368:. Typically, the APC responsible is a dendritic cell. If the antigen expresses appropriate molecular patterns (sometimes known as signal 0), it can induce maturation of the dendritic cell which results in enhanced expression of costimulatory molecules needed to activate T cells (see signal 2) and MHC Class II. Once at the lymph nodes, the APCs begin to present antigen peptides that are bound to Class II MHC, allowing CD4 T cells that express the specific TCRs against the peptide/MHC complex to activate.
332:). MHC Class II binding pockets are flexible with respect to the length of the peptides they hold. Generally, there are 9 core amino acid residues with several flanking amino acids which form a length of about 12–16 amino acids total but have been known to hold as many as 25 amino acids. By comparison, MHC Class I proteins are usually 9-10 peptides long. The activation of naive T cells is commonly explained in terms of the 3-signal model, elaborated upon below.
204:
387:, a co-receptor of the TCR complex, also binds to a different section of the MHC molecule. It is estimated that approximately 50 of these interactions are required for the activation of a helper T cell and assemblies known as microclusters have been observed forming between the TCR-CD3-CD4 complexes of the T cell and the MHC Class II proteins of the dendritic cell at the zone of contact. When these all come together, the CD4 is able to recruit a kinase called
38:
341:
779:
411:. CD45 activates Lck by dephosphorylating a tyrosine in its C-terminal tail, while Csk phosphorylates Lck at that site. The loss of CD45 produces a form of SCID because failure to activate Lck prevents appropriate T cell signaling. Memory T cells also make use of this pathway and have higher levels of Lck expressed and the function of Csk is inhibited in these cells.
485:. As naïve CD8 T cells have no true bias towards foreign sources, these T cells must rely on the activation of CD28 for confirmation that they recognize a foreign antigen (as CD80/CD86 is only expressed by active APC's). CD28 plays an important role in decreasing the risk of T cell auto-immunity against host antigens.
641:) can be essential for a successful outcome from infection. In order to be effective, helper T cells must determine which cytokines will allow the immune system to be most useful or beneficial for the host. Understanding exactly how helper T cells respond to immune challenges is currently of major interest in
1202:(TGF-β) and IL-10. Both cytokines are inhibitory to helper T cells; TGF-β suppresses the activity of most of the immune system. There is evidence to suggest that TGF-β may not suppress activated Th2 cells as effectively as it might suppress naive cells, but it is not typically considered a Th2 cytokine.
1579:
that would normally elicit a helper T cell response to bypass the immune system. While these complete bypass situations only occur when the helper T cell response is absolutely necessary for infection clearance, most infections increase in severity and/or duration because the immune system's helper T
1570:
that could potentially be detected. The depletion of CD4 T cells and the development of chronic inflammation are signature processes in HIV pathogenesis that propel progression to acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). CD4 T cell depleted to the cell count of less than 200cell/μL in blood during
1178:
One major difference between regulatory T cells and effector T cells is that regulatory T cells typically serve to modulate and deactivate the immune response, while effector T cell groups usually begin with immune-promoting cytokines and then switch to inhibitory cytokines later in their life cycle.
441:
activation (CD45RA to CD45RO), but whether this change in length influences activation is unknown. It has been proposed that the larger CD45RA may decrease the accessibility of the T cell receptor for the antigen-MHC molecule, thereby necessitating an increase in the affinity (and specificity) of the
1533:
It has been proposed that during the non-symptomatic phase of HIV infection, the virus has a relatively low affinity towards T cells (and has a higher affinity for macrophages), resulting in a slow kill rate of CD4 T cells by the immune system. This is initially compensated for via the production of
1311:
Considering the diverse and important role helper T cells play in the immune system, it is not surprising that these cells often influence the immune response against disease. They also occasionally generate non-beneficial responses. Very rarely, the helper T cell response could lead to the death of
450:
Having received the first TCR/CD3 signal, the naïve T cell must activate a second independent biochemical pathway, known as Signal 2. This verification step is a protective measure to ensure that a T cell is responding to a foreign antigen. If this second signal is not present during initial antigen
1018:
While we know about the types of cytokine patterns helper T cells tend to produce, we understand less about how the patterns themselves are decided. Various evidence suggests that the type of APC presenting the antigen to the T cell has a major influence on its profile. Other evidence suggests that
488:
Once the naïve T cell has both pathways activated, the biochemical changes induced by Signal 1 are altered, allowing the cell to activate instead of undergoing anergy. The second signal is then obsolete; only the first signal is necessary for future activation. This is also true for memory T cells,
1407:
both involve complications from auto-immune or low affinity antibodies. In both of these reactions, T cells may play an accomplice role in generating these auto-specific antibodies, although some of these reactions under Type 2 hypersensitivity would be considered normal in a healthy immune system
1590:
T cells are not stimulated as effectively during the AIDS stage of HIV infection, making AIDS patients very susceptible to most viruses, including HIV itself. This decline in killing of CD4 T cells results in the virus being produced for a longer period (the infected CD4 T cells are not killed as
1225:
producing cells were initially described as a pathogenic population implicated in autoimmunity but are now thought to have their own distinct effector and regulatory functions. Of note, some evidence suggest that functional plasticity is an intrinsic capacity of T helper cells. Indeed, a study in
1302:
Additional populations of memory T cells are now known to exist. These include tissue-resident memory T (Trm) cells and virtual memory T cells. The single unifying theme for all memory T cell subtypes is that they are long-lived and can expand quickly to large numbers of effector T cells upon
1550:
it binds to during infection), and the immune system is overwhelmed. Studies suggest that only ~5% of the lymphoid-derived CD4 T cells targeted by HIV are permissive and become productively infected with the virus. More than 95% of the CD4 T cells that die are resting and are unable to support
190:
cells are not a monolithic immunological entity because they are diverse in terms of function and their interaction with partner cells. In general, mature naive T cells are stimulated by professional antigen presenting cells to acquire an effector module. These are defined by the presence of a
315:
of the immune system but rather have a non-hematopoietic origin, and in general lack MHC Class II, meaning they are not true professional antigen-presenting cells; however, follicular dendritic cells may acquire MHC Class II proteins via exosomes that become attached to them). T cells require
1393:, focus on suppressing mast cells or other allergic cells; T cells do not play a primary role during the actual inflammatory response. It's important to note that the numeral allocation of hypersensitivity "types" does not correlate (and is completely unrelated) to the "response" in the T
1019:
the concentration of antigen presented to the T cell during primary activation influences its choice. The presence of some cytokines (such as the ones mentioned above) will also influence the response that will eventually be generated, but our understanding is nowhere near complete.
1102:
to apoptose virus-infected cells and to induce host as well as viral DNA fragmentation. IFN alpha/beta can suppress transcription to avoid virus replication and transmission. Overactivation of THαβ against autoantigen will cause type 2 antibody-dependent cytotoxic hypersensitivity.
455:(anergy is generated from the unprotected biochemical changes of Signal 1). Anergic cells will not respond to any antigen in the future, even if both signals are present later on. These cells are generally believed to circulate throughout the body with no value until they undergo
1498:
believes, by mistake, that a host antigen is foreign. As a result, the CD8 T cells treat the host cell presenting that antigen as infected, and go on to destroy all host cells (or in the case of transplant rejection, transplant organ) that express that antigen.
731:. They are triggered by the polarising cytokines IL-4 and IL-2, and their effector cytokines are IL-4, IL-5, IL-9, IL-10, IL-13 and IL-25. The main effector cells are eosinophils, basophils, and mast cells as well as B cells, and IL-4/IL-5 CD4 T cells. The key T
1011:
in helper T cells and IL-12 in dendritic cells and macrophages. The combined action of these two cytokines suggests that once the T cell has decided to produce these cytokines, that decision is preserved (and also encourages other T cells to do the same).
1626:
Inhibition of CD4 T-cell expansion during HIV infection may occur due to microbial translocation in an IL-10-dependent way. Triggering PD-1 expressed on activated monocytes by its ligand PD-L1, induces IL-10 production which inhibits CD4 T-cell function.
1446:
and cytokine release. Antibodies do not play a direct role in this allergy type. T cells play an important role in this hypersensitivity, as they activate against the stimulus itself and promote the activation of other cells; particularly macrophages via
1290:
Historically, memory T cells were thought to belong to either the effector or central memory subtypes, each with their own distinguishing set of cell surface markers. Central memory T cells reside in the lymph nodes while effector memory T cells lack the
1331:
The immune system must achieve a balance of sensitivity in order to respond to foreign antigens without responding to the antigens of the host itself. When the immune system responds to very low levels of antigen that it usually shouldn't respond to, a
195:, though the term has been criticized for being too reductive). The loss of function in a lineage specifying transcription factor results in the absence of the corresponding class of helper T cell which can be devastating for the health of the host.
1174:
subset of helper T cells. Terms such as "regulatory" and "suppression" have become ambiguous after the discovery that helper CD4 T cells are also capable of regulating (and suppressing) their own responses outside of dedicated regulatory T cells.
1551:
productive infection. These cells undergo abortive infection with HIV. Cell death is triggered when the host cell detects HIV foreign DNA intermediates and initiates a suicidal death pathway in an attempt to protect the host, leading to
616:
generated a murine monoclonal antibody, 5c8 that inhibited contact-dependent T cell helper function in human cells which characterized the 32 kDa surface protein transiently expressed on CD4 T cells. Richard
Armitage at
2756:
Toscano MA, Bianco GA, Ilarregui JM, Croci DO, Correale J, Hernandez JD, et al. (August 2007). "Differential glycosylation of TH1, TH2 and TH-17 effector cells selectively regulates susceptibility to cell death".
235:). Of note, only a very small minority of T cells egresses from the thymus (estimates commonly range from 1–5% but some experts feel even this is generous). Maturation of RTE in SLO results in the generation of mature
2985:
Harrington LE, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Turner H, Murphy TL, Murphy KM, Weaver CT (November 2005). "Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages".
