999). "EGF promotes development of a differentiated trophoblast phenotype having c-myc and junB proto-oncogene activation."
371:
580:
110:
573:
560:
253:
The primary function of an interstitial cytotrophoblast is to anchor the growing fetus to the maternal uterine tissue. These cells may invade the whole
98:
511:
Yang, M., Lei, Z. M., & Rao, Ch. V. (2003). "The central role of human chorionic gonadotropin in the formation of human placental syncytium."
188:
An undifferentiated cytotrophoblastic stem cell will differentiate into a villous cytotrophoblast, which is what constitutes primary
334:
273:
237:
The invasive lineage creates cytotrophoblasts that are essential in the process of implantation and forming a fully functional
537:
Genbacev, O., DiFederico, E., McMaster, M., & Fisher, S. (1999). "Invasive cytotrophoblast apoptosis in pre-eclampsia."
105:
210:
311:
169:
165:. The fusion lineage yields syncytiotrophoblast and the invasive lineage yields interstitial cytotrophoblast cells.
93:
625:
162:
450:
Bischof, P; Irminger-Finger, I (January 2005). "The human cytotrophoblastic cell, a mononuclear chameleon".
202:
752:
117:
61:
557: – Histology Learning System at Boston University - "Female Reproductive System: placental villi"
318:
221:
747:
783:
620:
377:
Section through embryonic area of
Vespertilio murinus to show the formation of the amniotic cavity.
181:
146:
653:
703:
467:
427:
353:
693:
602:
554:
459:
417:
409:
762:
668:
649:
357:
230:
226:
189:
56:
757:
698:
688:
680:
642:
422:
397:
338:
206:
352:
Conversely, if there is too much invasion of uterine tissue by the trophoblast then a
268:, they lose their ability to proliferate and become invasive. This departure from the
777:
330:
292:
283:
Interstitial cytotrophoblasts may also transform into endovascular cytotrophoblasts.
565:
663:
291:
The primary function of the endovascular cytotrophoblast is to penetrate maternal
463:
610:
398:"New insights into the regulation of human cytotrophoblast cell differentiation"
342:
254:
138:
742:
413:
269:
258:
150:
295:
and route the blood flow through the placenta for the growing embryo to use.
632:
299:
242:
157:
471:
431:
337:. Clinical symptoms of pre-eclampsia in the mother are most commonly high
721:
238:
197:
264:
Once these cells penetrate through the first few layers of cells of the
123:
726:
637:
277:
265:
658:
346:
298:
They arise from interstitial cytotrophoblasts from the process of
220:
81:
40:
28:
569:
452:
528:(pp. 53, 4th Ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone.
195:
Syncytialization of cytotrophoblastic cells can be induced
156:
The cytotrophoblast is considered to be the trophoblastic
168:
Cytotrophoblastic cells play an important role in the
145:) or the cells that live there. It is interior to the
735:
714:
679:
601:
104:
92:
80:
75:
67:
55:
50:
21:
137:is the name given to both the inner layer of the
201:through multiple signalling molecules including
581:
8:
588:
574:
566:
39:
27:
445:
443:
441:
421:
45:Secondary chorionic villi. Diagrammatic.
388:
367:
329:The most common associated disorder is
121:
33:Primary chorionic villi. Diagrammatic.
18:
7:
402:Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology
272:seems to be due to factors such as
14:
596:Membranes of the fetus and embryo
370:
149:and external to the wall of the
335:intrauterine growth restriction
257:and the proximal third of the
1:
396:Handwerger, S (8 July 2010).
464:10.1016/j.biocel.2004.05.014
287:Endovascular cytotrophoblast
249:Interstitial cytotrophoblast
211:human chorionic gonadotropin
172:of an embryo in the uterus.
312:Implantation (human embryo)
802:
309:
555:Histology image: 19908loa
526:Larsen's Human Embryology
524:Schoenwolf, G.C. (2009).
414:10.1016/j.mce.2009.12.015
116:
38:
26:
626:Intermediate trophoblast
153:in a developing embryo.
203:epidermal growth factor
234:
118:Anatomical terminology
224:
180:The formation of all
325:Associated disorders
306:Role in implantation
225:Histopathology of a
753:Reichert's membrane
621:Syncytiotrophoblast
182:syncytiotrophoblast
147:syncytiotrophoblast
654:Intervillous space
539:Human Reproduction
502:. Res., 11, 35–49.
235:
111:83042 83039, 83042
16:Layer of an embryo
771:
770:
748:Heuser's membrane
561:Diagram at McGill
515:, 144, 1108–1120.