1597:
declines significantly once helper T cell function fails. The immune system loses its ability to improve the affinity of their antibodies, and are unable to generate B cells that can produce antibody groups such as
755:, and leukotriene to cause broncho-constriction, intestinal peristalsis, gastric fluid acidification to expel helminths. IL-5 from CD4 T cells will activate eosinophils to attack helminths. IL-10 suppresses T
1610:
2 cytokines (and less interactions by helper T cells). All of these complications result in an increased susceptibility to aggressive bacterial infections, especially in areas of the body not accessible by
1606:. These effects are primarily due to the loss of any helper T cell that can interact with the B lymphocyte correctly. Another symptom of AIDS is the reduction in antibody levels due to a decrease in T
1249:
2 model is enlightening and gives insight into the functions of helper T cells, it is far too simple to define its entire role or actions. Some immunologists question the model completely, as some
275:
complex. The T cell receptor (TCR) consists of both constant and variable regions. The variable region determines what antigen the T cell can respond to. CD4 T cells have TCRs with an affinity for
700:
1 transcription factors are STAT4 and T-bet. IFN-γ secreted by CD4 T cells can activate macrophages to phagocytose and digest intracellular bacteria and protozoa. In addition, IFN-γ can activate
1566:
At this point chronic inflammation ensues, and functional CD4 T cell levels begin to decrease, eventually to a point where the CD4 T cell population is too small to recognize the full range of
767:
which is an allergic reaction mediated by IgE. Allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, and asthma belong to this category of overactivation . In addition to expressing different cytokines, T
692:), typically against intracellular bacteria and protozoa. They are triggered by the polarising cytokine IL-12 and their effector cytokines are IFN-γ and IL-2. The main effector cells of T
481:
Although the verification stage is necessary for the activation of naïve helper T cells, the importance of this stage is best demonstrated during the similar activation mechanism of CD8
1412:
during child-birth is a normal immune response against child antigens). The understanding of the role of helper T cells in these responses is limited but it is generally thought that T
1623:
they will succumb usually to either cancers or infections; the immune system finally reaches a point where it is no longer coordinated or stimulated enough to deal with the disease.
3537:
403:
and then itself becomes phosphorylated, wherein it orchestrates the downstream signaling required for T cell activation. Lck activation is controlled by the opposing actions of
1261:
model has still played an important part in developing our understanding of the roles and behaviour of helper T cells and the cytokines they produce during an immune response.
4214:
1696:
433:
It is unknown what role the relatively bulky extracellular region of CD45 plays during cell interactions, but CD45 has various isoforms that change in size depending on the T
2440:
Armitage RJ, Fanslow WC, Strockbine L, Sato TA, Clifford KN, Macduff BM, et al. (May 1992). "Molecular and biological characterization of a murine ligand for CD40".
3276:"CD4 virtual memory: Antigen-inexperienced T cells reside in the naïve, regulatory, and memory T cell compartments at similar frequencies, implications for autoimmunity"
1241:
Many of the cytokines in this article are also expressed by other immune cells (see individual cytokines for details), and it is becoming clear that while the original T
1147:
subsets in humans. Human IL-10 (hIL-10) suppresses the proliferation and cytokine production of all T cells and the activity of macrophages, but continues to stimulate
3080:"Multiparameter grouping delineates heterogeneous populations of human IL-17 and/or IL-22 T-cell producers that share antigen specificities with other T-cell subsets"
3223:
Sallusto F, Lenig D, Förster R, Lipp M, Lanzavecchia A (October 1999). "Two subsets of memory T lymphocytes with distinct homing potentials and effector functions".
1506:, where both antibodies and immune cells are known to play a role in the pathology. Generally the immunology of most auto-immune diseases is not well understood.
392:
1099:
132:
for those cytokines. These cells help polarize the immune response depending on the nature of the immunological insult (for example; virus vs. extracellular
613:
442:
T cell for activation. However, once the activation has occurred, CD45 shortens, allowing easier interactions and activation as an effector T helper cell.
128:
cells contain and release cytokines to aid other immune cells. Cytokines are small protein mediators that alter the behavior of target cells that express
112:
cells that express the surface protein CD4. Genetic variation in regulatory elements expressed by CD4 cells determines susceptibility to a broad class of
2828:"Interleukin-10 production by Th1 cells requires interleukin-12-induced STAT4 transcription factor and ERK MAP kinase activation by high antigen dose"
207:
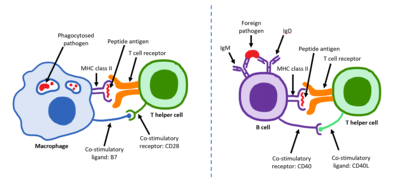
T-cell dependent B-cell activation, showing TH2-cell (left) B-cell (right) and several interaction molecules self-made according to
Janeway et al,
4207:
493:. Faster responses occur upon reinfection because memory T cells have already undergone confirmation and can produce effector cells much sooner.
1691:
2080:"The Length Distribution of Class I-Restricted T Cell Epitopes Is Determined by Both Peptide Supply and MHC Allele-Specific Binding Preference"
3844:
2809:
2136:
1303:
encountering their cognate antigen. By this mechanism they provide the immune system with "memory" against previously encountered pathogens.
3545:
1681:
1321:
4063:
4200:
799:
525:
or IL-2R), enabling a fully functional receptor that can bind with IL-2, which in turn activates the T cell's proliferation pathways.
747:
2 cells differentiation. Besides, IL-4 stimulates B-cells to produce IgE antibodies, which in turn stimulate mast cells to release
3758:"Transcriptional and epigenetic control of T helper cell specification: molecular mechanisms underlying commitment and plasticity"
2393:"Identification of a novel surface protein on activated CD4+ T cells that induces contact-dependent B cell differentiation (help)"
4546:
4099:
1992:
Unanue ER, Turk V, Neefjes J (May 2016). "Variations in MHC Class II Antigen
Processing and Presentation in Health and Disease".
1072:
17 cells are especially good at fighting extracellular pathogens and fungi, particularly during mucocutaneous immunity against
807:
704:(inducible nitric oxide synthase) to produce nitric oxide free radicals to directly kill intracellular bacteria and protozoa. T
427:
244:
4541:
2029:"Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Class I and MHC Class II Proteins: Conformational Plasticity in Antigen Presentation"
81:
775:
1 cells in their cell surface glycans (oligosaccharides), which makes them less susceptible to some inducers of cell death.
4484:
4022:
1292:
1162:
There are also other types of T cells that can influence the expression and activation of helper T cells, such as natural
665:
Proliferating helper T cells that develop into effector T cells differentiate into two major subtypes of cells known as T
4678:
4144:
4114:
4094:
3568:"Programmed death-1-induced interleukin-10 production by monocytes impairs CD4+ T cell activation during HIV infection"
4132:
4127:
3967:
1155:
2 response in humans, but acts to prevent over-stimulation of helper T cells while still maximising the production of
633:
Helper T cells are capable of influencing a variety of immune cells, and the T cell response generated (including the
408:
2493:"A 39-kDa protein on activated helper T cells binds CD40 and transduces the signal for cognate activation of B cells"
4370:
304:
4673:
3837:
988:, an important cytokine associated with the Type 2 response, and thus it also acts to preserve its own response.
622:
474:(B7.2) on the professional APCs. Both CD80 and CD86 activate the CD28 receptor. These proteins are also known as
224:
1636:
1594:
1491:
1400:
953:
709:
645:, because such knowledge may be very useful in the treatment of disease and in increasing the effectiveness of
1522:(HIV) infection. HIV mainly targets lymphoid CD4 T cells, but can infect other cells that express CD4 such as
1502:
Some of this section is a simplification. Many auto-immune diseases are more complex. A well-known example is
1086:
THαβ helper cells provide the host immunity against viruses. Their differentiation is triggered by IFN α/β or
3930:
1238:. A subsequent study furthermore showed that extensive T helper cell plasticity is also prominent in humans.
4688:
4550:
4308:
4171:
1894:
van den Broek T, Delemarre EM, Janssen WJ, Nievelstein RA, Broen JC, Tesselaar K, et al. (March 2016).
1576:
1427:
1404:
1351:
791:
764:
353:
284:
160:
129:
1546:(or T-tropic) however, it begins to infect CD4 T cells far more efficiently (likely due to a change in the
1253:
studies suggest that individual helper T cells usually do not match the specific cytokine profiles of the T
4668:
4572:
4290:
4226:
4014:
1663:
clearance. Despite the reduced levels of CD4, COVID-19 patients with severe disease had higher levels of T
1620:
931:
681:
608:
In 1991, three groups reported discovering CD154, which is the molecular basis of T cell helper function.
490:
70:
1583:
Two components of the immune system are particularly affected in AIDS, due to its CD4 T cell dependency:
1486:
The mechanism that killer T cells use during auto-immunity is almost identical to their response against
4663:
4519:
4375:
4353:
4053:
4030:
4006:
1183:
3 cells, which transform into a regulatory subset after its initial activation and cytokine production.
1151:, ensuring that antibody production still occurs. As such, hIL-10 is not believed to truly promote the T
945:
701:
324:
on MHC Class II (in the case of helper T cells because they express CD4) or MHC class I (in the case of
260:
256:
1716:
Burren OS, Rubio García A, Javierre BM, Rainbow DB, Cairns J, Cooper NJ, et al. (September 2017).
1467:. Helper T cells are required to fuel the development of these diseases. In order to create sufficient
4653:
4648:
4536:
4469:
4380:
4304:
4077:
3894:
3830:
3442:
3385:
3232:
2504:
2449:
1591:
quickly), increasing the proliferation of the virus, and accelerating the development of the disease.
1503:
1464:
317:
4192:
1475:
must be produced, and this is supplied by CD4 T cells. CD4 T cells can also stimulate cells such as
4658:
4596:
4531:
4514:
4348:
4266:
4086:
3925:
3091:
2972:
Microarray analysis of PBMC gene expression profiles after
Plasmodium falciparum malarial infection
2027:
Wieczorek M, Abualrous ET, Sticht J, Álvaro-Benito M, Stolzenberg S, Noé F, Freund C (2017-03-17).
1656:
1644:
1476:
1460:
1417:
1341:
1094:
as well as CD8 T cells, IgG B cells, and IL-10 CD4 T cells. The key THαβ transcription factors are
1091:
625:
generated an antibody that bound a 39 kDa protein on murine T cells and inhibited helper function.
171:
proteins, a CD4 cell will aid those cells through a combination of cell to cell interactions (e.g.
1851:
van den Broek T, Borghans JA, van Wijk F (June 2018). "The full spectrum of human naive T cells".
976:
by dendritic cells and macrophages, and via positive feedback, IL-12 stimulates the production of
621:
cloned a cDNA encoding CD154 by screening an expression library with CD40-Ig. Randolph Noelle at
4683:
4416:
4058:
4045:
3815:
3256:
3205:
3113:
3011:
2952:
2782:
2555:"Thymic and Postthymic Regulation of Naïve CD4(+) T-Cell Lineage Fates in Humans and Mice Models"
2473:
2185:
1876:
1494:. Cellular auto-immune disease occurs because the host antigen recognition systems fail, and the
1187:
1163:
361:
113:
85:
3325:"Abortive HIV infection mediates CD4 T cell depletion and inflammation in human lymphoid tissue"
2293:
Courtney AH, Shvets AA, Lu W, Griffante G, Mollenauer M, Horkova V, et al. (October 2019).
1108:
696:
1 immunity are macrophages as well as CD8 T cells, IgG B cells, and IFN-γ CD4 T cells. The key T
203:
2709:"Glycans in the immune system and The Altered Glycan Theory of Autoimmunity: a critical review"
1676:
383:
complex binds strongly to the peptide-MHC complex present on the surface of professional APCs.
303:(at all times). Some APCs also bind native (or unprocessed) antigens to their surface, such as
4464:
4230:
4109:
3990:
3909:
3889:
3787:
3744:
3690:
3649:
3597:
3519:
3468:
3411:
3354:
3305:
3248:
3197:
3162:
3105:
3060:
3003:
2944:
2909:
2857:
2805:
2774:
2738:
2689:
2640:
2586:
2532:
2465:
2422:
2373:
2324:
2275:
2234:
2177:
2142:
2132:
2109:
2078:
Trolle T, McMurtrey CP, Sidney J, Bardet W, Osborn SC, Kaever T, et al. (February 2016).
2060:
2009:
1974:
1925:
1868:
1833:
1798:
1769:"Master regulators or lineage-specifying? Changing views on CD4+ T cell transcription factors"
1749:
1359:
1104:
155:. CD4 T cells are generally treated as having a pre-defined role as helper T cells within the
37:
3431:"IFI16 DNA sensor is required for death of lymphoid CD4 T cells abortively infected with HIV"
1659:
admission, and CD4 cell count was the only parameter that predicted length of time for viral
4643:
4584:
4524:
4496:
4491:
4459:
4446:
4436:
3982:
3958:
3777:
3769:
3734:
3726:
3680:
3639:
3631:
3587:
3579:
3509:
3499:
3458:
3450:
3401:
3393:
3344:
3336:
3323:
Doitsh G, Cavrois M, Lassen KG, Zepeda O, Yang Z, Santiago ML, et al. (November 2010).
3295:
3287:
3240:
3189:
3152:
3144:
3095:
3050:
3042:
2995:
2936:
2927:
Tangye SG, Puel A (2023). "The Th17/IL-17 Axis and Host
Defense Against Fungal Infections".
2899:
2891:
2847:
2839:
2766:
2728:
2720:
2707:
Maverakis E, Kim K, Shimoda M, Gershwin ME, Patel F, Wilken R, et al. (February 2015).
2679:
2671:
2630:
2622:
2576:
2566:
2522:
2512:
2457:
2412:
2404:
2363:
2355:
2314:
2306:
2265:
2224:
2216:
2169:
2099:
2091:
2050:
2040:
2001:
1964:
1956:
1915:
1907:
1860:
1825:
1788:
1780:
1739:
1729:
1686:
1651:
counts decline, but both CD4 and CD8 cells decline to a far greater extent. Indicating that
1612:
1603:
1599:
1587:
1480:
1456:
1431:
1333:
1206:
1074:
1037:
1032:
1008:
977:
969:
879:
856:
724:
689:
557:
482:
380:
345:
325:
192:
89:
1420:(SLE) and other auto-immune diseases of similar nature can be linked to the production of T
4479:
3974:
3773:
3618:
Huang W, Berube J, McNamara M, Saksena S, Hartman M, Arshad T, et al. (August 2020).
3274:
Marusina AI, Ono Y, Merleev AA, Shimoda M, Ogawa H, Wang EA, et al. (February 2017).
3078:
Larsen M, Arnaud L, Hié M, Parizot C, Dorgham K, Shoukry M, et al. (September 2011).
2220:
2005:
1829:
1527:
1386:
1191:
1167:
451:
exposure, the T cell presumes that it is auto-reactive. This results in the cell becoming
376:
300:
288:
268:
3094:
Institut
National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (Inserm) UMR-S 945: 2596–2605.
803:
437:
cell's activation and maturation status. For example, CD45 shortens in length following T
414:
The binding of the antigen-MHC to the TCR complex and CD4 may also help the APC and the T
3446:
3389:
3372:
Doitsh G, Galloway NL, Geng X, Yang Z, Monroe KM, Zepeda O, et al. (January 2014).
3236:
2508:
2453:
223:, these cells (termed recent thymic emigrants (RTE)) egress from the thymus and home to
4506:
4451:
4392:
4312:
4285:
3782:
3757:
3739:
3714:
3644:
3619:
3592:
3567:
3514:
3487:
3463:
3430:
3406:
3373:
3349:
3324:
3300:
3275:
3157:
3132:
3055:
3030:
2904:
2879:
2852:
2827:
2733:
2708:
2684:
2659:
2635:
2610:
2581:
2554:
2417:
2392:
2368:
2343:
2319:
2294:
2229:
2204:
2104:
2079:
2055:
2028:
1969:
1944:
1920:
1896:"Neonatal thymectomy reveals differentiation and plasticity within human naive T cells"
1895:
1793:
1768:
1744:
1717:
1222:
1140:
1087:
1065:
1061:
1057:
1000:
973:
921:
917:
891:
581:
475:
321:
312:
172:
137:
3429:
Monroe KM, Yang Z, Johnson JR, Geng X, Doitsh G, Krogan NJ, Greene WC (January 2014).
2826:
Saraiva M, Christensen JR, Veldhoen M, Murphy TL, Murphy KM, O'Garra A (August 2009).
1718:"Chromosome contacts in activated T cells identify autoimmune disease candidate genes"
778:
4637:
4474:
4363:
4181:
4163:
4001:
3884:
2956:
2527:
2492:
1495:
1472:
1409:
1285:
1269:
1004:
992:
985:
913:
909:
905:
901:
887:
819:
815:
634:
609:
553:
518:
510:
264:
156:
3566:
Said EA, Dupuy FP, Trautmann L, Zhang Y, Shi Y, El-Far M, et al. (April 2010).
3488:"NLRP3 inflammasome induces CD4+ T cell loss in chronically HIV-1-infected patients"
3117:
3029:
Hirota K, Duarte JH, Veldhoen M, Hornsby E, Li Y, Cua DJ, et al. (March 2011).
3015:
2786:
2205:"Molecular control of steady-state dendritic cell maturation and immune homeostasis"
2189:
340:
4441:
4426:
4421:
4358:
4256:
3996:
3899:
3260:
3209:
2477:
1880:
1556:
1468:
1443:
1416:
2 cytokines would promote such disorders. For example, studies have suggested that
1148:
713:
276:
272:
236:
168:
93:
31:
2491:
Noelle RJ, Roy M, Shepherd DM, Stamenkovic I, Ledbetter JA, Aruffo A (July 1992).
2895:
2843:
2626:
2270:
2253:
1483:, encouraging these cytotoxic cells to kill host cells in certain circumstances.
4176:
3879:
3874:
1655:
attacks the CD4 cells during infection. Low CD4 predicted greater likelihood of
1547:
1539:
1523:
1439:
1435:
1390:
1371:
935:
646:
597:
506:
357:
292:
283:. Class II MHC proteins are generally only found on the surface of professional
232:
101:
3730:
3685:
3668:
3486:
Zhang C, Song JW, Huang HH, Fan X, Huang L, Deng JN, et al. (March 2021).
3340:
3291:
2940:
2724:
2497:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
1945:"The ins and outs of MHC class II-mediated antigen processing and presentation"
548:
cells receiving both signals of activation and proliferation will then become T
395:(ITAMs) present on the CD3 gamma, delta, epsilon, and zeta chains. The protein
299:, although dendritic cells are the only cell group that expresses MHC Class II
4564:
4317:
4223:
3853:
3148:
2359:
2310:
2146:
1864:
1734:
1652:
1648:
1560:
1296:
1265:
1264:
Studies by
Stockinger et al. revealed that another T helper subset may exist.
865:
852:
811:
685:
642:
400:
365:
191:
lineage-determining (or lineage-specifying) transcription factor (also called
105:
97:
2675:
2095:
2045:
1490:, and some viruses have been accused of causing auto-immune diseases such as
344:
Antigen presentation stimulates naïve CD8+ and CD4+ T cells to become mature
4622:
4327:
4149:
4104:
3952:
3454:
2517:
2391:
Lederman S, Yellin MJ, Krichevsky A, Belko J, Lee JJ, Chess L (April 1992).
2160:
Guy B (July 2007). "The perfect mix: recent progress in adjuvant research".
1572:
1552:
1385:
2 response during helper T cell development. Preventive treatments, such as
1367:
1299:(CD62L) receptors, which prevents them from trafficking to the lymph nodes.
1257:
model, and many cells express cytokines from both profiles. That said, the T
991:
The Type 2 response promotes its own profile using two different cytokines.
869:
752:
748:
728:
533:
529:
514:
456:
243:
that they are programmed to respond to), but naive T cells now lack or have
180:
74:
17:
3807:
3791:
3748:
3694:
3653:
3601:
3523:
3472:
3415:
3358:
3309:
3252:
3201:
3166:
3109:
3064:
3007:
2948:
2913:
2861:
2778:
2742:
2693:
2644:
2590:
2571:
2408:
2377:
2328:
2279:
2238:
2181:
2113:
2064:
2013:
1978:
1929:
1872:
1837:
1802:
1753:
430:
on the APC are the primary molecules of adhesion in this cell interaction.
279:, and CD4 is involved in determining MHC affinity during maturation in the
3100:
3079:
2536:
2469:
2426:
4612:
4397:
4385:
4343:
4297:
4261:
3918:
3869:
3635:
3374:"Cell death by pyroptosis drives CD4 T-cell depletion in HIV-1 infection"
1378:
1273:
1199:
1156:
957:
883:
638:
573:
133:
3397:
3193:
2173:
673:
2 cells (also known as Type 1 and Type 2 helper T cells, respectively).
4617:
4431:
4280:
4251:
4137:
1567:
1487:
1337:
949:
790:
2 Model for helper T cells. An antigen is ingested and processed by an
544:'s via the IL-2R thus driving proliferation and clonal expansion. The T
296:
240:
164:
3504:
3180:
Tato CM, Cua DJ (December 2008). "Alternative lifestyles of T cells".
1090:. Their key effector cytokine is IL-10. Their main effector cells are
942:
T cells. Also promotes the production of IgG, an opsonizing antibody.
4589:
4577:
4322:
4273:
3940:
3904:
3861:
2461:
1911:
1640:
1535:
1363:
1355:
1098:
and STAT3 as well as IRFs. IL-10 from CD4 T cells activate NK cells'
861:
509:. It achieves this by releasing a potent T cell growth factor called
452:
280:
228:
220:
216:
78:
66:
3583:
3046:
1960:
1784:
3031:"Fate mapping of IL-17-producing T cells in inflammatory responses"
2999:
2770:
1135:
2 model can be more complicated in some animals. For example, the T
30:"Th2" redirects here. For the professional wrestling tag team, see
3244:
1095:
984:
1 profile. IFNγ also inhibits the production of cytokines such as
777:
740:
736:
618:
517:
fashion. Activated T cells also produce the alpha sub-unit of the
423:
404:
396:
202:
176:
36:
1336:
response occurs. Hypersensitivity is believed to be the cause of
247:(reduced) expression of the RTE-related surface markers, such as
3620:"Lymphocyte Subset Counts in COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis"
1816:
Fink PJ (2013-03-21). "The biology of recent thymic emigrants".