364:Additional images
354:hydatidiform mole
143:layer of Langhans
135:"Cytotrophoblast"
132:
131:
127:
87:cytotrophoblastus
791:
694:Umbilical artery
590:
583:
576:
567:
542:
535:
529:
522:
516:
509:
503:
495:
489:
482:
476:
475:
447:
436:
435:
425:
393:
374:
319:coagulation plug
227:chorionic villus
217:Invasive lineage
124:edit on Wikidata
99:E6.0.1.1.4.0.5
43:
31:
19:
801:
800:
794:
793:
792:
790:
789:
788:
774:
773:
772:
767:
763:Gestational sac
731:
710:
704:Wharton's jelly
675:
650:Chorionic villi
616:Cytotrophoblast
597:
594:
551:
546:
545:
536:
532:
523:
519:
510:
506:
496:
492:
483:
479:
449:
448:
439:
395:
394:
390:
385:
378:
375:
366:
358:choriocarcinoma
327:
314:
308:
293:spiral arteries
289:
251:
231:tubal pregnancy
219:
207:glucocorticoids
190:chorionic villi
178:
128:
46:
34:
22:Cytotrophoblast
17:
12:
11:
5:
799:
798:
795:
787:
786:
776:
775:
769:
768:
766:
765:
760:
758:Vitelline duct
755:
750:
745:
739:
737:
733:
732:
730:
729:
724:
718:
716:
712:
711:
709:
708:
707:
706:
701:
699:Umbilical vein
696:
689:Umbilical cord
685:
683:
677:
676:
674:
673:
672:
671:
666:
656:
647:
646:
645:
643:Decidual cells
635:
630:
629:
628:
623:
618:
607:
605:
599:
598:
595:
593:
592:
585:
578:
570:
564:
563:
558:
550:
549:External links
547:
544:
543:
530:
517:
504:
490:
488:, 20, 119–126.
477:
437:
387:
386:
384:
381:
380:
379:
376:
369:
365:
362:
339:blood pressure
326:
323:
310:Main article:
307:
304:
288:
285:
250:
247:
218:
215:
177:
176:Fusion lineage
174:
130:
129:
120:
114:
113:
108:
102:
101:
96:
90:
89:
84:
78:
77:
73:
72:
69:
65:
64:
59:
57:Carnegie stage
53:
52:
48:
47:
44:
36:
35:
32:
24:
23:
15:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
797:
796:
785:
782:
781:
779:
764:
761:
759:
756:
754:
751:
749:
746:
744:
741:
740:
738:
734:
728:
725:
723:
720:
719:
717:
713:
705:
702:
700:
697:
695:
692:
691:
690:
687:
686:
684:
682:
678:
670:
667:
665:
662:
661:
660:
657:
655:
651:
648:
644:
641:
640:
639:
636:
634:
631:
627:
624:
622:
619:
617:
614:
613:
612:
609:
608:
606:
604:
600:
591:
586:
584:
579:
577:
572:
571:
568:
562:
559:
556:
553:
552:
548:
540:
534:
531:
527:
521:
518:
514:
513:Endocrinology
508:
505:
501:
494:
491:
487:
481:
478:
473:
469:
465:
461:
457:
453:
446:
444:
442:
438:
433:
429:
424:
419:
415:
411:
408:(1): 94–104.
407:
403:
399:
392:
389:
382:
373:
368:
363:
361:
359:
355:
350:
348:
344:
340:
336:
332:
331:pre-eclampsia
324:
322:
320:
313:
305:
303:
301:
296:
294:
286:
284:
281:
279:
275:
271:
267:
262:
260:
256:
248:
246:
244:
240:
232:
228:
223:
216:
214:
212:
208:
204:
200:
199:
193:
191:
186:
183:
175:
173:
171:
166:
164:
159:
154:
152:
148:
144:
141:(also called
140:
136:
125:
119:
115:
112:
109:
107:
103:
100:
97:
95:
91:
88:
85:
83:
79:
74:
70:
66:
63:
60:
58:
54:
49:
42:
37:
30:
25:
20:
615:
541:, 14, 59-66.
538:
533:
525:
520:
512:
507:
499:
493:
485:
480:
455:
451:
405:
401:
391:
351:
328:
315:
300:phenocopying
297:
290:
282:
263:
252:
236:
196:
194:
187:
179:
170:implantation
167:
155:
142:
134:
133:
86:
715:Circulatory
611:Trophoblast
458:(1): 1–16.
360:may arise.
343:proteinuria
255:endometrium
139:trophoblast
76:Identifiers
784:Embryology
743:Blastocoel
383:References
270:cell cycle
259:myometrium
151:blastocyst
633:Allantois
243:syncytium
158:stem cell
778:Category
722:Placenta
500:Trophobl
486:Placenta
472:15381142
432:20036312
239:placenta
198:in vitro
163:invasive
727:Chorion
638:Decidua
423:2874088
278:decorin
266:decidua
229:, in a
51:Details
669:cavity
659:Amnion
603:Embryo
470:
430:
420:
209:, and
736:Other
681:Fetus
347:edema
274:TGF-β
122:[
82:Latin
468:PMID
428:PMID
345:and
276:and
68:Days
664:sac
460:doi
418:PMC
410:doi
406:323
356:or
106:FMA
780::
466:.
456:37
454:.
440:^
426:.
416:.
404:.
400:.
349:.
341:,
321:.
261:.
245:.
213:.
205:,
94:TE
62:5a
652:/
589:e
582:t
575:v
474:.
462::
434:.
412::
233:.
126:]
71:8
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.