1434:, are caused via the over-stimulation of immune cells, commonly
522:
471:
467:
463:
252:
248:
4196:
3826:
501:
Once the two-signal activation is complete the T helper cell (T
3822:
3756:
Kanno Y, Vahedi G, Hirahara K, Singleton K, O'Shea JJ (2012).
1660:
1543:
1519:
1515:
1375:
1044:
are a subset of T helper cells developmentally distinct from T
939:
388:
384:
329:
148:
999:
2 cytokines (including itself; it is auto-regulatory), while
716:
and Type 1 diabetes belong to this category of autoimmunity.
287:(APCs). Professional antigen-presenting cells are primarily
3131:
Nakayamada S, Takahashi H, Kanno Y, O'Shea JJ (June 2012).
1347:
Hypersensitivity reactions can be divided into four types:
759:
1 cells differentiation and function of dendritic cells. T
600:
and carry out many other functions of the immune response.
73:. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing
3715:"Dissecting How CD4 T Cells Are Lost During HIV Infection"
798:
0, is a T helper cell. The fragment is presented to it by
375:
cell encounters and recognizes the antigen on an APC, the
1619:
If the patient does not respond to (or does not receive)
960:
production (IgG, IgM and IgA as well as IgE antibodies).
1205:
The novel characterisation of another T helper subtype,
794:. It presents fragments from it to T cells. The upper, T
360:
antigens (typically bacteria or viruses), which undergo
2929:
Journal of
Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice
1563:(a highly inflammatory form of programmed cell death).
1166:, along with less common cytokine profiles such as the
2880:"Th17 cytokines in mucosal immunity and inflammation"
2660:"GATA3: a master of many trades in immune regulation"
2553:
Belizário JE, Brandão W, Rossato C, Peron JP (2016).
2295:"CD45 functions as a signaling gatekeeper in T cells"
995:
acts on helper T cells to promote the production of T
2873:
2871:
727:, typically against extracellular parasites such as
88:
in dendritic cells, in the activation and growth of
4605:
4563:
4505:
4406:
4336:
4244:
4237:
4162:
4085:
4076:
4044:
3939:
3860:
1697:
List of distinct cell types in the adult human body
239:(naïve meaning they have never been exposed to the
41:
Activation of macrophage or B cell by T helper cell
1060:(IL-17), a pro-inflammatory substance, as well as
1003:(IL-10) inhibits a variety of cytokines including
708:1 overactivation against autoantigens will cause
462:The second signal involves an interaction between
1667:1 CD4 cells than patients with moderate disease.
3669:"COVID-19 poses a riddle for the immune system"
3613:
3611:
2548:
2546:
1272:)–producing T cell subset focused on defending
393:immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs
2344:"Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death"
1580:cells provide less efficient immune response.
1514:Perhaps the best example of the importance of
743:. IL-4 is the positive feedback cytokine for T
4208:
3838:
2800:Rang HP, Dale MM, Riter JM, Moore PK (2003).
1127:The interactions between cytokines from the T
629:Determination of the effector T cell response
364:, then travel from the infection site to the
8:
1575:to escape T cell recognition, thus allowing
763:2 overactivation against antigen will cause
712:or delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction.
588:1 cell production. Conversely, IL-4 drives T
399:can bind these phosphorylated ITAMs via its
2611:"CD4 T cells: fates, functions, and faults"
1767:Oestreich KJ, Weinmann AS (November 2012).
894:production has been reported in activated T
4241:
4215:
4201:
4193:
4082:
3945:
3845:
3831:
3823:
2604:
2602:
2600:
1455:Other cellular hypersensitivities include
980:in helper T cells, thereby promoting the T
422:cell activation, but the integrin protein
3781:
3738:
3684:
3643:
3591:
3513:
3503:
3462:
3405:
3348:
3299:
3156:
3099:
3054:
2974:(Ph.D. thesis). Johns Hopkins University.
2903:
2851:
2732:
2683:
2634:
2580:
2570:
2526:
2516:
2416:
2367:
2318:
2269:
2228:
2103:
2054:
2044:
1968:
1919:
1792:
1743:
1733:
1530:(both groups express CD4 at low levels).
1354:includes common immune disorders such as
1213:17) has cast further doubt on the basic T
536:secretion of IL-2 can bind to that same T
3133:"Helper T cell diversity and plasticity"
934:. Maximizes the killing efficacy of the
824:
552:0 (T helper 0) cells that secrete IL-2,
339:
2254:"Why is there so much CD45 on T cells?"
1708:
1479:and macrophages via cytokines such as
1143:inhibits cytokine production of both T
592:2 cell production and IFN-γ inhibits T
564:0 cells will then differentiate into T
348:and "helper" CD4+ cells respectively .
3774:10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-075058
3492:The Journal of Clinical Investigation
2221:10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-074929
2006:10.1146/annurev-immunol-041015-055420
1900:The Journal of Clinical Investigation
1830:10.1146/annurev-immunol-032712-100010
952:into proliferation, to induce B-cell
354:professional antigen-presenting cells
267:. Like all T cells, they express the
7:
2804:. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.
2397:The Journal of Experimental Medicine
1692:Cancer vaccine targeting CD4 T cells
680:1 helper cells lead to an increased
513:(IL-2) which acts upon itself in an
4064:Mucosal associated invariant T cell
1322:CD4+ T cells and antitumor immunity
938:and the proliferation of cytotoxic
466:on the CD4 T cell and the proteins
77:. They are considered essential in
69:that play an important role in the
3713:Doitsh G, Greene WC (March 2016).
1682:CD4 T cells and antitumor immunity
199:Activation of naive helper T cells
147:cells express the surface protein
25:
2609:Zhu J, Paul WE (September 2008).
1943:Roche PA, Furuta K (April 2015).
4100:Lymphokine-activated killer cell
320:into short fragments which form
136:vs. intracellular bacterium vs.
2884:Current Opinion in HIV and AIDS
1200:transforming growth factor-beta
956:, and to increase neutralizing
255:, Complement Receptor 1 and 2 (
4542:Immunoglobulin class switching
3084:European Journal of Immunology
2203:Hammer GE, Ma A (2013-03-21).
1374:. These reactions all involve
311:the same type of cells as the
1:
3137:Current Opinion in Immunology
2878:Guglani L, Khader SA (2010).
2252:Zamoyska R (September 2007).
1518:T cells is demonstrated with
1432:delayed type hypersensitivity
1293:C-C chemokine receptor type 7
596:2 cells. These cytokines are
4145:Type 3 innate lymphoid cells
4133:Type 2 innate lymphoid cells
4128:Type 1 innate lymphoid cells
4115:Uterine natural killer cells
4095:Cytokine-induced killer cell
2896:10.1097/COH.0b013e328335c2f6
2844:10.1016/j.immuni.2009.05.012
2627:10.1182/blood-2008-05-078154
2271:10.1016/j.immuni.2007.08.009
2162:Nature Reviews. Microbiology
1534:new helper T cells from the
1520:human immunodeficiency virus
1463:, and a similar phenomenon;
1179:The latter is a feature of T
972:increases the production of
808:transforming growth factor β
735:2 transcription factors are
3762:Annual Review of Immunology
2209:Annual Review of Immunology
1994:Annual Review of Immunology
1818:Annual Review of Immunology
928:Immune stimulation promoted
576:environment. IFN-γ drives T
352:During an immune response,
4705:
4371:Polyclonal B cell response
3731:10.1016/j.chom.2016.02.012
3686:10.1038/d41586-020-02379-1
3341:10.1016/j.cell.2010.11.001
3292:10.1016/j.jaut.2016.11.001
2941:10.1016/j.jaip.2023.04.015
2725:10.1016/j.jaut.2014.12.002
1949:Nature Reviews. Immunology
1853:Nature Reviews. Immunology
1773:Nature Reviews. Immunology
1542:). Once the virus becomes
1319:
1283:
1268:are claimed to be an IL9 (
1030:
771:2 cells also differ from T
497:Differentiation (signal 3)
305:follicular dendritic cells
29:
4123:
3948:
3667:Perlman S (August 2020).
3149:10.1016/j.coi.2012.01.014
2559:Mediators of Inflammation
2360:10.1080/01926230701320337
2311:10.1126/scisignal.aaw8151
1865:10.1038/s41577-018-0001-y
1735:10.1186/s13059-017-1285-0
1230:17 cells transform into T
1111:belong to this category.
723:2 helper cells lead to a
225:secondary lymphoid organs
140:vs. fungus vs. protist).
2676:10.1016/j.it.2014.04.002
2096:10.4049/jimmunol.1501721
2046:10.3389/fimmu.2017.00292
1637:coronavirus disease 2019
1595:Antibody class switching
1577:opportunistic infections
1492:Type 1 diabetes mellitus
1226:mice demonstrated that T
954:antibody class switching
623:Dartmouth Medical School
580:1 cell production while
505:) then allows itself to
489:which is one example of
476:co-stimulatory molecules
318:antigens to be processed
285:antigen-presenting cells
263:) and the production of
108:. CD4 cells are mature T
82:antibody class switching
4172:Hematopoietic stem cell
3931:Lymphoplasmacytoid cell
3719:Cell Host & Microbe
3455:10.1126/science.1243640
3280:Journal of Autoimmunity
2713:Journal of Autoimmunity
2518:10.1073/pnas.89.14.6550
2129:Janeway's immunobiology
2033:Frontiers in Immunology
1442:, resulting in chronic
1428:Type 4 hypersensitivity
1410:Rhesus factor reactions
1405:Type 3 hypersensitivity
1352:Type 1 hypersensitivity
765:Type I hypersensitivity
725:humoral immune response
161:antigen-presenting cell
159:. For example, when an
151:and are referred to as
4485:Tolerance in pregnancy
4227:adaptive immune system
2409:10.1084/jem.175.4.1091
2342:Elmore S (June 2007).
932:Cellular immune system
849:Main partner cell type
822:
682:cell-mediated response
349:
346:"cytotoxic" CD8+ cells
212:
120:Structure and function
71:adaptive immune system
42:
4520:Somatic hypermutation
4354:Polyclonal antibodies
4349:Monoclonal antibodies
4078:Innate lymphoid cells
4054:Natural killer T cell
3101:10.1002/eji.201041131
2348:Toxicologic Pathology
2084:Journal of Immunology
1538:(originally from the
1198:produce the cytokine
946:Humoral immune system
781:
572:2 cells depending on
540:cell or neighboring T
391:which phosphorylates
343:
336:Activation (signal 1)
206:
40:
4537:Junctional diversity
4305:Antigen presentation
3636:10.1002/cyto.a.24172
2664:Trends in Immunology
2658:Wan YY (June 2014).
2572:10.1155/2016/9523628
1571:AIDS allows various
1504:rheumatoid arthritis
1477:natural killer cells
1465:transplant rejection
1115:Limitations to the T
968:The Type 1 cytokine
418:cell adhere during T
265:interleukin 8 (IL-8)
92:, and in maximizing
4679:Infectious diseases
4532:V(D)J recombination
4515:Affinity maturation
4267:Antigenic variation
4046:Innate-like T cells
3926:Transitional B cell
3447:2014Sci...343..428M
3398:10.1038/nature12940
3390:2014Natur.505..509D
3237:1999Natur.401..708S
3194:10.1038/ni1208-1323
2509:1992PNAS...89.6550N
2454:1992Natur.357...80A
2174:10.1038/nrmicro1681
2131:. Garland Science.
1657:intensive care unit
1645:natural killer cell
1461:auto-immune disease
1381:, which require a T
1342:auto-immune disease
1068:. This means that T
827:
714:Tuberculin reaction
614:Columbia University
446:Survival (signal 2)
114:autoimmune diseases
27:Type of immune cell
3816:Cardiff University
1316:Antitumor immunity
1188:regulatory T cells
1164:regulatory T cells
876:Cytokines produced
826:Th1/Th2 dichotomy
825:
823:
584:and IL-4 inhibit T
426:on the T cell and
350:
213:
63:CD4-positive cells
43:
4631:
4630:
4559:
4558:
4309:professional APCs
4190:
4189:
4158:
4157:
4072:
4071:
3679:(7821): 345–346.
3624:Cytometry. Part A
3505:10.1172/JCI138861
3441:(6169): 428–432.
3384:(7484): 509–514.
3231:(6754): 708–712.
3035:Nature Immunology
2994:(11): 1123–1132.
2988:Nature Immunology
2811:978-0-443-07145-4
2759:Nature Immunology
2503:(14): 6550–6554.
2305:(604): eaaw8151.
2299:Science Signaling
2138:978-0-8153-4551-0
2127:Murphy K (2017).
1360:allergic rhinitis
1207:T helper 17 cells
1105:Myasthenia gravis
1082:THαβ helper cells
1056:17 cells produce
1016:
1015:
690:cytotoxic T cells
604:Effector function
483:cytotoxic T cells
326:cytotoxic T cells
90:cytotoxic T cells
57:), also known as
16:(Redirected from
4696:
4674:Lymphatic system
4525:Clonal selection
4497:Immune privilege
4492:Immunodeficiency
4447:Cross-reactivity
4437:Hypersensitivity
4242:
4217:
4210:
4203:
4194:
4110:Adaptive NK cell
4083:
3946:
3847:
3840:
3833:
3824:
3819:
3795:
3785:
3752:
3742:
3699:
3698:
3688:
3664:
3658:
3657:
3647:
3615:
3606:
3605:
3595:
3563:
3557:
3556:
3554:
3553:
3544:. Archived from
3534:
3528:
3527:
3517:
3507:
3483:
3477:
3476:
3466:
3426:
3420:
3419:
3409:
3369:
3363:
3362:
3352:
3320:
3314:
3313:
3303:
3271:
3265:
3264:
3220:
3214:
3213:
3177:
3171:
3170:
3160:
3128:
3122:
3121:
3103:
3075:
3069:
3068:
3058:
3026:
3020:
3019:
2982:
2976:
2975:
2967:
2961:
2960:
2935:(6): 1624–1634.
2924:
2918:
2917:
2907:
2875:
2866:
2865:
2855:
2823:
2817:
2815:
2797:
2791:
2790:
2753:
2747:
2746:
2736:
2704:
2698:
2697:
2687:
2655:
2649:
2648:
2638:
2621:(5): 1557–1569.
2606:
2595:
2594:
2584:
2574:
2550:
2541:
2540:
2530:
2520:
2488:
2482:
2481:
2462:10.1038/357080a0
2437:
2431:
2430:
2420:
2403:(4): 1091–1101.
2388:
2382:
2381:
2371:
2339:
2333:
2332:
2322:
2290:
2284:
2283:
2273:
2249:
2243:
2242:
2232:
2200:
2194:
2193:
2157:
2151:
2150:
2124:
2118:
2117:
2107:
2090:(4): 1480–1487.
2075:
2069:
2068:
2058:
2048:
2024:
2018:
2017:
1989:
1983:
1982:
1972:
1940:
1934:
1933:
1923:
1912:10.1172/JCI84997
1906:(3): 1126–1136.
1891:
1885:
1884:
1848:
1842:
1841:
1813:
1807:
1806:
1796:
1764:
1758:
1757:
1747:
1737:
1713:
1481:interferon-gamma
1471:killer T cells,
1457:cytotoxic T cell
1430:, also known as
1334:hypersensitivity
1327:Hypersensitivity
1033:T helper 17 cell
880:Interferon gamma
828:
637:signals such as
558:interferon gamma
491:learned immunity
193:master regulator
65:, are a type of
21:
4704:
4703:
4699:
4698:
4697:
4695:
4694:
4693:
4634:
4633:
4632:
4627:
4601:
4555:
4501:
4480:Clonal deletion
4408:
4402:
4332:
4233:
4221:
4191:
4186:
4154:
4119:
4068:
4040:
4034:
4026:
4018:
4010:
3986:
3978:
3971:
3935:
3913:
3856:
3851:
3806:
3803:
3798:
3755:
3712:
3708:
3706:Further reading
3703:
3702:
3666:
3665:
3661:
3617:
3616:
3609:
3584:10.1038/nm.2106
3572:Nature Medicine
3565:
3564:
3560:
3551:
3549:
3536:
3535:
3531:
3485:
3484:
3480:
3428:
3427:
3423:
3371:
3370:
3366:
3322:
3321:
3317:
3273:
3272:
3268:
3222:
3221:
3217:
3179:
3178:
3174:
3130:
3129:
3125:
3077:
3076:
3072:
3047:10.1038/ni.1993
3028:
3027:
3023:
2984:
2983:
2979:
2969:
2968:
2964:
2926:
2925:
2921:
2877:
2876:
2869:
2825:
2824:
2820:
2812:
2799:
2798:
2794:
2755:
2754:
2750:
2706:
2705:
2701:
2657:
2656:
2652:
2608:
2607:
2598:
2552:
2551:
2544:
2490:
2489:
2485:
2448:(6373): 80–82.
2439:
2438:
2434:
2390:
2389:
2385:
2341:
2340:
2336:
2292:
2291:
2287:
2251:
2250:
2246:
2202:
2201:
2197:
2159:
2158:
2154:
2139:
2126:
2125:
2121:
2077:
2076:
2072:
2026:
2025:
2021:
1991:
1990:
1986:
1961:10.1038/nri3818
1942:
1941:
1937:
1893:
1892:
1888:
1850:
1849:
1845:
1815:
1814:
1810:
1785:10.1038/nri3321
1779:(11): 799–804.
1766:
1765:
1761:
1715:
1714:
1710:
1705:
1673:
1666:
1633:
1609:
1559:, thus causing
1528:dendritic cells
1512:
1450:
1423:
1415:
1396:
1387:corticosteroids
1384:
1329:
1324:
1318:
1309:
1307:Role in disease
1288:
1282:
1260:
1256:
1248:
1244:
1233:
1229:
1221:2 model. These
1220:
1216:
1212:
1195:
1182:
1171:
1154:
1146:
1138:
1134:
1130:
1125:
1122:
1118:
1109:Graves' disease
1084:
1071:
1062:interleukins 21
1055:
1051:
1047:
1042:17 helper cells
1041:
1035:
1029:
1027:17 helper cells
1026:
998:
983:
965:Other functions
897:
843:
836:
797:
789:
785:
774:
770:
762:
758:
746:
734:
722:
707:
699:
695:
679:
672:
668:
663:
660:
656:
631:
606:
595:
591:
587:
579:
571:
567:
563:
551:
547:
543:
539:
504:
499:
448:
440:
436:
421:
417:
374:
338:
322:linear epitopes
313:dendritic cells
289:dendritic cells
269:T cell receptor
201:
189:
146:
127:
122:
111:
86:cross-tolerance
54:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
4702:
4700:
4692:
4691:
4689:Cell signaling
4686:
4681:
4676:
4671:
4666:
4661:
4656:
4651:
4646:
4636:
4635:
4629:
4628:
4626:
4625:
4620:
4615:
4609:
4607:
4603:
4602:
4600:
4599:
4594:
4593:
4592:
4582:
4581:
4580:
4569:
4567:
4561:
4560:
4557:
4556:
4554:
4553:
4544:
4539:
4534:
4529:
4528:
4527:
4522:
4511:
4509:
4507:Immunogenetics
4503:
4502:
4500:
4499:
4494:
4489:
4488:
4487:
4482:
4477:
4472:
4467:
4455:
4454:
4452:Co-stimulation
4449:
4444:
4439:
4434:
4429:
4424:
4419:
4412:
4410:
4404:
4403:
4401:
4400:
4395:
4393:Immune complex
4389:
4388:
4383:
4378:
4373:
4368:
4367:
4366:
4361:
4356:
4351:
4340:
4338:
4334:
4333:
4331:
4330:
4325:
4320:
4315:
4313:Dendritic cell
4301:
4300:
4295:
4294:
4293:
4291:Conformational
4288:
4277:
4276:
4271:
4270:
4269:
4264:
4259:
4248:
4246:
4239:
4235:
4234:
4222:
4220:
4219:
4212:
4205:
4197:
4188:
4187:
4185:
4184:
4179:
4174:
4168:
4166:
4160:
4159:
4156:
4155:
4153:
4152:
4147:
4142:
4141:
4140:
4130:
4124:
4121:
4120:
4118:
4117:
4112:
4107:
4102:
4097:
4091:
4089:
4080:
4074:
4073:
4070:
4069:
4067:
4066:
4061:
4056:
4050:
4048:
4042:
4041:
4039:
4038:
4037:
4036:
4032:
4028:
4024:
4020:
4016:
4012:
4008:
3999:
3994:
3984:
3976:
3969:
3961:
3955:
3949:
3943:
3937:
3936:
3934:
3933:
3928:
3923:
3922:
3921:
3911:
3907:
3902:
3897:
3892:
3887:
3882:
3877:
3872:
3866:
3864:
3858:
3857:
3852:
3850:
3849:
3842:
3835:
3827:
3821:
3820:
3808:"T-cell Group"
3802:
3801:External links
3799:
3797:
3796:
3753:
3725:(3): 280–291.
3709:
3707:
3704:
3701:
3700:
3659:
3630:(8): 772–776.
3607:
3578:(4): 452–459.
3558:
3529:
3478:
3421:
3364:
3335:(5): 789–801.
3315:
3266:
3215:
3188:(12): 1323–5.
3172:
3143:(3): 297–302.
3123:
3070:
3041:(3): 255–263.
3021:
3000:10.1038/ni1254
2977:
2962:
2919:
2890:(2): 120–127.
2867:
2838:(2): 209–219.
2818:
2810:
2792:
2771:10.1038/ni1482
2765:(8): 825–834.
2748:
2699:
2670:(6): 233–242.
2650:
2596:
2542:
2483:
2432:
2383:
2354:(4): 495–516.
2334:
2285:
2264:(3): 421–423.
2244:
2215:(1): 743–791.
2195:
2168:(7): 505–517.
2152:
2137:
2119:
2070:
2019:
2000:(1): 265–297.
1984:
1955:(4): 203–216.
1935:
1886:
1859:(6): 363–373.
1843:
1808:
1759:
1722:Genome Biology
1707:
1706:
1704:
1701:
1700:
1699:
1694:
1689:
1684:
1679:
1672:
1669:
1664:
1632:
1629:
1617:
1616:
1607:
1592:
1555:activation in
1511:
1508:
1453:
1452:
1448:
1425:
1421:
1413:
1408:(for example,
1398:
1394:
1382:
1328:
1325:
1320:Main article:
1317:
1314:
1308:
1305:
1284:Main article:
1281:
1278:
1258:
1254:
1246:
1242:
1231:
1227:
1218:
1214:
1210:
1193:
1180:
1169:
1152:
1144:
1136:
1132:
1128:
1124:
1120:
1116:
1113:
1083:
1080:
1069:
1058:interleukin 17
1053:
1049:
1045:
1039:
1031:Main article:
1028:
1024:
1021:
1014:
1013:
1001:interleukin 10
996:
989:
981:
974:interleukin 12
966:
962:
961:
943:
929:
925:
924:
922:interleukin 13
918:interleukin 10
899:
895:
892:interleukin 10
877:
873:
872:
859:
850:
846:
845:
841:
838:
834:
831:
795:
787:
783:
772:
768:
760:
756:
744:
732:
720:
705:
697:
693:
684:(primarily by
677:
670:
666:
662:
658:
654:
651:
630:
627:
605:
602:
593:
589:
585:
577:
569:
565:
561:
560:(IFN-γ). The T
549:
545:
541:
537:
502:
498:
495:
447:
444:
438:
434:
419:
415:
372:
337:
334:
328:which express
301:constitutively
211:(Berlin, 2002)
200:
197:
187:
179:) and through
173:CD40 (protein)
144:
125:
121:
118:
109:
52:
47:T helper cells
26:
24:
14:
13:
10:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
4701:
4690:
4687:
4685:
4682:
4680:
4677:
4675:
4672:
4670:
4669:Immune system
4667:
4665:
4662:
4660:
4657:
4655:
4652:
4650:
4647:
4645:
4642:
4641:
4639:
4624:
4621:
4619:
4616:
4614:
4611:
4610:
4608:
4604:
4598:
4595:
4591:
4588:
4587:
4586:
4583:
4579:
4576:
4575:
4574:
4571:
4570:
4568:
4566:
4562:
4552:
4548:
4545:
4543:
4540:
4538:
4535:
4533:
4530:
4526:
4523:
4521:
4518:
4517:
4516:
4513:
4512:
4510:
4508:
4504:
4498:
4495:
4493:
4490:
4486:
4483:
4481:
4478:
4476:
4475:Clonal anergy
4473:
4471:
4468:
4466:
4463:
4462:
4461:
4457:
4456:
4453:
4450:
4448:
4445:
4443:
4440:
4438:
4435:
4433:
4430:
4428:
4425:
4423:
4420:
4418:
4414:
4413:
4411:
4405:
4399:
4396:
4394:
4391:
4390:
4387:
4384:
4382:
4379:
4377:
4374:
4372:
4369:
4365:
4364:Microantibody
4362:
4360:
4357:
4355:
4352:
4350:
4347:
4346:
4345:
4342:
4341:
4339:
4335:
4329:
4326:
4324:
4321:
4319:
4316:
4314:
4310:
4306:
4303:
4302:
4299:
4296:
4292:
4289:
4287:
4284:
4283:
4282:
4279:
4278:
4275:
4272:
4268:
4265:
4263:
4260:
4258:
4255:
4254:
4253:
4250:
4249:
4247:
4243:
4240:
4236:
4232:
4228:
4225:
4218:
4213:
4211:
4206:
4204:
4199:
4198:
4195:
4183:
4182:Prolymphocyte
4180:
4178:
4175:
4173:
4170:
4169:
4167:
4165:
4164:Lymphopoiesis
4161:
4151:
4148:
4146:
4143:
4139:
4136:
4135:
4134:
4131:
4129:
4126:
4125:
4122:
4116:
4113:
4111:
4108:
4106:
4103:
4101:
4098:
4096:
4093:
4092:
4090:
4088:
4084:
4081:
4079:
4075:
4065:
4062:
4060:
4057:
4055:
4052:
4051:
4049:
4047:
4043:
4035:
4029:
4027:
4021:
4019:
4013:
4011:
4005:
4004:
4003:
4002:Memory T cell
4000:
3998:
3995:
3992:
3988:
3980:
3972:
3965:
3962:
3960:
3959:Cytotoxic CD8
3956:
3954:
3951:
3950:
3947:
3944:
3942:
3938:
3932:
3929:
3927:
3924:
3920:
3917:
3916:
3915:
3908:
3906:
3903:
3901:
3898:
3896:
3895:Marginal zone
3893:
3891:
3888:
3886:
3883:
3881:
3878:
3876:
3873:
3871:
3868:
3867:
3865:
3863:
3859:
3855:
3848:
3843:
3841:
3836:
3834:
3829:
3828:
3825:
3817:
3813:
3809:
3805:
3804:
3800:
3793:
3789:
3784:
3779:
3775:
3771:
3767:
3763:
3759:
3754:
3750:
3746:
3741:
3736:
3732:
3728:
3724:
3720:
3716:
3711:
3710:
3705:
3696:
3692:
3687:
3682:
3678:
3674:
3670:
3663:
3660:
3655:
3651:
3646:
3641:
3637:
3633:
3629:
3625:
3621:
3614:
3612:
3608:
3603:
3599:
3594:
3589:
3585:
3581:
3577:
3573:
3569:
3562:
3559:
3548:on 2015-04-15
3547:
3543:
3539:
3533:
3530:
3525:
3521:
3516:
3511:
3506:
3501:
3497:
3493:
3489:
3482:
3479:
3474:
3470:
3465:
3460:
3456:
3452:
3448:
3444:
3440:
3436:
3432:
3425:
3422:
3417:
3413:
3408:
3403:
3399:
3395:
3391:
3387:
3383:
3379:
3375:
3368:
3365:
3360:
3356:
3351:
3346:
3342:
3338:
3334:
3330:
3326:
3319:
3316:
3311:
3307:
3302:
3297:
3293:
3289:
3285:
3281:
3277:
3270:
3267:
3262:
3258:
3254:
3250:
3246:
3245:10.1038/44385
3242:
3238:
3234:
3230:
3226:
3219:
3216:
3211:
3207:
3203:
3199:
3195:
3191:
3187:
3183:
3176:
3173:
3168:
3164:
3159:
3154:
3150:
3146:
3142:
3138:
3134:
3127:
3124:
3119:
3115:
3111:
3107:
3102:
3097:
3093:
3092:UPMC Paris 06
3089:
3085:
3081:
3074:
3071:
3066:
3062:
3057:
3052:
3048:
3044:
3040:
3036:
3032:
3025:
3022:
3017:
3013:
3009:
3005:
3001:
2997:
2993:
2989:
2981:
2978:
2973:
2970:Hu W (2007).
2966:
2963:
2958:
2954:
2950:
2946:
2942:
2938:
2934:
2930:
2923:
2920:
2915:
2911:
2906:
2901:
2897:
2893:
2889:
2885:
2881:
2874:
2872:
2868:
2863:
2859:
2854:
2849:
2845:
2841:
2837:
2833:
2829:
2822:
2819:
2813:
2807:
2803:
2796:
2793:
2788:
2784:
2780:
2776:
2772:
2768:
2764:
2760:
2752:
2749:
2744:
2740:
2735:
2730:
2726:
2722:
2718:
2714:
2710:
2703:
2700:
2695:
2691:
2686:
2681:
2677:
2673:
2669:
2665:
2661:
2654:
2651:
2646:
2642:
2637:
2632:
2628:
2624:
2620:
2616:
2612:
2605:
2603:
2601:
2597:
2592:
2588:
2583:
2578:
2573:
2568:
2564:
2560:
2556:
2549:
2547:
2543:
2538:
2534:
2529:
2524:
2519:
2514:
2510:
2506:
2502:
2498:
2494:
2487:
2484:
2479:
2475:
2471:
2467:
2463:
2459:
2455:
2451:
2447:
2443:
2436:
2433:
2428:
2424:
2419:
2414:
2410:
2406:
2402:
2398:
2394:
2387:
2384:
2379:
2375:
2370:
2365:
2361:
2357:
2353:
2349:
2345:
2338:
2335:
2330:
2326:
2321:
2316:
2312:
2308:
2304:
2300:
2296:
2289:
2286:
2281:
2277:
2272:
2267:
2263:
2259:
2255:
2248:
2245:
2240:
2236:
2231:
2226:
2222:
2218:
2214:
2210:
2206:
2199:
2196:
2191:
2187:
2183:
2179:
2175:
2171:
2167:
2163:
2156:
2153:
2148:
2144:
2140:
2134:
2130:
2123:
2120:
2115:
2111:
2106:
2101:
2097:
2093:
2089:
2085:
2081:
2074:
2071:
2066:
2062:
2057:
2052:
2047:
2042:
2038:
2034:
2030:
2023:
2020:
2015:
2011:
2007:
2003:
1999:
1995:
1988:
1985:
1980:
1976:
1971:
1966:
1962:
1958:
1954:
1950:
1946:
1939:
1936:
1931:
1927:
1922:
1917:
1913:
1909:
1905:
1901:
1897:
1890:
1887:
1882:
1878:
1874:
1870:
1866:
1862:
1858:
1854:
1847:
1844:
1839:
1835:
1831:
1827:
1823:
1819:
1812:
1809:
1804:
1800:
1795:
1790:
1786:
1782:
1778:
1774:
1770:
1763:
1760:
1755:
1751:
1746:
1741:
1736:
1731:
1727:
1723:
1719:
1712:
1709:
1702:
1698:
1695:
1693:
1690:
1688:
1685:
1683:
1680:
1678:
1677:CD4/CD8 ratio
1675:
1674:
1670:
1668:
1662:
1658:
1654:
1650:
1646:
1642:
1638:
1630:
1628:
1624:
1622:
1621:HIV treatment
1614:
1605:
1601:
1596:
1593:
1589:
1586:
1585:
1584:
1581:
1578:
1574:
1569:
1564:
1562:
1558:
1557:inflammasomes
1554:
1549:
1545:
1541:
1537:
1531:
1529:
1525:
1521:
1517:
1510:HIV infection
1509:
1507:
1505:
1500:
1497:
1496:immune system
1493:
1489:
1484:
1482:
1478:
1474:
1473:interleukin-2
1470:
1469:auto-reactive
1466:
1462:
1458:
1445:
1441:
1437:
1433:
1429:
1426:
1419:
1411:
1406:
1402:
1399:
1392:
1388:
1380:
1377:
1373:
1369:
1365:
1362:(hay fever),
1361:
1357:
1353:
1350:
1349:
1348:
1345:
1343:
1339:
1335:
1326:
1323:
1315:
1313:
1306:
1304:
1300:
1298:
1294:
1287:
1286:Memory T cell
1280:Memory T cell
1279:
1277:
1275:
1271:
1270:interleukin 9
1267:
1262:
1252:
1239:
1237:
1224:
1208:
1203:
1201:
1197:
1189:
1184:
1176:
1173:
1165:
1160:
1158:
1150:
1142:
1114:
1112:
1110:
1106:
1101:
1097:
1093:
1089:
1081:
1079:
1077:
1076:
1067:
1063:
1059:
1052:2 lineages. T
1043:
1034:
1022:
1020:
1010:
1006:
1005:interleukin 2
1002:
994:
993:Interleukin 4
990:
987:
986:interleukin 4
979:
975:
971:
967:
964:
963:
959:
955:
951:
948:. Stimulates
947:
944:
941:
937:
933:
930:
927:
926:
923:
919:
915:
914:interleukin 9
911:
910:interleukin 6
907:
906:interleukin 5
903:
902:Interleukin 4
900:
893:
889:
888:Interleukin 2
885:
881:
878:
875:
874:
871:
867:
863:
860:
858:
854:
851:
848:
847:
839:
832:
830:
829:
821:
820:interleukin 4
817:
816:interleukin 2
813:
809:
805:
801:
793:
780:
776:
766:
754:
750:
742:
738:
730:
726:
717:
715:
711:
703:
691:
687:
683:
674:
652:
650:
648:
644:
640:
636:
635:extracellular
628:
626:
624:
620:
615:
611:
610:Seth Lederman
603:
601:
599:
583:
575:
559:
555:
535:
531:
526:
524:
520:
519:IL-2 receptor
516:
512:
511:interleukin 2
508:
496:
494:
492:
486:
484:
479:
477:
473:
469:
465:
460:
458:
454:
445:
443:
431:
429:
425:
412:
410:
406:
402:
398:
394:
390:
386:
382:
378:
369:
367:
363:
359:
355:
347:
342:
335:
333:
331:
327:
323:
319:
314:
310:
306:
302:
298:
294:
290:
286:
282:
278:
274:
270:
266:
262:
258:
254:
250:
246:
245:downregulated
242:
238:
237:naive T cells
234:
230:
226:
222:
218:
210:
205:
198:
196:
194:
184:
182:
178:
174:
170:
166:
162:
158:
157:immune system
154:
150:
141:
139:
135:
131:
119:
117:
115:
107:
103:
99:
95:
91:
87:
83:
80:
76:
72:
68:
64:
60:
56:
48:
39:
33:
19:
4664:Cell biology
4442:Inflammation
4427:Alloimmunity
4422:Autoimmunity
4407:Immunity vs.
4359:Autoantibody
4257:Superantigen
3963:
3811:
3765:
3761:
3722:
3718:
3676:
3672:
3662:
3627:
3623:
3575:
3571:
3561:
3550:. Retrieved
3546:the original
3542:www.aids.gov
3541:
3532:
3495:
3491:
3481:
3438:
3434:
3424:
3381:
3377:
3367:
3332:
3328:
3318:
3286:(2): 76–88.
3283:
3279:
3269:
3228:
3224:
3218:
3185:
3181:
3175:
3140:
3136:
3126:
3087:
3083:
3073:
3038:
3034:
3024:
2991:
2987:
2980:
2971:
2965:
2932:
2928:
2922:
2887:
2883:
2835:
2831:
2821:
2802:Pharmacology
2801:
2795:
2762:
2758:
2751:
2716:
2712:
2702:
2667:
2663:
2653:
2618:
2614:
2562:
2558:
2500:
2496:
2486:
2445:
2441:
2435:
2400:
2396:
2386:
2351:
2347:
2337:
2302:
2298:
2288:
2261:
2257:
2247:
2212:
2208:
2198:
2165:
2161:
2155:
2128:
2122:
2087:
2083:
2073:
2036:
2032:
2022:
1997:
1993:
1987:
1952:
1948:
1938:
1903:
1899:
1889:
1856:
1852:
1846:
1824:(1): 31–50.
1821:
1817:
1811:
1776:
1772:
1762:
1725:
1721:
1711:
1647:, and total
1634:
1625:
1618:
1582:
1565:
1548:co-receptors
1544:lymphotropic
1532:
1513:
1501:
1485:
1454:
1451:1 cytokines.
1444:inflammation
1424:2 cytokines.
1370:(hives) and
1346:
1330:
1310:
1301:
1289:
1276:infections.
1263:
1250:
1240:
1235:
1204:
1185:
1177:
1161:
1149:plasma cells
1126:
1085:
1073:
1036:
1017:
804:interferon γ
718:
675:
664:
632:
607:
527:
500:
487:
480:
461:
449:
432:
413:
370:
351:
308:
277:Class II MHC
214:
208:
185:
169:MHC class II
152:
142:
123:
96:activity of
94:bactericidal
62:
58:
50:
46:
44:
32:The Hybrid 2
18:CD4+ T cells
4654:Macrophages
4649:Human cells
4565:Lymphocytes
4224:Lymphocytic
4177:Lymphoblast
3875:Plasmablast
3854:Lymphocytes
3768:: 707–731.
3538:"CD4 Count"
3182:Nat Immunol
2719:(6): 1–13.
2565:: 9523628.
1687:CD8 T cells
1639:(COVID-19)
1615:antibodies.
1540:bone marrow
1524:macrophages
1440:macrophages
1436:lymphocytes
1391:montelukast
1372:anaphylaxis
1295:(CCR7) and
1139:2 cytokine
936:macrophages
882:(IFNγ) and
686:macrophages
647:vaccination
598:pleiotropic
507:proliferate
366:lymph nodes
307:(these are
293:macrophages
233:lymph nodes
217:development
209:Immunologie
167:antigen on
163:displays a
153:CD4 T cells
106:neutrophils
102:macrophages
84:, breaking
4659:Phagocytes
4638:Categories
4606:Substances
4470:Peripheral
4458:Inaction:
4337:Antibodies
4318:Macrophage
4231:complement
3991:Regulatory
3964:Helper CD4
3890:Follicular
3552:2015-04-30
2147:1020120603
1728:(1): 165.
1703:References
1653:SARS-Cov-2
1649:lymphocyte
1561:pyroptosis
1379:antibodies
1312:the host.
1297:L-selectin
1157:antibodies
866:eosinophil
857:CD8 T cell
853:Macrophage
812:macrophage
643:immunology
470:(B7.1) or
401:SH2 domain
362:processing
358:endocytose
215:Following
98:phagocytes
4684:Apoptosis
4623:Cytolysin
4613:Cytokines
4460:Tolerance
4409:tolerance
4328:Immunogen
4150:LTi cells
4105:Null cell
3953:Thymocyte
2957:258380150
1573:pathogens
1553:caspase-1
1459:mediated
1368:urticaria
1340:and some
1266:Th9 cells
870:mast cell
840:Type 2/ T
833:Type 1/ T
806:; TGF-β,
802:. IFN-γ,
753:serotonin
749:histamine
729:helminths
639:cytokines
534:paracrine
530:autocrine
515:autocrine
457:apoptosis
181:cytokines
134:bacterium
130:receptors
75:cytokines
59:CD4 cells
4573:Cellular
4417:Immunity
4415:Action:
4398:Paratope
4386:Idiotype
4376:Allotype
4344:Antibody
4298:Mimotope
4262:Allergen
4245:Antigens
4238:Lymphoid
4138:Nuocytes
4087:NK cells
3919:B10 cell
3792:22224760
3749:26962940
3695:32807916
3654:32542842
3602:20208540
3524:33720048
3473:24356113
3416:24356306
3359:21111238
3310:27894837
3253:10537110
3202:19008928
3167:22341735
3118:24092508
3110:21688259
3065:21278737
3016:11717696
3008:16200070
2949:37116791
2914:20543588
2862:19646904
2832:Immunity
2816:Page 223
2787:41286571
2779:17589510
2743:25578468
2694:24786134
2645:18725574
2591:27313405
2378:17562483
2329:31641081
2280:17892852
2258:Immunity
2239:23330953
2190:25647540
2182:17558426
2114:26783342
2065:28367149
2014:26907214
1979:25720354
1930:26901814
1873:29520044
1838:23121398
1803:23059426
1754:28870212
1671:See also
1631:COVID-19
1568:antigens
1274:helminth
1234:1 cells
1092:NK cells
958:antibody
898:1 cell.
818:; IL-4,
814:; IL-2,
574:cytokine
371:When a T
143:Mature T
138:helminth
100:such as
4644:T cells
4618:Opsonin
4597:NK cell
4585:Humoral
4465:Central
4432:Allergy
4381:Isotype
4281:Epitope
4252:Antigen
3941:T cells
3870:B1 cell
3862:B cells
3812:T-Cells
3783:3314163
3740:4835240
3645:7323417
3593:4229134
3515:7954596
3464:3976200
3443:Bibcode
3435:Science
3407:4047036
3386:Bibcode
3350:3026834
3301:6066671
3261:4378970
3233:Bibcode
3210:6691974
3158:3383341
3056:3040235
2905:2892849
2853:2791889
2734:4340844
2685:4045638
2636:2518872
2582:4904118
2537:1378631
2505:Bibcode
2478:4336943
2470:1374165
2450:Bibcode
2427:1348081
2418:2119166
2369:2117903
2320:6948007
2230:4091962
2105:4744552
2056:5355494
2039:: 292.
1970:6314495
1921:4767338
1881:3736563
1794:3584691
1745:5584004
1488:viruses
1338:allergy
1251:in vivo
1236:in vivo
1196:3 cells
1123:2 model
1075:Candida
1048:1 and T
950:B-cells
710:Type IV
669:1 and T
661:2 model
619:Immunex
453:anergic
356:(APCs)
297:B cells
241:antigen
219:in the
165:peptide
4590:B cell
4578:T cell
4323:B cell
4286:Linear
4274:Hapten
3885:Memory
3880:Plasma
3790:
3780:
3747:
3737:
3693:
3673:Nature
3652:
3642:
3600:
3590:
3522:
3512:
3471:
3461:
3414:
3404:
3378:Nature
3357:
3347:
3308:
3298:
3259:
3251:
3225:Nature
3208:
3200:
3165:
3155:
3116:
3108:
3063:
3053:
3014:
3006:
2955:
2947:
2912:
2902:
2860:
2850:
2808:
2785:
2777:
2741:
2731:
2692:
2682:
2643:
2633:
2589:
2579:
2535:
2525:
2476:
2468:
2442:Nature
2425:
2415:
2376:
2366:
2327:
2317:
2278:
2237:
2227:
2188:
2180:
2145:
2135:
2112:
2102:
2063:
2053:
2012:
1977:
1967:
1928:
1918:
1879:
1871:
1836:
1801:
1791:
1752:
1742:
1641:B cell
1536:thymus
1401:Type 2
1397:model.
1364:eczema
1356:asthma
862:B-cell
810:; mø,
568:1 or T
397:ZAP-70
281:thymus
229:spleen
227:(SLO;
221:thymus
79:B cell
67:T cell
3997:Naïve
3905:Pre-B
3900:Naïve
3498:(6).
3257:S2CID
3206:S2CID
3114:S2CID
3090:(9).
3012:S2CID
2953:S2CID
2783:S2CID
2615:Blood
2528:49539
2474:S2CID
2186:S2CID
1877:S2CID
1418:lupus
1223:IL-17
1186:Both
1141:IL-10
1096:STAT1
1088:IL-10
1078:spp.
884:TNF-β
741:GATA3
737:STAT6
582:IL-10
424:LFA-1
177:CD40L
55:cells
4229:and
3957:αβ (
3914:cell
3788:PMID
3745:PMID
3691:PMID
3650:PMID
3598:PMID
3520:PMID
3469:PMID
3412:PMID
3355:PMID
3329:Cell
3306:PMID
3249:PMID
3198:PMID
3163:PMID
3106:PMID
3061:PMID
3004:PMID
2945:PMID
2910:PMID
2858:PMID
2806:ISBN
2775:PMID
2739:PMID
2690:PMID
2641:PMID
2587:PMID
2563:2016
2533:PMID
2466:PMID
2423:PMID
2374:PMID
2325:PMID
2276:PMID
2235:PMID
2178:PMID
2143:OCLC
2133:ISBN
2110:PMID
2061:PMID
2010:PMID
1975:PMID
1926:PMID
1869:PMID
1834:PMID
1799:PMID
1750:PMID
1602:and
1526:and
1438:and
1403:and
1389:and
1190:and
1100:ADCC
1064:and
1009:IFNγ
1007:and
978:IFNγ
970:IFNγ
890:and
800:MHC2
739:and
702:iNOS
688:and
556:and
554:IL-4
528:The
523:CD25
472:CD86
468:CD80
464:CD28
428:ICAM
407:and
405:CD45
295:and
253:PTK7
249:CD31
231:and
175:and
104:and
45:The
4551:HLA
4547:MHC
3912:reg
3778:PMC
3770:doi
3735:PMC
3727:doi
3681:doi
3677:584
3640:PMC
3632:doi
3588:PMC
3580:doi
3510:PMC
3500:doi
3496:131
3459:PMC
3451:doi
3439:343
3402:PMC
3394:doi
3382:505
3345:PMC
3337:doi
3333:143
3296:PMC
3288:doi
3241:doi
3229:401
3190:doi
3153:PMC
3145:doi
3096:doi
3051:PMC
3043:doi
2996:doi
2937:doi
2900:PMC
2892:doi
2848:PMC
2840:doi
2767:doi
2729:PMC
2721:doi
2680:PMC
2672:doi
2631:PMC
2623:doi
2619:112
2577:PMC
2567:doi
2523:PMC
2513:doi
2458:doi
2446:357
2413:PMC
2405:doi
2401:175
2364:PMC
2356:doi
2315:PMC
2307:doi
2266:doi
2225:PMC
2217:doi
2170:doi
2100:PMC
2092:doi
2088:196
2051:PMC
2041:doi
2002:doi
1965:PMC
1957:doi
1916:PMC
1908:doi
1904:126
1861:doi
1826:doi
1789:PMC
1781:doi
1740:PMC
1730:doi
1661:RNA
1635:In
1613:IgM
1604:IgA
1600:IgG
1588:CD8
1516:CD4
1376:IgE
1245:1/T
1217:1/T
1131:1/T
1119:1/T
1107:or
940:CD8
792:APC
786:1/T
657:1/T
612:at
532:or
409:Csk
389:Lck
385:CD4
381:CD3
377:TCR
330:CD8
309:not
273:CD3
261:CR2
257:CR1
149:CD4
61:or
4640::
4311::
4059:γδ
4033:VM
4025:RM
4017:EM
4009:CM
3989:/
3987:17
3981:/
3973:/
3970:FH
3966:/
3814:.
3810:.
3786:.
3776:.
3766:30
3764:.
3760:.
3743:.
3733:.
3723:19
3721:.
3717:.
3689:.
3675:.
3671:.
3648:.
3638:.
3628:97
3626:.
3622:.
3610:^
3596:.
3586:.
3576:16
3574:.
3570:.
3540:.
3518:.
3508:.
3494:.
3490:.
3467:.
3457:.
3449:.
3437:.
3433:.
3410:.
3400:.
3392:.
3380:.
3376:.
3353:.
3343:.
3331:.
3327:.
3304:.
3294:.
3284:77
3282:.
3278:.
3255:.
3247:.
3239:.
3227:.
3204:.
3196:.
3184:.
3161:.
3151:.
3141:24
3139:.
3135:.
3112:.
3104:.
3088:41
3086:.
3082:.
3059:.
3049:.
3039:12
3037:.
3033:.
3010:.
3002:.
2990:.
2951:.
2943:.
2933:11
2931:.
2908:.
2898:.
2886:.
2882:.
2870:^
2856:.
2846:.
2836:31
2834:.
2830:.
2781:.
2773:.
2761:.
2737:.
2727:.
2717:57
2715:.
2711:.
2688:.
2678:.
2668:35
2666:.
2662:.
2639:.
2629:.
2617:.
2613:.
2599:^
2585:.
2575:.
2561:.
2557:.
2545:^
2531:.
2521:.
2511:.
2501:89
2499:.
2495:.
2472:.
2464:.
2456:.
2444:.
2421:.
2411:.
2399:.
2395:.
2372:.
2362:.
2352:35
2350:.
2346:.
2323:.
2313:.
2303:12
2301:.
2297:.
2274:.
2262:27
2260:.
2256:.
2233:.
2223:.
2213:31
2211:.
2207:.
2184:.
2176:.
2164:.
2141:.
2108:.
2098:.
2086:.
2082:.
2059:.
2049:.
2035:.
2031:.
2008:.
1998:34
1996:.
1973:.
1963:.
1953:15
1951:.
1947:.
1924:.
1914:.
1902:.
1898:.
1875:.
1867:.
1857:18
1855:.
1832:.
1822:31
1820:.
1797:.
1787:.
1777:12
1775:.
1771:.
1748:.
1738:.
1726:18
1724:.
1720:.
1643:,
1366:,
1358:,
1344:.
1209:(T
1159:.
1066:22
920:,
916:,
912:,
908:,
904:,
886:.
868:,
864:,
855:,
844:2
751:,
649:.
478:.
459:.
291:,
259:,
251:,
183:.
116:.
4549:/
4307:/
4216:e
4209:t
4202:v
4031:T
4023:T
4015:T
4007:T
3993:)
3985:h
3983:T
3979:3
3977:h
3975:T
3968:T
3910:B
3846:e
3839:t
3832:v
3818:.
3794:.
3772::
3751:.
3729::
3697:.
3683::
3656:.
3634::
3604:.
3582::
3555:.
3526:.
3502::
3475:.
3453::
3445::
3418:.
3396::
3388::
3361:.
3339::
3312:.
3290::
3263:.
3243::
3235::
3212:.
3192::
3186:9
3169:.
3147::
3120:.
3098::
3067:.
3045::
3018:.
2998::
2992:6
2959:.
2939::
2916:.
2894::
2888:5
2864:.
2842::
2814:.
2789:.
2769::
2763:8
2745:.
2723::
2696:.
2674::
2647:.
2625::
2593:.
2569::
2539:.
2515::
2507::
2480:.
2460::
2452::
2429:.
2407::
2380:.
2358::
2331:.
2309::
2282:.
2268::
2241:.
2219::
2192:.
2172::
2166:5
2149:.
2116:.
2094::
2067:.
2043::
2037:8
2016:.
2004::
1981:.
1959::
1932:.
1910::
1883:.
1863::
1840:.
1828::
1805:.
1783::
1756:.
1732::
1665:h
1608:h
1449:h
1447:T
1422:h
1414:h
1395:h
1383:h
1259:h
1255:h
1247:h
1243:h
1232:h
1228:h
1219:h
1215:h
1211:h
1194:h
1192:T
1181:h
1172:3
1170:h
1168:T
1153:h
1145:h
1137:h
1133:h
1129:h
1121:h
1117:h
1070:h
1054:h
1050:h
1046:h
1040:h
1038:T
1025:h
1023:T
997:h
982:h
896:h
842:h
837:1
835:h
796:h
788:h
784:h
782:T
773:h
769:h
761:h
757:h
745:h
733:h
721:h
719:T
706:h
698:h
694:h
678:h
676:T
671:h
667:h
659:h
655:h
653:T
594:h
590:h
586:h
578:h
570:h
566:h
562:h
550:h
546:h
542:h
538:h
521:(
503:h
439:h
435:h
420:h
416:h
379:-
373:h
271:-
188:h
186:T
145:h
126:h
124:T
110:h
53:h
51:T
49:(
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.